Biochemistry - Module 12 2027 Ratio
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
B. Acetyl CoA
The macronutrients are digested and metabolize in this common product before being oxidized to the Kreb cycle.
A. Lactate
B. Acetyl CoA
C. Ketone bodies
D. Free fatty acids
B. Hepatic glycogenolysis
During an overnight fast, which would be the major source of glucose?
A. Ketogenesis
B. Hepatic glycogenolysis
C. Muscle glycogenolysis
D. Proteolysis
B. There is an increase secretion of insulin in response to increase the glucose in the portal blood.
During the fed state, which of the following is true?
A. Resting muscle uses glucose as metabolic fuel
B. There is an increase secretion of insulin in response to increase the glucose in the portal blood.
C. Glucagon acts to increase synthesis of glycogen from glucose
D. Plasma glucose is maintained because of hexokinase in the liver.
A. Liver
Which organ plays a central role in metabolism?
A. Liver
B. Kidneys
C. Brain
D. Muscle
A. Glycolysis
Which of the following metabolic pathways is active in a patient who is just finishing a 100 m dash run?
A. Glycolysis
B. Gluconeogenesis
C. Lipolysis
D. Ketogenesis
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the clinic complaining of fatigue and lightheadedness. The mother is complaining that she is losing weight despite her voracious appetite. Physical examination reveals a thin girl with a BMI of 18 after computing. Which of the following metabolic processes is active in this patient?
A. Fatty acid synthesis
B. Glycogenesis
C. Glycolysis
D. Ketogenesis
A. Glucose will enter the cell and either be used in glycolysis or stored as glycogen.
Which of the following biochemical reactions is occurring in a person who has just taken breakfast?
A. Glucose will enter the cell and either be used in glycolysis or stored as glycogen.
B. Proteins are not catablized after breakfast
C. Free fatty acids are utilized
D. Lactic acid is produced
C. Plasma glucose is being maintained by the process of gluconeogenesis
A castaway diva lived for 3 months without food, but she was able to find water. Which of the following statements is true about the patient’s condition?
A. The muscle can take up glucose for use as a metabolic fuel in response to glucagon
B. There is increased secretion of insulin in response to increased glucose in the portal blood
C. Plasma glucose is being maintained by the process of gluconeogenesis
D. There is increase in the metabolic rate in the fasting state
C. Increased mobilization and oxidation of fats for the use of energy
A 20-year old unconscious female rushed to the ER. Patient is febrile, dry skin, breathing heavily. Lab tests show the RBS of 400, Blood pH of 6.8, and +40 ketonuria, what is the expected reaction of this patient?
A. Deficiency in carnitine
B. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis
C. Increased mobilization and oxidation of fats for the use of energy
Ketone body consumption by brain increases
A scholar medical-student was unable to eat for 3 days due to financial constraints. Which of the following biochemical activities are occurring in the body?
Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
During stress situations, which of the following metabolic processes are stimulated?
B. Translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane is decreased in the muscle and adipose tissue
Biochemical activity almost always present in patients with type II diabetes.
A. Hyperglycemia is present but there is excessive production of insulin from pancreatic beta cells
B. Translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane is decreased in the muscle and adipose tissue
Increase free fatty acids in the circulation
A 45-year-old female consulted you due to difficulty sleeping. The patient is 5 feet tall, and weighs 200 pounds. Lab tests show FBS of 150, triglycerides of 350, and cholesterol of 200. What condition is the patient having?
Liver is always in a gluconeogenic and ketogenic state because the insulin-glucagon ratio cannot increase
A 27-year-old male was rushed to the hospital in a coma, dehydrated. Lab tests show RBS of 300, pH of 7.2, and increased ketonemia. Which of the following biochemical reactions is occurring in this patient?
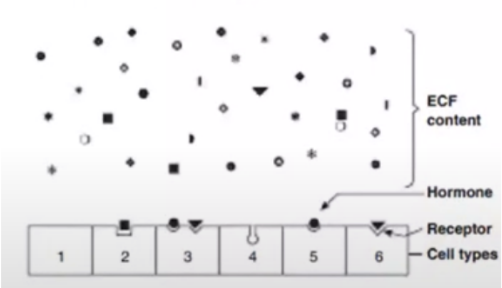
C. It is possible that a cell has no hormone receptor.
The figure below shows the binding of the molecules from the extracellular fluid (ECF) to the cell receptor. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Binding of a specific cell receptor and hormone can produce a biologic response at low concentration.
B. Hormones can bind to protein receptors regardless of their structures.
C. It is possible that a cell has no hormone receptor.
D. Signal transduction may occur even if there is no binding of the hormone with the receptor.
A. Cholesterol
Which of the following compounds is used as the starting material in the biosynthesis of estriol and estrone?
A. Cholesterol
B. Tyrosine
C. Iodine
D. Arachidonic acid
D. DHEA
Which is the primary precursor of natural estrogen?
A. ACTH
B. DHT
C. OHSD
D. DHEA
B. Progesterone
Based on the steroidogenesis pathway, which can be
considered as precursor of testosterone?
A. Aldosterone
B. Progesterone
C. Estrone
D. DHT
A. Decrease in testosterone production
Which is a possible result of the inhibition of 17B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17B-OHSD) in the testicular steroidogenesis?
A. Decrease in testosterone production
B. No significant effect
C. Increase in DHT
D. Apoptosis of Leydig cells
C. Estradiol
In postmenopausal women, circulating testosterone is a precursor for which of the following steroids?
A. Cortisol
B. Androstenedione
C. Estradiol
D. Dehydroepiandrosterone
D. By addition of methyl group to nitrogen atom
How does the enzyme PNMT convert epinephrine to adrenaline?
A. By addition of -OH to the side chain
B. By addition of -OH to the ring hydroxylation
C. By removal of -COOH
D. By addition of methyl group to nitrogen atom
A. Prevents oxidation of iodide
How do thiourea drugs work as a treatment for hyperthyroidism?
A. Prevents oxidation of iodide
B. Activates thyroperoxidase
C. Increases diiodotyrosine and monoiodotyrosine
D. Deactivates thyroglobulin
B. To control its synthesis
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is synthesized from prepropressophysin, a large precursor protein. Which is a plausible reason why our body does not make it from smaller molecules?
A. Due to structural purposes
B. To control its synthesis
A. Several days
How long is insulin supply stored in the cell?
A. Several days
B. Several hours
C. Several weeks
D. None
B. Cytosol
Where does a steroid hormone bind the receptor?
A. Cell membrane
B. Cytosol
C. Nucleus
D. Nucleus membrane
A. By binding to cell receptors and the use of second messengers to reach the target organ
How do polypeptide hormones initiate a response?
A. By binding to cell receptors and the use of second messengers to reach the target organ
B. By penetrating the cell membranes and interaction with the nucleus
C. By forming complexes with cofactors which is transported in the bloodstream
D. By catabolism to produce energy
A. The N-terminal chain is extracellular and C- terminal chain is intracellular
Which of the following statements is true about G-protein couple receptors?
A. The N-terminal chain is extracellular and C- terminal chain is intracellular
B. It contains 5-transmembrane hydrophobic sections
C. There are more extracellular loops that intracellular loops
D. The binding region for G-protein involves 2 extracellular loops
C. They interact with heterotrimeric guanine binding proteins
Which of the following describes G-protein coupled receptors?
A. They catalyze the production of cAMP
B. They catalyze the production of cGMP
C. They interact with heterotrimeric guanine binding proteins
D. They remove cAMP from the cytoplasm.
D. Receptor tyrosine kinases
Which of the following plasma membrane receptors activate signaling pathways usually by forming molecular dimers that result in protein phosphorylation reactions upon binding of their specific ligand?
A. Steroid hormone receptors
B. Ligand-ion gated channels
C. G protein-coupled receptors
D. Receptor tyrosine kinases
B. Type II serine/threonine kinase receptor
What does transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) attach in the activation of serine threonine kinase receptor?
A. SMAD protein
B. Type II serine/threonine kinase receptor
C. Type I serine/threonine kinase receptor
A. Inhibition of cGMP phosphodiesterase
Activation of guanylyl cyclase considerably increases the amount of cGMP. Which of the following can also cause an increase in the cGMP concentration and is considered a vasodilator?
A. Inhibition of cGMP phosphodiesterase
B. Interaction with inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate
C. Activation of glycogenolysis
D. Release of calcitonin
D. It is translocated to the nucleus to enable transcription of a specific gene
After binding of the ligand to cytokine receptors in the presence of JAK and STAT, what happens to the phosphorylated STAT?
A. This leads to the activation of interleukin-2 (IL-2)
B. It dimerizes and reacts with GTP
C. This stimulates the dephosphorylation of subsequent proteins in the signaling pathway
D. It is translocated to the nucleus to enable transcription of a specific gene
B. Mutation of gene
Aberrant kinase activity is one of the drivers of cancer progression. Which of the following could cause an unusual increase in kinase activity?
A. Presence of cofactors
B. Mutation of gene
C. An increase in metabolism
D. Glycogenolysis
A. Cell development
A phosphorylated protein via the action of a protein kinase is able to attract other proteins. This is to promote certain cell processes. Which of the following can be affected by an abnormal protein kinase activity?
A. Cell development
B. Osmosis
C. Cell transport
D. Cell diffusion