7- all ceramic restorations
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the two main approaches to achieving strength in ceramic restorations?
Bilayered ceramics – Strong but non-aesthetic core- like zirconia or alumina, veneered with aesthetic porcelain.
Monolithic ceramics – Single material like monolithic zirconia combining high strength with good aesthetics, without needing extra thickness to mask color
What are the advantages vs aesthetic limitations of monolithic zirconia restorations?
Very strong
Acceptable aesthetics for posterior
Less tooth reduction
Less wear of opposing enamel
non-uniform colouring due to limited translucency
colour change after adjustment if glazed layer removed
What are the general advantages vs disadvantages of dental ceramics?
Very aesthetic
Biocompatible
Brittle
Can fracture when seating or during function- caused by fabrication defects or surface cracks
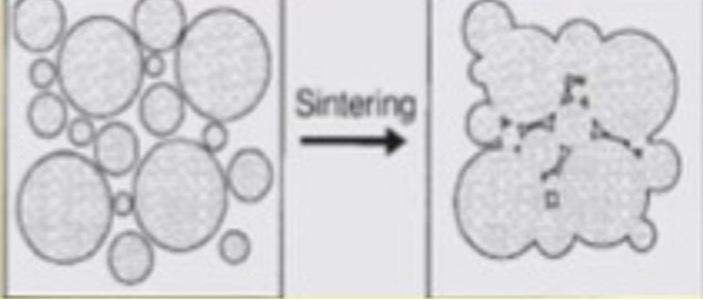
When are fabrication defects created?
During sintering- heating compacted ceramic particles to bond them together and increase density and decrease surface area
Defects include voids or inclusions
What factors contribute to porosity and microcracks in dental ceramics?
Porosity- when condensation of ceramic slurry is done by hand, vacuum sintering reduces it from 5.6% to 0.56%
Microcracks- form in leucite-containing ceramics due to thermal contraction mismatch between leucite crystals and the glassy matrix
How are surface cracks induced?
Machining or grinding
Which 4 methods are used to improve the strength and clinical performance of dental ceramics?
Crystalline reinforcement
Chemical strengthening
Stress-induced transformation
Glazing
How does crystalline reinforcement strengthen dental ceramics?
By adding a high proportion of crystalline phase- resist crack propagation via-
Weak grain interfaces in single-phase ceramics due to incomplete sintering
Residual strains in two-phase ceramics from mismatch between crystals and glass matrix
How does chemical strengthening improve the strength of dental ceramics?
By ion exchange of alkali salts that have a mp lower than the glass transition temp
This creates compressive stresses that resist crack propagation
Can increase flexural strength of feldspathic porcelain by up to 80%
How is the chemical strengthening technique limited?
time, temperature, and ionic radius of the exchanged ions
How does stress-induced transformation strengthen polycrystalline zirconia?
Stress triggers a transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic zirconia, increasing grain volume near crack tips and resisting crack growth.
How does glazing strengthen ceramics, and what is self-glazing in dental ceramics?
It creates a low expansion surface layer at a high temp- compresses the ceramic and reduces size of surface flaws
Extra firing in air without applying a glaze
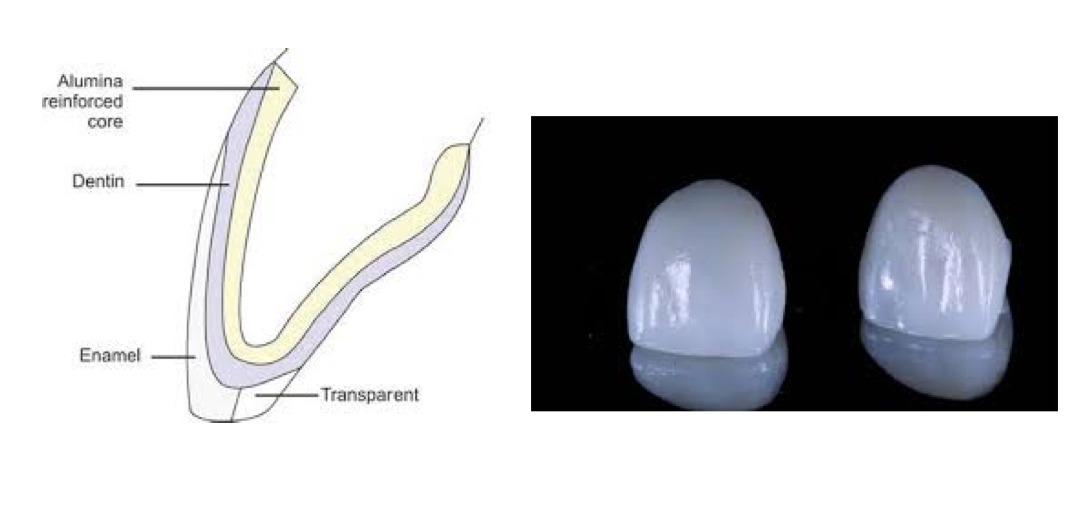
What are aluminous core ceramics, and how did McLean’s technique increase strength in dental restorations?
Ceramics with alumina crystals in a glass matrix
McLean’s technique used a 50% alumina core veneered with porcelains making restorations ~40% stronger than feldspathic porcelain