PVD part 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the 2 main types of Peripheral Vascular Disease? (PVD)
Arterial and Venous
What are the 3 main Arterial PVD?
Stenosis/Occlusion
Aneurysm
Dissection
What are the 2 main Venous PVD?
Stasis/Insufficiency
Thromboembolism
PE and DVT
What is an Aneurysm?
Part of artery wall weakens, allowing it to ballon out or widen abnormally
Where are Aneurysms more common? (4)
Any Vessel
Brain
Heart
Thoracic Aorta
Abdominal Aorta
What is a Dissection?
Tear in INTIMA layer allows blood to leak through >> Separating inner and middle layers
2 Primary S/S of Dissecting Aneurysm?
Sudden severe chest or upper back pain
Sudden severe stomach pain
Sudden Severe Chest or Upper Back Pain of a Dissecting Aneurysm is often described as what?
" Tearing or Ripping" that can spread to the neck or down the back
Other S/S of Dissecting Aneurysm: cope? breath? Issues similar to what? Unilateral weak/strong what?
Syncope
SOB
Sudden vision problems, difficult speaking, weakness or hemiparesis (Similar to CVA)
Unilateral weak pulse in one arm or thigh
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)? Which reduces what?
Narrowing or occlusion of arteries OUTSIDE of the heart
Reduced blood flow to extremities, gut, kidneys, head
What is primary cause of PAD? And what else may develop?
Atherosclerosis
Collateral circulation may develop if atherosclerosis is gradual
What’s collateral circulation?
Body generates new blood vessels
What are risk factors for PAD? Habit? BP? Hyper what? Body? Diet? Age? Disease?
Smoking
HTN
Hyperlipidemia
Obesity
Diabetes
Older age (15-20% over age 70)
Coronary artery disease
Main PAD symptom:
Intermittent Claudication!
What is Intermittent Claudication?
Limb pain or cramping w exercise, resolves w rest (just like angina)
What are other s/s of PAD? In what position? What’s on the LE? Hot/cold?
Pain (burning, aching) at rest, lying flat/LE elevated
Ulcers/sores/wounds on toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly, poorly, or not at all
Coldness in affected extremity
What are other s/s of PAD? What’s the skin color like? Possible what? What’s weak/absent?
Pale or cyanotic, dusky red color
Possible numbness
Weak or absent pulses (Dorsalis Pedis and Post Tib)
Claudication Scale: (1-4)****
1 >> Initial Discomfort (Established but minimal)
2 >> Moderate Discomfort but attention can be diverted
3 >> Intense Pain (Attention cannot be diverted)
4 >> Excruciating and Unbearable Pain
Is it okay to exercise if pt has pain? And why?
YES <<
Exercise through pain to drive blood to periphery
If pt stays stationary, pt will get worse
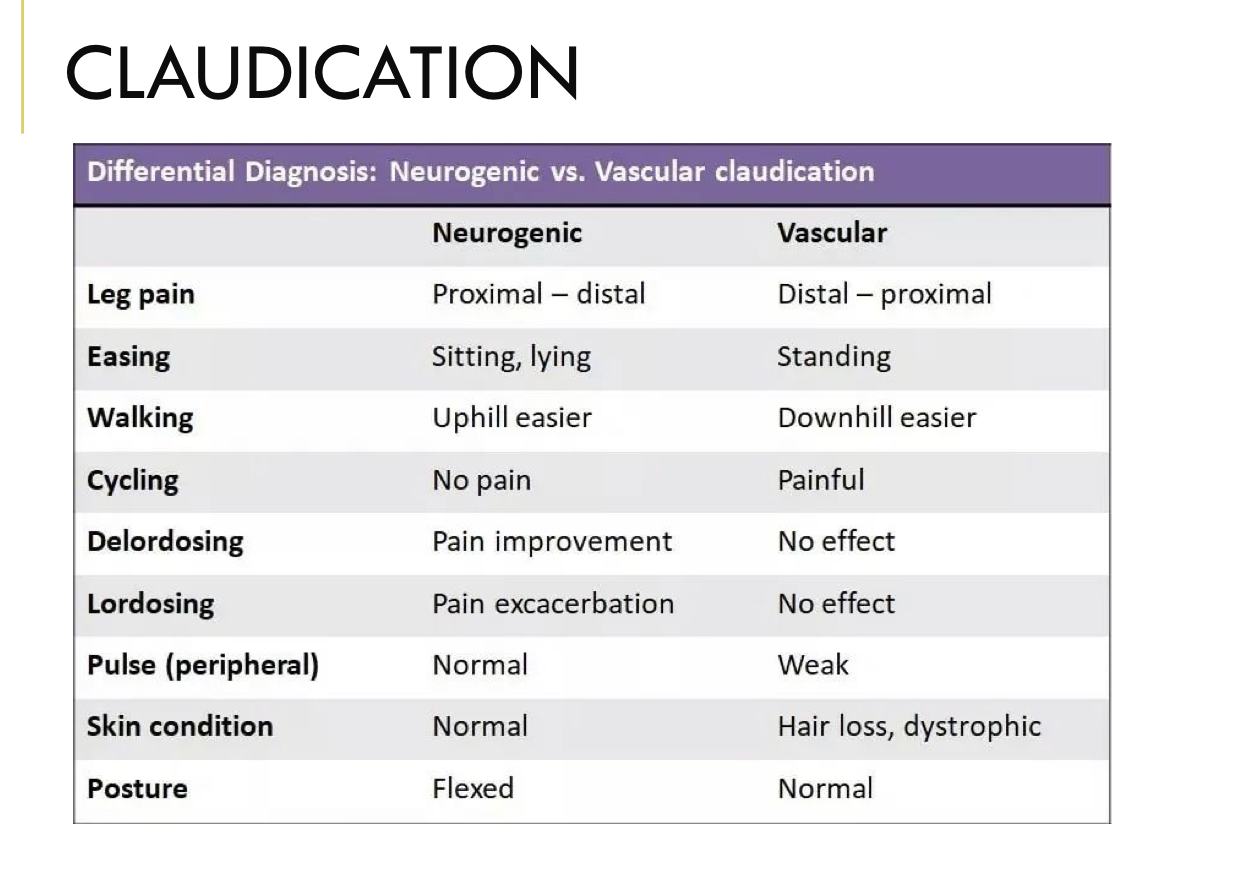
Study this?
Differential Dx - Claudication: Delordosing
Neurogenic: Pain Improvement
Vascular: No Effect
Differential Dx - Claudication: Lordosing
Neurogenic: Pain Exacerbation
Vascular: No Effect
What are the 2 main EMERGENT PAD Complications?
Acute Limb Ischemia and Osteomyelitis
What are the 3 NON-EMERGENT PAD Complications?
Critical Limb Ischemia >> Chronic
Stroke
MI
What is Acute Limb Ischemia?
Sudden decrease in limb perfusion, potentially threatening limb variability
Acute Limb Ischemia S/S (The 6 P's)
Pn
Pallor
Paresthesias
Poikilothermia (Coldness)
Pulselessness
Paralysis
What is Acute Limb Ischemia due to?
Embolism or Thrombosis
3 Critical Limb Ischemia - Chronic S/S:
Pn at rest, w elevation
Arterial Insufficiency Ulcers
Gangrene
PT Management of Arterial PAD: maximize what 3 things?
Maximize quality of life, general health and well-being
Maximize aerobic capacity, O2 transport
Maximize general strength, peripheral O2 extraction
Education
What should the PT Educate the pt who has PAD? What should they assess daily?
Atherosclerosis/heart disease process, CAD/cardiac risk factors, disease prevention, self-management
Good foot and skin care (assess daily for signs of skin breakdown)
Chief Complaints/Impairments of Arterial PAD: (Pt 1) (4)
Pain > claudication
Poor/non-healing wound or ulcer
Decreased exercise/activity tolerance
Impaired peripheral circulation (ABI, Palpation)
Chief Complaints/Impairments of Arterial PAD: (Pt 2) (3)
Impaired muscle function/strength
Impaired aerobic capacity/endurance
Impaired respiration/gas exchange (PE)
What to INSPECT during Vascular Exam for PAD pts? (4)
Color
Ulcers
Edema
Symmetry
What to PALPATE during Vascular Exam for PAD pts? (2)
Temp and Pulses
Palpation: What special tests can a PT do on a PAD pt? (6)
ABI
Rubor Dependency
Capillary Refill
Pitting Edema
Venous Filling Time
Calf Girth
Arterial PAD Skin Changes presentation (Pt 1) (4) gets worse with what?
Shiny, tight, dry, hairless
Thickened toenails
Cool/cold to touch
Pallor, pale or bluish color to skin (peripheral cyanosis) >> worse with elevation
Arterial PAD Skin Changes presentation: what comes out on the LE? What tests for arterial insufficiency?
Ulcers and Rubor of Dependency
Ulcer Presentation: may or not be what? What does it do to the skin? Where? Is it fast/slow?
May or may not be painful
Ischemic, gangrene (tissue necrosis)
Result of trauma - common in toes and heel
Develop rapidly
What are the 7 main Arteries to palpate for Arterial PAD?
Dorsalis Pedis
Post Tib
Femoral
Popliteal
Radial
Brachial
Carotid
Pulses Scale
4+ = bounding
3+ = increased
2+ = normal
1+ = diminished
0 = absent, unable to palpate
Changes in pulse is the most important sign of what?
Arterial Insufficiency
How to perform Capillary Refill test? What’s the normal wait time?
-Compress nailbeds until blanched
Normal flesh coloration returns in 3-5 sec
Capillary Refill Test: What does Prolonged time (~ 15-20 secs) mean?
Arterial Insufficiency
What does Rubor of Dependency assess?
Arterial Insufficiency
What to watch out for in Rubor Dependency Test? (2)
Pallor w Elevation
Deep red color in 20-30 sec in dependent position
What needs to be competent in order to perform Rubor of Dependency Test?
Veins
Step 1 of Rubor Dependncy Test and the grades?****
Elevate LE 60 deg for 1 min
0 = normal, no pallor
1 = definite pallor in 60 sec
2 = pallor in 30-60 sec
3 = pallor in < 30 sec
4 = pallor without elevation
Step 2 of Rubor Dependency Test and what do you assess?****
Put limb in LE dependent
Assess time for normal flesh color to return
Step 2: what are the 3 Timeframes for Normal Flesh Color to Return
Normal: 10-15 sec
Moderate Occlusive Disease: 15-25 sec
Severe Ischemia: > 40 sec
What color indicates Arterial Insufficiency?****
DEEP RED COLOR >> in 20-30 secs