lab practical II
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
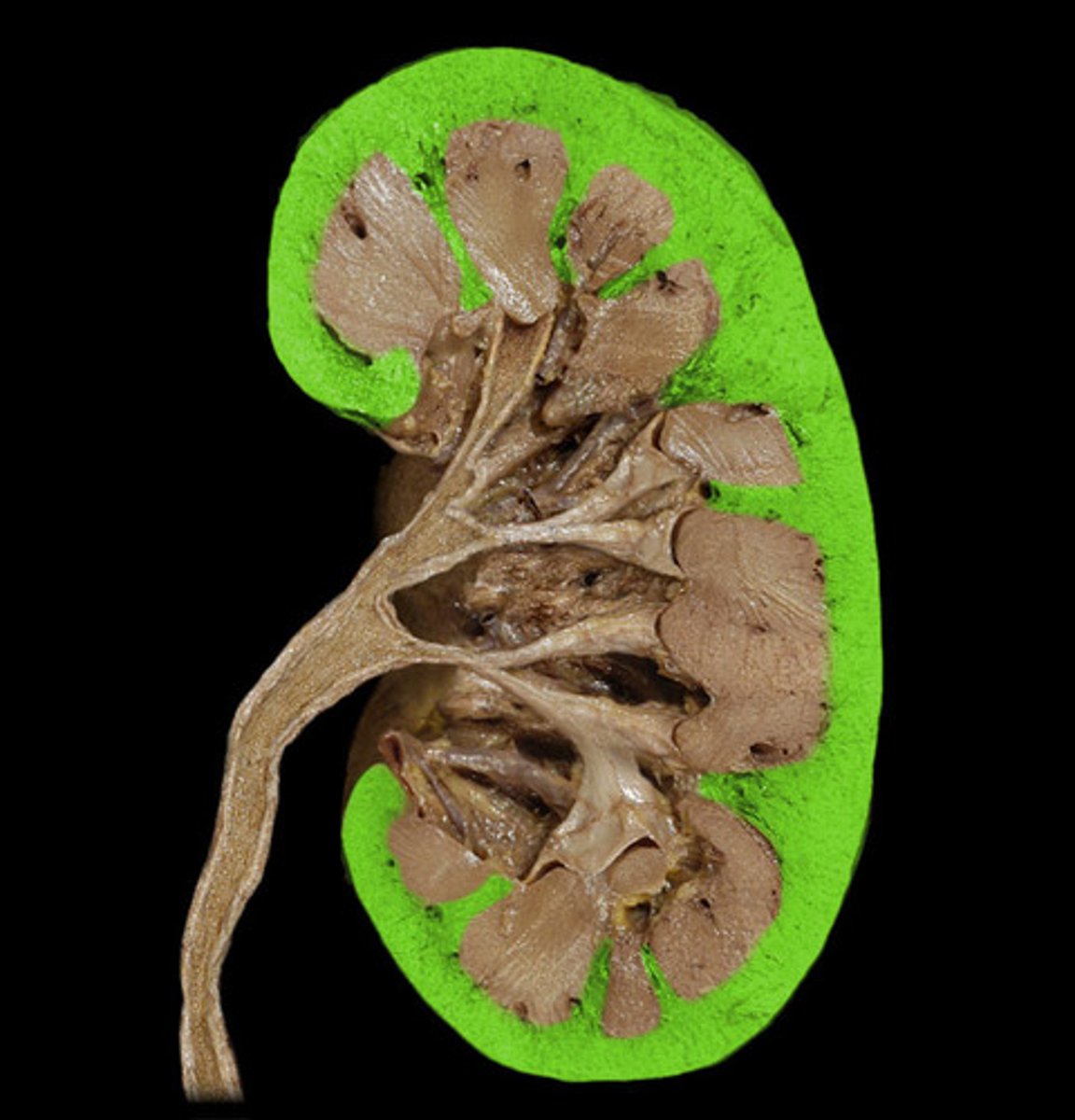
renal cortex
outer region of the kidney; filtration and reabsorption
renal medulla
inner portion of the kidney; contains renal pyramids; reabsorption and collection
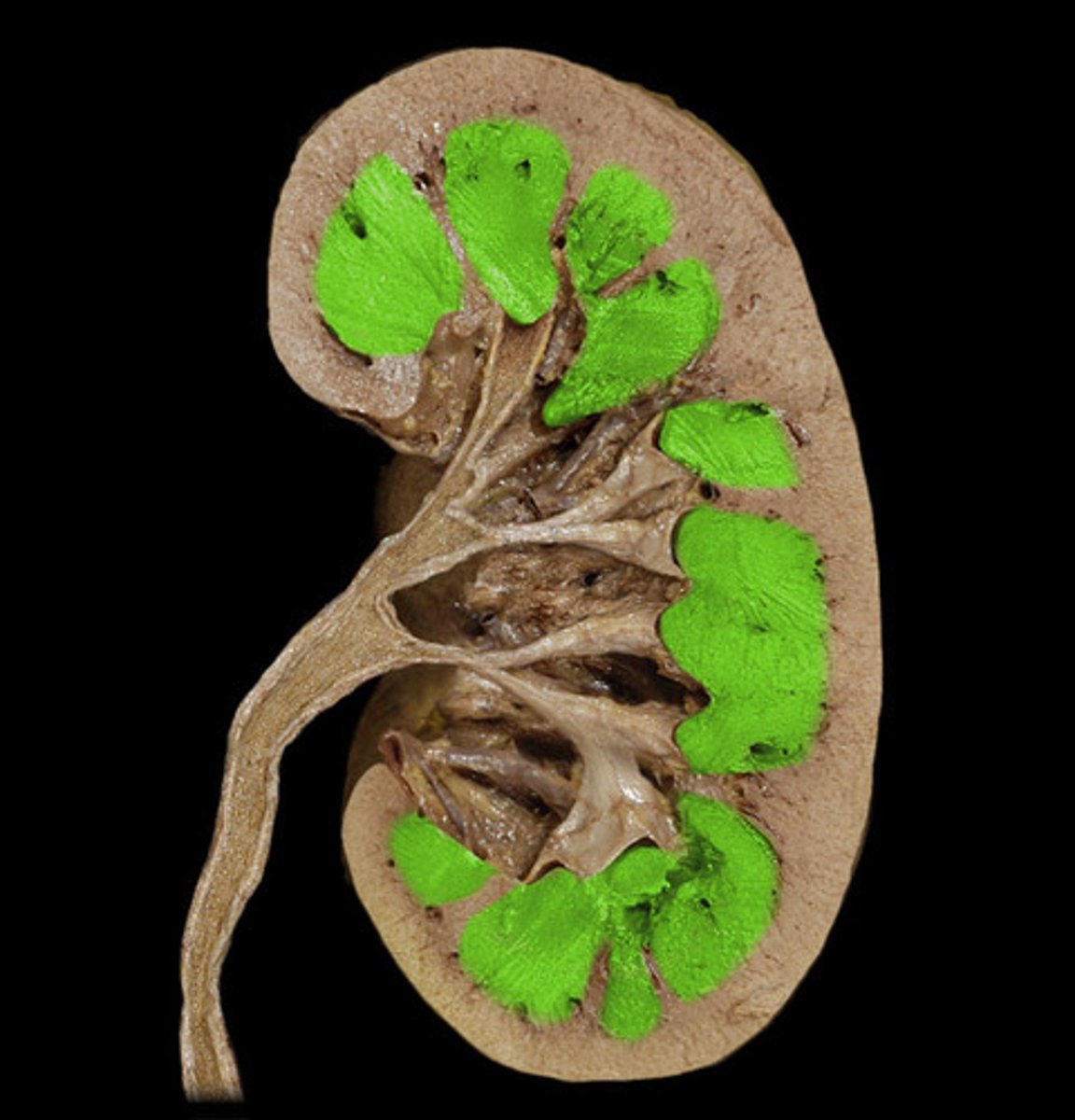
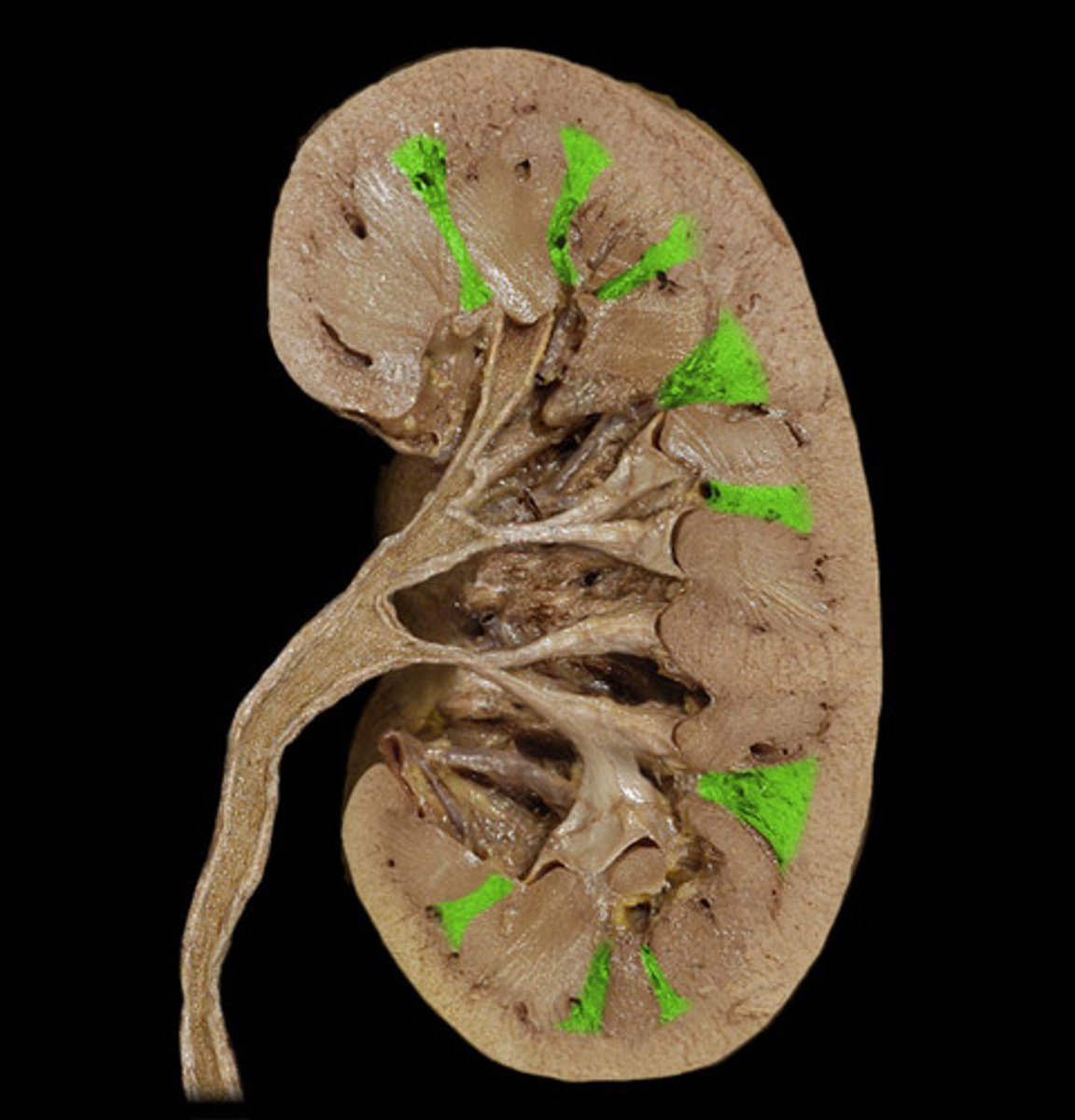
renal pyramids
triangular-shaped areas in the medulla of the kidney
renal pelvis
funnel-shaped reservoir that collects the urine and passes it to the ureter; collection
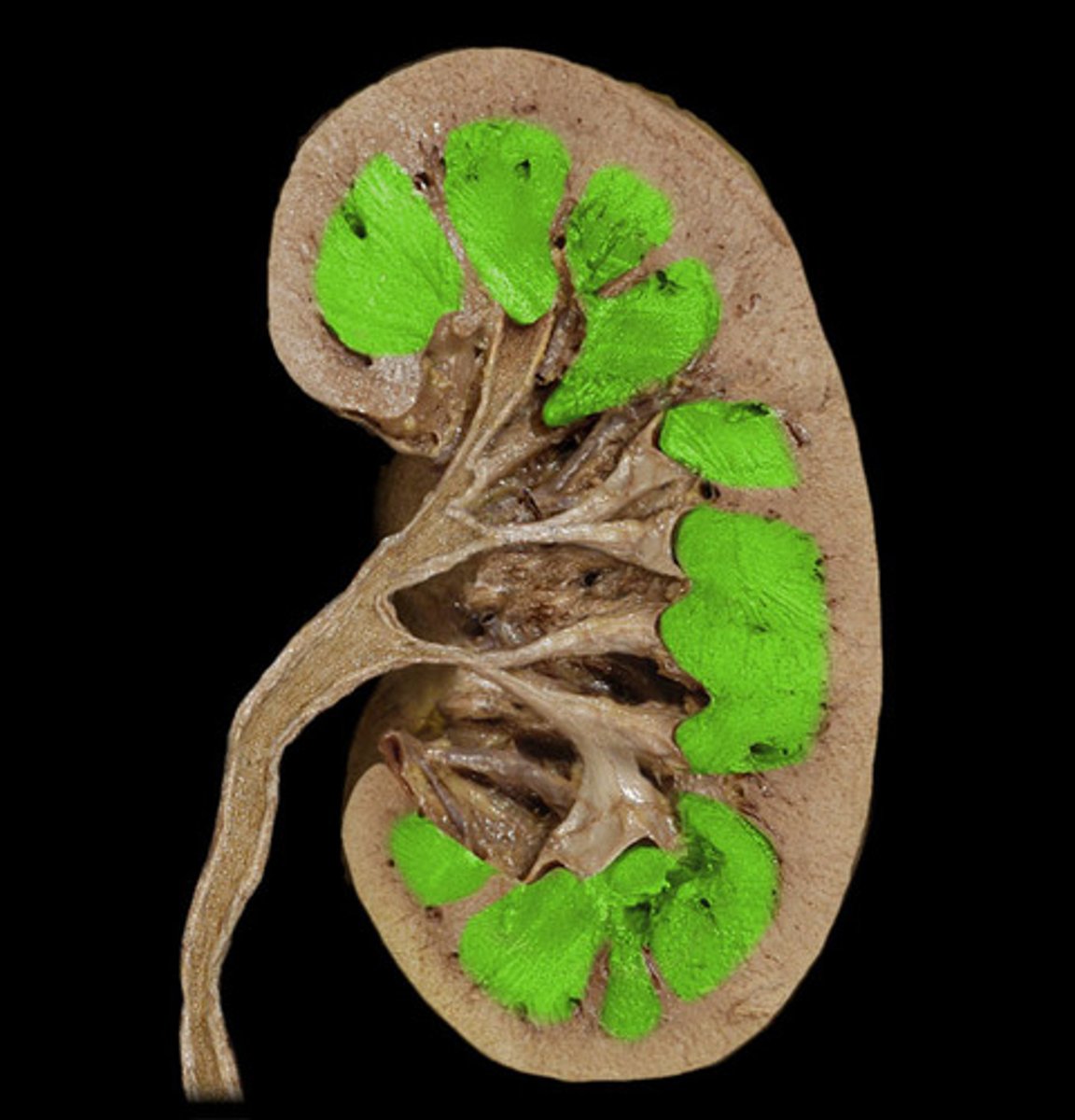
renal columns
Inward extensions of the cortex tissue separating the renal pyramids.
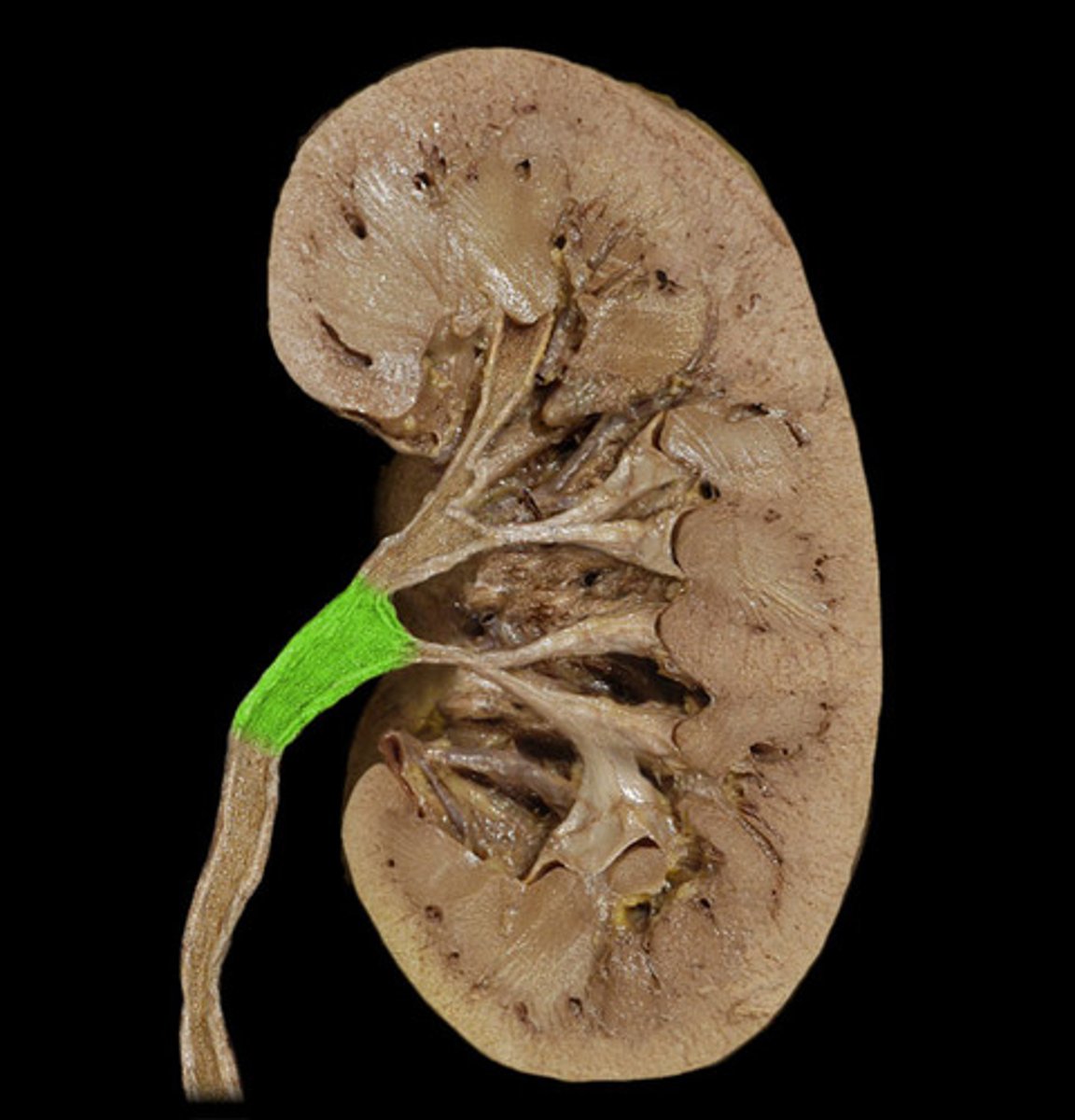
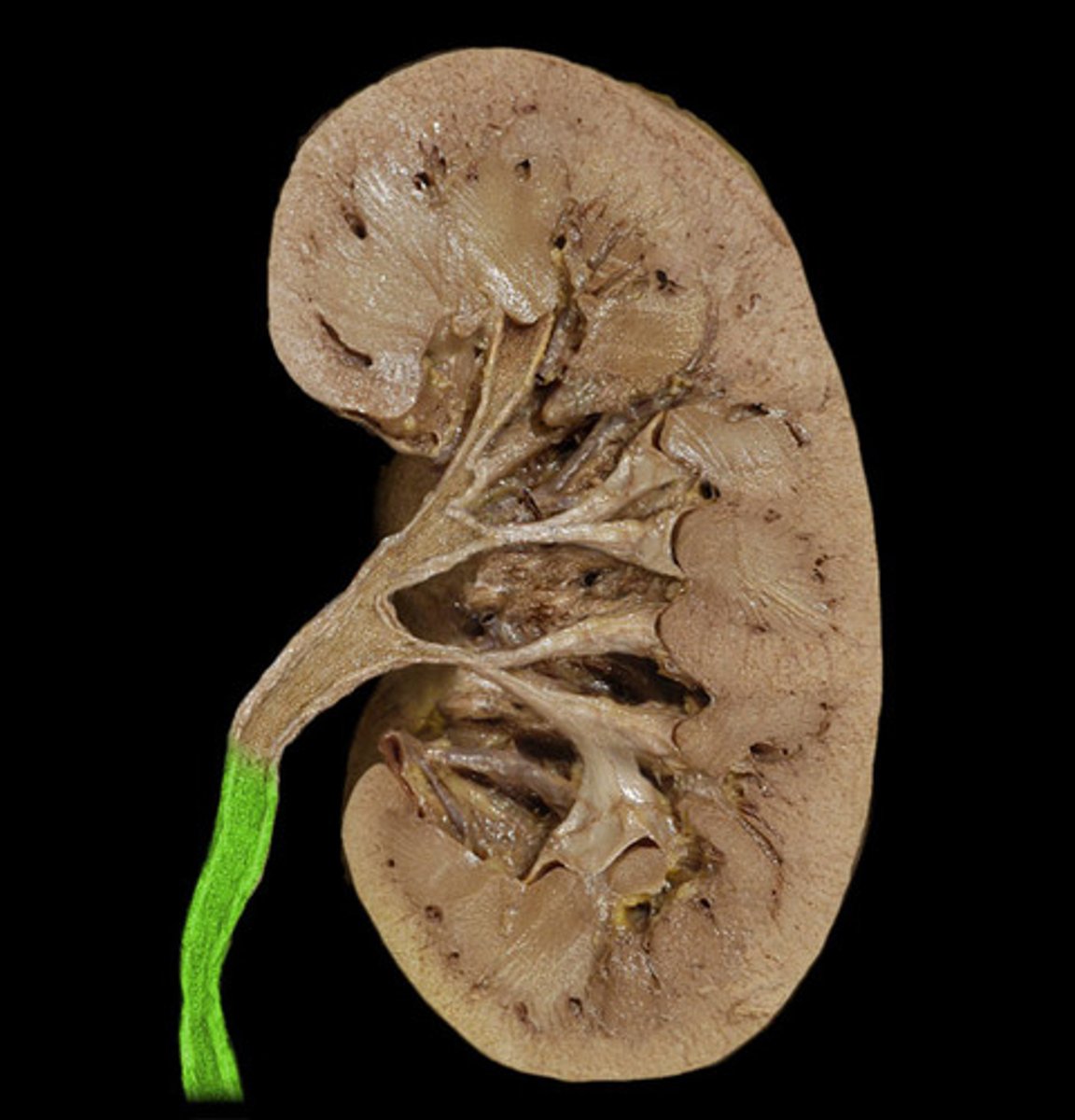
ureter
tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
Renal pyramid
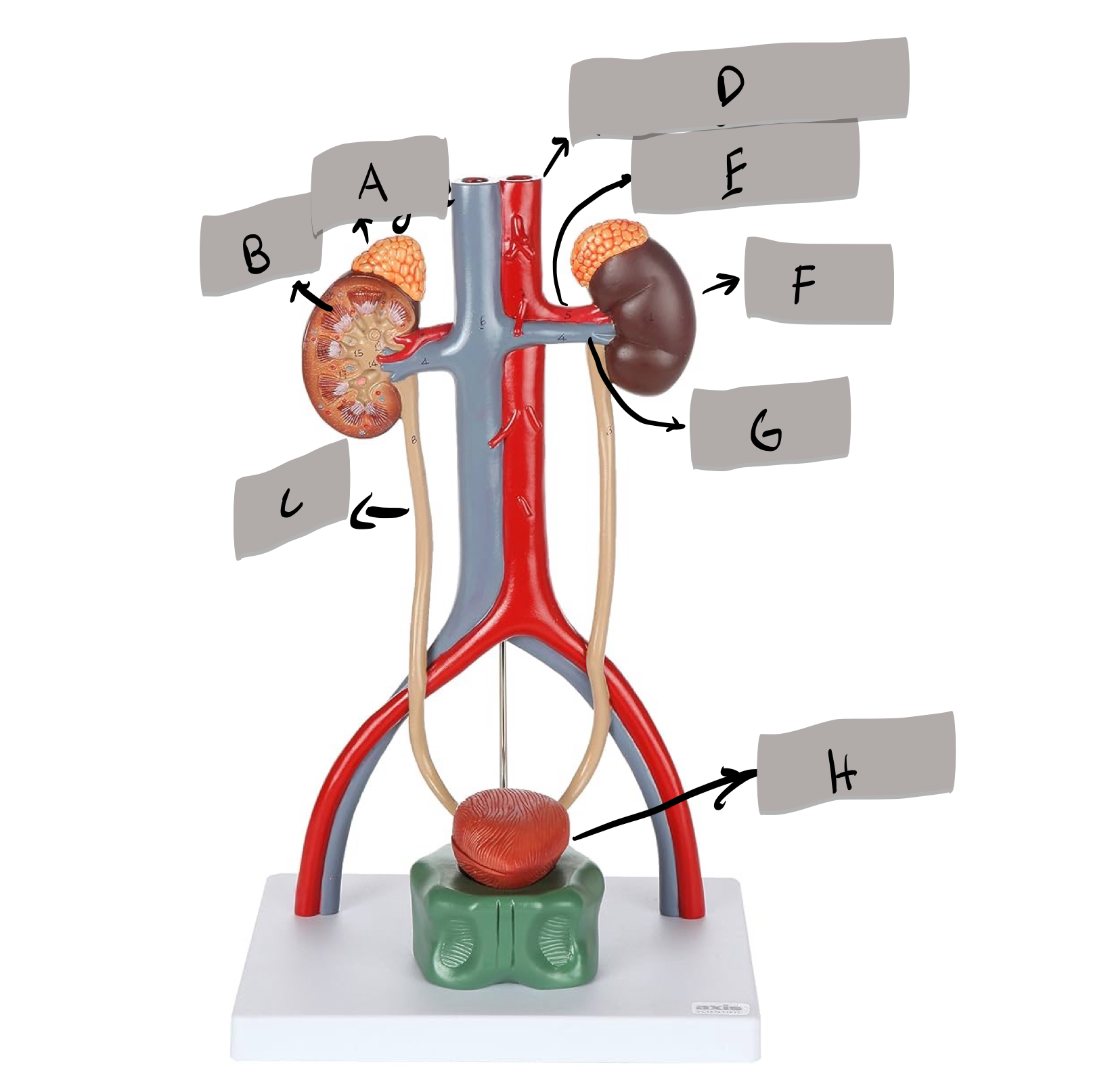
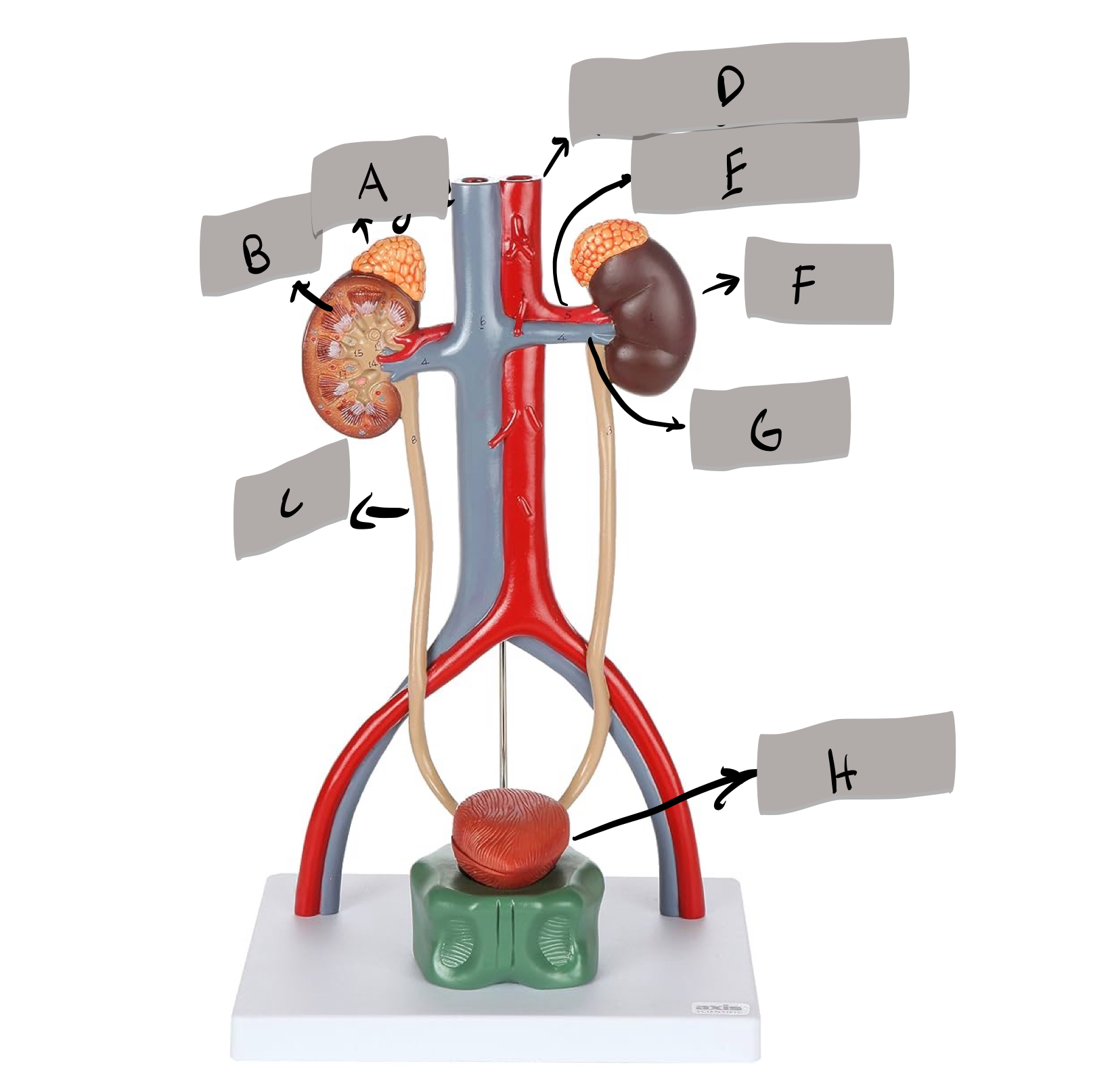
Label B
Ureter
Label c ?
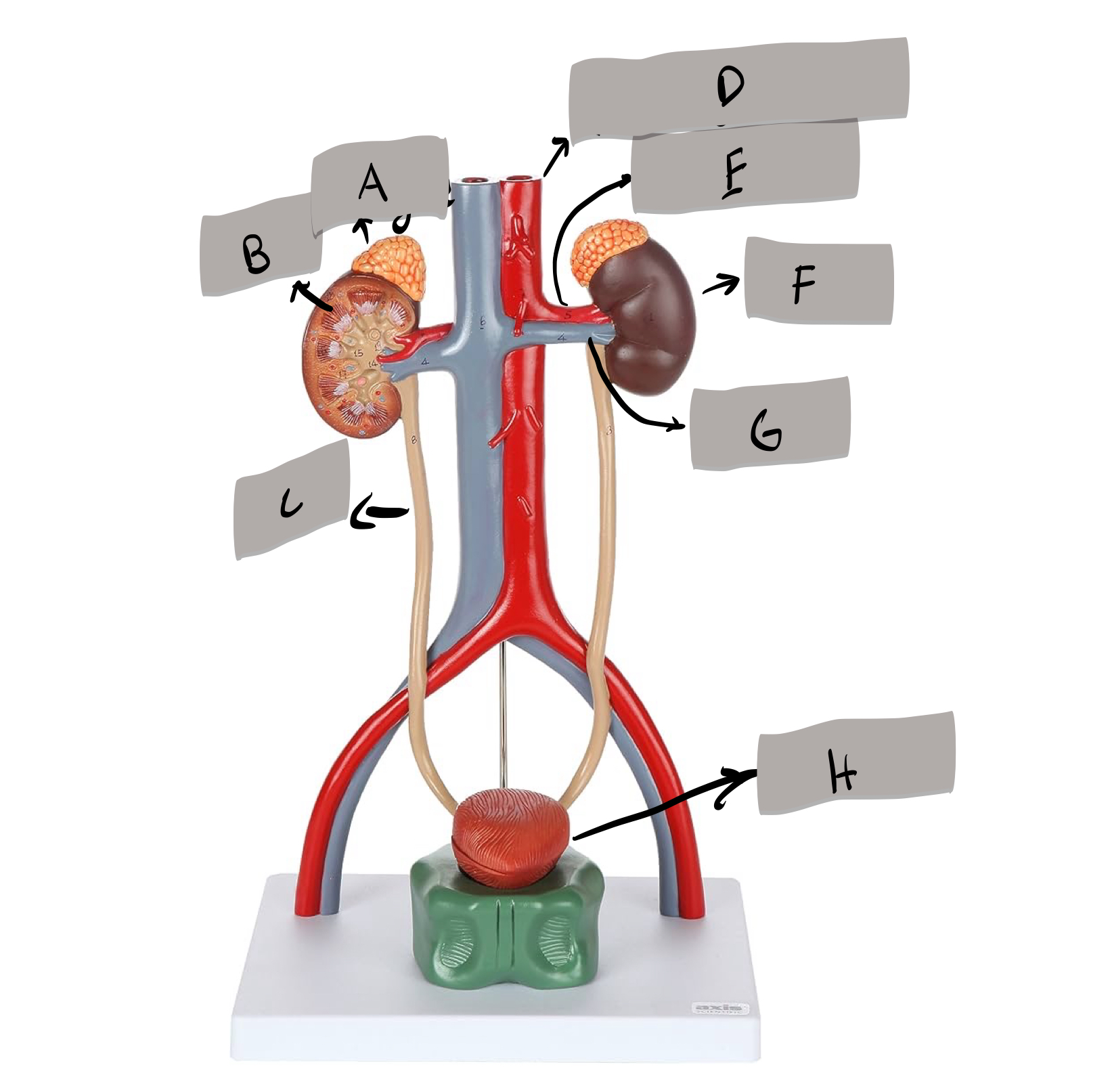
Descending aorta
Label D
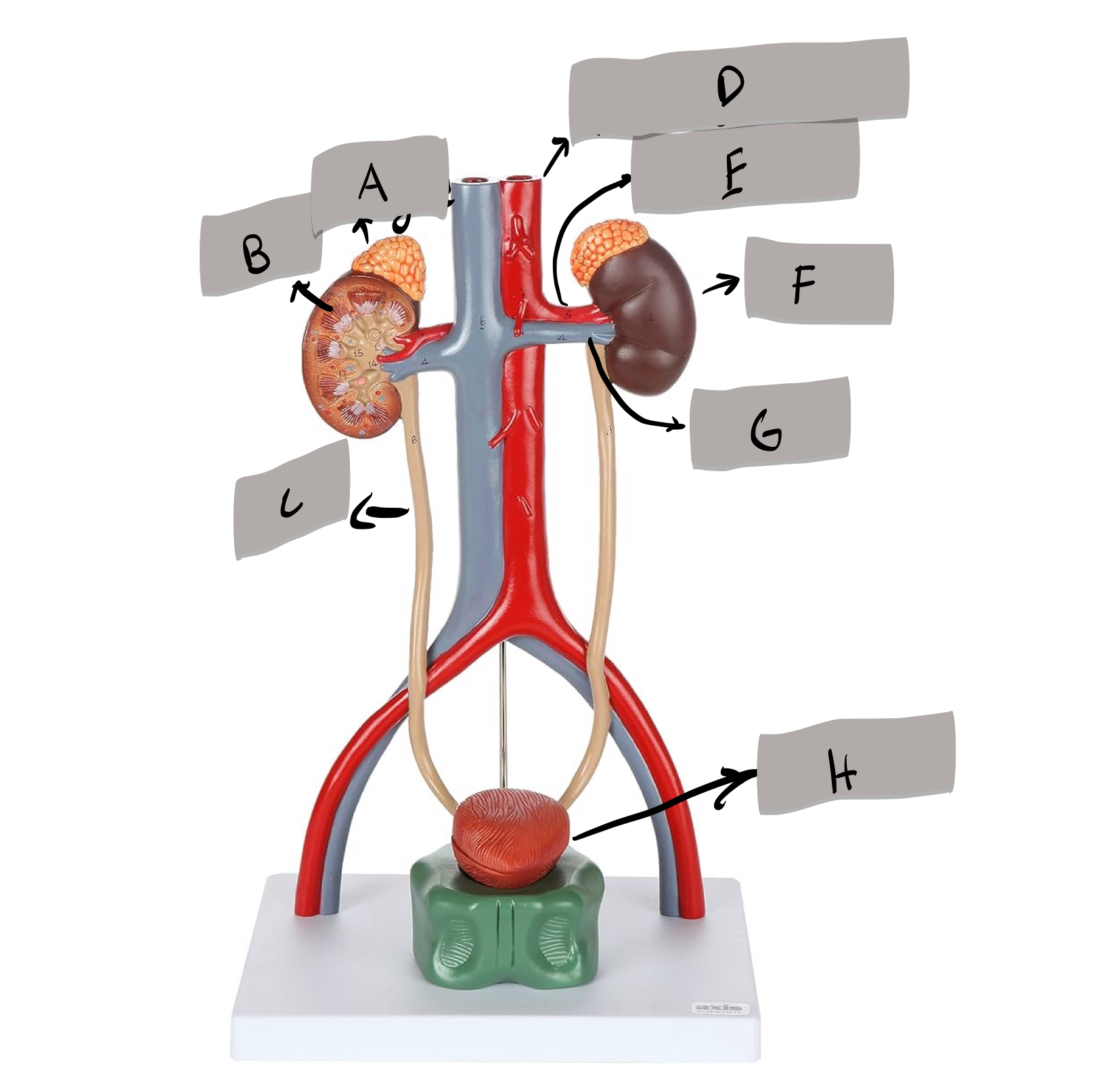
Renal artery
Label E
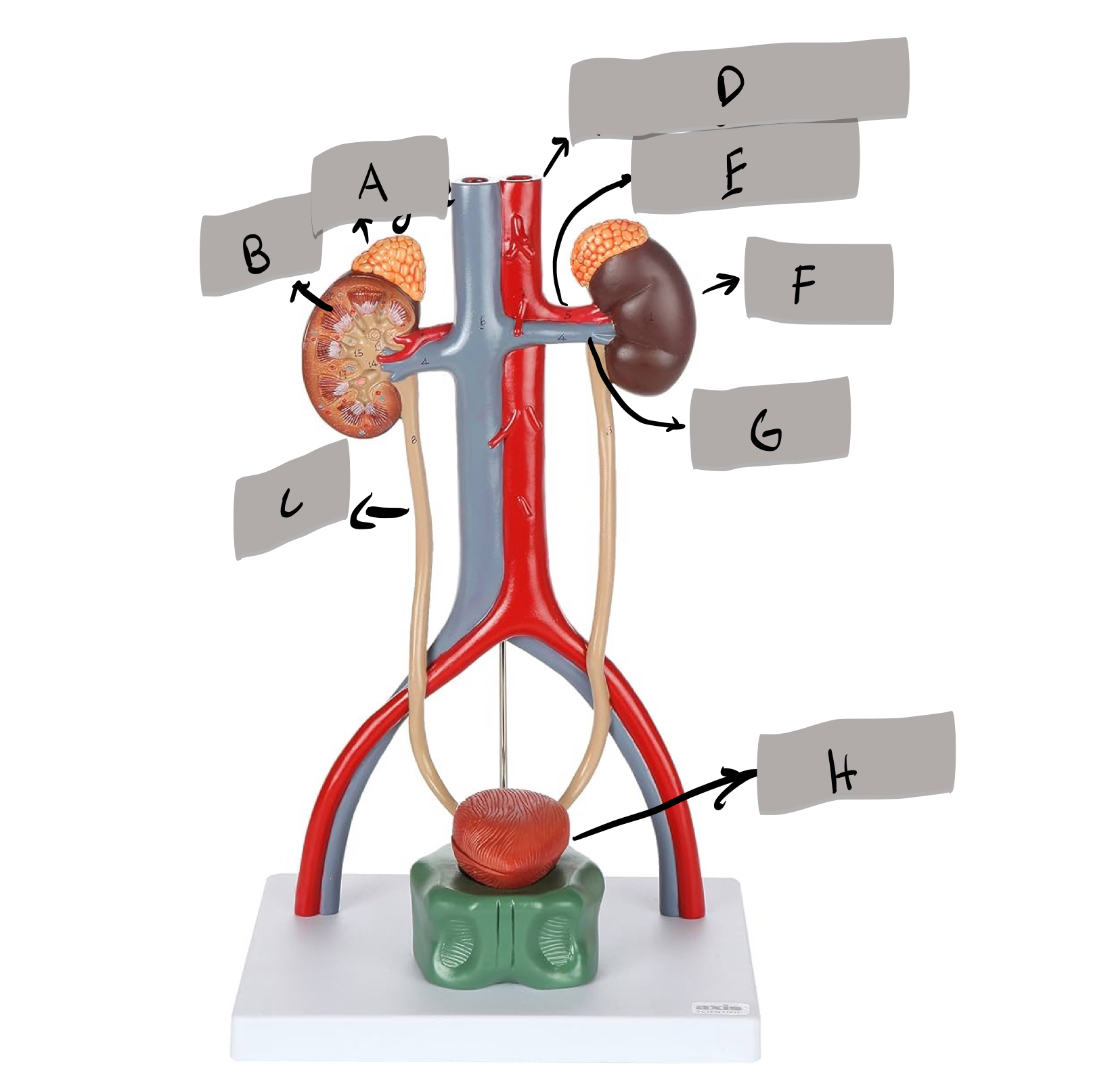
Kidney
Label F
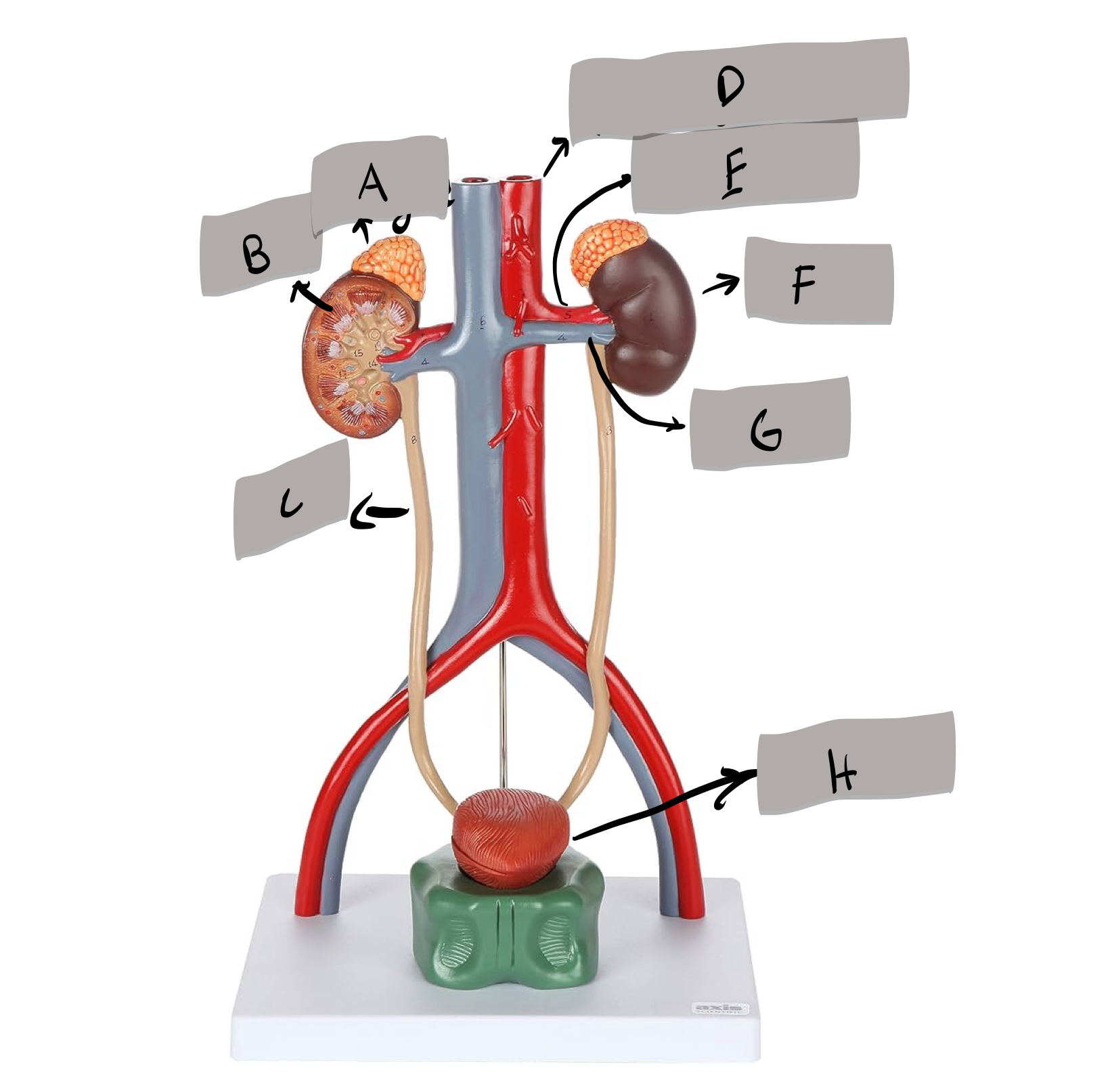
Renal vein
Label G
Urinary bladder
Label H
Proximal tubule
Label A
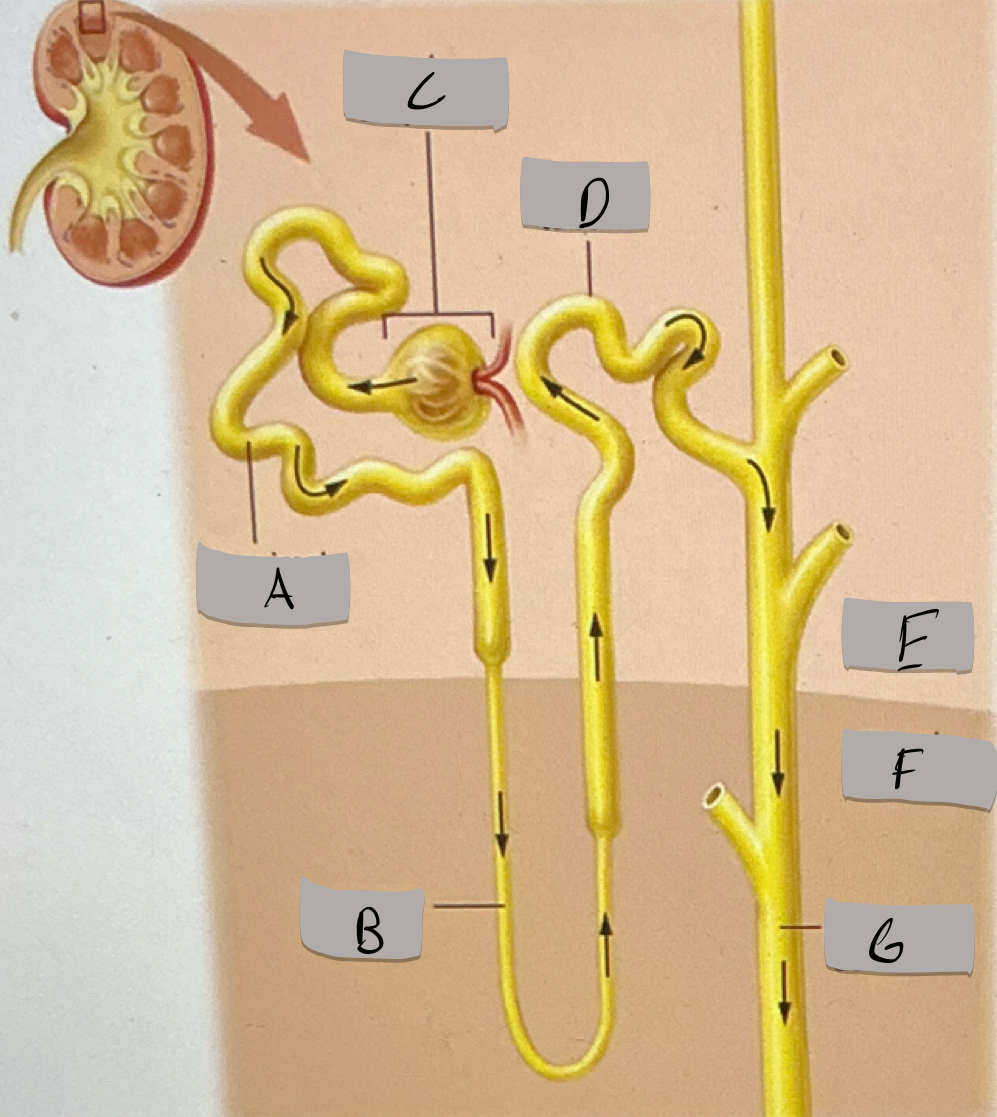
Nephron loop
Label B
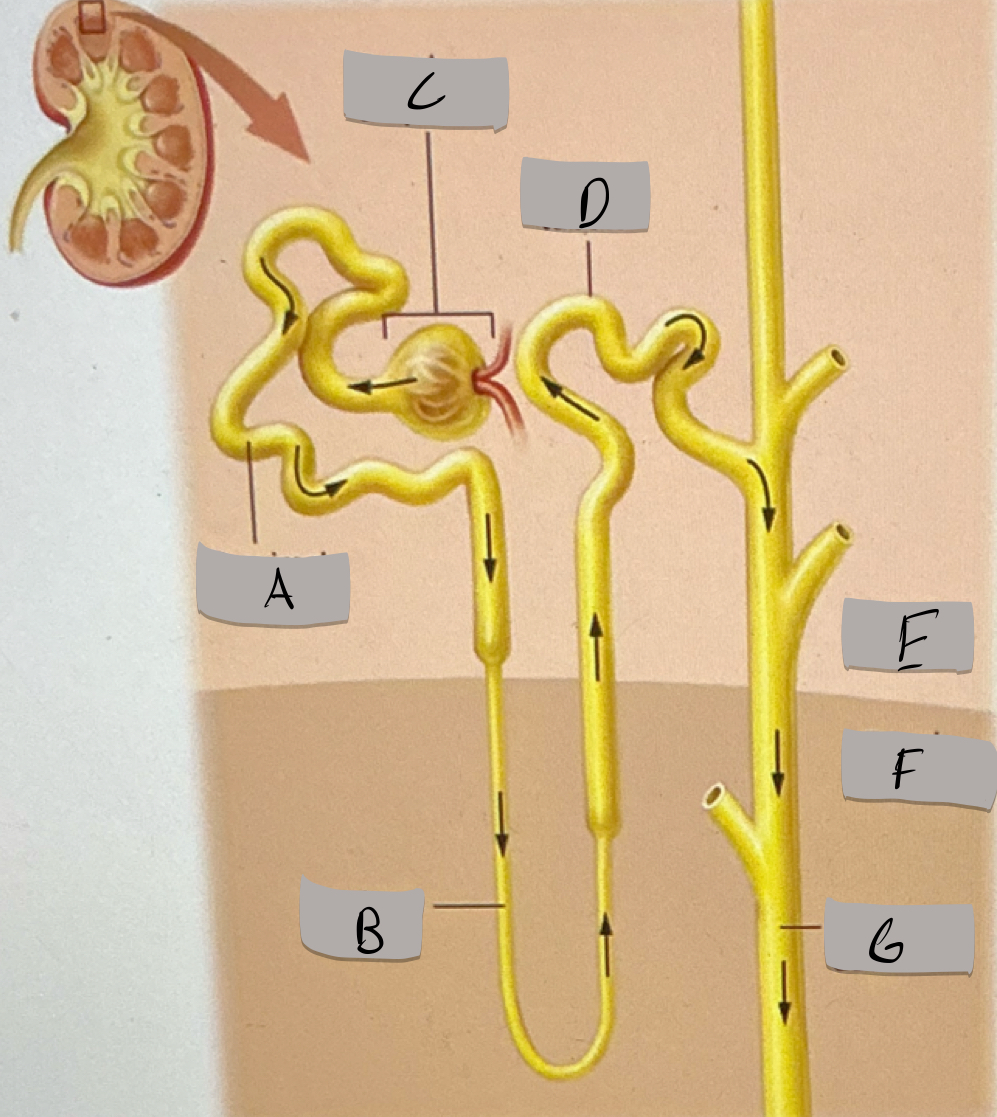
Renal corpuscle
Label c
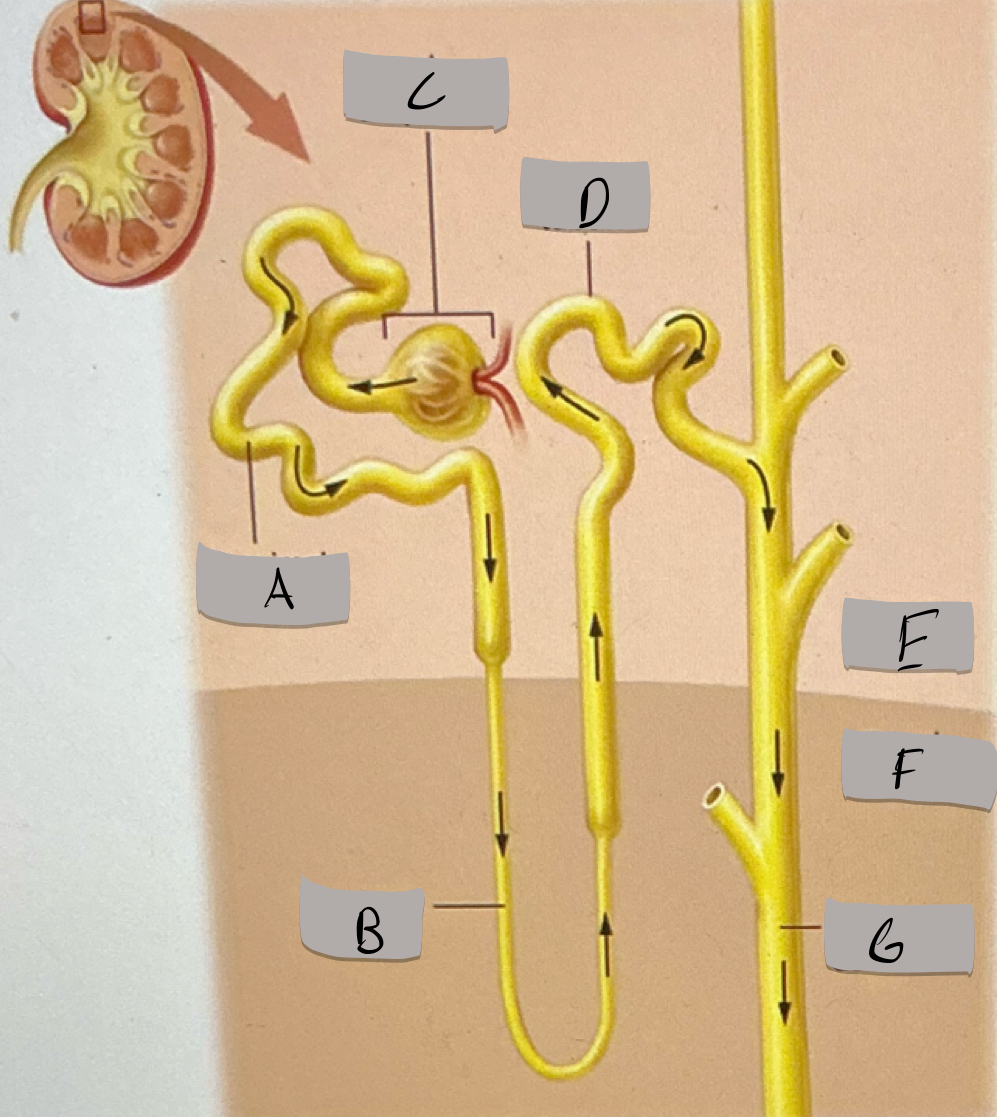
Distal tubule
Label D
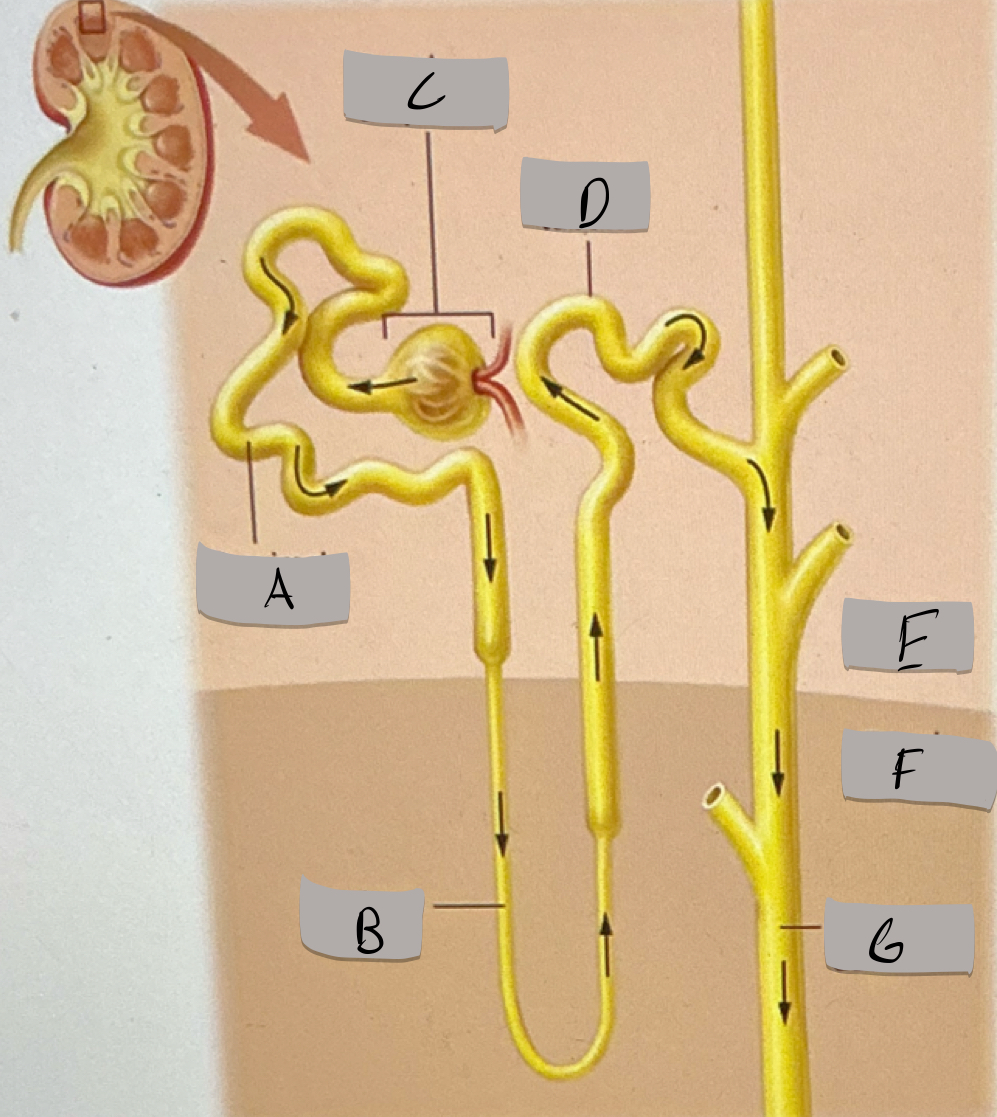
Renal cortex
Label E
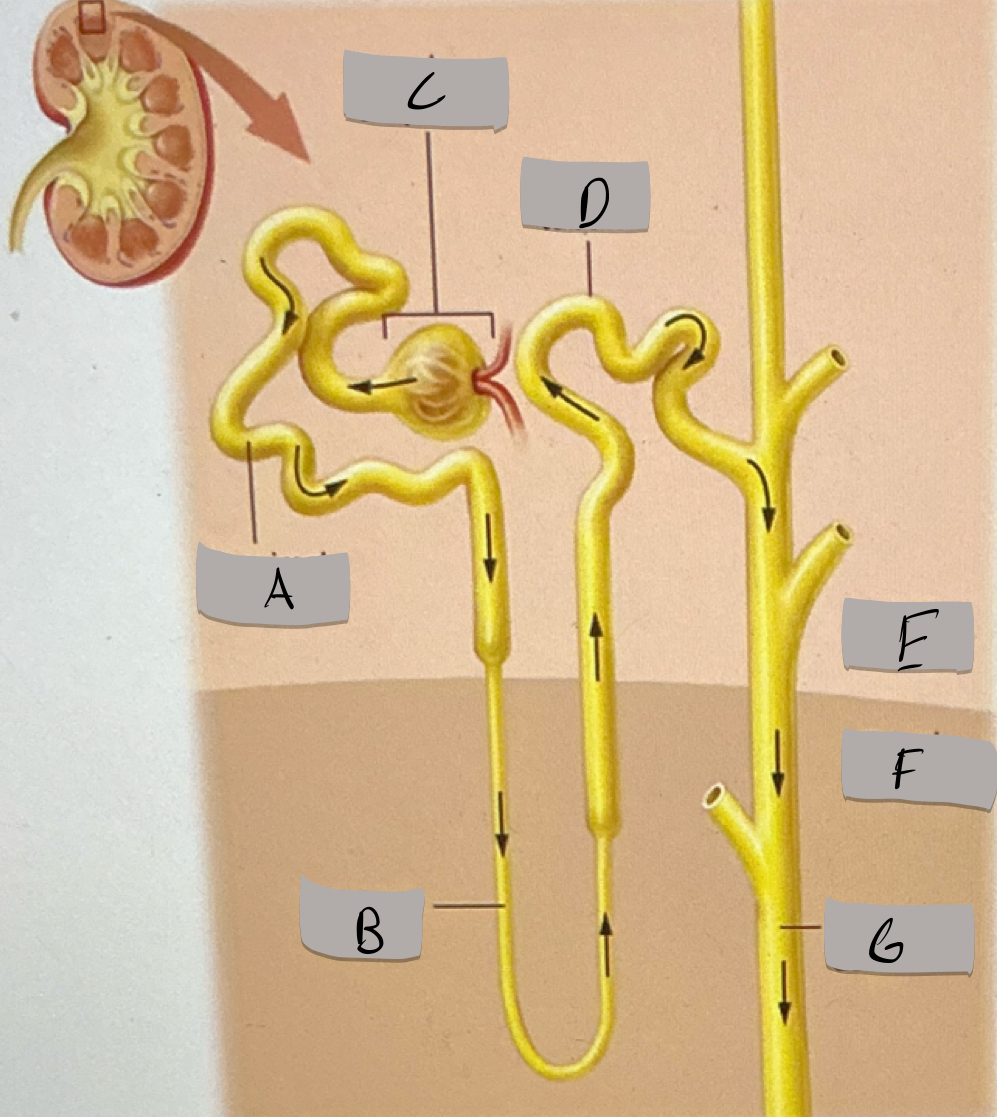
Renal medulla
Label F
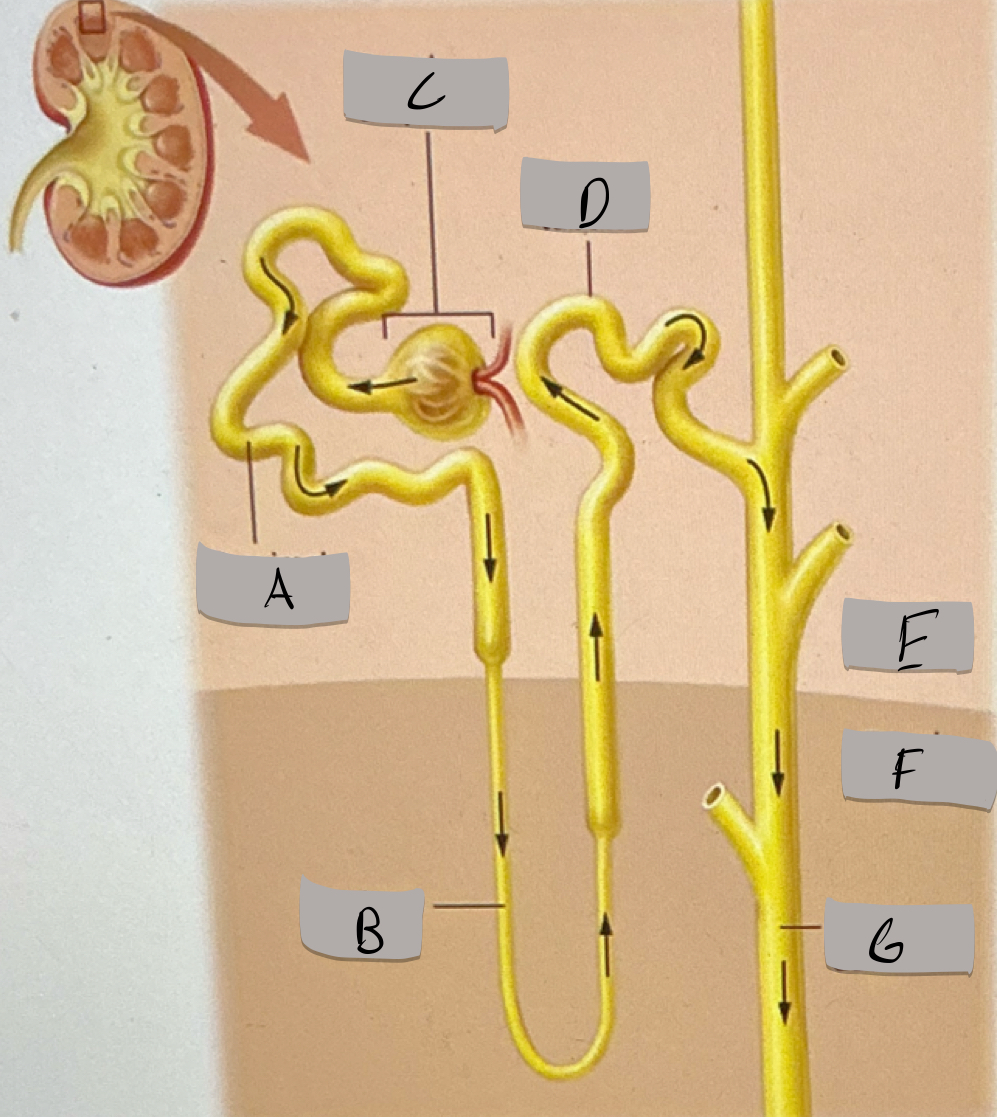
Collecting duct
Label G
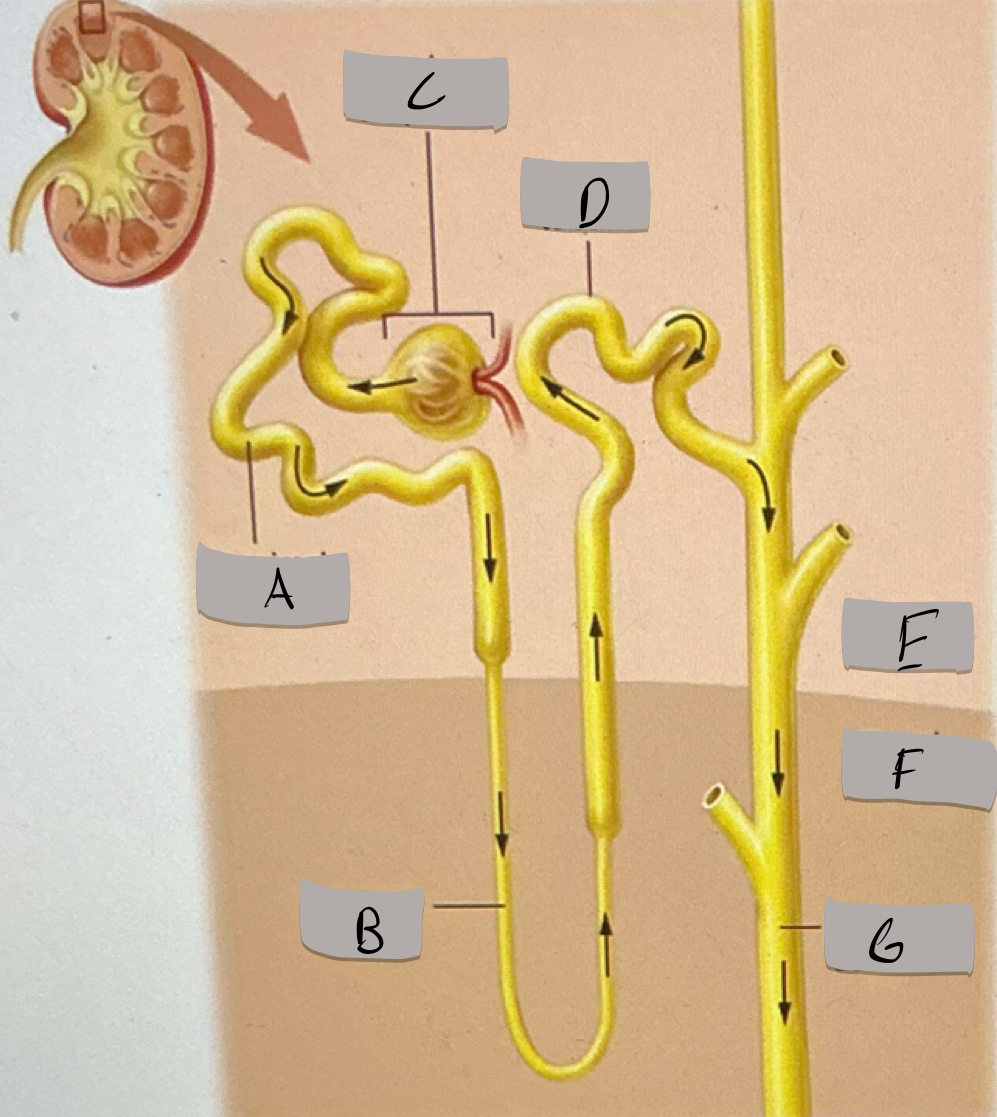
Blood flow pathway
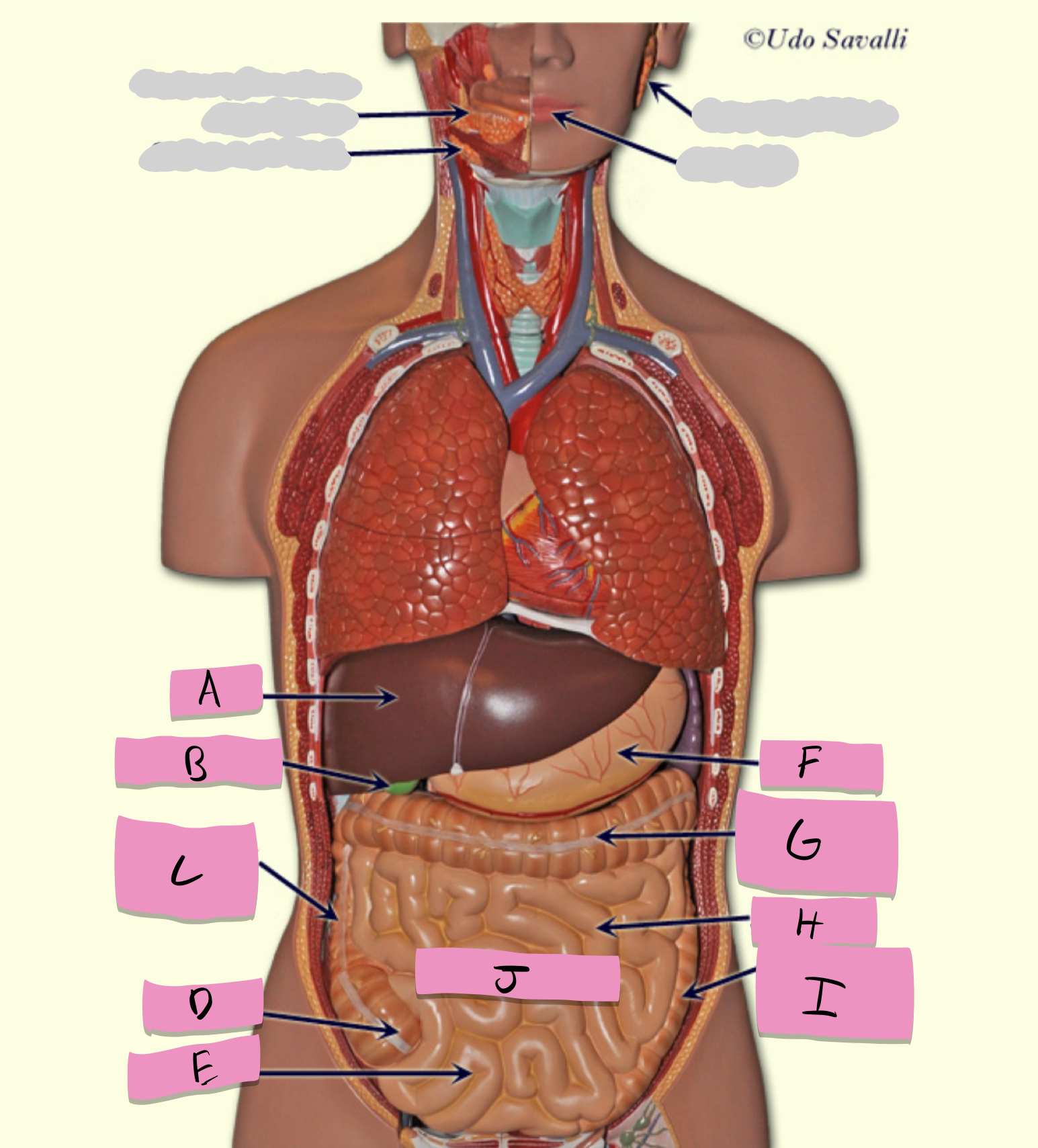
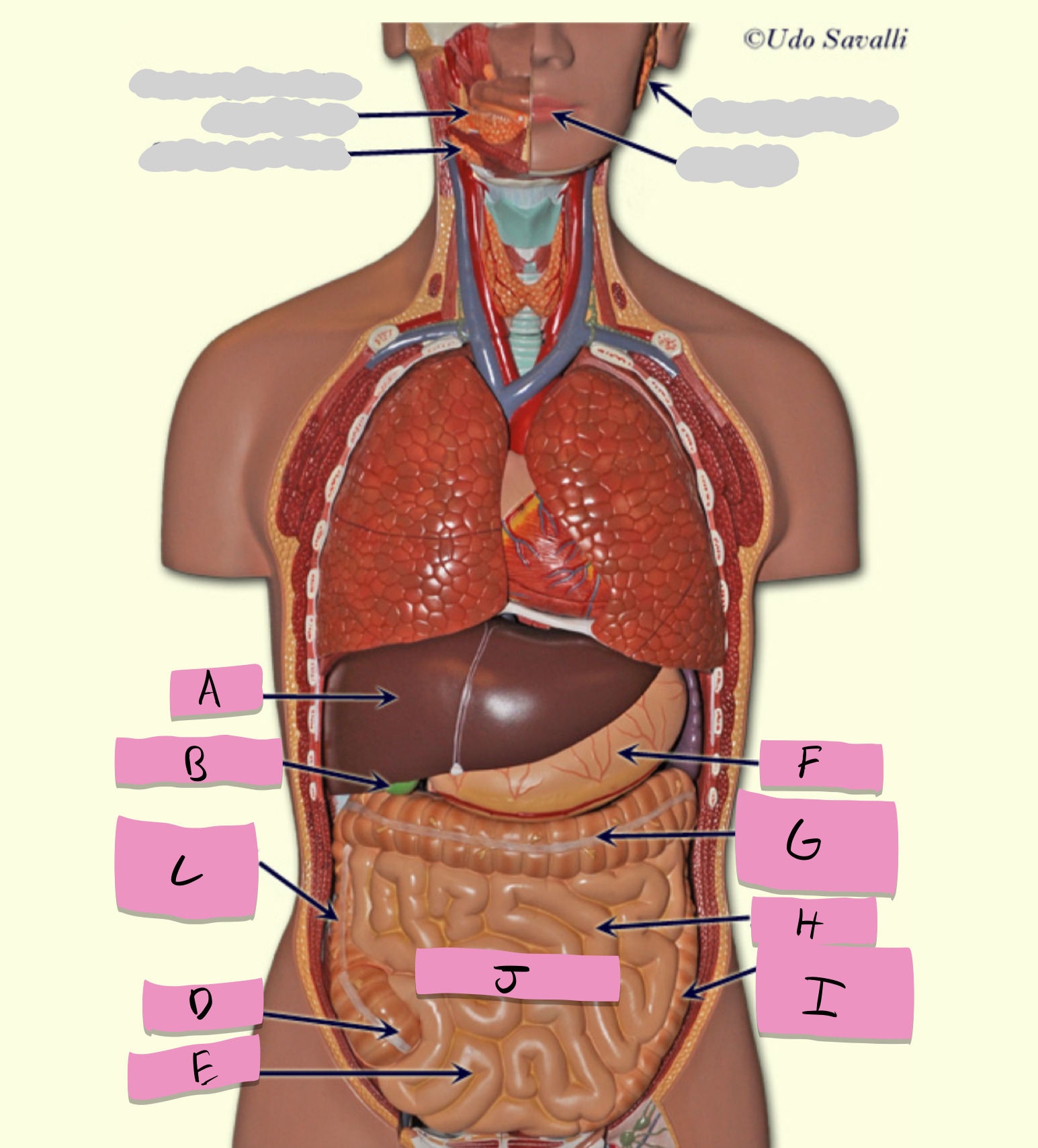
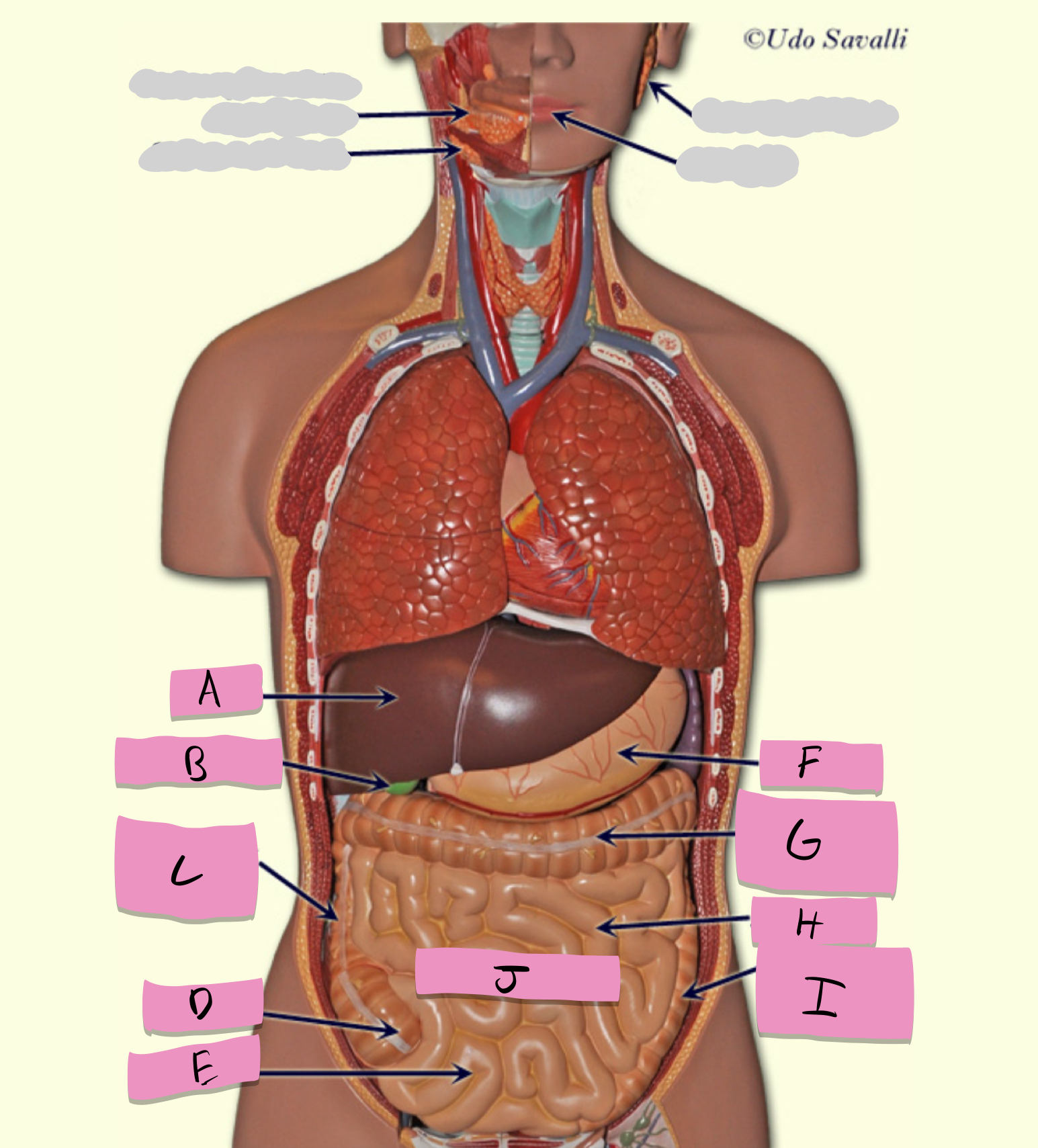
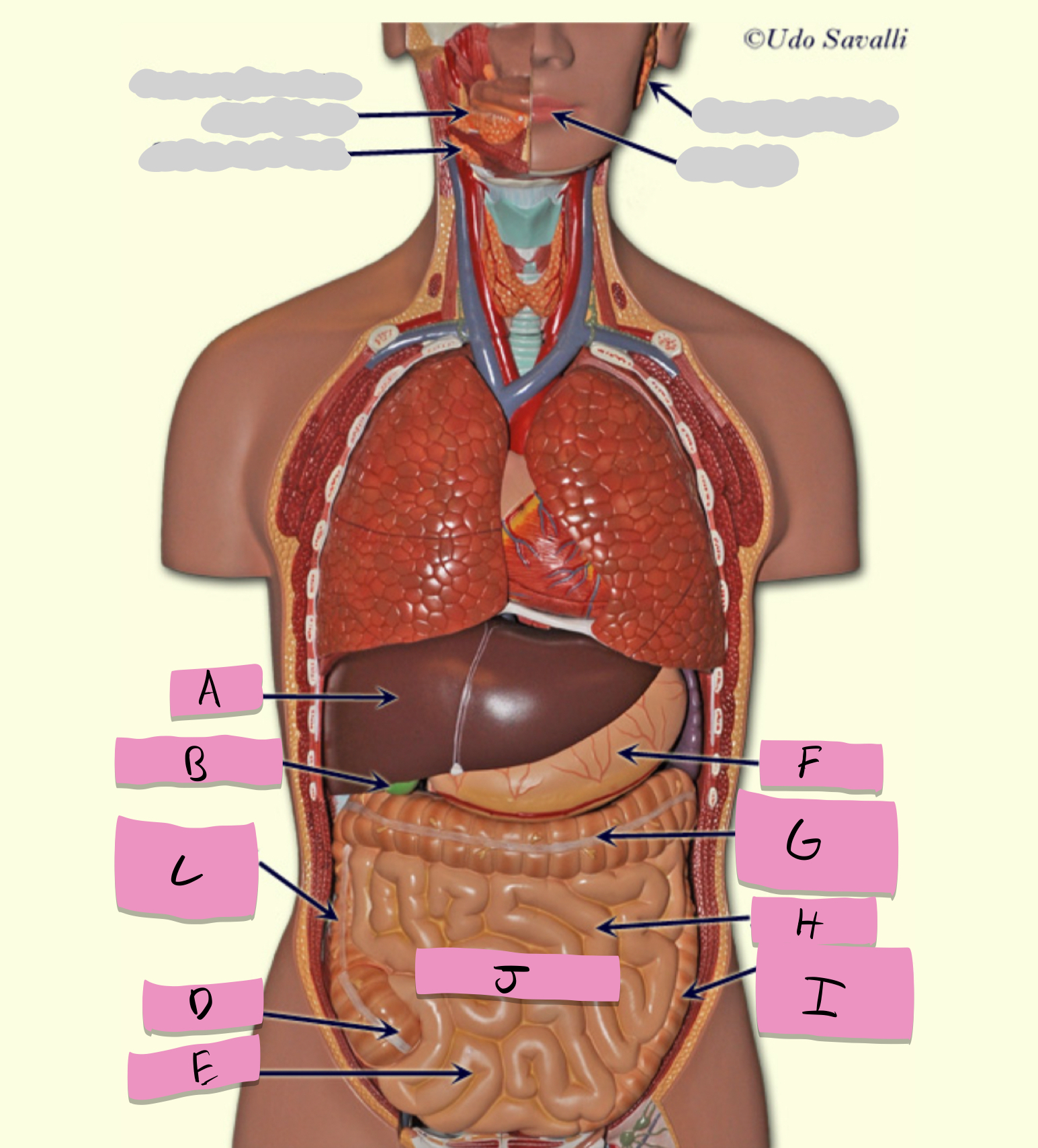
oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
pathway of food through the digestive tract
oral cavity
ingestion, mechanical processing, moistening, mixing with salivary secretions
pharynx
passageway for food
esophagus
moves food to stomach via peristalsis
stomach
chemical breakdown of materials by acid and enzymes; secretes gastric juice; creates chyme
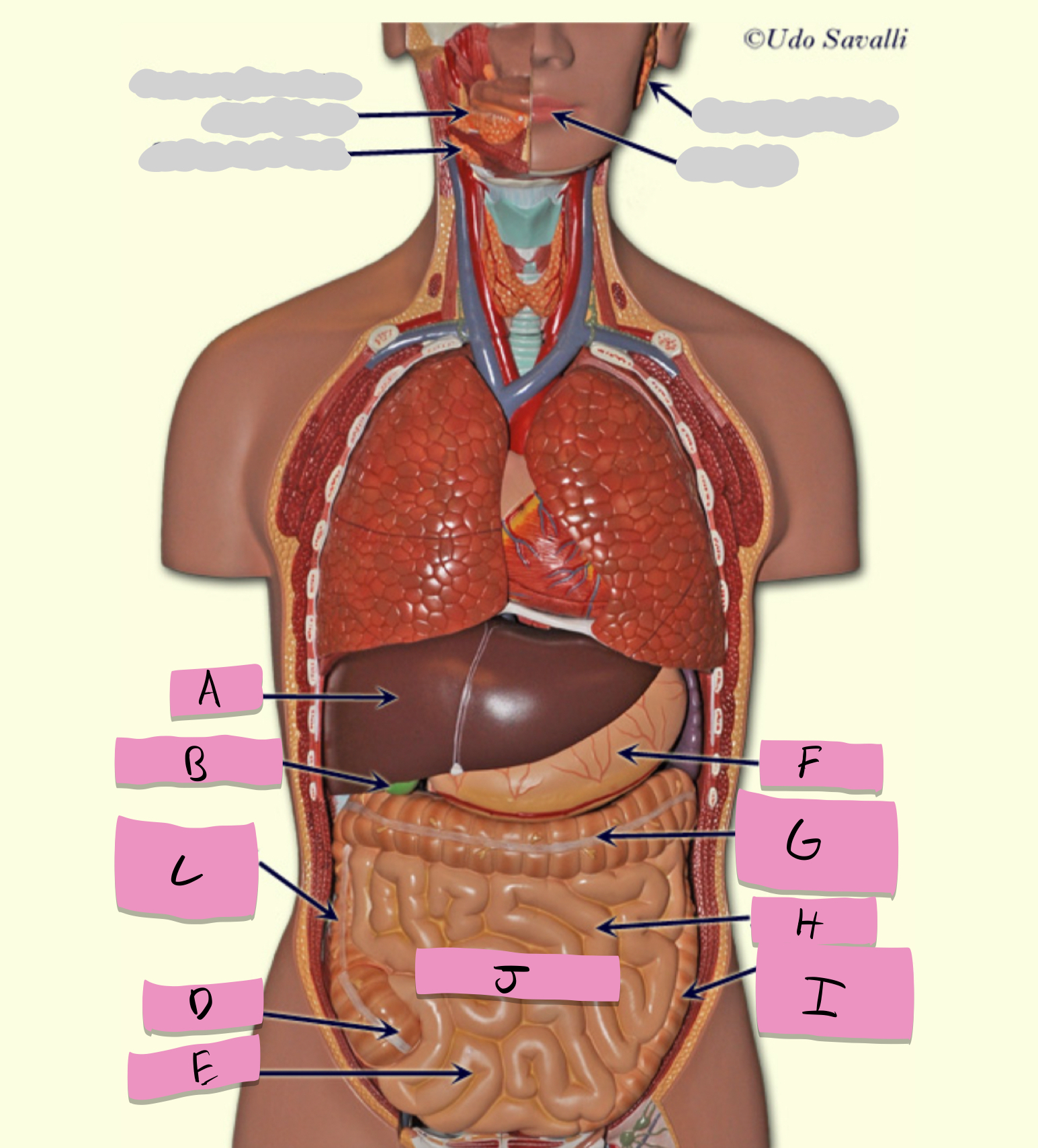
stomach function
chemical breakdown of materials by acid and enzymes; secretes gastric juice; creates chyme
small intestine
absorption of nutrients (label J)
jejunum
Label H
Ileum
Label E
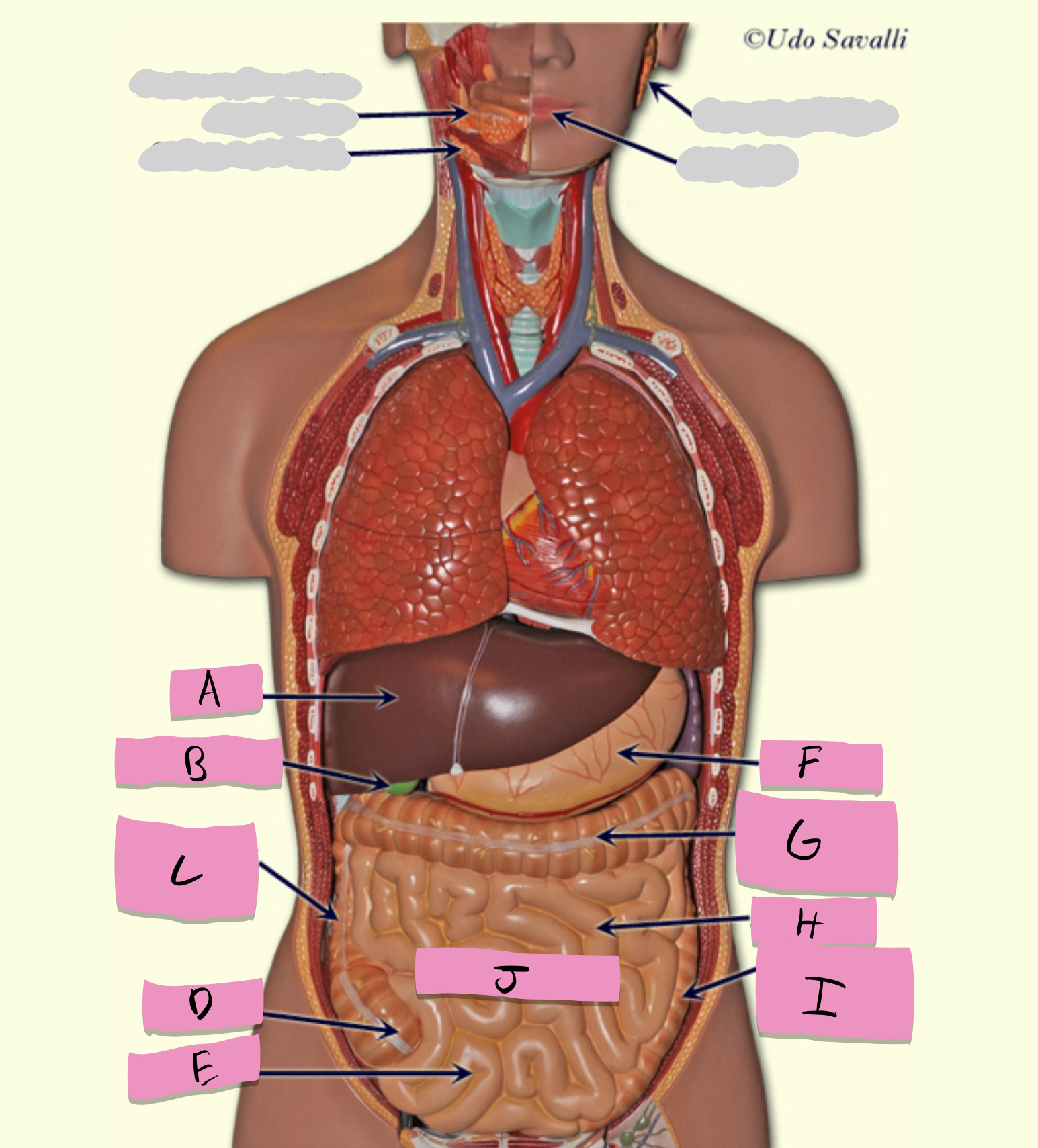
large intestine
Absorbs water and forms feces
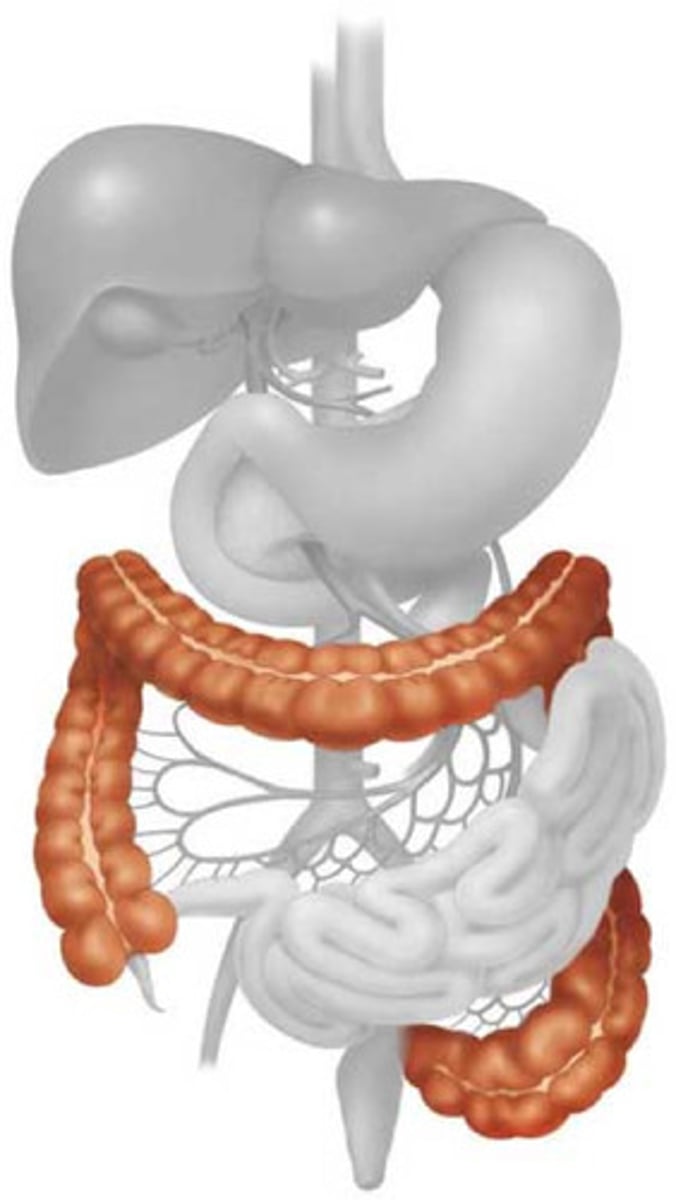
transverse colon
Label G
descending colon
Label I
Cecum
Label D
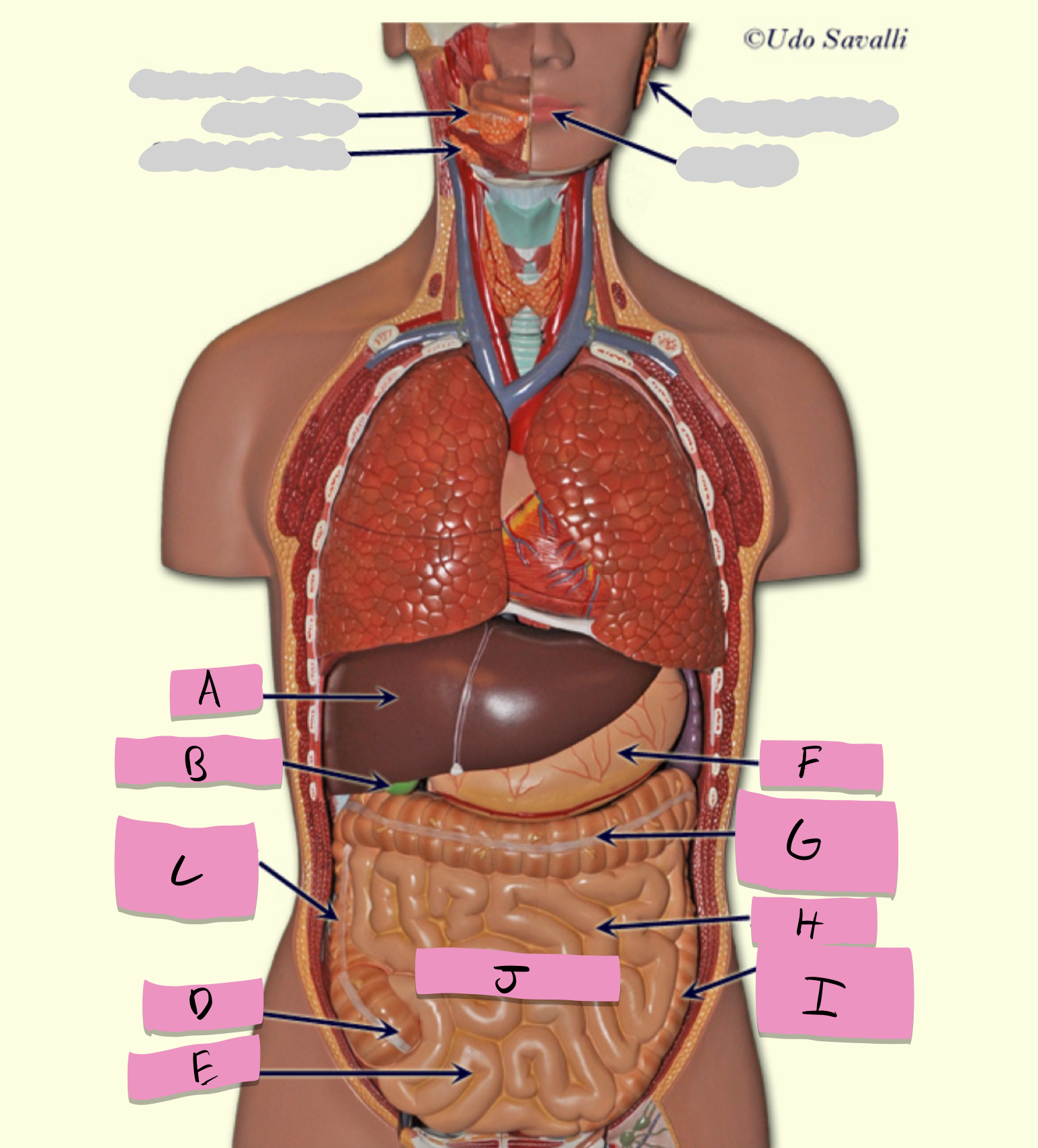
teeth
mechanical digestion
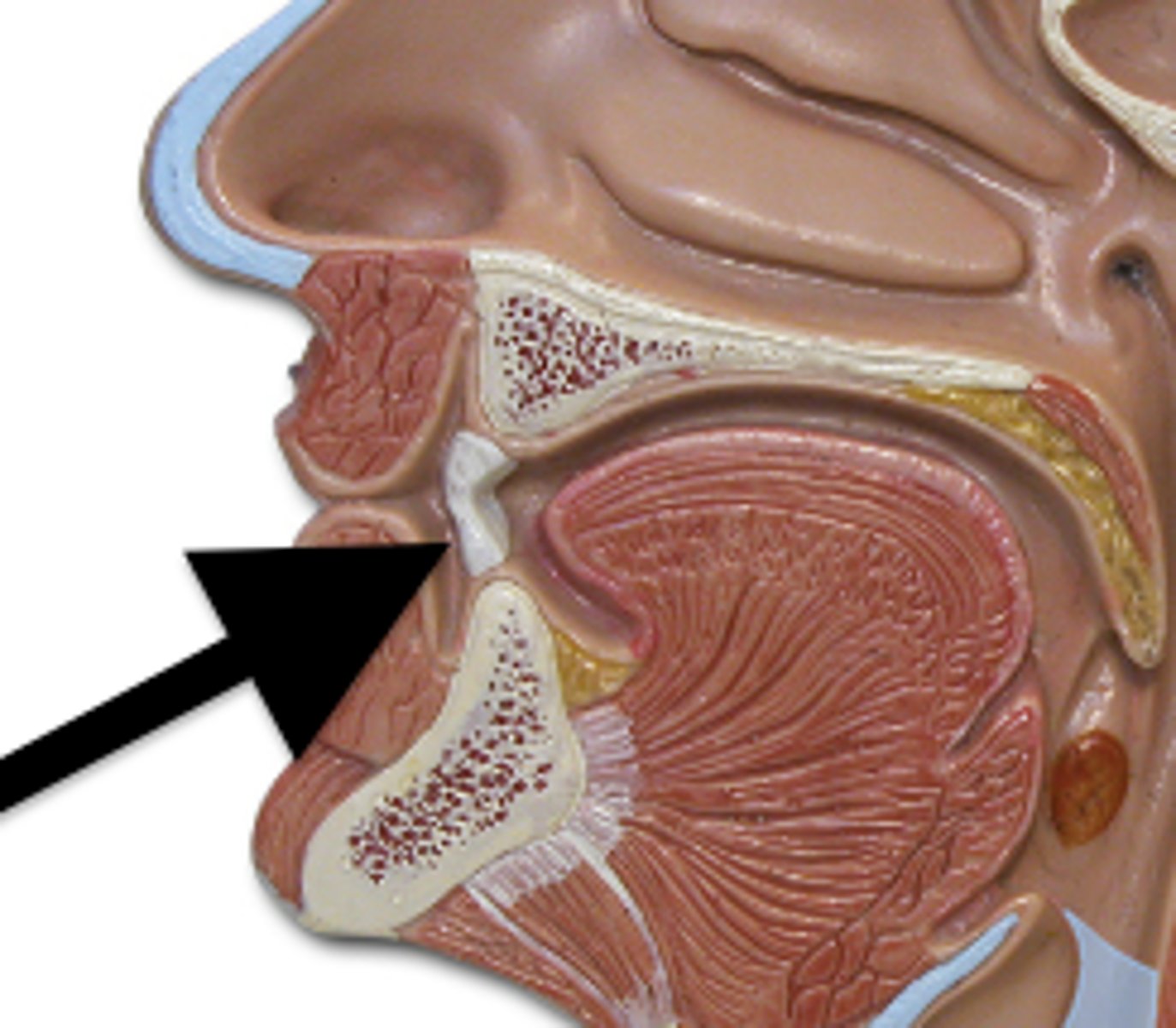
tongue
moves food around; aids in bolus formation; initiates swallowing
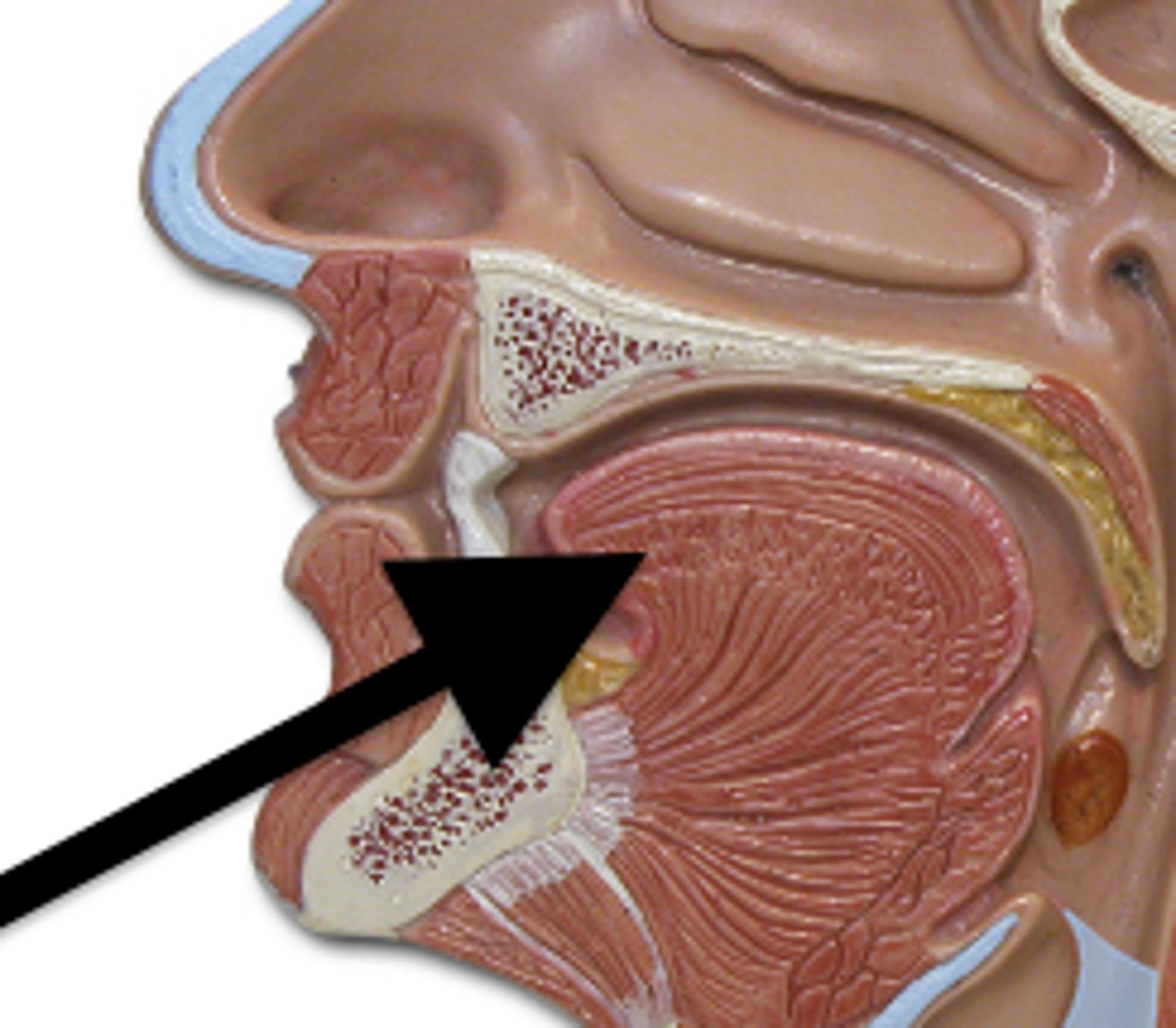
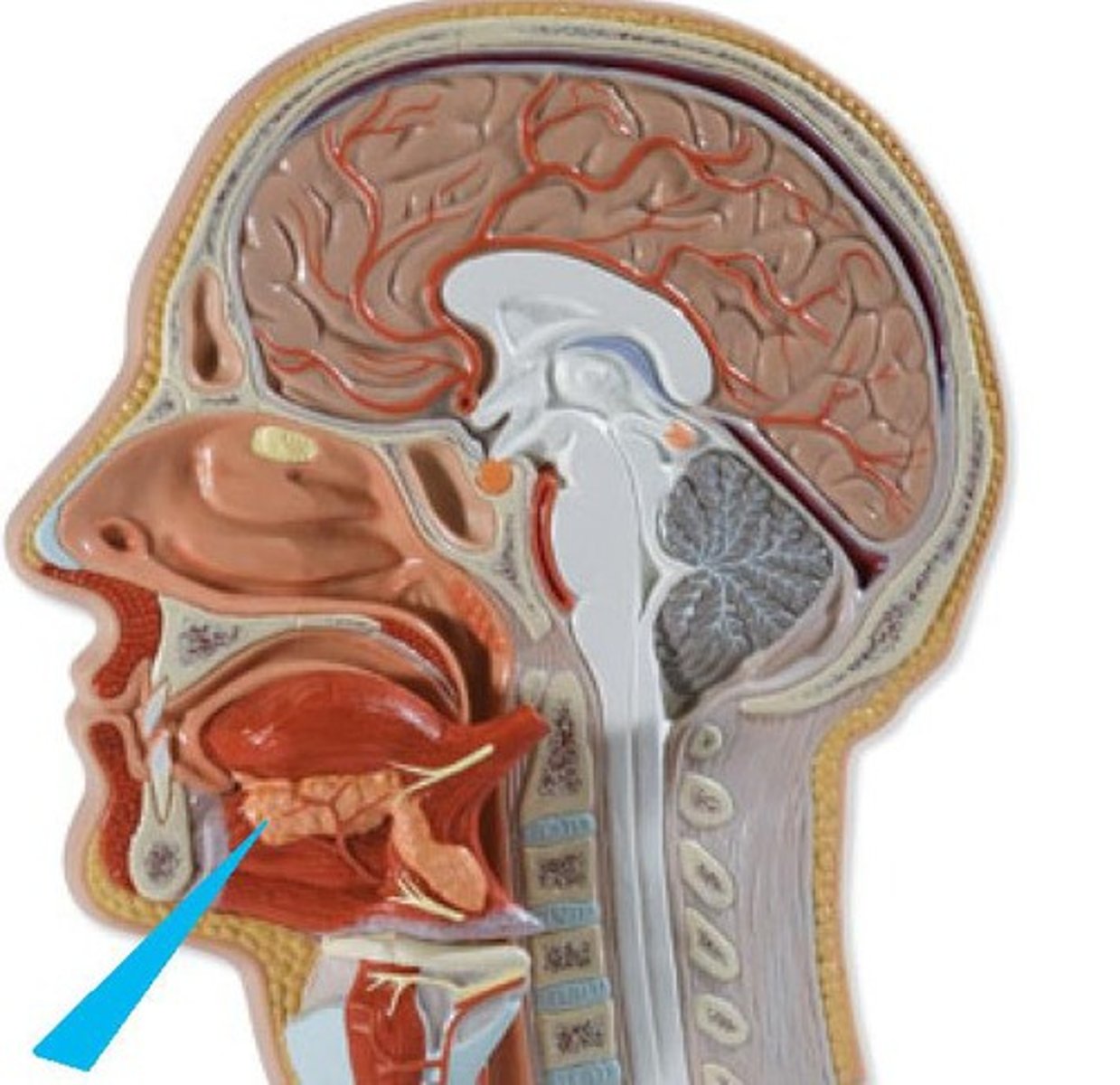
salivary glands
produce saliva
liver
produces bile
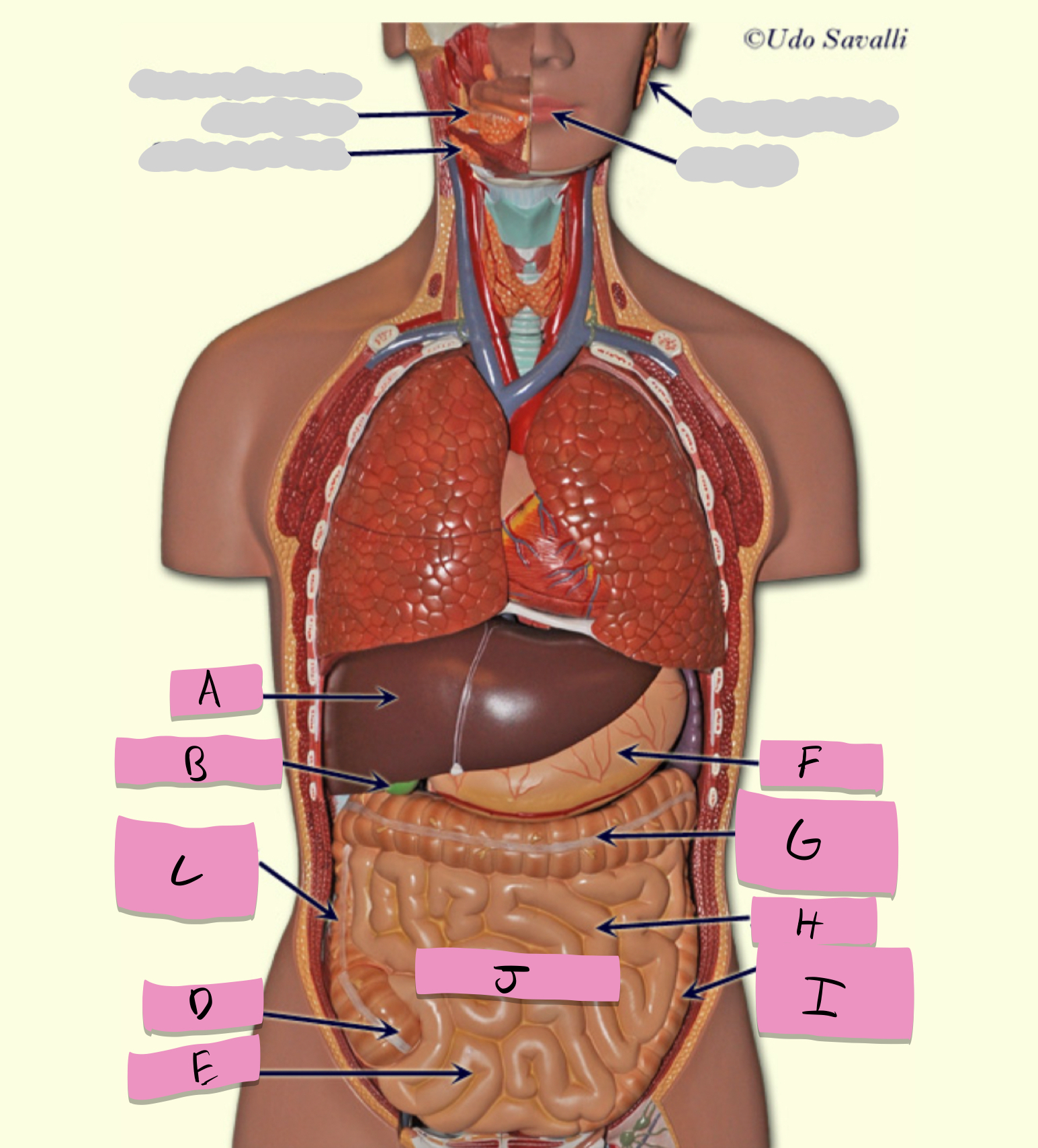
gallbladder
stores bile
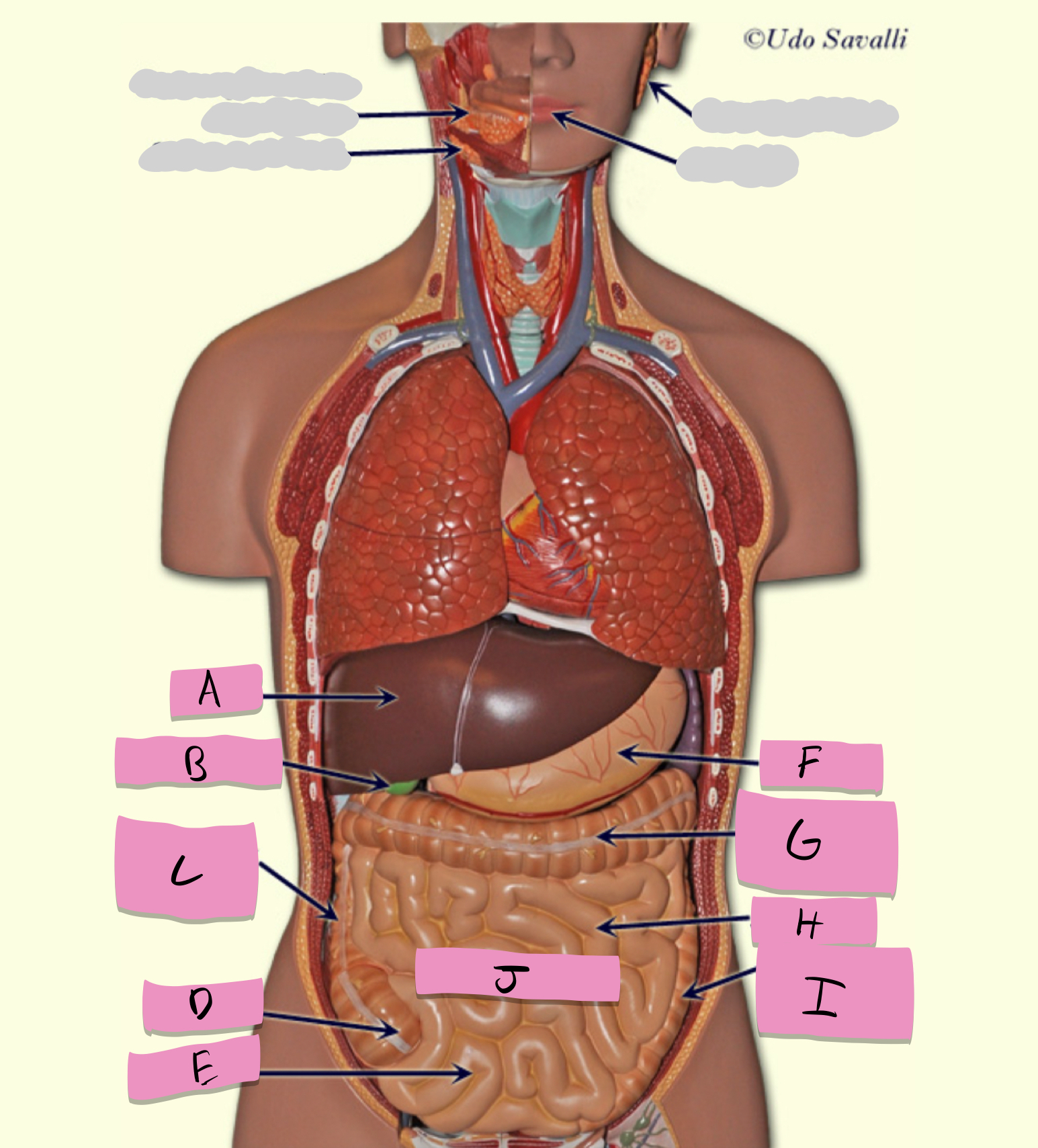
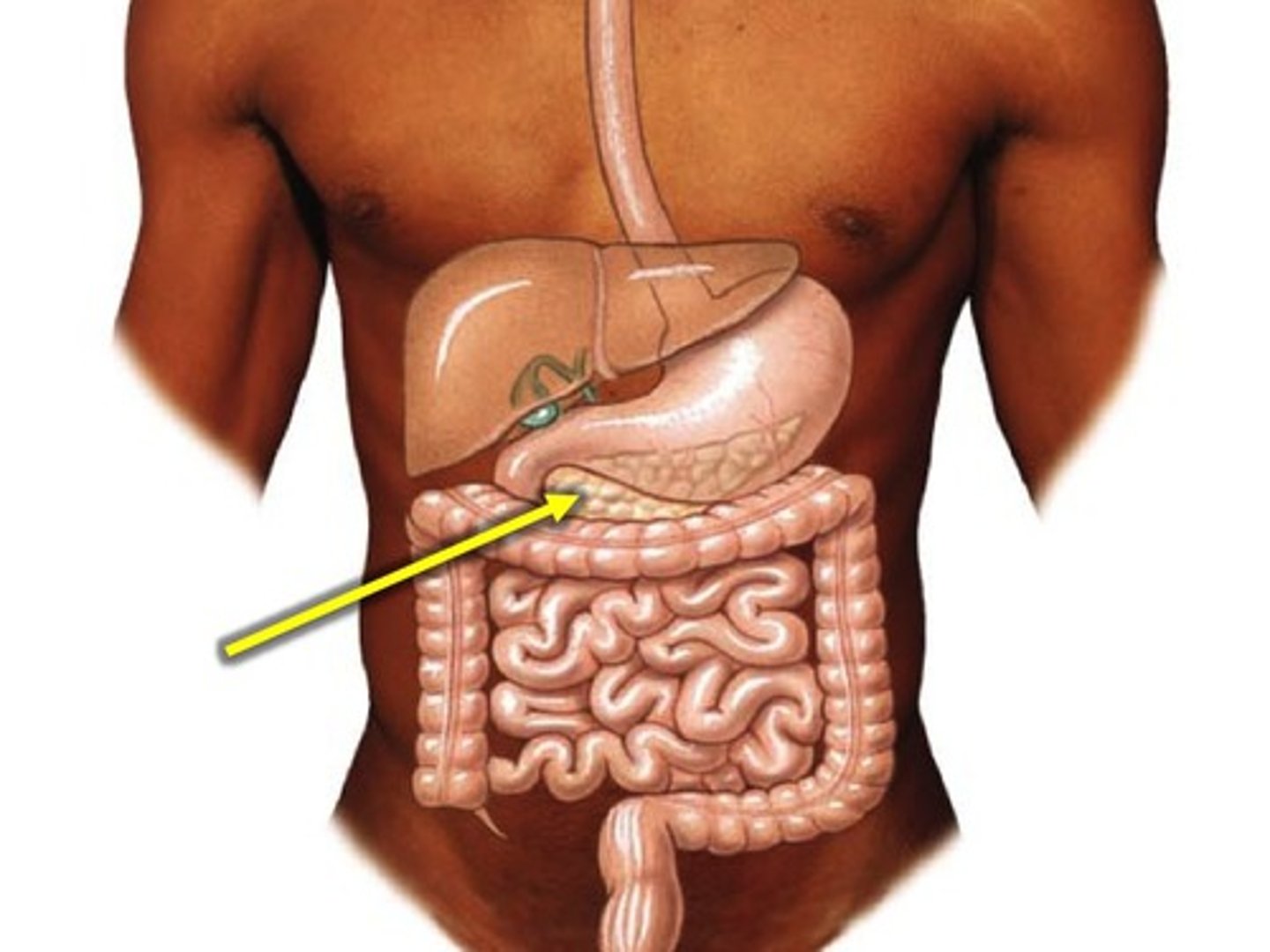
pancreas
production of enzymes (pancreatic juice) for digestion/absorption in small intestine
solid food
state of material when entering oral cavity
bolus (chewed mass)
state of material when exiting oral cavity
bolus
state of material in pharynx
bolus
state of material in esophagus
bolus
state of material when entering the stomach
chyme
state of material when exiting the stomach
chyme
state of material in the small intestine
semi-solid
state of material when entering the large intestine
feces
state of material when exiting the large intestine
1. ingestion
2. propulsion
3. mechanical digestion
4. chemical digestion
5. absorption
6. defecation
digestive processes
mucosa
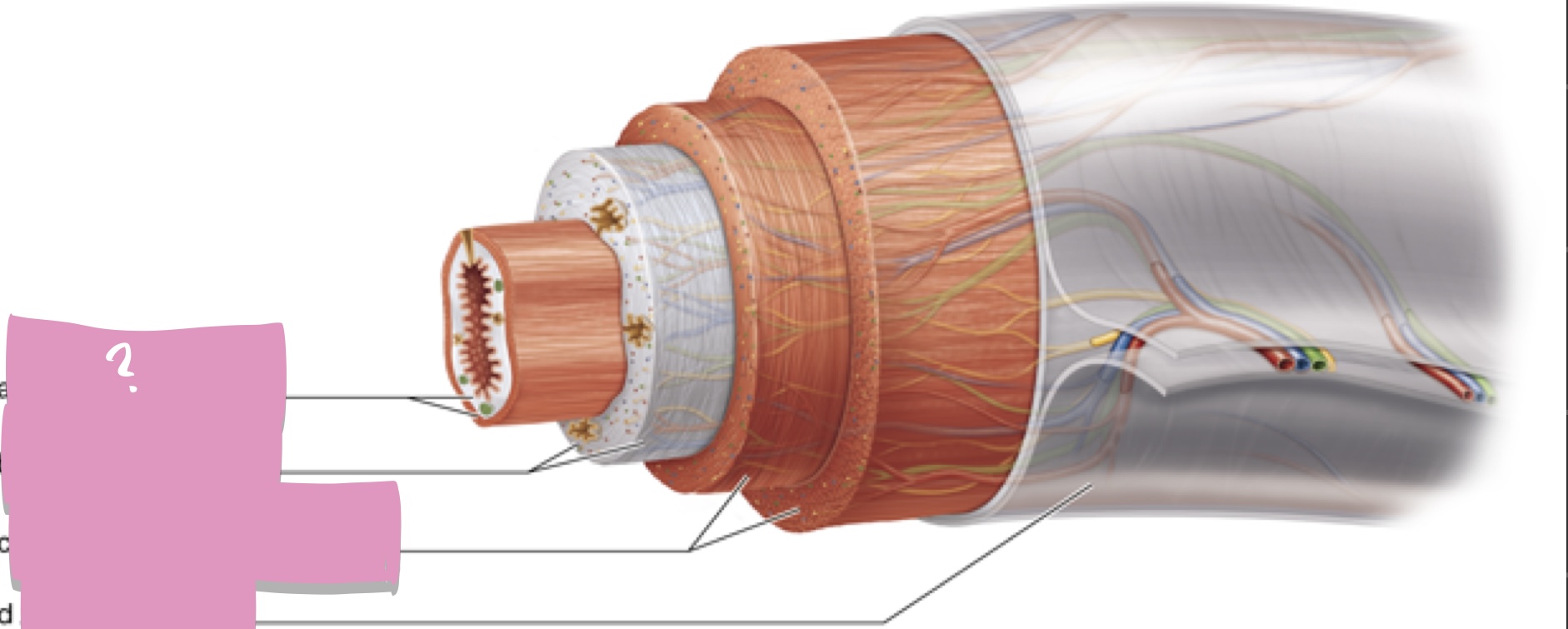
Submucosa
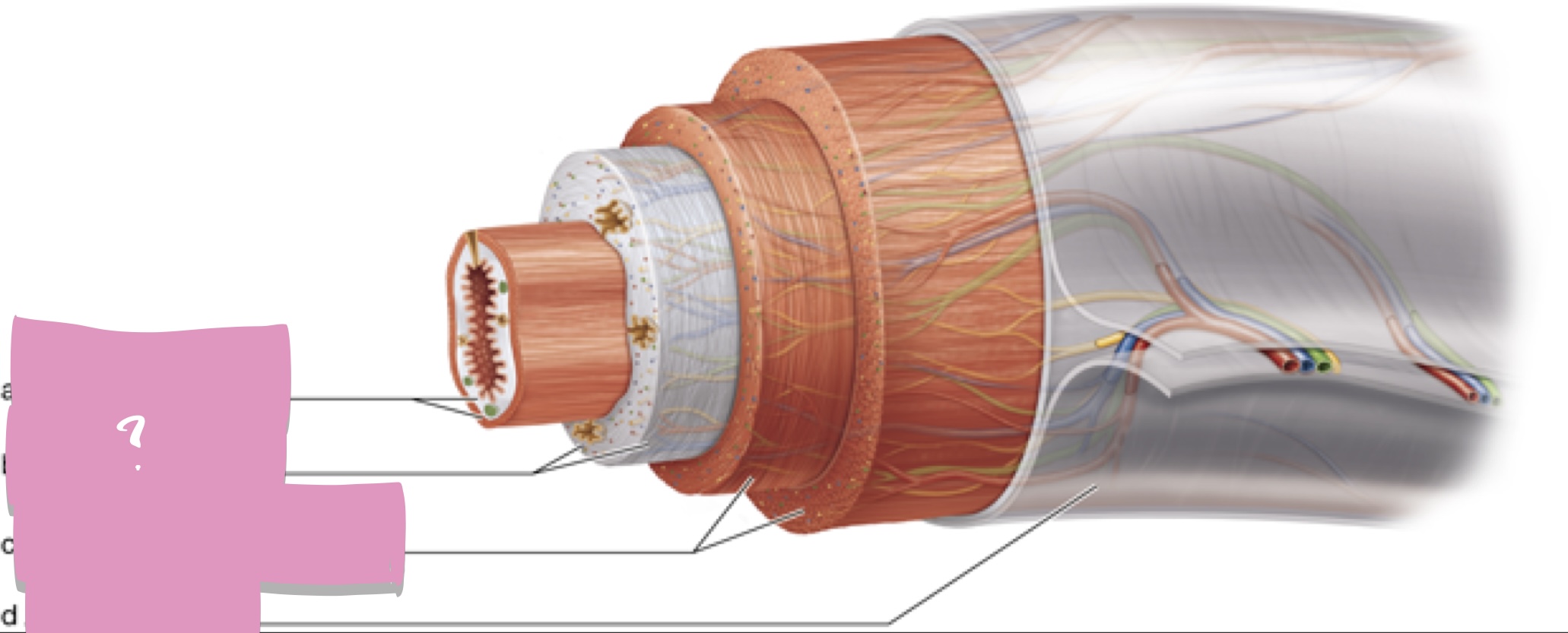
muscularis externa
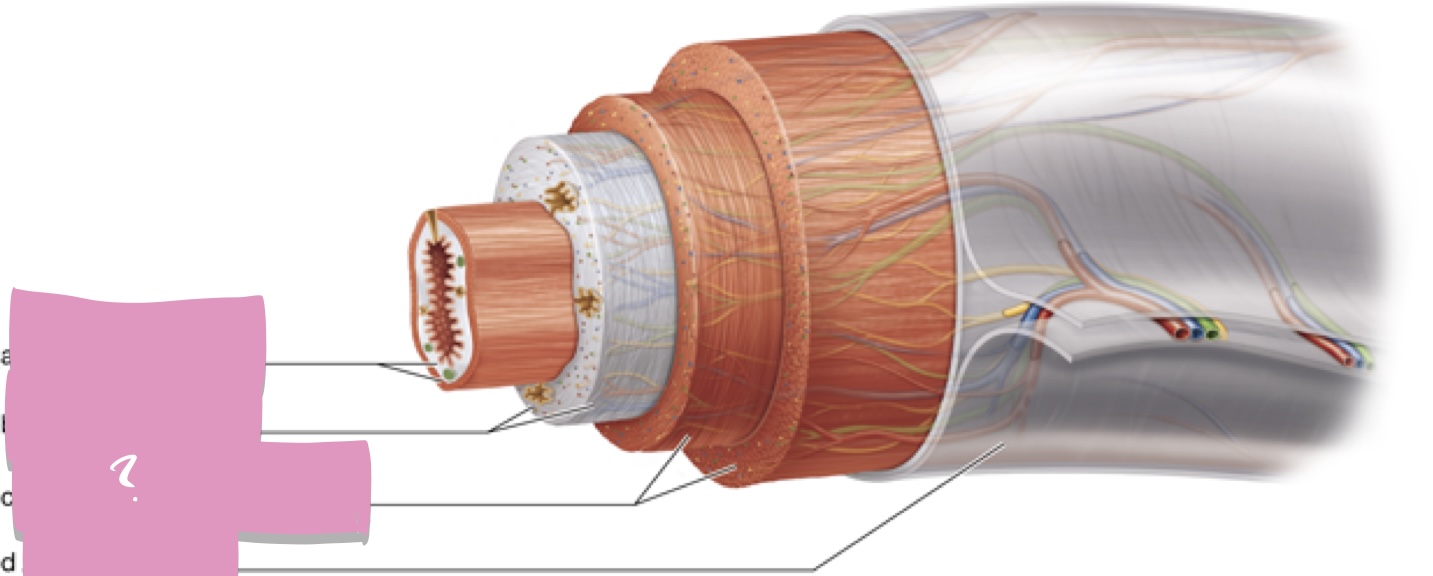
Serosa
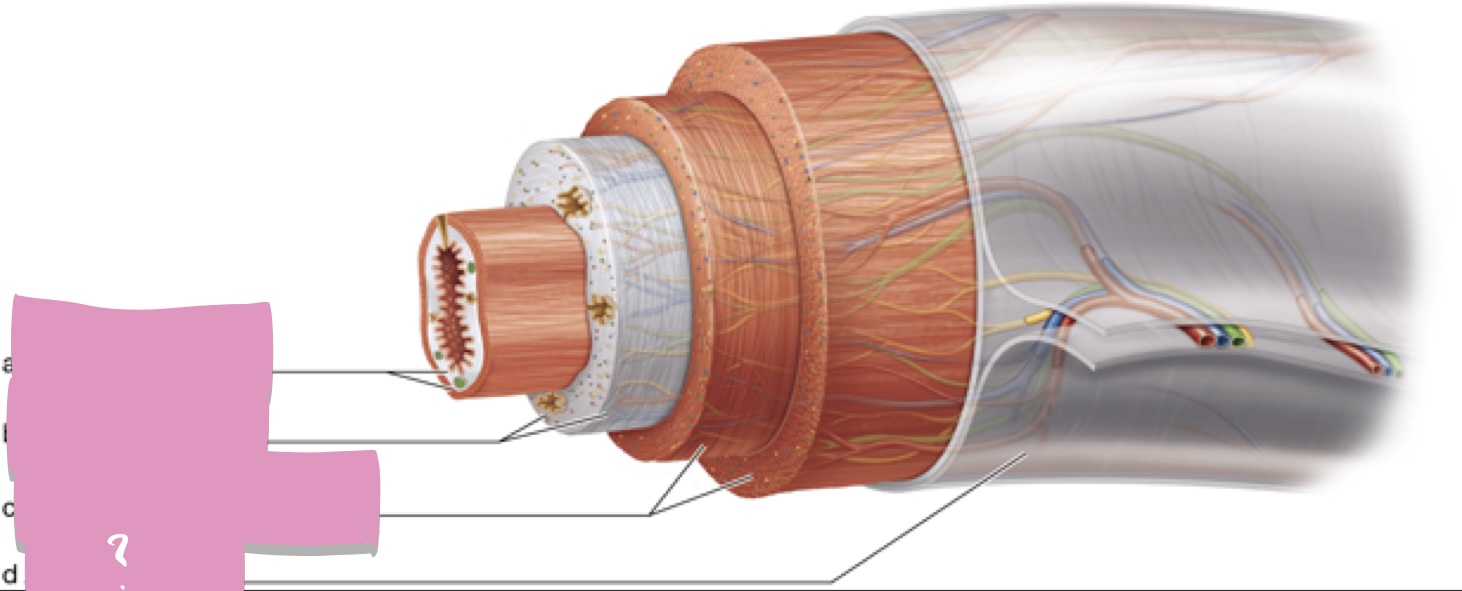
hepatocytes
cells of the liver
acinar cells
cells of pancreas
brush border cells (enterocytes), duodenal cells
small intestine cells
chief cells, parietal cells
cells of the stomach
Renal cortex
Connecting tissue wrapping that surrounds kidney
Renal pyramid
Renal capsule
Outer region of kidney
Renal pelvis
Kidney region continuous with the ureter
Renal artery
Supplies the kidney with blood
Renal vein
Drains blood from the kidneys
Ureter
Transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
Nephron
Microscopic, functional unit of kidney
Renal medulla
Houses renal pyramids
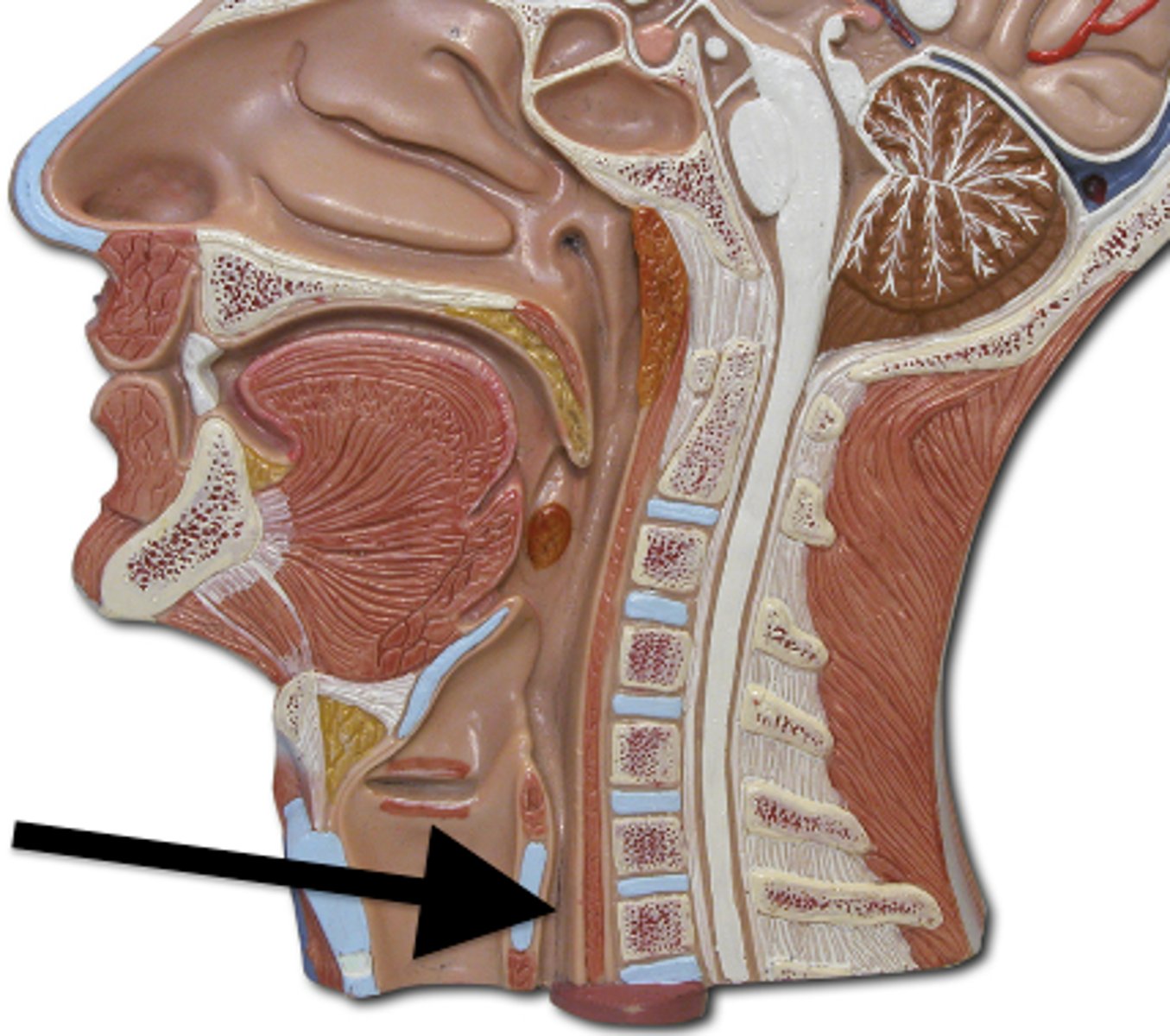
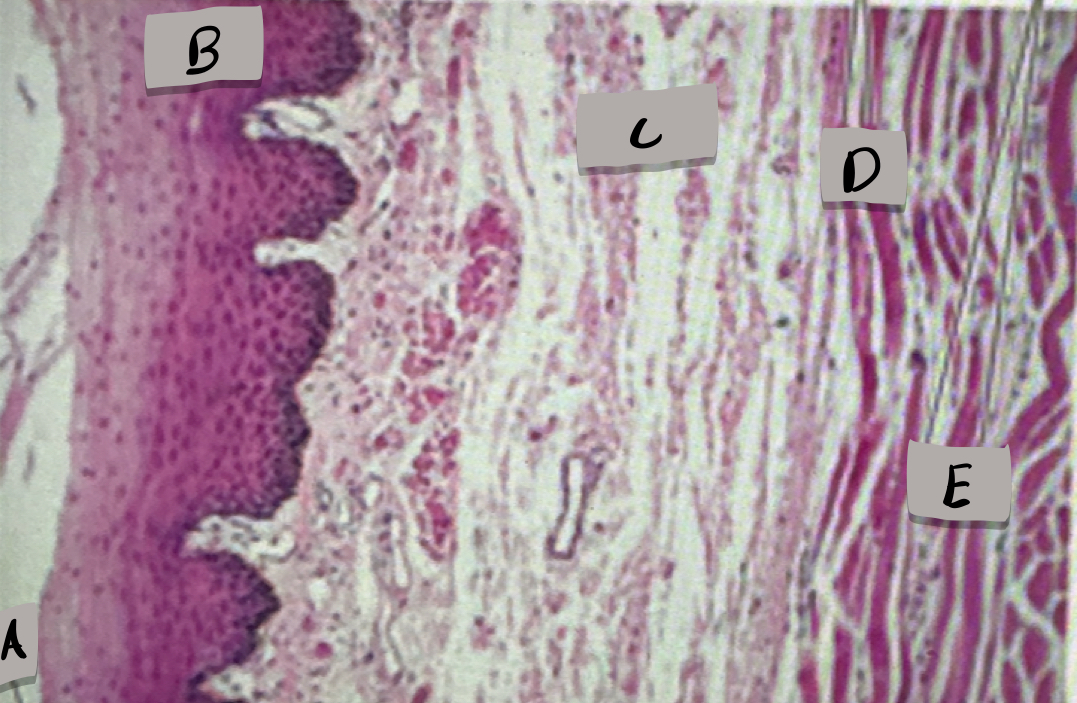
esophagus histology
only one with stratified squamous epithelium; adventitia (outermost layer)
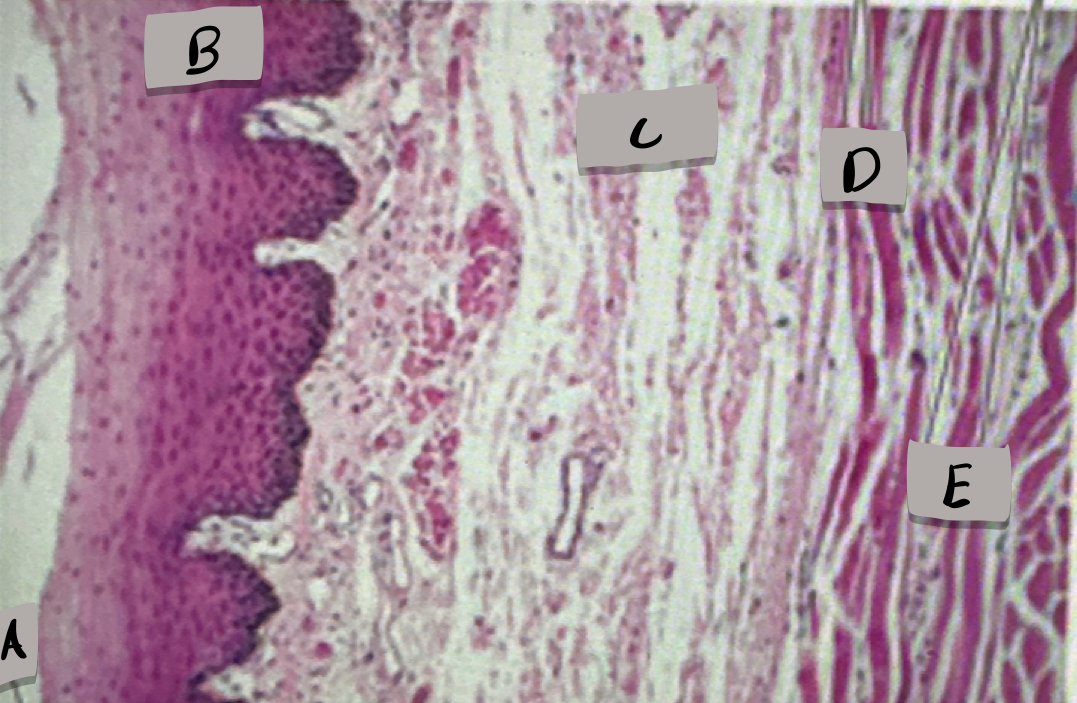
Lumen
What does label A show?
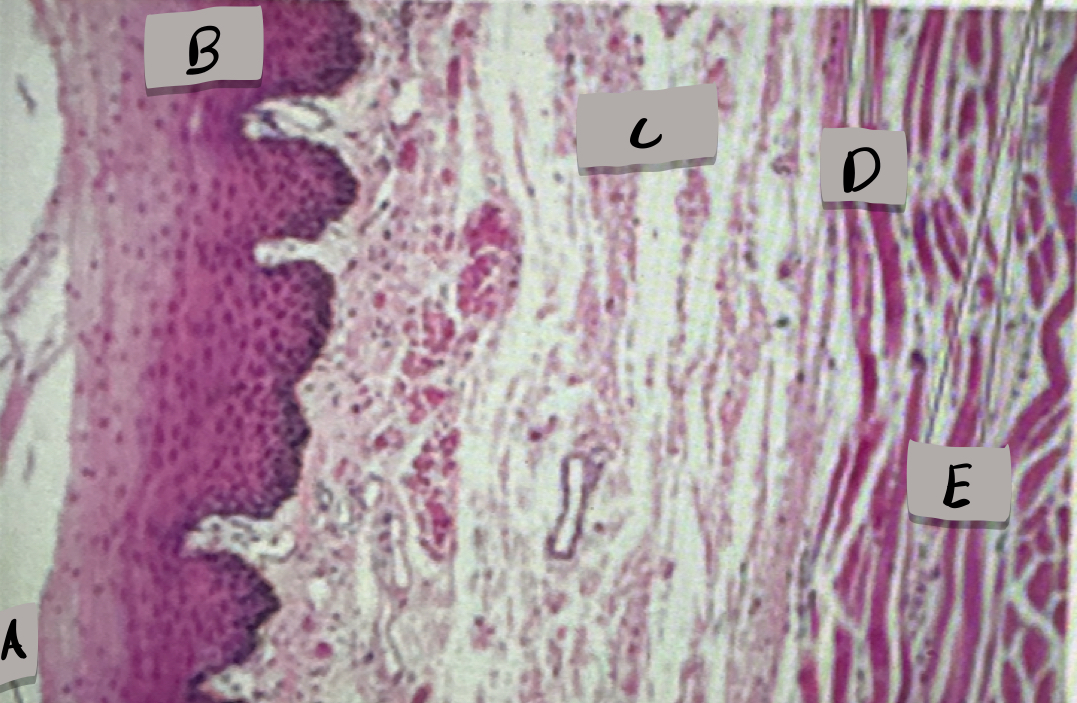
Mucosa, stratified squamous epithelium
what layer is label B and what is it made of?
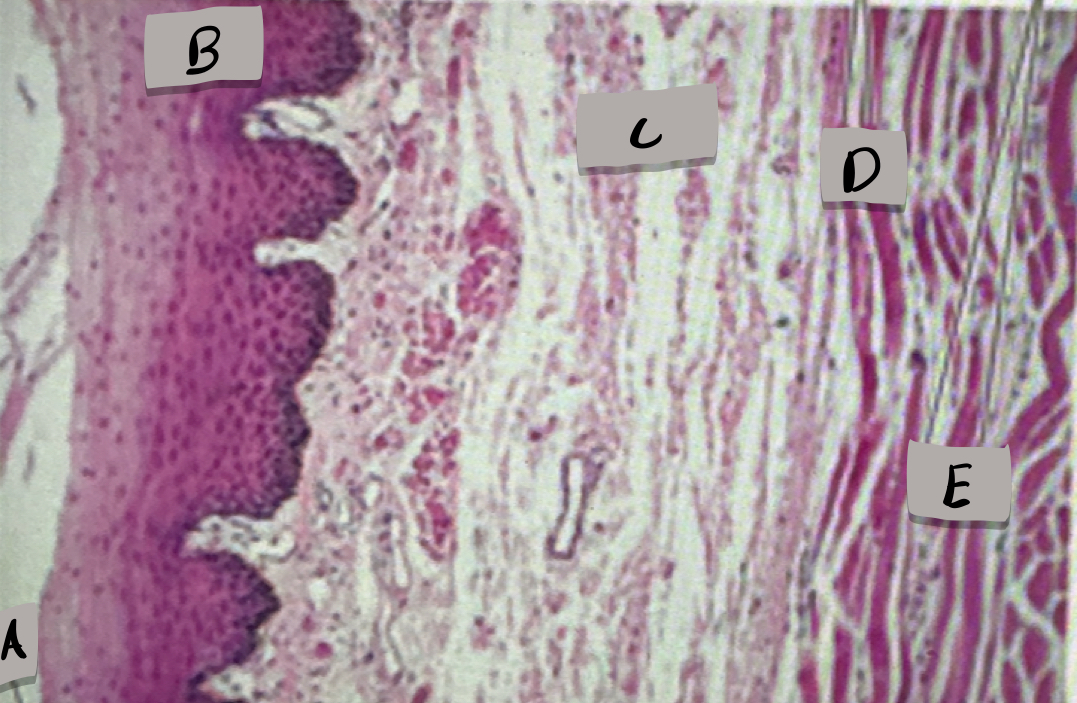
submucosa
what layer is label C ?
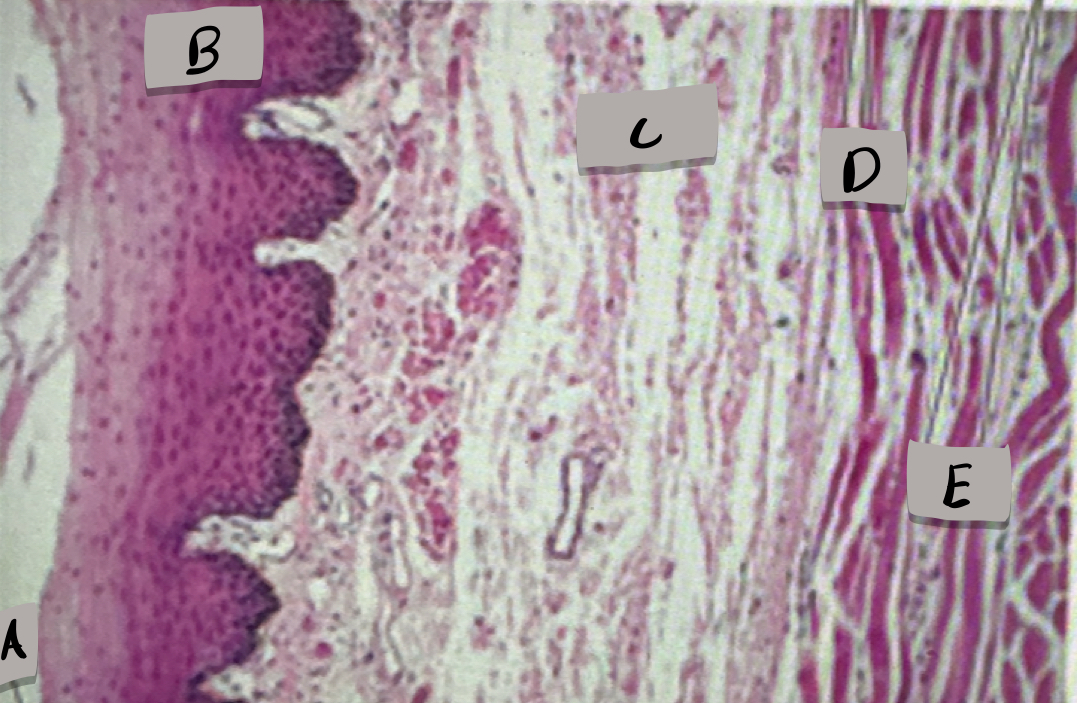
skeletal muscle cells
what cell type does label D show ?
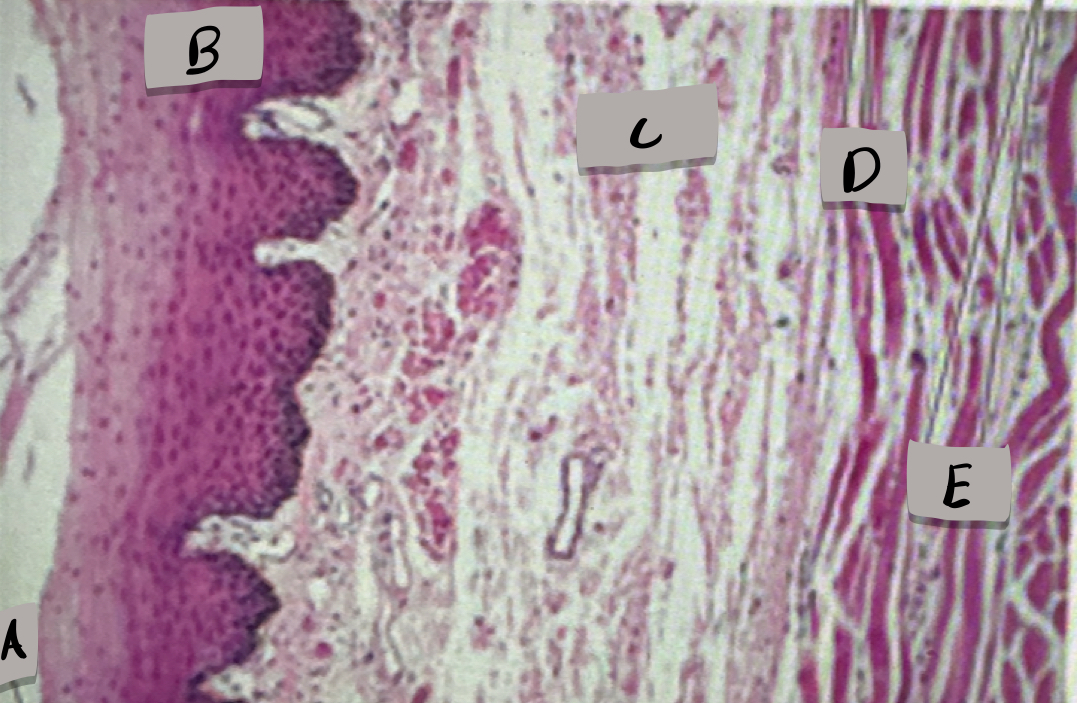
smooth muscle cells
what does cell type does label D show ?
stomach (histology)
gastric pits towards the top, glands towards the bottom; mucosa cells, parietal cells, chief cells, endocrine cells; oblique muscle of muscularis externa
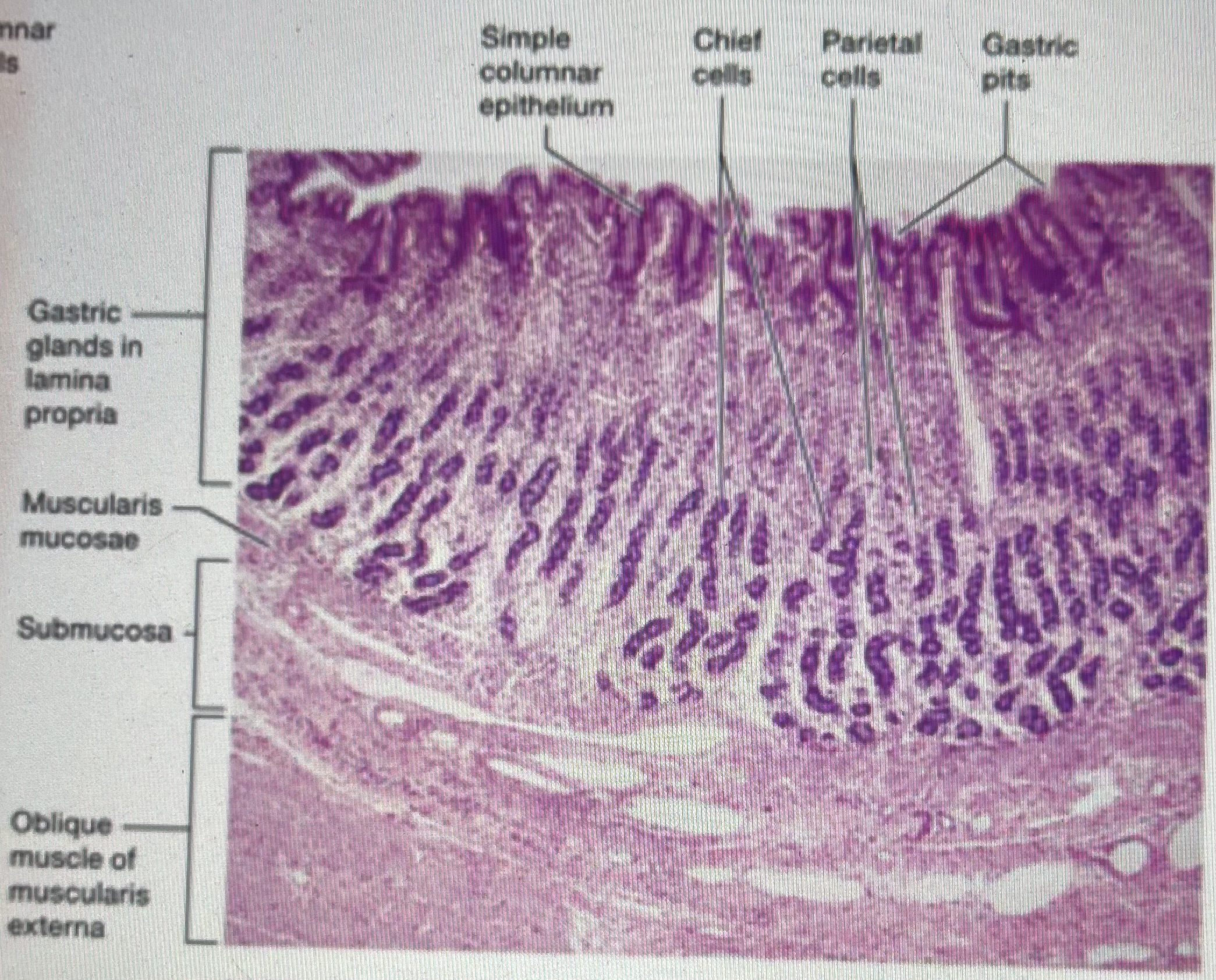
gastric pits
What does label A represent?
parietal cells
what does label B represent ?
chief cells
what does label C represent ?
muscularis mucosae
what does label D represent ?
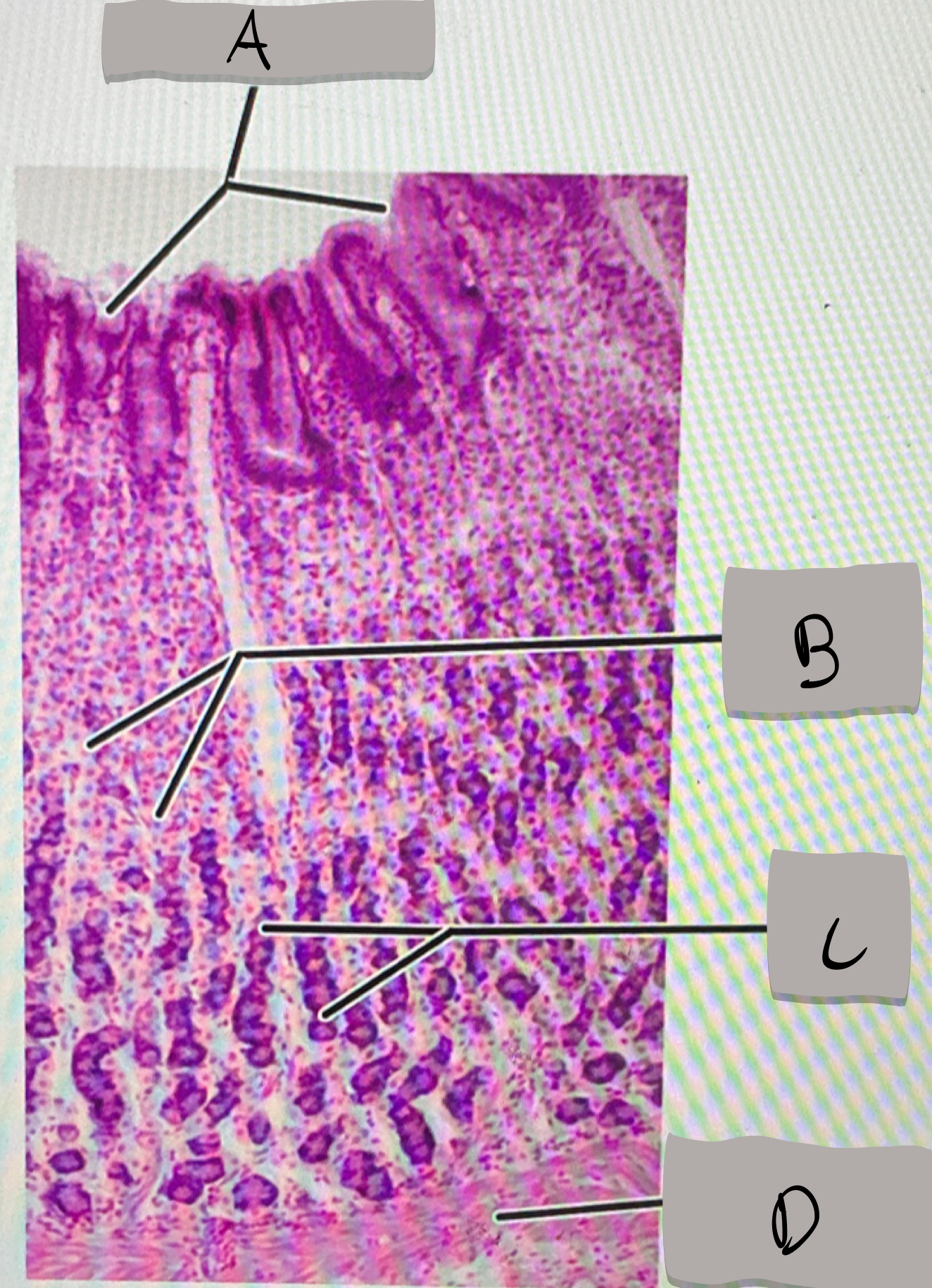
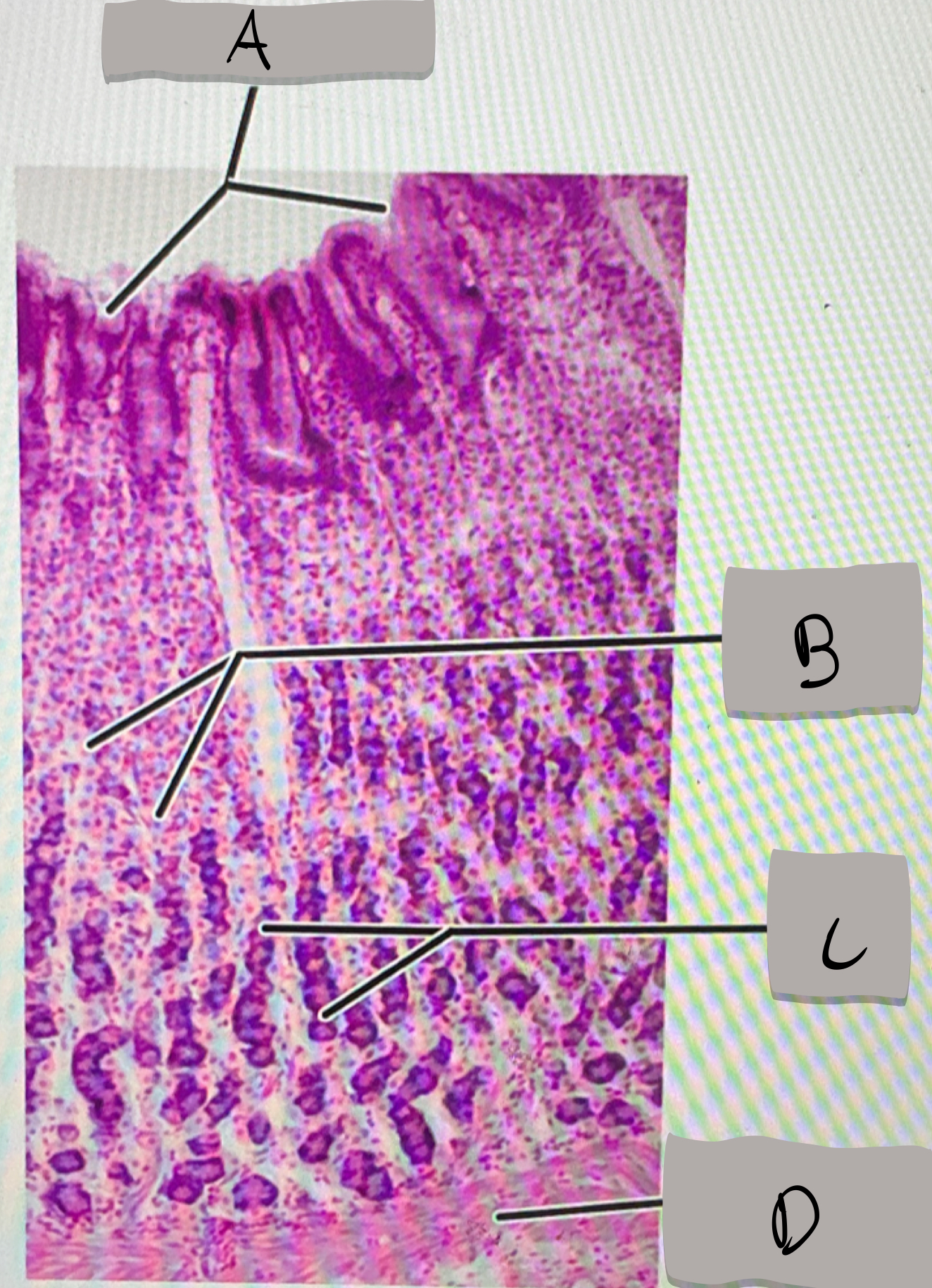
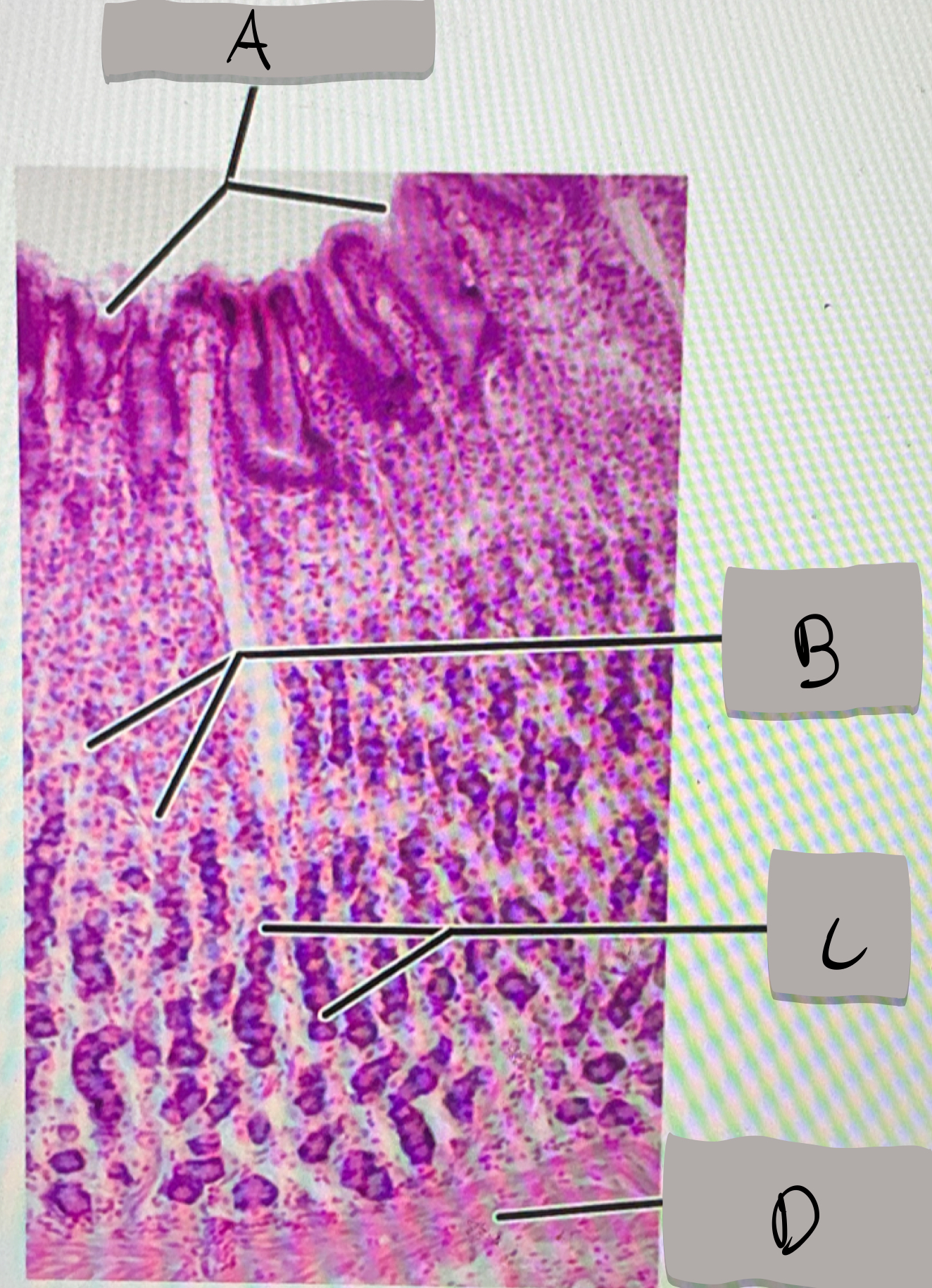
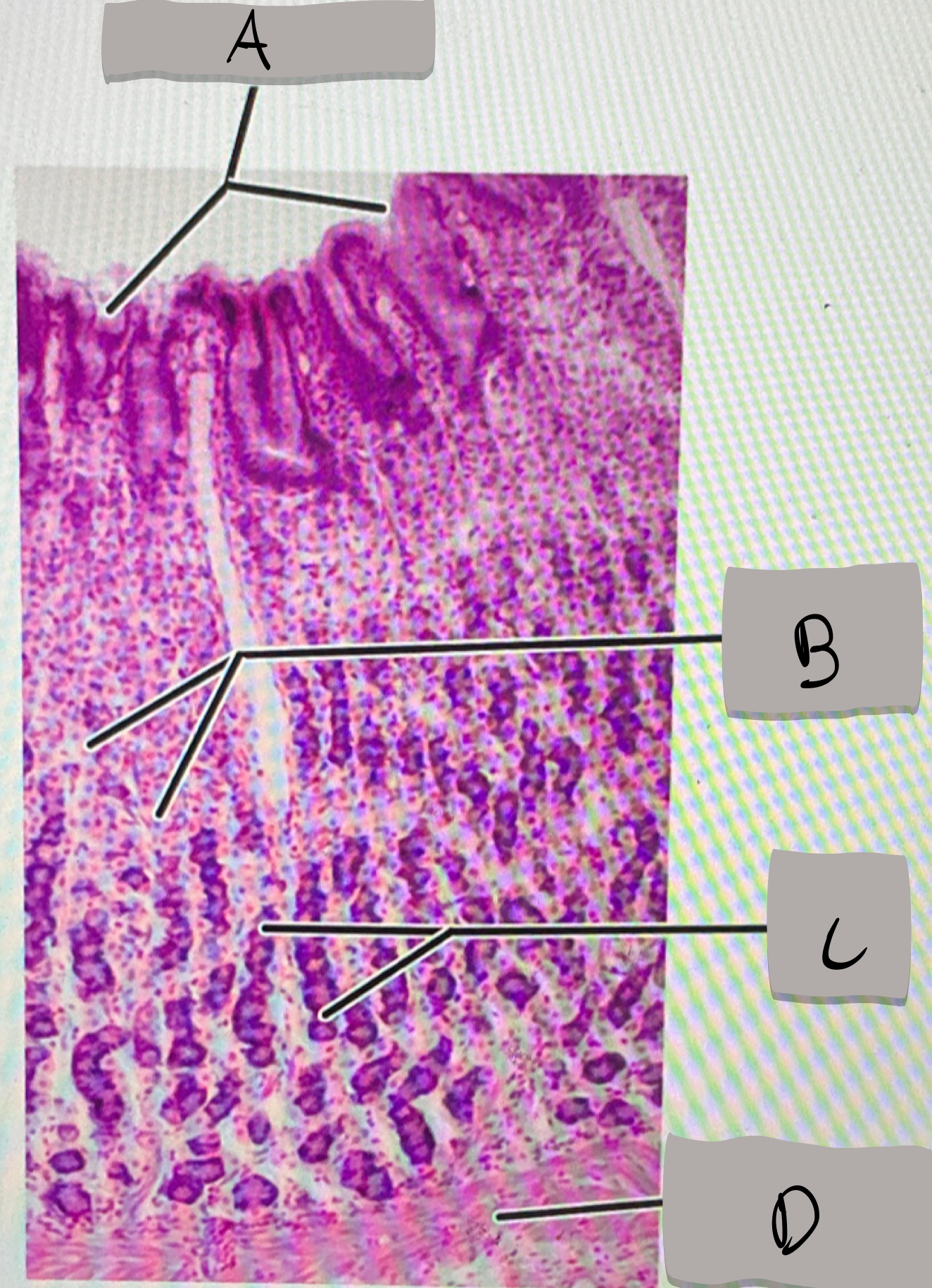
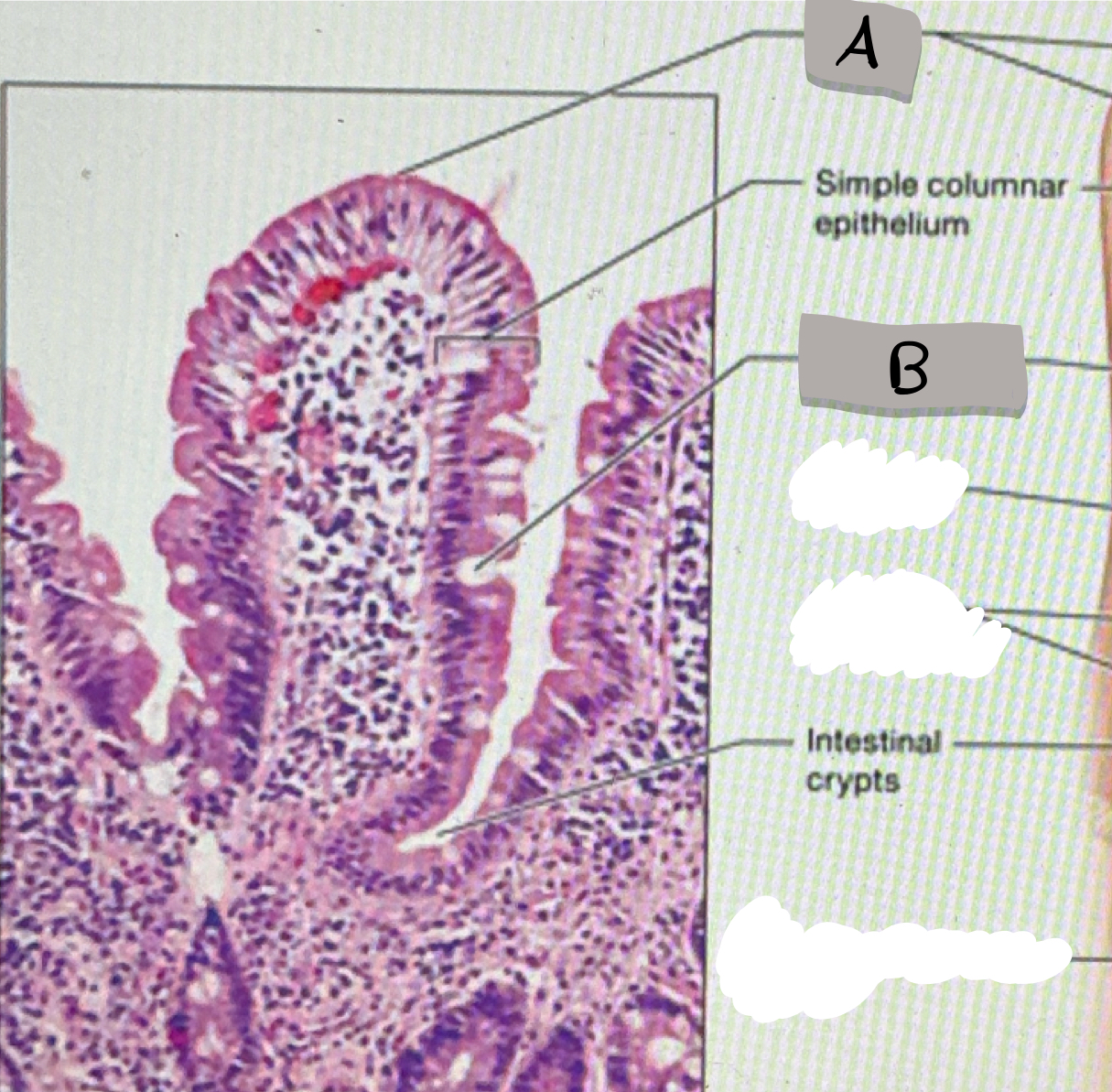
small intestine (histology)
villi; microvilli; adventitia
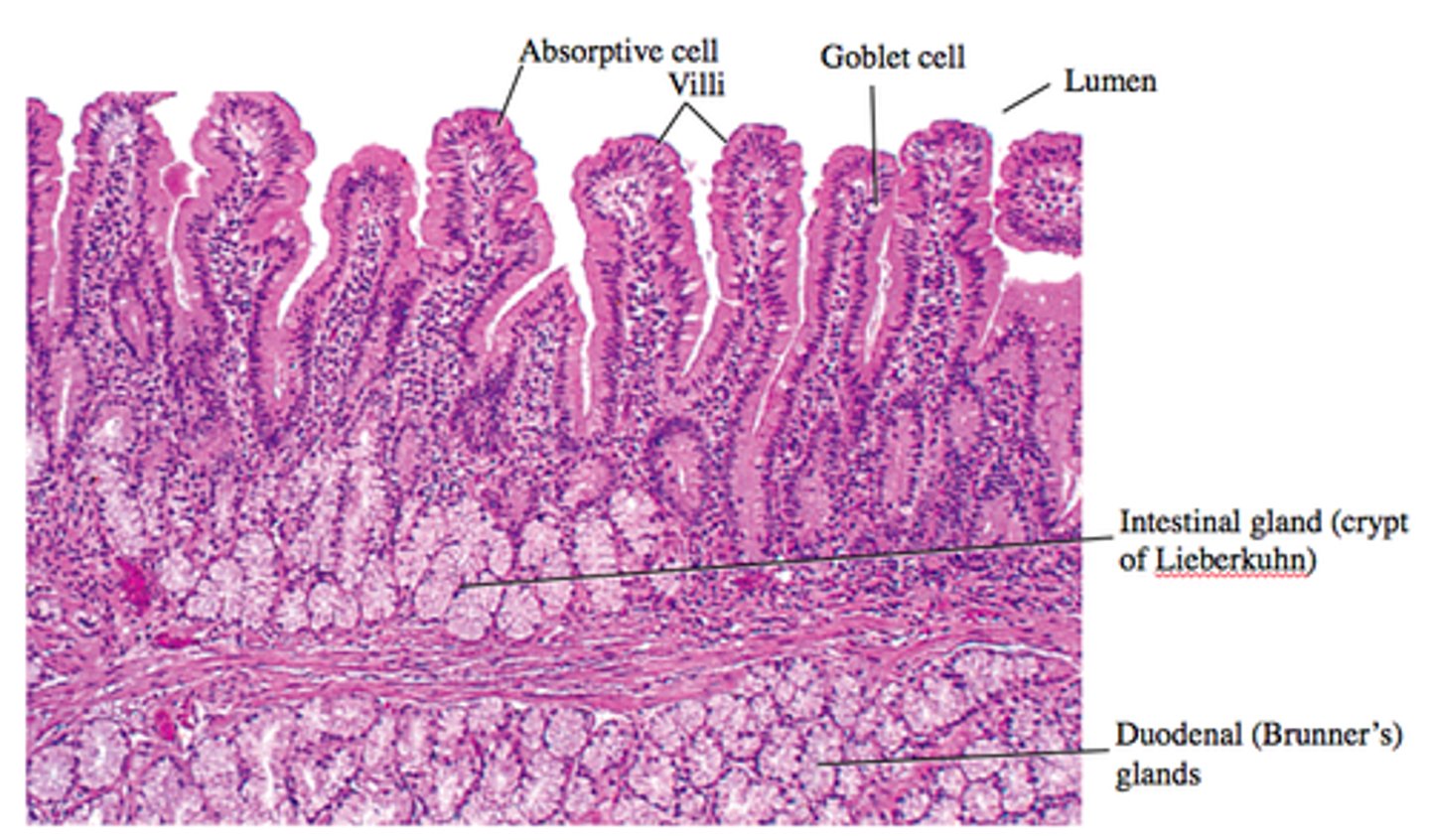
jejunum
what part of the small intestine this photomicrograph represent ?
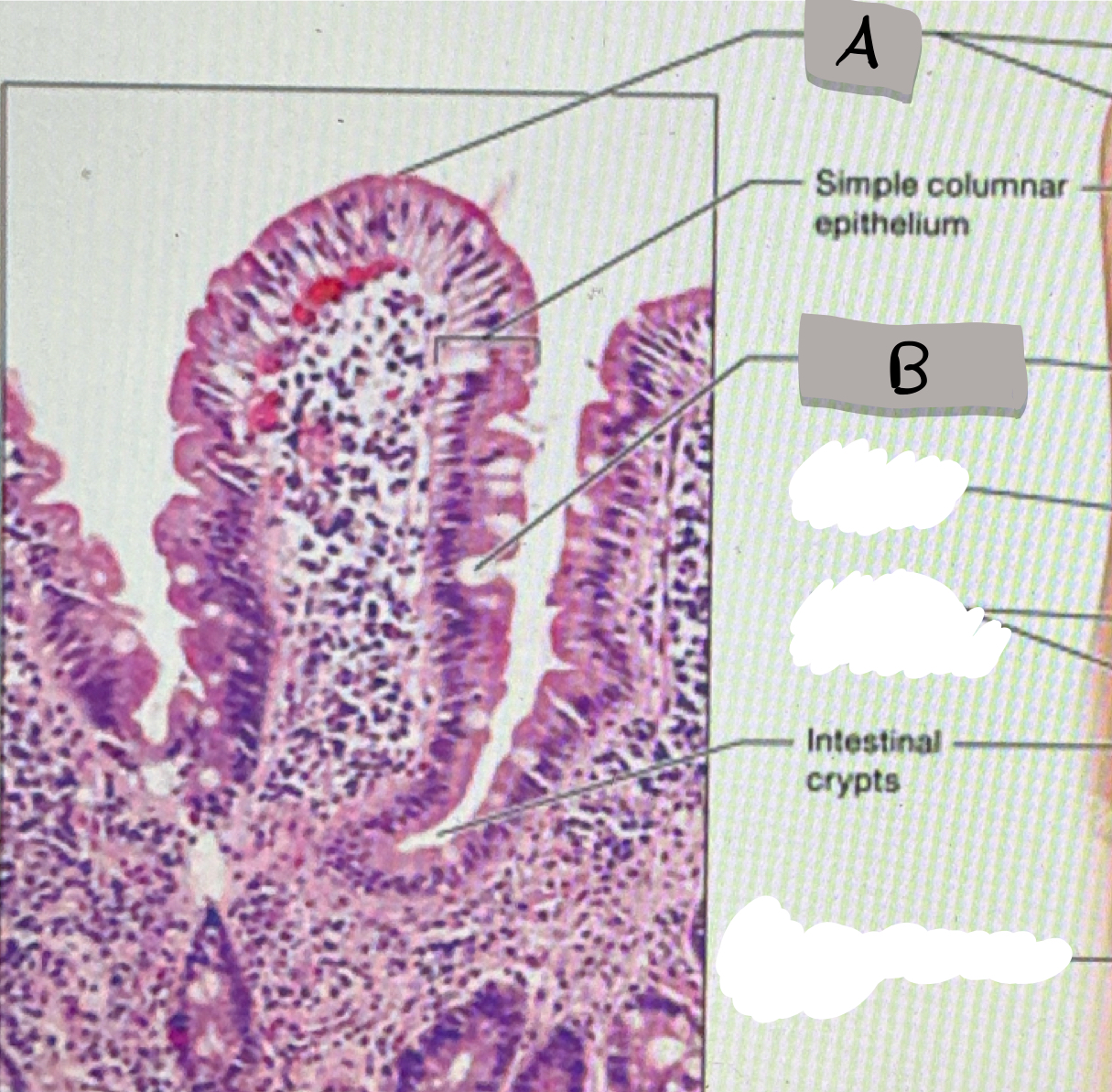
villi
what does label A represent ?
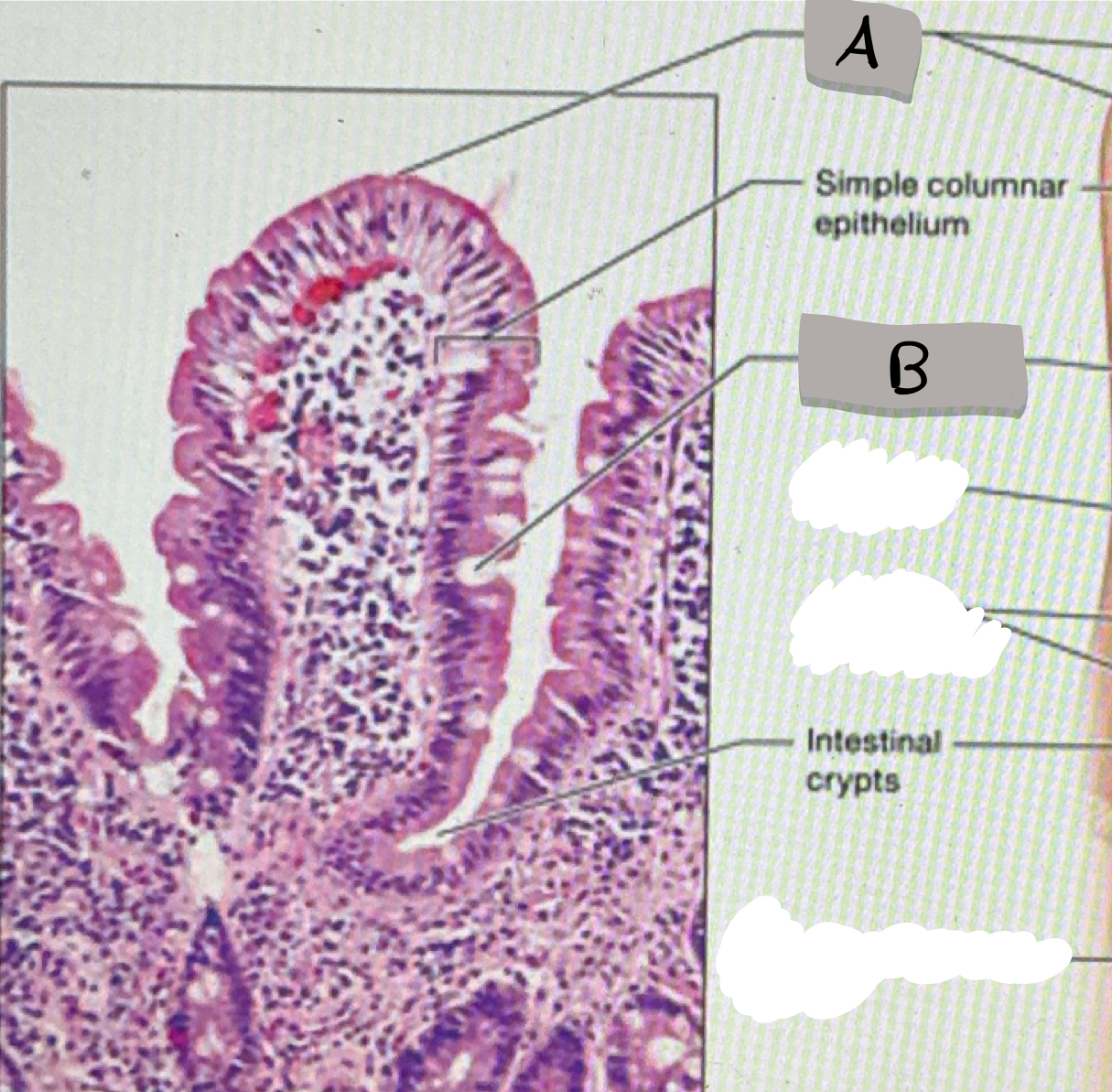
goblet cells
what does label B represent ?
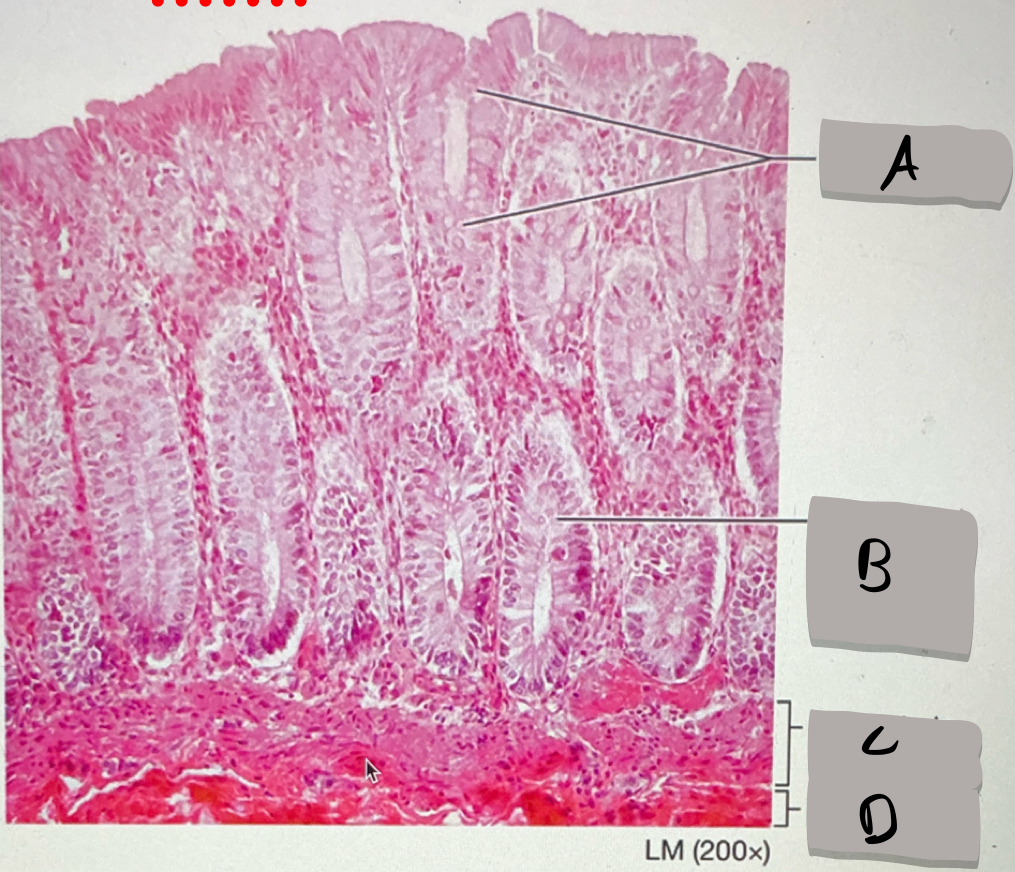
large intestine (histology)
what does this photomicrograph represent ?
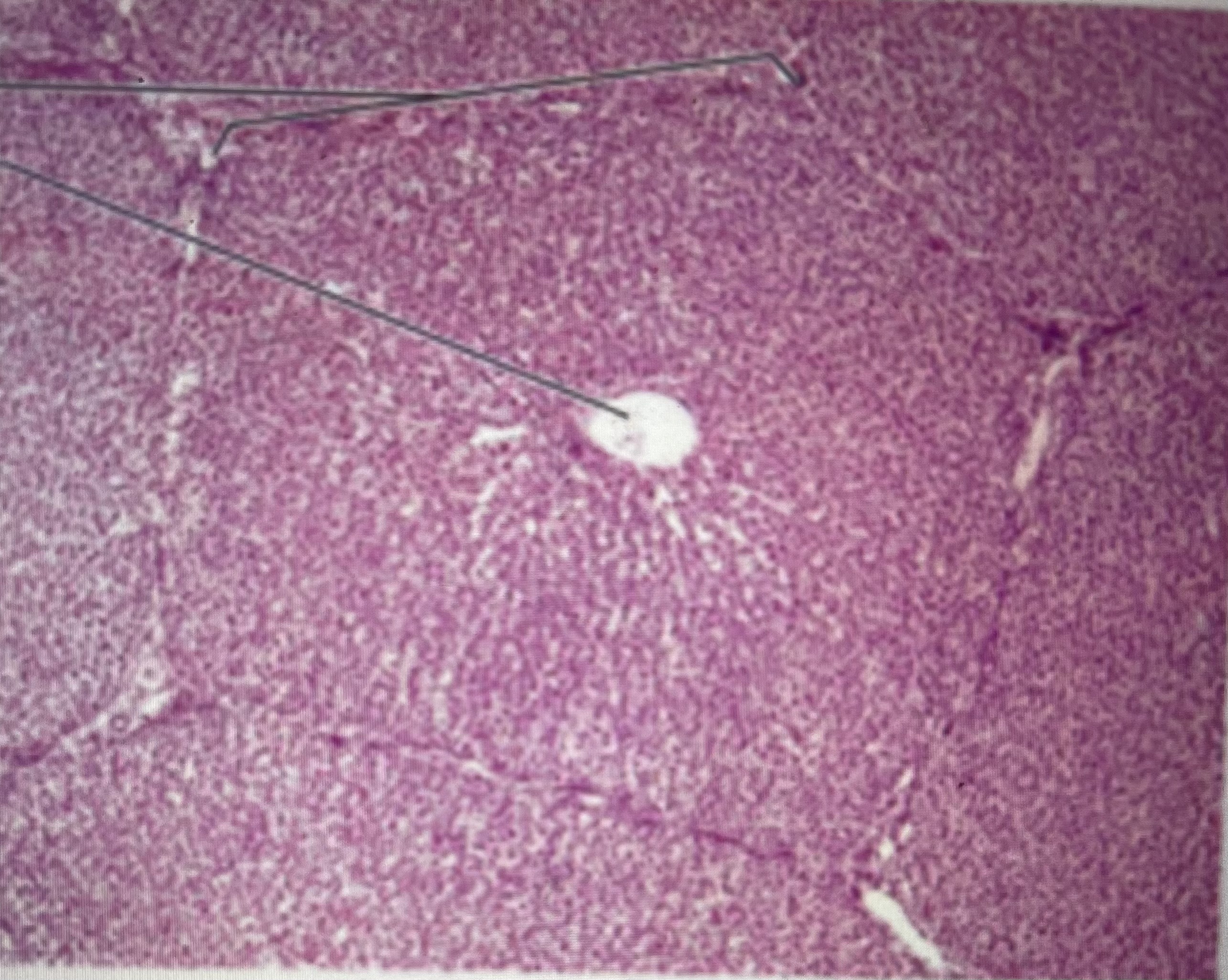
liver (histology)
(donut shaped) hepatocytes; arterioles; venules
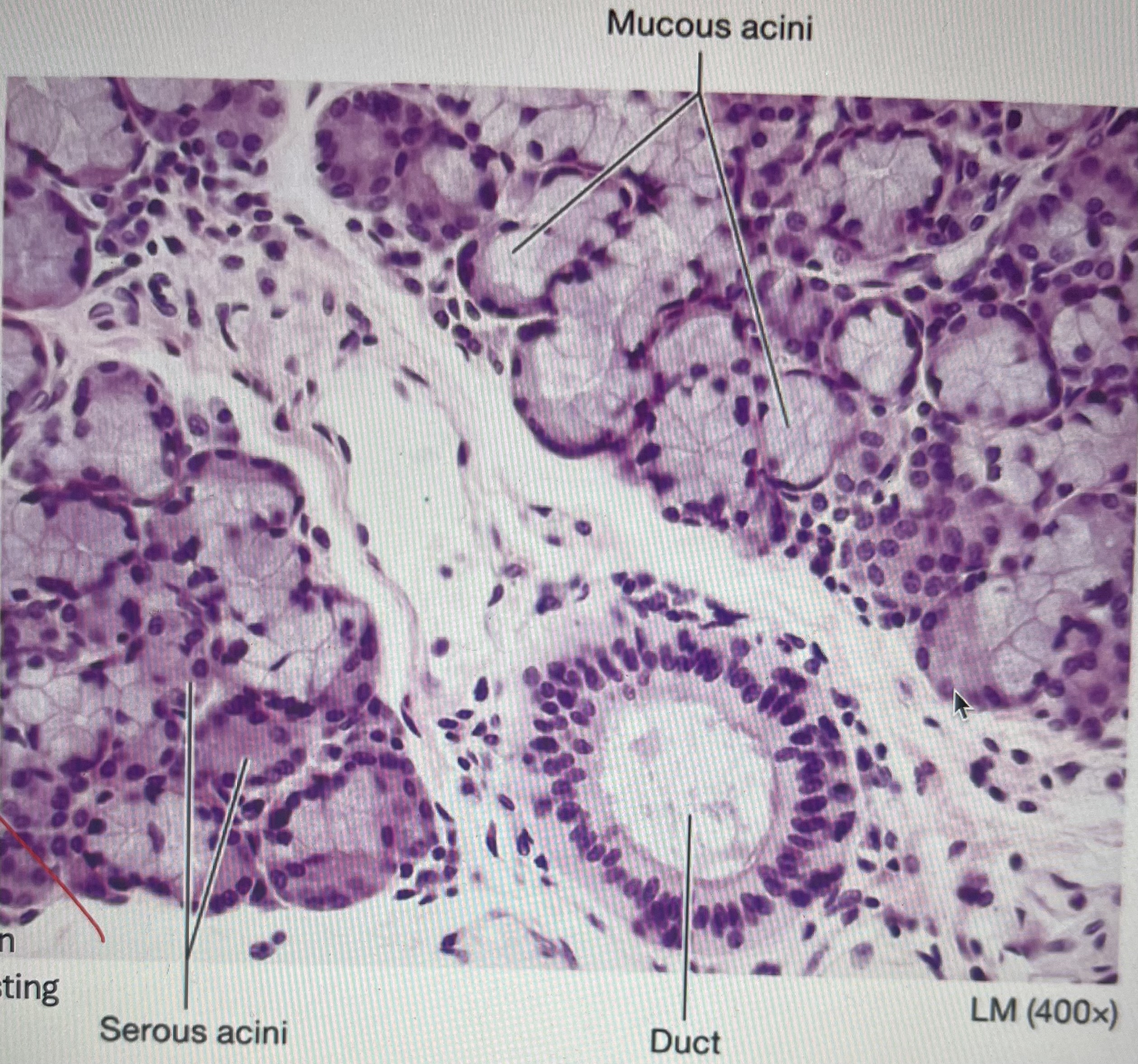
submandibular gland (histology)
serous acini: produces saliva (dark pink circles
mucous acini: produces lubricating mucus (light circles)
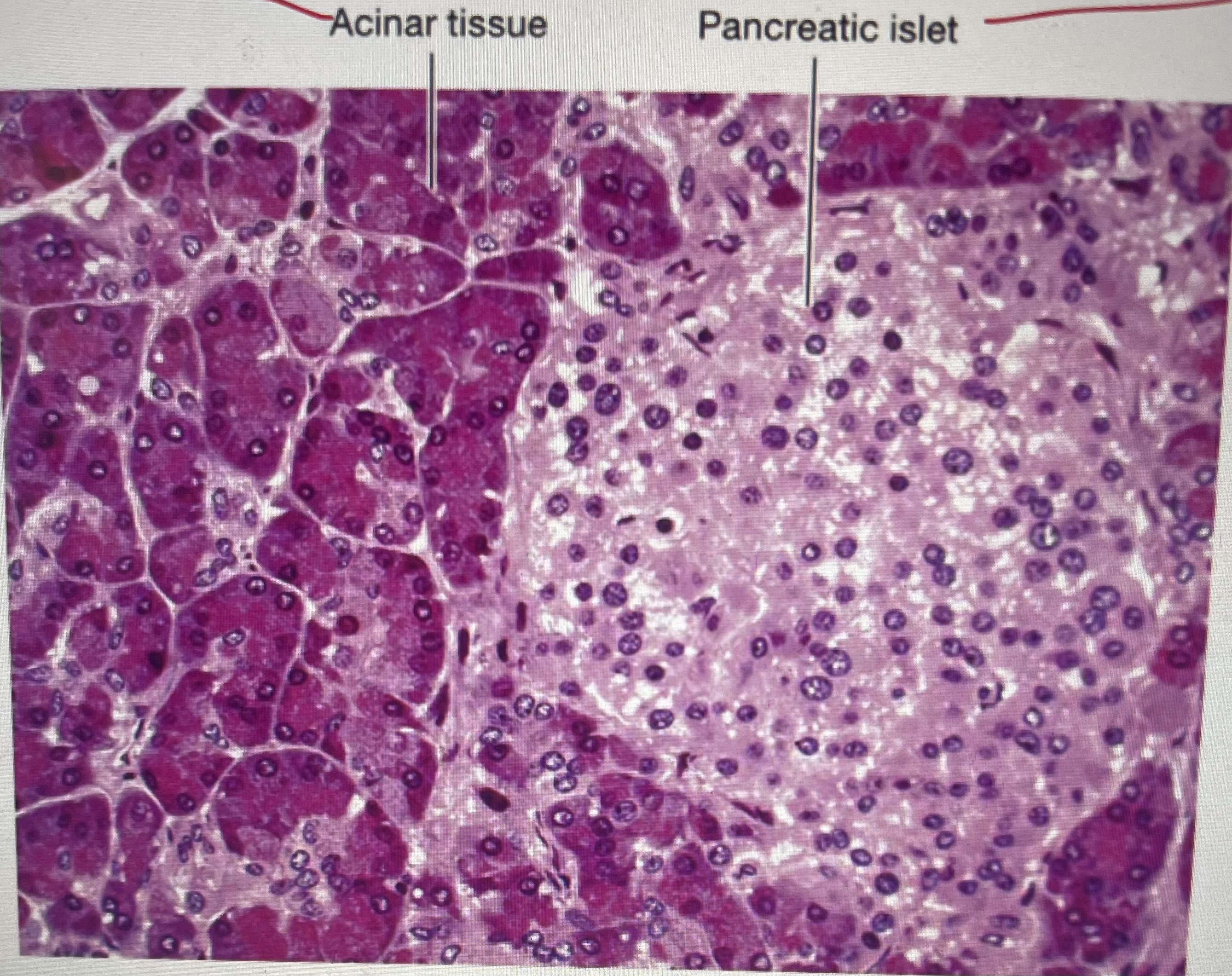
pancreas (histology)
pancreatic islet: controls glucose blood level (lighter pink area)
acinar tissue: produces pancreatic juice (darker pink)
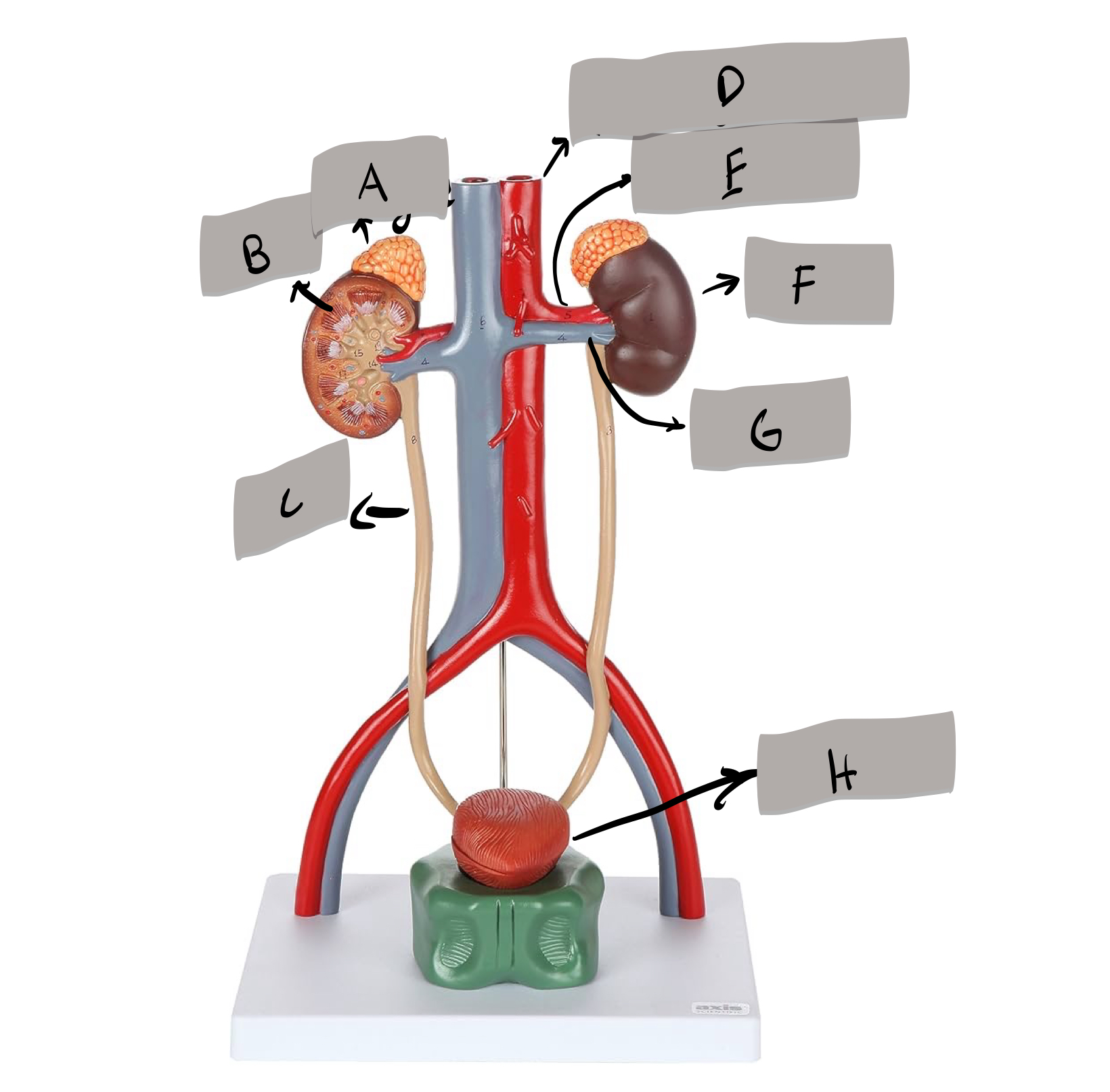
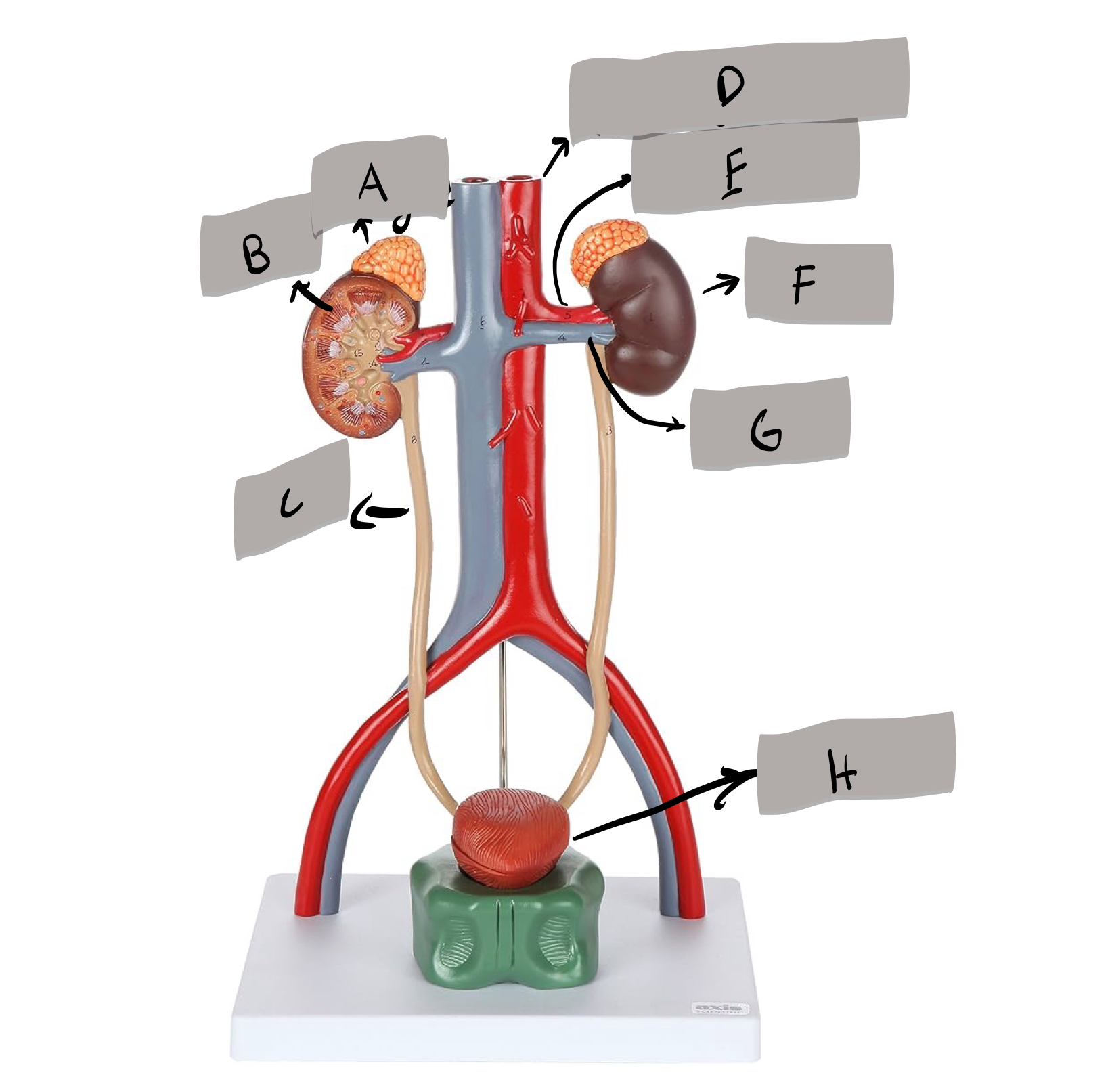
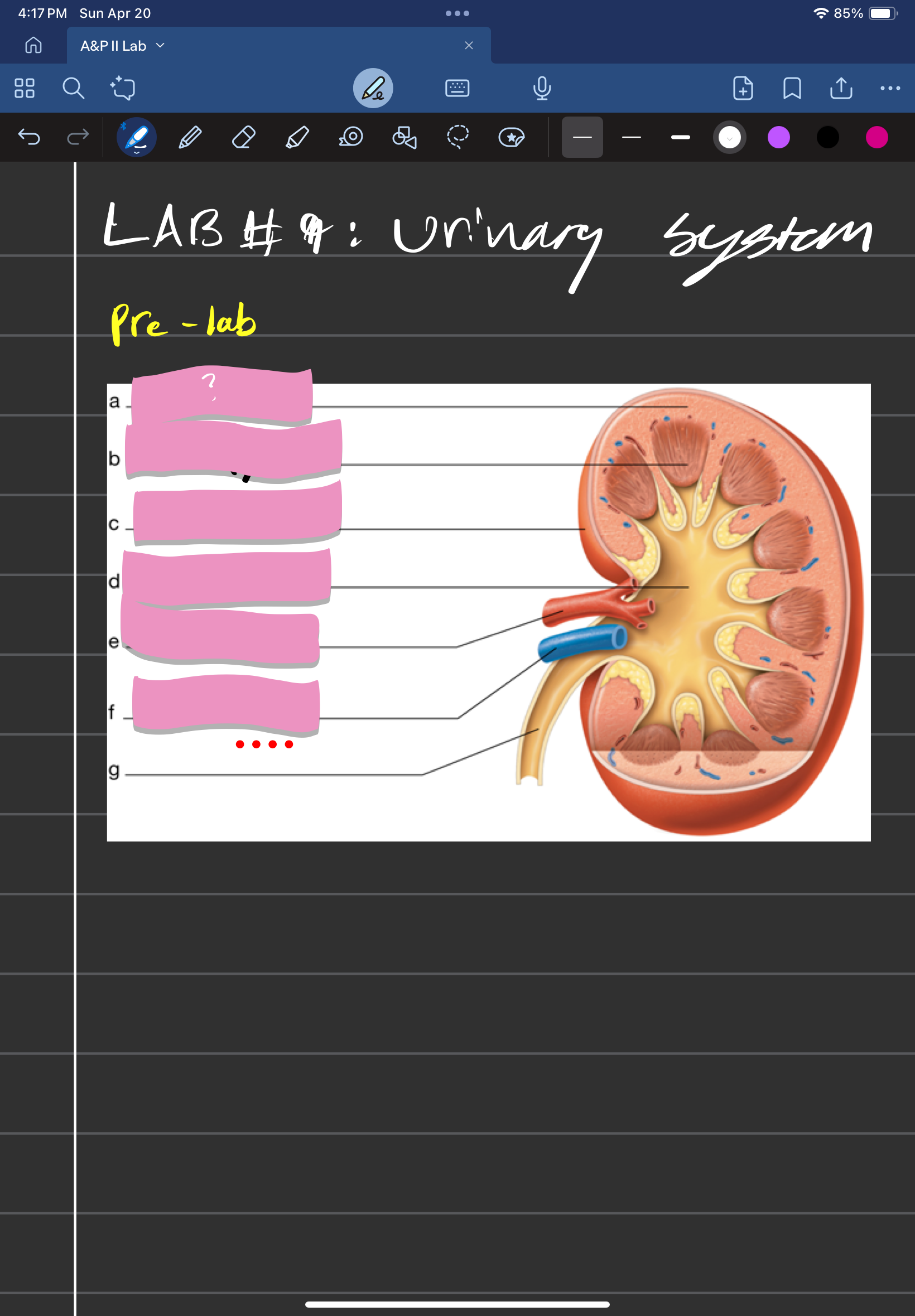
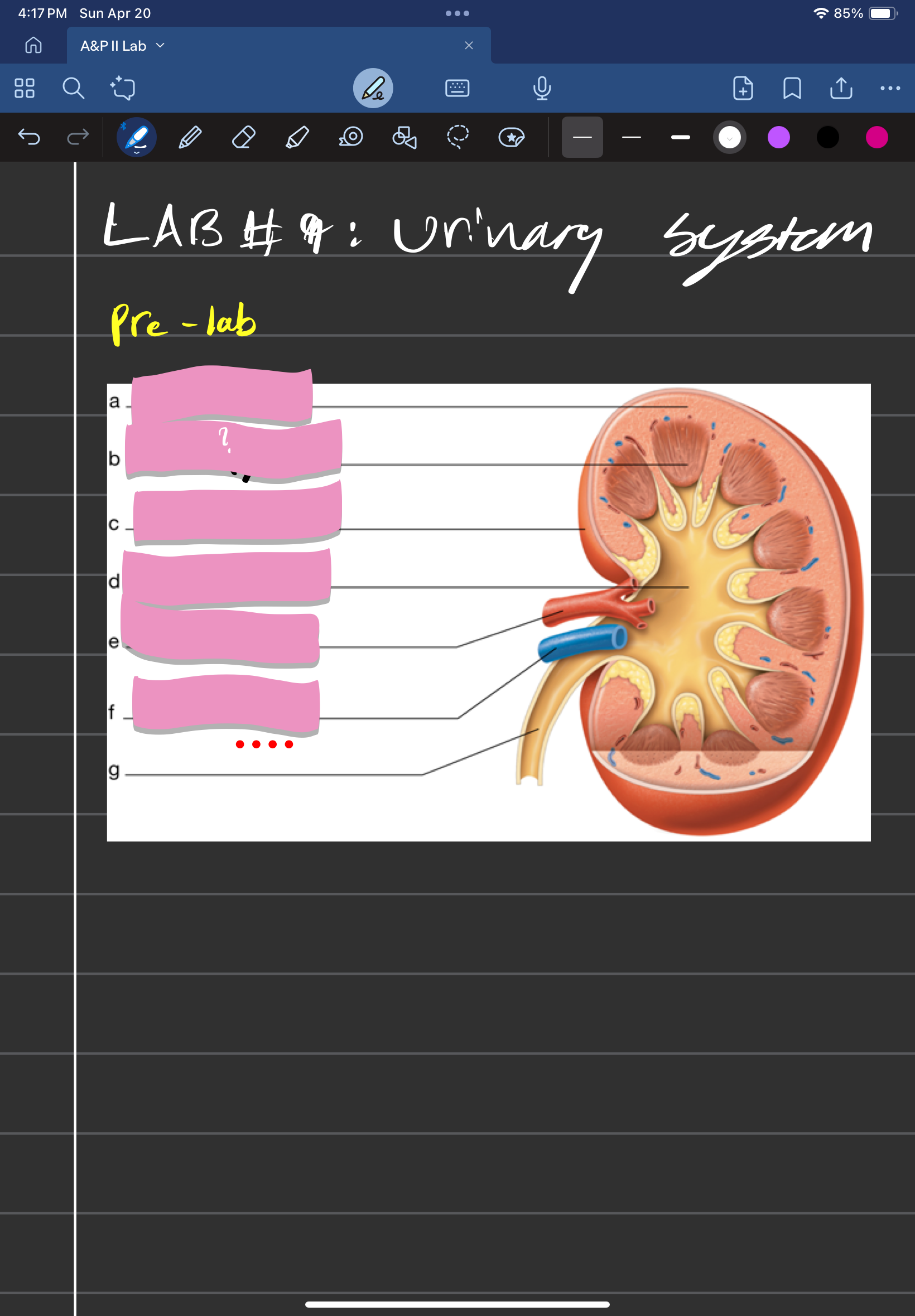
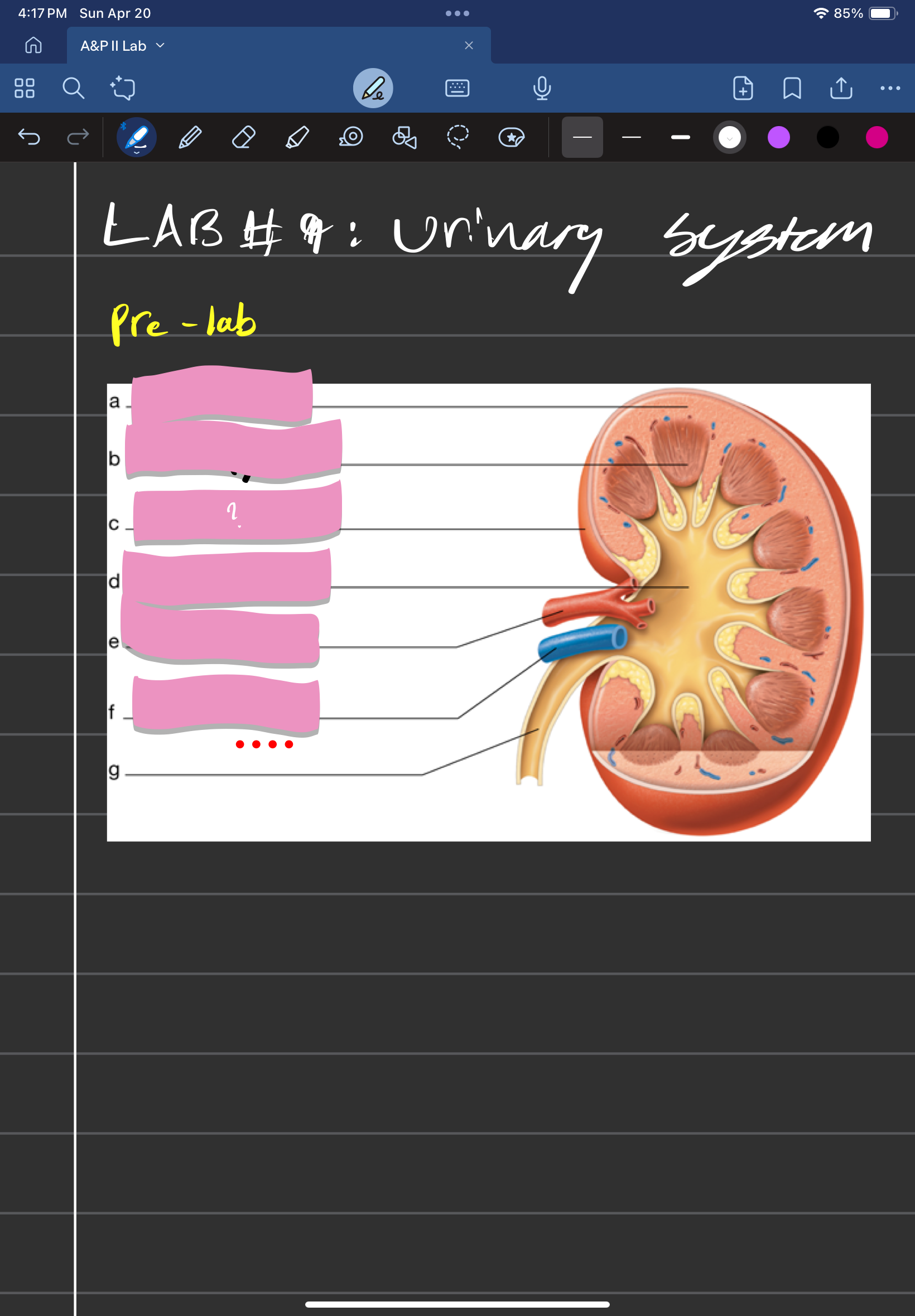
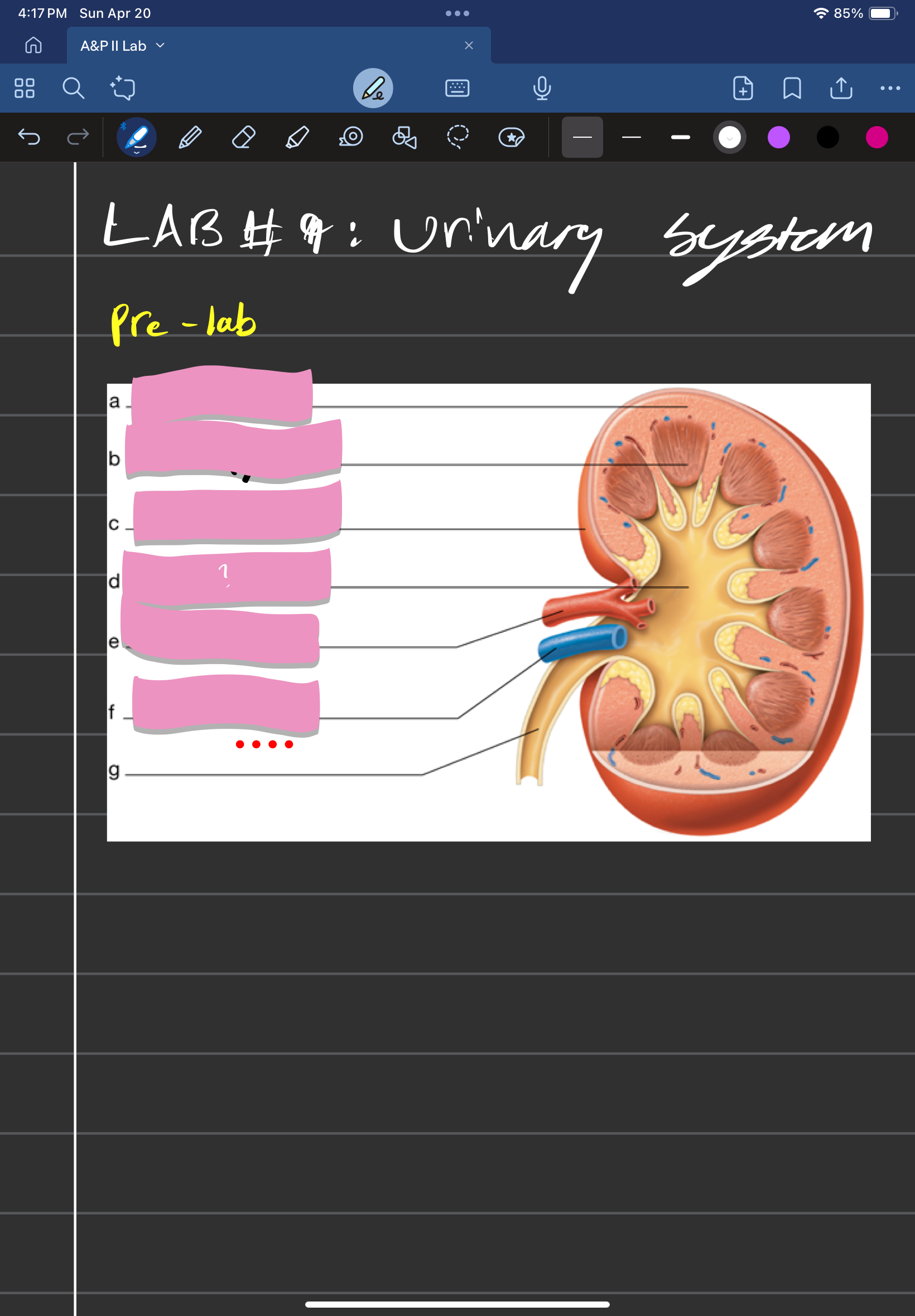
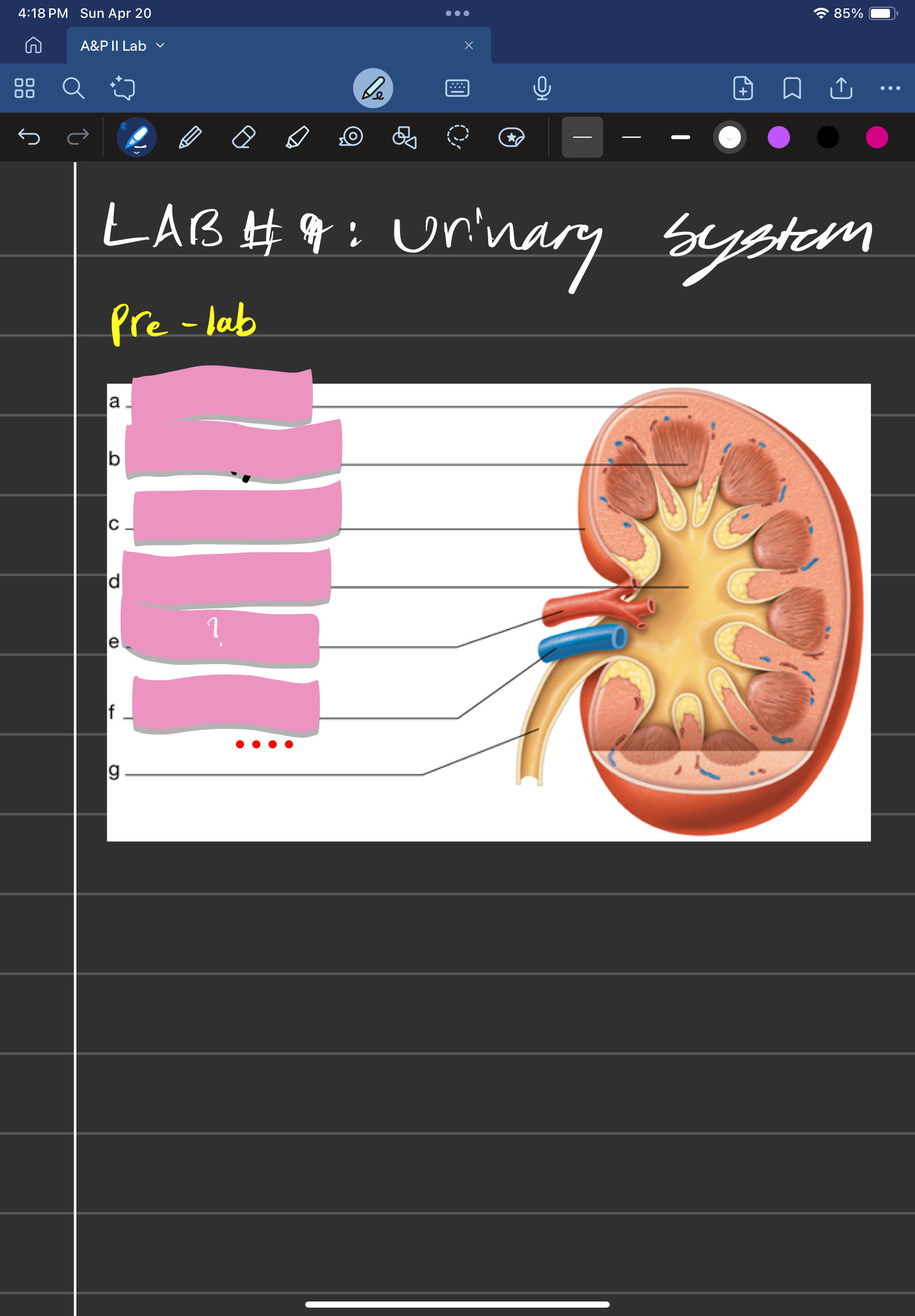
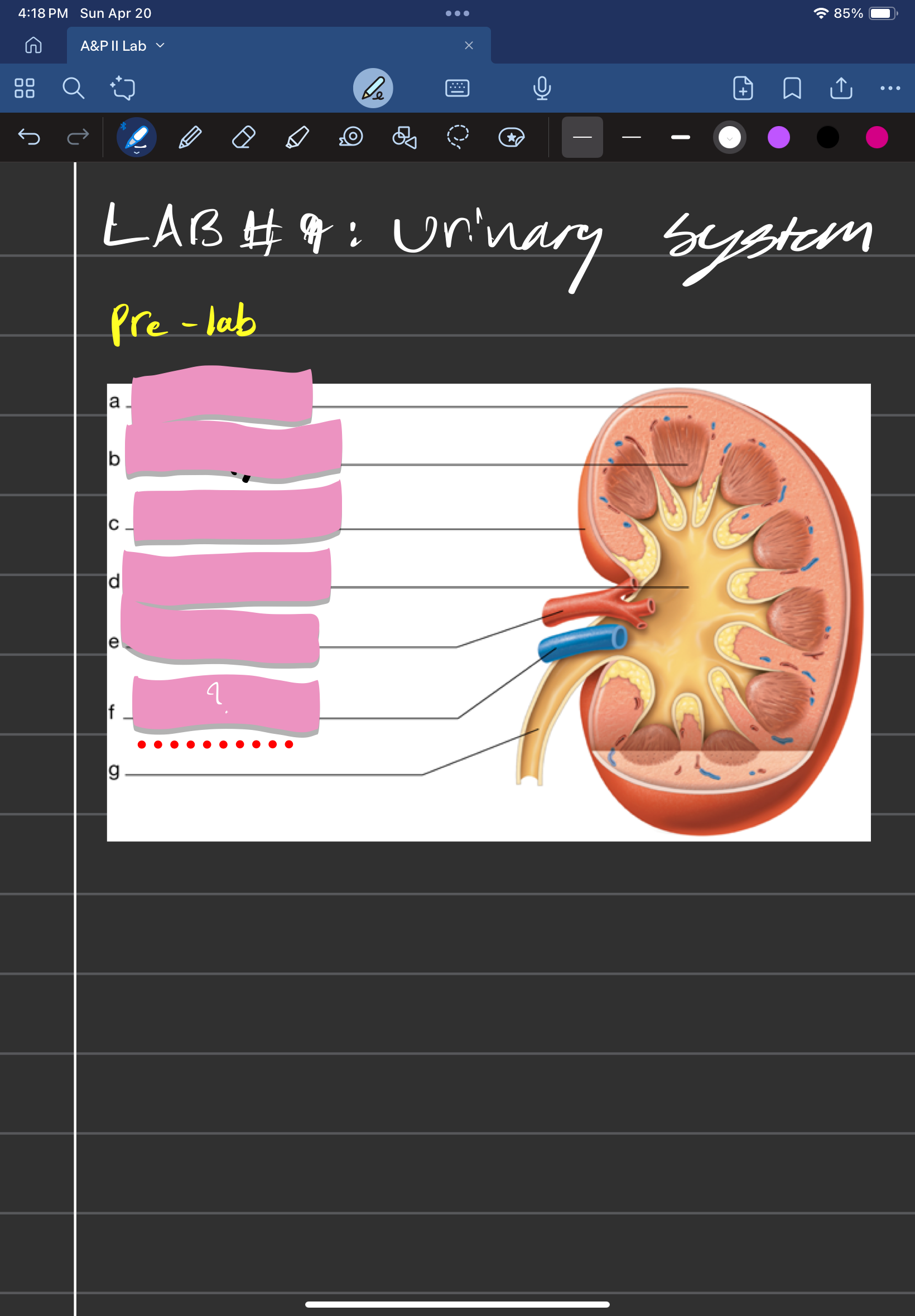
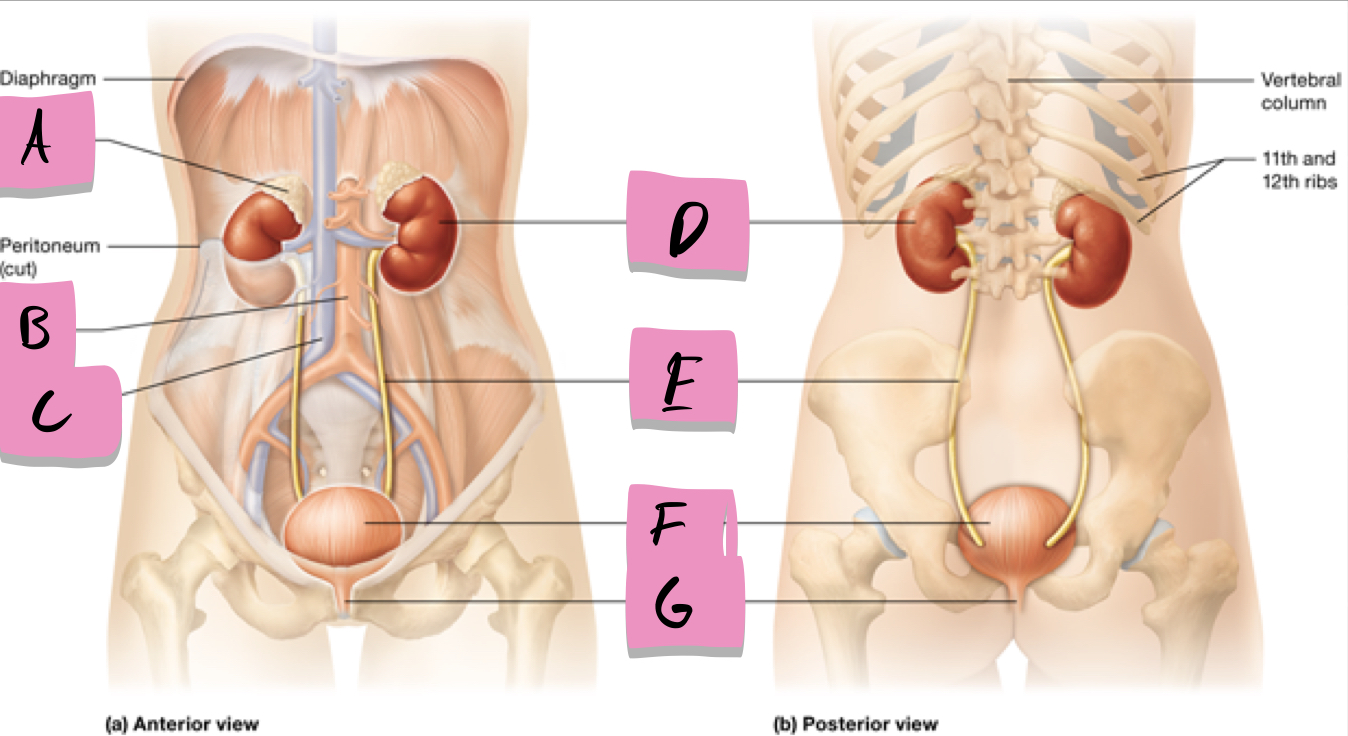
adrenal gland
label A
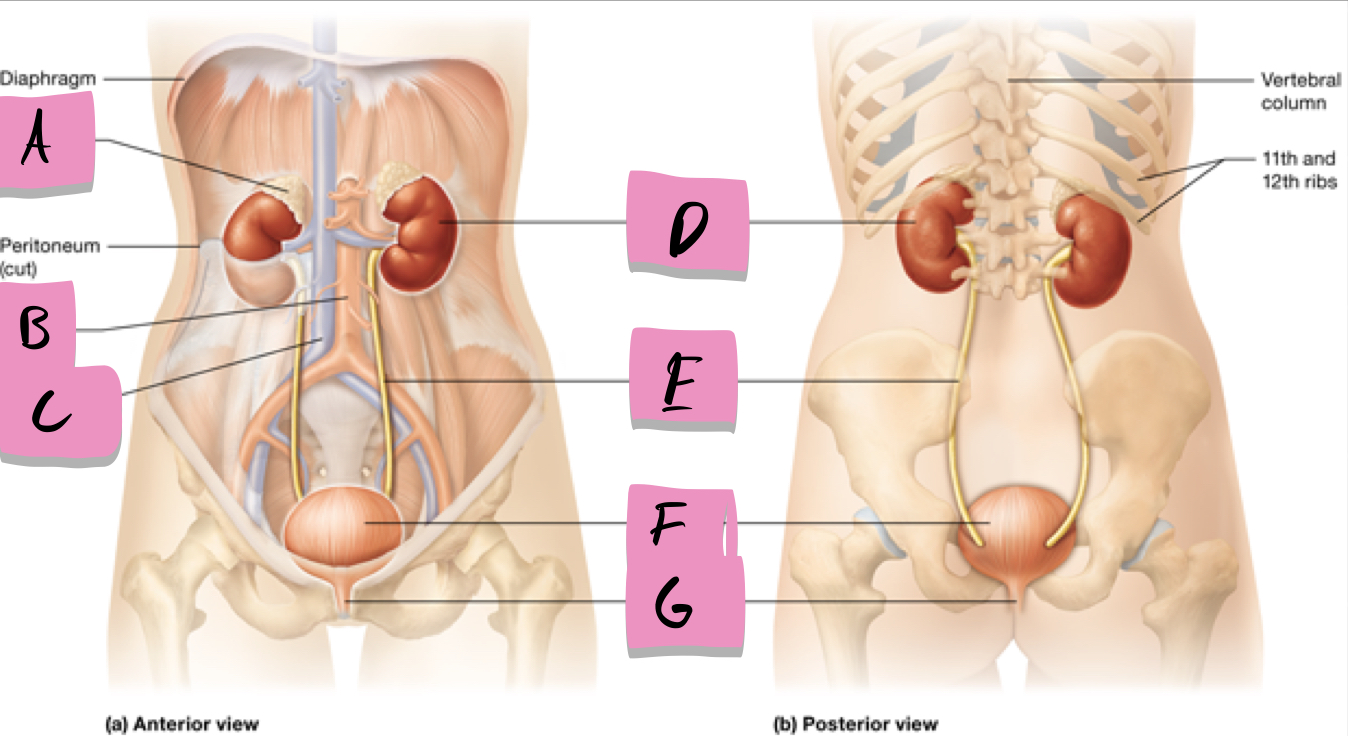
kidney
label D
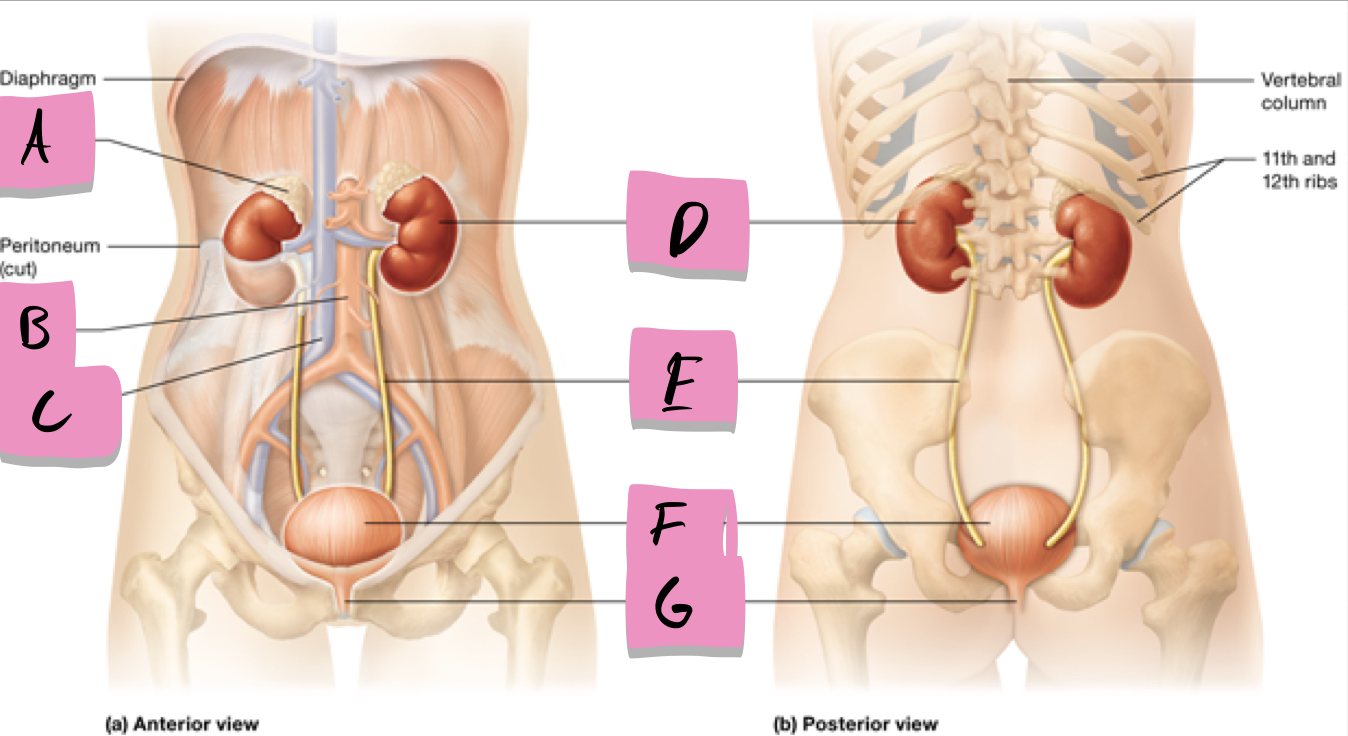
ureter
label e
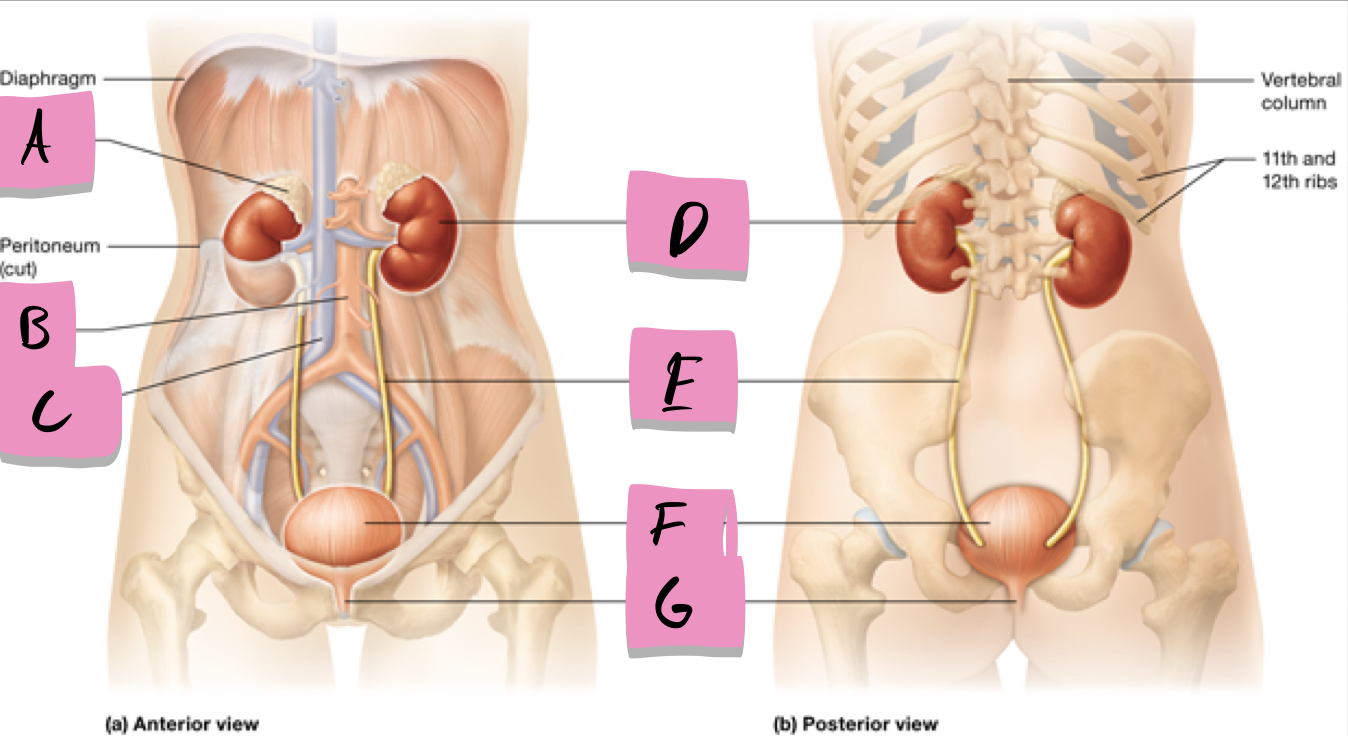
urinary bladder
stores urine; label f
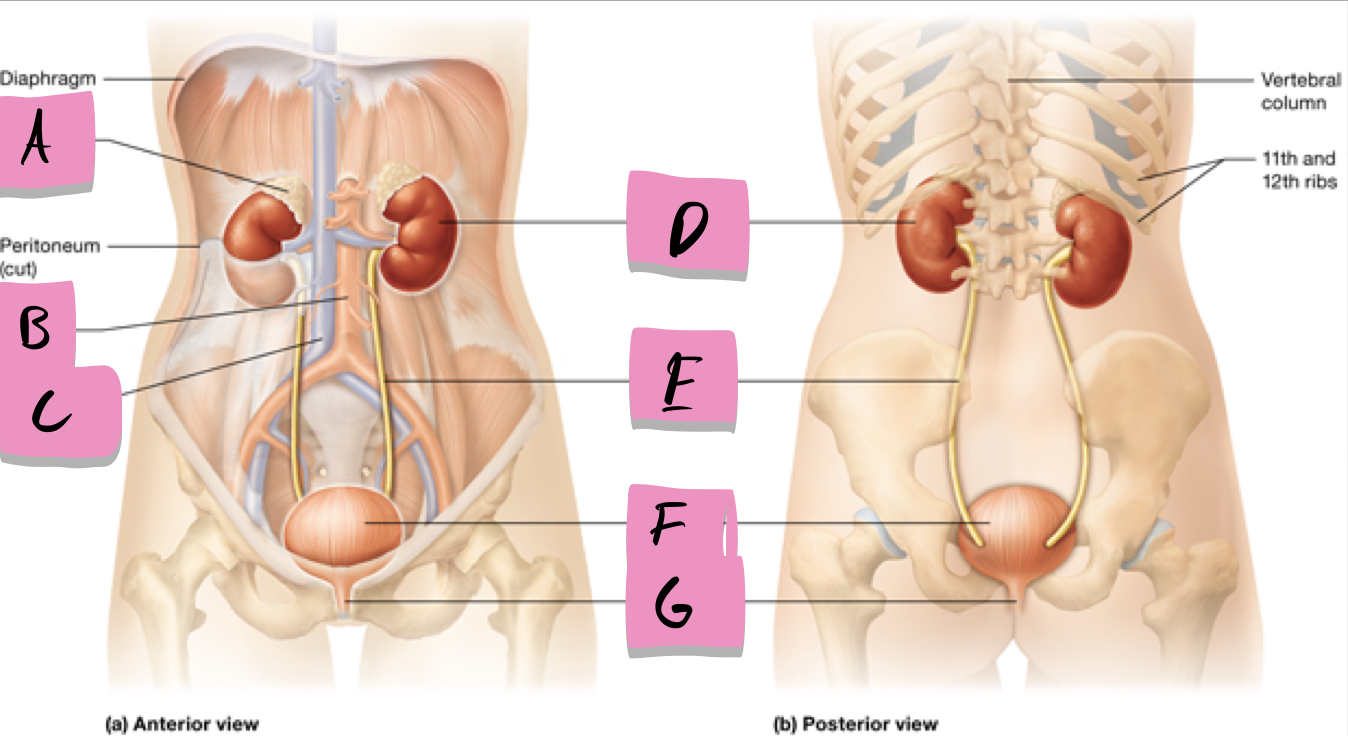
urethra
conveys urine to the outside of the body; label g
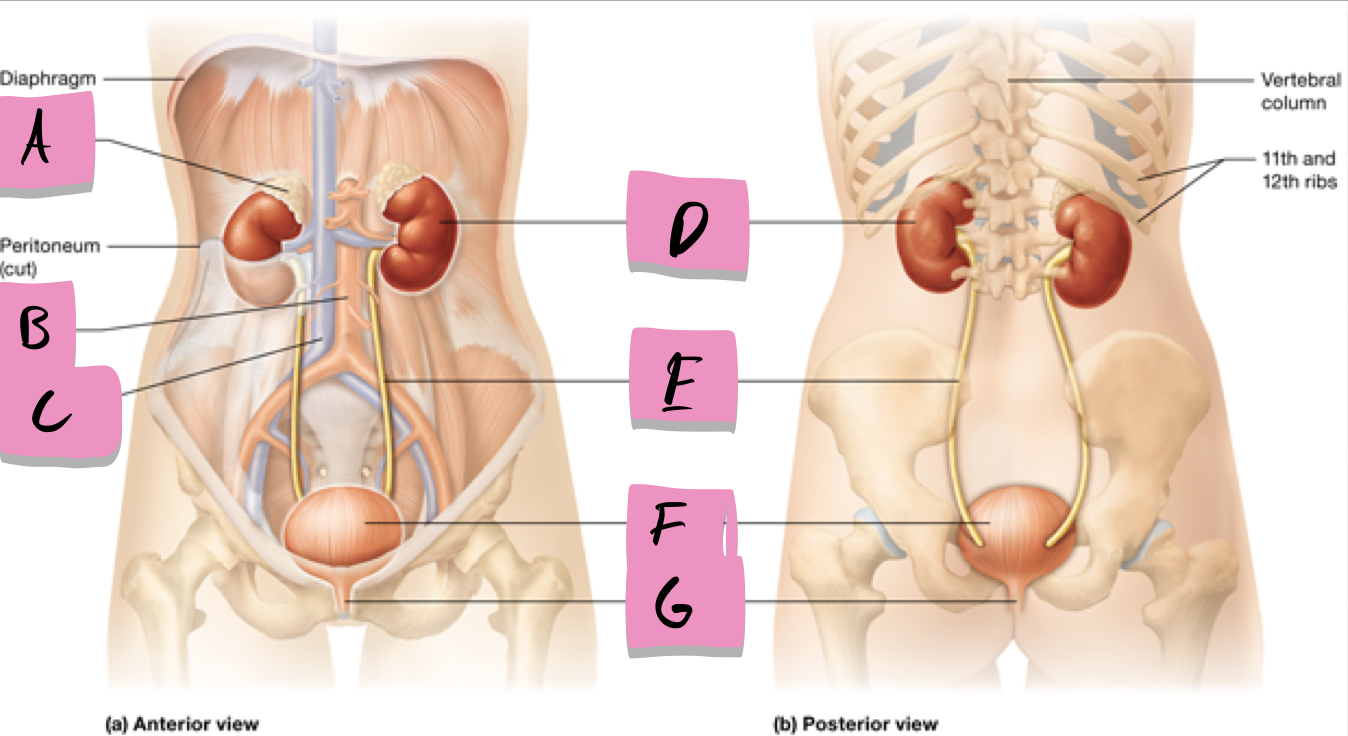
aorta
label b
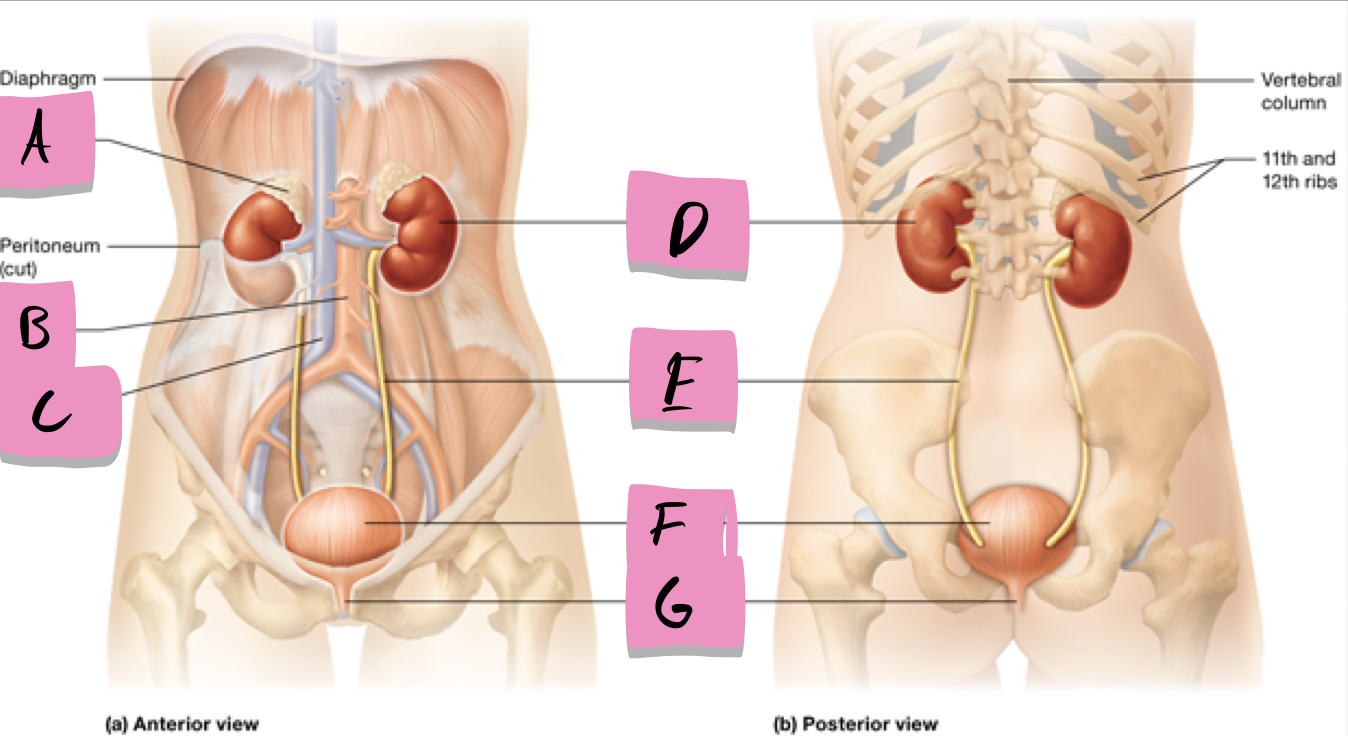
inferior vena cava
Label c
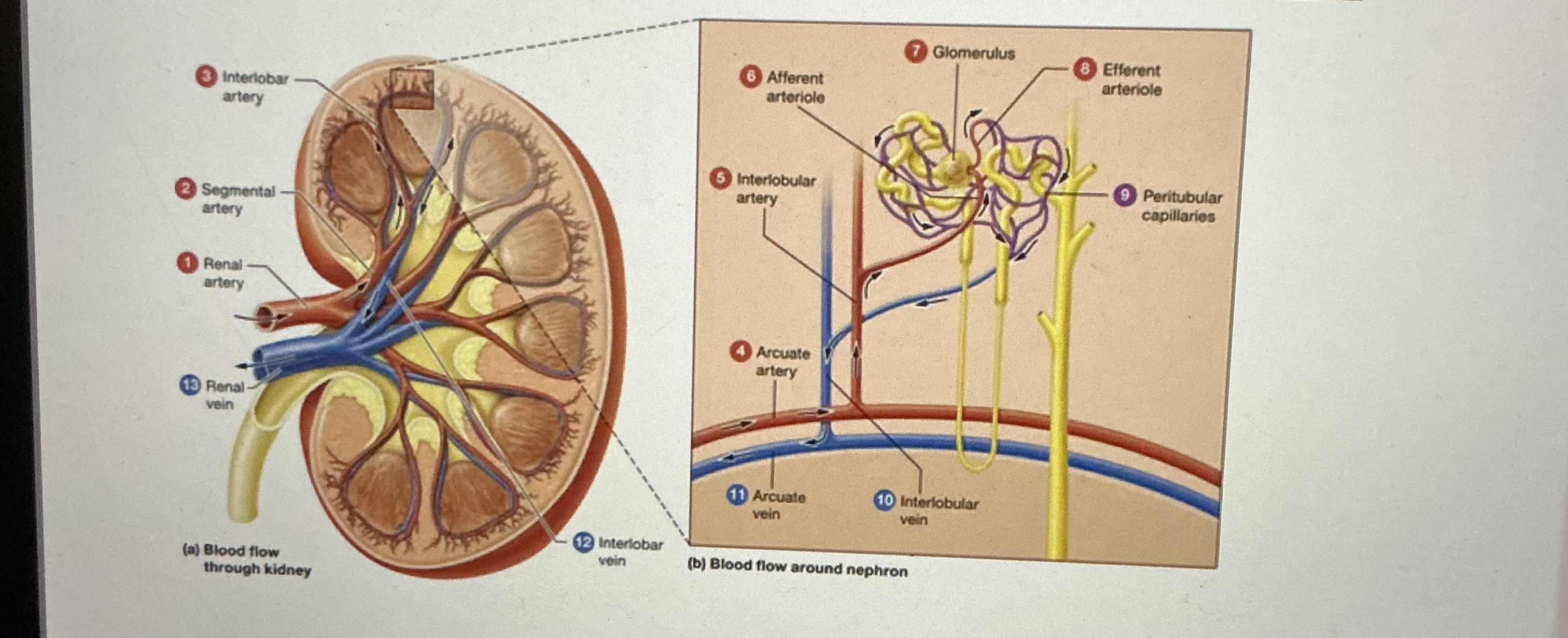
abdominal aorta -> renal artery -> segmental arteries -> interlobar arteries -> Arcuate arteries -> interlobular arteries -> afferent arterioles -> glomeruli -> efferent arterioles -> peritubular capillaries
arterial path of kidneys
Venous path of kidneys
peritubular capillaries -> interlobular veins -> arcuate veins -> interlobar veins -> renal vein -> inferior vena cava
urinary bladder (histology)
mucosa is transitional epithelium
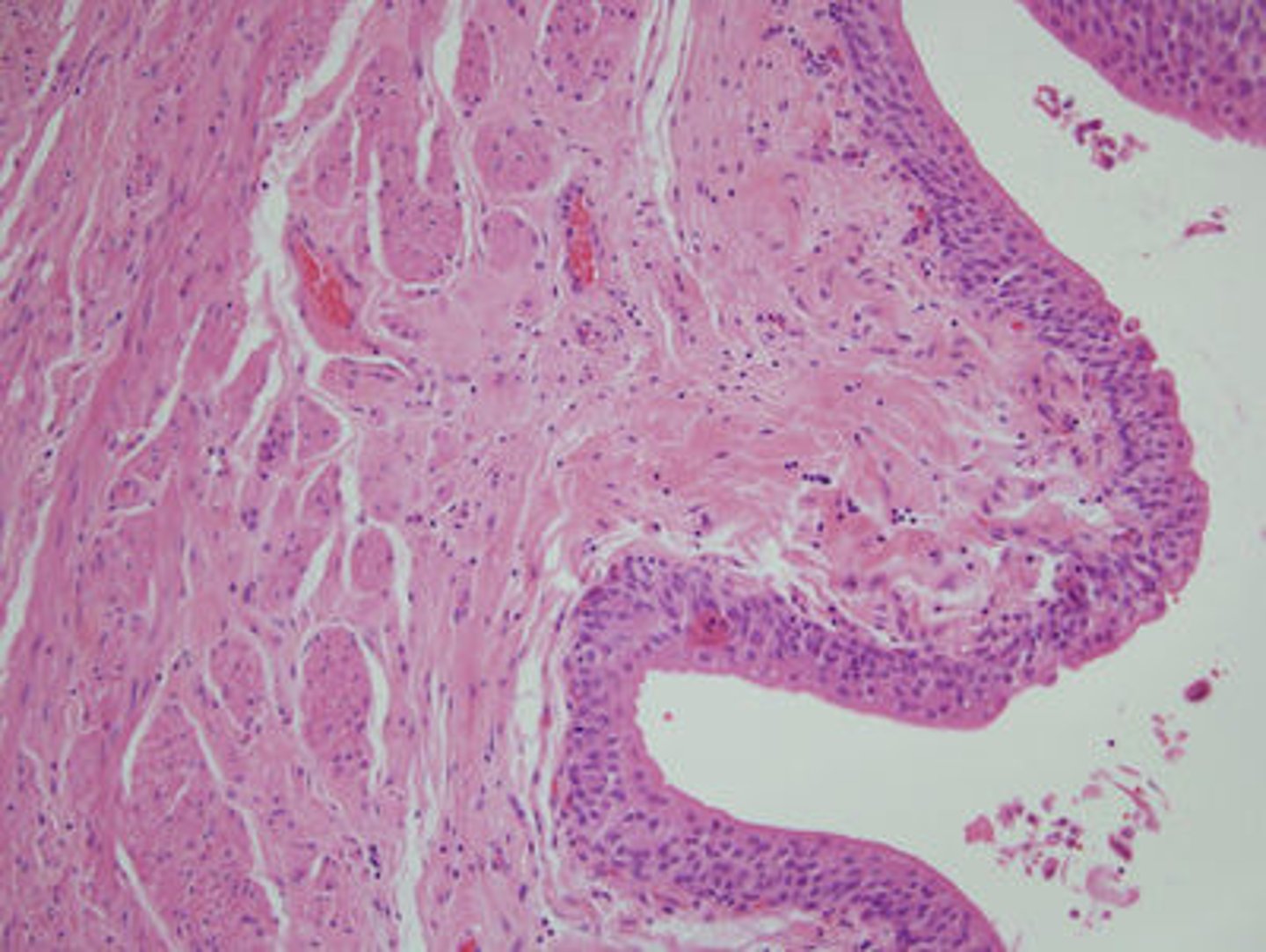
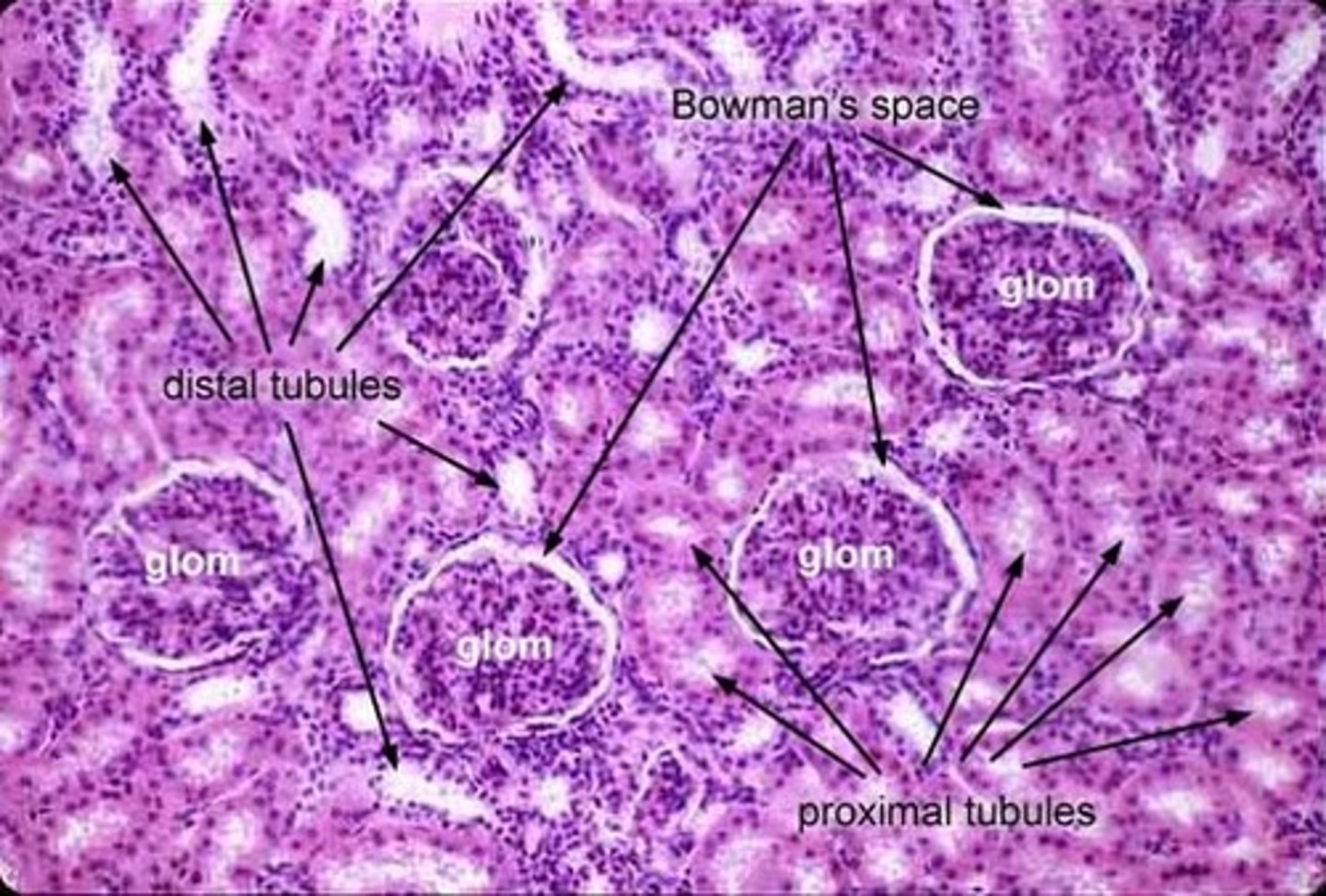
kidney (histology)
Kidney is composed of nephrons and a collecting system
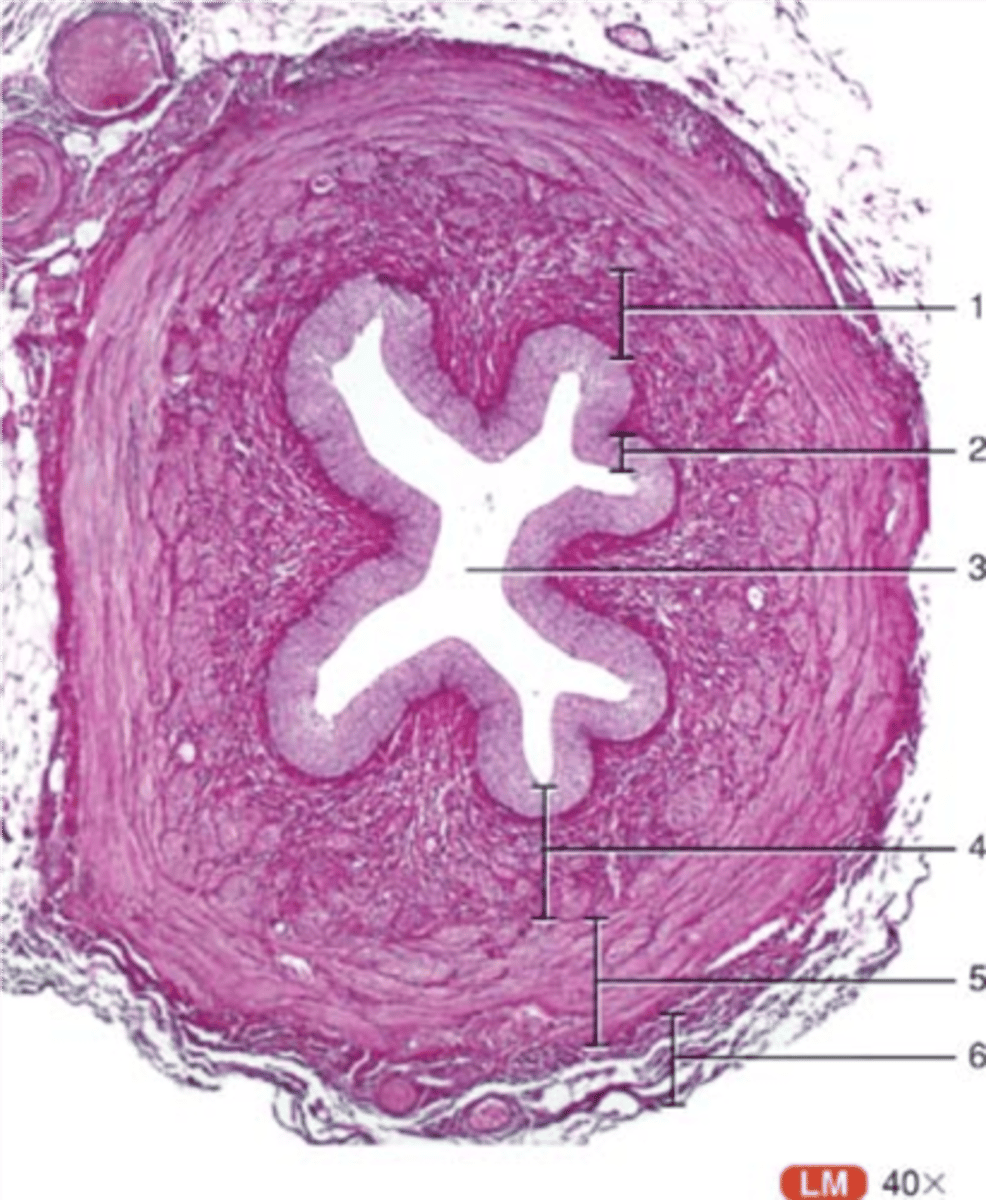
ureter (histology)
transitional epithelium
renal cortex
outer region of the kidney