14. Color Vision 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
retinal organization is
centripetal
- Photoreceptor → bipolar → RGC →CN II (optic nerve) → dorsal LGN (midbrain) via the parallel pathways (Magno pathway-axons from M cells/parasol cells; Parvo pathway-axons from P cells/midget ganlion cells; Konio pathway) → primary visual cortex/ V1/Brodman’s Area 17/striate visual cortex
- from striate cortex, it no longer remains centripetal because it can go in different directions
lateral
–Horizontal and amacrine cells
-Cells influencing signal before it even leaves the eye
What is the purkinje shift?
change in peak sensitivity observed when shifting from scotopic to photopic vision
Red vs green photopigment is a ________ genetically
small difference
There used to be one long wave photopigment and then over the centuries it evolved and it split into 2
Now we have 2 photopigments that have slightly different peaks at the long end of visual spectrum
1) each cone type responds to a
2) Is there overlap?
3) Are peaks evenly spaced?
1) wide range of wavelengths
2) Some overlap
3) Peaks not evenly spaced
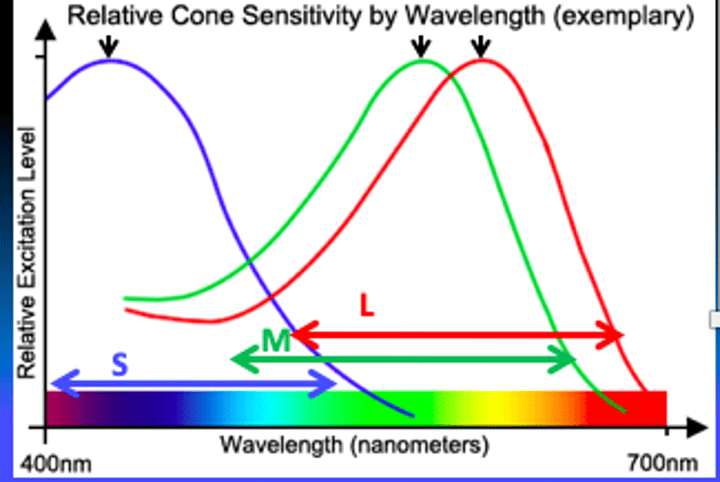
What do we need in order to distinguish between wavelengths?
need input of all three cone types
principle of univariance
“A photon is a photon is a photon….”
•The absorption of a long wavelength (low frequency, low energy) quantum has the same effect on a receptor as the absorption of a short wavelength (high frequency, high energy) quantum. Once a quantum of light is absorbed, all information about wavelength is lost. (Like how all eminems taste the same)
When does the probability of absorption change?
-wavelength
-photoreceptor class
(blue cones absorb short wavelength photons more easily than long ones)
What is true about wavelength vs color?
Color is to wavelength as...
-wavelength is a physical attribute
-color is a perceptual attribute
brightness is to intensity
Illuminant color is related to?
the wavelengths of light emitted
What is object color related to?
Red bucket example
wavelengths of light reflected from an object
White light of all wavelengths hits a colored red bucket, but red wavelengths are reflected back towards light
- Rest of light absorbed by pigment in paint
What is illuminant color related to?
wavelengths of light emitted
What are the two types of color mixing?
What comes into play here?
additive and subtractive
Abney's law
What system uses additive color mixing?
RGB
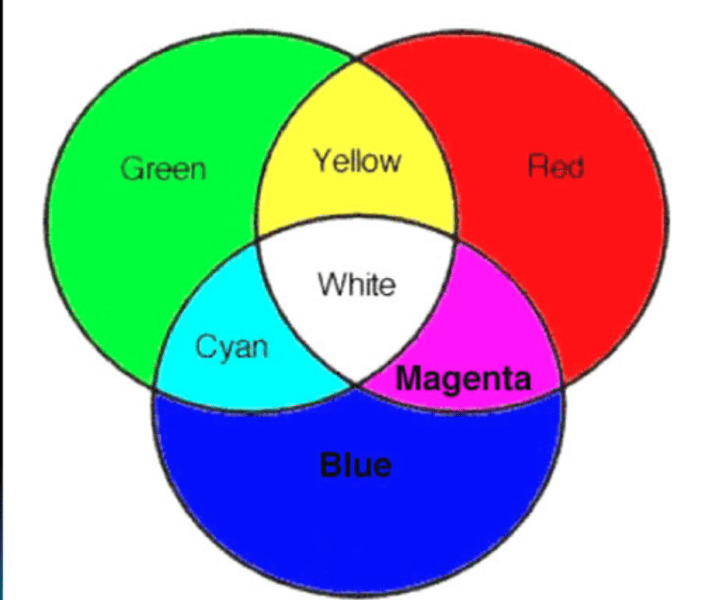
What system uses subtractive color mixing ?
CMYK
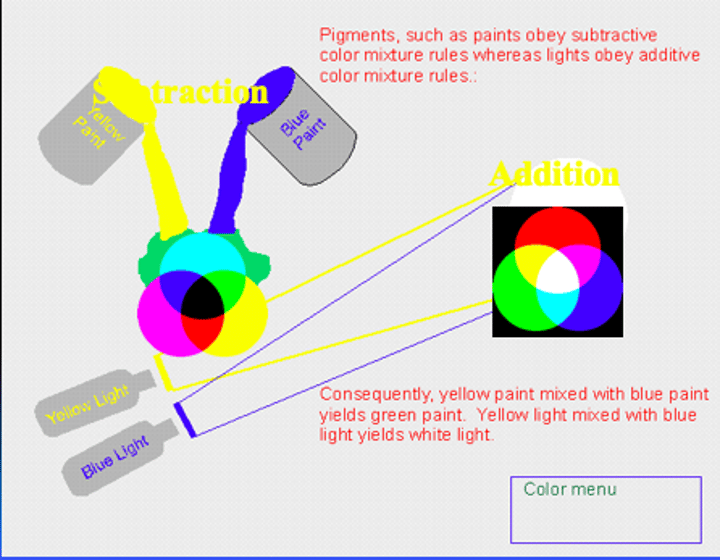
pigments, such as paints obey ________ where as lights obey _____
Consequently...
subtractive color mixture rules, additive color mixture rules
yellow paint mixed with blue paint yields green paint. Yellow light mixed with blue light yields white light.
What is abney's law?
Total luminance of light composed of several wavelengths is equal to the sum of luminances of its monochromatic components
Metamers
two lights that have different wavelength distributions but are perceptually identical
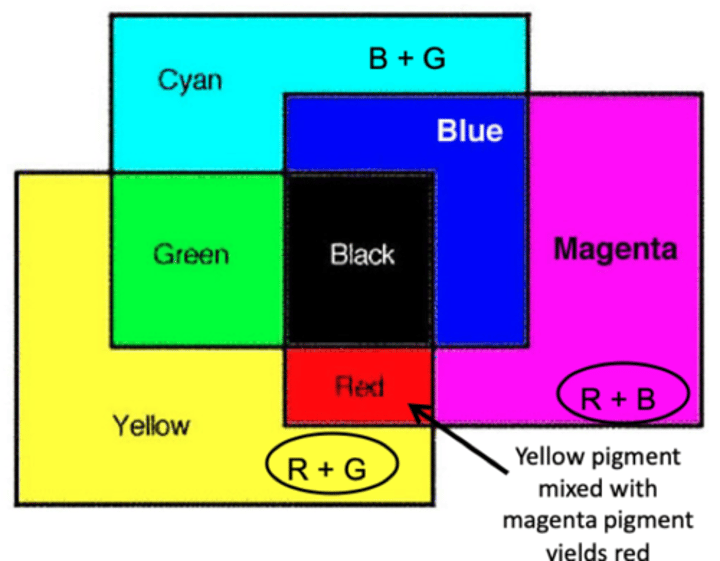
cyan =
blue + green
magenta =
red + blue
yellow =
red + green
K =
whiteness
To get the answer when subtracting colors, you take away
what they don’t have in common.
Yellow pigment mixed with magenta pigment yields red
-yellow = R + G
-magenta = R + B
-both have red in common
To get the answer when subtracting colors (like paint), you....
Take away what they don't have in common, Whats left is what they have in common
How is spectral color obtained?
directly by prismatic decomposition of sunlight
How is nonspectral color obtained?
What colors does it include?
Are these colors present in sunlight?
1) only by mixing spectral colors
2) some purples
3) not present in sunlight
1) What are metamers?
2) What can affect this?
3) Why does color appearance change with different light sources?
1) two or more stimuli that have the same color but different wavelength compositions
2) differences in luminance of light (light sources)
3) If wavelength is not in light shining upon object then that object can’t reflect that wavelength back
Each square has two different patches of paint.
Paint chips look the same color when you shine sunlight on them
If we change illuminant, then you can see a color difference
Color appearance depends upon light shining upon object
what are grassman's laws
Scalar Property of Metamers
Additive Property of Metamers
Associative Property of Metamers
What is the scalar property of metamers?
if you increase the intensity of two metamers, they will still be metamers
What is the additive property of metamers?
add same wavelength to two metamers and the results will still be metamers
What is the associative property of metamers?
if a 3rd metamer is created for one of a pair of metamers, all three will be metamers
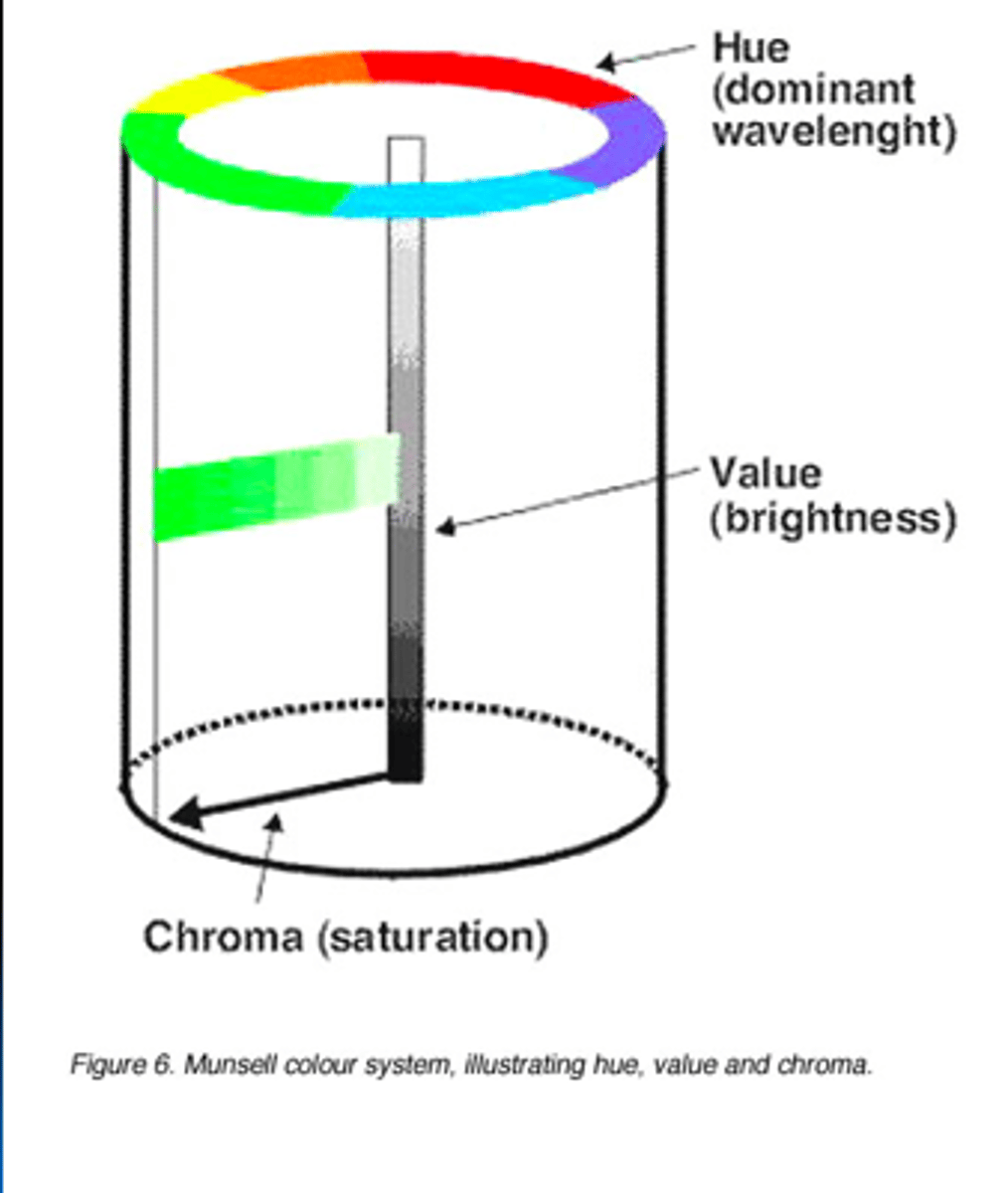
What are attributes of color?
-Hue
-Saturation (chroma)
-Brightness (value)
Munsell system
The standard system of measuring color in archaeology, based on hue, chroma, and value
What is the benefit of Newtons color circles?
1) What does it provide?
2) What does it show?
3) What else does it show?
provides a qualitative description of color matches
shows why two colors alone may not be sufficient to make color matches
Shows the need to use “negative” colors.
example of color matching
- B + G = 500 nm, but desaturated.
- To make the left side of bipartite field (500 nm) visually match right side (B+G), need to add some red to 500 nm to saturate the 500 nm
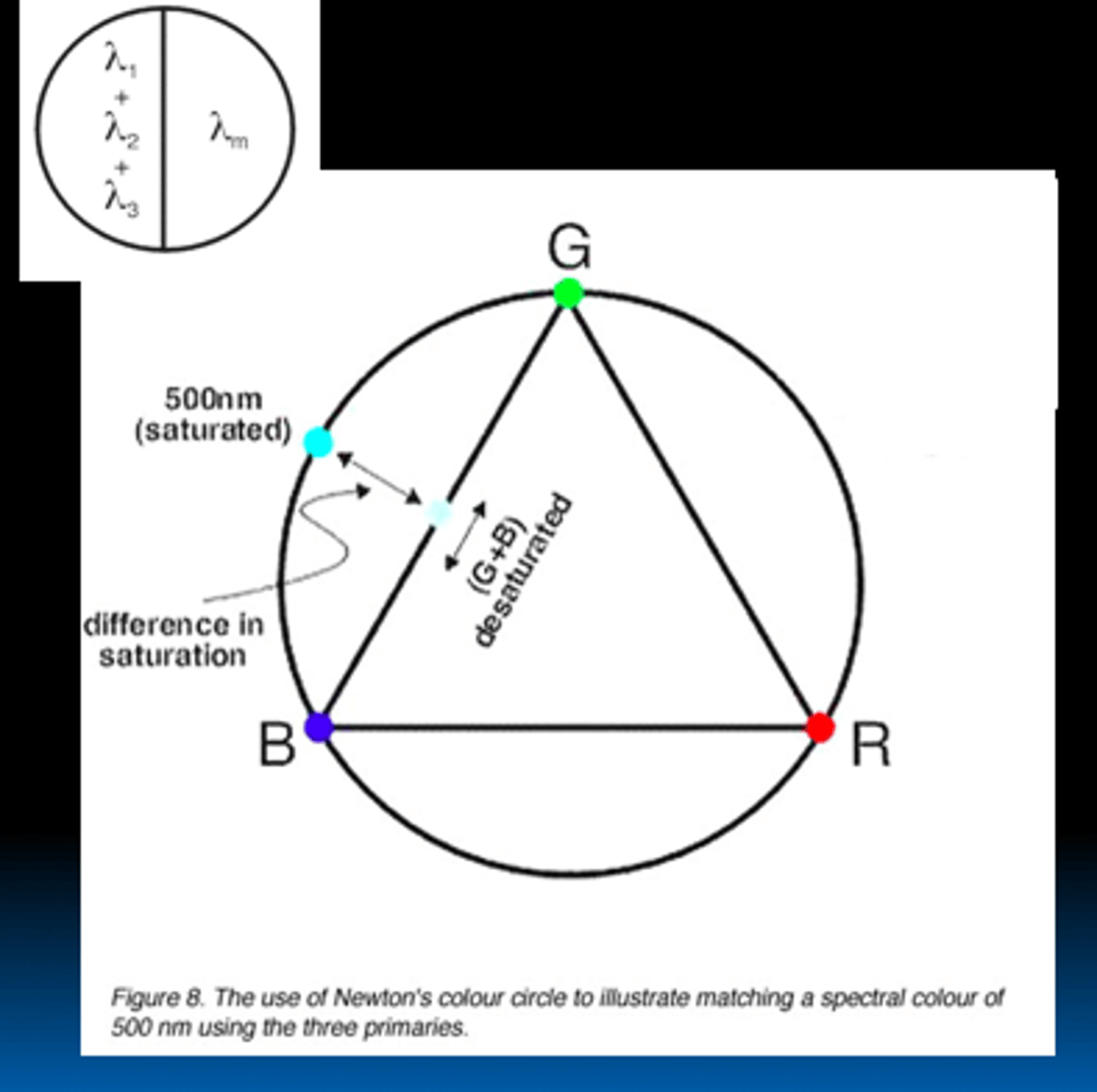
Why do we use "negative" colors?
need to add some of a certain color wavelength to allow the mixed sample to match a certain saturation
top right diagram:
- Cant get same saturation in right and left side unless you take out a certain wavelength from one side and put it on the other side
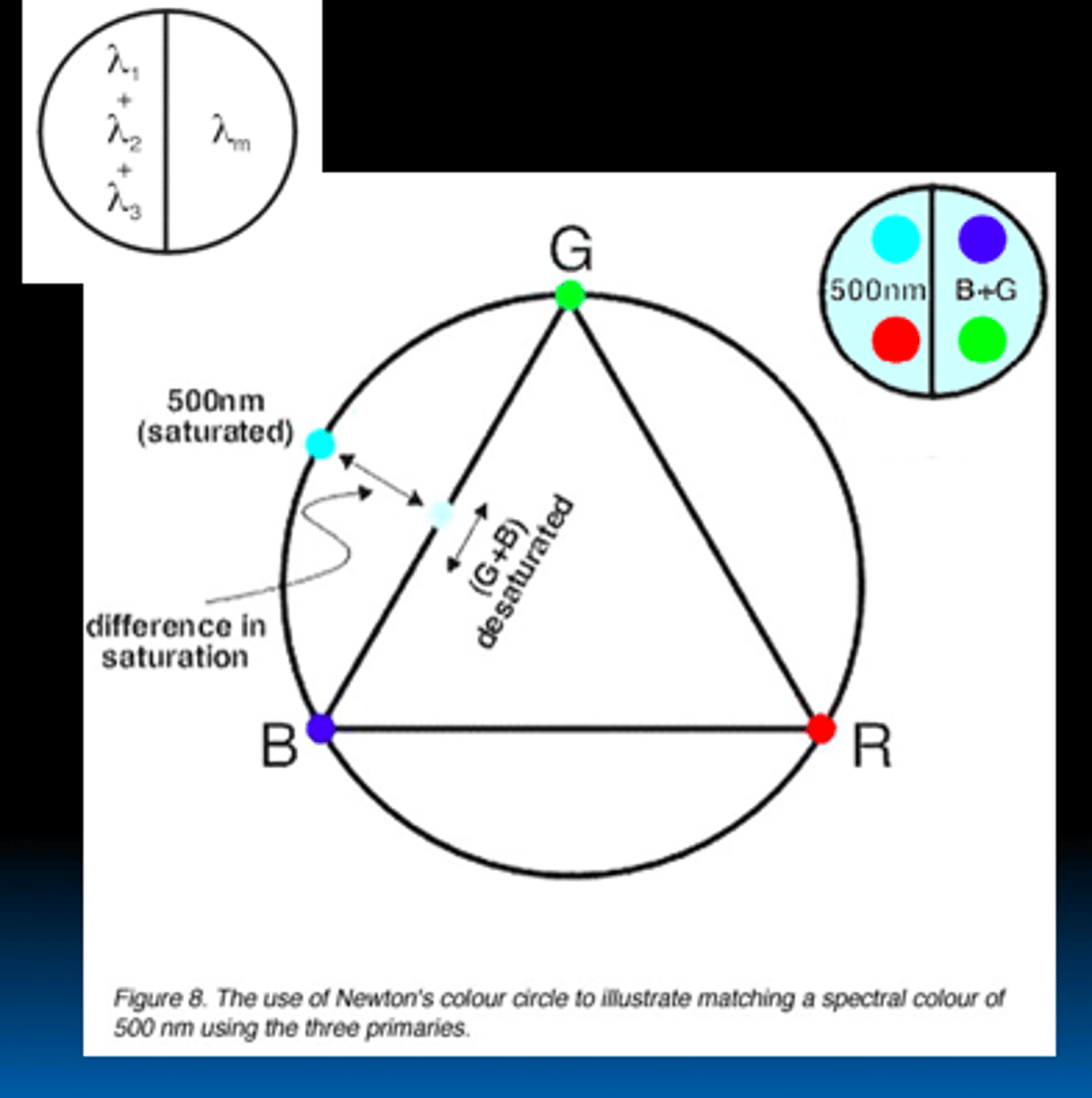
What are complimentary colors?
two colors that when added together, produce a neutral color (i.e. black-gray-white)
(opposite sides of a color wheel)
What is hue associated with?
wavelength
What is brightness (Munsell value) associated with?
perceived intensity of a color

What is saturation (Munsell chroma) associated with?
degree to which a color appears to differ from an equally bright gray

What is a color's perceived colorimetric purity?
the saturation
colormetric purity describes
“Saturation” is the
proportion of pure, dominant spectral wavelength energy relative to the amount of achromatic (white/grey) luminance objectively present in a color sample
perceptual attribute most closely related to the physical attribute of “colorimetric purity”
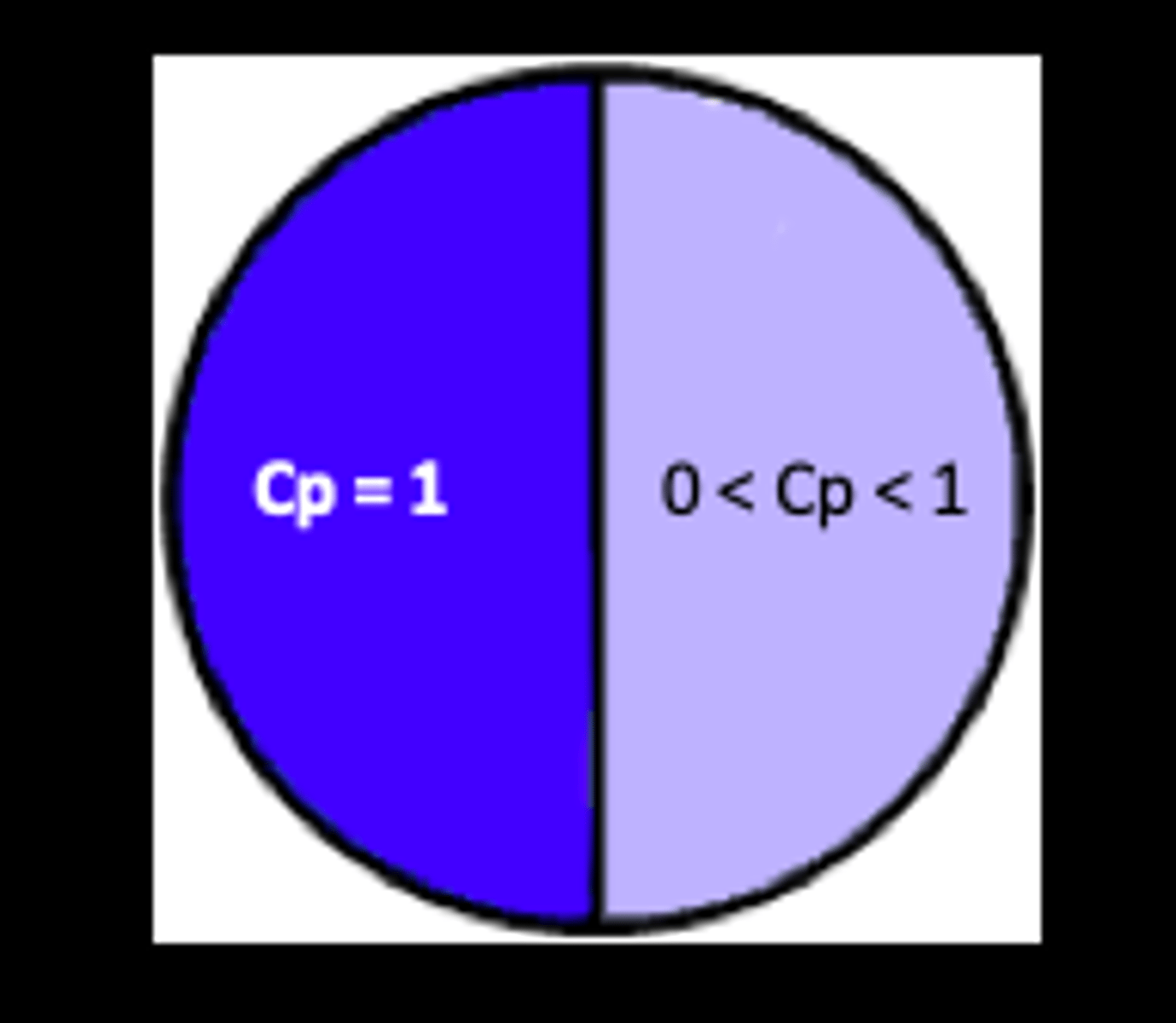
What does a colormetric purity of a pure color relate to?
Pure white/gray?
1
0
What is the equation for colorimetric purity?
cp = Lλ/ (Lλ+Lw)
T/F: saturation is the perceptual attribute most closely related to the physical attribute of colorimetric purity?
True
the munsell color system
What are the three parts?
one of the first people to try uniform way to specify colors on an international basis
hue sectors
chroma (saturation)
value (lightness, intensity)
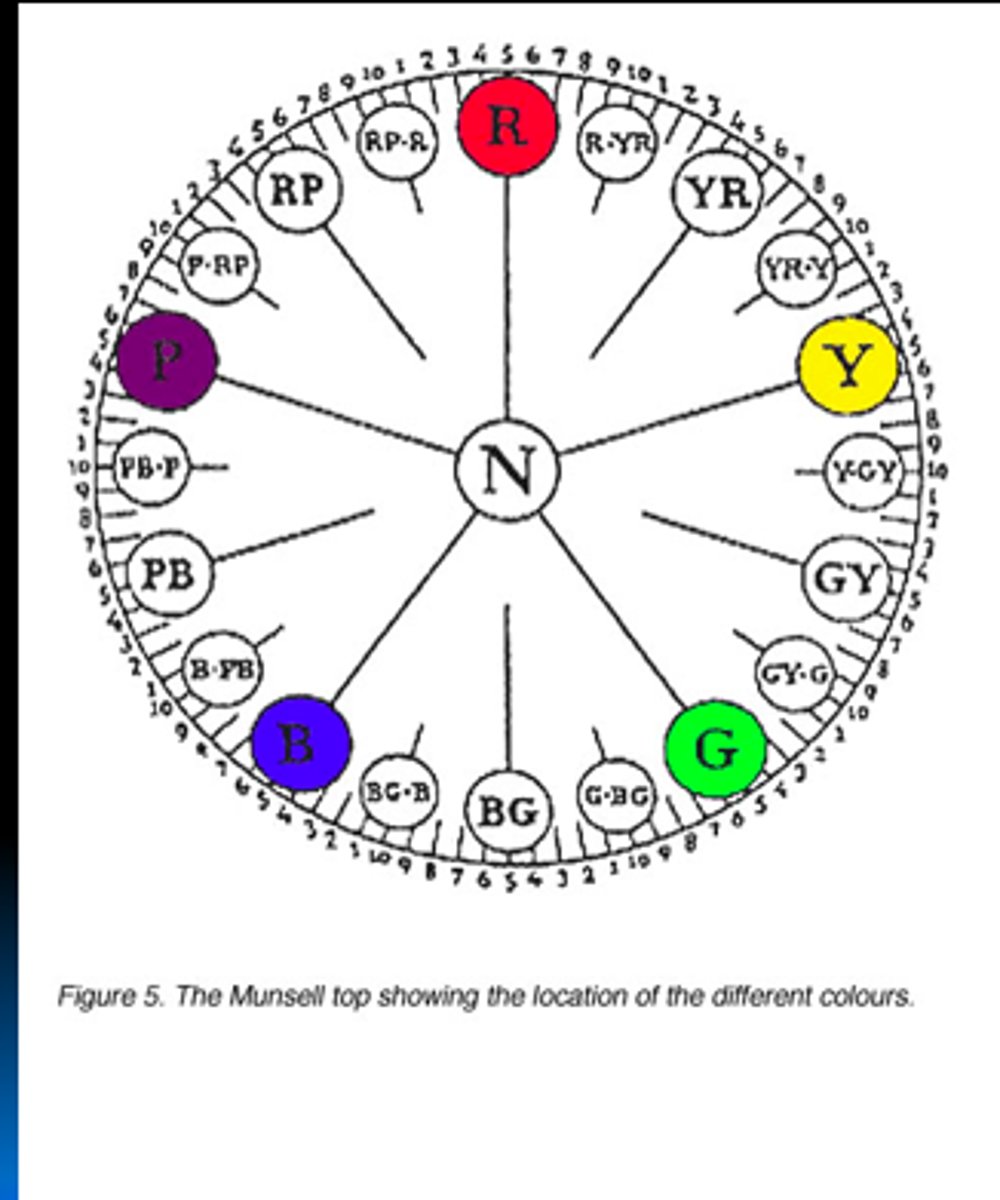
munsell hue sectors
(R, YR, Y, GY, G, BG, B, PB, P and RP)
10 equally distinguishable steps per sector (#1-10: Middle of red sector is 5R)
1) munsell chroma (saturation)
2) Where does it stretch from?
3) What has happened to it?
1) (Approximately) visually uniform scale
2) 0 – 30+
3) increased as new, highly saturated (e.g., fluorescent) colors are added
munsell value (lightness/intensity)
Black > White: scale of 0 - 10
How can we generate C.I.E diagrams?
-RGB color matching functions
-XYZ color matching functions
-xyz chromaticity coordinates
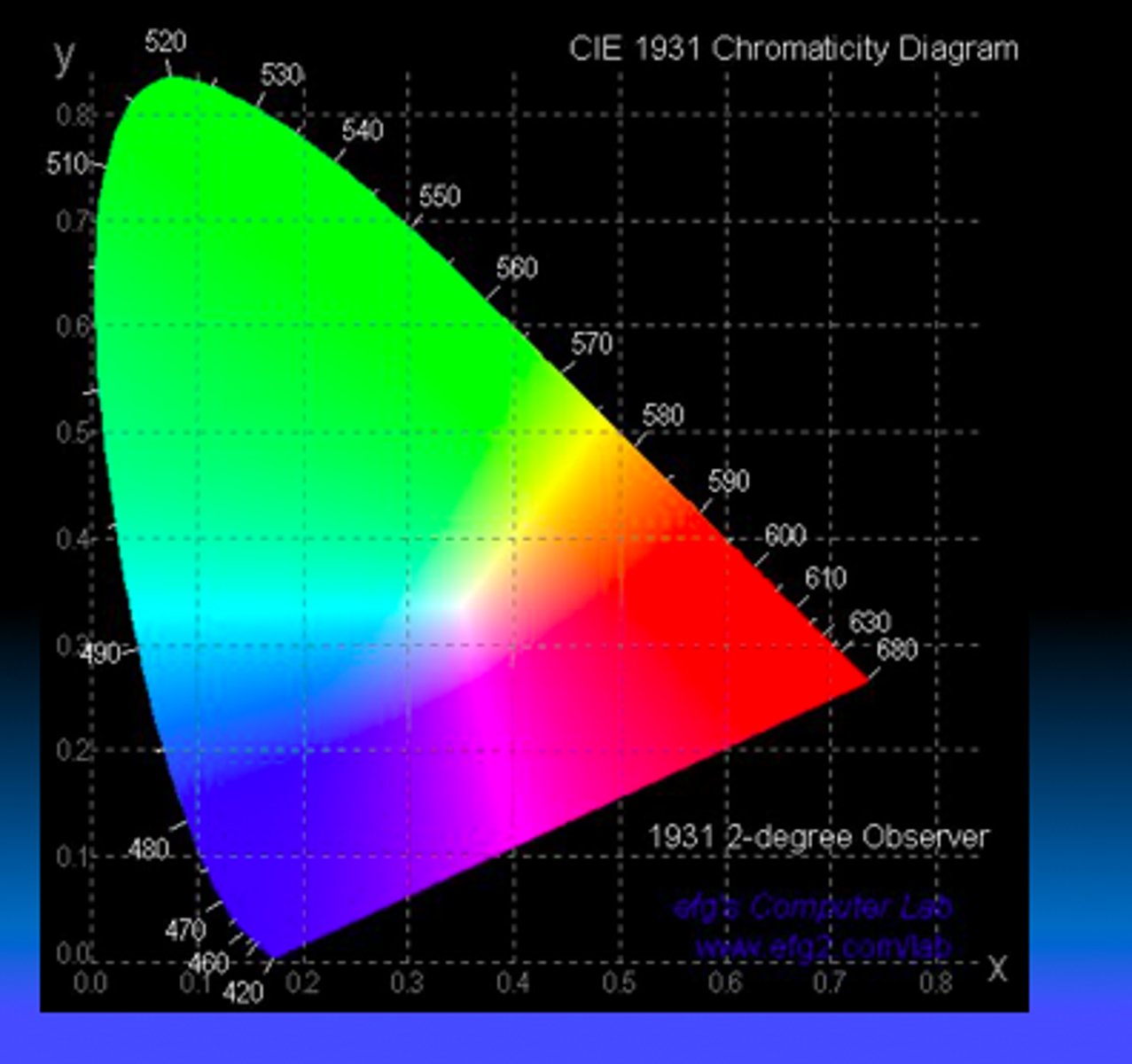
what are features of CIE diagram
•additivity & linearity
•spectral, non-spectral (purple), & Planckian locus
•dominant & complementary wavelength
•equal energy white, excitation purity
•MacAdam ellipses
What are uniform color spaces?
CIELUV & CIELAB
two colors that are equally distant in color space (i.e. on the diagram) are also perceptually equidistant
What does a person with normal color vision need to match any color?
they need to mix only 3 suitably chosen primary colors in different proportions
How can a color matching function be obtained?
So… for each single wavelength matched, there is a set of
What are these values referred to as?
having a normal observer match each monochromatic wavelength with some mixture of the same 3 primaries
3 proportional values (adding up to 1.0) specifying the proportion of each primary color.
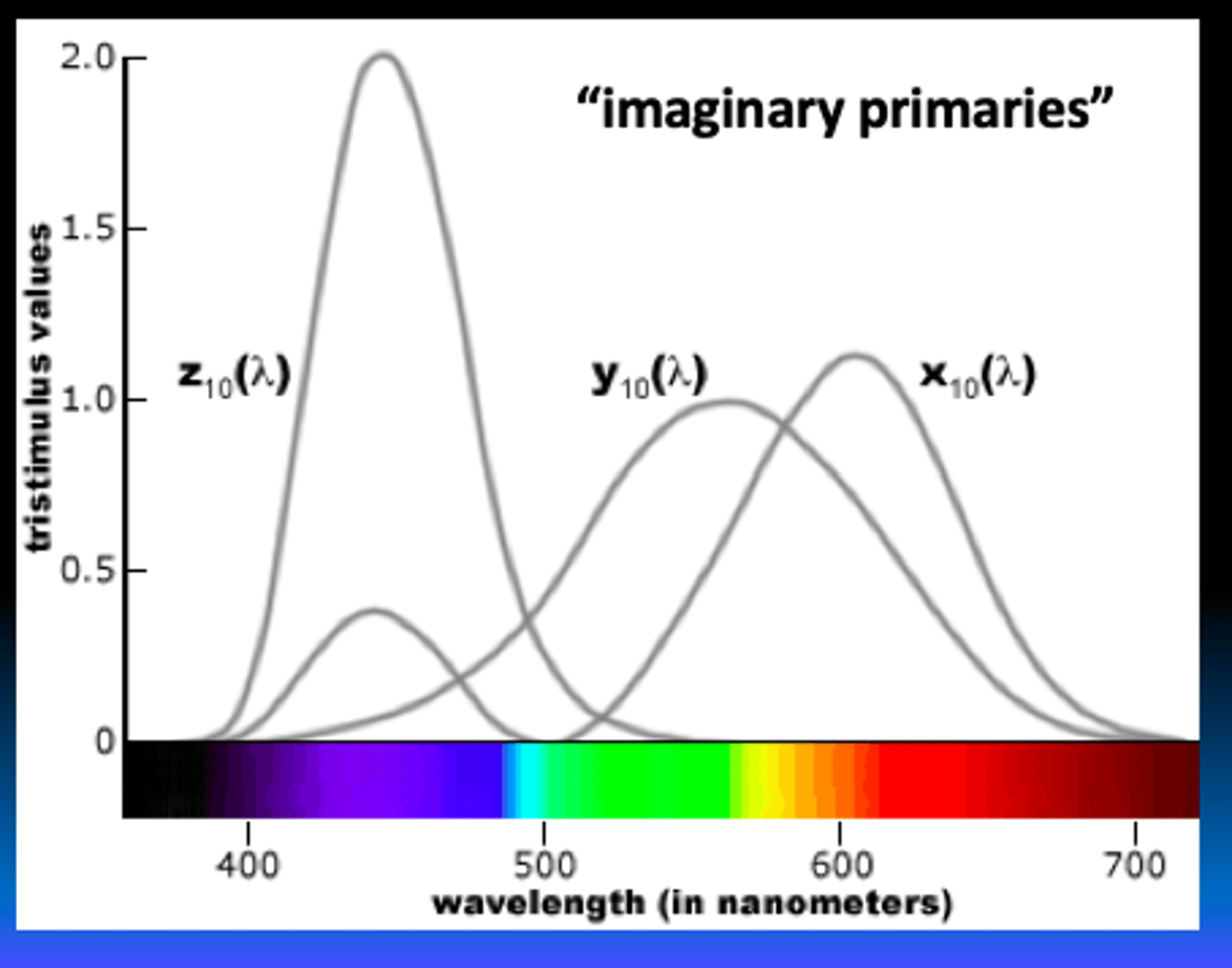
These values are referred to as “tristimulus values”, and plotting them against the (spectral) wavelengths they match yields three “color-matching functions”.
RGB color matching functions
How did they measures this?
What are the real primaries
380-780 > 360-830 nm.
2 degree foveal, bipartite field
REAL PRIMARIES
- 435.8 nm (blue)
- 546.1 nm (green)
- 700.0 nm (red)
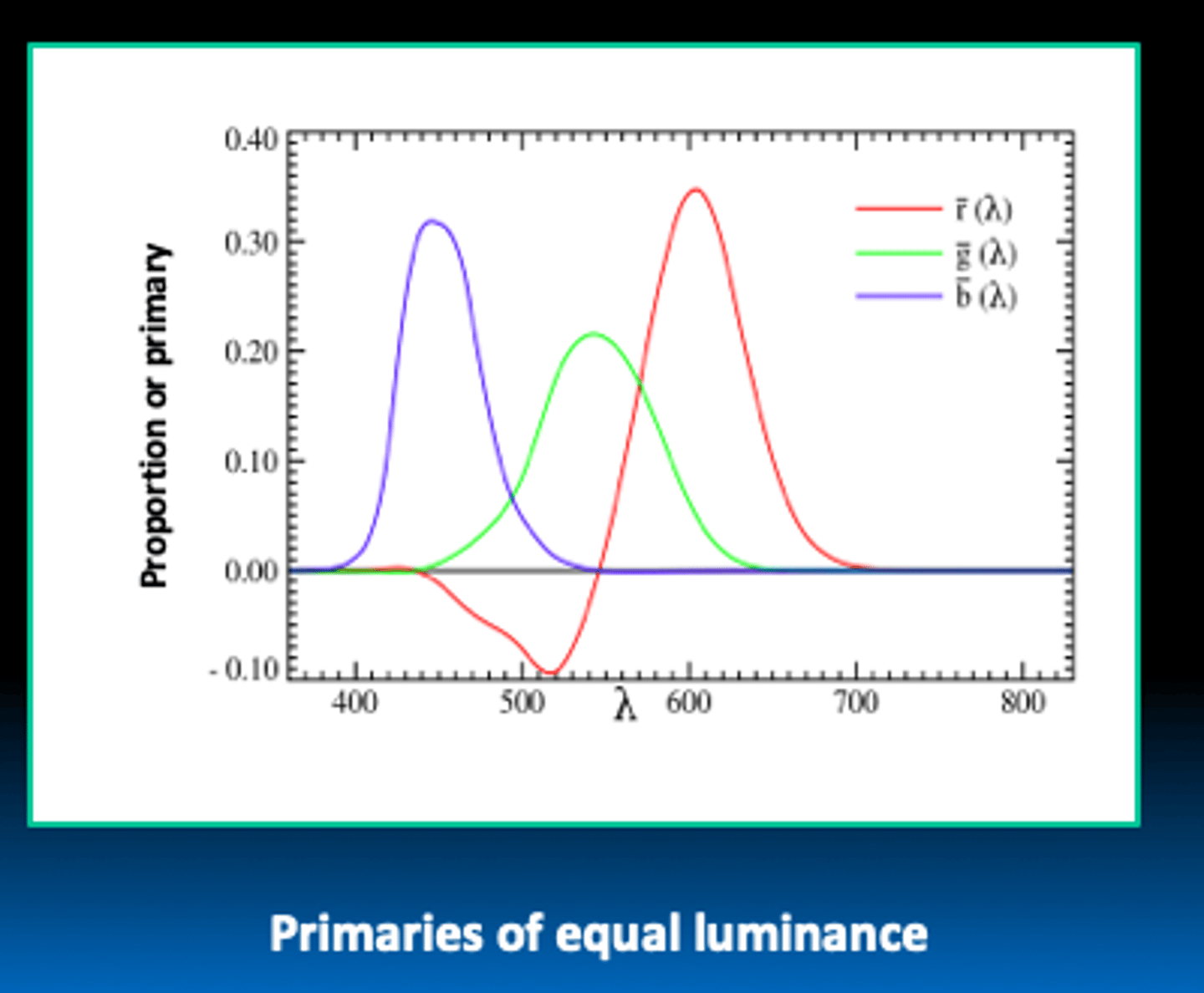
X, Y, and Z are trisimulus values, what do they indicate?
how much of each primary is needed to match a given wavelength
What does the Y tristimulus value represent?
total brightness of the light
What do you use to locate a given color in the CIE color space?
divide the tristimulus value for each primary by the sum of the 3 values for that color
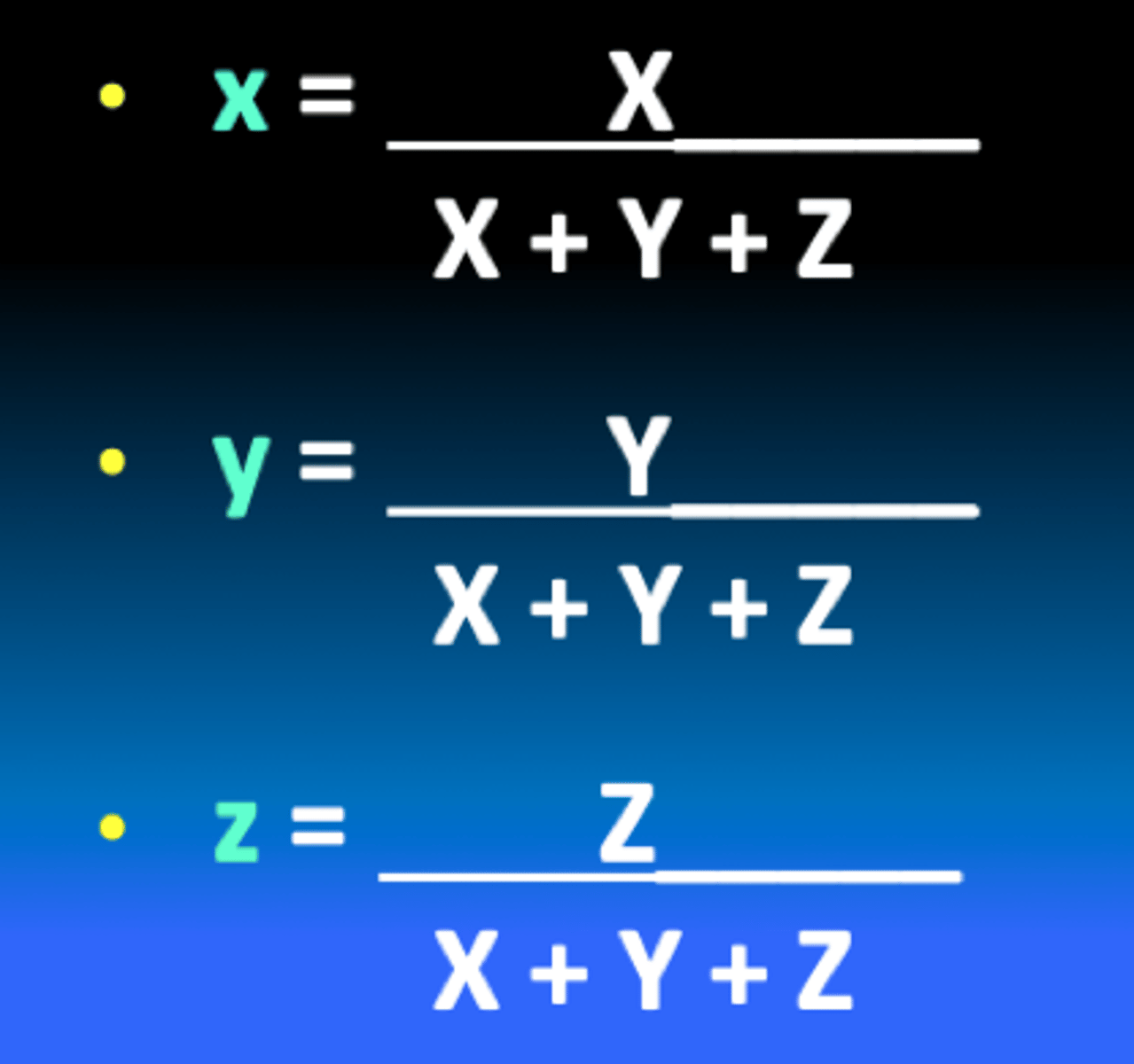
What should x+y+z equal?
because of this, all essential information can be represented by...
Graphing y against x yields a...
1.00
any two of the three parameters (The 3rd can be calculated by subtracting the other two from 1.0).
2-dimensional plot of human color space: the CIE Chromaticity Diagram.
Loci on CIE chromaticity diagram
1) What is the curve?
2) What is the flat part?
3) What is the part in the middle?
Spectral Locus
Purple Locus
- non-spectral purples
Planckian Locus
- blackbody radiators (where white is found)
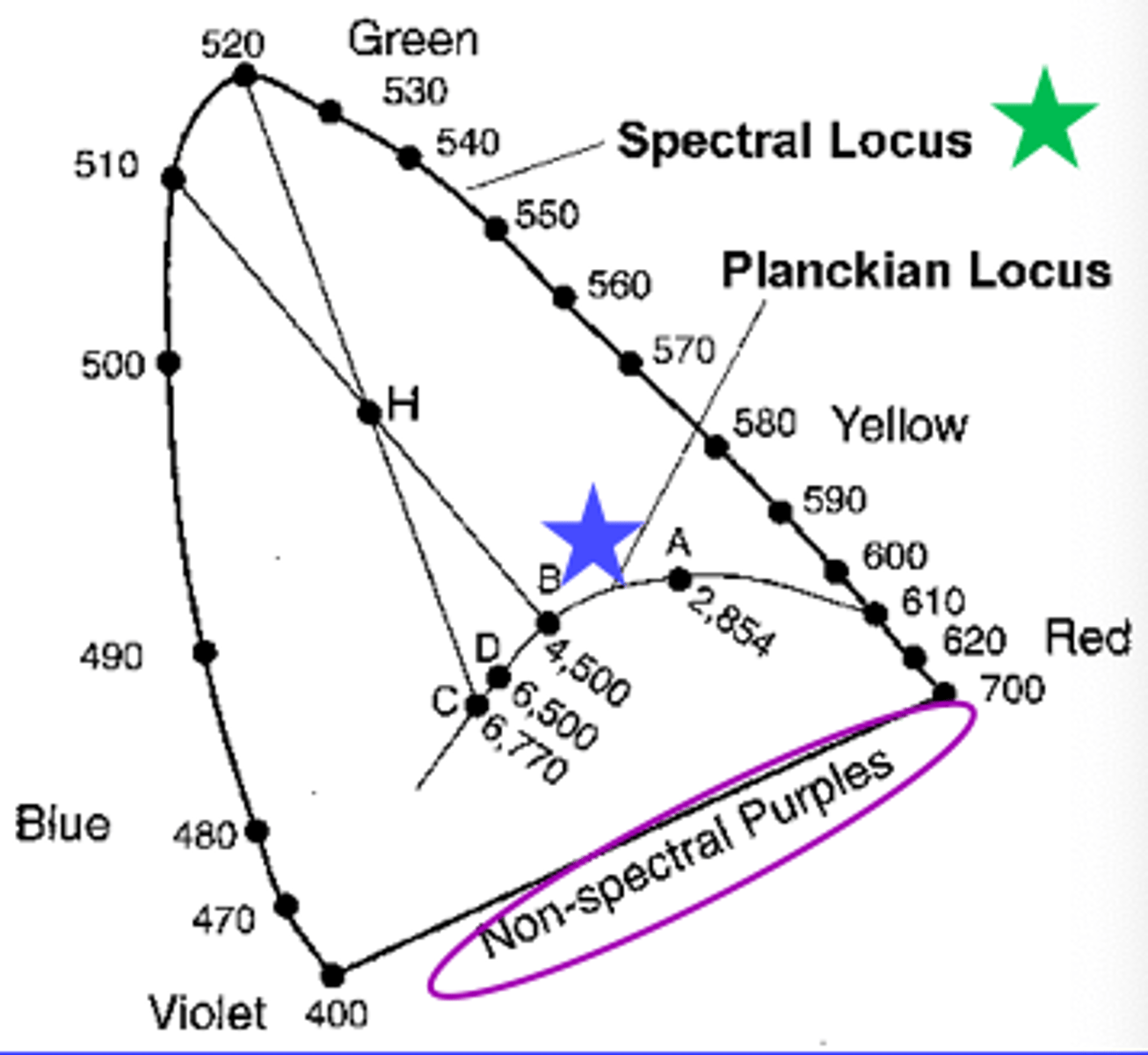
What do the temperatures mean for the planckian locus?
Where a white light of that temp would be plotted.
how do you find dominant wavelength on CIE diagram?
Draw line from white light of interest through color to spectral locus
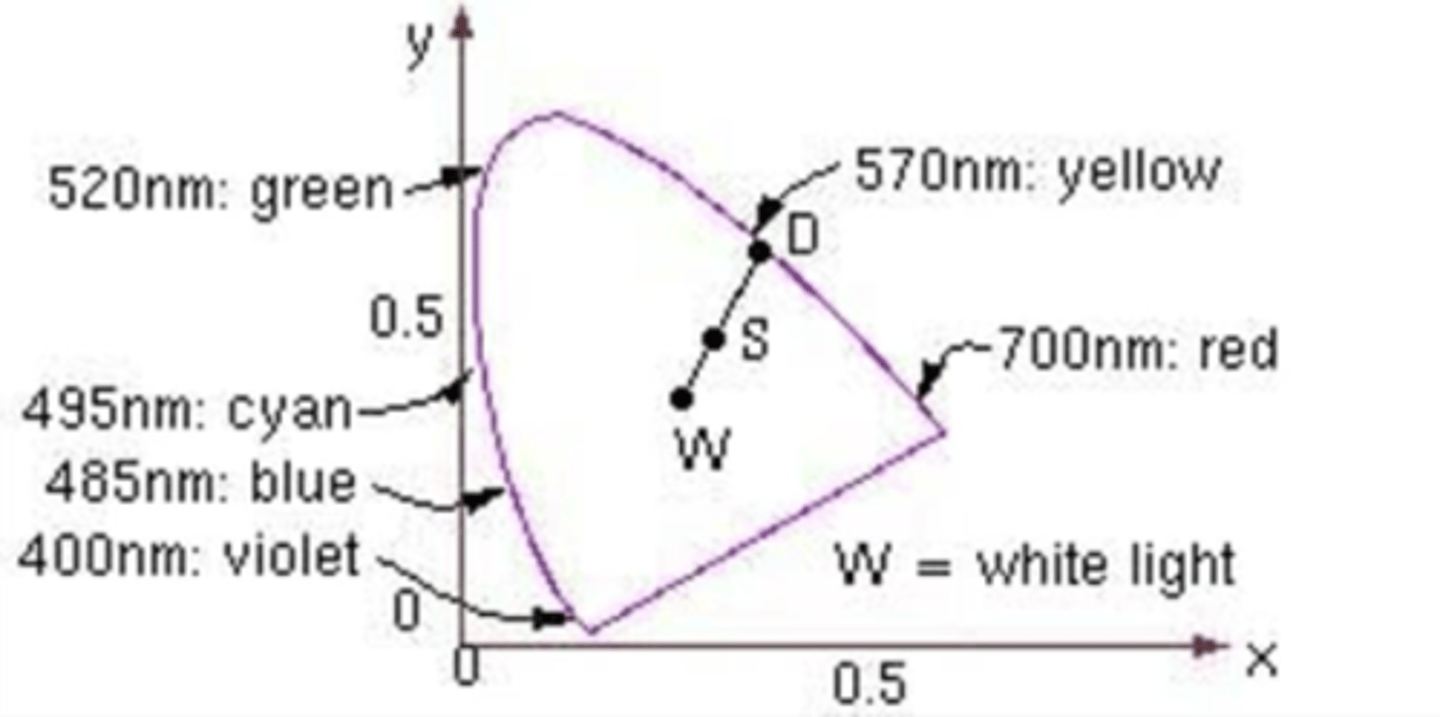
how do you find complementary wavelength on CIE diagram
Draw line from one wave- length through white light of interest to opposite side of diagram
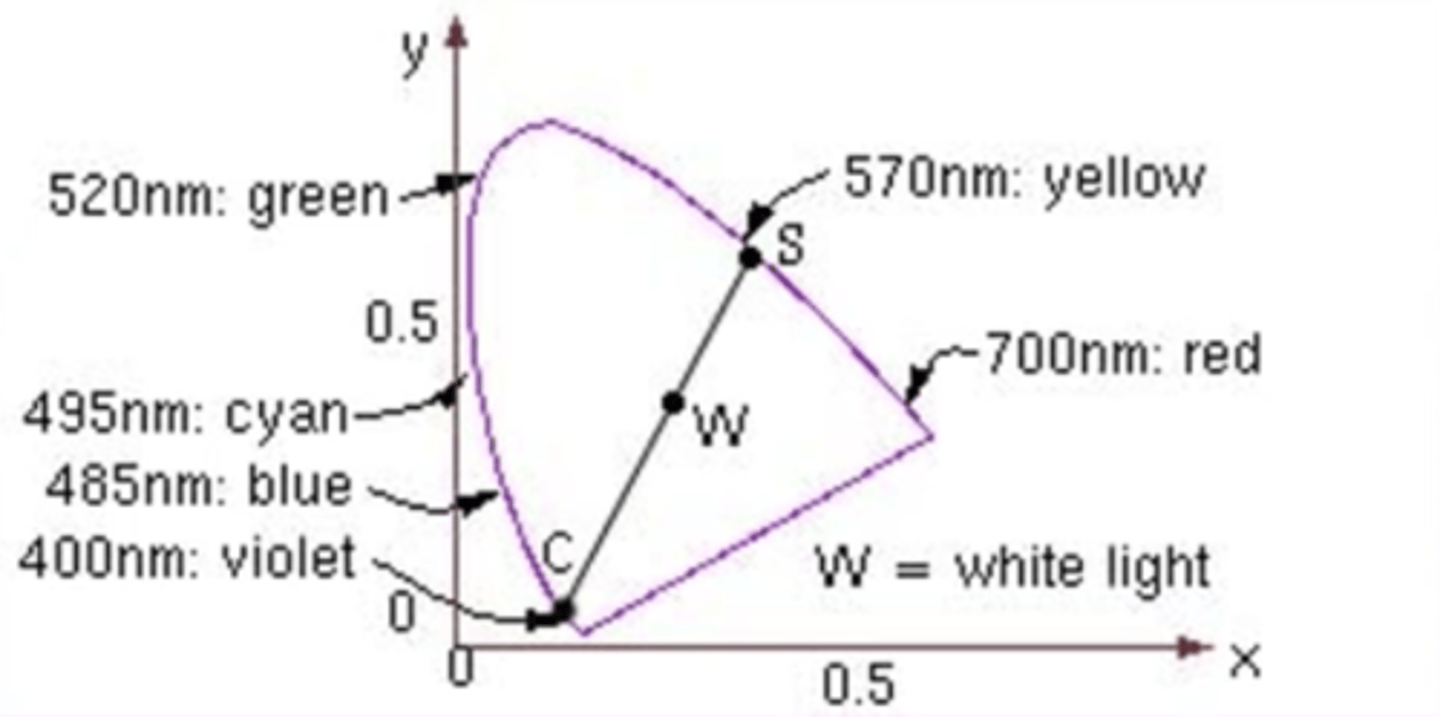
excitation purity
For a given point on the CIE diagram, what is it labeled as?
Excitation purity =
a correlate to "saturation"
"S":
a / (a + b)
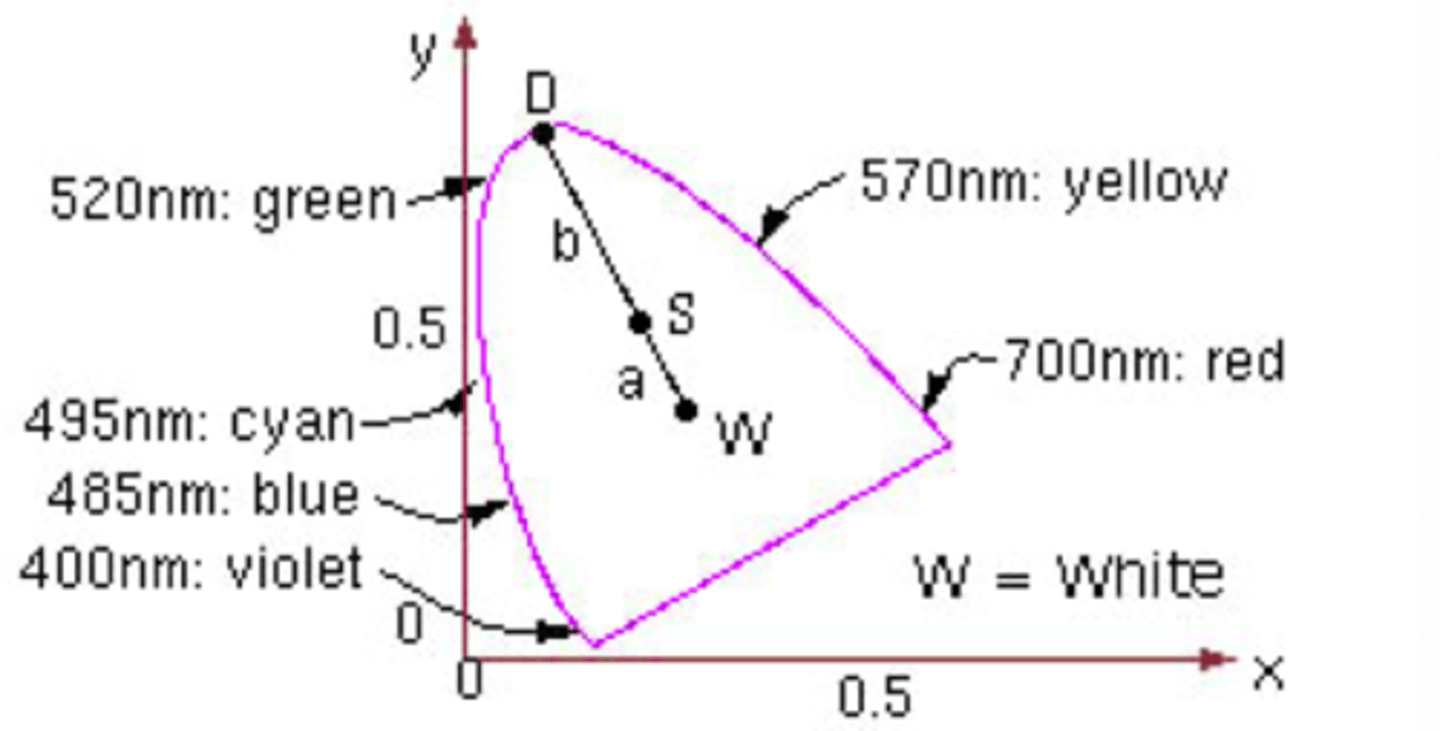
On a CIE diagram what happens when you move S closer to W?
Less saturation so reducing the purity
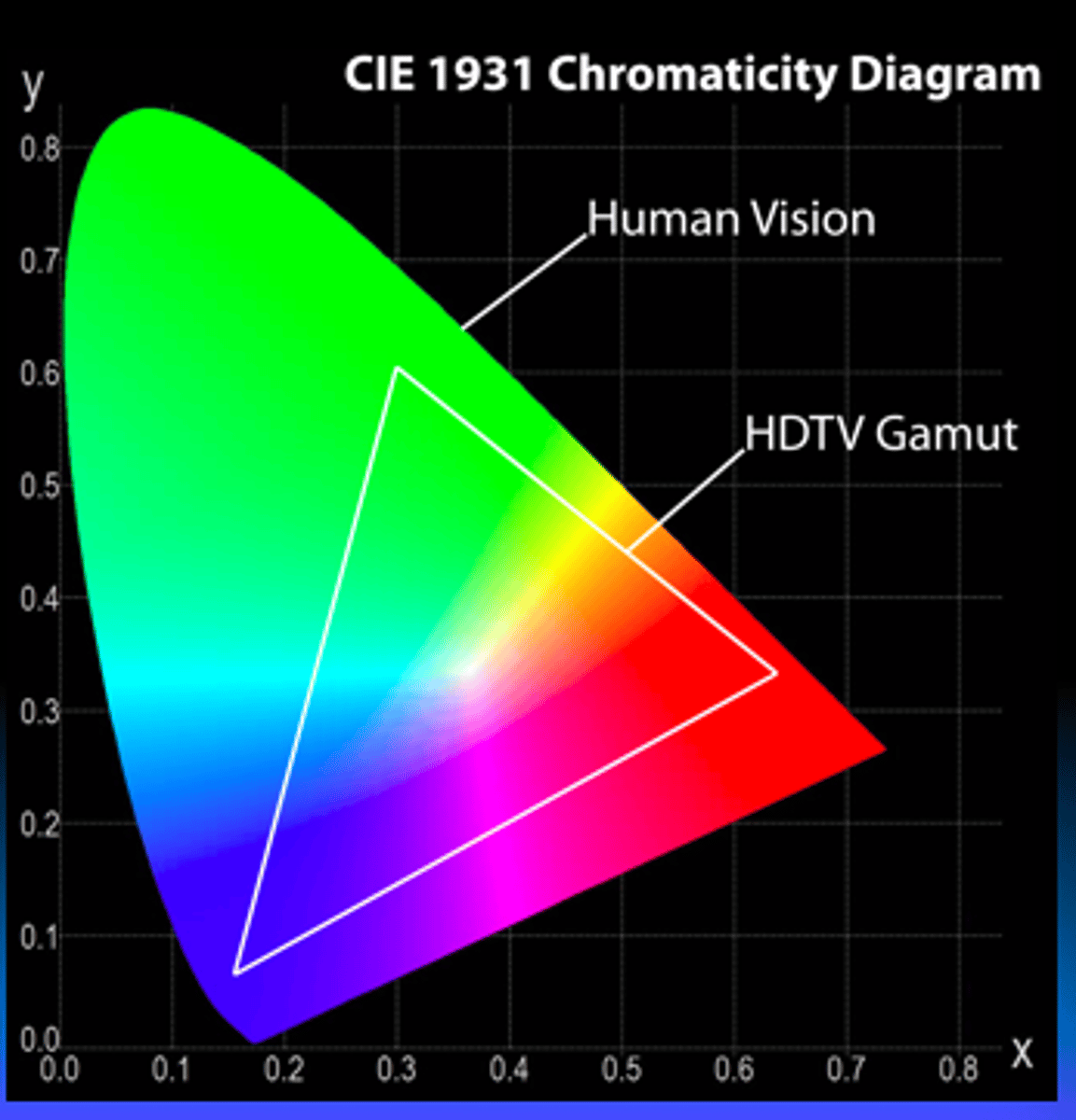
What is a color gamut?
-This set of primaries (the triangle in the graph) can be a subset of the
set of all colors that can be obtained from all possible mixtures of a specified set of primary colors
CIE diagram.
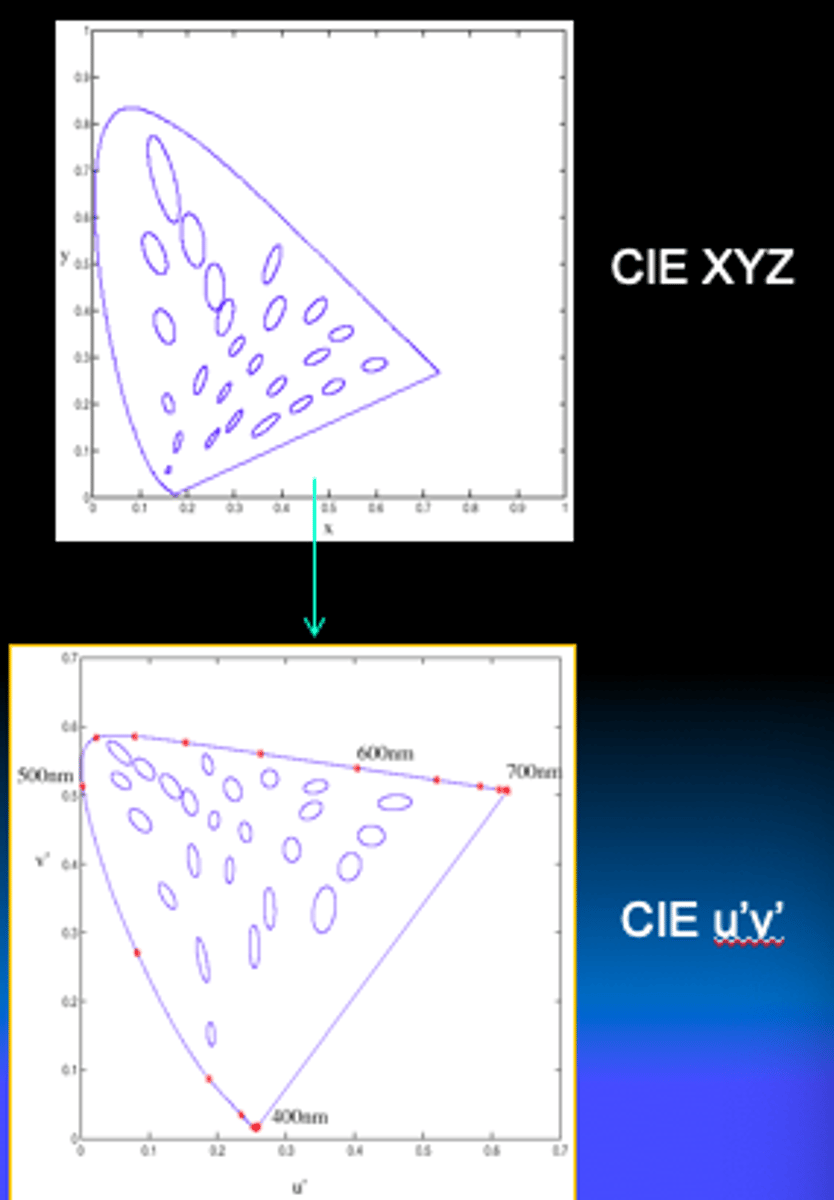
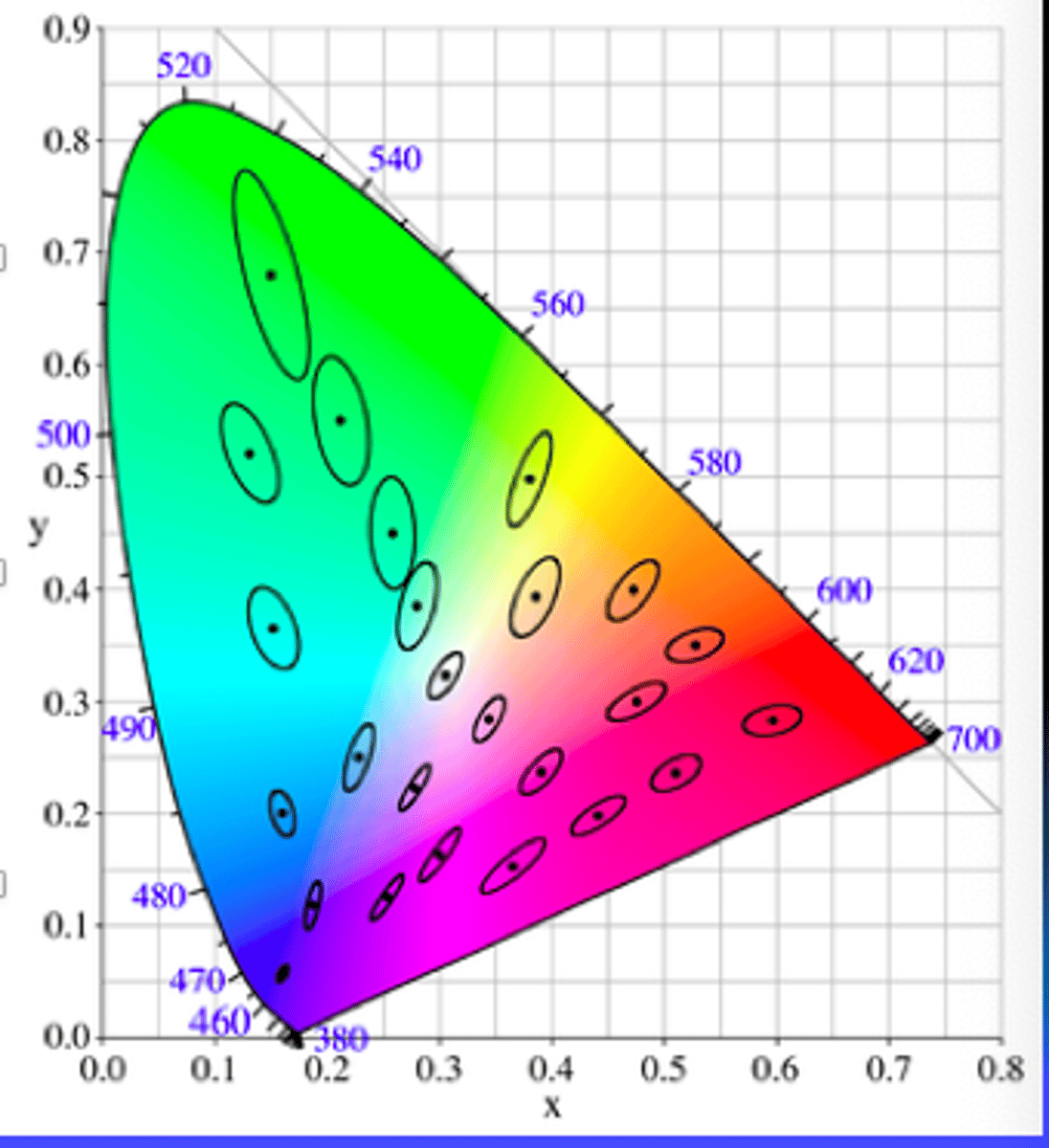
macadam ellipses
Where can u make less of a change and the person will detect the color change?
JNDs for chromaticity for a person with normal color vision
- how much of a change in color is needed for a person to tell the color has changed
blue and red areas
what is unequal about the CIE diagram?
What does the CIE (u', v') do?
there is a large amount of green
Attempts to make PERCEIVED chromaticity difference between two points on the chart the same as for any other two points that are separated by the same distance.
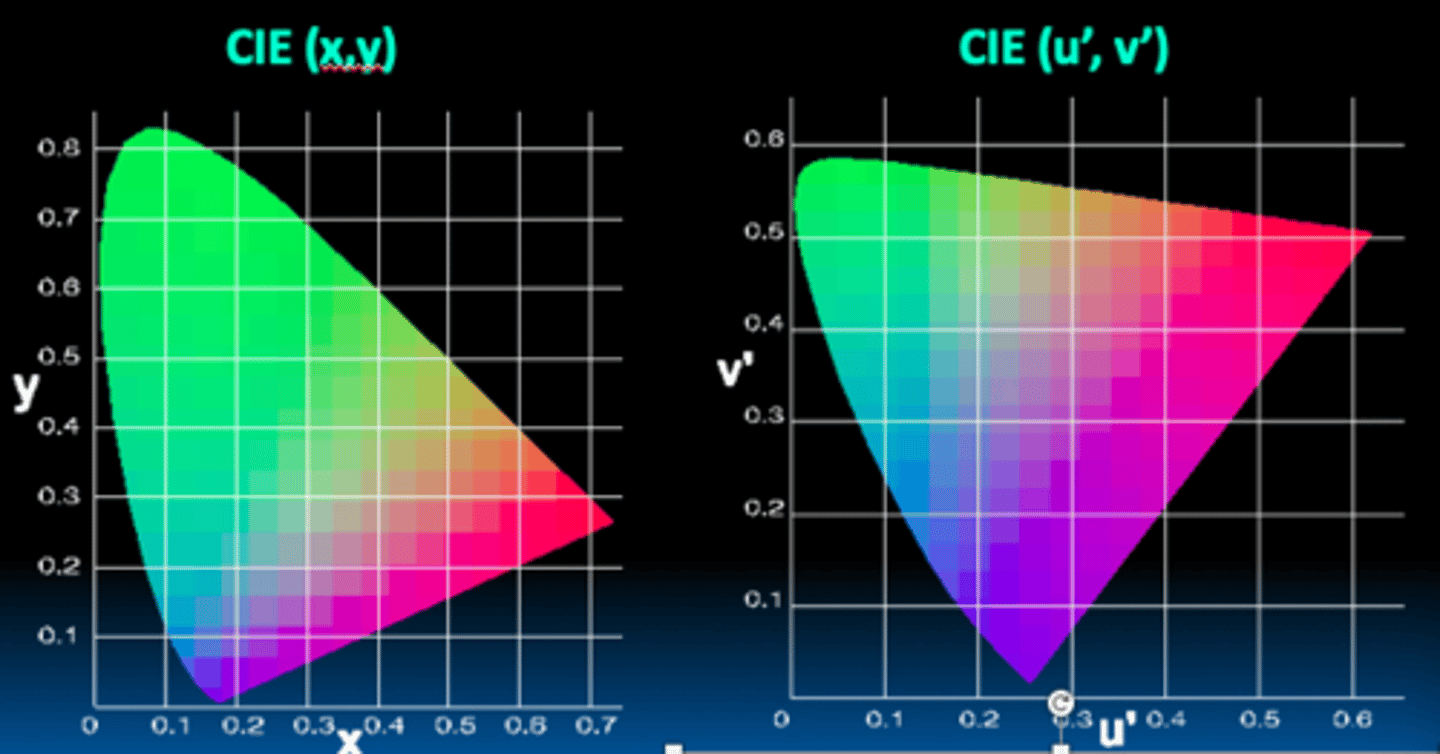
uniform color spaces
•Attempt to correct this limitation by remapping color space so that just-noticeable differences are contained by circles -> distances more perceptually meaningful.
•Examples:
–CIE u’v’
–CIE Lab