Biology Week 1 Gathering
1/503
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
504 Terms
What is iodine essential for
thryoid gland (for T3 and T4)
What can cross the membrane without a transporter
cortisol
what has both endo and exocrine functions
Pancreas
where are steroid hormones made in the body
adrenal cortex or gonads
how does estrogen attack certain cells
freely corsses, binds to nuclear receptors and bind to DNA sequences
what does the hypothalamus connect to
Post. Pituitary
what hormones does the hypothalamus make
oxytocin and antidueritic
what does antidiuretic or ADH do
increases water perm. of collecting ducts
what can bind a hormone to secondary messenger
G protein coupled reactor
what is a secondary messenger in signal transduction
Calcium
What organ lowers blood calcium levels
Thyroid
What cells release calcitonin
C cells
what does calcitonin do
decreases osteoblast activity
What organ decreases blood glucose concentrations
Pancreas
What does glucagon do
released by alpha due to low glucose. It raises glucose levels
What does insulin do
released by beta due to high glucose. decreases glucose levels.
Somatostatin
released by delta cells and stops growth hormone
what hormones are water soluble
peptide
What does IP3 do
Increases cystolic calcium levels which leads to many enzymes activating
what does prolactin do
stim. milk production
what hormones are water soluble
epinephrine, insulin, and HGH
what hormones are lipid soluble
cortisol, aldosterone, and sex hormones
what hormones does the anterior pituatary gland make
FLAT PiG. FSH, LH, TSH, Prolactin, Growth, and Adrenocorti…
what hormones does the post. pituitary make
stores and releases antidueretic and oxytocin
what causes goiter
iodine dificiency
what hormone increases cellular metabolism levels
thyroxine
what organ makes epinephrine
adrenal medulla
what adrenal cortex hormone increases blood pressure
aldosterone
what does vasopressin target
kidneys (increases water reabsorption)
What does GRH target
anterior pituatary (releases LH and FSH)
what is ACTH released by
anterior pit. (targets adrenal and releases cortisol)
what are the diff. between the ant and post pituitary
the anterior is connected to hypothalamus through blood vessels while posterios is connected through nuerons
what makes a hormone that increases blood calcium levels
parathyroid
what hormones increases blood glucose levels
cortisol
what hormones does the post pit make
vaso and oxytocin
what sturcure makes steroids
adrenal cortex
how do distant cells communicate
hormones
how is the production of test. stimulated
LH targets the Leydig Cells
what hormone stim. another to release another hromone
ACTH
what is correlated with the adrenal medulla
sympathetic nervous system
what cna explain how fish gills absorb oxygrn from water
countercurrent exchange
what is at the bottom of the thoriac cavity
diaphragm
how is reparation controlled
controlled by medulla oblongata and pons of brainstem
what causes a respiratory center response
accumulation of carbon dioxide
what decreases O2 binding
high CO2, low pH, 23 BPG, High temp
what increases O2 binding
low CO2, high pH, fetal hemo, and low temp
how to remeber oxygen curve
CADET, FACE RIGHT! - increase in cadet means it will shfift to the right
what is a major intracellular buffer in humans
phosphate (regulate fluid pH)
when biocarbonate diffuses out, what enters to balance the charge
Chlorine (Cl)
what is the passage of air
trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
what does surfactant do in the resp. system
reduces surface tension
what do goblet cells do
secret mucus to trap debris
what do ciliated epith. cells do
move mucus and debris away from the lungs
what is the response to metabolic acidosis
breathing increases
how many lobes of the lungs
left 2 right three
what is cooperativity
the more O2 binds, the easier it becomes
how does Co2 go from tissues to blood to lungs
simple diffusion
what is the H zone.
The middle part of a muscle.
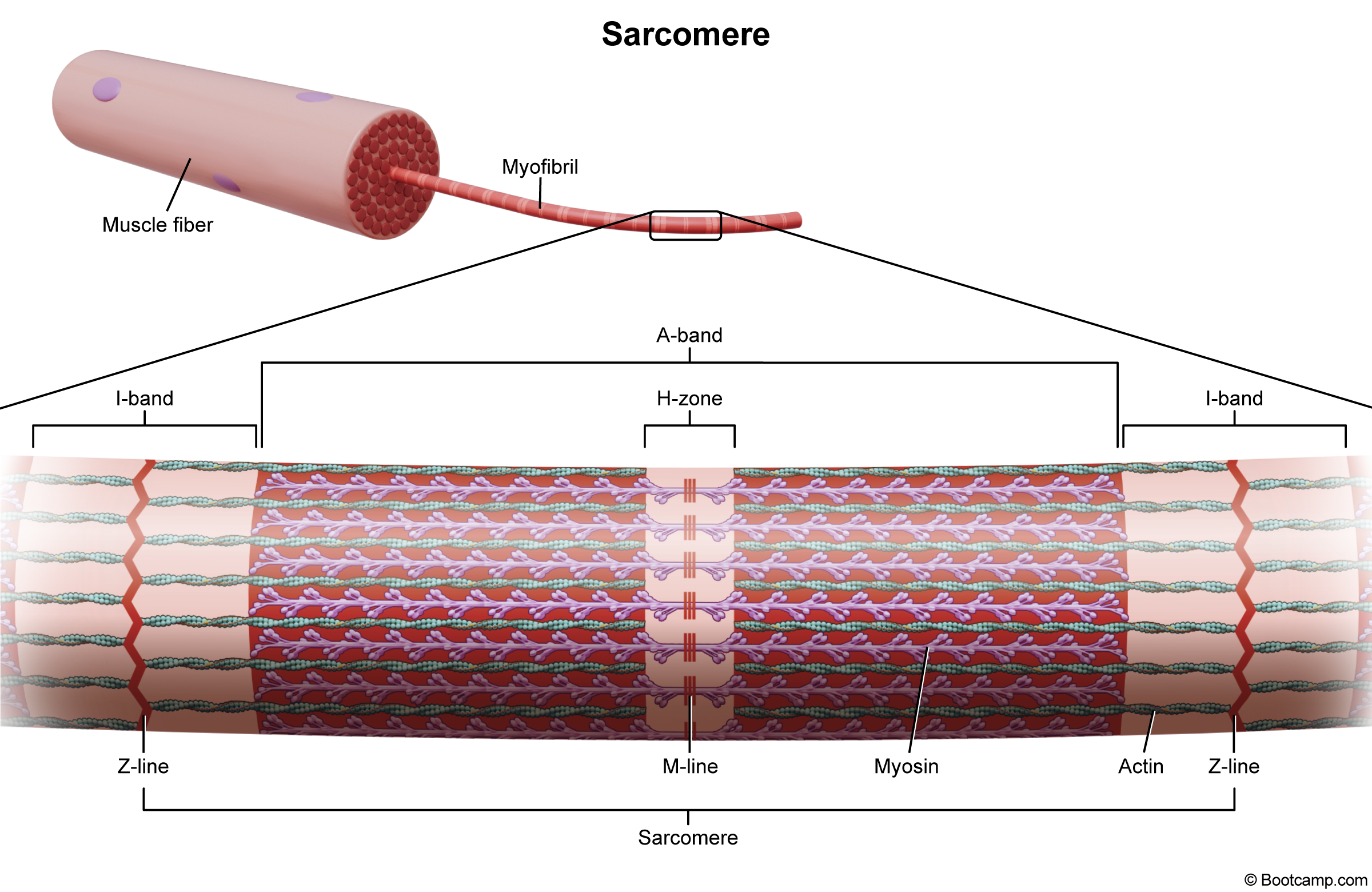
what are the breakdowns of a muscle
muscle fibet - myofibril - sacromere
what is the outer part of a sacromore
I band and has a Z line
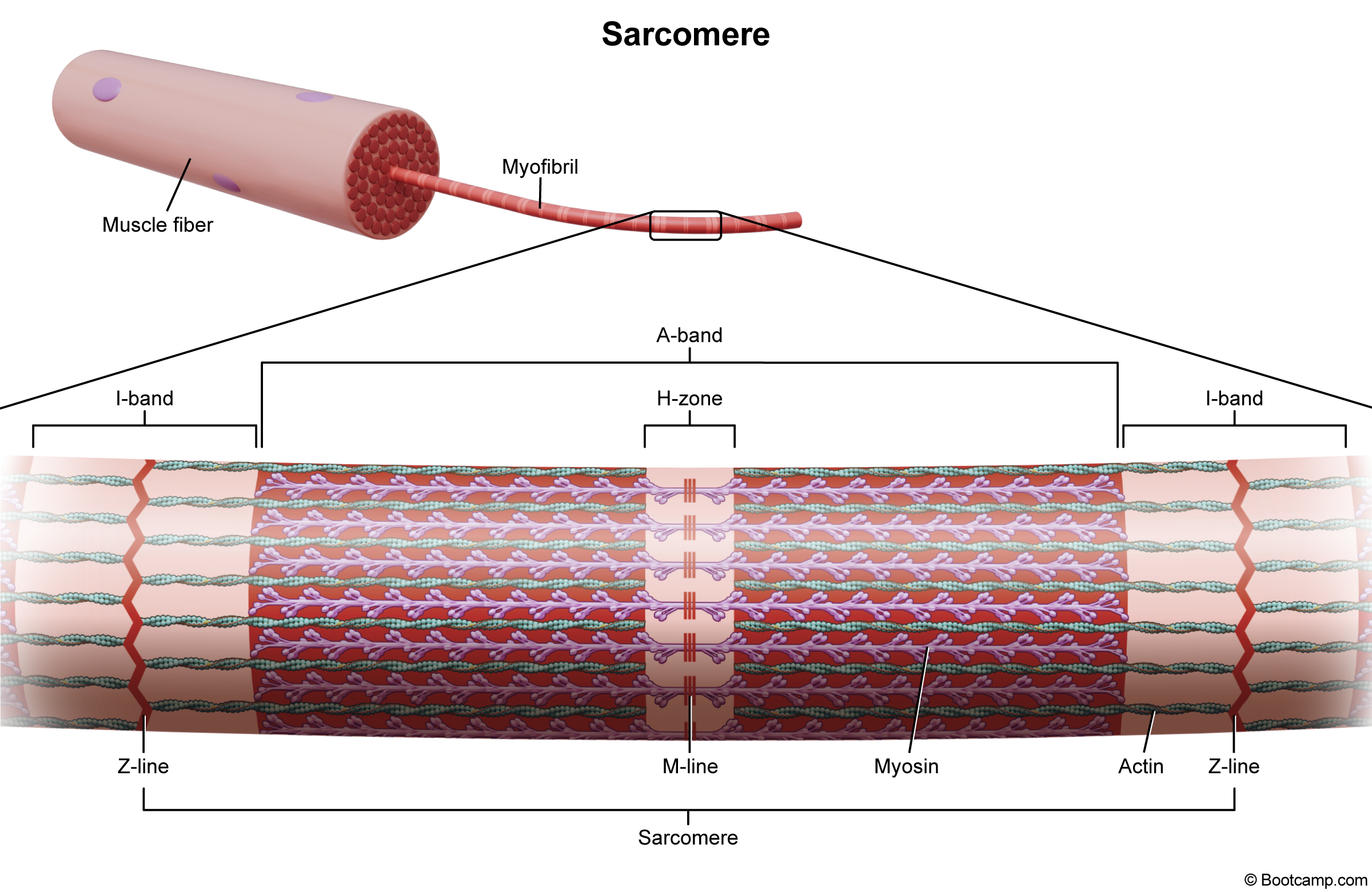
What is the entire big middle section called and contains
Called the A band

what are the major contractile proteins that help with contractions
actin and myosin
what is the first step of muscle contraction
action potential gets to the end nueron
what is the second step of a contraction
acetylcholine is released onto muscle fiber
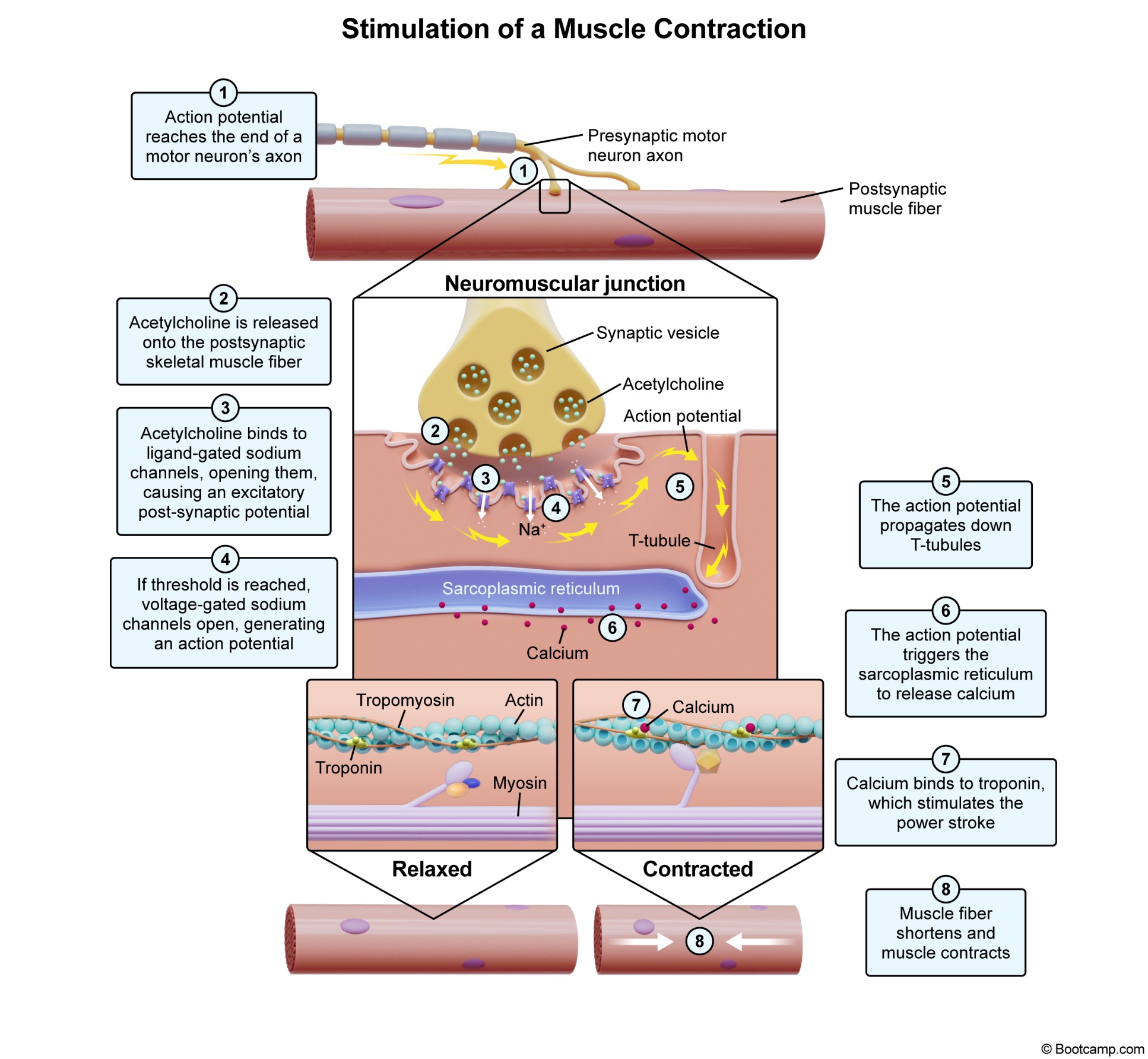
What is the third step to contraction
acetylcholine binds to ligand gated sodium channels, making a potential

What is the forth step of contraction
threshold is met and gates are open, making a action potential

what is the fifth step to contraction
action potential goes down T tubules

what is the sixth step to contraction
action potential triggers sarco. reticulum to release calcium
what is the 7th step to contraction
calcium binds to troponin which stimulates the power stroke.

what happens after calcium binds to troponin
Myosin and actin bind
what happens after myosin and actin bind
sliding motion causes fibers to shorten
how do the cross bridges unbind after they bind
ATP binds to myosin
What is the most common nuerotrans. in muscular
Acetylcholine
what part of sacromore shortens
H zone
what is the functional unit of muscle
sacromere
what are thick and thin filaments made of
myosin thick, actin thin
what actually helps in contraction
troponin
what does acetylcholinesterase do
hydrolyzes acetylcholine
what part of the brain does cortical arousal
reticular formation
what is part of the cerebral cortex
all the lobes
what does the brainstem contain
medulla, pons, midbrain, and reticular
what does the limbic system contain
thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala
what does the cerebellum do
coordinates movement
what does the amygdala do
emotional reaction
hippocampus
memory
what does the hypothalamus do
hormones
what does the thalamus do
relay center: sensory and motor signals
what does the medulla do
heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, toxins
what do pons do
relay messages
what does the midbrain do
relays senses to other parts of brain
what does parietal lobe do
spatial perception and sensation
what does occ lobe do
sight
what does temporal lobe do
speech and hearing
what does the Na/K pump do
three Na out / two K in
what is part of the outer ear
tympanic membrane
what is in the middle ear
ossicles
what is in the inner ear
cochlea and semicircular canals
what does depolarization entail
Na+ channels open