Unit 0-Foundations (8,000-600 BCE)-APWH
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Neolithic Era
The period of the "New Stone Age" associated with the first Agricultural Revolution (onset of planting crops & domesticating herds). It follows the Paleolithic period.
pastoralism
A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic herding and the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter.
agrarian
concerning farms, farmers, or the use of land
archaeology
the study of human history and prehistory through the excavation of sites and the analysis of artifacts and other physical remains.
metallurgy
the science of working with metals

rural
relating to farm areas and life in the countryside

urban
in, relating to, or characteristic of CITIES or TOWNS

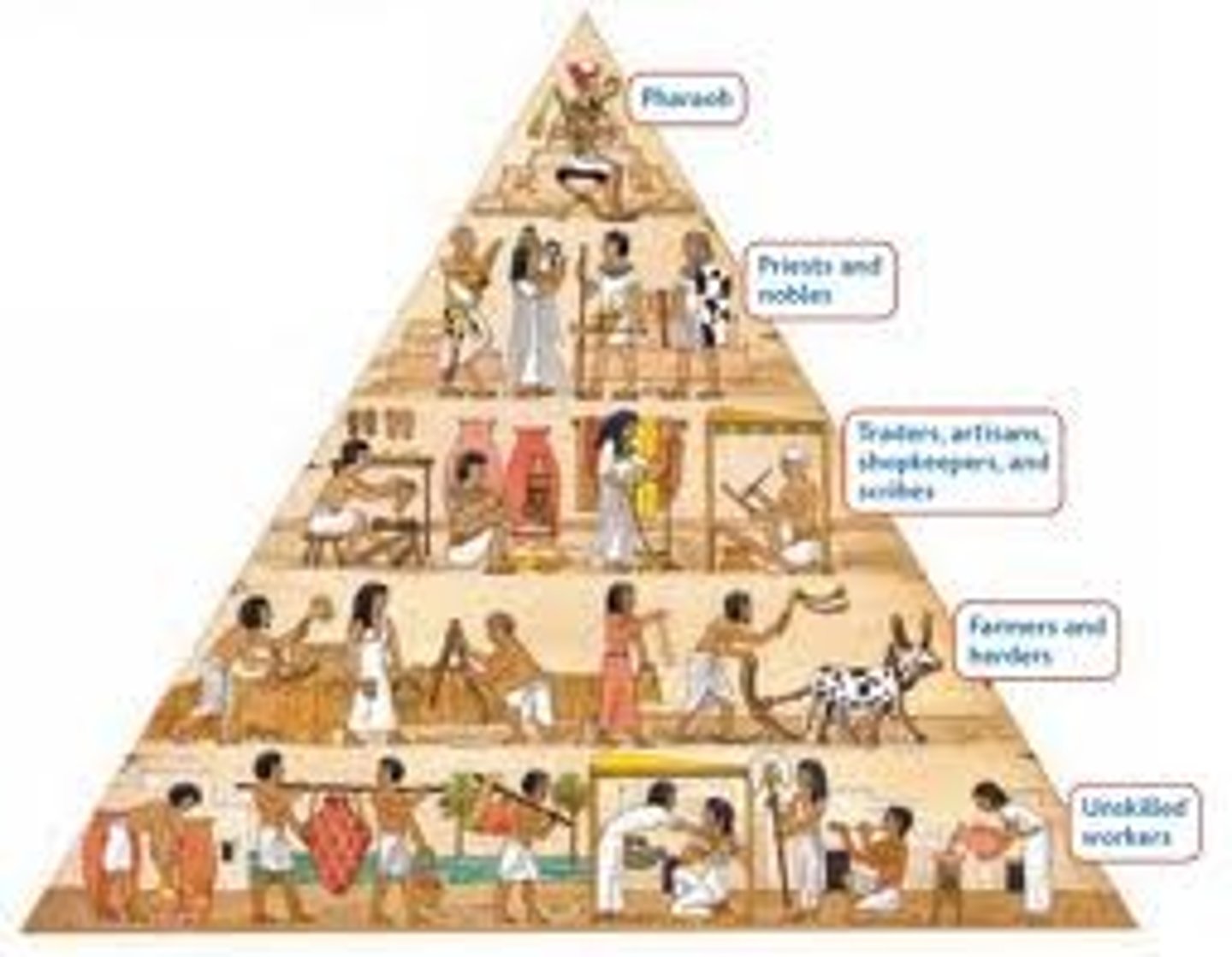
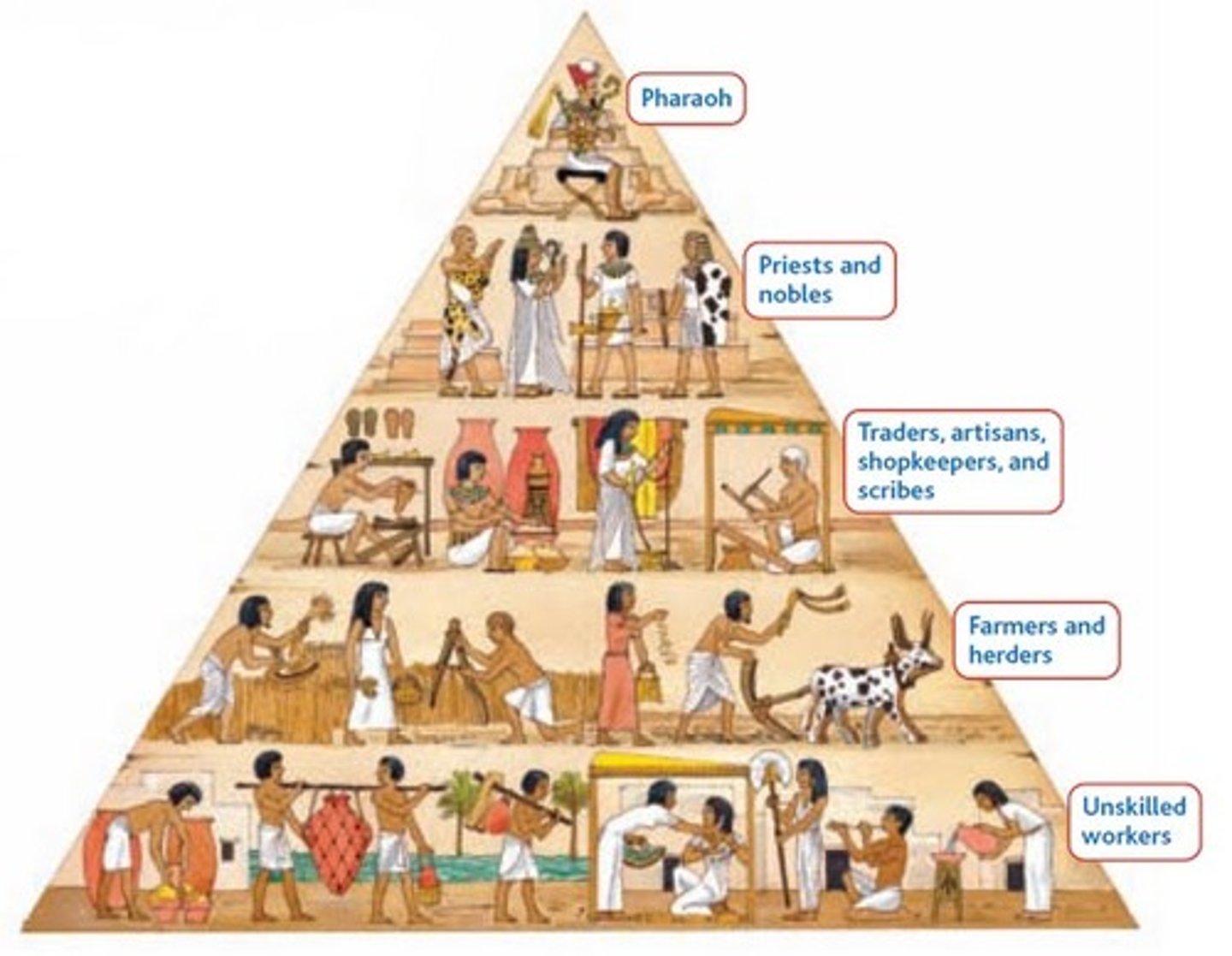
civilization
A society with cities, complex institutions, government/political authority, job specialization, and stratified social classes
job specialization
The process by which a division of labor occurs as different workers specialize in different tasks over time

social hierarchy
an order or ranking of social classes, usually with laborers/producers at the bottom and leaders, kings, or other elites at the top
patriarchal
relating to a society in which men hold the greatest legal and moral authority

city-state
A sovereign state comprising of a single city (urban area) and its immediate hinterland

imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, or economically (empire-building)

bureaucracy
A system of organizing and managing a complex government through departments and agencies, run by appointed officials

monumental architecture
large man-made structures generally created for the public to remember or revere an event or individual

alphabet
writing system in which each letter represents a single basic sound that can be combined with other letter sounds to form words; developed first by the Phoenicians around 1,000 BCE

Cuneiform
A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge shaped stylus and clay tablets.

Heiroglyphs
a writing system used in Egypt by using pictures and symbols to tell stories and events

Code of Hammurabi
set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi in the 18th c. BCE; emphasized the concept of "lex talionis", or law of retaliation (ex: "an eye for an eye")

polytheism
the belief in or worship of more than one god.

monotheism
belief in a single God

Judaism
monotheistic religion of the Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles embodied chiefly in the Torah and the Talmud
prophet
a person regarded as an inspired teacher or proclaimer of the will of God
Covenant
A solemn agreement between God and Abraham, in which God promised Abraham and his followers the land of Canaan, in return for their obedience and faith
Torah and Talmud
Holy books for Jewish faith
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation (samsara) and a supreme being (Brahman) who takes many forms
Vedas
Collections of hymns, songs, prayers, and rituals honoring the various gods of the Aryans; early sacred texts of Hinduism
caste system
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society
Zoroastrianism
A religion that developed in early Persia and stressed the fight between the forces of good and evil (and how eventually the forces of good would prevail)
Dynastic Cycle
rise and fall of Chinese dynasties according to the Mandate of Heaven
Mandate of Heaven
a political theory of ancient China in which those in power were given the right to rule from a divine source
ritual bloodletting
fundamental part of Mayan religion; Mayan rulers gave their blood to nourish the gods; done through self-mutilation
maize
An early form of corn grown by ancient Mesoamericans

Austronesian migrations
The last phase of the great human migration; Austronesian peoples settled in the Pacific Islands (Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia) and Madagascar in a series of seaborne migrations beginning around 3,500 years ago.
identify
To give the name and/or the defining characteristics of (in a list)
compare and contrast
to examine the qualities of in order to determine SIMILARITIES or DIFFERENCES
prioritize
To arrange or rank items in order of importance
analyze
To break down a complex whole to study the nature and relationships of the parts
evaluate
To determine the significance or quality of; to assess
political
relating to government, laws, or public policy

intellectual
relating to the ability to think and understand ideas and information
religious
relating to spiritual beliefs & practices

artistic
relating to the arts (visual arts, music, literature) and monumental architecture

technology
The application of scientific knowledge and innovation for practical purposes (to make life and work more efficient)

economic
relating to the system in a society or state that involves the use of resources, land, and labor to make, buy, and sell goods
social
relating to a society and its organization (ex: class hierarchy, gender roles, family structure, etc.)