Bio 132 - Digestive System Part 5: Pancreas, Small intestine, Intestinal motility, Peristalsis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
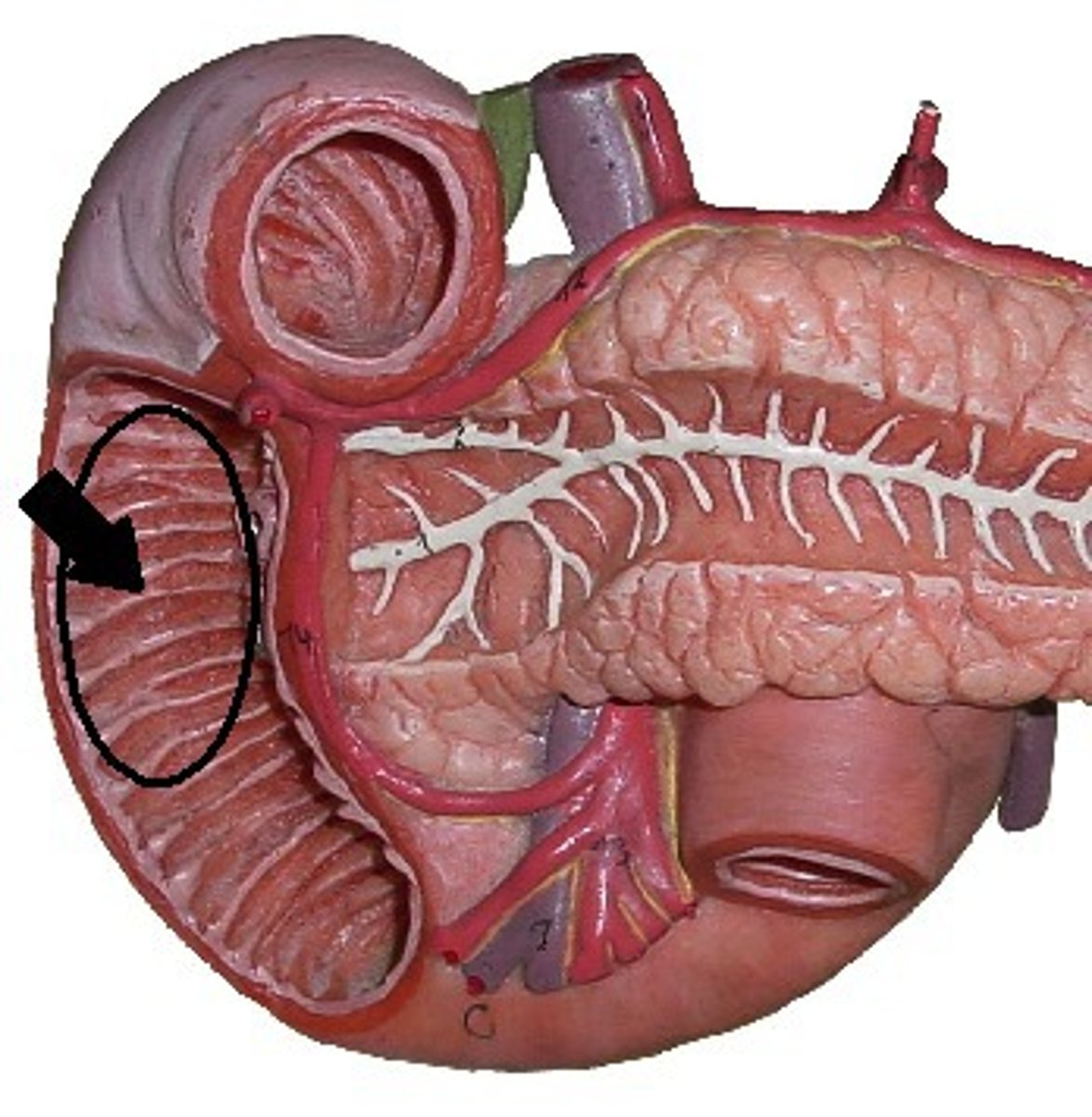
pancreas
spongy gland embedded in mesentery adjacent to duodenum
-12 to 15 cm long, and 2.5 cm thick
-head encircled by duodenum, body, and a tail on the left
-both an endocrine and exocrine gland
pancreas endocrine portion
pancreatic islets that secrete insulin and glucagon
pancreas exocrine portion
99% of pancreas - secretes pancreatic juice
-small ducts converge on the main pancreatic duct
pancreatic duct runs
lengthwise through middle of the gland
-joins the bile duct at hepatopancreatic ampulla
-hepatopancreatic sphincter controls release of both bile & pancreatic juice into the duodenum
accessory pancreatic duct
smaller duct that branches from the main pancreatic duct
•opens independently into the duodenum
•bypasses the sphincter and allows pancreatic juice to be released without bile
pancreatic juice
Alkaline mixture of water, enzymes, zymogens, sodium bicarbonate and other electrolytes
pancreatic zymogens
trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase.
proelastase
Trypsinogen
•secreted into intestinal lumen
•converted to trypsin by enterokinase, an enzyme secreted by mucosa of small intestine
•trypsin is autocatalytic - makes more trypsin
Chymotrypsinogen
converted to chymotrypsin by trypsin
procarboxypeptidase
converted to carboxypeptidase by trypsin
proelastase
converted to active elastase by trypsin
pancreatic enzymes
pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase,
ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease
pancreatic amylase
digests starch
pancreatic lipase
digests fat
ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease
digest RNA and DNA
pancreatitis
•Inflammation of the pancreas
• often from alcohol abuse, or untreated gallstones
• sometimes cause is unknown
• common in dogs after a large, high fat meal
• pancreas releases trypsin and starts digesting itself - can be life-threatening
• diagnosis can be made by detecting high levels of amylase and lipase in the blood
small intestine
-coiled mass filling most of the abdominal cavity inferior to the stomach & liver
-nearly all chemical digestion & nutrient absorption occurs in sm. intestine
-the longest part of the digestive tract
•2.7 to 4.5 m long in a living person
-"small" intestine refers to the diameter, not length
3 regions of small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
duodenum
the first 25 cm
•begins at the pyloric valve
•ends at a sharp bend called the duodenojejunal flexure
•receives stomach contents, pancreatic juice, and bile
•stomach acid is neutralized here
•fats are physically broken up (emulsified) by the bile acids
•pepsin is inactivated by increased pH
•pancreatic enzymes take over the job of chemical digestion
jejunum
first 40% of small intestine beyond duodenum
•has large, tall, closely spaced circular folds
•its wall is relatively thick and muscular
•especially rich blood supply - red color
•most digestion & nutrient absorption occurs here
ileum
last 60% of the postduodenal small intestine
•thinner, less muscular, less vascular, and paler pink color
•Peyer patches
Peyer patches
prominent lymphatic nodules in clusters on the side opposite the mesenteric attachment
ileocecal junction
the end of the small intestine
-where the ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine
ileocecal valve
a sphincter formed by the thickened muscularis of the ileum
-regulates passage of food residue into the large intestine
small intestine tissue layers have modifications for nutrient digestion and absorption
lumen lined with simple columnar epithelium
large internal surface area for effective digestion and absorption
•great length and three types of internal folds or projections
- circular folds
- villi
- microvilli
Circular folds (plicae circulares)
-from the duodenum to the middle of the ileum
-cause chyme flow in spiral path
-promote more thorough mixing & nutrient absorp.
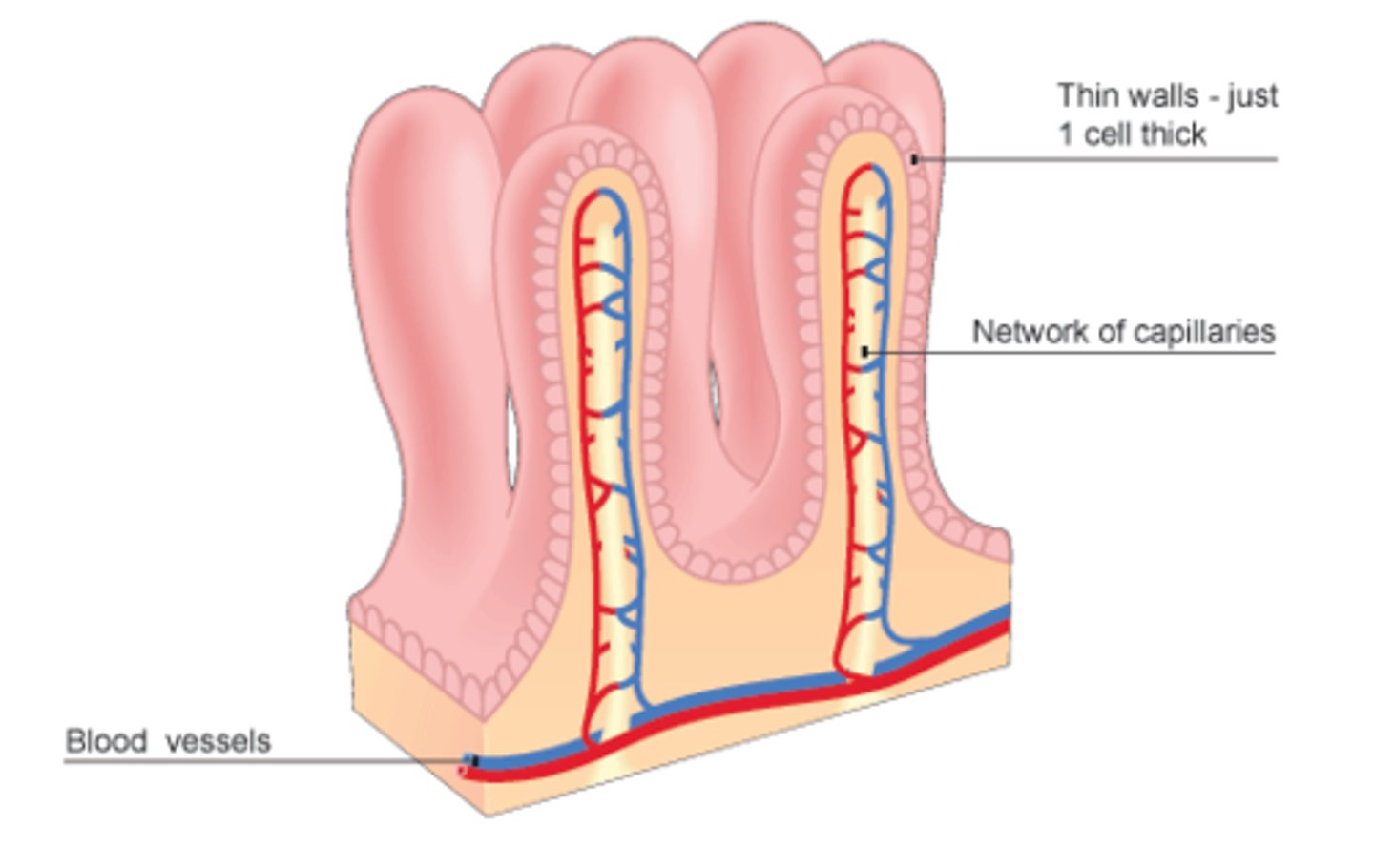
villi
fingerlike projections 0.5 to 1 mm tall
-make mucosa look fuzzy
-covered with two types of epithelial cells:
•absorptive cells (enterocytes)
•goblet cells - secrete mucus
-core of villus filled with areolar tissue
•embedded in this tissue are an arteriole, a capillary network, a venule, and a lymphatic capillary called a lacteal
Microvilli
fuzzy border of microvilli on apical surface of each absorptive cell
-"the brush border" - increases absorptive surface area
-brush border enzymes
brush border enzymes
in the plasma membrane of microvilli
•carry out some of the final stages of enzymatic digestion
•not released into the lumen
•contact digestion - the chyme must contact the brush border for digestion to occur
•intestinal churning of chyme ensures contact with the mucosa
contractions of small intestine serve 3 functions
-to mix chyme with intestinal juice, bile, & pancreatic juice
-to churn chyme and bring it in contact w/ mucosa
-to move residue toward large intestine
segmentation
movement in which stationary ringlike constrictions appear in places along the intestine
-they relax and new constrictions form elsewhere
-most common kind of intestinal contraction
-when most nutrients have been absorbed and little remains but undigested residue, segmentation declines and peristalsis begins
purpose of segmentation
mix and churn, not to move material along as in peristalsis
Peristalsis
•gradual movement of contents towards colon
•peristaltic wave begins in the duodenum, travels 10-70 cm and dies out
•followed by another wave starting further down the tract
•ileocecal valve usually closed
-food in stomach triggers gastroileal reflex that enhances segmentation in the ileum and relaxes the valve