Radiology Quiz #1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
radiology
specialty of medicine that uses imaging technology to diagnose and treat diseases
1. diagnostic radiology
2. interventional radiology
What are the 2 subdivisions of radiology?
diagnostic radiology
Type of Radiology:
the use of special imaging studies to interpret and then possibly diagnose a patient
"wet read"
a very simple read done by a non-radiologist provider
interventional radiology
Type of Radiology:
performing minor procedures using radiology
positron emission tomography
what PET scan stands for
computed tomography
computerized axial tomography
What does CT scan stand for? How about its alternative name, CAT scan?
magnetic resonance imaging
what MRI stands for
radiology technologist
Health Professional:
- perform various radiology exams (x-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, mammograms, etc.)
- receive formal training in various types of programs
nurses
Health Professional:
- help with complex procedures (i.e. procedures that need anesthesia)
- help with procedures that need IV meds, contrast, or nuclear substances
- assess, watch, and note a person's status
- often involved in interventional radiology to monitor vital signs, administer meds, etc
medical physicist
Health Professional:
- make sure of the safe/accurate use of radiation therapy
- work with radiology team in treatment planning
- set guidelines and check safety for radiation doses
- research/development of new technologies
ionizing radiation
type of energy used in CT, fluoroscopy, and X-rays to capture diagnostic images; can have harmful effects if used in excess or in certain situations
1. transmitted
2. absorbed
3. scatter
What are the three fates of radiation during an imaging procedure?
transmitted radiation
Fate of Radiation:
- passes through patient and interacts with detector to create image
- ~5-15% of radiation produced by source becomes this
absorbed radiation
Fate of Radiation: -
interacts with tissues of patient, depositing its energy in those tissues
- source of the patient's radiation exposure
scatter radiation
Fate of Radiation:
- not transmitted OR absorbed by the patient
- can change original path and leave the patient in a different course than entry
- can degrade quality of the image and exposure source to personnel
1. directly damaging molecules
2. indirectly creating free radicals to disrupt cellular metabolisms
What are the 2 ways that radiation can cause biologic effects on a cellular level?
deterministic effects (nonrandom)
Type of Biologic Effect:
- damage that occurs when threshold is met
- relatively rare
- occur when level of radiation-induced cell damage > cell's ability to repair damage
- most come from nuclear warfare, bombs, etc.
Skin erythema, hair loss, sterility, cataracts, death
examples of nonrandom (deterministic effects):
Stochastic Effects (random)
Type of Biologic Effect:
- may occur at any level of exposure, without a threshold dose
- occur by chance
- due to damage of cellular components, usually DNA, by free radicals leading to abnormal cell function
- invisible damage and may not manifest until many years after exposure.
- can lead to development of cancers
10 mSv
the minimal dose that could statistically increase the risk of developing a radiation-induced cancer
False: 1 chest radiograph = 0.04 mSv
requires 10 mSv to really affect a person
True/False:
Even just one radiograph on the chest, where there's many important, vulnerable organs, can automatically increase the chance of developing cancer.
10-20 year latent period
How long is the latent period after being exposed to radiation therapy and hitting 10 mSv? (why geriatrics can get more imaging - will probs die before latent period is over anyways) - latent period after which cancer develops from radiation exposure.
American College of Radiology (ACR)
the professional medical organization that has established the Appropriateness Criteria to aid providers in selecting appropriate imaging procedure
- also provides info on relative radiation levels (RRL) associated with different modalities.
computerized tomography (CT) and fluoroscopy can use a relatively larger dose of radiation, whereas ultrasound and MR do not use any ionizing radiation
Relative Radiation Doses of Different Modalitites: modalities such as computerized tomography (CT) and fluoroscopy can use how much radiation? Ultrasound an MR use how much ionizing radiation?
ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) principle
What's the name of the principle we use to practice radiation safety in order to prevent deterministic effects and limit stochastic effects?
High-quality images should be obtained by using the lowest possible dose to limit the exposure of patients and healthcare workers
1. manage time of exposure
2. increase distance from x-ray source
3. use appropriate shielding materials
What are the 3 major radiation safety practices meant to limit radiation dose?
Managing time of exposure
Limiting exposure duration to a level that still produces a clinically useful examination
This has led to an effective dose-reduction effort in CT exams:
● Monitoring the dose
● Increasing the speed of the table top movement to shorten
the exposure
● Adjusting parameters based on patient size and age
Practices for radiation safety: dose reduction in CT - what it led to?
True
True/False:
Children are 3-5x higher risk of mortality from radiation-induced cancer than adults due to increased organ sensitivity, longer life expectancy, and longer latent period to develop cancer.
Ionizing radiation
The use of _____ in pediatric populations is monitored carefully and utilized only when necessary
US (ultrasound) and MRI (no ionizing radiation)
What radiographic tools are used when possible for pediatric populations to practice radiation safety?
children, pregnant women
What are some at-risk groups of radiation exposure?
-An inquiry about pregnancy status
-pregnancy testing is performed if there is any doubt
-If a woman is pregnant, exposure is limited and modalities that do not use ionizing radiation are employed when possible (US and MRI)
Imaging a woman of childbearing age requires:
Conventional radiograph. plain films, plain radiographs, radiographs
Correct term for an X-ray is? What are other names?
Depends on its density
How X-rays work: X-ray beam is released from a generator and passes through the body. Body tissues absorb and/or block the beam in varying amounts. What does it depend on?
Relatively inexpensive, quick to perform, can be portable, lower amount of radiation than CT scan, well tolerated
Benefits of X-rays?
All X-rays may cause alteration of cellular division and other intracellular processes. potentially harm to the human body
What are the risks of X-rays?
correct patient name?
correct patient DOB?
correct date?
correct images/views ordered?
correct quality?
Interpretation basics: what do we need to know for patient information?
Gas/air, Fat, Water/soft tissue, Mineral/bone, Metal
Interpretation basics: density - what are the 5 conventional radiograph densities from black to white?
Absorbs the least amount of X-rays
Appears black
How does gas/air show up on the X-ray and why?
Dark gray
What color does fat appear on the X-ray?
Appears light gray because is it very dense
What color does water/soft tissue appear on the X-ray and why?
Appears dark white on X-ray. Absorbs the most X-rays. most dense
What color does mineral/bone appear on the X-ray and why?
Appears whitest, bright white. Usually absorbs all X-rays
What color does metal appear on the X-ray and why?
- evidence of upper airway obstruction on exam
- concern for radiopaque foreign body (may have hard time breathing, have mild stridor, appear to be choking)
- +/- severe throat pain
What are some indications that you should order a soft tissue neck x-ray?
- quicker
- patient too unstable for CT
- airway compromised if lying flat
- decreased neck radiation
- cheaper!
What are some reasons why you would order a soft tissue neck x-ray over a CT?
radiopaque
describes a substance does not allow x-rays to pass through and appears white or light gray on the resulting film
retropharyngeal abscess
a life-threatening infection posterior to the pharynx and anterior to the cervical spine; has the potential to occlude the breathing pathway
False; can see them, but not what we would order to dx a cervical spine abnormality. HOWEVER, if you notice a bony abnormality on an x-ray, you are still responsible for it!!
True/False:
A soft tissue neck x-ray is a good imaging study to order to diagnose and determine any cervical spine abnormalities.
AP, lateral
the 2 views typically ordered for a soft tissue neck x-ray
C - confirm details & quality of study
H - hypopharynx (is it abnormally distended or wide?)
E - epiglottis (is it unusually large?)
S - subglottis (is it unusually narrow? is there a foreign body?)
S - spine (is the prevertebral space usually wide? is the cervical spine lordosis unusually straight?)
Systematic Approach to Interpretation: When evaluating a soft tissue neck X-ray, we use the pneumonic CHESS to follow our appropriate order of analysis. What does each letter stand for? What do you have to consider for each letter?
Confirm correct patient name, DOB, date, images ordered.
Must be performed at end-inspiration and with the neck extended
Explain how we confirm the details and quality of the study
Using the C1-C3 50% and C4-T1 100% rule
What rule do we assess when looking at the prevertebral space?
retropharyngeal space soft tissue infection
What is a prevertebral space enlargement on a STNX-ray usually indicative of?
retropharyngeal space
Prevertebral space enlargement is an important and ominous sign of ______________ soft tissue infections
no more than 50% the width of the associated vertebral bodies
no more than 100% the width of associated vertebral bodies
retropharyngeal abscess
How do we compare the width of the prevertebral space to the adjacent vertebral bodies when evaluating a STNX-ray?
Finish these sentences to answer this question:
- The space anterior to disk spaces C1-C3 should be ____________________ the width of the associated vertebral bodies.
- The space anterior to disk spaces C4-T1 should be _________________ the width of the associated vertebral bodies.
A space wider than this is concerning for __________ or a prevertebral hematoma
eliglottitis
inflammation of the epiglottis & adjacent supraglottic structures
- primarily due to infection (can be due to trauma tho)
- Without treatment, can progress to life-threatening airway obstruction
May present as a URI (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea)
Severe sore throat (100%)
Trouble swallowing (94%)
Difficulty swallowing own secretions (63%)
What is the presentation of Epiglottitis in adults?
Respiratory distress (late)
Stridor (late)
Tripod posturing
Difficulty swallowing own secretions
Muffled voice
Anxiety
What is the presentation of Epiglottitis in children?
endotracheal intubation or advanced airways
The imaging study of choice is the lateral neck radiograph, which should be exposed in the upright position only, as the supine position may close off the airways.
Epiglottitis:
Patient should be accompanied everywhere by someone experienced in __________ or _________
What is the imaging study of choice?
thumbprint sign, thickening of aryepiglottic folds, and sometimes there will also be circumferential narrowing of the subglottic portion of the trachea during inspiration.
What are the imaging findings in Epiglottitis?
Haemophilus influenzae
What is the main bacteria that causes the infection that leads to epiglottitis?
- presents as URI (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea)
- severe sore throat
- trouble swallowing
- difficulty swallowing own secretions --> drooling
Epiglottitis most often occurs in kids between 2-8 years old, but can present at any age. What are the S/S often seen in adults with epiglottitis?
- tripod posturing
- difficulty swallowing own secretions
- muffled voice
- anxiety
- respiratory distress & stridor
Epiglottitis most often occurs in kids between 2-8 years old. What are the S/S often seen in children with epiglottitis?
False - you don't NEED STN X-ray to diagnose epiglottitis
True/False:
Epiglottitis is severe, but treatable. If a young child (4 y/o) presents with the signs of epiglottitis (tripod posturing, muffled voice, difficulty swallowing saliva, some lung sounds), your next move of action should be to order a STN X-ray, as there is no other way to diagnose epiglottitis.
thumbprint sign
the manifestation of an edematous and enlarged epiglottis seen on a lateral STN X=ray; typically indicative of epiglottitis
1. you don't need STN X-ray to diagnose her w epiglottitis
2. DO NOT leave a patient you suspect has epiglottitis alone with personnel untrained in endotracheal intubation!!!
3. the supine position the x-ray was taken in would close off the airway
(i'm surprised she even survived for you to find the thumbprint sign. you'd fs be sued for this)
What's wrong with the following scenario?
A 5 y/o girl presents to the ER with her mother. You notice she has tripod posturing and a muffled voice. Her mother says she's been drooling and complaining of a sore throat, and seems very anxious lately. Once you examine her, you hear stridor in her lungs and suspect epiglottitis, but can't diagnose her with it until you send her for a STN X-ray. You find a brand new medical assistant to escort them down to radiology. Once at radiology, the MA works with the radio technician and tells the child to lie supine to get the image done. Sure enough, the image shows a thumbprint sign indicating epiglottitis.
thickening of aryepiglottic folds
the important component of airway obstruction & true cause of stridor in epiglottitis
croup
a respiratory illness characterized by inspiratory stridor, cough, and hoarseness
- symptoms result from laryngeal and subglottic airway inflammation (usually parainfluenza virus)
- usually mild and self-limited illness, but can cause resp distress/death
viral - parainfluenza
What is the most common cause of croup?
croup
If a 2 y/o child presented with the following symptoms, what would be your most likely differential diagnosis, before you even order any imaging?
- harsh, "barking" cough
- hoarseness
- inspiratory stridor
- low-grade fever
NO, Dx is made based on clinical findings
are imagine studies required to diagnose Croup?
- distention (widening) of hypopharynx
- distention of laryngeal ventricle
- haziness/narrowing of subglottic trachea
What are the 3 things you may see in a lateral STN X-ray view of a child with croup?
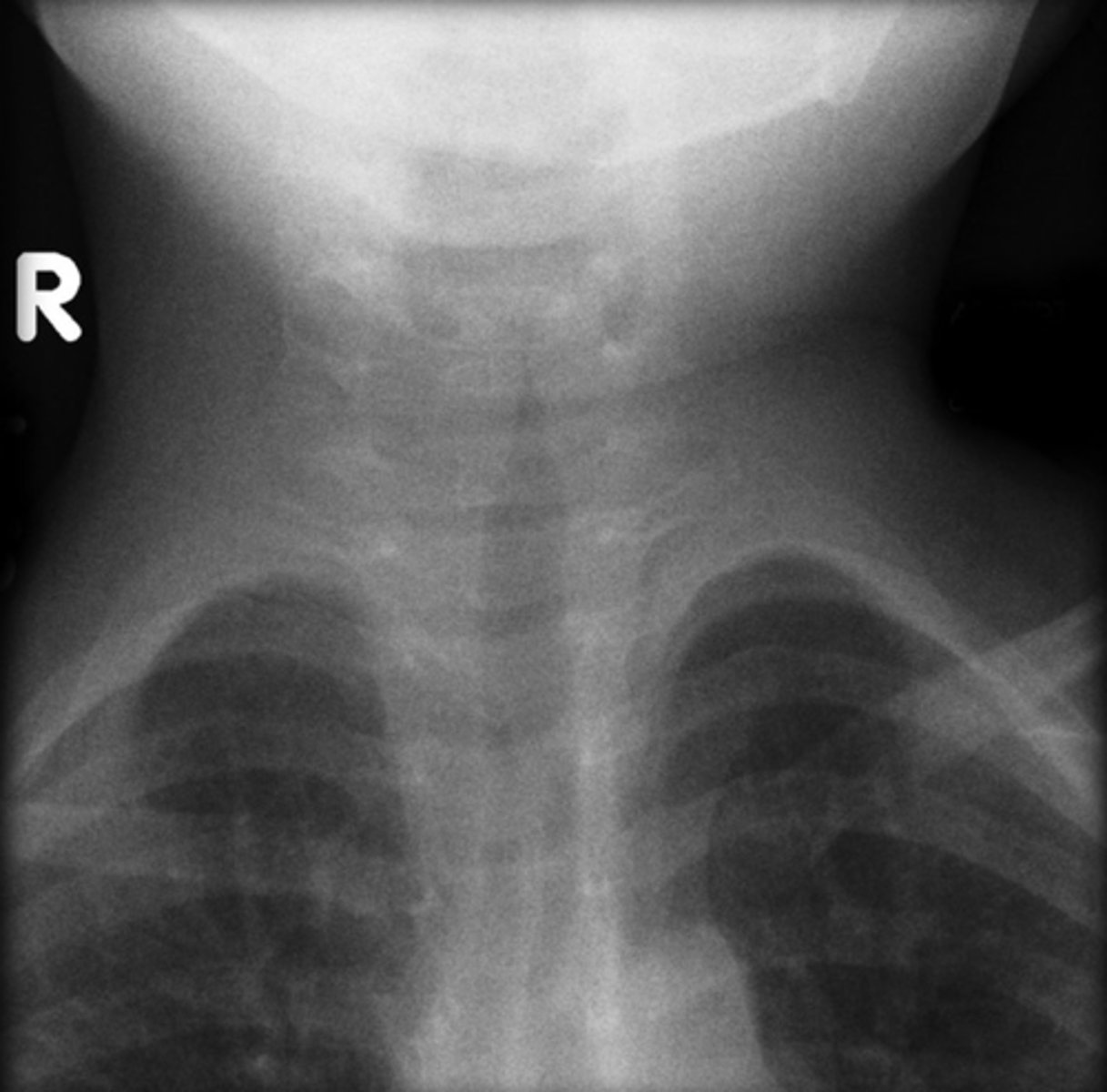
steeple sign
What is the #1 imaging indication that suggests croup, which is seen on a STN X-ray frontal view?
steeple sign
indicative of croup;
- refers to the tapering of the upper trachea on AP STN X-ray or frontal CXR
Between 6mo and 6years. Coins and button batteries are commonly injected. A coin or button battery may appear differently on XR views
Foreign Bodies:
Majority of foreign body injections occur between what ages?
What is most commonly injected? and do they appear differently on XR views?
trachea
A person presents to the ER with difficulty breathing and you suspect a foreign body is lodged in their airway. You get a STN X-ray done and confirm that there is a coin there. In the frontal (AP) view, you see the side of the coin; in the lateral view, you can see the face of the coin. Is this coin stuck in the patient's trachea or esophagus?
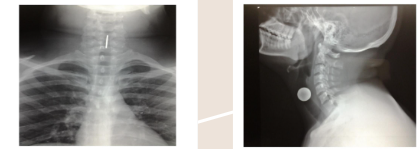
esophagus
You order a STN X-ray for a patient with a suspected foreign body. When you get the image back, the frontal view shows the face of the coin. The lateral view shows the side of the coin. Is the coin stuck in this patient's trachea or esophagus?
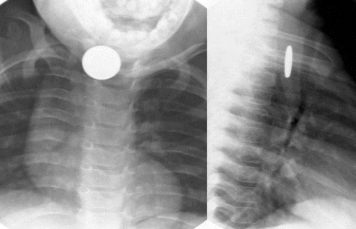
- battery has double-ring or "halo" sign = the bordering around the circle
- battery more see-through and thinner than coin
You're on your ER clinical rotation when your preceptor pimps you: how can you tell the difference between a coin and a button battery in a person's airway from radiologic studies?
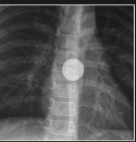
retropharyngeal abscess
a potentially life-threatening infection involving the retropharyngeal space
- requires prompt diagnosis and aggressive therapy
- more common in children
- S/S: generalized irritability, fever, refusal to eat, drooling, fever, neck swelling, stridor
- soft tissue swelling posterior to pharynx, with widening of prevertebral soft tissue
- loss of normal cervical lordosis
- increased width of prevertebral soft tissue at upper cervical spine
-The oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx and upper trachea are displaced anteriorly by the soft tissue thickening
What are some key imaging findings that would indicate a retropharyngeal abscess?
thumbprint sign; epiglottitis
What abnormality is shown here in this soft tissue neck x-ray? What would you diagnose this patient with?
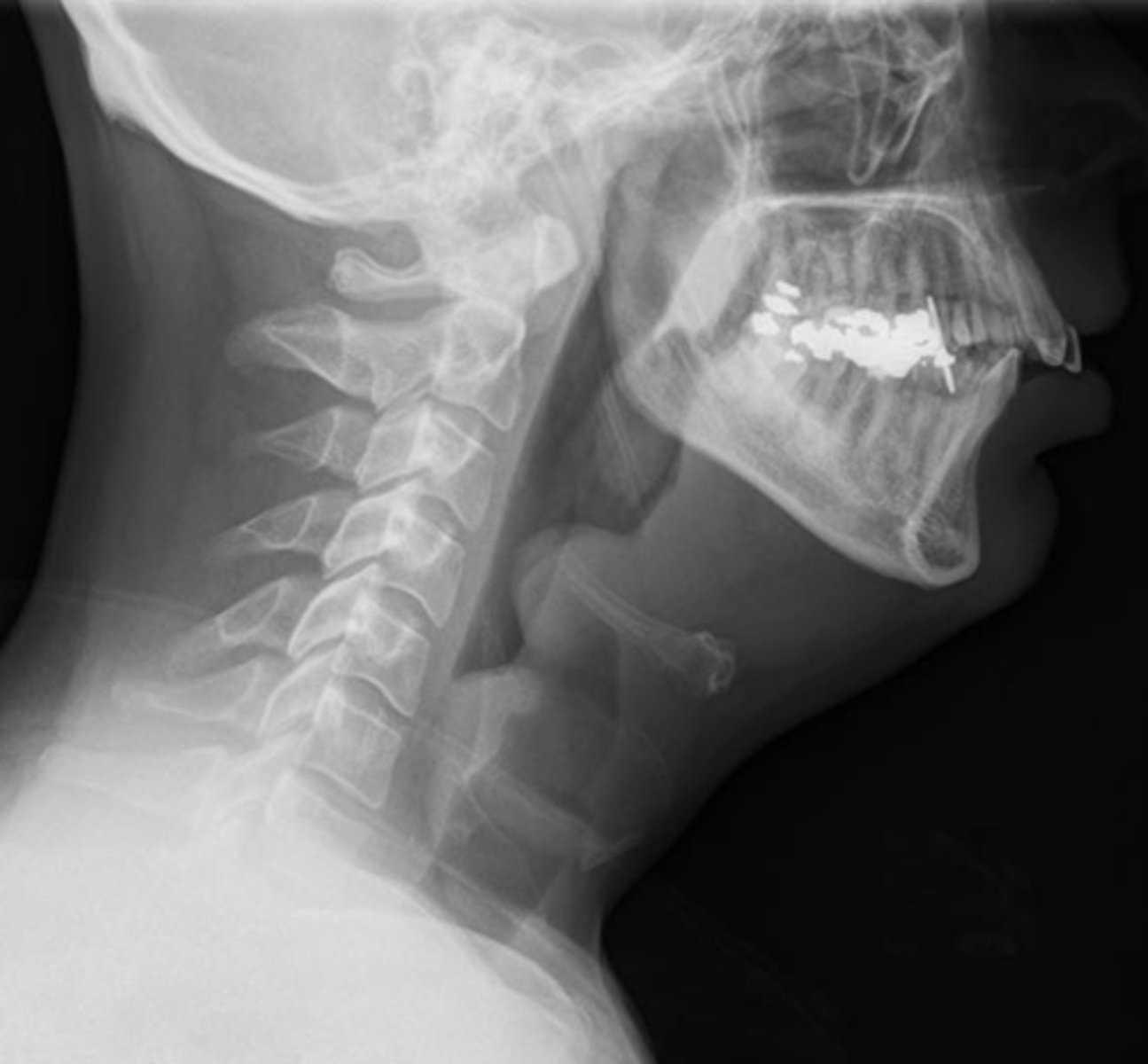
thumbprint sign; epiglottitis
What abnormality is shown here in this soft tissue neck x-ray? What would you diagnose this patient with?
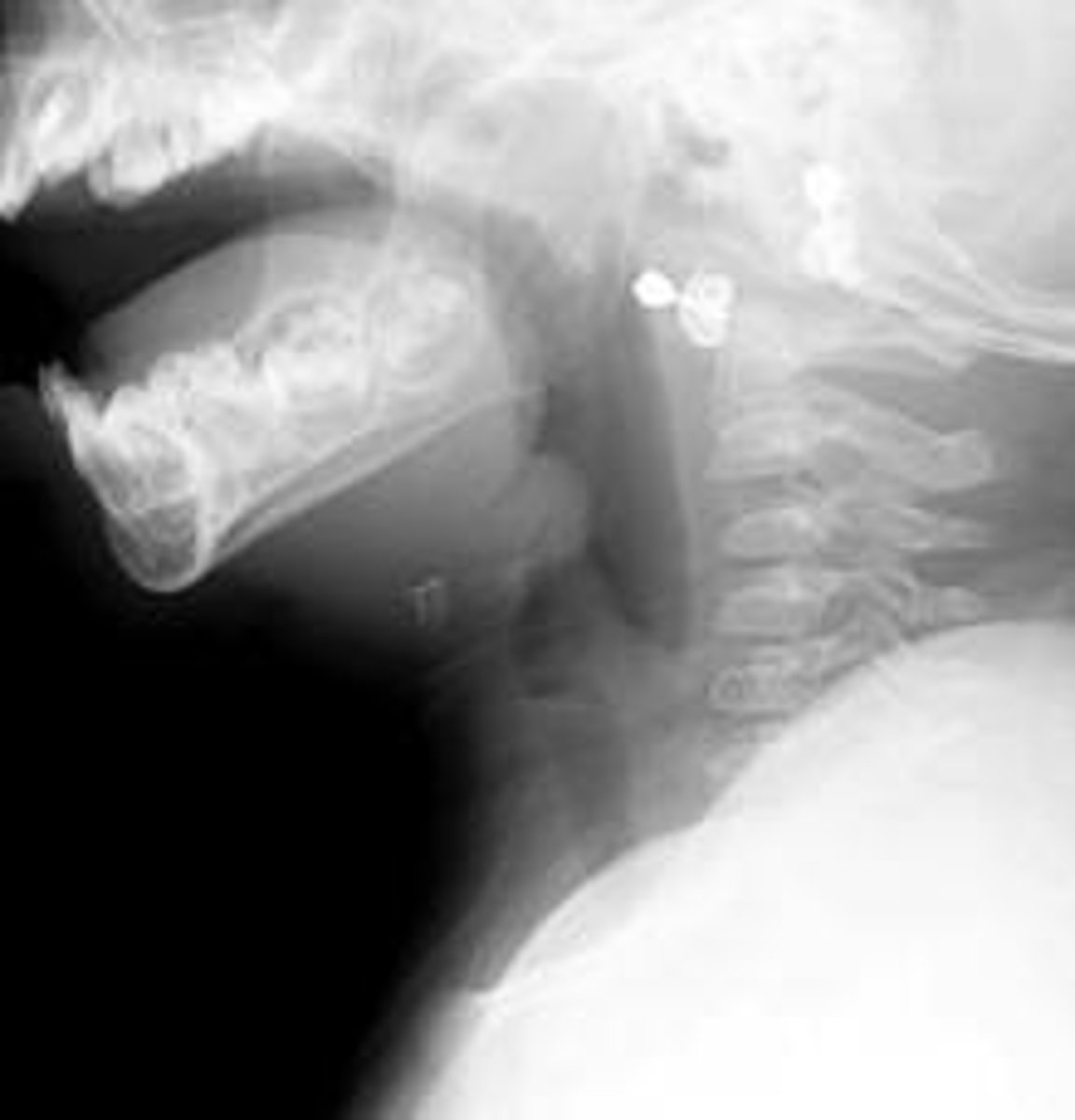
steeple sign; croup
What abnormality is shown here in this soft tissue neck x-ray? What would you diagnose this patient with?
density
An X-ray beam is released from a generator and passed through the body. Body tissues absorb and/or block the beam in varying amounts; what does its absorbance depend on?
1. ordering provider (us)
2. hospital transport (if being obtained in a hospital)
3. radiology technician (performs X-ray)
4. radiologist (helps to interpret results)
Who are the 4 main people that are involved in ordering radiologic studies?
"wet" read
the initial read done by the ordering provider before there's input from the radiologist
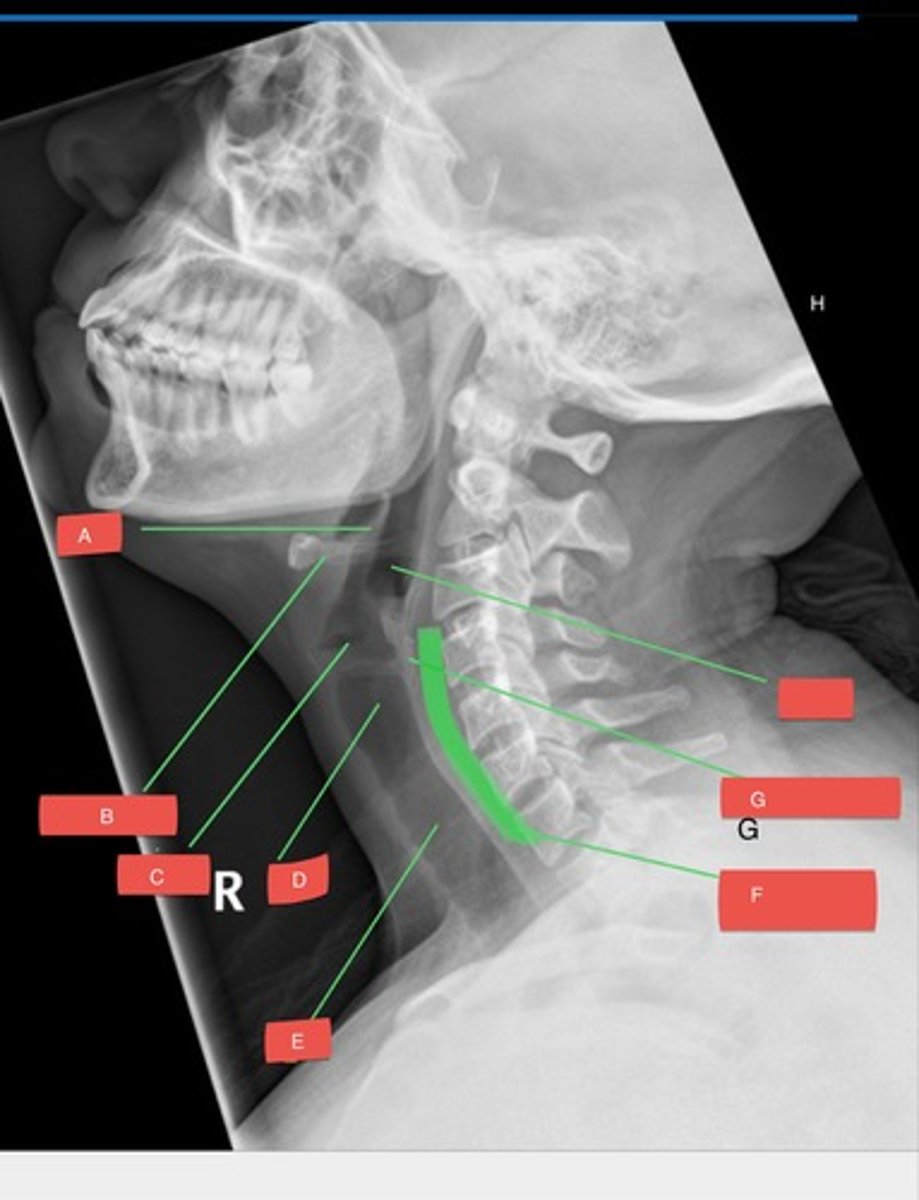
A - epiglottis
A?
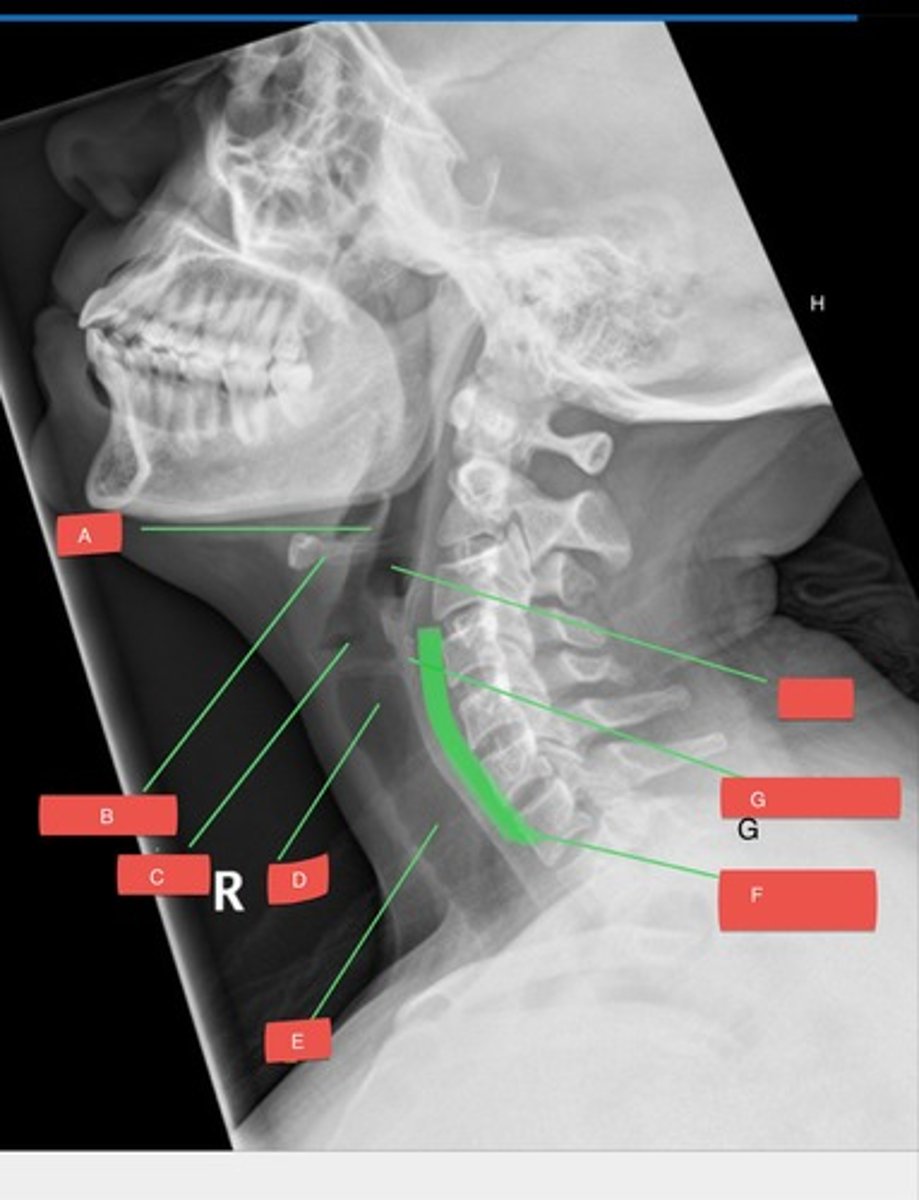
B - hyoid bone
B?
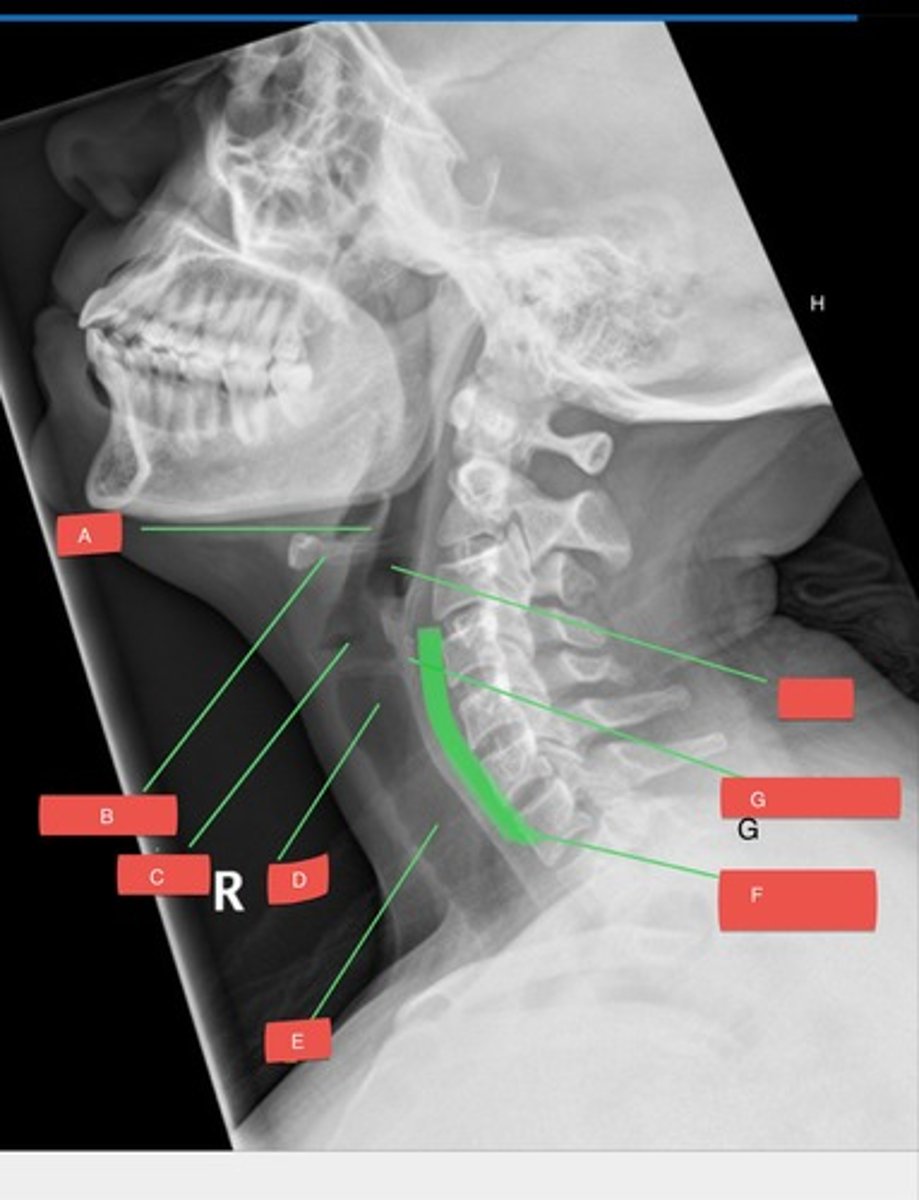
C - glottis
C?
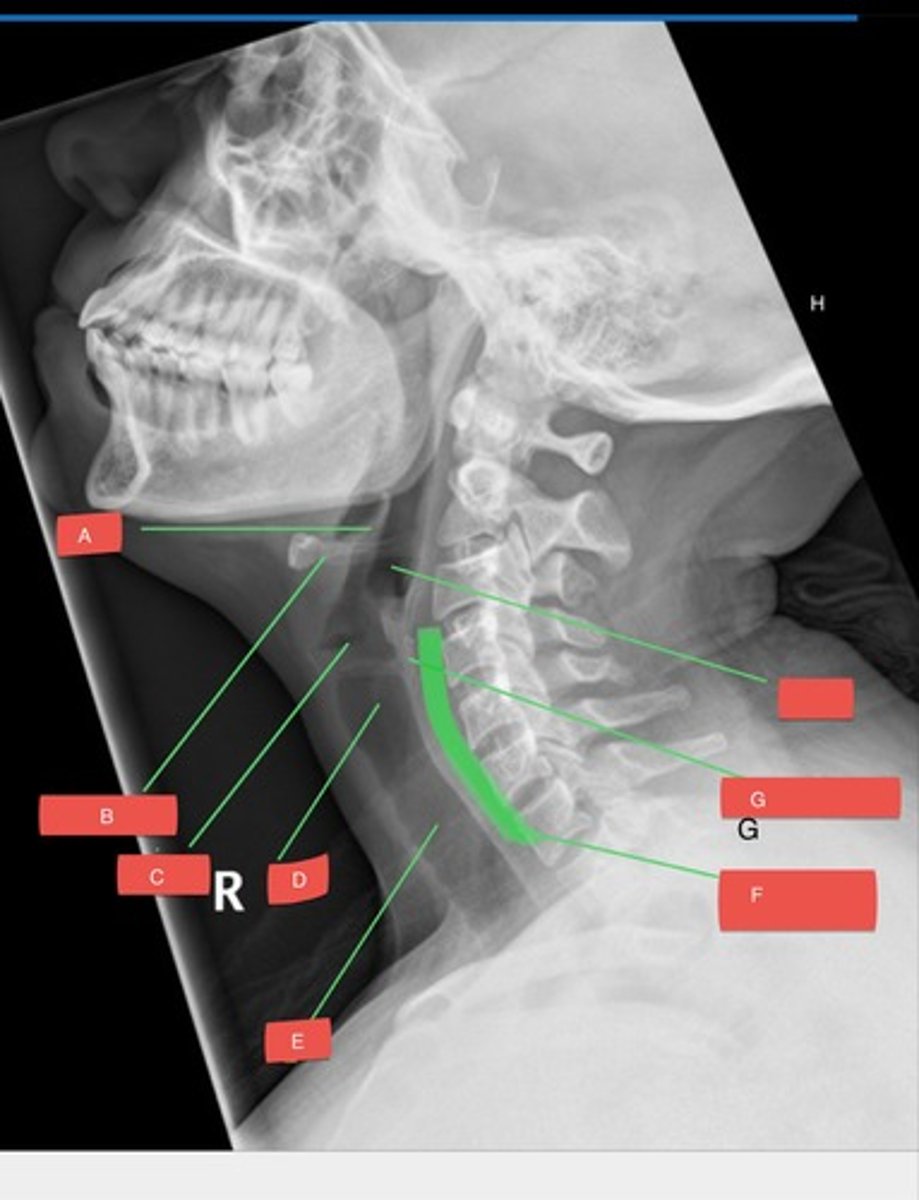
D - subglottis
D?
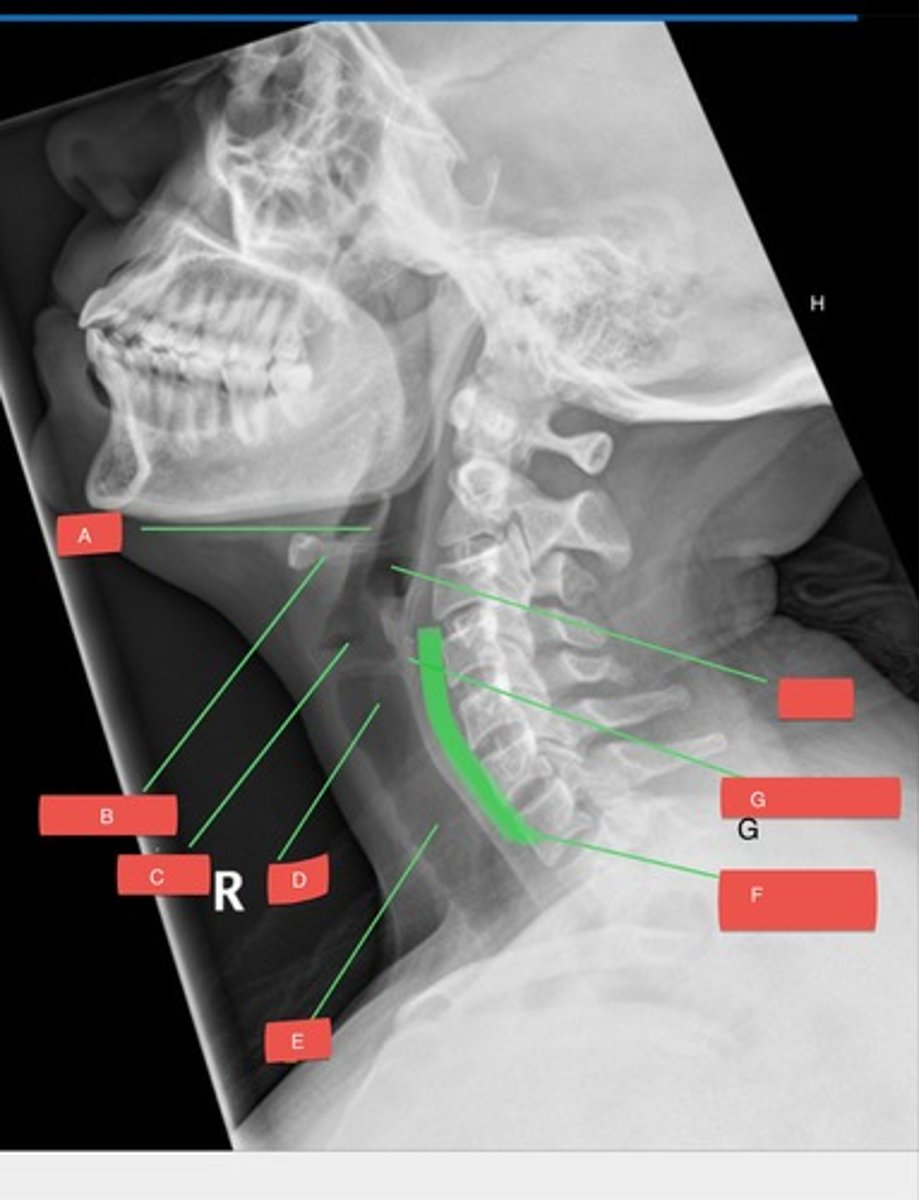
E - trachea
E?
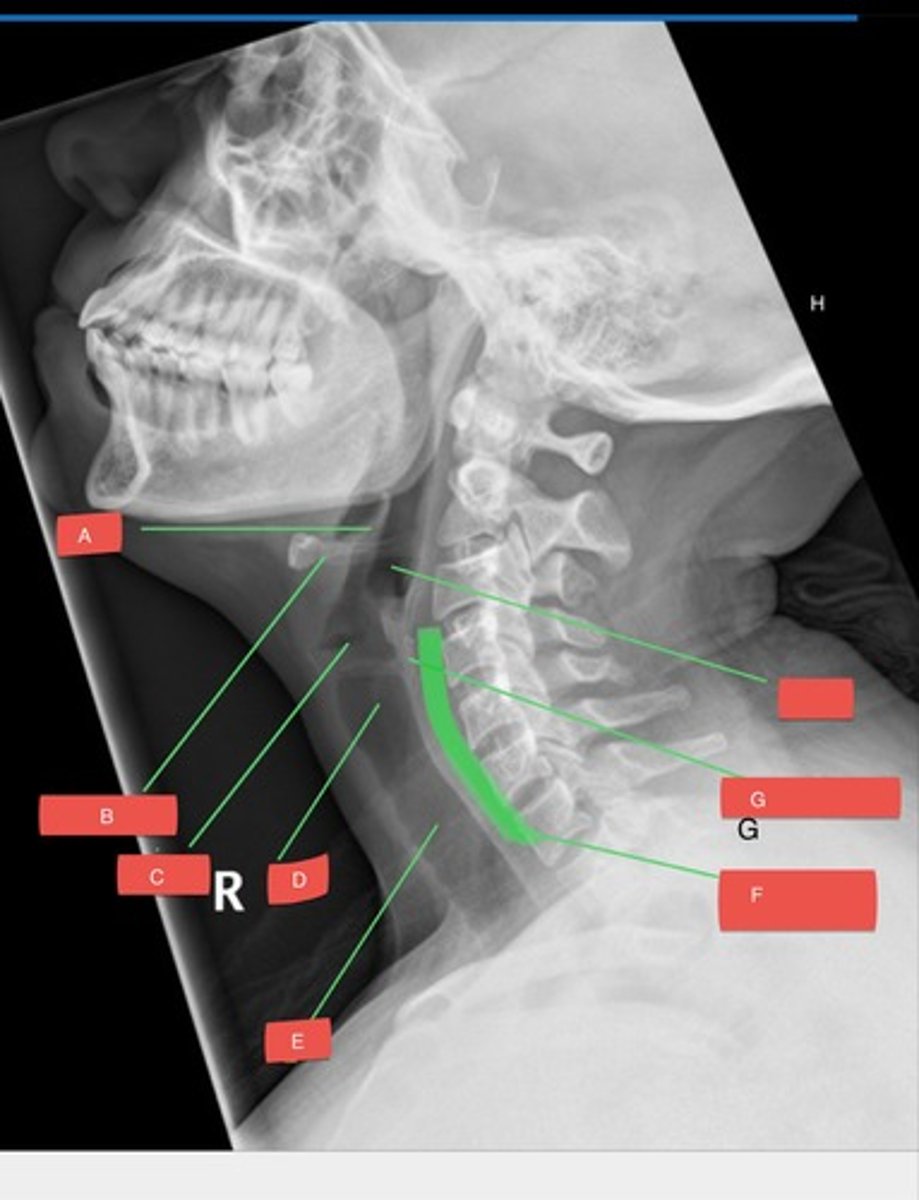
F - prevertebral space
F?
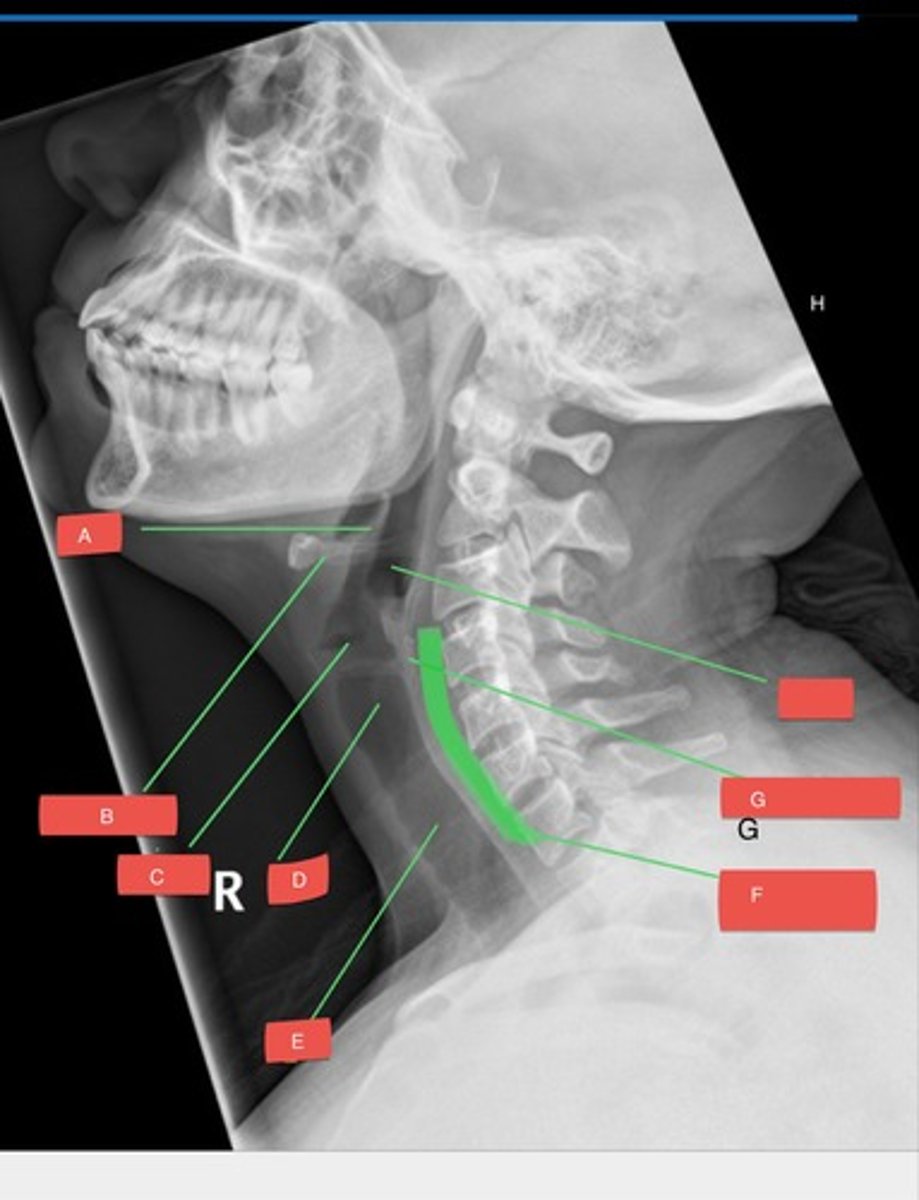
G - cricoid cartilage
G?
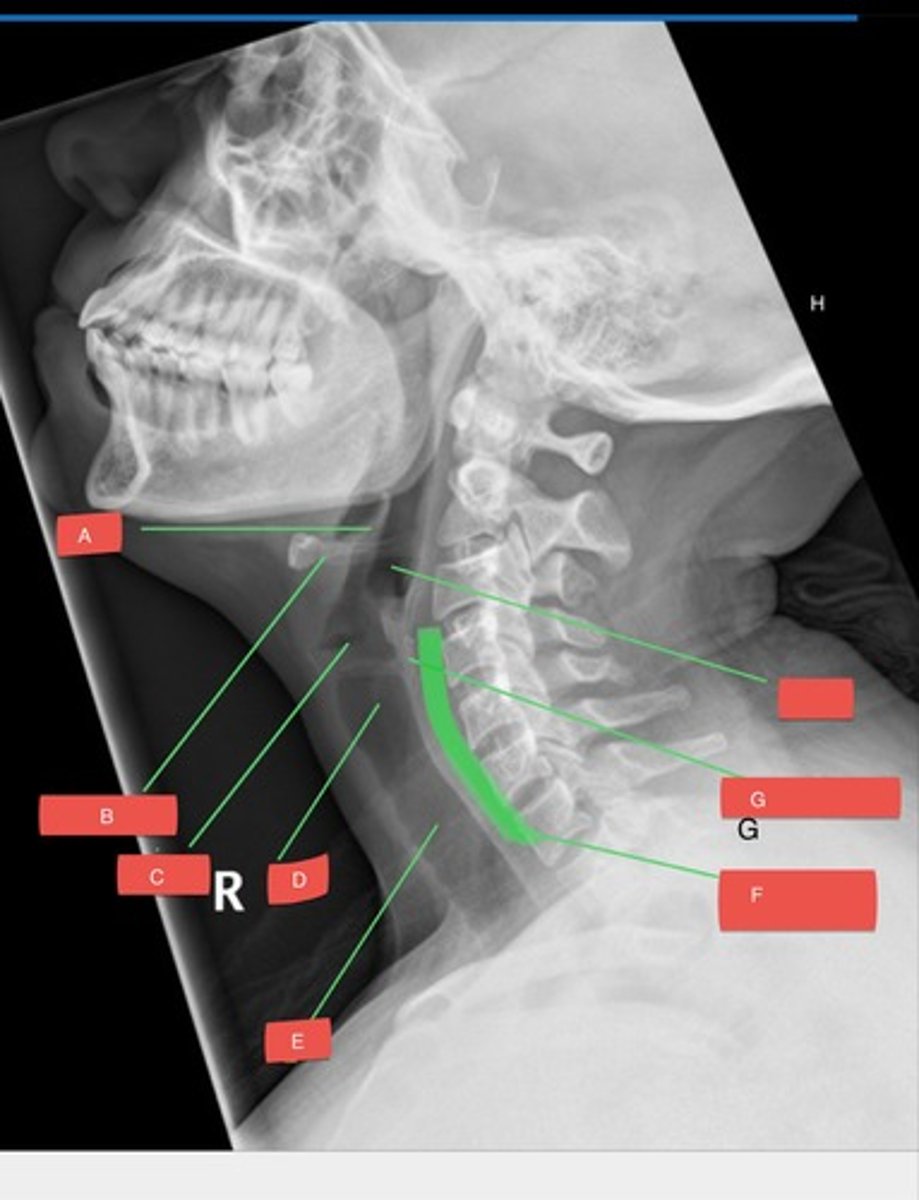
H - hypopharynx
H?