CPIM Module 1.2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Crafting and Executing Strategy
the range of activities that a firm performs internally, the breadth of its product and service offerings
Product-Market Growth Matrix
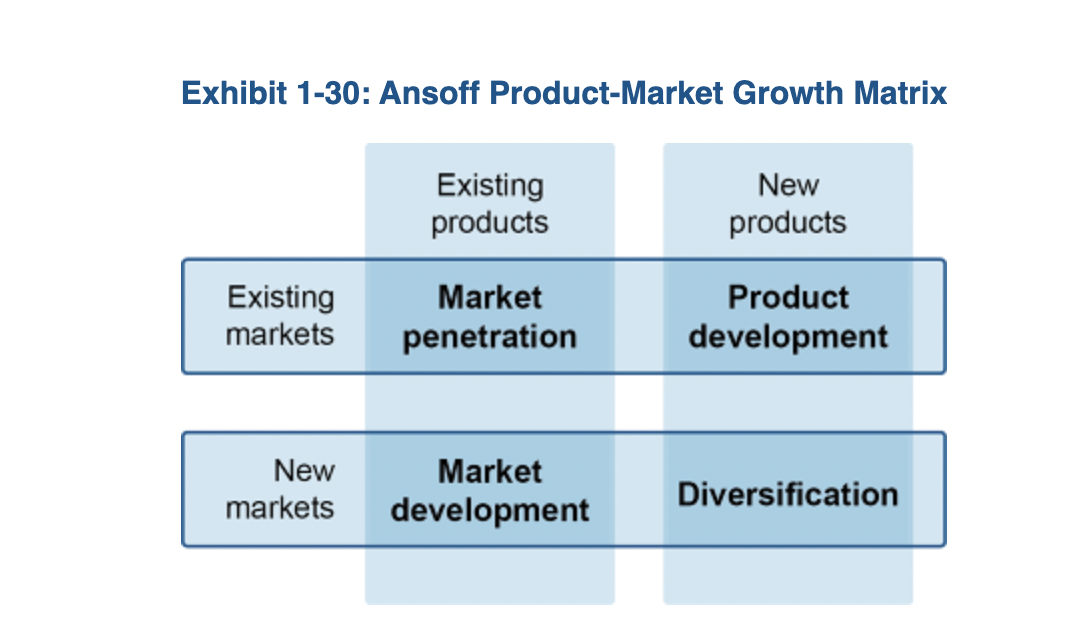
Market penetration
pursuing a larger market share in the exisitng market with the same product, by being more aggressive with the competitors or by being different than the competitors
Product development
The organization focuses on growing within its existing market by introducing new products
Market development
Decision to sell your products to a new market
Diversification
Extending scope to start performing entirely new activities.
An expansion of the scope of the product line to exploit new markets. A key objective of a diversification strategy is to spread the company’s risk over several product lines in case there should be a downturn in any one product’s market.
Related diversification strategy - aiming for Strategic Fit
potential for sharing expertise or assets that will have synergistic effects
assets can be shared to lower costs
brand identity can be transferred to support consumer recognition
Unrelated Diversification Strategy
involving organizations with different value chains and/or different types of resources
Assessment of Diversification Opportunities
Industry Attractiveness
Cost of Entry
Better-off test (assessing synergies)
Multi-Factorial Matrices
Profit sanctuary
created when an organization expands into a foreign market and enjoys a strong and protected competitive position, which then supports competitive activities in the organization’s domestic and foreign markets.
Because of that the company can behave more aggressively on the market - due to the income from other markets
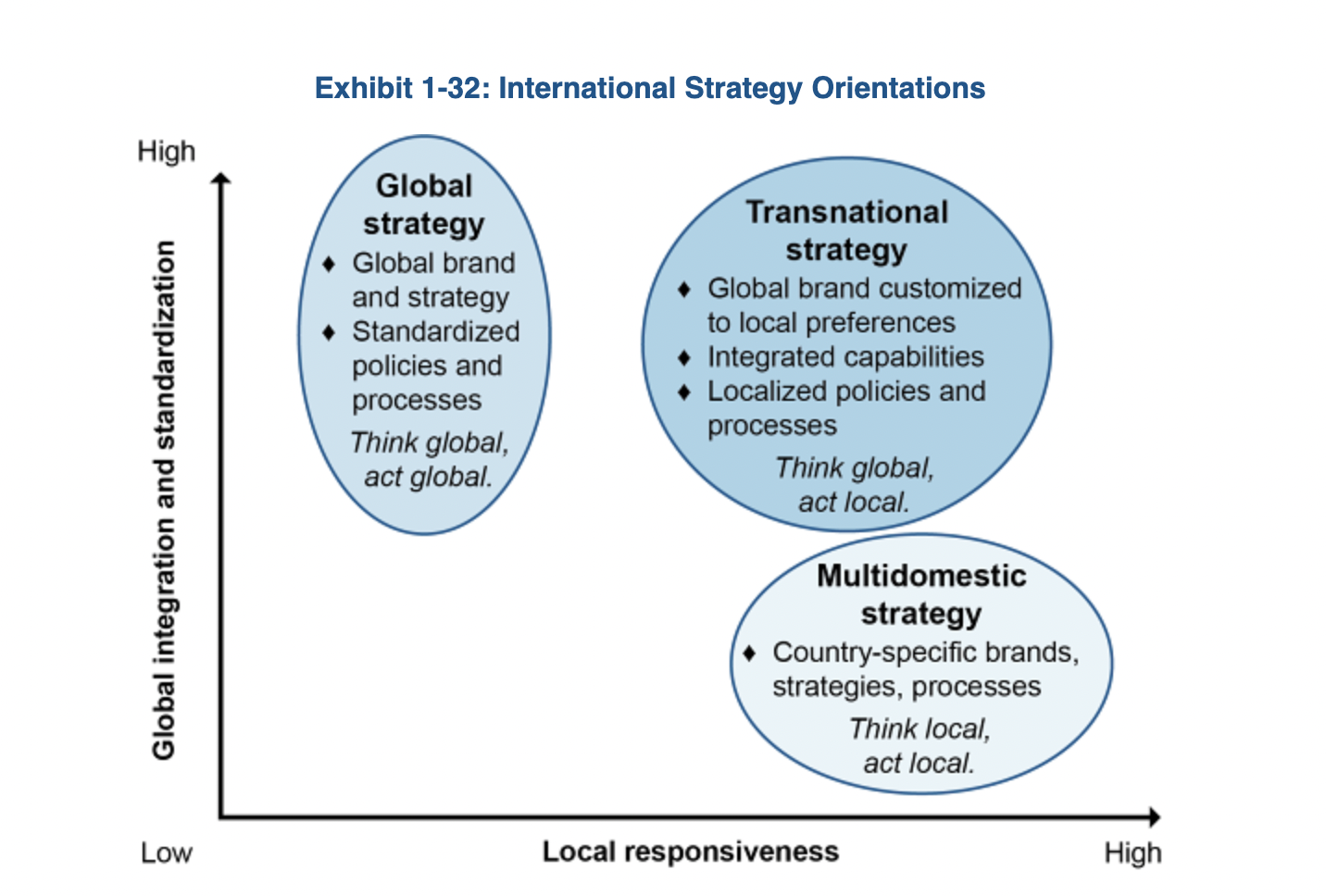
International Strategy Orientations
Horizontal Integration
produces or sells similar products in various geographical locations. Horizontal integration in marketing occurs more frequently than horizontal integration in production
Vertical Integration
Functions that were previously performed by suppliers…are now done internally.
The degree to which a firm has decided to directly produce multiple value-adding stages from raw materials to the sale of the product to the ultimate consumer. The more steps in the sequence, the greater the vertical integration.
Horizontal Scope of Operations
Horizontal Scope - the range of product and service segments that the firm serves within its product or service market.
5 objectives of M&A
Creating cost efficiencies
Expanding geographical coverage
Extending product offerings
Gaining access to technology, resources or capabilities
Supporting the organization’s ability to adapt to the evelotion of its industry
Directions of Vertical Integration
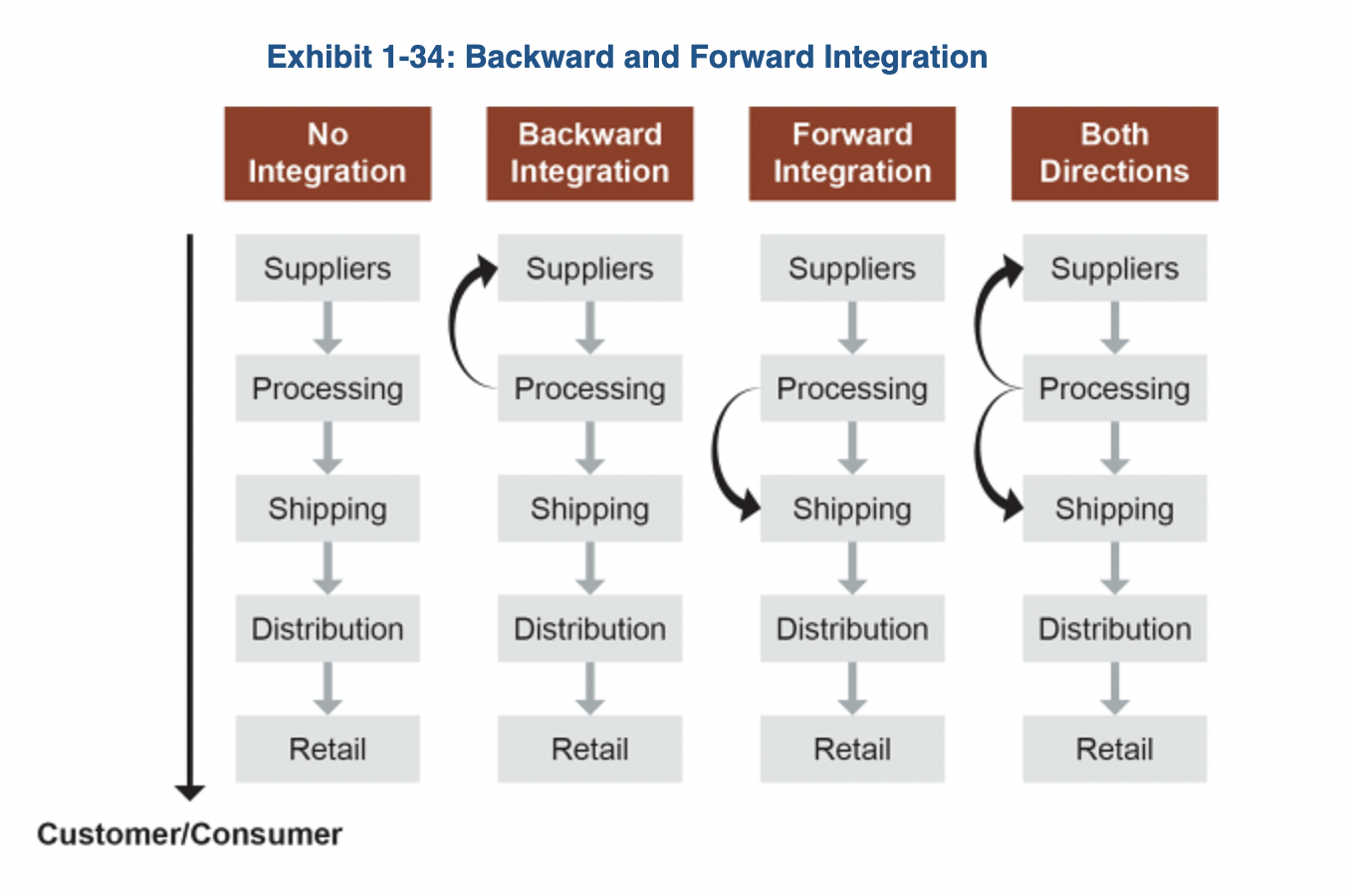
Backward Integration
the process of buying or owning elements of the production cycle and channel of distribution back toward raw material suppliers
Forward Integration
1) Process of buying or owning elements of the production cycle. 2) The channel of distribution forward toward the final customer.
Outsourcing
The process of having suppliers provide goods and services that were previously provided internally. Outsourcing involves substitution - the replacement of internal capacity and production by that of the supplier.
Market segmentation
a marketing strategy in which the total market is disaggregated into submarkets, or segments, that share some measurable characteristic based on demographics, psychographics, lifestyle, geography, benefits, and so forth.
Customer segmentation
the practice of dividing a customer base into groups of individuals who are similar in specific ways relevant to marketing. Traditional segmentation focuses on identifying customer groups based on demographics and attributes such as attitude and psychological profiles.
Customer Lifetime Value Analysis
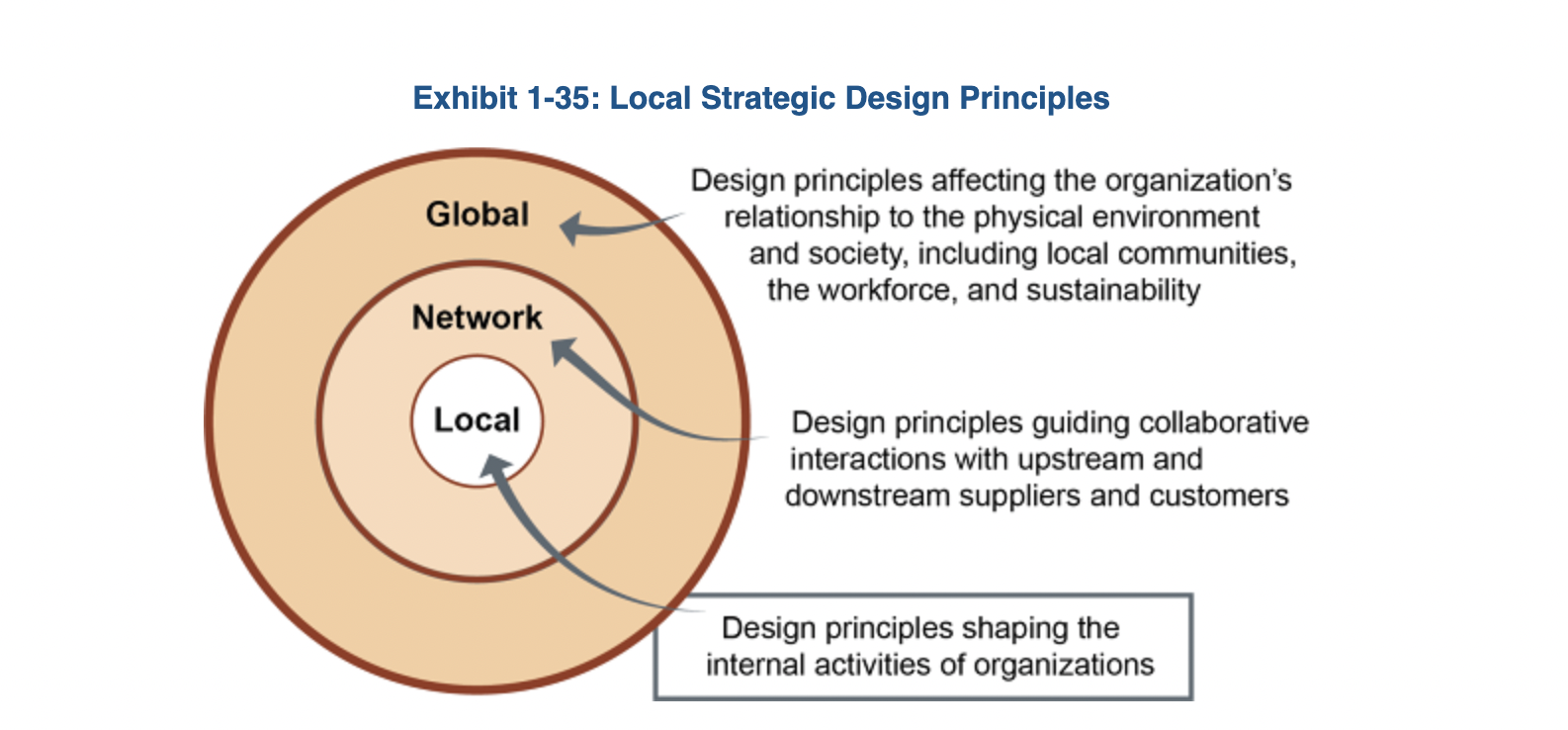
Strategic Design Principles
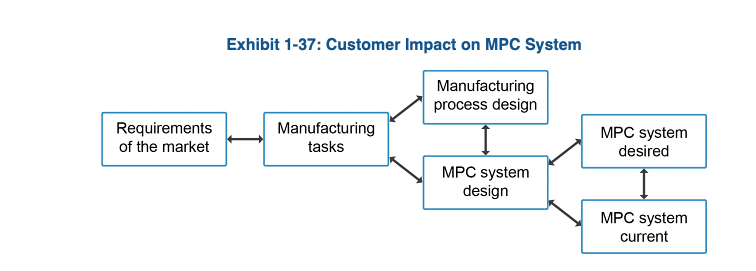
Customer Impact on MPC System
performance objectives
measurements that enable the firm to monitor whether or not the firm’s strategy is being accomplished
Integrated Measurement Model
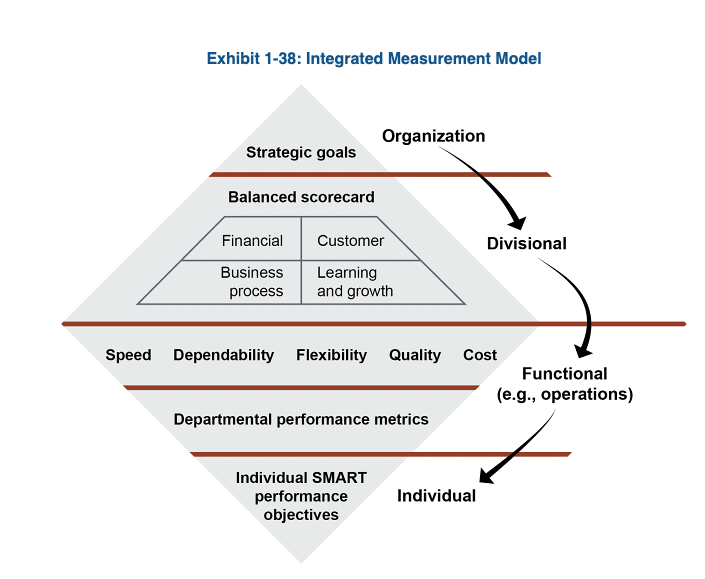
Balanced Scorecard
Financial; Customer; Business process; Learning and growth
Functional Strategy Level Objectives (FSLO)
Speed
Dependability (resilience)
Flexibility (agility)
Quality
Cost
FSLO - Speed
Time to market, short lead times, high output per time period, and/or fast delivery
FSLO - Dependability
Promise fulfillment, on-time delivery (neither early nor late), and/or products that can take a certain level of wear and tear
FSLO - Flexibility
Ability to ramp up or down in volume quickly or change what is being produced without significant disruption