The Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nervous System Overview
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the three overlapping functions of the nervous system?
1. Sensory input: Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes. 2. Integration: Processing and interpretation of sensory input. 3. Motor output: Activation of effector organs (muscles and glands) produces a response.
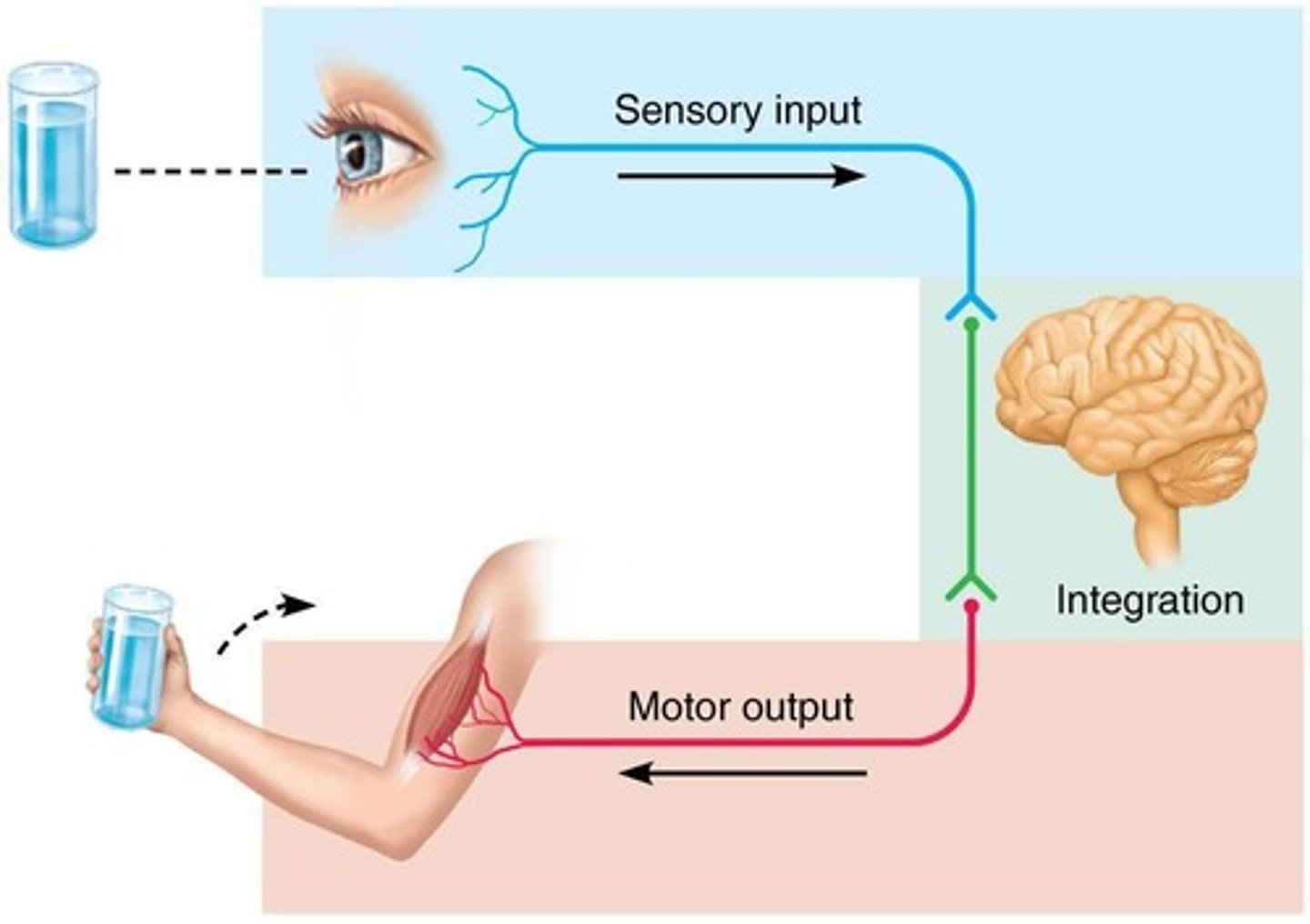
What is the role of afferent and efferent divisions in the nervous system?
Afferent division carries sensory information towards the central nervous system (CNS), while the efferent division carries motor information out of the CNS.
What structures protect the brain?
1. Meninges & Bone 2. Cerebral Spinal Fluid 3. The Blood Brain Barrier.
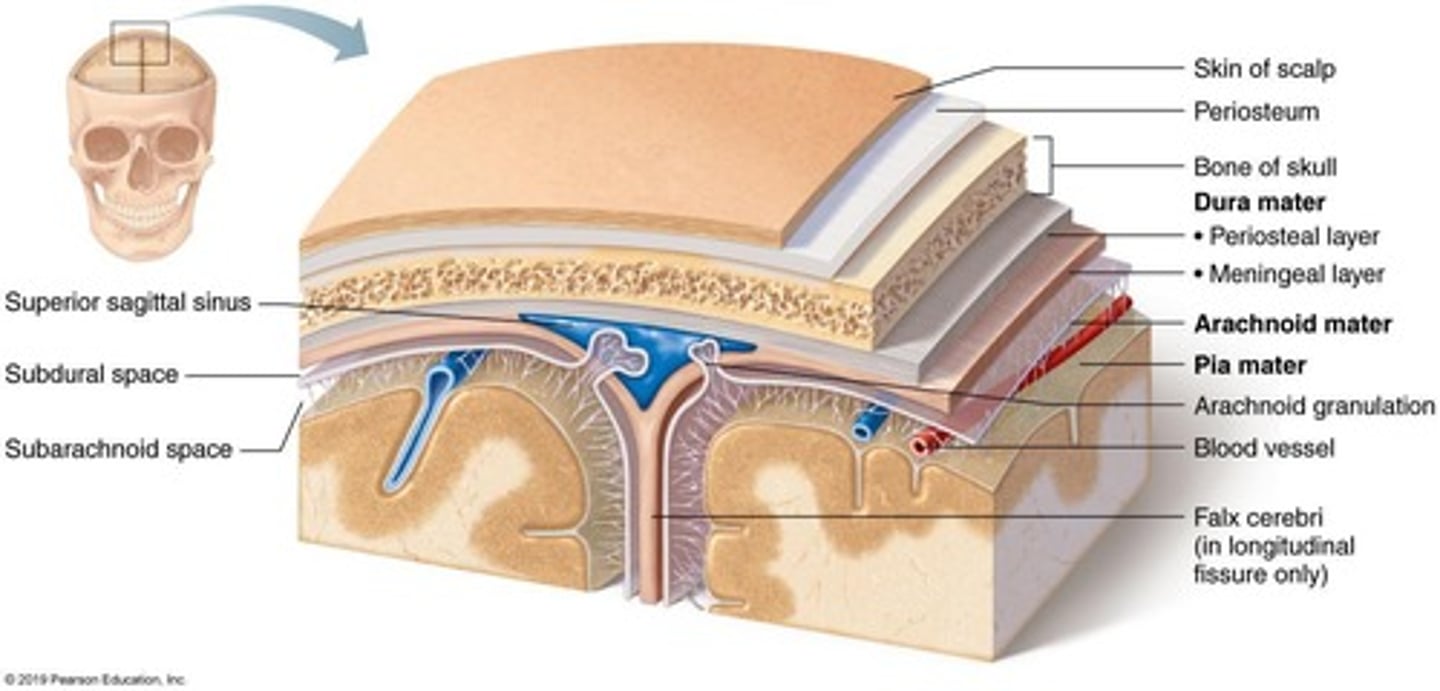
What are the layers of the meninges?
1. Dura mater: Superficial, double-layered. 2. Arachnoid mater: Middle layer with trabeculae. 3. Pia mater: Deep layer that follows the contours of the brain.
What is the function of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)?
CSF provides physical and chemical protection, carries oxygen, glucose, and other substances from the blood to nervous tissue cells.
Where does the spinal cord begin and end?
The spinal cord starts at the medulla and ends at L1 or L2 at the conus medullaris.
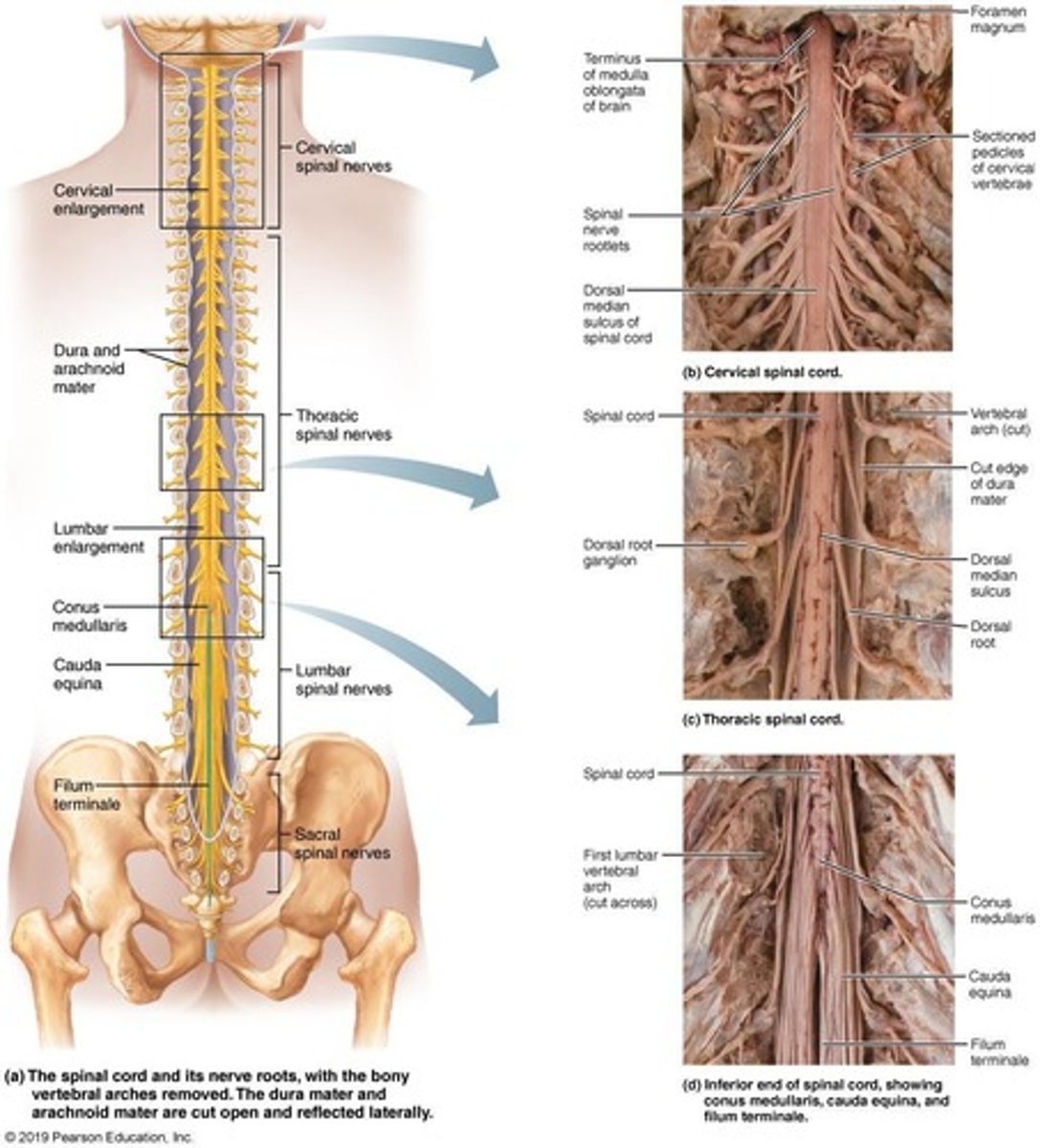
What is the function of the filum terminale?
The filum terminale anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx.
What is the cauda equina?
The cauda equina is a bundle of spinal nerves that extends to the base of the vertebrae.
What are the cervical and lumbar enlargements?
Cervical and lumbar enlargements house nerves that service the upper and lower limbs, respectively.
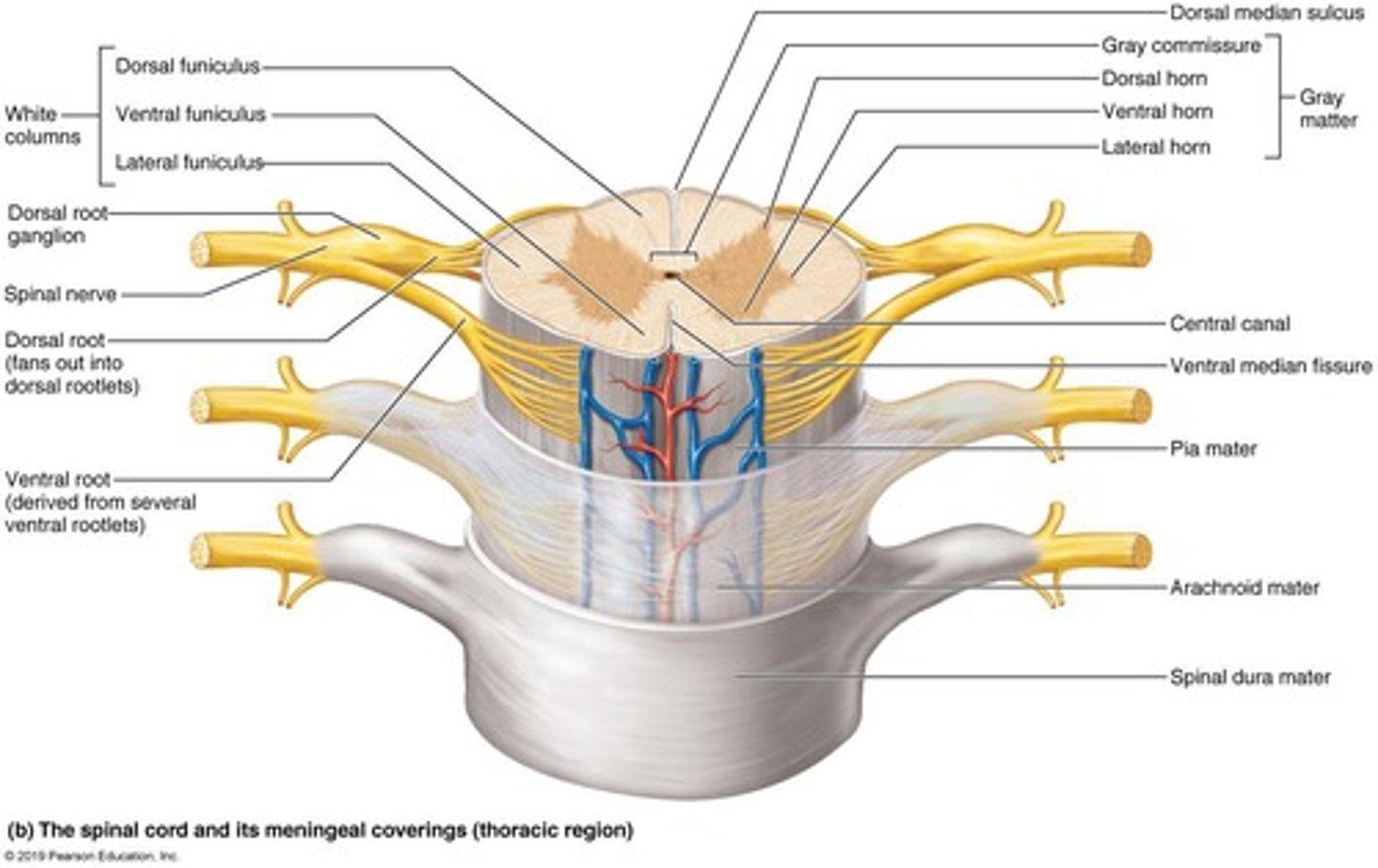
What is the structure of the spinal cord in terms of grey and white matter?
The spinal cord has grey matter on the inside and white matter on the outside, with ascending and descending pathways connecting the brain and body.

What are the roles of the dorsal and ventral roots in the spinal cord?
The dorsal root carries sensory (afferent) input to the spinal cord, while the ventral root carries motor (efferent) output from the spinal cord.
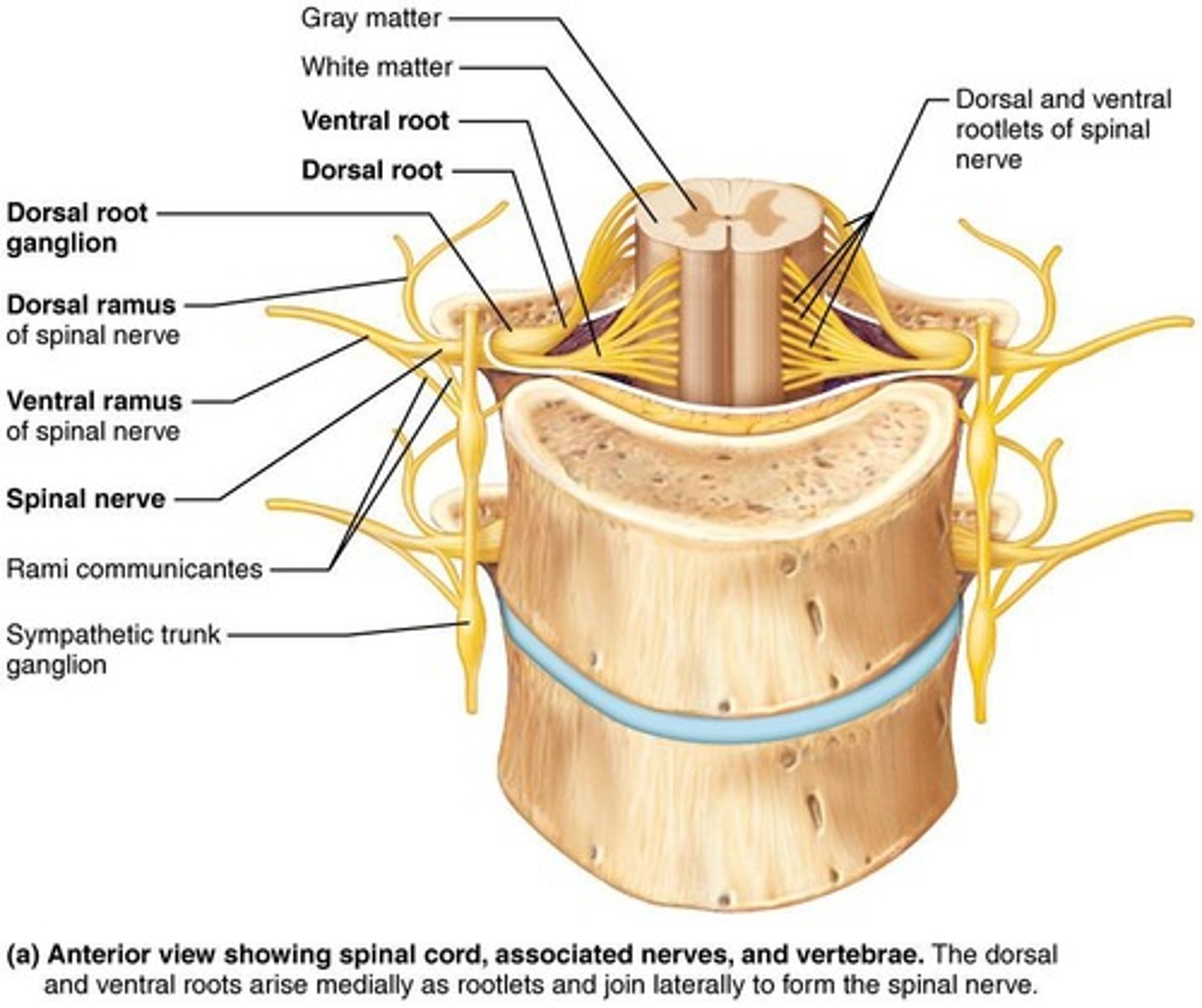
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there, and how are they classified?
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, classified as: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal.
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral rami?
Dorsal rami innervate the skin and back muscles, while ventral rami innervate the rest of the trunk and limbs.
What are nerve plexuses, and what are the four main types?
Nerve plexuses are branching networks of nerves formed by ventral rami. The four main types are: Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar, and Sacral.
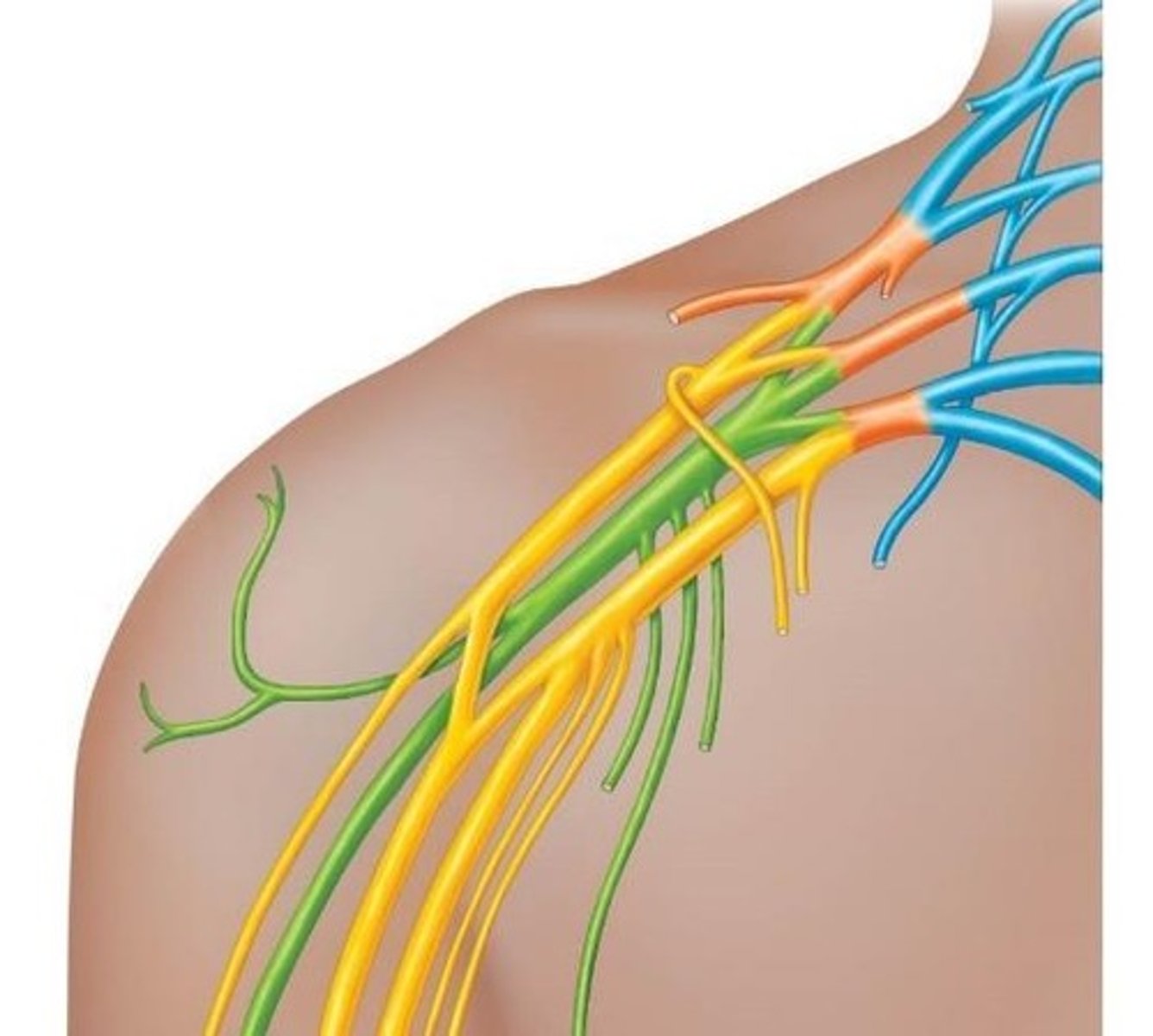
What is the significance of overlapping territories in nerve plexuses?
Overlapping territories ensure that each part of the skin/muscle receives input from more than one spinal nerve, which is important if spinal nerves are damaged.
What are cranial nerves, and how many pairs are there?
Cranial nerves originate from the brain and there are 12 pairs, which can be sensory, motor, or mixed.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is involved in involuntary bodily functions, including the regulation of internal organs.
What is the function of the enteric nervous system?
The enteric nervous system is involved in the regulation of digestion.
What is the epidural space?
The epidural space is the area between the dura mater and vertebrae, containing fat and a network of veins.
What is the purpose of an epidural injection?
Epidural injections are used for pain relief by injecting into the epidural space.
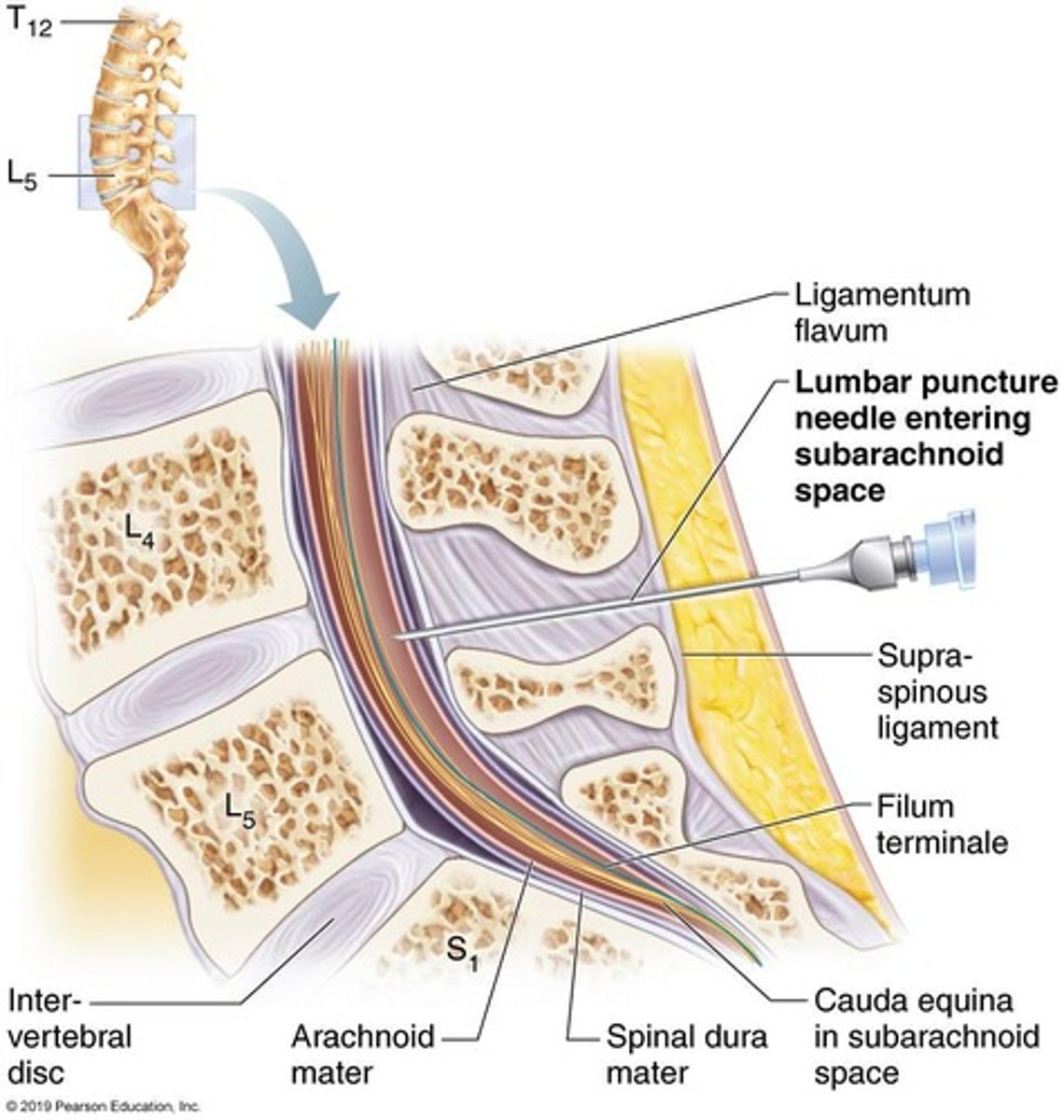
What is a lumbar puncture used for?
A lumbar puncture penetrates the dura to access CSF for pathological testing or drug administration.
What are the functions of the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass through.
What is the central canal of the spinal cord?
The central canal runs the length of the spinal cord and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What are the functions of the dorsal horn, lateral horn, and ventral horn in the spinal cord?
The dorsal horn processes sensory information, the lateral horn contains autonomic neurons, and the ventral horn contains motor neurons.
What is the significance of the dura mater's structure?
The dura mater has a double layer, with the outer layer fused to the bone and the inner layer forming dural venous sinuses that collect venous blood.