ADVANCED BIOLOGY - Cardiovascular/Blood Vessels/Anatomy and Physiology: Final Term (2nd SEM)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Cardiovascular System
Organ system that distributes blood to all parts of the body
Fists
Human heart is approximately the size of a __________ and weighs less than a pound
Inferior mediastinum
The heart is enclosed within the_________________________, the medial cavity of the thorax and flanked on each side by the lungs
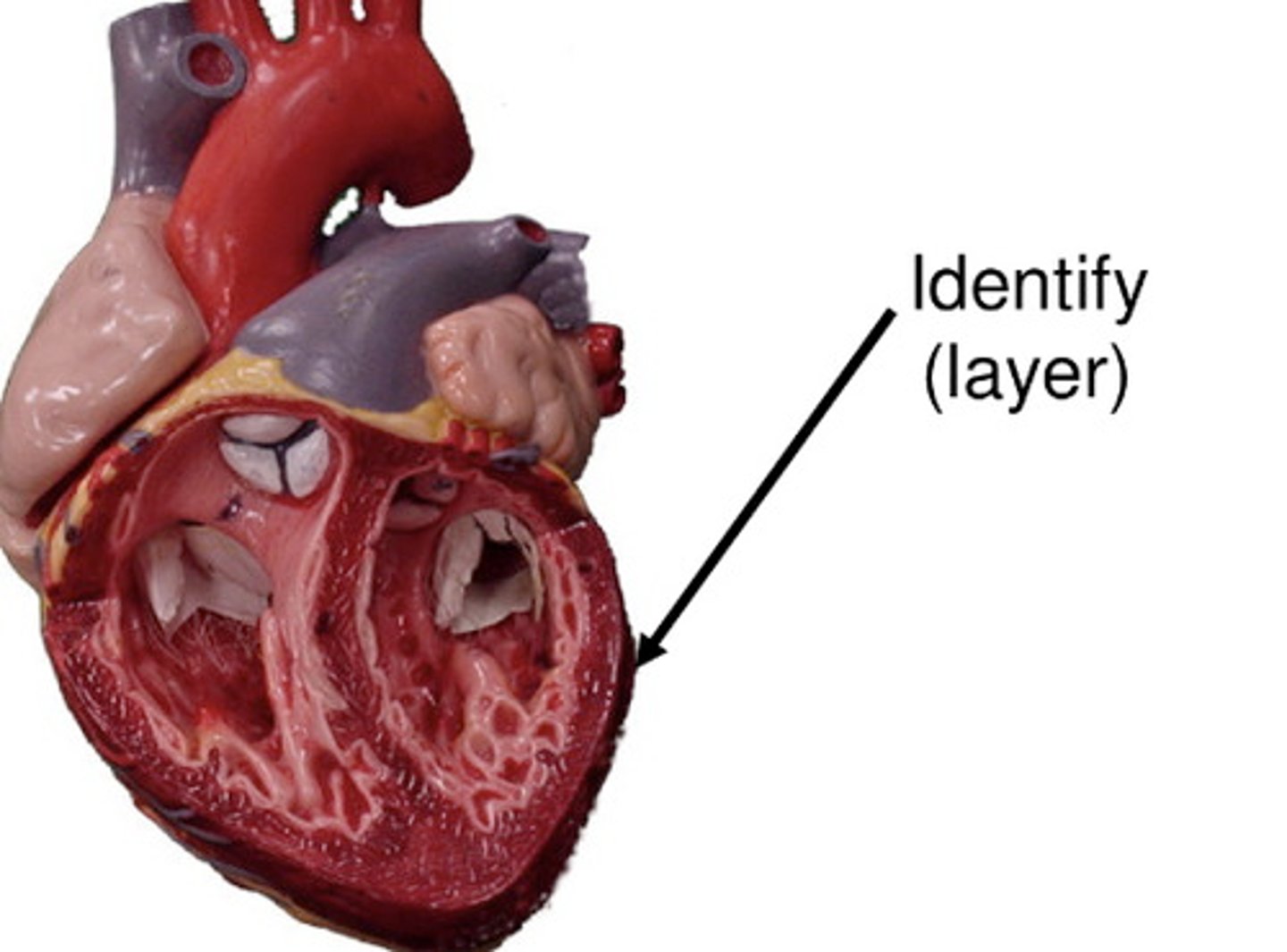
pericardium
A double-walled sac that encloses the heart
Fibrous pericardium
superficial loosely fitted part that protects and anchors the heart
serous pericardium
slippery, two-layer that is deep to the fibrous pericardium
parietal layers
lines the interior of the fibrous pericardium
Epicardium
the parietal layer attaches to the large arteries leaving the heart and then makes a U-turn and continues inferiorly over the heart surface as the visceral layer
serous pericardial membranes
Produces a slippery lubricating fluid which allows the heart to beat easily in a relative frictionless environment
pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium that results in a decrease in the serous fluid
pericarditis
causes the pericardial layers to stick, forming painful adhesions that interfere with heart movements
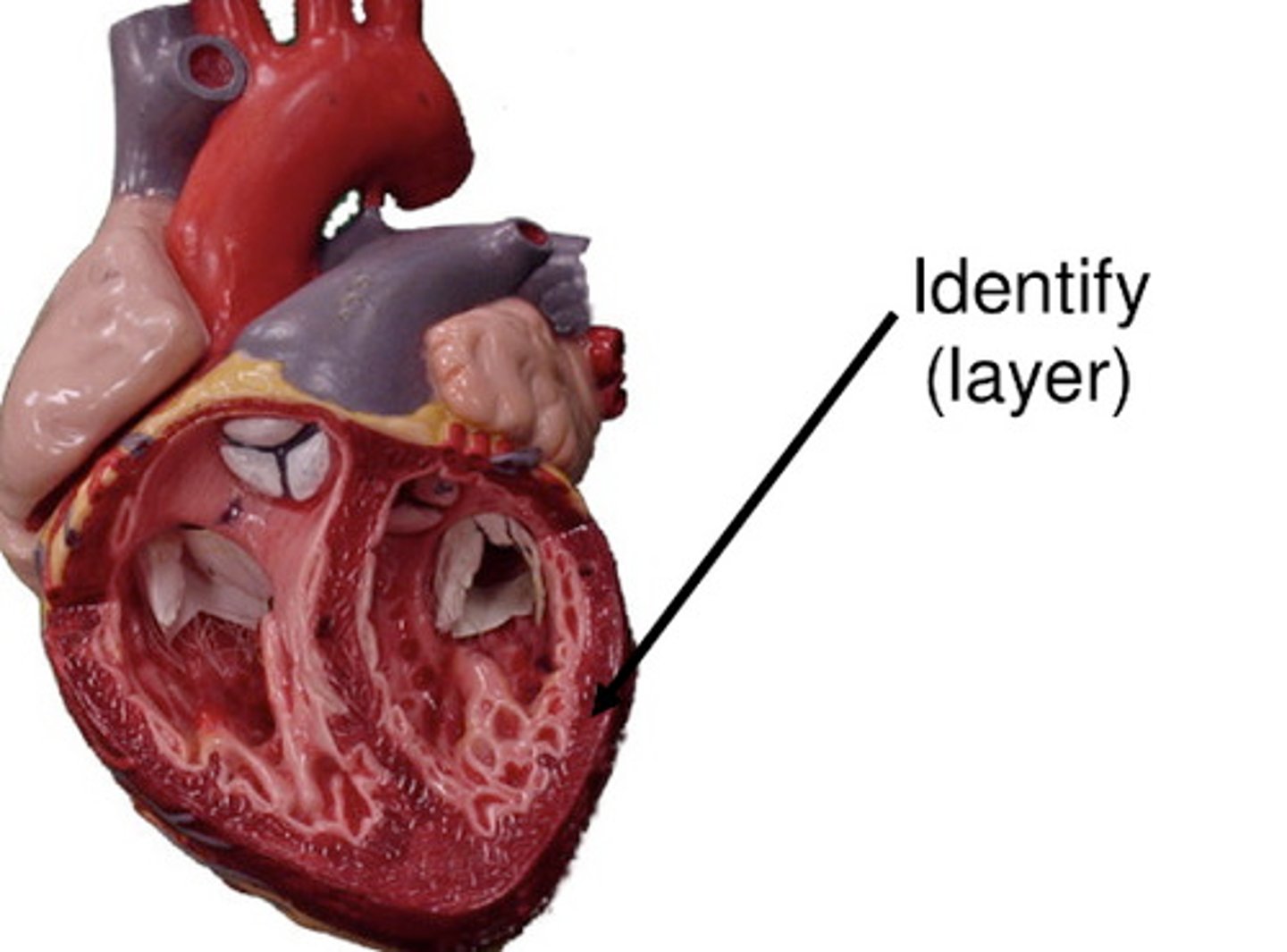
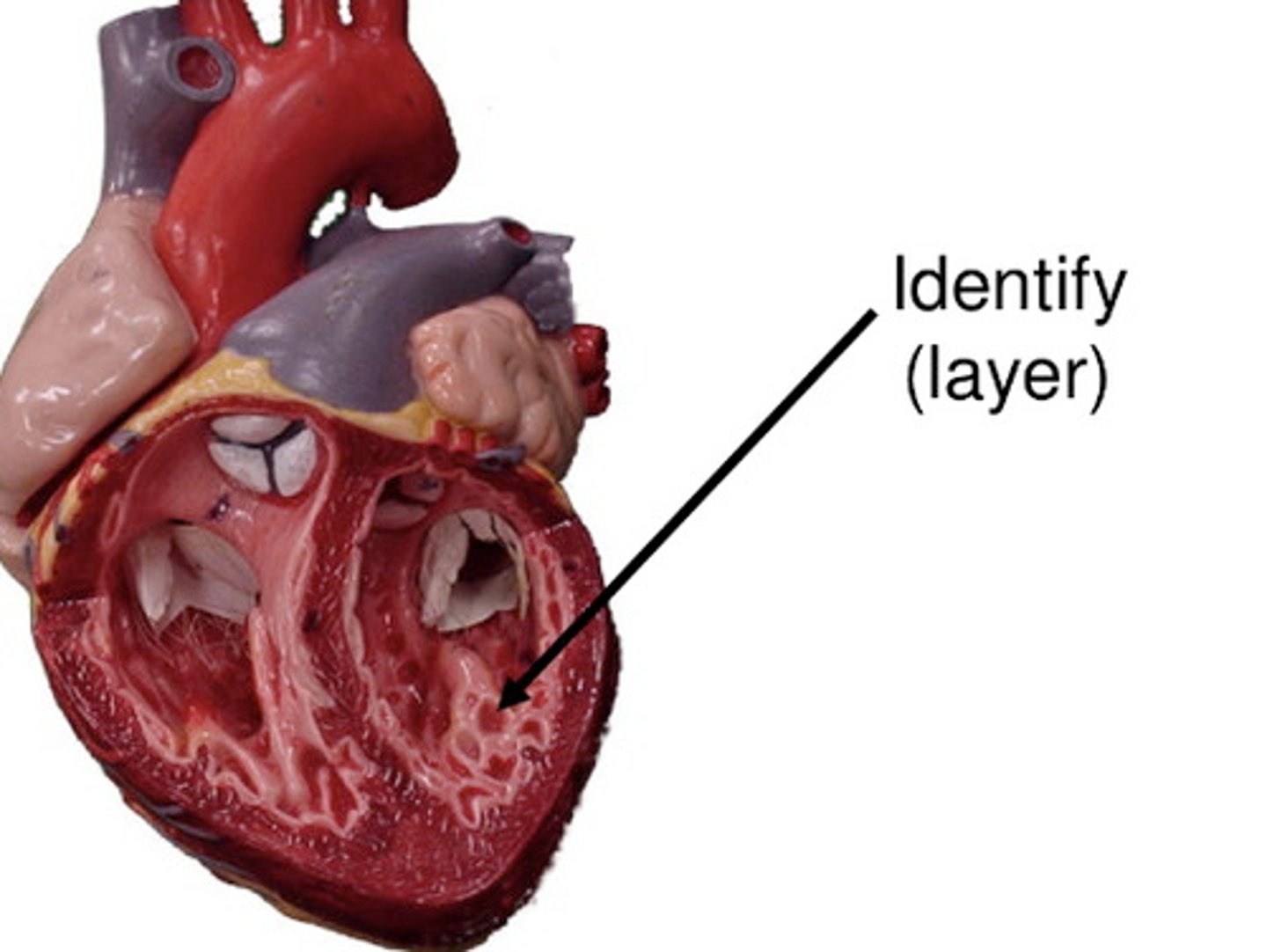
myocardium
consists of thick bundles of the cardiac muscle twisted into ringlike arrangements
myocardium
-layer of the heart that actually contracts
-reinforced by dense, fibrous connective tissue
endocardium
a thin, glistening sheet of endothelium that lines the heart chambers
endocardium
continuous with the linings of the blood vessels leaving and entering the hear
atria
It is where the Blood follows into under low pressure from the veins, and continues into the ventricles
ventricle
-thick-walled discharging chambers
-they are pumps of the heart
-when they contract, blood is propelled out of the heart and into circulation
anterior surface
forms most of the heart's anterior surface
left ventricle
forms the apex
Interventricular/Interatrial Septum
septum that divides the heart longitudinally based on the chambers it separates
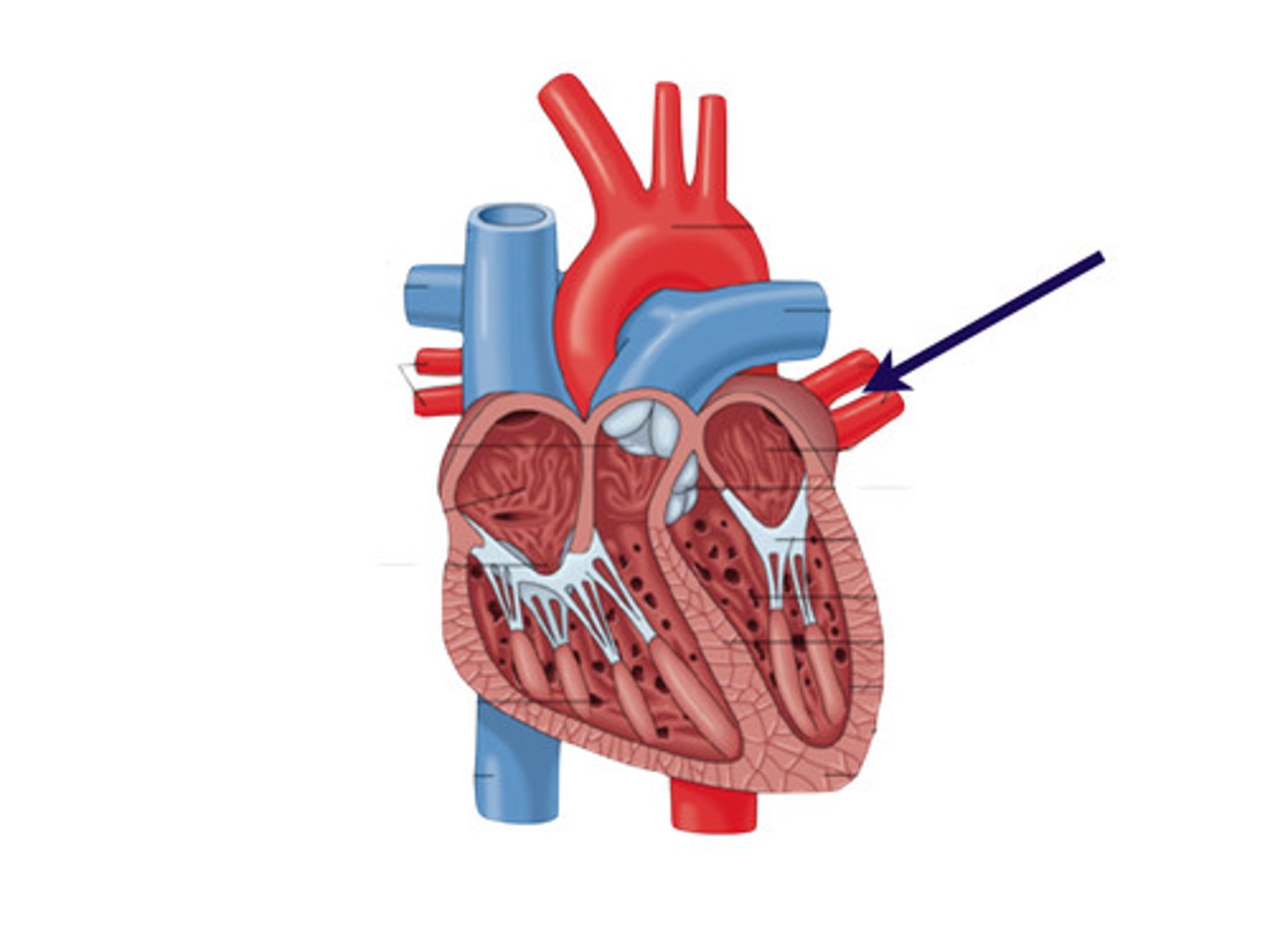
pulmonary arteries
this carry blood to the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is unloaded
pulmonary circulation
its only function is to carry blood to the lungs for gas exchange and then return it to the heart
systematic circulation
oxygen-poor blood circulates from the tissues back to the right atrium via the systemic veins, which empty their blood into either the superior or inferior vena cava
to prevent backflow
What does the valves do?
apex
is directed toward the left hip and rests at about the fifth intercostal space
base
points toward the right shoulder and lies beneath shoulder and lies beneath the second rib
fibrous pericardium
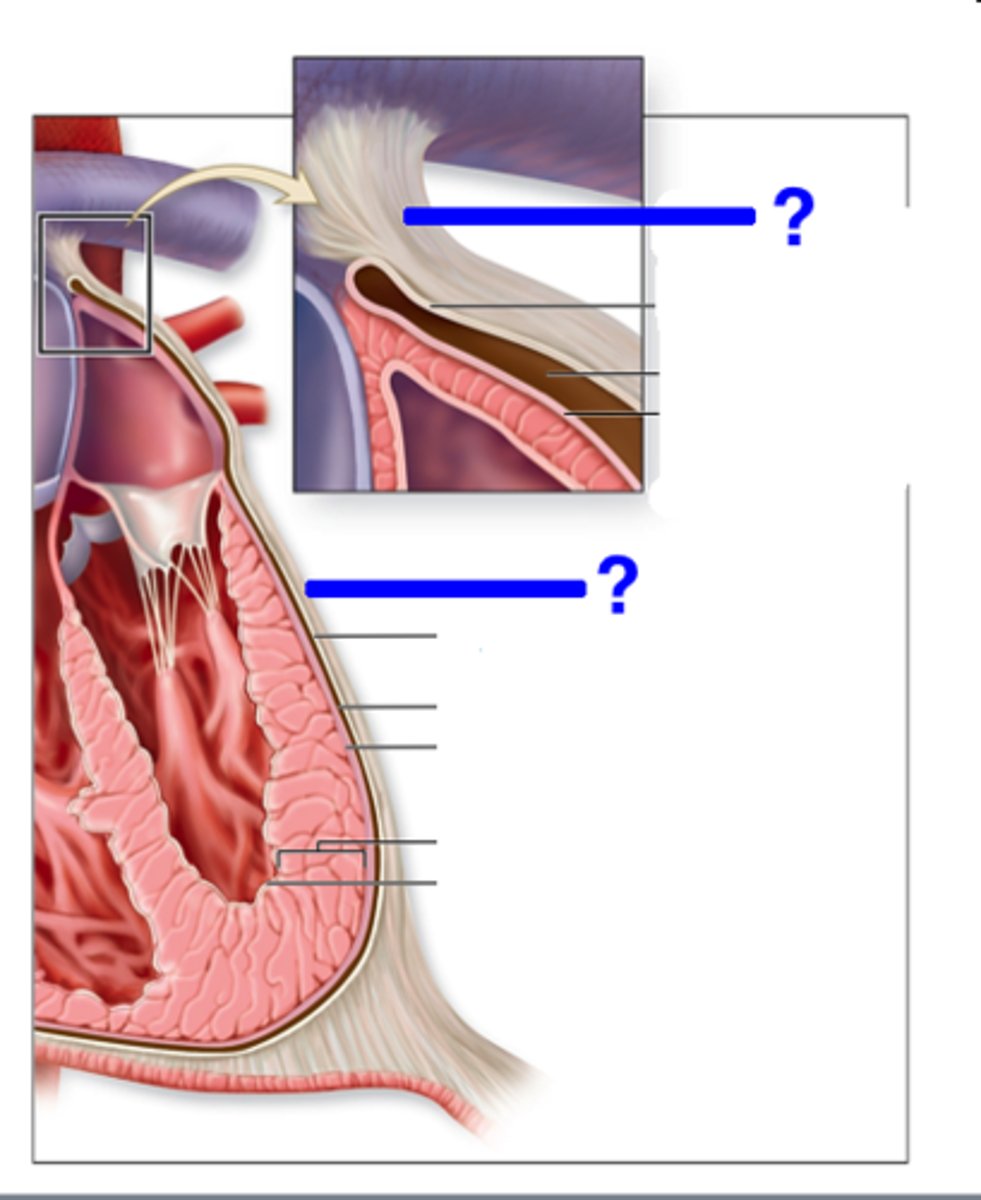
pericardium
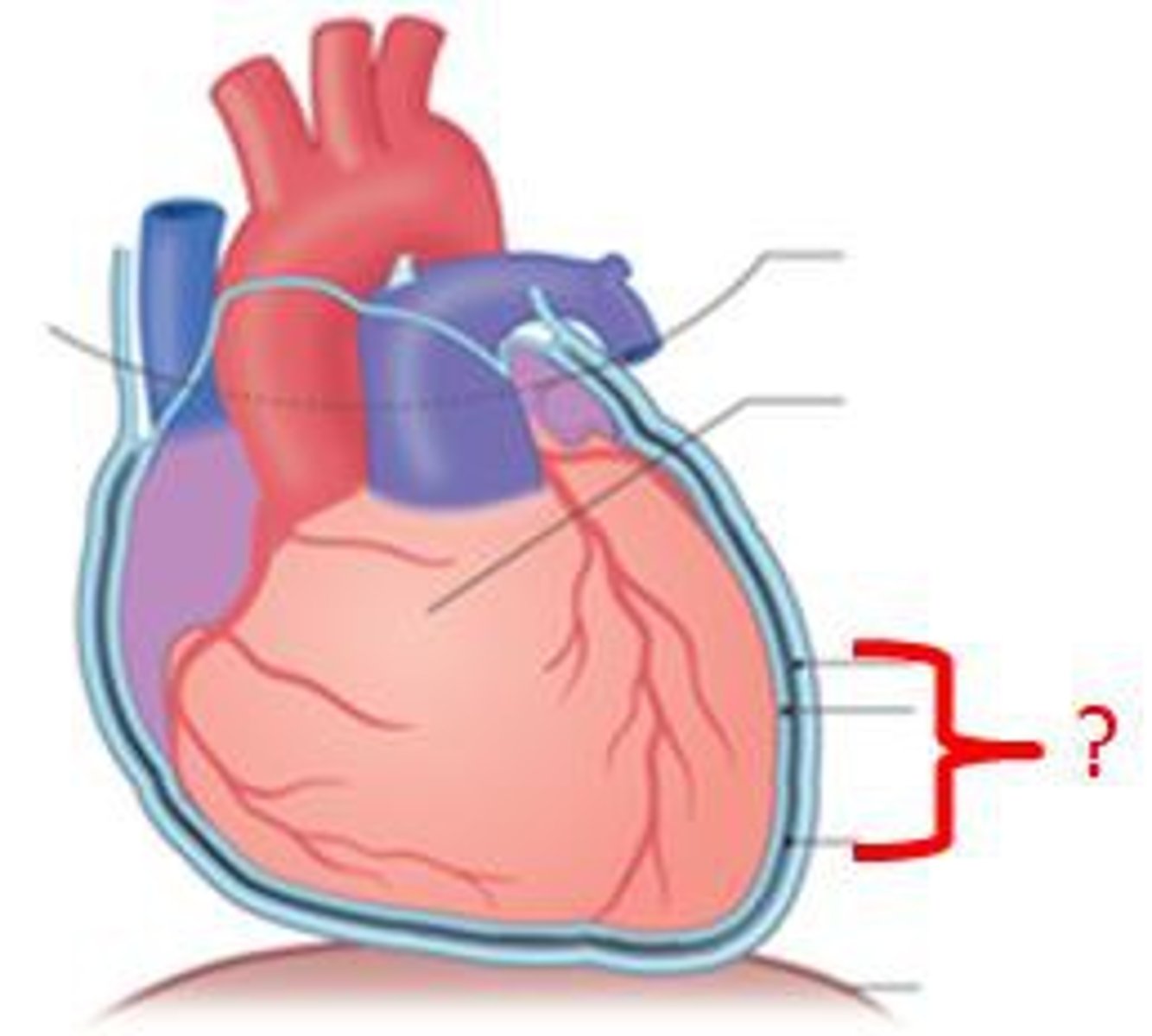
myocardium
endocardium
visceral pericardium
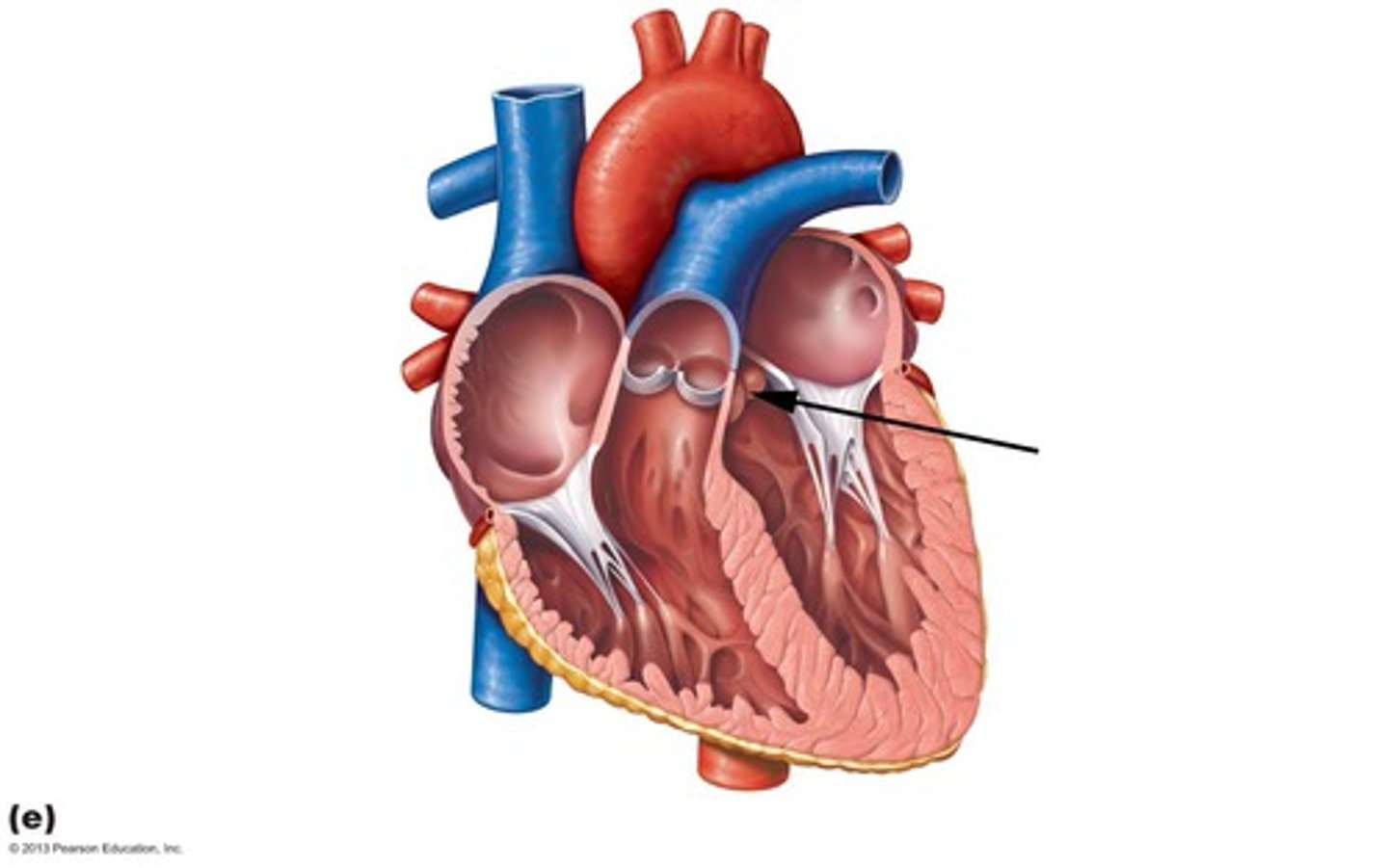
right atrium
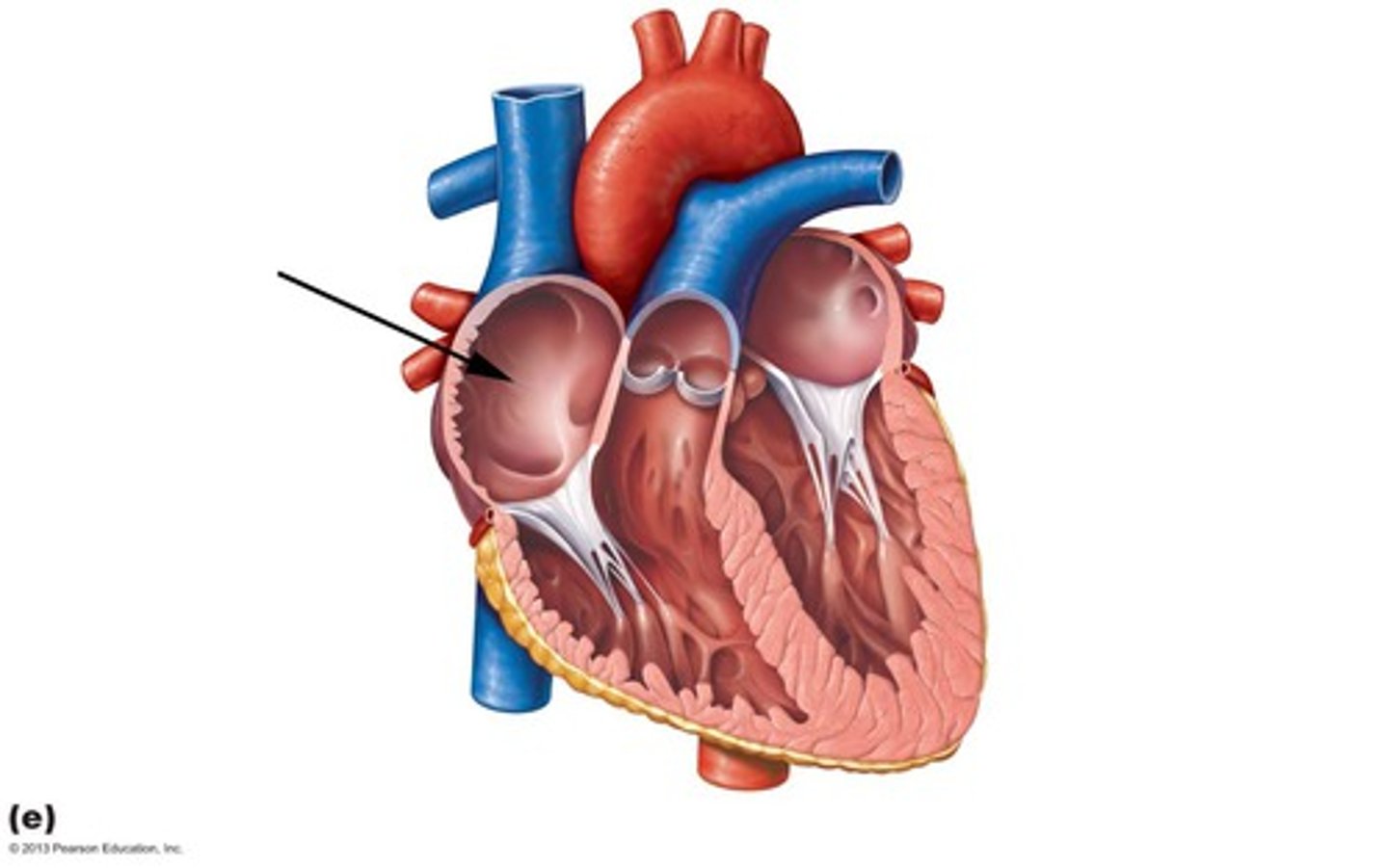
right ventricle
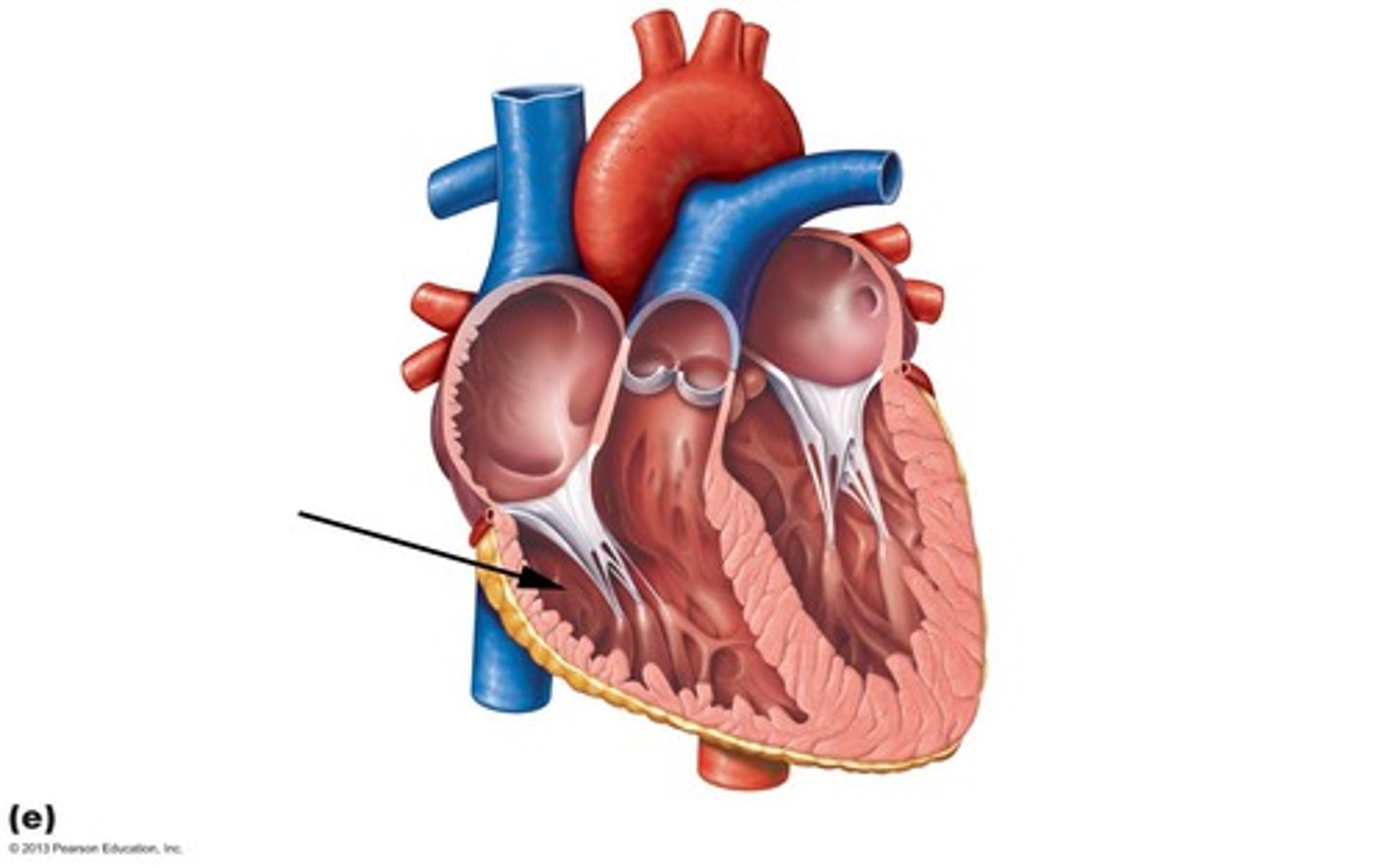
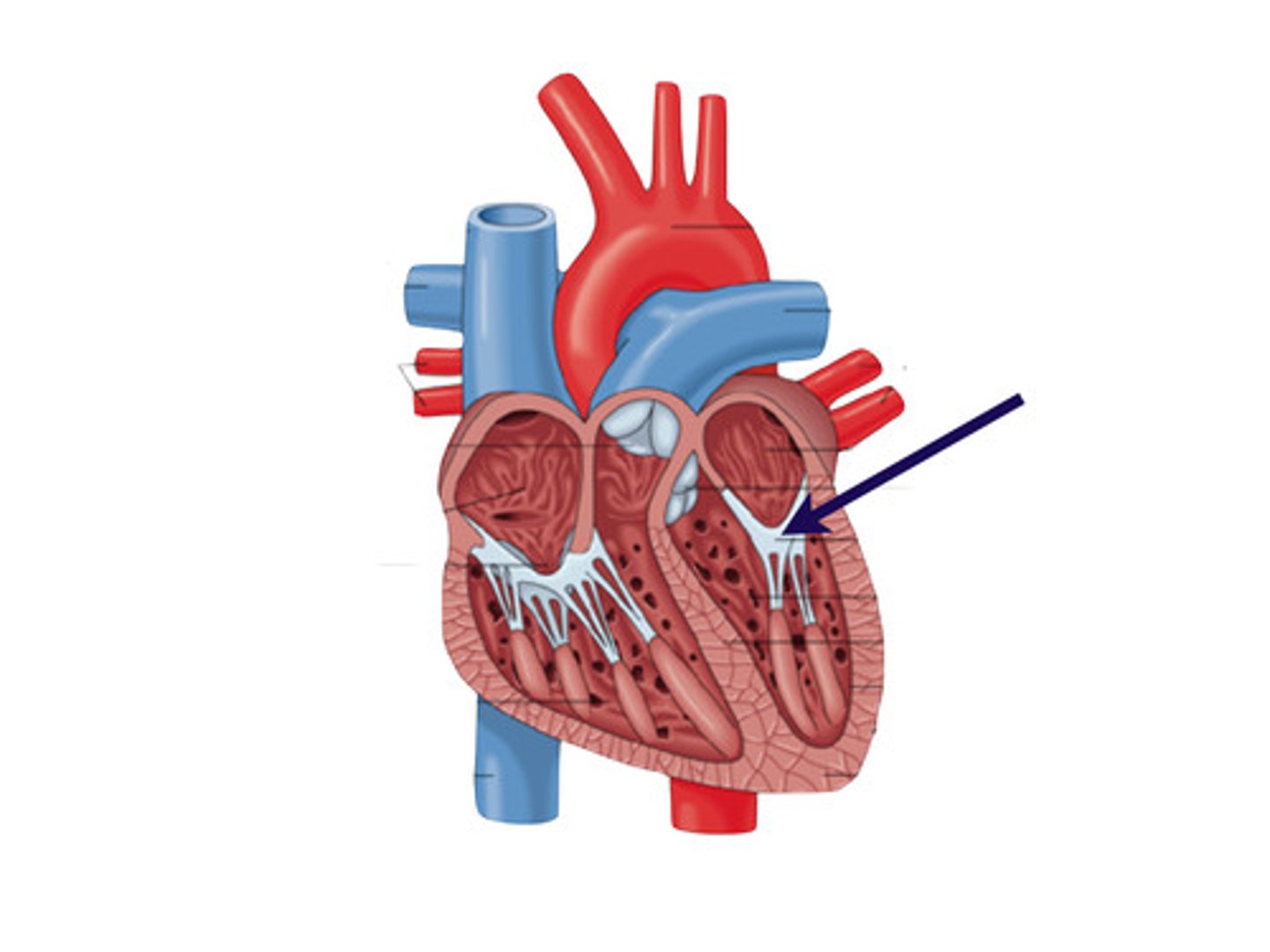
left atrium
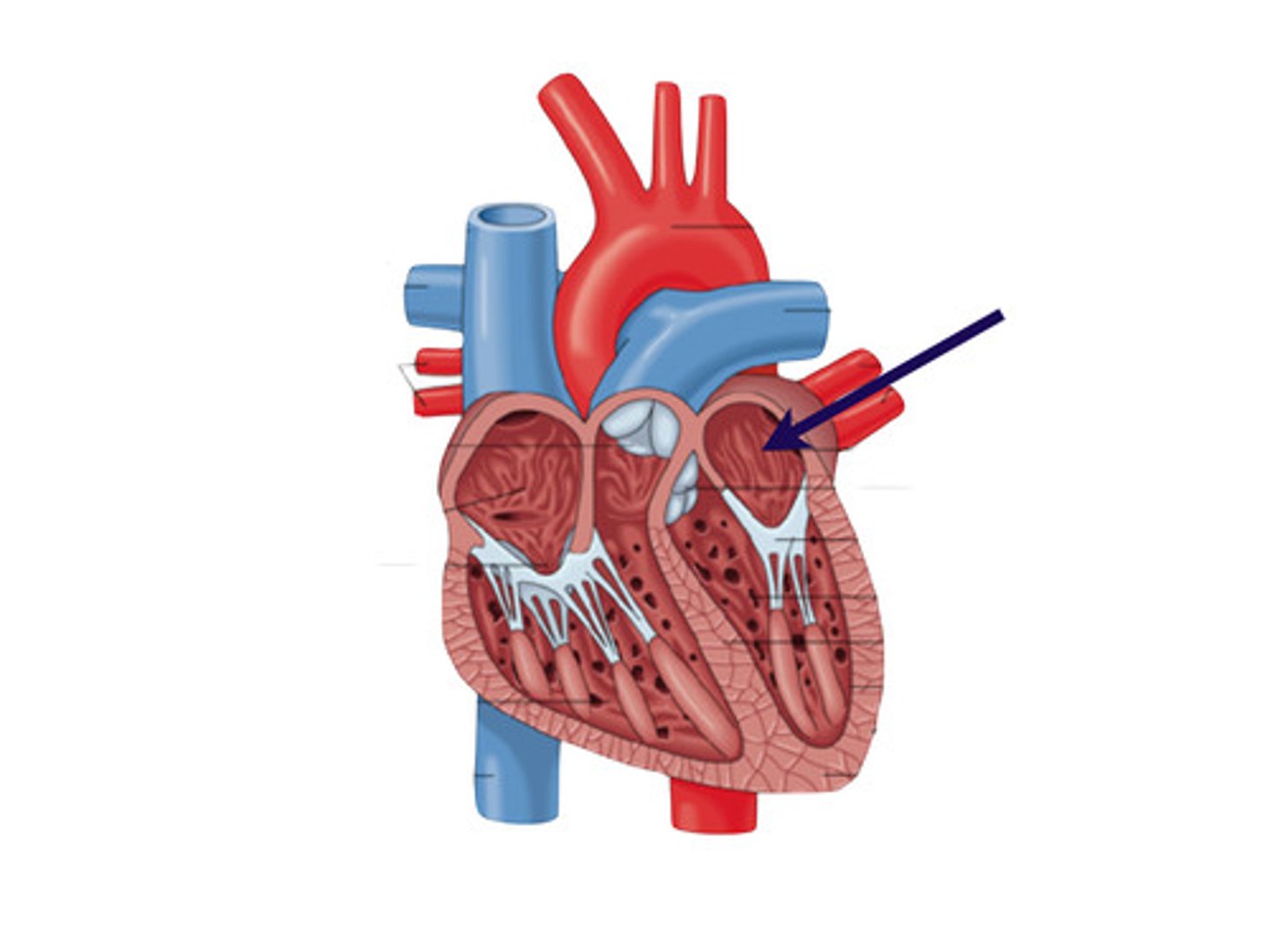
left ventricle
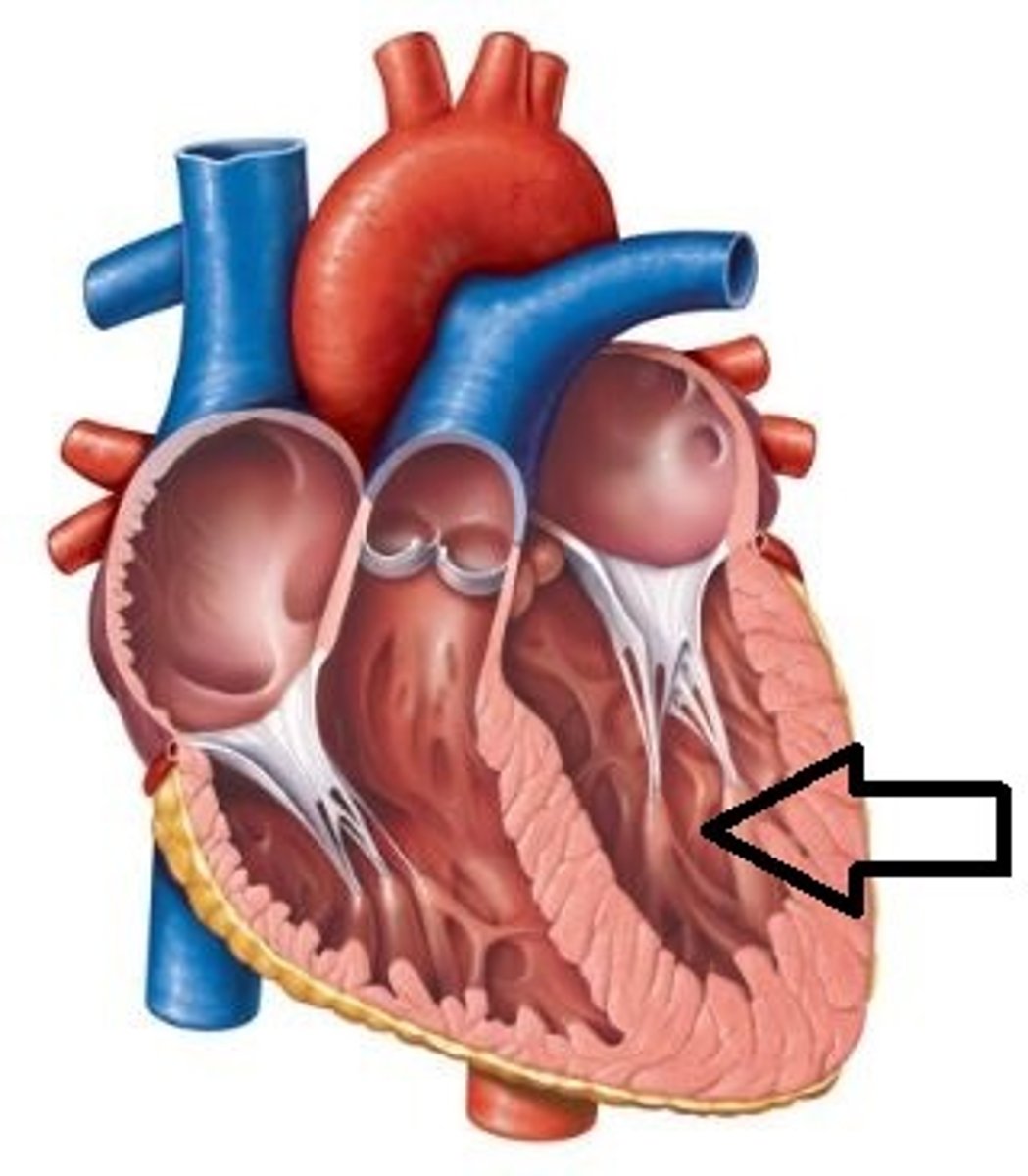
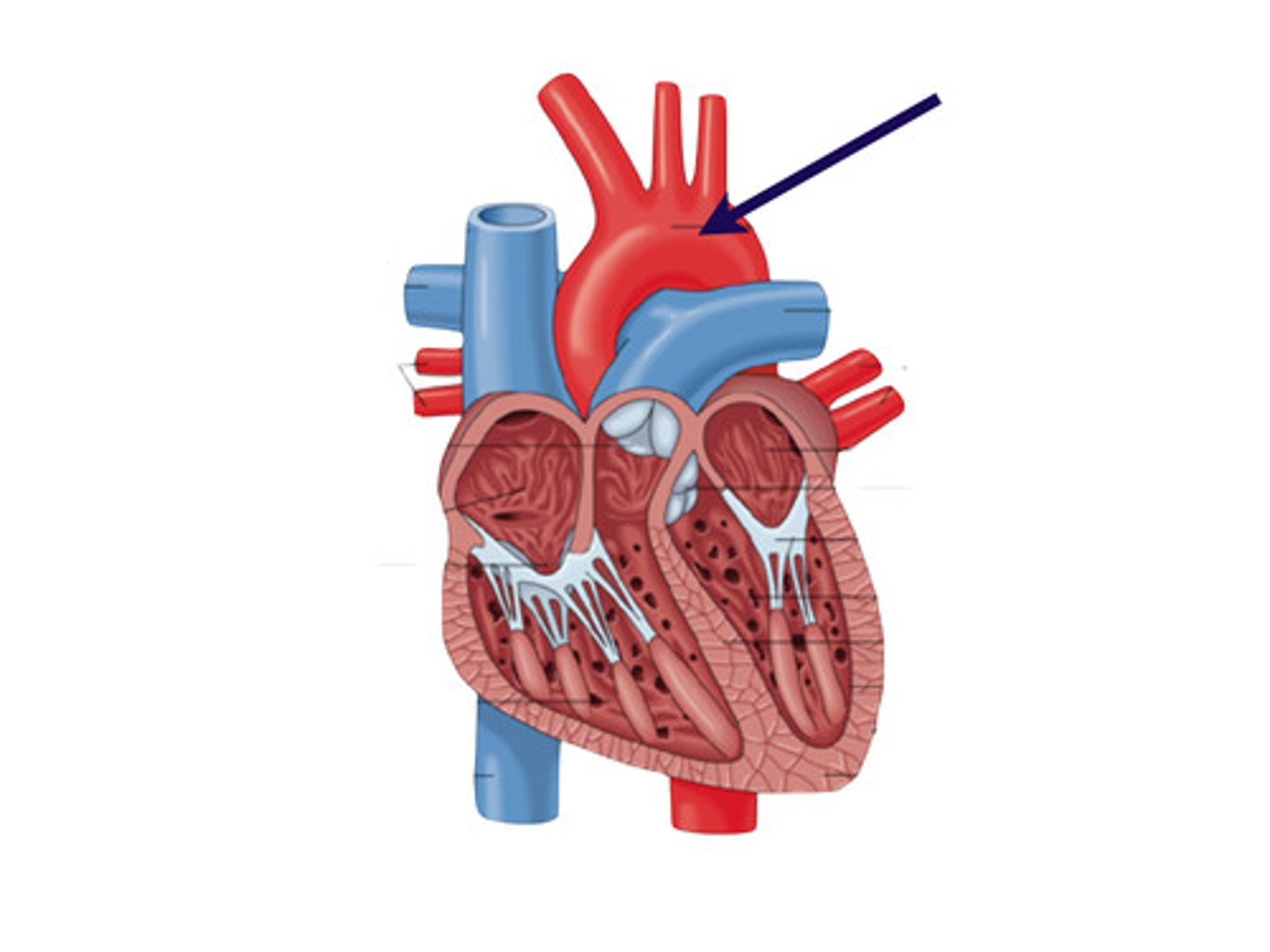
aorta
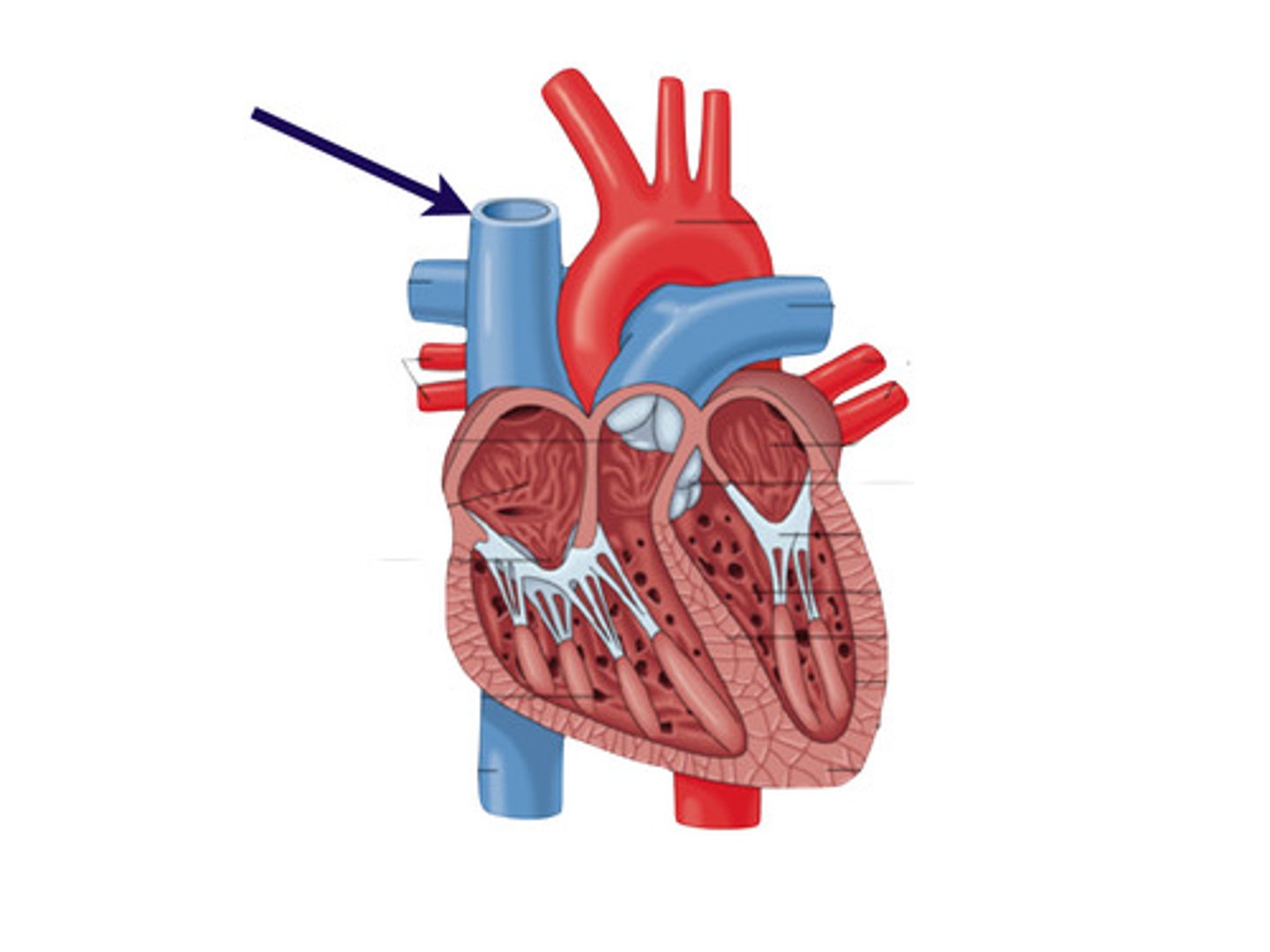
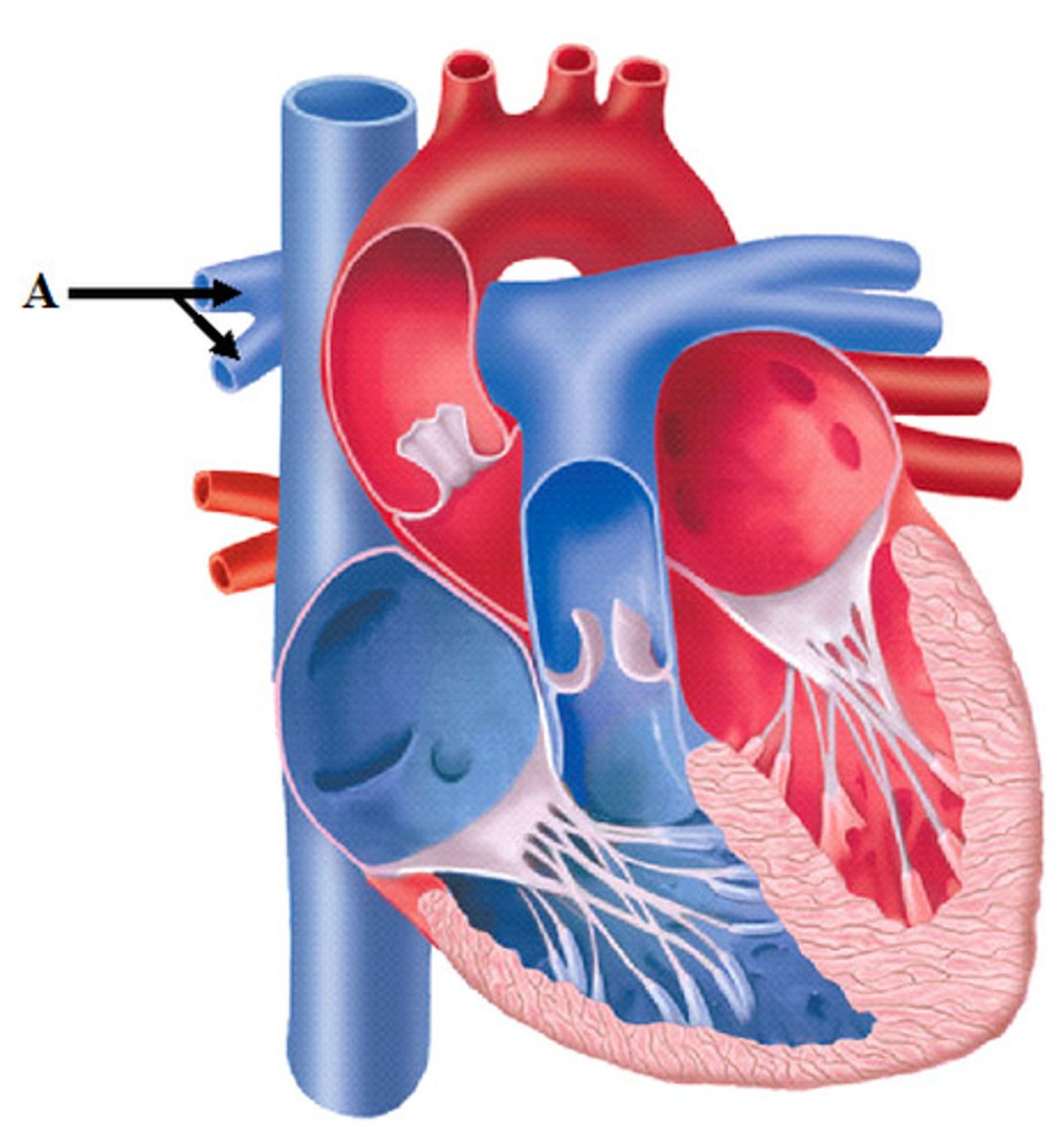
superior vena cava
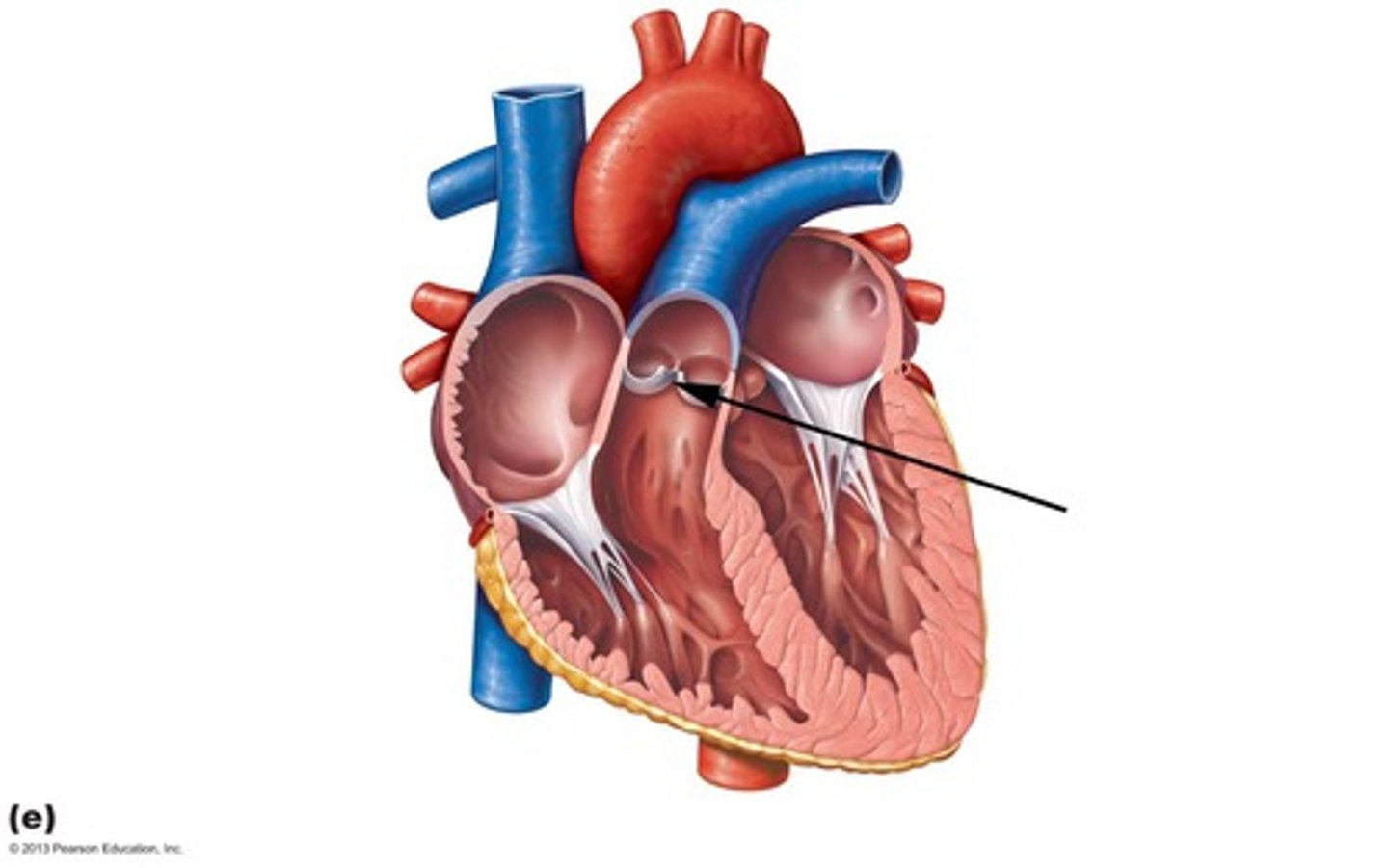
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
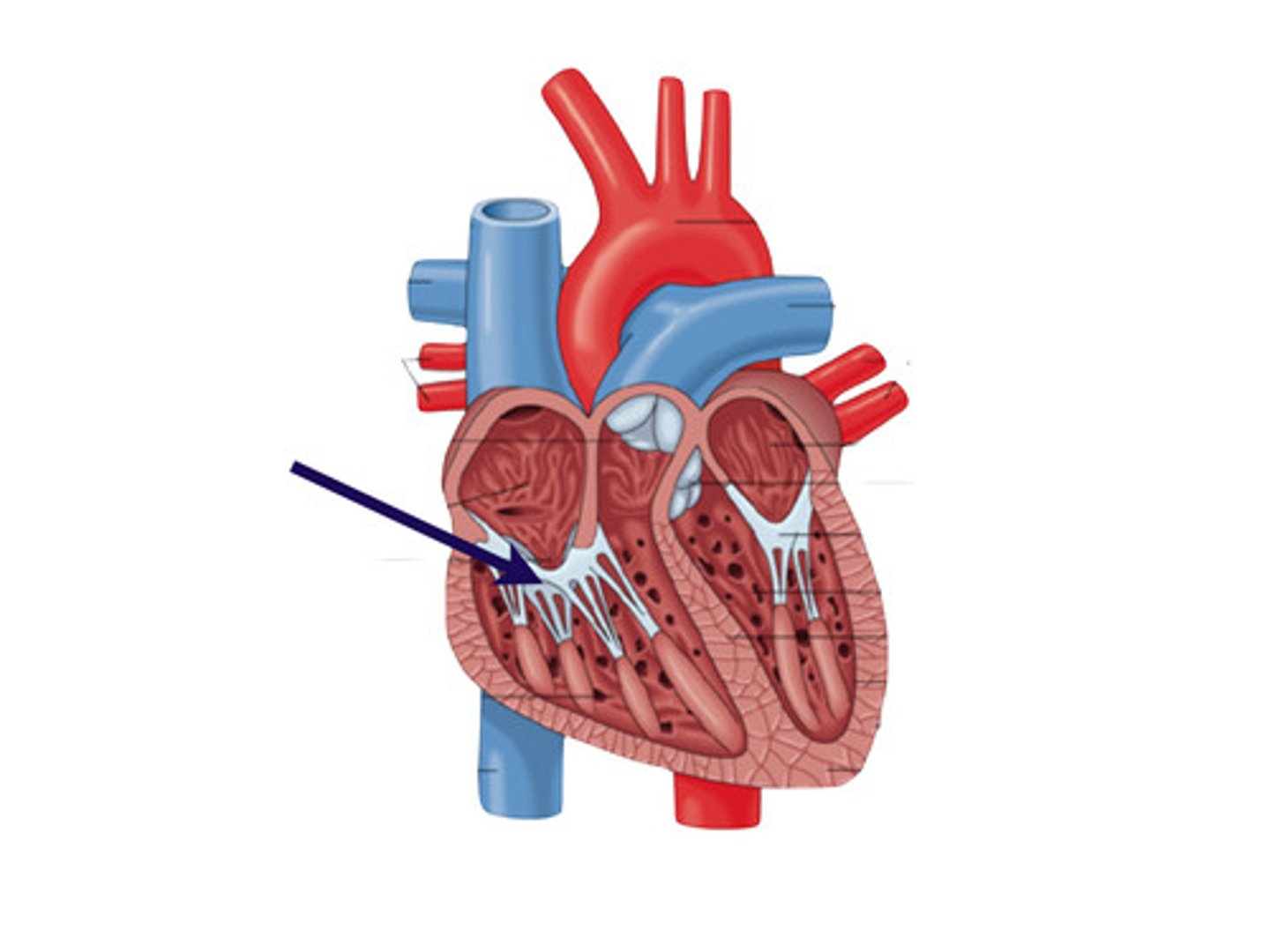
pulmonary artery
pulmonary vein
mitral valve
aortic valve
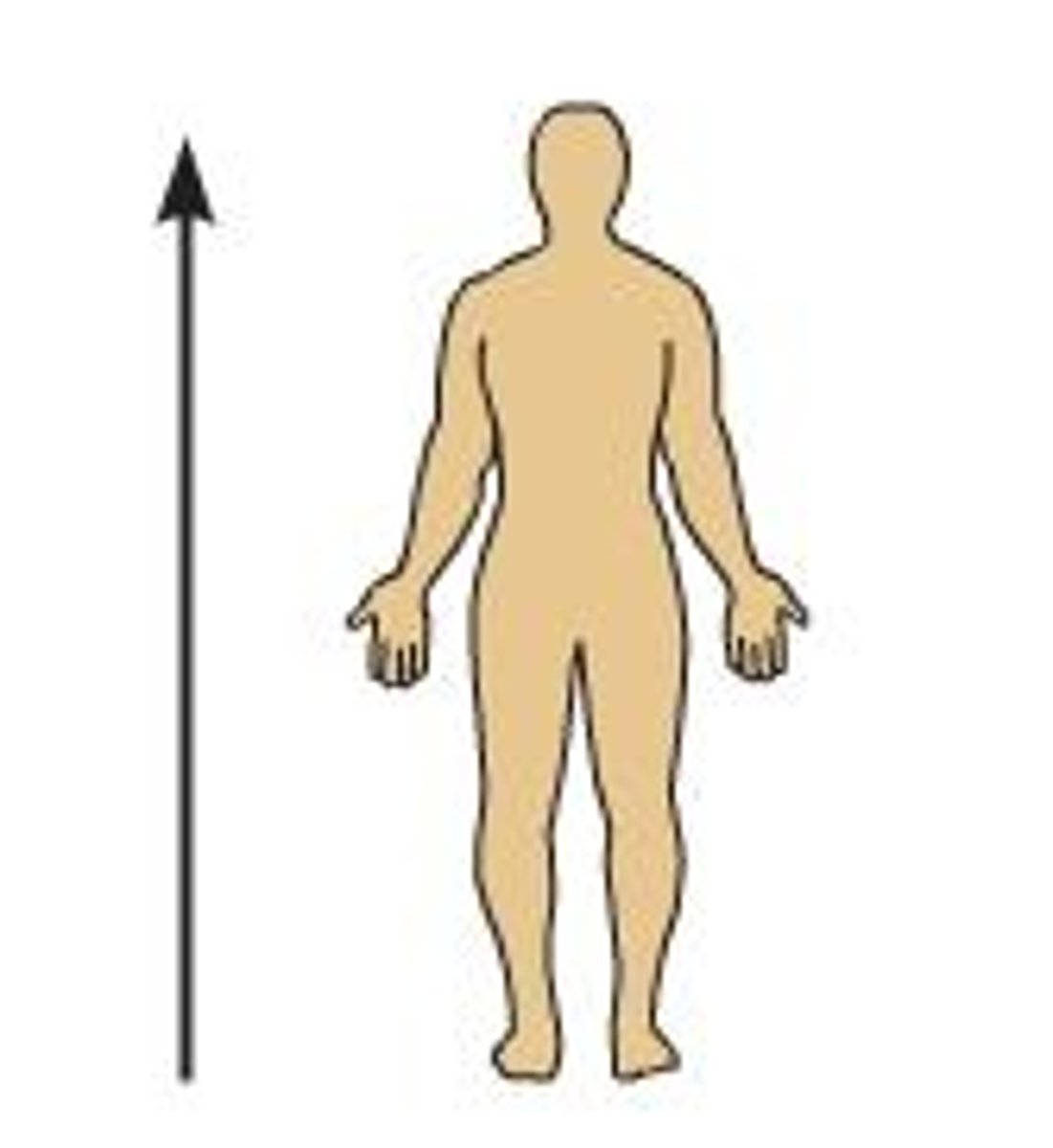
Superior
What position of the body is shown?
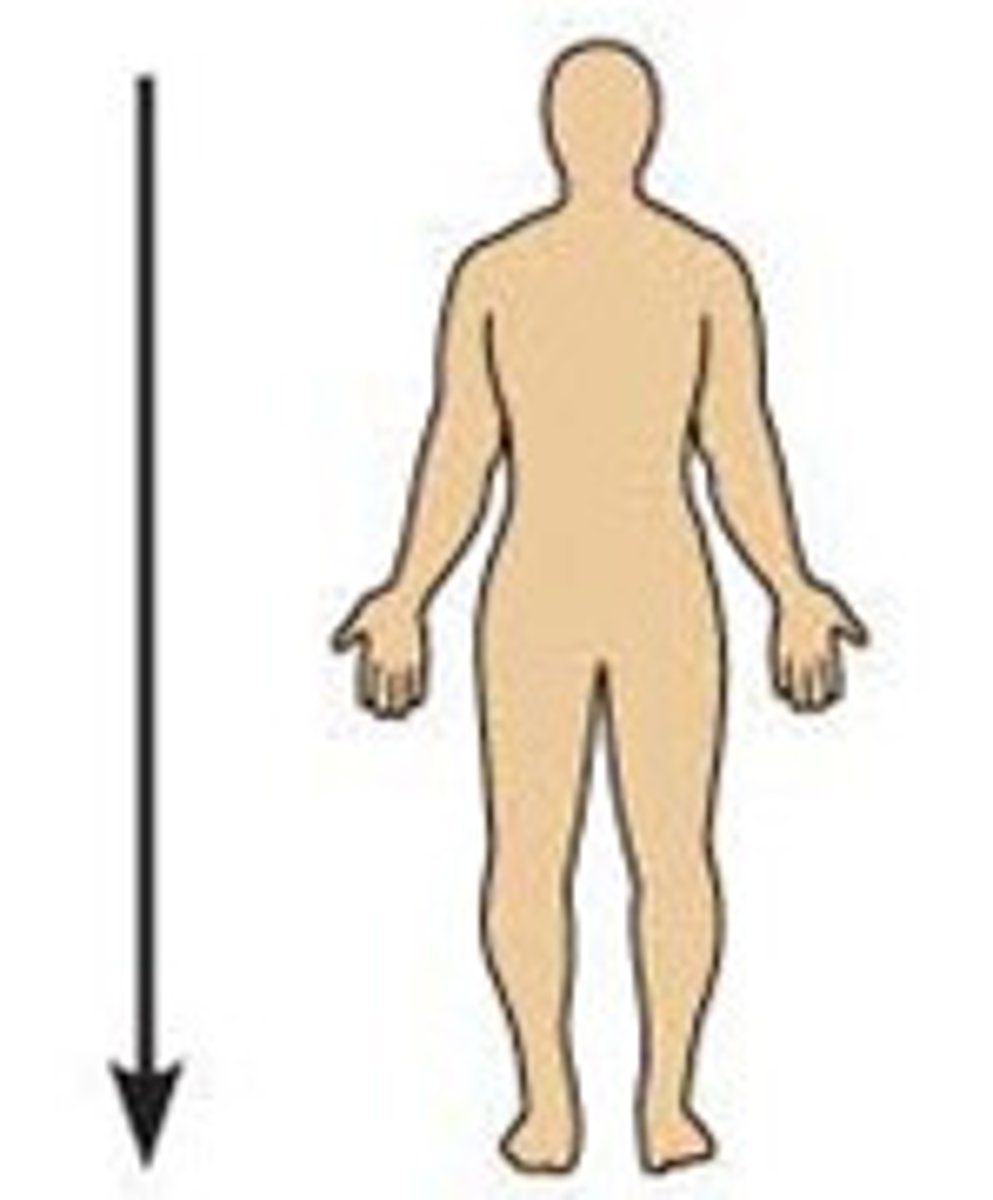
Inferior
What position of the body is shown?
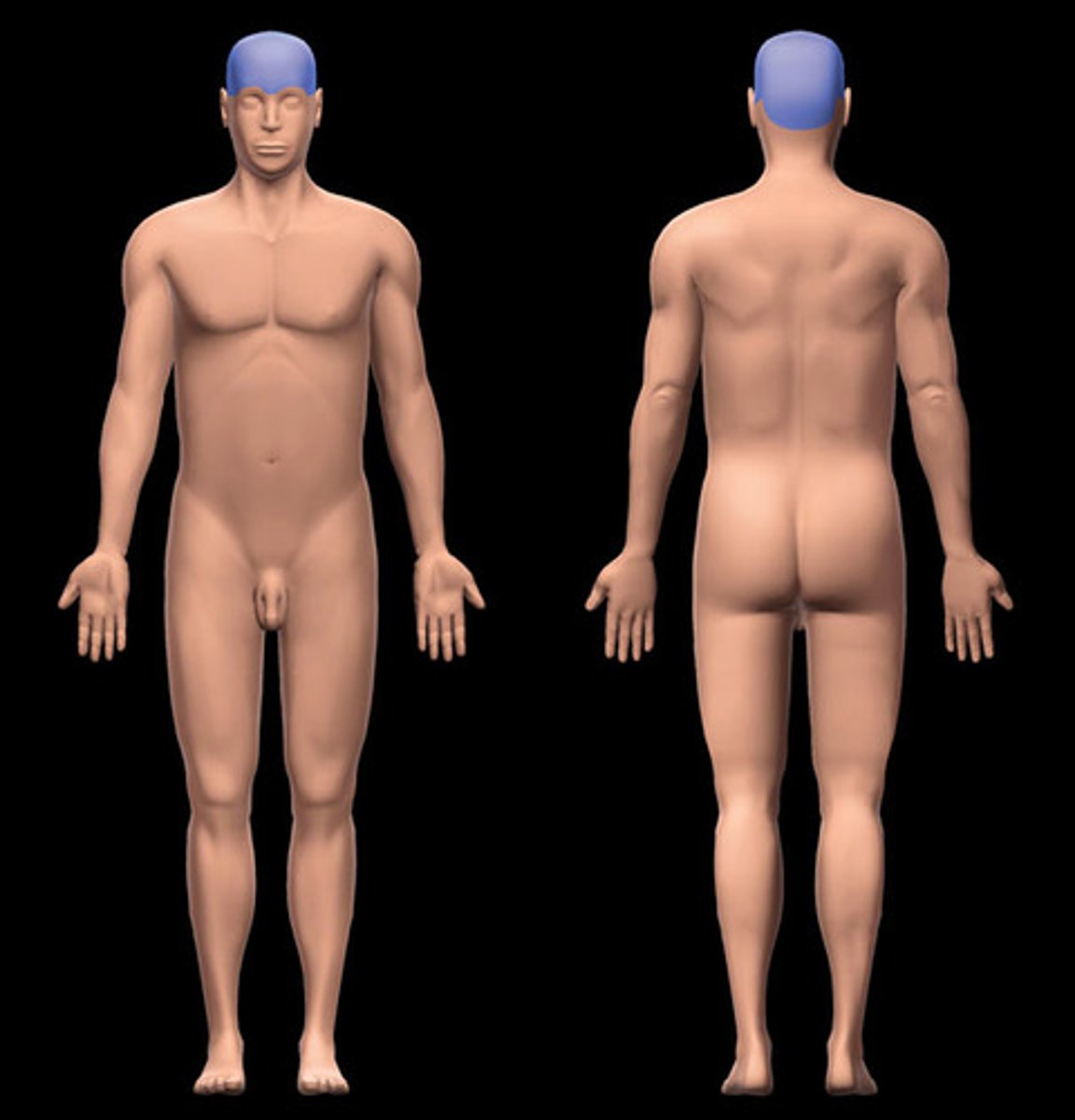
Cranial
What position of the body is shown?
Sagittal plane
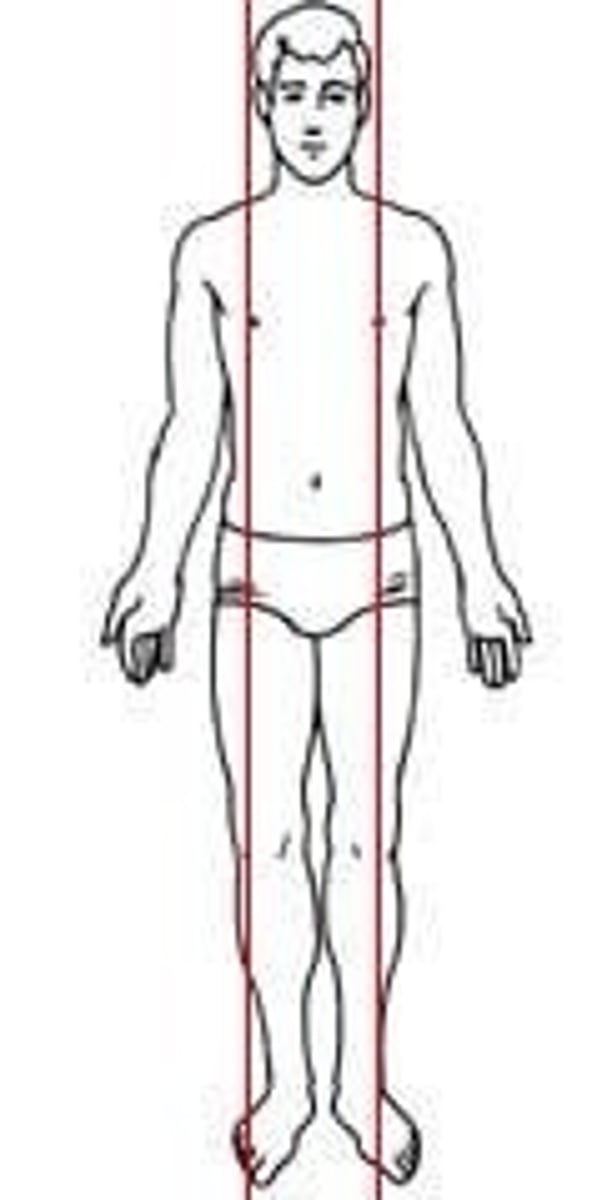
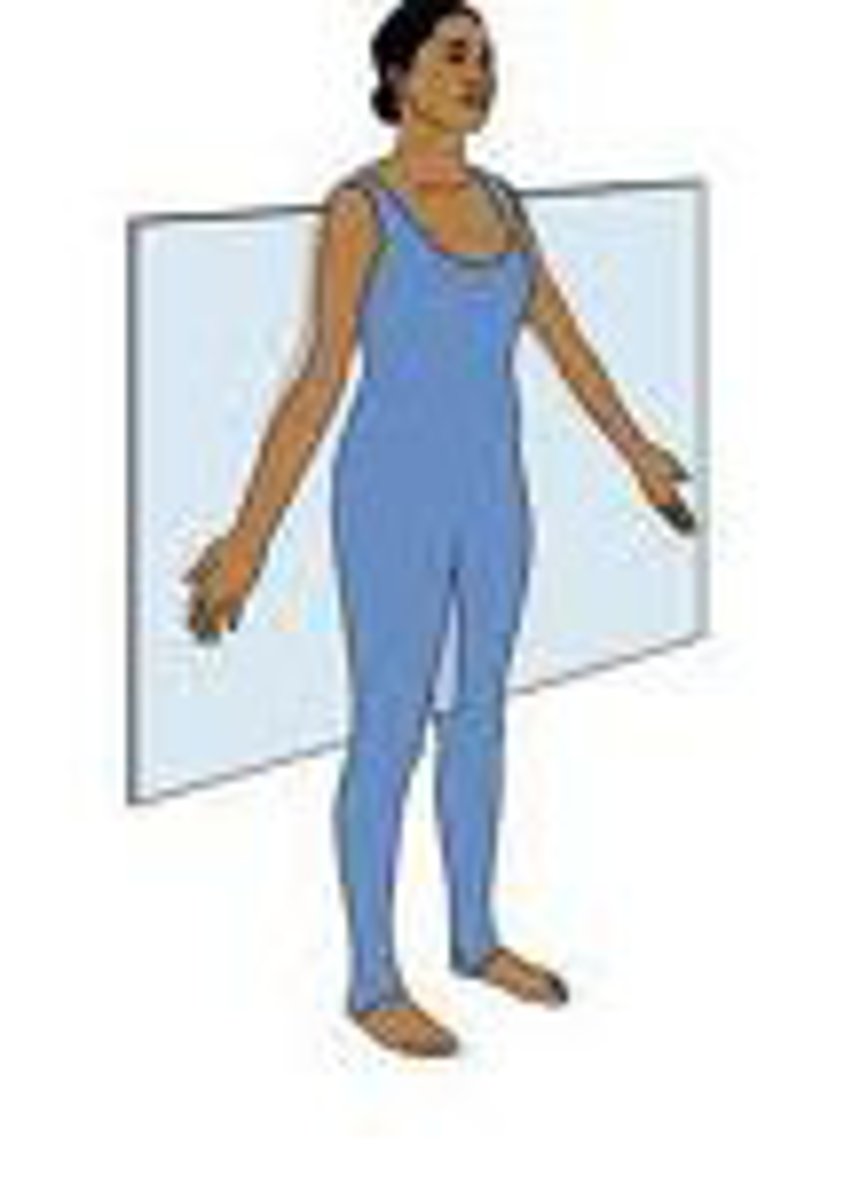
Frontal/Coronal plane

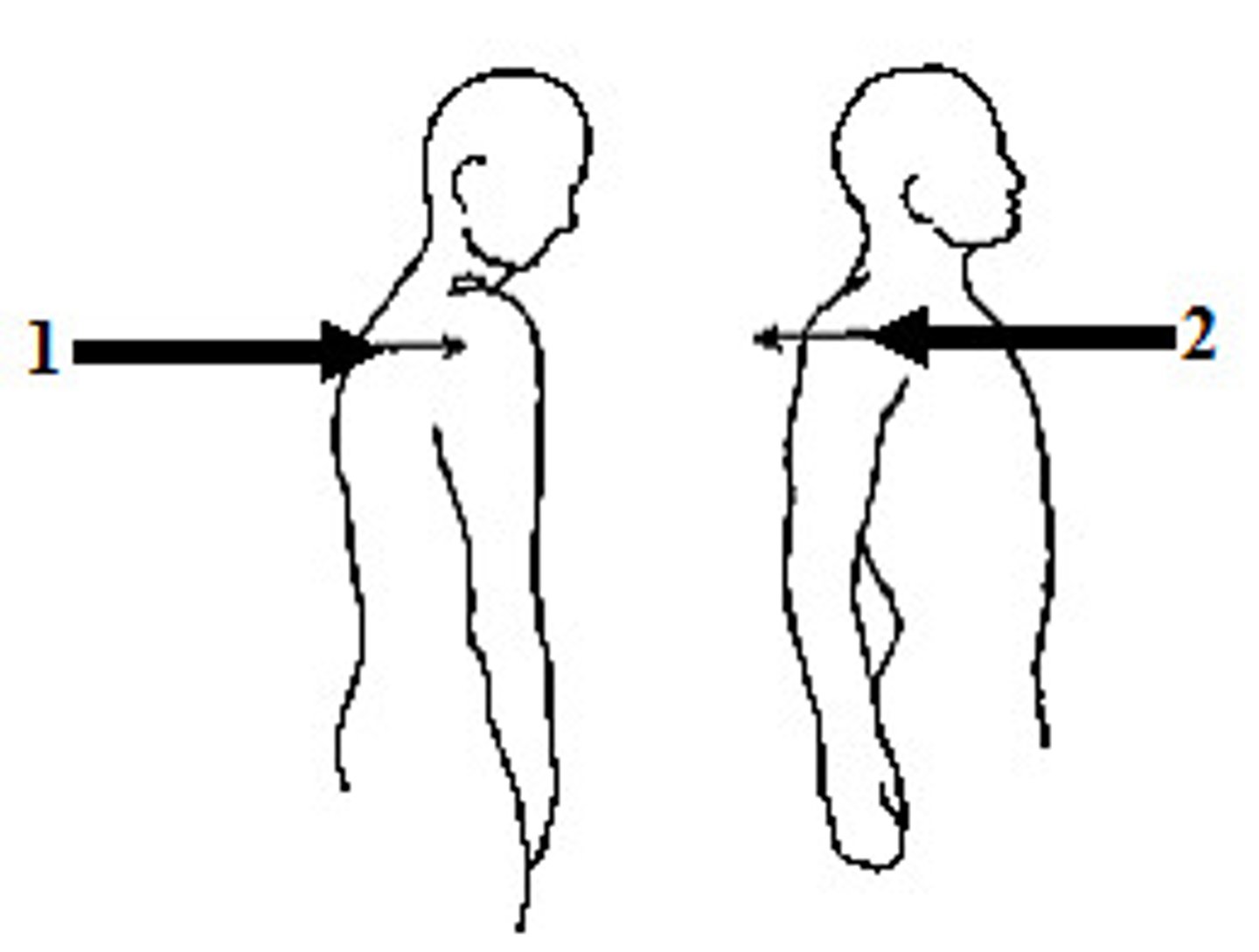
Protraction/Retraction
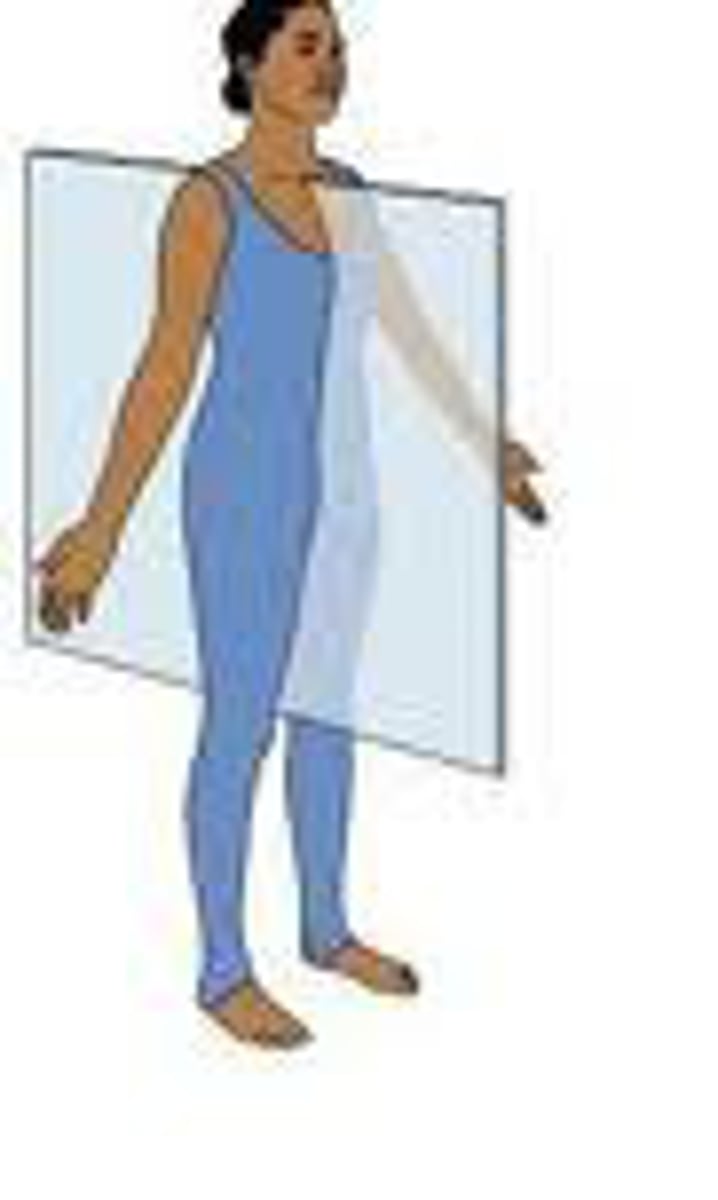
midsagittal/median plane
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE.
The wall of blood vessels consists of 3 layers or tunics
Arteries
The muscular and elastic tunica media is very thick to comply to the high pressure blood flow
Elastic Arteries
Largest arteries in the body with large diameters
Muscular arteries
tunica media contains smooth muscle and fewer elastic fibers
femoral arteries
a major blood vessel which carries blood from the bottom of your abdomen down to your lower limbs
Arterioles
means small arteries
arterioles
play a major role in regulating blood flow from arteries to capillaries by regulating resistance
Capillaries
This is the smallest blood vessels
Capillaries
the part that connects arterial flow to venous return
Venules
These blood vessels have thin walls and don't maintain shape
postcapillary venules
venules receive blood vessels from capillaries
veins
in general has thin walls and has all three layers