Applied Cognition 1, 2
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is Cognitive Psychology?
The study of thinking, attention, memory, perception, etc.
What is the timeline of events that led to the development of Cognitive Psychology?
Behaviorism was widely accepted. The Cognitive Revolution marked a shift in ideology and research. Leading to the Physiological approach.
What is a key factor of Cognitive Psychology? What does this factor mean?
It is interdisciplinary. It involved different disciplines that overlap, Neuroscience, Philosophy, Psychology, Computer Science, etc
What was Franciscus Donders known for?
Mental chronometry and his reaction time experiment, including simple and choice reaction
What was Wilhelm Wundt known for?
Father of Psychology who has the first Psych Lab and looked at analytical introspection
What was Hermann Helmholtz known for?
Unconscious inference, based on past experiments. The rectangle experiment we did in class
What was Hermann Ebbinghaus known for?
Nonsense syllables experiment and the forgetting curve
What was the Little Albert experiment and who performed it?
John Watson classically conditioned a baby to fear rats
What is Noam Compsky known for?
He believed language was innate and reinforced
What is the idea behind Behaviorism? How does it differ from Cognitive Psychology?
Measure a relationship between an observable stimulus and the environment. NOT DONE
What was the information processing approach? What tech did it compare to?
We receive information input by storing, retrieving, and encoding this information. We are compared to computers.
What is a neuron?
Specialized cells of our nervous system
What is a Node of Ranvier (Ron-vee-air)
French; execrates information on the axon, located in those tiny gaps
What is a dendrite?
Receives signals from other neurons like a sticky hand
What is a cell body?
It contains the nucleus and keeps the cell alive
What is the myelin sheath?
It allows quicker transmission of information, effectively, and increases insulation
What are Schwann cells?
They produce myelin
What is an axon?
The long body that carries signals away from the cell body
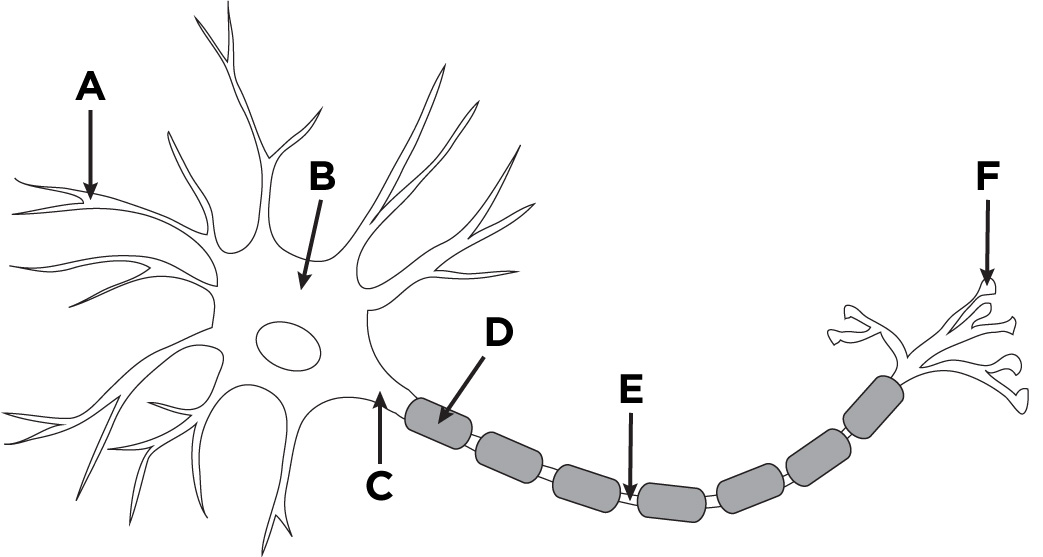
Fill in the blank
A: dendrites B: cell body C: axon D: Schwann cells/myelin sheath E: node of Raniver F: axon terminal
What are sensory receptors and what do they do?
Structures that take information from environment and communicate with the different neurons
What is transduction?
The process of turning chemical energy to electrical energy
What is action potential?
When a neuron sends information down an axon. It happens or it doesn’t.
No size
Rate of firing
When does action potential occurs? What happened when it does?
???
What is a synapse?
Area between the end of axon and next neuron
What affects the speed of mental processing?
The rate of firing or action potential
High rate is fast
Low rate is slow
What’s the difference between excitatory and inhibitory signals in neurons?
Excitatory signals increase the chance a neuron will fire an action potential, while inhibitory signals decrease that chance
What is the relationship between neural processing and neural circuits?
Neurons bind together to form circuits. The more neural circuits we have, the more connections, the faster the processing
What is a neural circuit?
A group of interconnected neurons
How is convergence related to excitatory and inhibitory signals?
Depending on the signal of excitatory or inhibitory, it will communicate an increase or decrease of neurons
What is convergence?
When one neuron receives many signals from many neurons
What is a feature detector?
Neurons that respond to specific features of stimuli
What is a grandmother cell?
It was a belief that there was a 1-1 ratio for neurons - stimuli, which is not true
What is distributive coding?
A neuron stimulates an entire network of information, like the activity done in class
What are the 4 lobes of the brain?
Frontal, Occipital, Temporal, Parietal
What is the Cerebellum?
Controls balance and motor movement
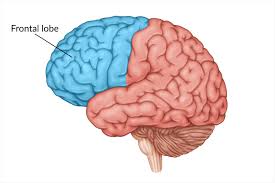
What are the main functions of the frontal lobe?
Higher cognitive functions, motor control, located in front of head
What are the main functions of the temporal lobe?
Hearing, language, memory, located by ears
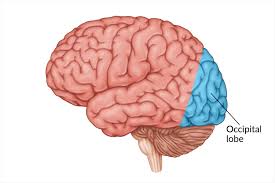
What are the main functions of the occipital (aux-si-puh-tuhl) lobe?
Processing visual info, located back of head
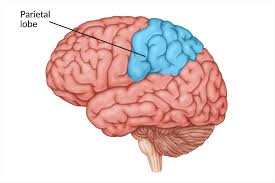
What is the main functions of the parietal (pa-ry-a-tuhl) lobe?
Receives and processes sensory information. located at the topish area of head
What is the cerebral cortex?
The thick outer layer of the brain
What is the localization of function? And how does we know it exists
Organization of the brain into different areas that respond to different functions. If someone is missing the brain part then the function also is missing.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Low dose of radioactive tracker to measure blood flow in brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI
Uses iron in the blood to measure brain activity
What is experience-dependent plasticity?
When neurons adapt to respond best to new environments Basically rewiring
What 2 factors are needed for perception to occur?
Attention and Sensation
What is Top-down processing? How does it from bottom-up processing?
A whole that is familiar vs unfamiliar That is built piece by piece to form a whole
What are the 6 laws of Gestalt Psychology?