Chemistry Honors Wilson Chapter 3 & 4
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element.
Dalton's (Billiard Ball) model
The atom is a solid, indivisible sphere; atoms of different elements differ in mass and properties.
Thomson's (Plum Pudding) model
The atom is a positively charged "pudding" with negatively charged electrons embedded throughout.
Rutherford's (Nuclear) model
The atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space where electrons move.
Bohr's (Planetary) model
Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels (like planets orbiting the sun).
Quantum Mechanical model
Electrons exist in probability regions called orbitals, not fixed paths; their positions are described by wave functions.
Thomson's Cathode Ray Tube experiment
It revealed the existence of electrons — negatively charged particles smaller than atoms.
Millikan's Oil Drop experiment
It measured the charge and mass of the electron.
Rutherford's Gold Foil experiment
Most of an atom is empty space, with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus.
Hydrogen Emission Spectrum
Electrons occupy specific energy levels; light is emitted or absorbed when electrons change levels.
Electron movement and energy
When electrons absorb energy, they move to higher energy levels; when they fall back, they release energy as light.
Electromagnetic spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays, arranged by wavelength or frequency.
Subatomic particle locations
Proton: nucleus; Neutron: nucleus; Electron: electron cloud.
Mass and charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons
Proton: +1 charge, ≈1 amu; Neutron: 0 charge, ≈1 amu; Electron: -1 charge, ≈0 amu.
Atomic number, mass number, and neutrons relationship
Mass number = protons + neutrons; Atomic number = protons; Neutrons = mass number - atomic number.
Finding number of electrons in an ion
Electrons = protons - charge.
Calculating average atomic mass
Multiply each isotope's mass by its percent abundance (as a decimal) and add them together: (mass₁ × %₁) + (mass₂ × %₂) + ...
Alpha, beta, gamma, and positron radiation
Alpha (α): +2 charge, heavy (4 amu); Beta (β⁻): -1 charge, tiny mass; Gamma (γ): no charge, no mass (energy only); Positron (β⁺): +1 charge, tiny mass.
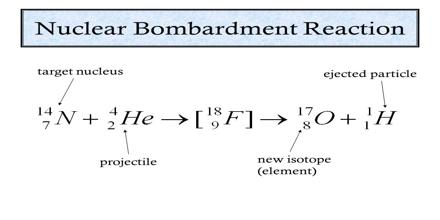
Balancing a nuclear equation
Both the mass numbers and atomic numbers on each side of the equation.
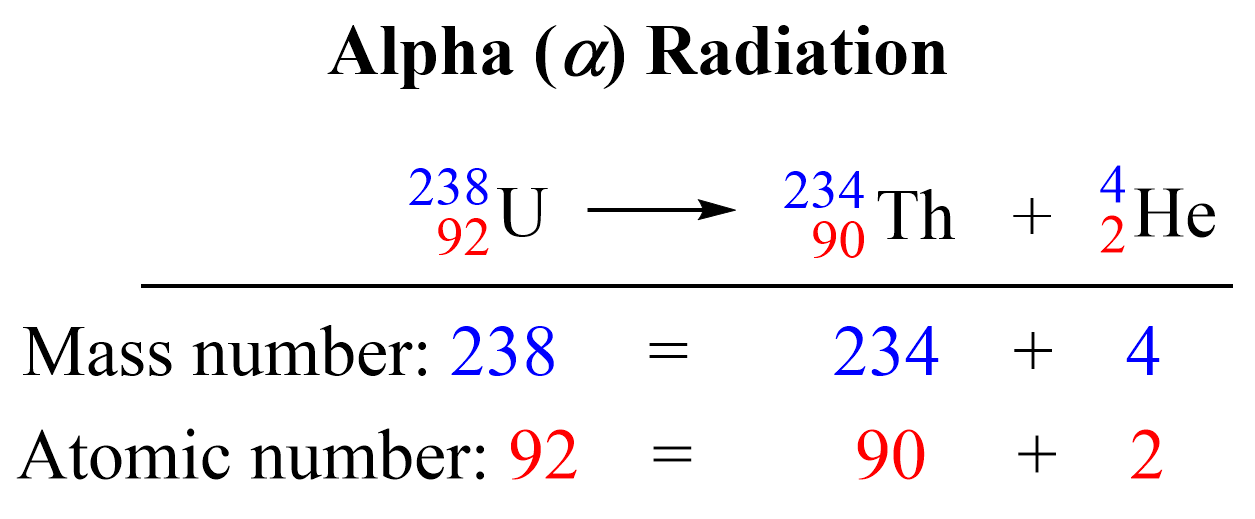
Nuclear equation for alpha decay of Uranium-238
²³⁸₉₂U → ⁴₂He + ²³⁴₉₀Th
Factors influencing nuclear stability
Strong nuclear force, neutron-to-proton (N/P) ratio, and band of stability.
When alpha decay occurs
In very heavy nuclei that need to reduce mass and charge.
When beta decay (β⁻) occurs
When a nucleus has too many neutrons; a neutron turns into a proton and emits an electron.
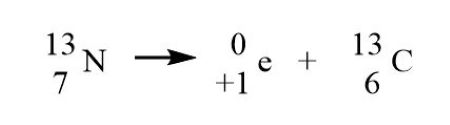
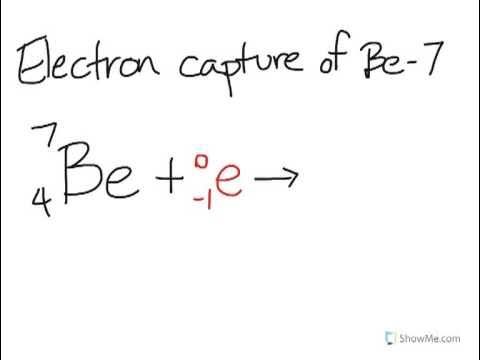
When positron emission (β⁺) or electron capture occurs
When a nucleus has too many protons; a proton changes to a neutron.
Critical mass
The minimum amount of fissionable material needed to sustain a nuclear chain reaction.
Subcritical, critical, and supercritical conditions
Subcritical: reaction dies out; Critical: reaction sustains itself; Supercritical: reaction grows uncontrollably.
How nuclear reactors generate electricity
Through fission — splitting large nuclei (like U-235) to release energy that heats water and produces steam to spin turbines.
Safety measures controlling nuclear reactions
Control rods absorb excess neutrons; coolant removes heat; containment structures prevent radiation leaks.
Half-life
The time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay.
Ways to solve half-life problems
1. Chart method: halve the amount after each half-life. 2. Equation: A = A₀(½)^(t/t₁/₂).
alpha decay nuclear equation
beta decay nuclear equation
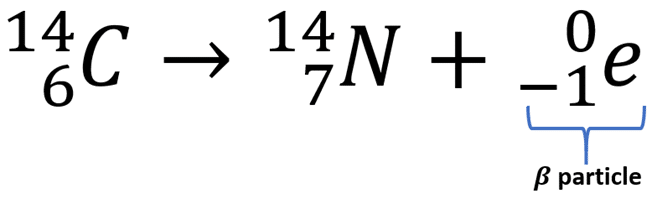
positron emission nuclear equation
electron capture nuclear equation
bombardment nuclear equation