Cytopenias (platelets and neutrophils)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
thrombocytopenia
low platelet
-clotting, bleeding, petechiae, purpura, easy bruising
thrombocytopenia classification
mild: >70
moderate: 20-70
severe: <20
easy bruising: <50
life threatening: <15
Thrombocytopenia: increased destruction of platelets
-Immune thrombocytopenia
-Thrombotic Microangiopathy
-Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
-Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Immune thrombocytopenia pathophysiology
-acquired autoimmune
-IgG bind to glycoproteins on platelets > spleen removes them from circulation
-no glycoprotein IIb/IIIa = no aggregation
-spleen marks them for destruction and removes
ITP in adults can also cause
- T-cell mediated platelets destruction
- impairment of production center of platelets
ITP epidemiology
Primary: idiopathic in most adults
Secondary: due to another disease
-lupus, lymphoma, meds, infections (HIV), vaccine
Immune thrombocytopenia etiology
Children: predominantly post infection, self limited, less chronic disorder, 2-5 IgM
Adults: idiopathic, secondary causes likely, chronic course, 20-30, >60, women IgG
Immune thrombocytopenia symptoms
- musculocutaneous bleedings: epistaxis
- asymptomatic - viral illness
- fatigue
- meds
Immune thrombocytopenia signs
- non-blanching petechial rash or purpura
- nose bleedings, buccal and gingival
Immune thrombocytopenia diagnosis
- only thrombocytopenia with everything else looking normal
Immune thrombocytopenia treatment
- <30000 or significant bleeding should be treated
First line: Prednisone with/o IVIG
Thrombotic Microangiopathy overview
- formation of small blood clots in tiny blood vessels > damage to organs and tissue
-the excessive platelets used to make little clots = decreased amount in circulation
Thrombotic Microangiopathy two main types
TTP: thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
HUS: hemolytic uremic syndrome
TTP pathophysiology
-autoantibodies against ADAMTS-13 > vWF are out of control > call platelets that stick together > microthrombi > decreased platelets willy is holding them all
TTP symptoms and signs
"FAT RN"
-fever
-anemia
-thrombocytopenia
-renal failure
-neurological symptoms
TTP diagnosis
-decreased ADAMTS-13 activity
-hemolytic anemia PBS: schistocytes
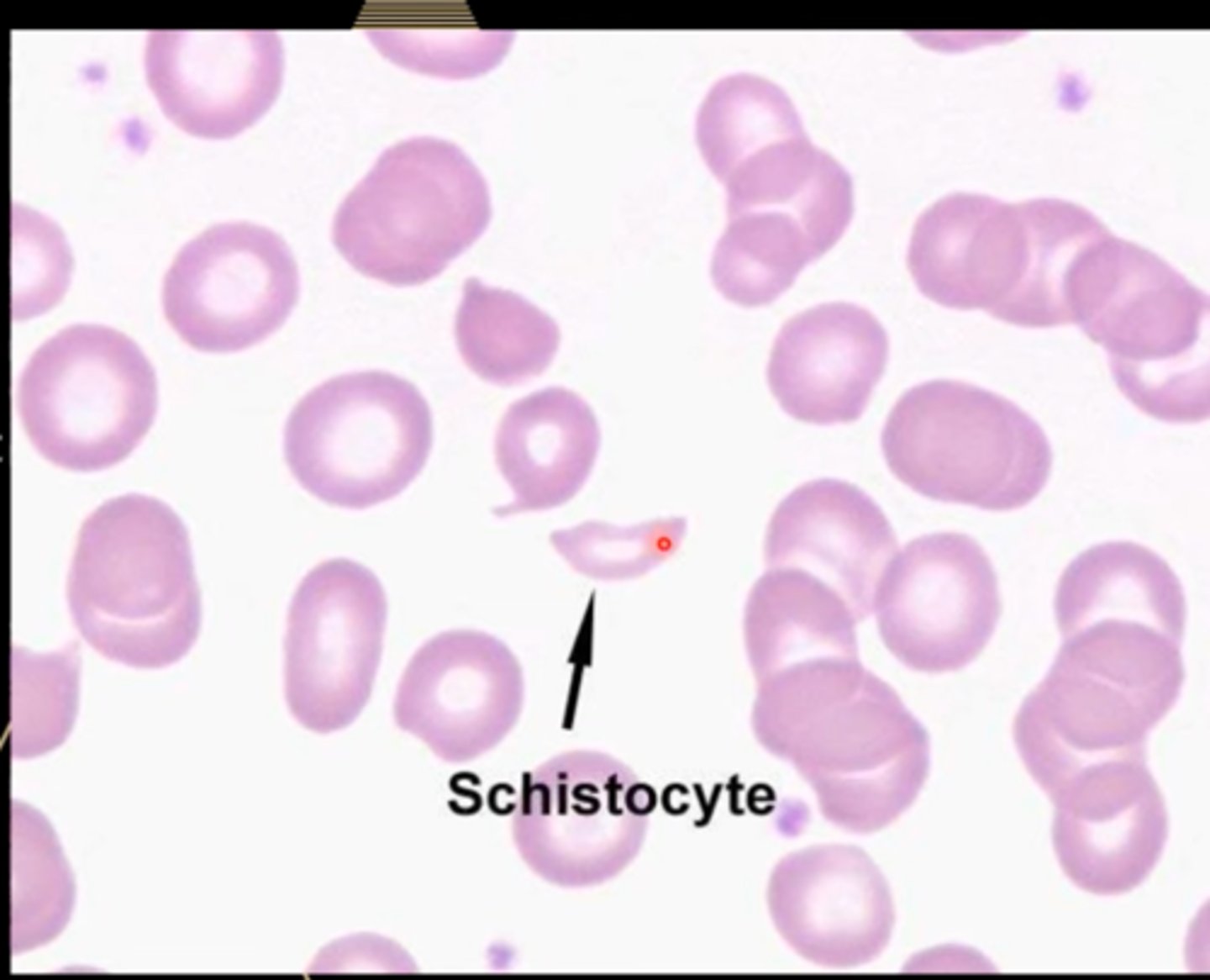
TTP treatment
-plasma exchange (TPE)
If relapse: plasma exchange reinstituted
-rituximab: if ineffective
HUS pathophysiology shiga-toxin
-shiga toxin- mediated HUS > toxin mediated endothelial damage from undercooked meat w E. coli > platelets go to site of damage > less platelets in circulation
HUS pathophysiology complement-mediated
-complement protein issues > genetic mutation leads dysregulation of complement
HUS symptoms and signs
"HUSS"
-hamburger
-urinary symptoms
-shitting
-school age
HUS diagnosis
complement-mediated: mutation of genes encoding complement proteins
Shiga: Positive E. coli, decreased antibodies to shiga toxin
-elevated creatine
HUS: complement- mediated treatment
-plasma exchange (TPE)
-infusion of the anti-complement C5 antibody eculizumab
HUS: Shiga-toxin treatment
-diarrhea associated HUS: supportive care
TIP treatment overview
Plasma exchange (TPE): TTP and complement-mediated
-remove pathogenic factors, replace factors, no more pathology
RBC transfusion: severe anemia
Hemodialysis: severe kidney injury
when can you give TIP patients platelets
- if there is a true life threatening bleeding
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) pathophysiology
-acquired disorder
-IgG antibodies to heparin-platelet factor 4 complex > activated platelets independent of physiological homeostasis > thrombocytopenia and thrombosis
HIP symptoms and signs
-asymptomatic
-thrombosis in 50% of patients 30 days post diagnosis
HIT diagnosis
-new onset thrombocytopenia 50% drop within 5-14 days of initial exposure to heparin
- low 4T score
- PF4 heparin antibody ELISA
-ultrasound
HIT treatment
-discontinue heparin
-DTI until platelets go up then warfarin
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) pathophysiology
- uncontrolled activation of coagulation > depletion of coagulation factors > thrombocytopenia bc platelets are activated instead
Disorders associated with DIC
-know its a very sick patient
-sepsis
-cancer
-trauma
-burns
-pregnancy
DIC symptoms and signs
-BLEEDING: catheter and IV
-thrombosis (trousseau syndrome)
DIC diagnosis
"DDIC"
- D-dimer increase
-Dripping blood
-Ill very
-Clotting got us here
-increased PT and PTT
- decrease fibrinogen levels
DIC treatment
-assess and treat underlying cause
-establish baseline
-transfuse blood products
-follow platelets 4-12hr
-consider heparin if persistent bleeding
Thrombocytopenia: decreased production
-bone marrow failure
-bone marrow infiltration
-chemo/rad
-nutritional deficiency
-cyclic thrombocytopenia
Bone marrow failure
-congenital or acquired
-replacement of normal bone marrow by leukemic cells, plasma cell myeloma, lymphoma or non hemolytic tumors, infection
-abnormalities in cell lines
bone marrow failure diagnosis
-bone marrow biopsy and aspirate
chemotherapy and radiation
- direct toxicity to megakaryocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells or both
nutritional deficiencies
-deficiency in folate
-deficiency in B12
nutritional deficiencies diagnosis
-serum folate
-serum B12
-serum iron
Neutropenia epidemiology
-white blood cell critical to host defense
-release cytokines
-large reserve stored in marrow
neutropenia is defined as
<1800
severe: <500
neutrophil count can be lower in certain pops
consequence of neutropenia
increased risk of infections
neutropenia etiology
-bone marrow: congenital, hairy cell leukemia, myelodysplasia
-non-bone marrow: meds, immune mediated, sepsis
neutropenia symptoms and signs
-stomatitis (inflammation in mouth)
-infection
-cellulitis, pneumonia
-neutropenic fever of unknown origin
neutropenia diagnosis
-CBC w Diff: <1800
-PBS: see forms of neutrophils
-medication review
neutropenia treatment
-identify and discontinue causative drugs
-myeloid growth factors
-condition specific treatment
-febrile neutropenia (fever) : fluoroquinolone
-fungal coverage: fluconazole