Biochemistry Lab#4 (Protein Denaturation) Midterm Reviewer
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
protein
are polymers of amino acids.
Denaturation
is the process of changing a protein’s conformation, either temporarily or permanently, by disrupting its stabilizing forces.
Biuret test
test for peptide bonds
Biuret test positive result
violet or purple color indicates the presence of peptide bonds
Biuret test negative result
no color change or blue color persists
coagulation test
using ethanol exploits the property of proteins to precipitate out of solution when ethanol is added.
ethanol
reduces the solubility of proteins in water, causing them to denature and aggregate, leading to visible precipitation.
coagulation test positive result (protein present)
Cloudiness or precipitate formation indicates proteins have coagulated.
coagulation test negative result (no protein present)
Clear solution with no precipitate indicates the absence of proteins.
Heller’s test
is based on the principle of protein denaturation and coagulation in the presence of a strong acid.
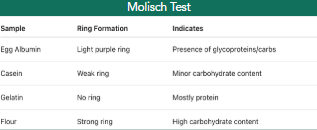
Molisch test
(carbohydrates presence)
molisch test
relies on dehydration and furfural formation, whereas protein detection tests involve protein denaturation and complex formation with specific reagents.
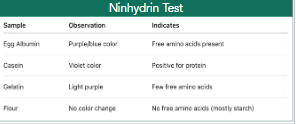
Ninhydrin test
(free amino group detection)
nihydrin test positive result
blue or purple: presence of free amino groups
nihydrin test negative result
pale or no change: lack of free amino acids
Nihydrin test
is a valuable qualitative method for detecting proteins and amino acids based on the reaction between ninhydrin and primary amino groups.
Litmus in Nitrogen test
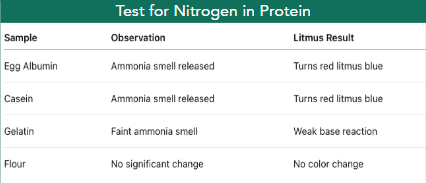
Detects released ammonia; turns red litmus blue, indicating a basic gas from protein breakdown.
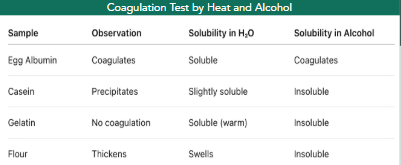
coagulation by heat/alcohol
Heat and alcohol disrupt protein structure, causing denaturation and aggregation due to loss of solubility.
ammonium sulfate use
high salt concentration decreases protein solubility, allowing separation based on solubility.
Nihydrin test
Reacts with free amino groups to produce a purple/blue color; confirms presence of amino acids or protein hydrolysis.
Biuret test
Changes from blue to purple because it detects peptide bonds; the copper ions form complexes with the nitrogen atoms in the bonds.
Biuret test
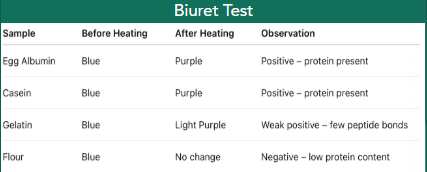
test for nitrogen in protein result
Coagulation test by heat and alcohol result
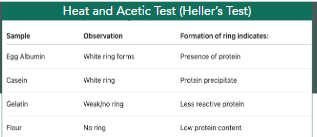
Heat and Acetic test (heller’s test) result
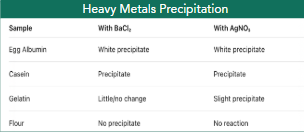
Heavy metals precipitation result
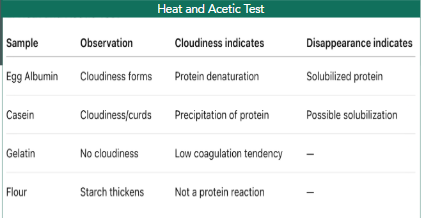
heat and Acetic test result
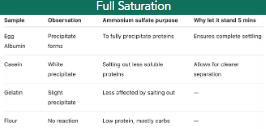
full saturation result
Half saturation result

Molisch test result
NIhydrin test result
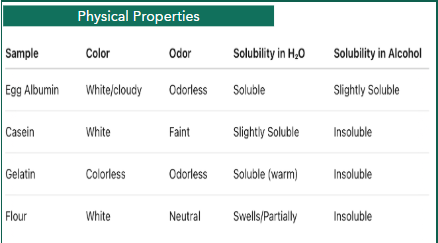
Solubility in H2O and alcohol result