PHYS1103_Unit 4: Circular Motion 낱말 카드 | Quizlet
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is angular velocity?
Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement and is measured in radians per second (rad/s).
How is angular acceleration calculated?
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity over time, measured in radians per second squared (rad/s²).
Define centripetal acceleration.
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path, keeping an object moving along the circular path.
How is tangential velocity related to angular velocity?
Tangential velocity (vt) is the product of the radius (r) and the angular velocity (ω), expressed as
vt = rω.
What is the formula for centripetal force?
Centripetal force is calculated as Fc = mv²/r, where m is mass, v is velocity, and r is the radius of the circular path.
How does Newton's second law apply to uniform circular motion?
In uniform circular motion, the net inward force (centripetal force) equals the mass times the centripetal acceleration (Fc = mac).
What does Kepler's first law state?
Kepler's first law states that the orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
Describe Kepler's second law of planetary motion.
Kepler's second law, or the law of equal areas, states that a line that connects a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
What is Kepler's third law?
Kepler's third law states that the square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit (T² ∝ a³).
How is rotational kinetic energy calculated?
Rotational kinetic energy is given by 1/2 Iω², where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
What is the relationship between linear and angular acceleration?
Linear acceleration along the circumference of a circular path (tangential acceleration) is the product of angular acceleration and the radius
(at = αr).
How is moment of inertia calculated for a solid sphere?
The moment of inertia for a solid sphere about an axis through its center is (2/5)mr², where m is mass and r is radius.
Explain the principle of conservation of angular momentum.
The total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external torques are applied.
What causes precession in a spinning top?
Precession is caused by the torque due to gravitational force acting on the center of mass of a top, which is not aligned with the pivot point.
What is the angular momentum of a particle moving in a circle?
The angular momentum L of a particle is given by L = r x p, where r is the radius vector and p is the linear momentum.
How do you convert angular speed from revolutions per minute to radians per second?
Multiply the angular speed in revolutions per minute by 2π and divide by 60.
What is the role of the radius in centripetal acceleration?
The radius inversely affects the magnitude of centripetal acceleration; as the radius increases, centripetal acceleration decreases for a given speed.
Define the term 'radian'.
A radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle.
How is gravitational force calculated between two masses?
Gravitational force is calculated using Newton's law of universal gravitation: F = G(m₁m₂/r²), where G is the gravitational constant, m₁ and m₂ are the masses, and r is the distance between their centers.
What is escape velocity?
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity needed for an object to break free from the gravitational attraction of a planet without further propulsion.
What factors affect the gravitational force between two objects?
The gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
How does mass affect rotational motion?
Mass distribution relative to the axis of rotation affects the moment of inertia, which in turn influences the angular acceleration for a given torque.
What is the difference between static and dynamic equilibrium in rotational motion?
Static equilibrium occurs when an object is at rest with no net torque, while dynamic equilibrium occurs when an object is moving with constant velocity without acceleration or net torque.
How can you increase the stability of a rotating object?
Increasing the moment of inertia (by distributing mass farther from the axis of rotation) enhances rotational stability.
What is the significance of the radius of gyration?
The radius of gyration is a measure of the distribution of an object's mass around an axis, representing how far from the axis all the mass would need to be concentrated to have the same moment of inertia.
What is the gravitational potential energy near the surface of Earth?
Near Earth's surface, gravitational potential energy is calculated as PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height above a reference level.
How does angular momentum conservation affect planetary orbits?
Angular momentum conservation implies that planets will move faster in their orbits when they are closer to the sun and slower when they are farther away, preserving the angular momentum.
What is the role of centripetal force in satellite motion?
Centripetal force is necessary to keep a satellite in orbit around a planet, counteracting the satellite's inertia that would otherwise cause it to move in a straight line.
How do you calculate the angular momentum of a rigid body?
For a rigid body, angular momentum is the product of its moment of inertia and its angular velocity, L = Iω.
What is the critical speed for a car turning on a flat curve to avoid skidding?
The critical speed can be calculated using the formula v = sqrt(rμg), where r is the radius of the curve, μ is the coefficient of static friction, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What is torque?
Torque is the rotational equivalent of force; it measures how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate.
How is torque calculated?
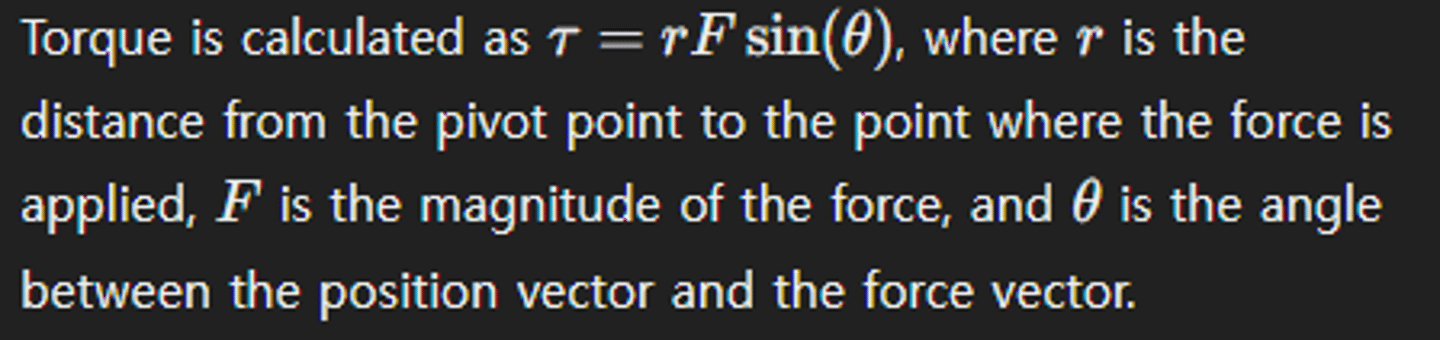
What is the SI unit of torque?
The SI unit for torque is the Newton-meter (N·m).
Describe Newton's first law in the context of rotational motion.
An object remains in its state of uniform rotational motion unless acted upon by an external torque.
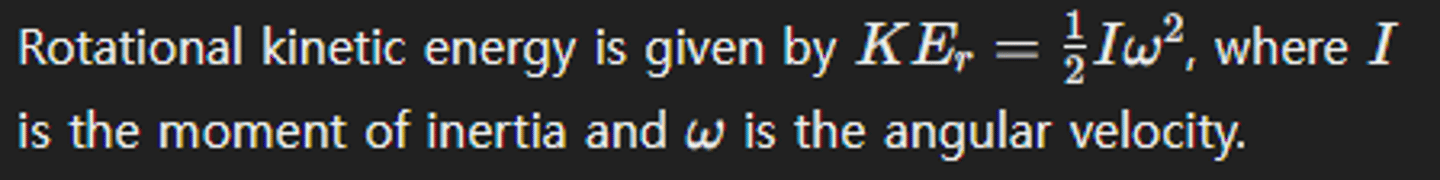
What does the rotational second law of motion state?

How is rotational kinetic energy calculated?
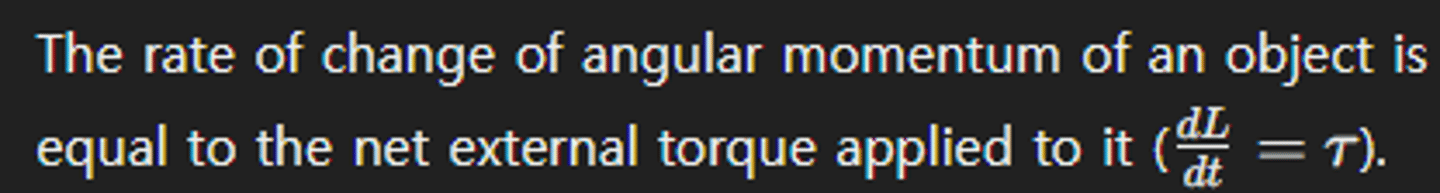
What is the relationship between angular momentum and torque?
Define angular momentum for a rotating object.
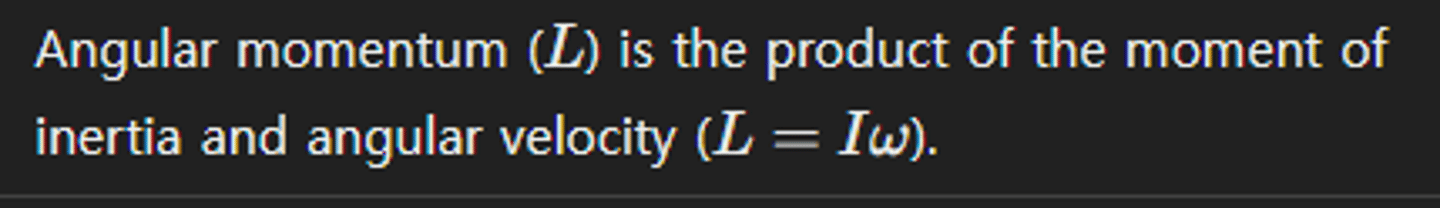
How is the moment of inertia calculated for a point mass at a distance rrr from the axis of rotation?
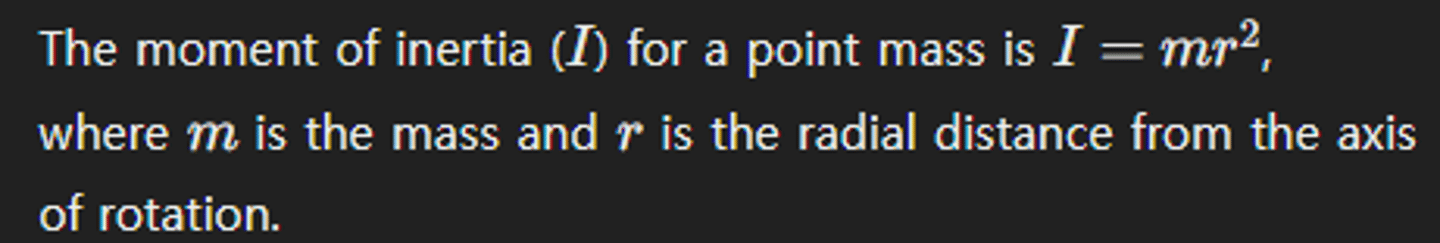
What is the conservation of angular momentum?
Angular momentum is conserved in an isolated system if no external torques are acting on it.
Describe the two conditions necessary for rotational equilibrium.
There must be no net external torque, and the net external force must be zero.
Explain how you determine the direction of torque using the right-hand rule.

What role does the radius play in the moment of inertia?

How does the distribution of mass affect the moment of inertia?
Objects with mass further from the axis of rotation have higher moments of inertia, indicating greater resistance to changes in their rotational state.
How does rotational kinetic energy relate to translational kinetic energy?
Rotational kinetic energy is associated with the rotation of an object around an axis, whereas translational kinetic energy is due to the object's linear motion.
What is the effect of an external torque on an object's rotation?
External torque changes the angular momentum, thus changing the angular velocity if the moment of inertia is constant.
Describe the effect of mass distribution on rotational dynamics.
Mass farther from the axis of rotation increases the moment of inertia, decreasing angular acceleration for the same torque.
Explain the principle behind gears using torque and angular acceleration.
Larger gears exert more torque, allowing more forceful rotational acceleration or the ability to move larger loads.
How is the center of mass calculated for a system of particles?
The center of mass is the weighted average of the positions of all particles, weighted by their masses.
How does torque affect an object's angular speed?
An increase in net external torque increases angular speed, while a decrease reduces it, depending on the direction of the torque.
How can angular momentum be used to calculate changes in rotational motion?
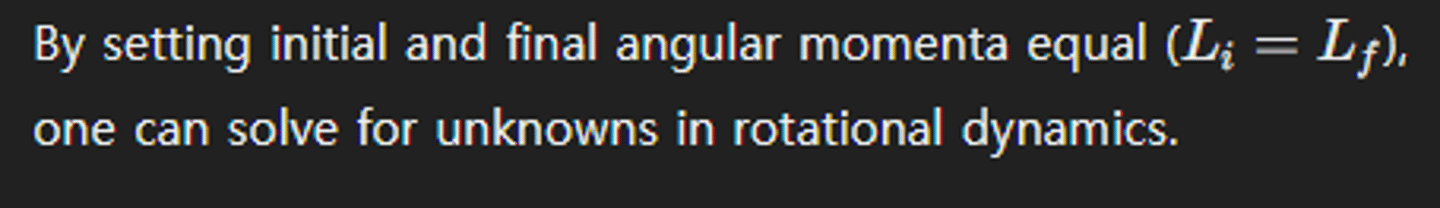
What is the significance of the lever arm in calculating torque?
The lever arm is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force, crucial for calculating torque.
Describe how conservation of angular momentum can explain the behavior of a spinning ice skater pulling in her arms.
As the skater pulls in her arms, she reduces her moment of inertia but her angular momentum must stay constant, so her angular velocity increases.
What is the relationship between torque and the angle of force application?
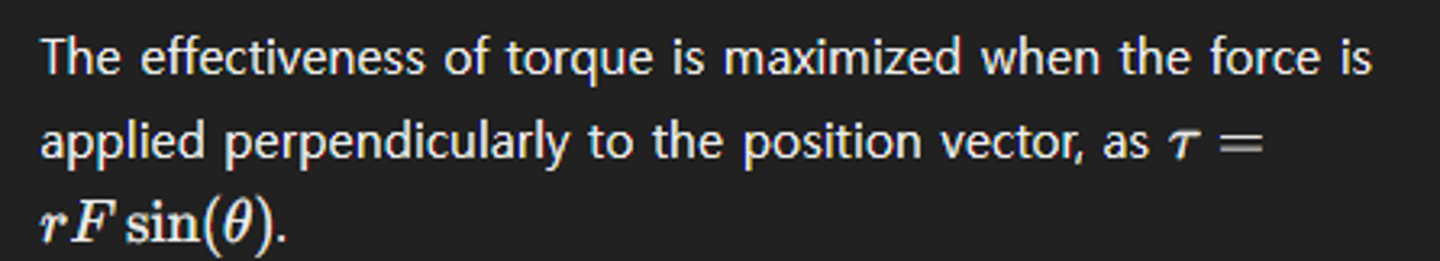
Explain why angular momentum conservation is important in astrophysics.
Conservation of angular momentum explains phenomena such as the increase in angular velocity of stars as they collapse into neutron stars.
How does the 'no-slip condition' relate translational and rotational motion?
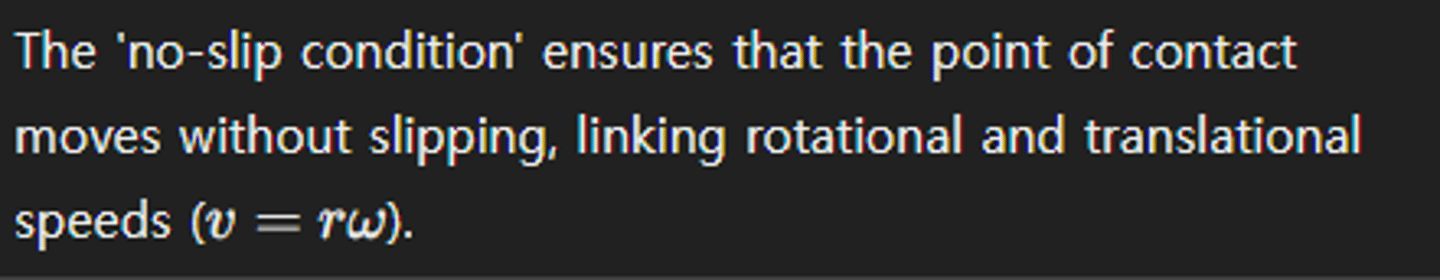
What role does rotational inertia play in everyday mechanical systems, such as vehicles?
Rotational inertia affects the acceleration and braking in vehicles; high rotational inertia in wheels can lead to slower acceleration and braking times.
How does changing the axis of rotation affect the moment of inertia?
Changing the axis of rotation generally changes the moment of inertia, which can alter the rotational dynamics of an object.
What experimental methods can determine the center of mass of an irregular object?
Techniques like suspending the object from different points and observing the plumb line can help locate the center of mass accurately.
Discuss the practical applications of rotational dynamics in engineering.
Rotational dynamics is crucial in designing and analyzing systems like turbines, engines, and rotating machinery to ensure efficiency and stability.