Vas week 4: LE segmental pressures & doppler waveforms, VPR, Exercise and stress testing LE bookwork
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Calcified vessels are often found in patients with
Diabetes
the difference between the 3-cuff versus 4-cuff method for arterial pressure measurements includes using another cuff at the:
Thigh level
What angle will produce the best arterial signal during CW Doppler testing?
45-60
There should be no more than _____ mmHg difference between the right and left brachial pressures
20
An ABI greater than ____ most likely suggests that the vessels are calcified and the index may be falsely elevated
1.30
A change of more than ____ in the ankle-brachial index from one exam to the next is significant
0.15
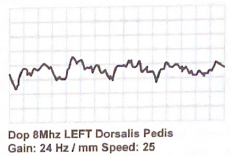
Describe the following pedal waveform:
monophasic
a pressure gradient between the calf and ankle cuffs indicated disease at which level?
Infrapopliteal
A thigh-brachial index less than 1.0 bilaterally suggests disease at which level?
Aortoiliac
A thigh-brachial index less than 1.0 unilaterally suggests disease at which level
iliac
An arterial occlusion is typically seen from one branch to the ______
Next
Vasospasm is an intermittent _____ of an artery
Constriction
The range that is considered a significant difference between arterial pressures between levels is _____ mmHg
20-30
the suggested rate for the appropriate deflation speed of the arterial cuff during a lower extremity pressure analysis should be ______ mmHg per second
2-4
The criterion range for a normal upper thigh-brachial index is between ____
1.2-1.4
Multilevel occlusive disease is suspected once the highest ankle-brachial index drops below ____
0.50
typically, the calf pressure should be greater or equal to ____ mmHg in order to heal a below-knee amputation
65-70
The arterial pressure will be falsely _____ if the cuff is too narrow for the width of the limb
Elevated
Do not take the blood pressure in the arm if the patient has a history of _____
Mastectomy or dialysis access conduit
In the equation for arterial brachial index, the highest ____ pressure is always used in the denominator
Brachial
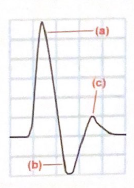
Label the 3 phases of this triphasic waveform
a. Peak systole
b. diastole flow reversal
c. late diastole
What is the purpose of giving the patient a “rest period” before beginning the exam?
In order for blood pressure to stabilize after “exercise”
Explain how collateral circulation can cause false negative results in lower extremity segmental pressure testing
Collateral vessels can provide enough blood flow to the area under the cuffs to make it seem as if the arterial pressures are normal even when the main/deep vessels are occluded
What makes an obstruction “hemodynamically significant”?
When stenosis/occlusion results in a significant decrease in blood pressure distal to obstruction. (difference of 20-30mmHg between cuff levels)
List 2 suggestion for capturing an arterial waveform using Doppler when there is vein interference
try a slightly more proximal or distal location or manually compress the proximal limb to temporarily stop venous return
What is the significance when the ankle pressure is higher than the calf pressure? how does this affect the accuracy of the ankle-brachial index?
arterial calcification is likely and the ABI is unreliable

What characteristics make the following waveform “monophasic”? use terms to describe upstroke, amplitude and flow reversal
Slow upstroke, low amplitude, broad peak and no flow reversal
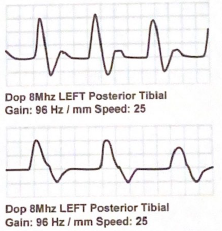
describe the difference between these waveforms
Top is triphasic while bottom is biphasic
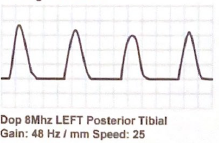
Describe the upstroke, amplitude, and flow reversal of the following waveform
Sharp upstroke, normal amplitude, no flow reversal
where is the most common location for obstruction in the lower extremity?
Distal superficial femoral artery at the adductor canal
Define “claudication”
Intermittent leg pain brought on by exercise that is relieved with rest
The absence of a dicrotic notch on a VPR (Volume pulse recording) waveform:
Is normal in some patients after exercise
The normal calf VPR tracing should be _____ greater than the thigh tracing
25%
An aortoiliac occlusion produces abnormal VPR waveforms:
At all levels
The calf VPR will display _____ augmentation when there is a tibial artery obstruction present
normal
Abnormal VPR waveforms are displayed
Distal to the obstruction
The normal amplitude for a lower extremity ankle VPR is:
The same as the thigh
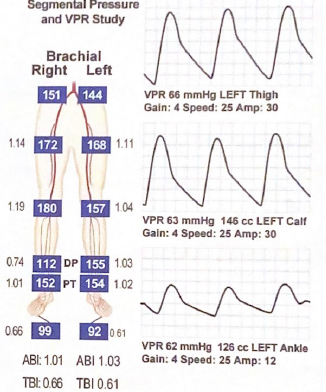
What does the following VPR exam suggest?
Left infrapopliteal artery obstruction
Air pressure or changes in limb volume are recorded by the VPR instrument as _____.
waveforms
One purpose of VPR testing is to isolate the _____ of disease.
segmental location or level
Collateralization can _____ the VPR waveform, especially in a short occlusion
normalize
When there is a dicrotic notch on the VPR waveform, ____ ____ can be excluded.
occlusive disease
A low amplitude thigh VPR that is abnormally shaped suggests _____ obstruction.
aortailliac or SFA
The VPR waveform will be _____ in the presence of small vessel disease.
Normal
Blood _____ is a physiologic variable that affects VPR amplitude.
pressure/volume
Tremors result in VPR tracing ____.
artifact
In a moderately abnormal VPR tracing, the upslope and downslope are _____.
Equal
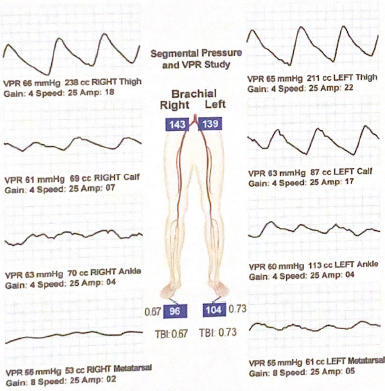
Identify the levels of disease in the following VPR exam:
Bilateral superficial femoral artery obstruction and infrapopliteal/ tibial disease is suspected
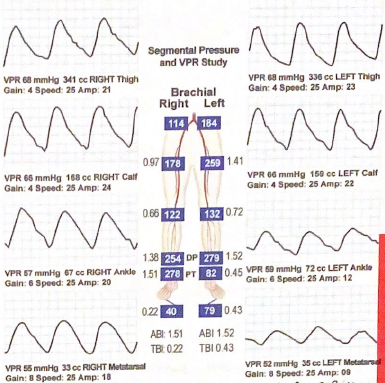
Explain the difference between the right and left ankle waveforms in this VPR tracing
Disease suspected on left side, infrapopliteal and tibial artery suspected due to decrease between the left calf and tibial tracing amplitude compared to the contralateral VPR waveforms
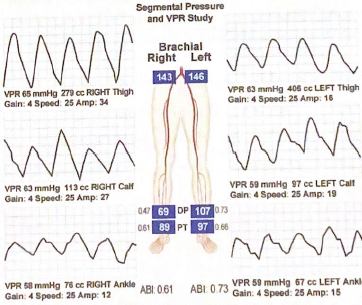
Does the right calf VPR waveform in this report suggest any disease?
Yes, amplitude of every peak/tracing recorded in the calf should be 25% greater than the thigh, suspected disease between thigh/calf
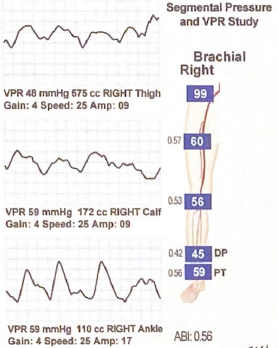
Is disease suspected between the calf and ankle level in this report? Explain why or why not.
No pressure decrease between amplitude or pressure between levels, so no additional disease suspected. VPR waveforms or ankle perfusion can improve due to presence of short collaterals
What VPR presentation is the most reliable sign of superficial femoral artery disease?
Calf amplitude is the same or lower than the ipsilateral thigh amplitude
Explain how VPR testing may be used to diagnose popliteal entrapment syndrome.
VPR should be normal at rest, then flatten with plantarflexion or dorsiflexion; as knee hyperextends, the gastric muscles contract compressing the popliteal artery
What is the normal gain setting used when recording a PPG waveform?
10
What is the appropriate width of the cuff used for digital testing?
2.5cm
how will using a cuff that is too small for the digit affect the arterial pressure?
pressure will be falsely elevated
It may not be possible to record a digital waveform when the pressure is less than:
20mmHg
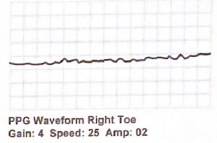
What term describes this digital PPG (photoplethysmography) waveform:
Absent
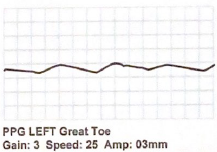
What term best describes this digital PPG waveform:
Reduced
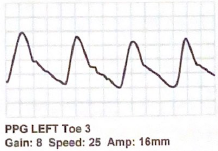
Describe this digital PPG waveform:
Normal
A patient presenting with “blue toe syndrome” should be examined for this condition
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
in older patients, more than _____ is an abnormal difference in pressure between the ankle and digital levels
64mmHg
Which condition is defined as an intermittent constriction of an artery?
Vasospasm
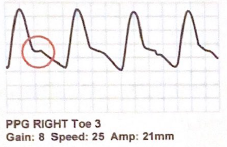
The highlighted area of the following PPG waveform is known as the ______ notch
Dicrotic
A _____ can be used to cover the foot to eliminate artifact when recording the PPG tracing.
Towel
calcification ____ affects digital pressures
Rarely
Each arterial pulse creates a change in blood _____ under the PPG sensor.
volume
Research shows that a toe-brachial index of ____(plus or minus 15 mmHg) often relates to a patients complaint of claudication.
0.35
The toe pressure needs to be greater than ____ mmHg in order to have a good chance of healing a digital ulcer.
30
The difference in pressure between the ankle and digital levels should be less than ____ in young patients
44mmHg
When the digital index falls below ____, a significant obstruction at or proximal to the digital level is suspected.
<0.60
The PPG recorder should run at ____ mm/s when recording the shape of the digital waveform.
25
The waveform is described as _____ when the PPG tracing reveals a flat line.
non pulsatile or absent
What does the abbreviation “TBI” stand for?
Toe-brachial index
What is the formula for calculating the TBI?
Toe pressure/ highest brachial = TBI
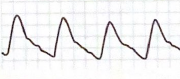
What characteristics make the following waveform “abnormal”? Use terms to describe the peak, amplitude and downslope of the waveform.
Prolonged onset to peak
Rounded peak
Downslope that bows away from baseline
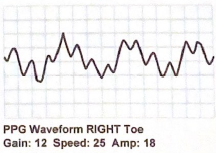
Use terms to describe the peak, amplitude and downslope of the following waveform.
Short onset to peak
downslope that bows toward baseline
dicrotic notch
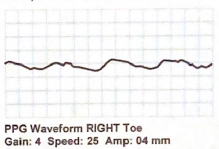
What could improve the following PPG waveform to make it easier to interpret?
use towel to get rid of artifact or tell patient to be still and rerecord
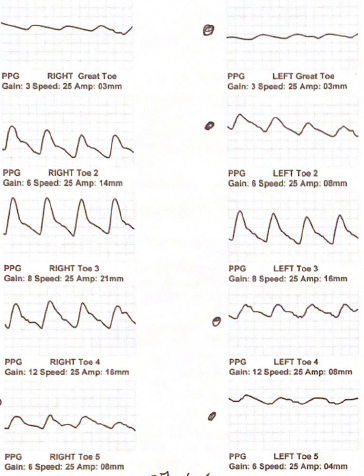
Which digital waveform display evidence of significant obstruction in this digital evaluation?
Right great and 5th toes
Left great, 2nd, 4th, and 5th toes
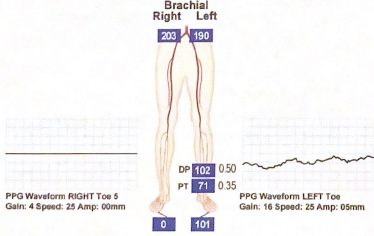
This patient has an above-knee amputation. calculate the TBI in both extremities for this case
Right cant be calculated due to amputation
Left TBI is 101/203 = 0.497
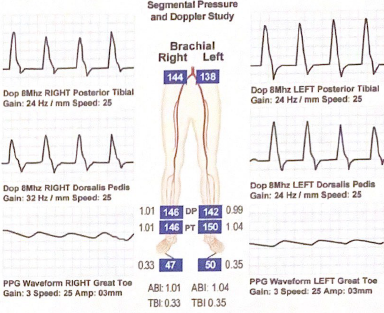
A 73 year old male patient presents with a diabetic foot ulcer on the right great toe. the results of his vascular lab exam are shown below. is his toe likely to heal according to his digital pressures? why or why not?
Yes because the absolute pressure gradient is >30mmHg
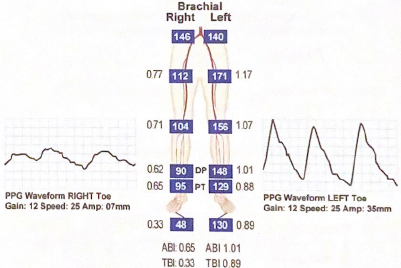
Describe the digital waveforms and categorize the severity of disease according to digital arterial pressures
Right toe waveform is reduced/abnormal and the TBI indicates severe decrease in digital perfusion
Left toe waveform is normal and the TBI indicates normal digital perfusion
What is the difference between AC and DC modes on the arterial waveform recording instrument?
DC mode records slow volume changes in the veins, while AC mode records quicker changes in the arterial vessels
What is a normal pressure drop post-occlusion in reactive hyperemia testing?
25%
How long does the cuff stay inflated on the thigh during reactive hyperemia testing?
3-5min
How does exercise normally affect blood flow?
Flow increases
Initially, the treadmill grade is set to:
10%
Patients typically begin walking on the treadmill at a speed of _____.
2 miles/hour
cuff inflation serves to create a period of _____ in the tissue
hypoxia
Patients should not need to walk longer than _____ during treadmill testing
5 minutes
With treadmill testing, single-level disease is reflected by a recovery time that is _____.
between 2-6 min
Retake ankle ankle and brachial pressures until return to within _____ of the baseline values
10mmHg
The expectation during post-exercise treadmill testing is to obtain all pressures (brachial and pedal) every _____ until reaching baseline or the time limit
2 min
Treadmill testing determines the _____ significance of arterial disease by measuring exercise ability.
Functional
post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) testing simulates exercise to create a brief period of limb _____.
Ischemia
The ankle-brachial index will _____ in the presence of arterial obstruction when flow demand is increased
decrease
marking the _____ of the arteries on the skin may help you locate vessels quicker during post- exercise pressure analysis
location
a pressure drop great than _____ of the resting pressure indicates a significant finding post-treadmill testing
20%
The thigh cuff needs to be inflated _____ mmHg above the highest brachial systolic pressure in reactive hyperemia testing.
40-50
Multilevel disease often results in a decrease in ankle pressure of more than _____ during a reactive hyperemia evaluation.
>50%