Urology Boards terms
1/297
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Memorize the below definitions for day of test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
298 Terms
Post obstructive diuresis
urine output > 200 mL/hour for two consecutive hours or > 3L/24 hours after the obstruction is relieved
PDE5 inhibitors are metabolized by cytochrome P450 pathway, therefore what drugs are concerning due to their ability to increase serum levels of PDE5 inhibitors.
Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors
“SICKFACES.COM”
S: odium valproate
I: soniazid/ INDINOVIR
C: imetidine
K: etoconazole
F: luconazole
A: lcohol
C: hloramphenicol
E: rythromycin
S: ulfonamides
C: iprofloxacin
O: meprazole
M: etronidazole/ MACROLIDES
According to AUA Best practice statement who gets antimicrobial prophylaxis at removal of catheter?
And what antibiotics are recommended?
Patients with risk factors (i.e., advanced age, anatomic anomalies of the urinary tract, chronic steroid use, smoking, etc.). The antimicrobials of choice are fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
What is solfenacin? and what is it used for?
Solifenacin (Vesicare) is a anticholinergic drug selective for M3.
First line for UUI
For men with non obstructive azoospermia, aka testis is the problem what do we see for FSH & testes size?
FSH > 7.6
testes small < 4.6 cm
Hydroceles form between what layers?
Parietal and visceral layers of the tunica vaginalis.
Congenital paraureteral diverticula are most frequently associated with
VUR
Gold standard for diagnosis = VCUG
Patient on Topiramate a 24 hour urine will show_______.
And they are likely to have what kinds of stone?
hypocitraturia
Calcium phosphate
An injury below vertebral level _____ would result in a sacral spinal cord injury.
What do we see in these patients
L1
1) Detrusor underactivity/hypocontractility
2) lack of volitional control of the external sphincter
3) SUI or overflow incontinence due to weak sphincter
Weakness, muscle cramps and fatigue are common side effects of thiazide therapy…what electrolyte changes cause this?
Diuretic-induced hypokalemia or hyponatremia.
In this clinical scenario, potassium and sodium levels should always be checked!!!!
Tx: hypokalemia —> potassium supplements or switching to a combined thiazide - potassium sparing diuretic preparation.
Tx if there is hyponatremia _→ STOP thiazide use, cation repletion, and oral fluid restriction.
What nerve is impacted during Laparoscopic varicocelectomy?
The Genitofemoral nerve lies directly atop the psoas muscle in close proximity to where the gonadal vessels are ligated during this procedure.
Approximately 4-5% of patients undergoing laparoscopic varicocelectomy will complain of either temporary or permanent alterations in the sensory innervation of the anterior thigh consistent with injury to the genitofemoral nerve.
Men with Congenital absence of Vas deferens/cystic fibrosis mutation have semen parameters consistent with a pattern seen with ejaculatory duct obstruction.
What are they?
Sperm count:
Semen volume:
Semen pH
Semen coagulum
Semen liquefaction:
Semen fructose level:
Azoospermia: 0 sperm on 2 centrifuged specimens
Low semen volume (< 1.5 mL)
Acidic semen pH (< 7.0)
Can’t form semen coagulum
Prolonged semen liquefaction >30 minutes
Semen fructose levels are low
Urinary retention in young women that is associated with abnormally increased EMG activity that results in impaired external sphincter relaxation.
What is this & what’s the tx?
Fowler’s Syndrome
Tx: Sacral neuromodulation
Patient has BCR s/p RT or ablative therapy what must you do do before any salvage therapy.
GET PROSTATE BIOPSY
BCR post focal ablation, clinicians should offer
whole gland treatment by RP or RT
Men with mCRPC who have mutations in DNA repair enzymes central to homologous recombination DNA repair ( EX. BRCA1/2) should get
PARP INHIBITORS
In patients with mismatch repair deficient or MSI-H mCRPC, clinicians should offer
Pembrolizumab
Who with advanced PCA gets bone protective agent denosumab or zoledronic acid ?
Metastatic Castrate resistant prostate cancer W/ BONY METS
To prevent skeletal related events
Post biopsy, if you see HGPIN, ASAP, or AIP (atypical intraductak proliferation) which of the following should have repeat testing that includes biopsy.
Who does NOT get a repeat biopsy without further evaluation.
ASAP & AIP
Who does NOT get a repeat biopsy without further evaluation.
HGPIN
T staging for PCA
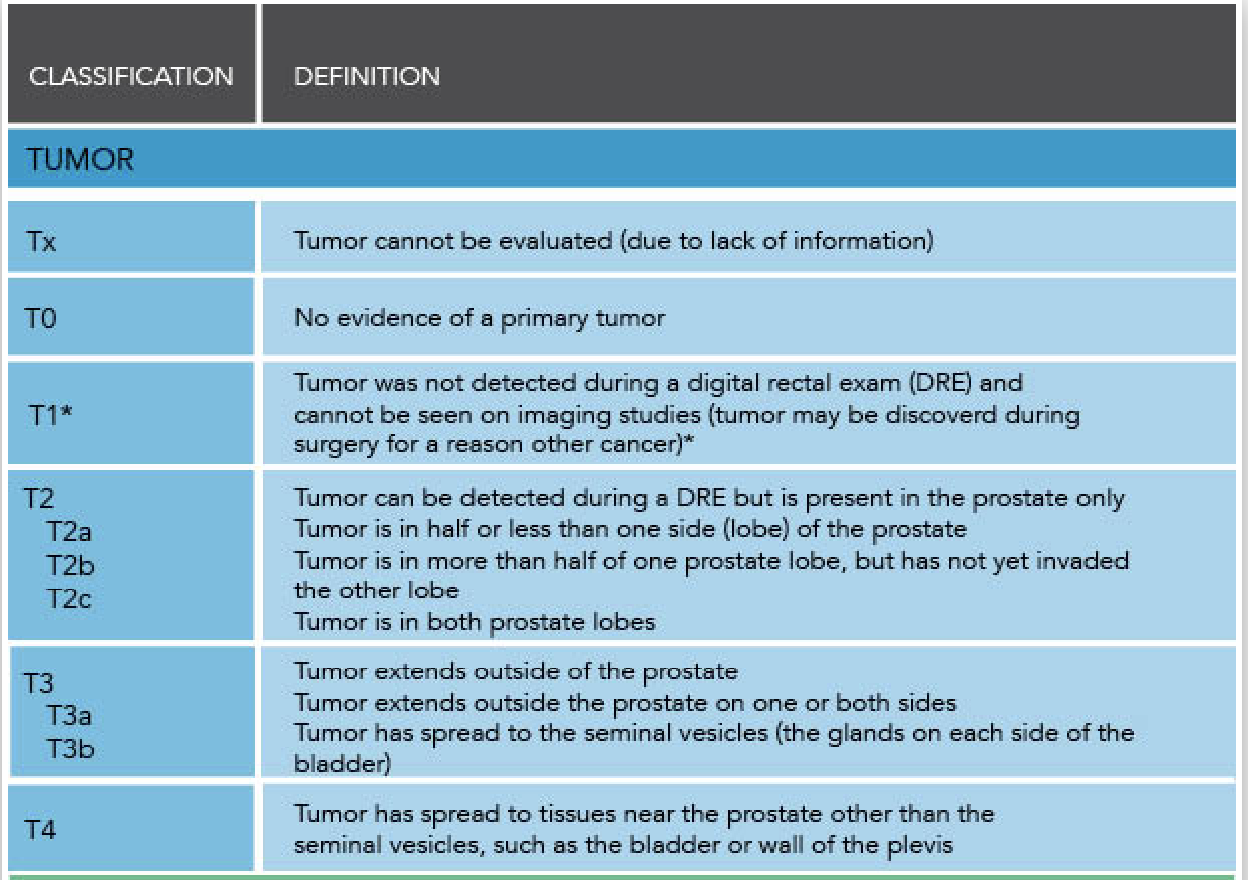
Describe Moderate hypo fractionated EBRT
Higher doses of RT given in fever sessions
What toxicity is of concern in with moderate hypofractionation in comparison to conventionally fractionated EBRT?
Small increased risk of ACUTE gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity with moderate hypofractionation.
GU toxicity (both acute & late) as well as Late GI are the same between types of RT!
What is Ultra hypo fractionated mean?
Its basically concept of higher dose with less frequency. Ultra-hypofractionation, referring to the use of fraction size ≥5 Gy, so even more given.
Ultra by-fractionation is NOT recommended to ______ unless clinical trial
High risk patients
Best predictor of pca mortality in the setting of recurrent disease post local therapy
PSA doubling time (< 10 months)
The SELECT trial showed selenium _____ against pca , and Vitamin E ______ risk of pca
SELECT trial showed selenium DOES NOT PREVENT against pca , and Vitamin E INCREASES risk of pca
voiding dysfunction post midurethral sling placement …what next?
Get cysto first prior to making any surgical decision because you want to r/o urethral erosion.
Global Polyuria
total daily urine production > 40 mL/kg (ex. 80 kg man = expected volume 2800 mL).
mag 3/renal Lasix scan cut offs for T 1/2
0-10: non obstructed
10-20 : equivocal
>20: obstructed
First line therapy for chancroid (H. Ducreyi)
Single-dose treatment with azithromycin 1 gram orally or ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscularly
Nocturnal polyuria index (NPi)
urine at night/ total 24-hour urine volume > 33%
Metastatic RCC: IMDC Risk factors
Karnofsky Performance < 80% |
Time from initial diagnosis to treatment < 1 year |
Dec. Hemoglobin |
Inc. corrected serum calcium |
Neutrophilia |
Thrombocytosis |
Sampling bias
Patients are enrolled in a non-random manner
Verification bias
study design foregoes testing of a subset of patients included in the study
Confirmation bias
occurs when there is dismissal of evidence that appears to go against preconceived notions
Dietl’s crisis
episodic abdominal pain and hydronephrosis caused by extrinsic pressure from an artery —> episodes usually happen after high fluid intake. Pyeloplasty resolves it.
Treatment for meatal vs. penile vs. bulbar strictures
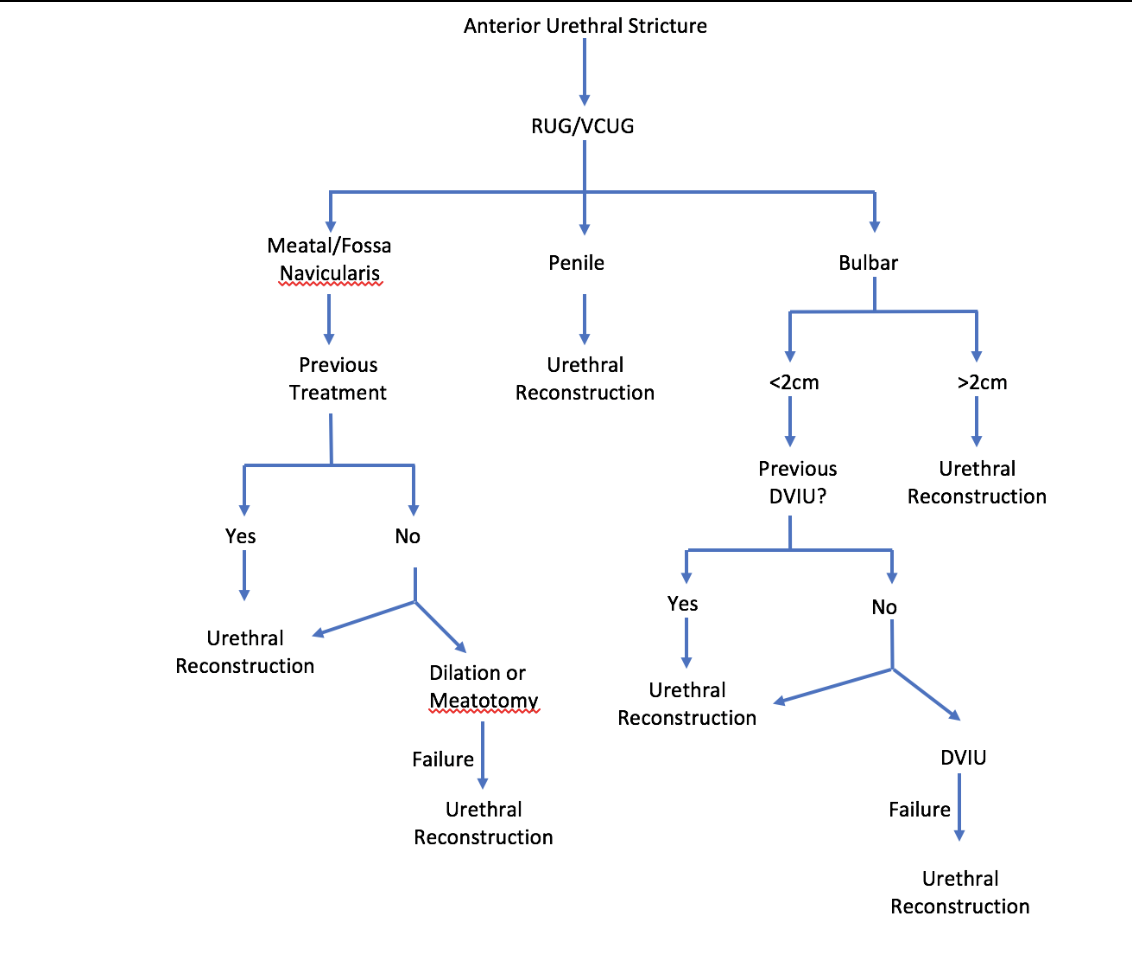
Anterior urethra includes …
urethral meatus, fossa navicularis, penile urethra, and bulbar urethra.
All parts of the urethra that are Associated with corpus spongiosum.
What is absent in the posterior urethra?
corpus spongiosum is absent in the posterior urethra
Imaging for posterior urethral stricture
if the stricture extends past the level of the bulbomembranous junction, RUG and VCUG at the same setting may be necessary to effectively characterize the stricture disease as the RUG alone poorly evaluates the posterior urethra
Normal urethral mucosa and its associated corpus spongiosum is replaced with scar tissue
Anterior urethral stricture disease
Abx contraindicated in peel (due to poor tissue penetration)
nitrofurantoin (dont use in peel or prostatitis)
MC SE of fluoroquinolone
GI upset, tendinopathy, QT prolongation, CNS effects (elderly), and risk of aortic aneurysm
Detrusor leak point pressure >_____ is associated with renal deterioration
>40
Bladder Outlet Obstruction Index (BOOI)
Pdet@Qmax – 2 x Qmax
- >40 = Obstructed
- 20-40 = equivocal
- <20 = unobstructed
PDet =
= Pves – Pabd
AUA symptom score/IPSS stratification
Symptom Score (Severity):
0 to 7 (Mild)
8 to 19 (Moderate)
20 to 35 (Severe)
What does IPSS include in addition?
Quality of Life Due to Urinary Symptoms
0 = delighted
6 = Terrible
When to give what alpha-1 blocker:
1) Person on antihypertensives/ or old with cardiac issues
Silodosin —> least impact on blood pressure
When to give what alpha-1 blocker:
Sexually active guy wants to maintain fertility
Doxazosin & Terazosin
When to give what alpha-1 blocker:
Man getting ready for cataracts surgery
All alpha-1 blockers carry risk for Intraoperative floppy Iris syndrome. But Tamsulosin is the worst!
Tamsulosin carried the highest risk for IFIS (40x that of alfusozin).
Discontinuation of tamsulosin 4 to 7 days prior to cataract surgery is routine practice, but it does not completely eliminate risk
5 - alpha reductase indicated in men with…(Hint 3 things).
1) prostate volume of > 30g on imaging
2) PSA > 1.5ng/mL, or
3) palpable prostate enlargement on (DRE)
Next step for patient with low risk NMIBC and a normal post op cystoscopy.
Cysto in 6- 9 months. NO cytology
NMIBC Guideline #10:
In a patient with a history of low-risk cancer and a normal cystoscopy, a clinician should not routinely use a urinary biomarker or cytology during surveillance.
What are storage symptoms?
Storage symptoms include frequency, urgency, nocturia and urinary incontinence.
Primary toxicity: Cisplatin
Nephrotoxicity & Ototoxicity
Chemo man = kidneys + ears are “C”
Primary toxicity: Bleomycin
Pulmonary fibrosis
Chemo man = Lungs are “B”
Primary toxicity: Vincristine + Taxanes (Docetaxel /Paclitaxel)
Peripheral neuropathy
Chemo man = Legs and arms are “ V”
Primary toxicity: Doxorubicin
Cardiotoxicity
Chemo man = heart is “D”
Primary toxicity: Cyclophosphamide
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Chemo man = Bladder is “P”
Primary toxicity: Methotrexate/ 5-flourauracil
Myelosuppresion
What chemotherapy is the least myelosuppresive
BLEOMYCIN!
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Transurethral cases (TURP/TURBT etc)
First line: Cefazolin (Ancef) or Bactrim
Second line:
amoxicillin/clavulanate
aminogylcoside ± ampicillin
Aztreonam ± ampicillin
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Transrectal prostate biopsy
First line:
flouroquinolone
3rd gen cephalosporin
1st/2nd gen cephalosporin ± aminoglycoside
Second line: Aztreonam
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
PCNL
First line:
1st/2nd gen cephalosporin
aminoglycoside + metronidazole
aminoglycoside + clindamycin
aztreonam + metronidazole
aztreonam + clindamycin
Second line:
Ampicillin/sulbactam
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Ureteroscopy
First line:
1st/2nd gen cephalosporin
Bactrim
Second line:
Aminoglycoside ± Ampicillin
Aztreonam ± Ampicillin
Amoxicillin/clavulanate
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Urethroplasty
First line: Cefazolin (Ancef)
Second line:
Cefoxitin
Cefotetan
Ampicillin/sulbactam
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Penile surgery/circumcision
None required
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Implanted device: AUS, IPP, sacral neurostimulator
First line:
Aminoglycoside + 1st/2nd gen cephalosporin
Aminoglycoside + Vancomycin
Aztreonam + 1st/2nd gen cephalosporin
Aztreonam + vancomycin
Second line:
Antibiotic Prophylaxis:
Vaginal surgery: slings, fistula repair, urethral diverticulectomy etc
First line:
2nd gen cephalosporins (Cefoxitan & cefotetan)
Cefazolin (Ancef) can be used in slings
Second line:
Aztrenomam, clindamycin, metronidazole
What stone is pathognomonic for hypercalciuria and elevated urinary pH
BRUSHITE STONE!!
Think primary hyperparathyroidism (resorptive hypercalciuria)
Renal hypercalciuria is associated with what type of stones?
calcium oxalate!!!
Equation for Child’s bladder capacity
average bladder capacity in mL = (age in years + 2) X 30
Patient has bilateral adrenalectomy → years later develops visual disturbances and has skin hyperpigmentation. The most likely explanation is:
NELSON’S SYNDROME!
Pituitary adenoma develops due to increased ACTH secretion.
Metabolic derangement associated with ileal conduit
hypokalemic, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
Metabolic derangement associated with stomach used for urinary diversion [Think: vomiting]
hypochloremic, hypokalemic, metabolic alkalosis
First line treatment for uncomplicated UTI in women: list the drug and duration of treatment
Nitrofurantoin: 5 days (100 mg BID)
TMP–SMX: 3 days (1 DS BID)
Fosfomycin: single dose (3 grams)
Bounce effect
PSA rise greater than 0.1 to 0.5 ng/mL followed by a durable decline and is especially common after brachytherapy,
Which antibiotic is preferred for UTI in pregnancy?
Amoxicillin-clavulanate, cephalexin, or fosfomycin.
What are the side effects of aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin)?
Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, neuromuscular blockade
What is the mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones?
Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, preventing DNA replication.
What are key side effects of TMP-SMX?
Hyperkalemia, rash (including Stevens-Johnson), bone marrow suppression, nephrotoxicity.
What antibiotic class should be avoided in patients on warfarin due to increased bleeding risk?
Flouroquinolones & Bactrim elevated INR —> bleeding
Which antibiotic is commonly used for epididymitis in men <35 years old?
Ceftriaxone (IM) + doxycycline (10 days) for gonorrhea/chlamydia coverage.
Sensitivity
Given you have disease, you tested positive.
True positive/ True positive + False negative
Specificity
Given you dont have disease, you tested negative.
True Negative/True negative + False positive
Positive vs. Negative Predictive value
PPV: probability a person has disease if test result is positive.
PPV = TP/(TP + FP)
NPV: probability a person does not have the disease if the test result is negative.
NPV = TN/(FN + TN)
Lose control/coordination of movement, blood pressure, and urination [ Hint: open bladder neck on filling seen on UDS]
Shy Drager = Multiple system atrophy
Penile Doppler what is normal arterial and end diastolic
Normal arterial inflows (peak systolic velocities > 30 cm/sec)
End diastolic velocities < 5 cm/sec
Peyronies + ED what do guidelines recommend for treatment?
what is the cutoff for curvature that impacts treatment?
Inflatable penile prosthesis implant results in curvature correction and restoration of satisfactory sexual function for most men with <60 degree curvature.
If man has > 60 deg curvature, adjunctive procedures are frequently necessary, penile plication or graft incision along With IPP
Histology: concentrically laminated calcific inclusions
Michaelis-Gutmann bodies
Histology: large histiocytes
Von Hansemann cells
Yellow, raised, and soft lesions of bladder associated with Michaelis-Gutmann bodies & Von Hansemann cells
Malakoplakia
Malakoplakia tx
Usually caused by E.coli UTI so Bactrim vs. flouroquinolones
Weigert - Meyer rule
For duplicated renal system.
Ureter of the upper pole moiety obstructs. The ectopic ureter and its orifice inserts medially and inferiorly to the ureter of the lower pole moiety, and frequently ends as a ureterocele.
Ureter from lower pole moiety of the kidney refluxes and inserts laterally and superiorly to the ectopic ureter of the upper pole moiety, and reflux at its level often causes pyelonephritis.
What does impedence mean in context of neurostim
Impedance refers to the resistance to flow of electrons through a circuit. If there is too much resistance, the flow is limited.
Vas deferens travels posterior along the spermatic cord then courses ______ to the epigastric vessels & _________ to the ureter
Lateral to epigastric
Anterior to ureter
Tibial nerve stimulation is associated with ….
flexion of the great toe and tickling of the sole of the foot
Tibial nerve travels behind the _______ of the ankle. Needle for PTNS is placed 3-4 cm ____ of the _______.
medial malleolus
3-4 cm cephalic (superior) to the medial malleolus.
Squamous cell Tx
cystectomy!!!!!