Radioactivity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Radioactivity (explanation)
Certain isotopes of elements have an unstable nucleus. The nucleus gives off energy to make itself stable it breaks up, shoots small pieces of itself off, and giving off energy
Radioactivity (definition)
The spontaneous breaking up of unstable nuclei with the emission of one or more types of radiation
History of radioactivity
Henri Bequerel discovered radioactivity. Pierre and Marie Curie were the first to discover radioactive elements (Polonium and Radium)
Alpha particles symbol
a
Alpha particles (explanation)
Consists of 2 protons + 2 neutrons (no electrons). Same as helium nucleus and is shown as 4 He 2 or He+2, due to no electrons. Heavy and slow
What do you need to remember when it comes to alpha particle calculations
Atomic mass number of parent element decreases by 4. Atomic number of parent element decreases by 2. Move back 2 on periodic table.
Draw the symbol for Beta particles in sketchbook
β
Beta particle (properties)
A singular electron, light and fast. shown as 0e-1
Beta particle/emission explanation
Neutron from nucleus turns into a proton + electron. Electron is shot off
What do you need to remember about Beta particles/emission calculations?
Mass number doesn't change. Move forward one space on the Periodic Table.
Radioactivity calculations (notes)
When selecting a symbol for the element, base it off atomic number and not atomic mass number due to isotopes
Gamma Radiation (explanation)
strong form of electromagnetic radiation. Travels at the speed of light. Dangerous due to high energy and speed. No changes to number of protons or electrons
Draw the symbol for gamma rays in sketchbook
γ
Note for penetration
lighter the radiation = more penetration/dangerous
Draw an alpha particle in the sketchbook app
...
Charge (Alpha particle)
positive
Penetrating power (Alpha particle)
Weak (stopped by paper)
Example/Use (Alpha particle)
Americium-241. Used in smoke detectors
Charge (Beta Particle)
negative
Draw a Beta particle in sketchbook
...

Penetrating power (Beta Particle)
Medium (Stopped by 4mm of aluminium)
Example/Use (Beta Particle)
Carbon-14. Used for radiocarbon/carbon-14 dating
Draw gamma ray in sketchbook
...
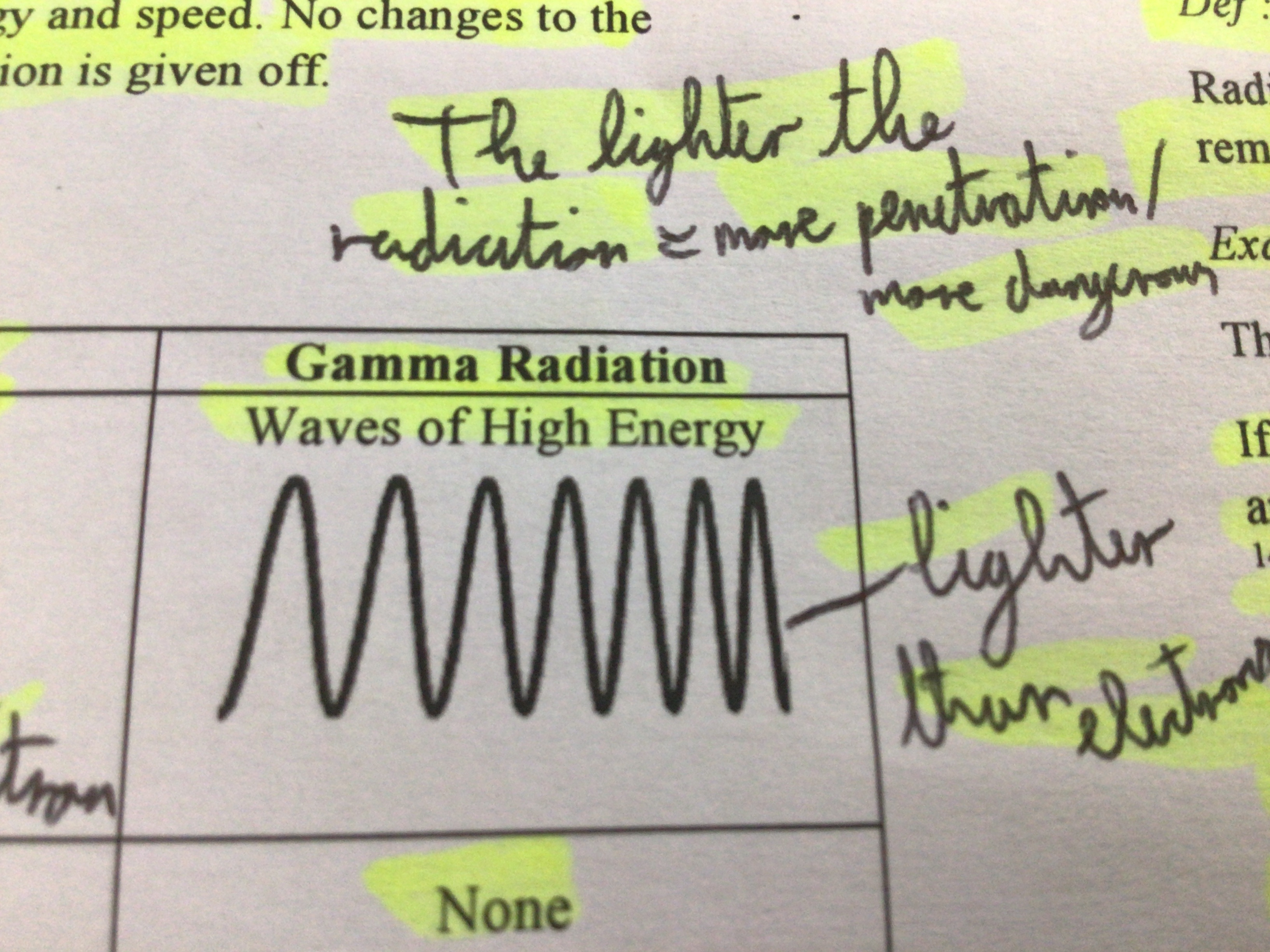
Charge (Gamma Ray)
None
Penetrating power (Gamma Ray)
Strong. (Stopped by several cms of lead)
Example/Use (Gamma Ray)
Cobalt-60. Used in cancer treatment
Features of Chemical Reactions
Involves electrons, No new element formed, No release of nuclear radiation. Bonds broken + formed.
Features of Nuclear Reactions
Involves nucleus. New elements formed. Release of nuclear radiation. No bonds broken + formed
Nuclear Reaction (definition)
A process that alters the composition, structure or energy of an atomic nucleus
Half-life (definition)
The time taken for half the nuclei of a radioactive sample to decay.
Half-life (explanation)
Half of the sample decays after one half life. Half of what remains (1/4 of the original sample) remains after two half lives etc.
Half-life (Example)
Half-life of Carbon-14 is 5730 years. If we start with 10g of Carbon-14, after 5730 years half the sample will have decayed to nitrogen leaving 5g of Carbon-14. After another 5730 years half of that will have decayed leaving 2.5g of Carbon-14
Radiocarbon/Carbon-14 Dating (definition)
A technique used to find the age of an object containing carbon. It is based on the ratio of Carbon-14: Carbon-12 in the object
What is a radioisotope?
Isotope with unstable nucleus
Half-life of a radioisotope (definition)
Time taken for half of the sample to decay.
One risk associated with exposure to alpha radiation
Causes cancer
Why are people who live in a house with americium-241 smoke detectors not at risk from alpha radiation?
Alpha radiation is not very penetrating
Does the americium-241 in a smoke detector need to be replaced often?
No, as it’s half-life is very long