greek art
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Minoan Culture
An early civilization from 2800-1400 BCE, known for its sailors and traders, centered on the island of Crete, marked by fine palaces and safe lifestyle.
Palace of Minos
A significant architectural structure located in Knossos, Crete, dating back to 1700-1350 BCE, featuring advanced plumbing and luxurious facilities.
Contrapposto
An artistic technique where the human figure is posed with weight shifted onto one leg, creating a sense of dynamic balance and naturalism.
Kouros
A type of free-standing ancient Greek statue representing a standing nude young man, used as a grave marker or cult object.
Arete
A key value in Greek culture that signifies excellence and reaching one's highest human potential.
Hellenistic Art
Art that emerged after Alexander the Great's conquests, focusing on individual emotions, realism, and dramatic expressions as opposed to ideal forms.
The Parthenon
A Doric temple on Athens' Acropolis dedicated to goddess Athena, known for its architectural perfection and the use of optical refinements.
Theatre of Epidaurus
An ancient Greek theater known for its exceptional acoustics and harmonious proportions, designed for large audiences.
The Cycladic Culture
An Aegean civilization characterized by simple marble figurines and an emphasis on aesthetics, prevalent around the 3rd millennium BCE.
Geometric Period
The era in Greek art (ca. 900-700 BCE) marked by geometric motifs and patterns in pottery and sculpture.
Classical Period
The period of Greek history from 480-323 BCE recognized for its political achievements, including the culmination of democracy in Athens and advancements in art and philosophy.
Electrum
A naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver used by the Greeks for coinage, particularly famous during the Lydian empire.
Black-Figured Style
An early Greek vase painting technique where figures are painted in a black slip and details incised to reveal the red clay.
Red-Figured Style
A later Greek vase painting technique that allowed for greater detail and realism, where the background is painted black leaving the figures in red.
Sappho
An ancient Greek poet from the island of Lesbos, noted for her lyric poetry focusing on personal themes, especially love and relationships.
when was the archaic period
600-480 BCE
what features do greek temples have?
order
compactness
symmetry
sense of proportion
numerical relationships and geometric rules
proportion in architecture and sculpture
reflections and embodiments of cosmic order
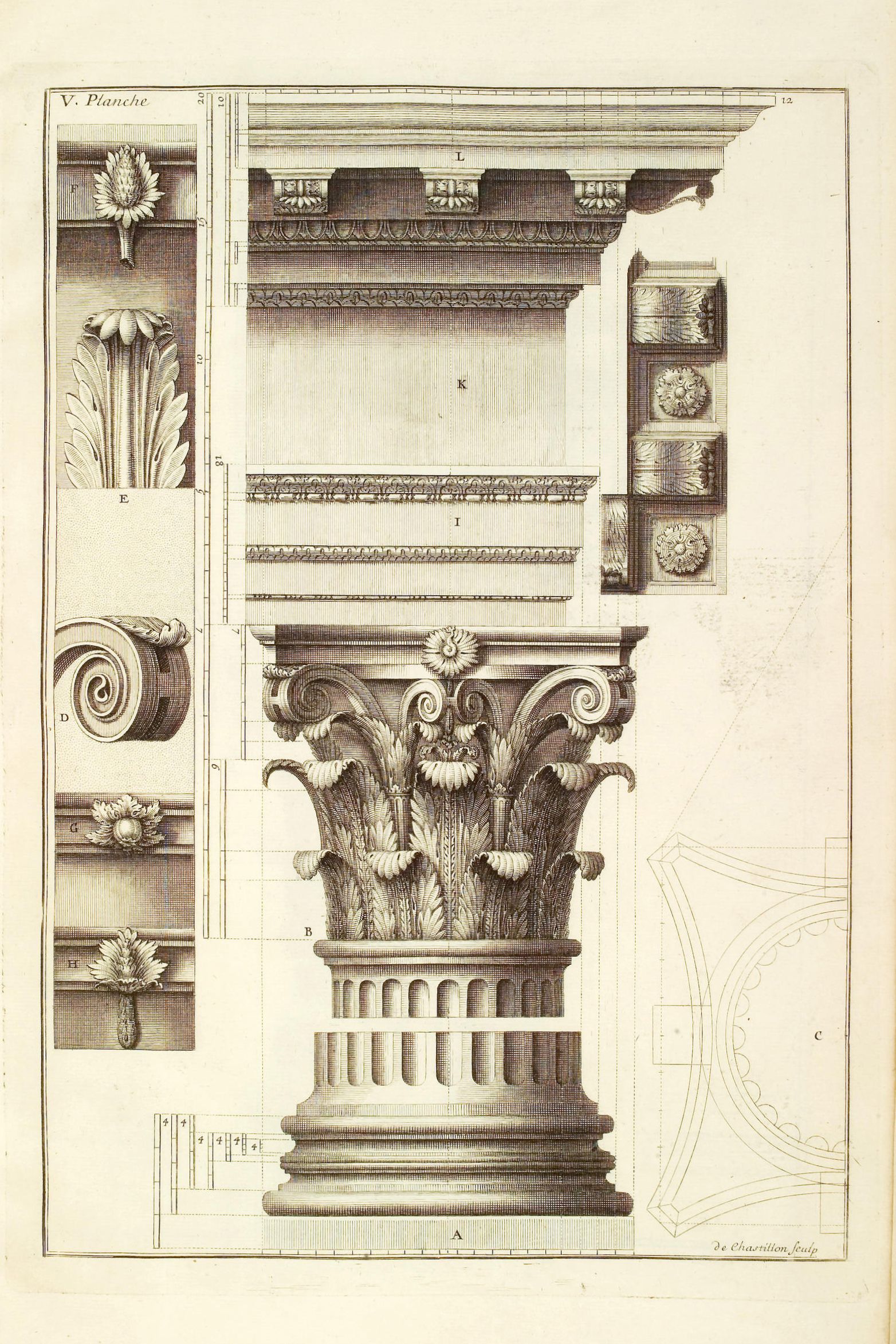
name the features of a pillar in a greek temple in corinthian order, top to bottom
cornice, frieze, architrave, capital, shaft, base
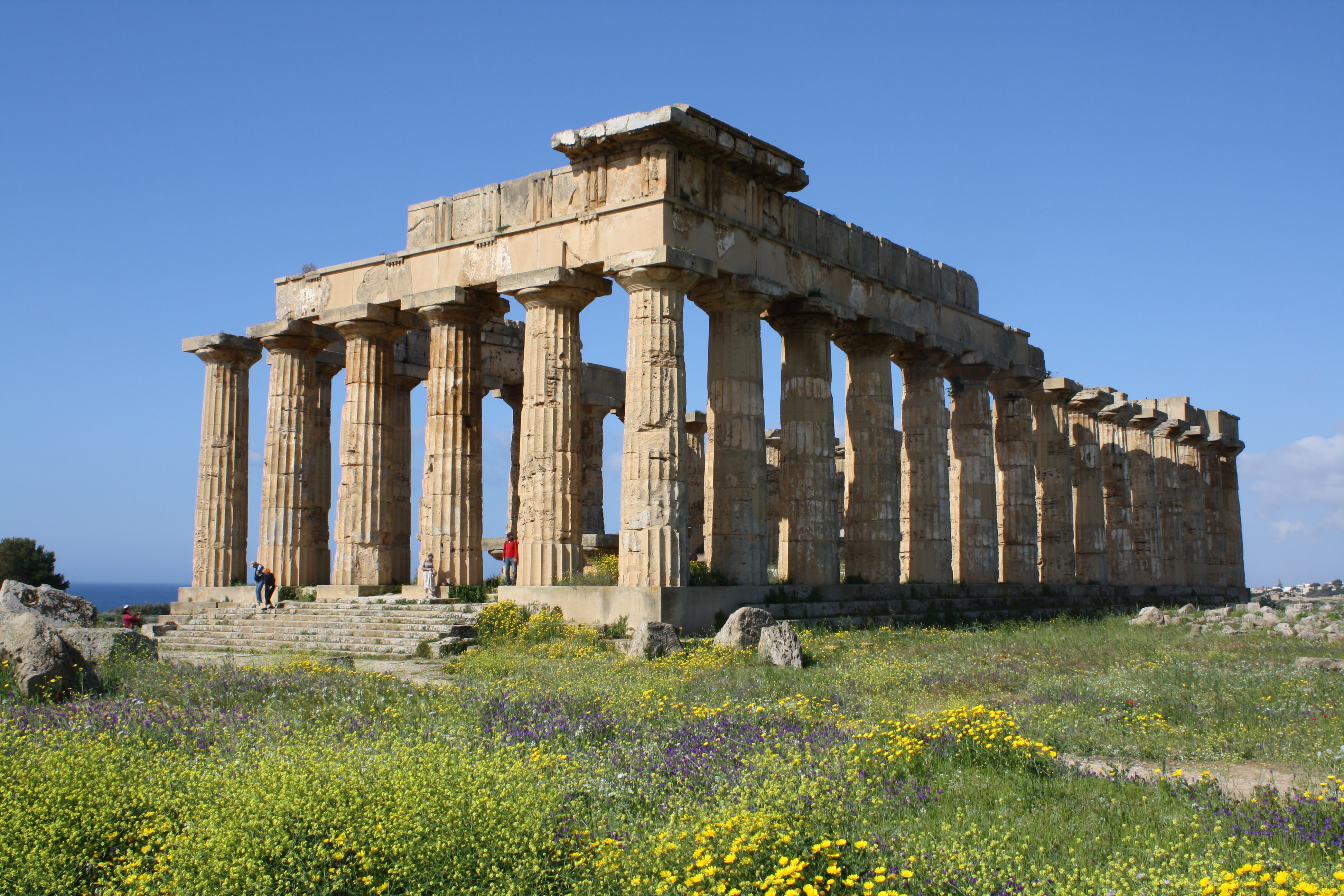

what style is the temple of hera in?
doric style, simple, severe and powerful in appearance

describe the similarities and differences of this to an Egptian statue
similarities
rigidly frontal
one foot forward, but body weight is evenly distributed on both feet
differences
greece was obsessed with motion, egypt was obsessed with permanence
greek figures are NAKED
enigmatic expression: “archaic smile”
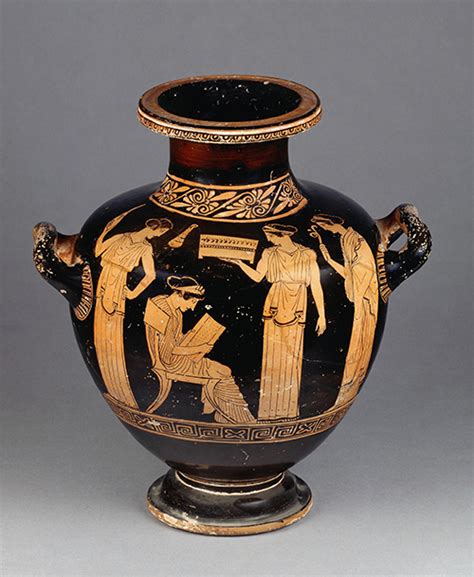

what is the context behind the woman in the middle? (sappho)
was poet who surrounded herself with a group of young women who engaged in the celebration of love (aphrodite), beauty (graces) and poetry (muses)
poetry was celebrated as female creativity
her lyric poems were on themes of love and personal relationships, often with other women
sung her songs to the accompaniment of a lyre
what was the reconstruction of athens and when did it happpen?
happened after the destruction of athens by the persians in 479 BCE
explosion of creativity that resulted in unparalleled level of excellence (art, architecture, poetry ect)
athens rebuilt with walls, agora (marketplace), house shops, stoa (covered walkways) that were supported by colonnades (rows of columns)
what was general characteristics of art produced during the reconstruction of athens?
balance and order in art
was a reaction to the extreme disorder of the world that they named “barbarians”
what features of architecture was observed?
monuments treated as large sculptures, with the same rules of symmetry and ideal proportions
public rites took place in front of temples, with elaborate sculptures telling the story of the temple’s deity
sculpted figures often protruded sharply from their background stone, usually painted red or blue

what is the parthenon and when was it built?
448-432 BCE
built by Pericles, using funds intended for Athen’s defense
doric temple, dedicated to Athena
Ultimate example of greek architecture, paradigm of perfection of its proportions
Golden Section: width 1.618 times height 8:5
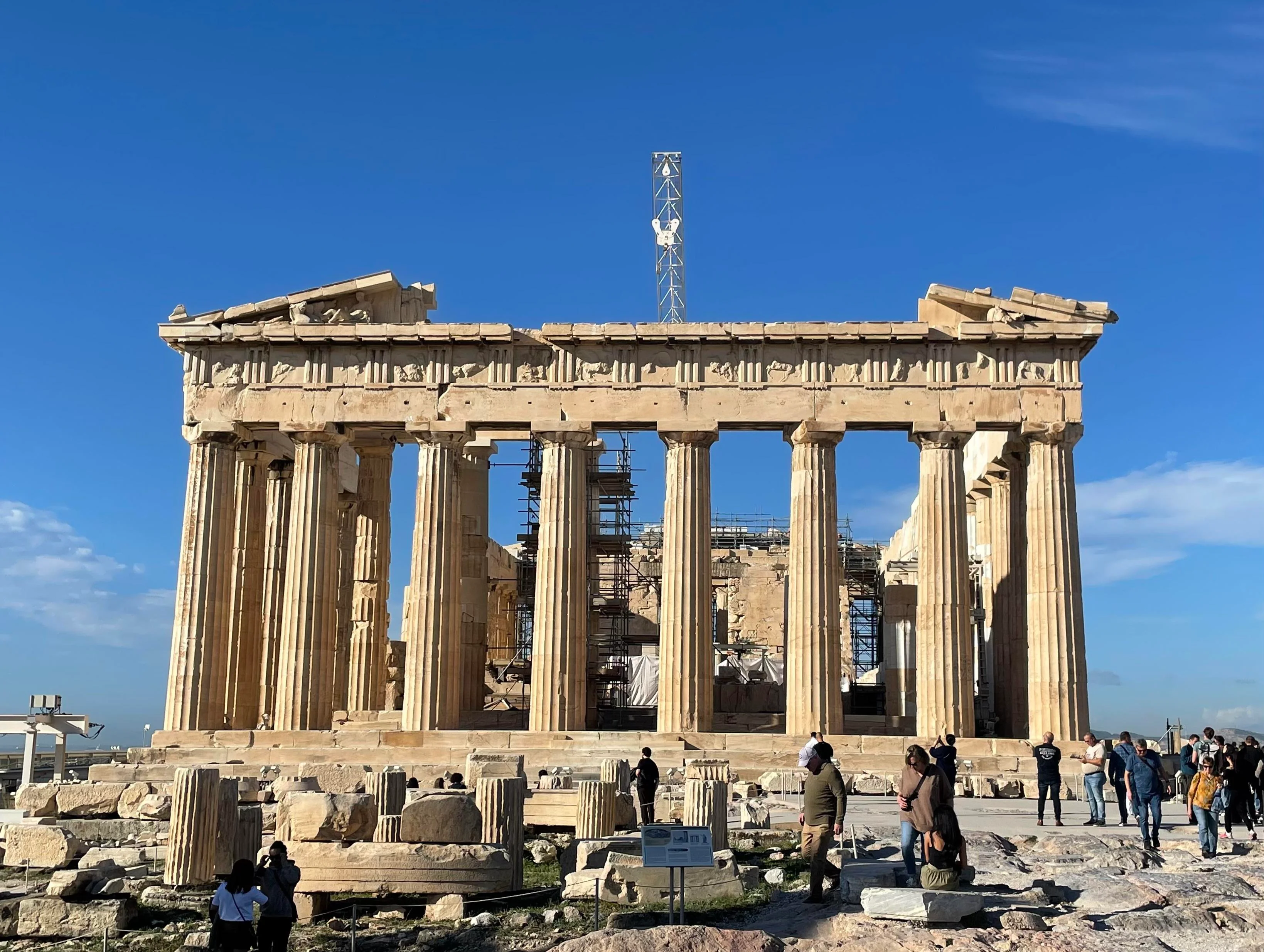

What was so special about the colonnades?
no straight lines, steps and entablature form convex curves
columns with “entasis” : slight bulge in the column shaft
bent straight lines give illusion of upward thrust and solid support for central mass
what were the 3 types of sculptures found on the Parthenon?
Frieze (low relief, made of marble)
procession of women: asthetic principal of unity and variety
physically young and strong, idealized rather than individualized
east pediment
three goddesses
classical balance between idealism and naturalism
perfectly and powerfully proportioned bodies revealed by naturalistic drapery folds (appears wet)
erechtheion (never finished)
asymmetrical ionic temple
needed to incorporate elements from previous shrines, including an oliva tree grown by athena, different rooms and functions
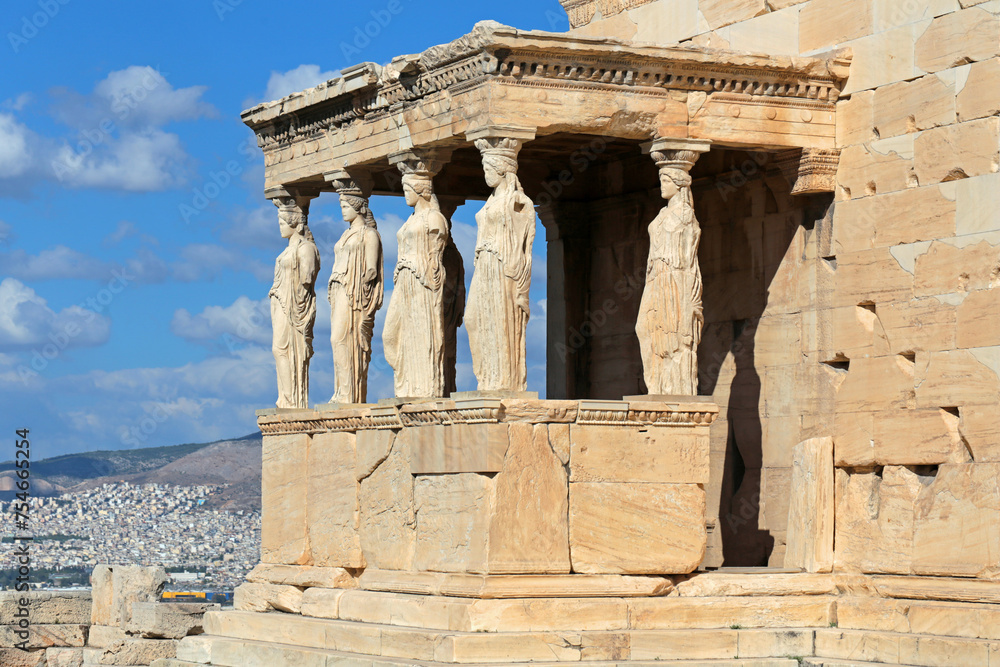

what are the 6 caryatids?
female figures used as architectural supports. the statues are meant to blend in with the building
reflects unity and variety
contrapposto pose: supporting leg hidden by drapery of their dress that stimulate the fluting of a column
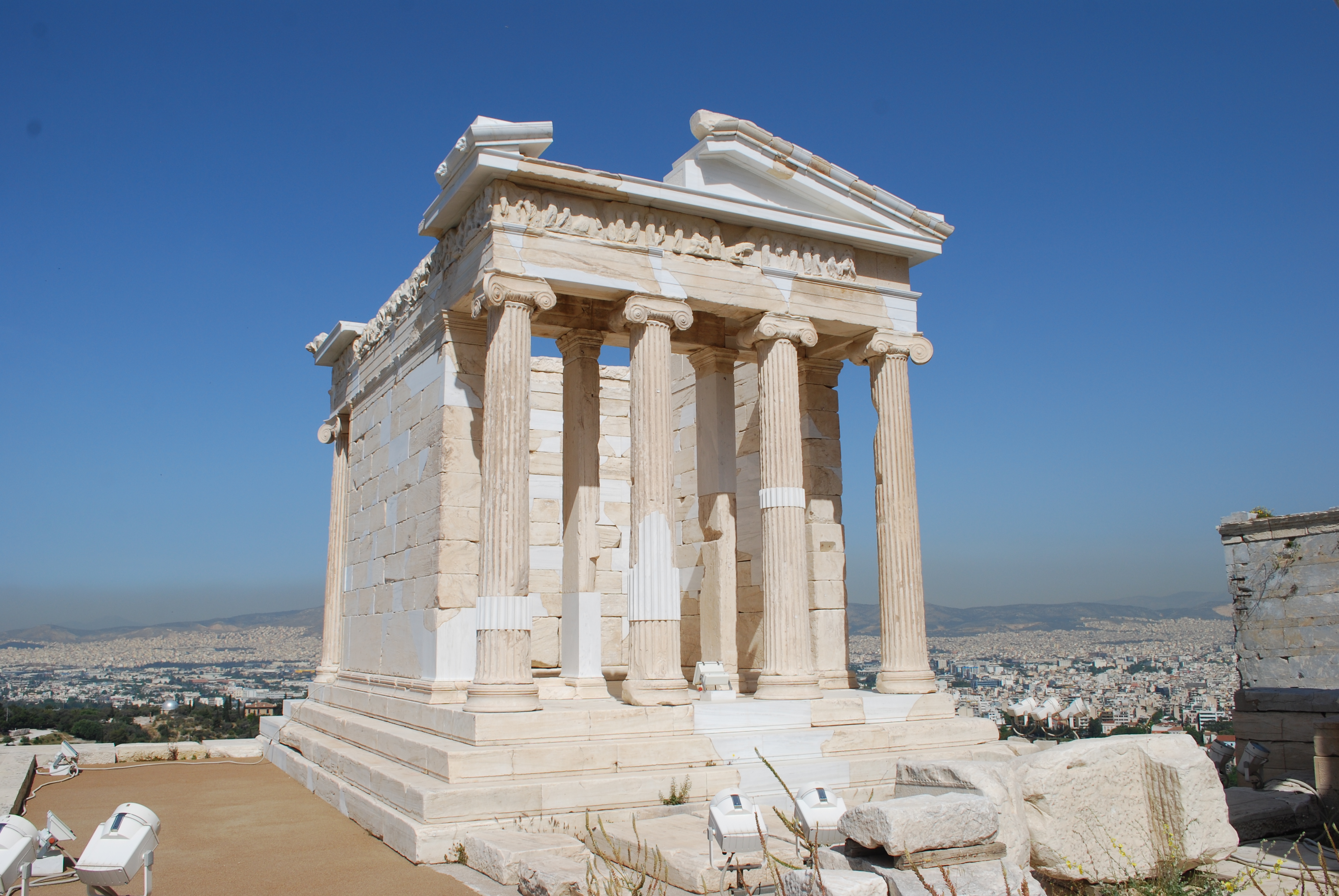

what was the purpose of this temple?
temple of athena nike
commemorates victory over persians, nike is the winged goddess of victory
4 ionic columns in front and behind

what was different about this statue compared to statues before it? (480 BCE)
accurate anatomical details
first statue to show how a person naturally stands
archaic smile gone, serious now
new sense of movement that broke free from previous frontality (Egypt)
spine forms a gentle S curve, one hip raised slightly, weight falling on a single leg [contrapposto] → separates classical from archaic statues
what were common features of greek statues?
relaxed and natural contrapposoto pose
weight on 1 leg, hips and shoulders not parallel, spine in gentle S curve
harmonic proportions: sought to portray the perfect man/woman and to impose order on human mvt

what is different about this statue of aphrodite and statues of male gods?
modest (covers herself)
sensuality is not suppressed
350 BCE → female nudity was not yet popularized (only towards the Hellenistic period)
when did drama emerge?
400 BCE
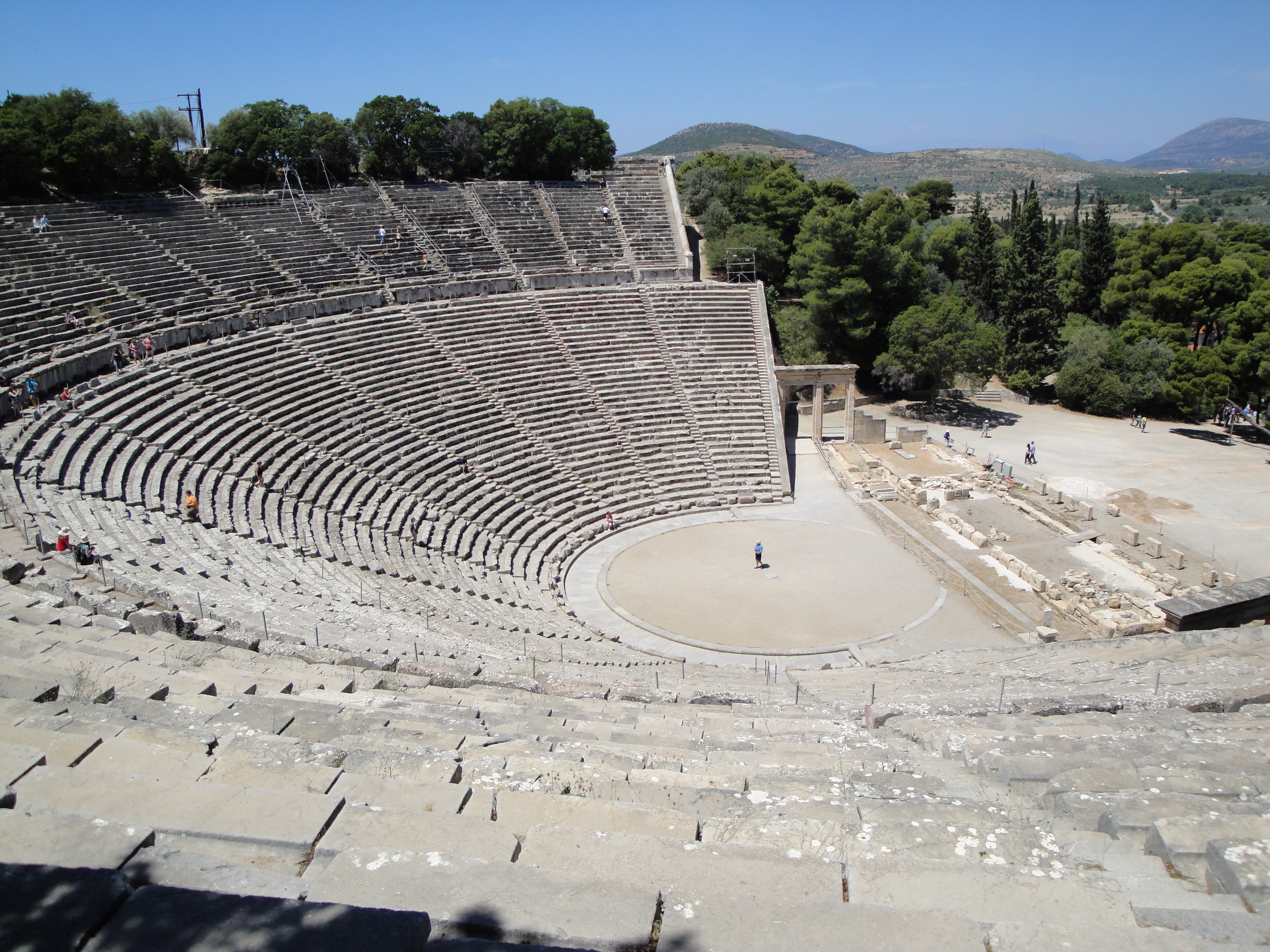

what was so incredible about this theatre?
harmony of proportions
limestone absorbs low-frequency sounds and amplifies high-frequency sounds from the stage
excellent acoustics
what did alexander the great’s death trigger? (323 BCE)
mingling of eastern-western cultures through policies and conquests
generals were governors
political, artistic, social and economic dominance shifted from mainland greece to the hellenistic kingdoms
characteristics of hellenistic art
focused on the individual (classical art focused on balance, order and idealization)
emotional states of the person
united by international culture and same language (greek)
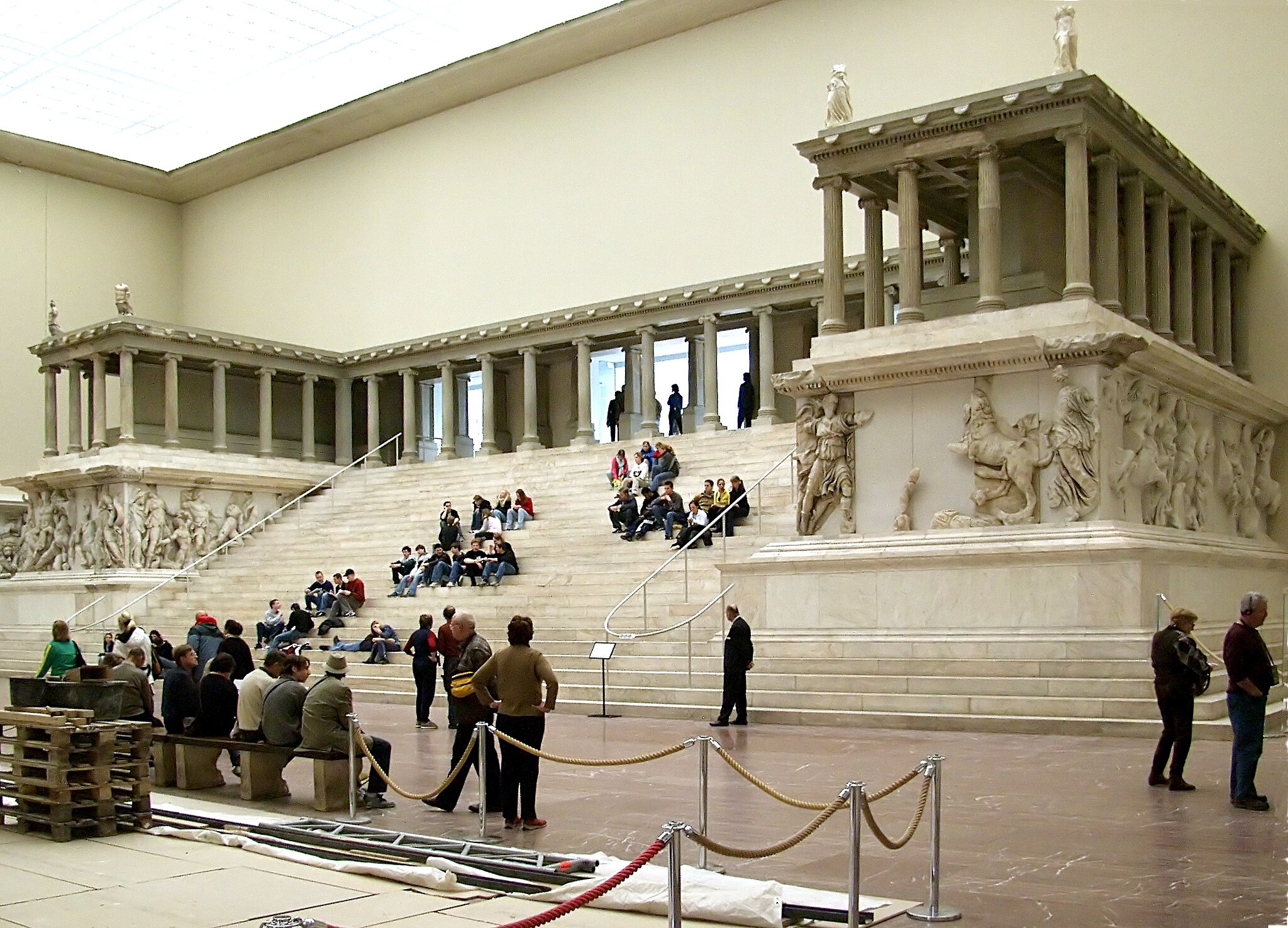

what is this art piece and why was it so significant? (175 BCE)
built by King Attalos in Asia Minor to commemorate victory over the barbarians
depicts the battle of Zeus and the gods against the giants
larger-than-life size, embellished with a profusion of ornament
theatricality, expression and large-scale
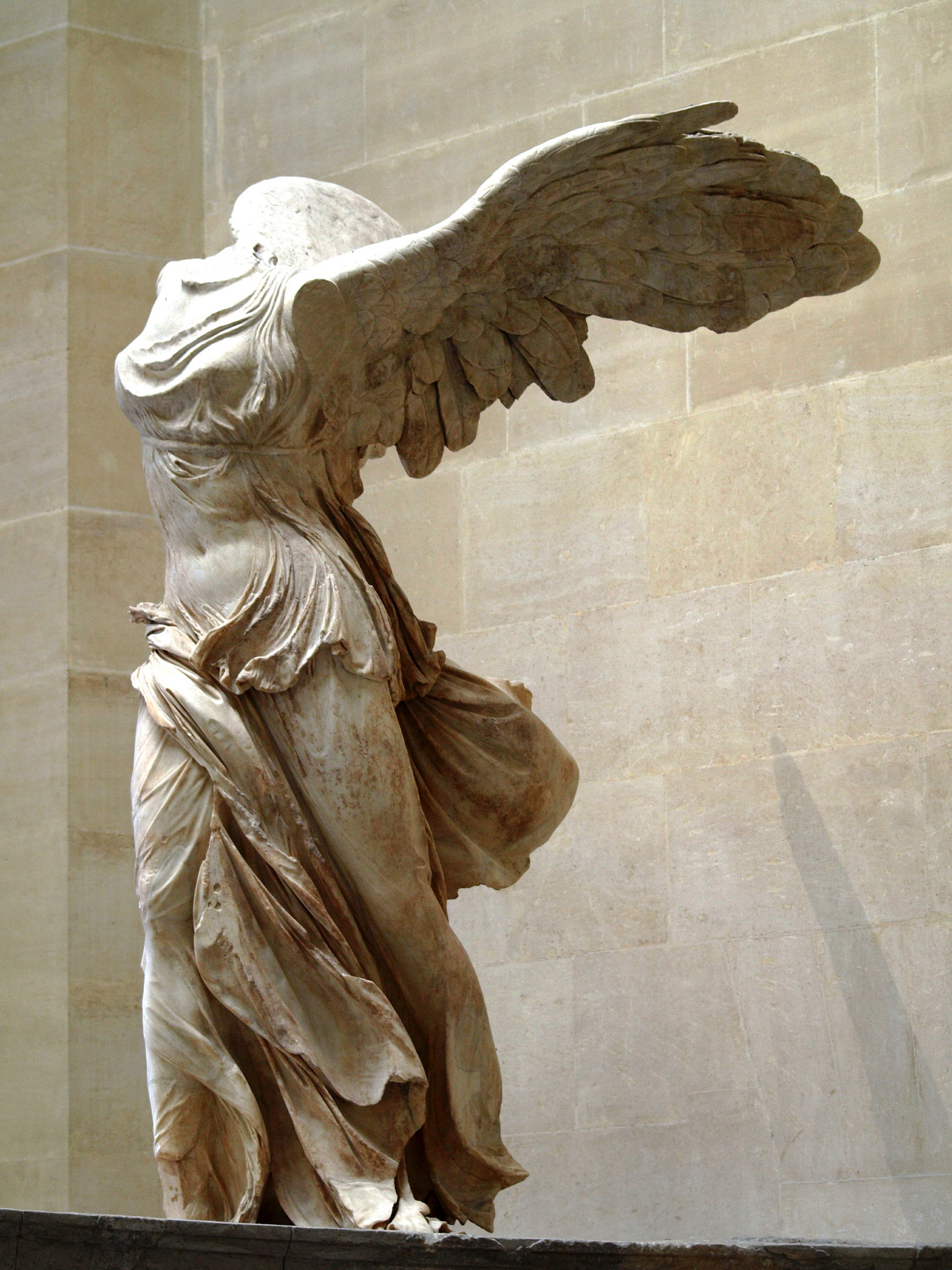

what was the purpose and signifiance of this statue? (200-190 BCE)
nike of samothrace (winged victory)
movement through space
revealed the treatment of drapery
originally placed at the prow of a stone ship at Samothrace: to crown the victorious command and crew
head turned to face the sea
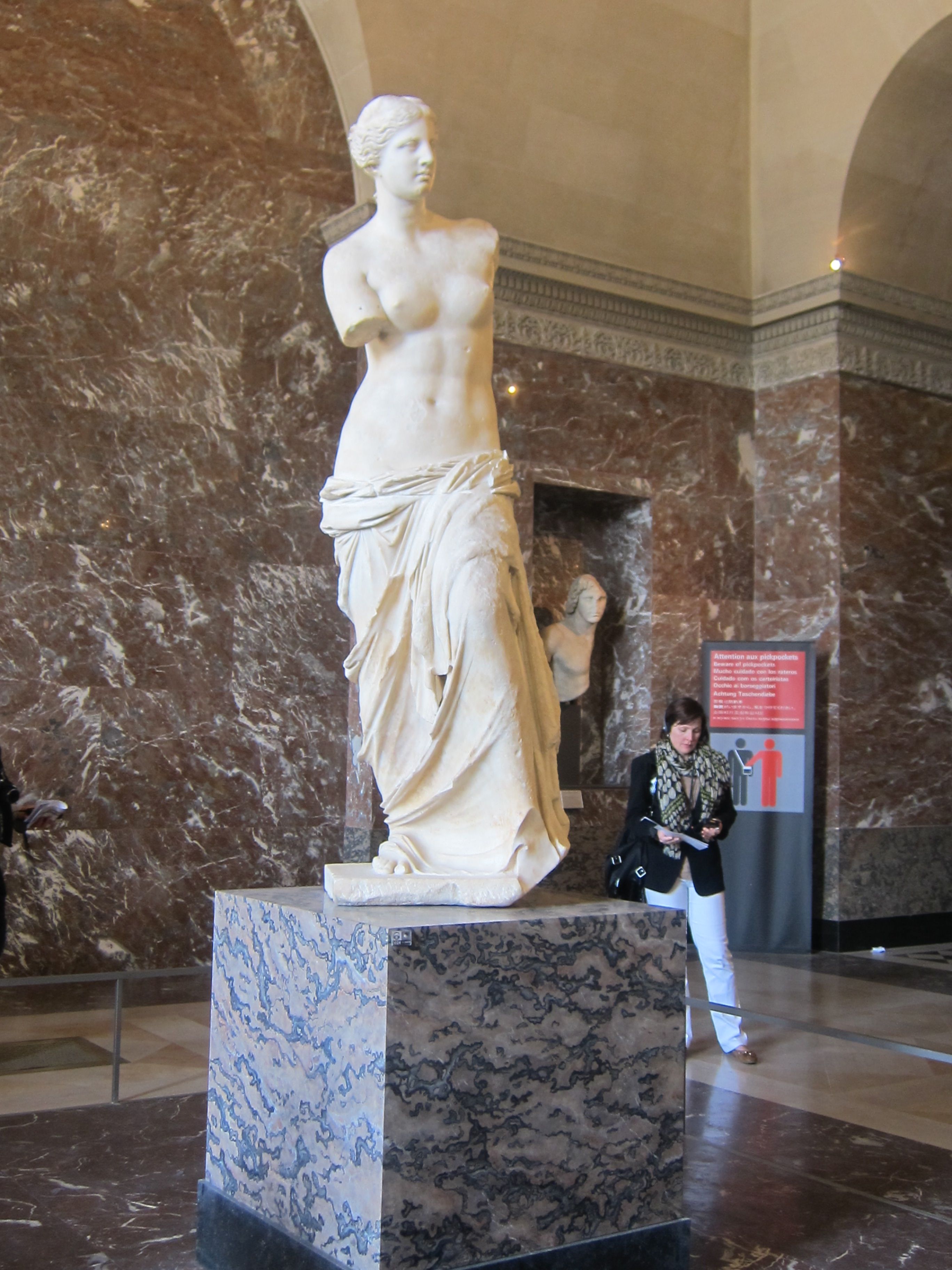

what was the significance of this statue?
overtly sexual, eroticism of the nude female form explored
teasing spectator with the partially draped body that is slipping
contrapposto
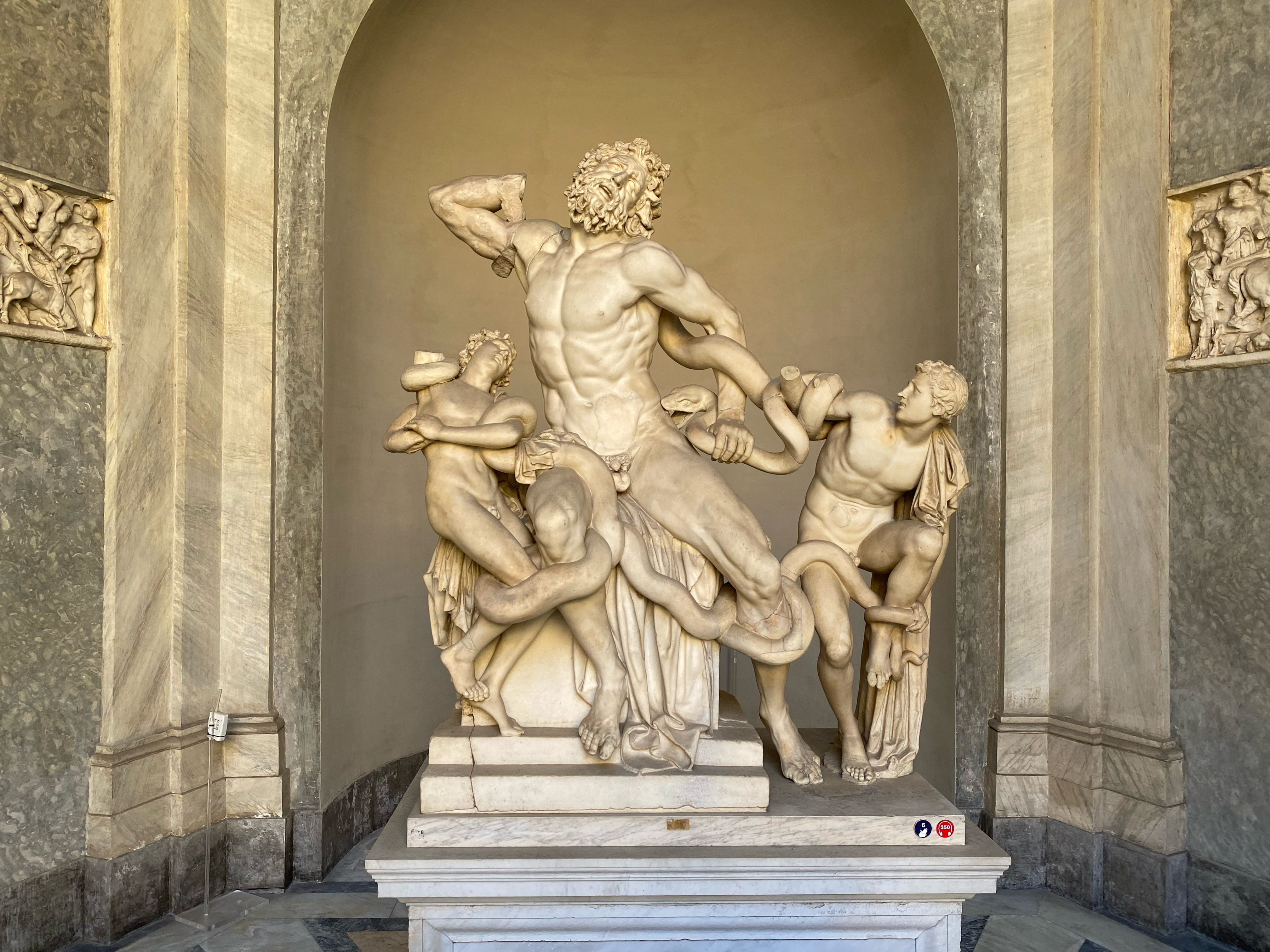

what does this sculpture depict? (150-100 BCE)
Laocoon was a priest of Apollo temple of Troy
Gods favoured Greece in the way against troy. Laocoon tried to warn the Trojans against accepting the wooden horse.
the snakes are strangling him and his sons as his punishment for betraying the Greeks
figures are bound by the serpent and writhe in agony
extraordinary dynamism