Architectural Appreciation Final Exam Review - W. Briar Jones
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
What does Architecture Respond To?
Architecture responds to the needs of its users and rises to the level of art
Architecture is Connected to What?
Architecture is connected to a particular place and relates to the specifics of geography, climate and the surroundings
Why is Architecture Important?
Because architecture permanently records a civilization’s aesthetic tastes, material resources, political and social aspirations
Architecture helps define ________
place
What are the Three Principles Vitruvius Felt are Essential to Architecture?
1. Firmness (structure)
2. Commodity (function)
3. Delight (beauty)
Example of a Representative Sketch
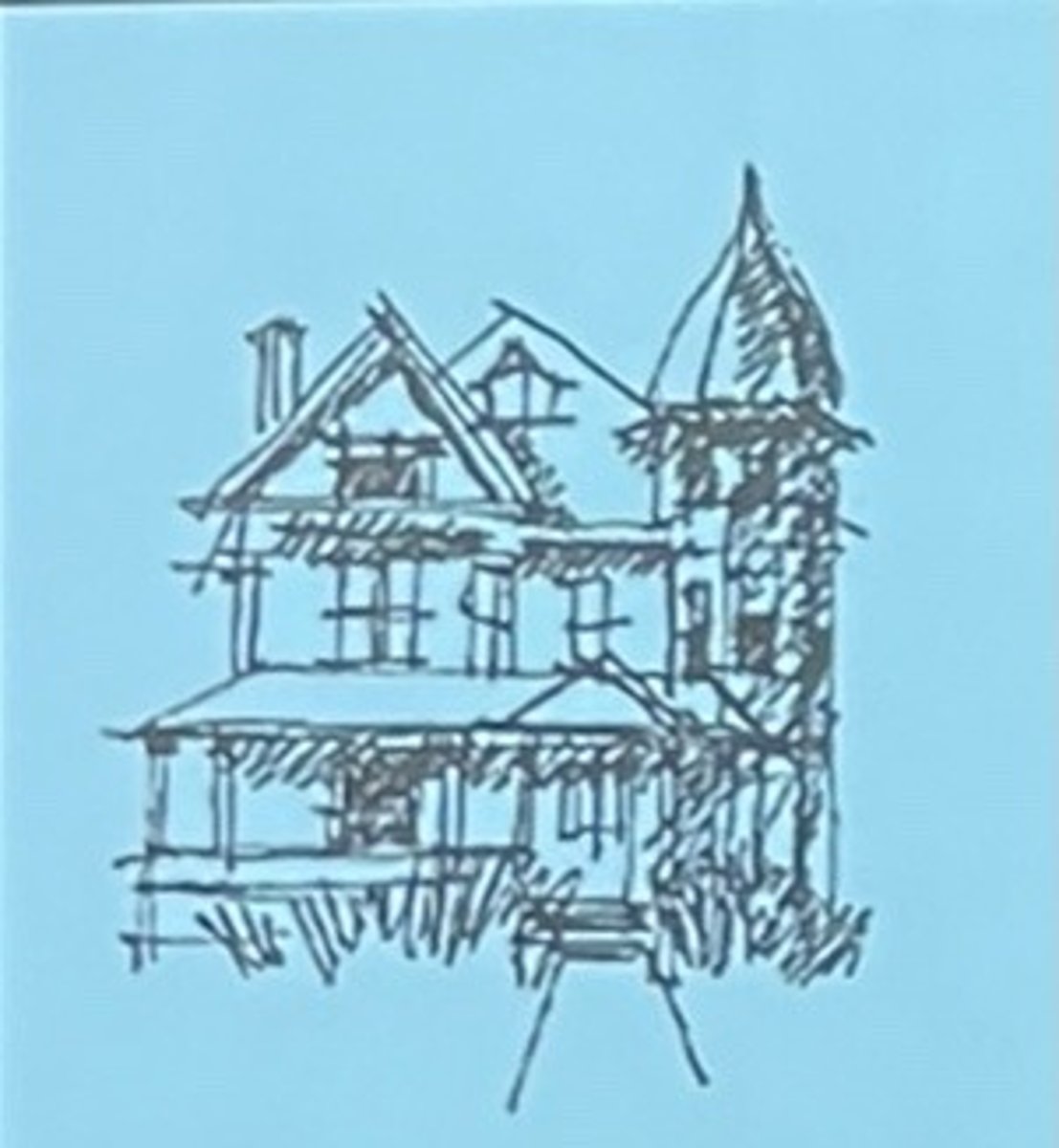

Example of an Abstract Sketch
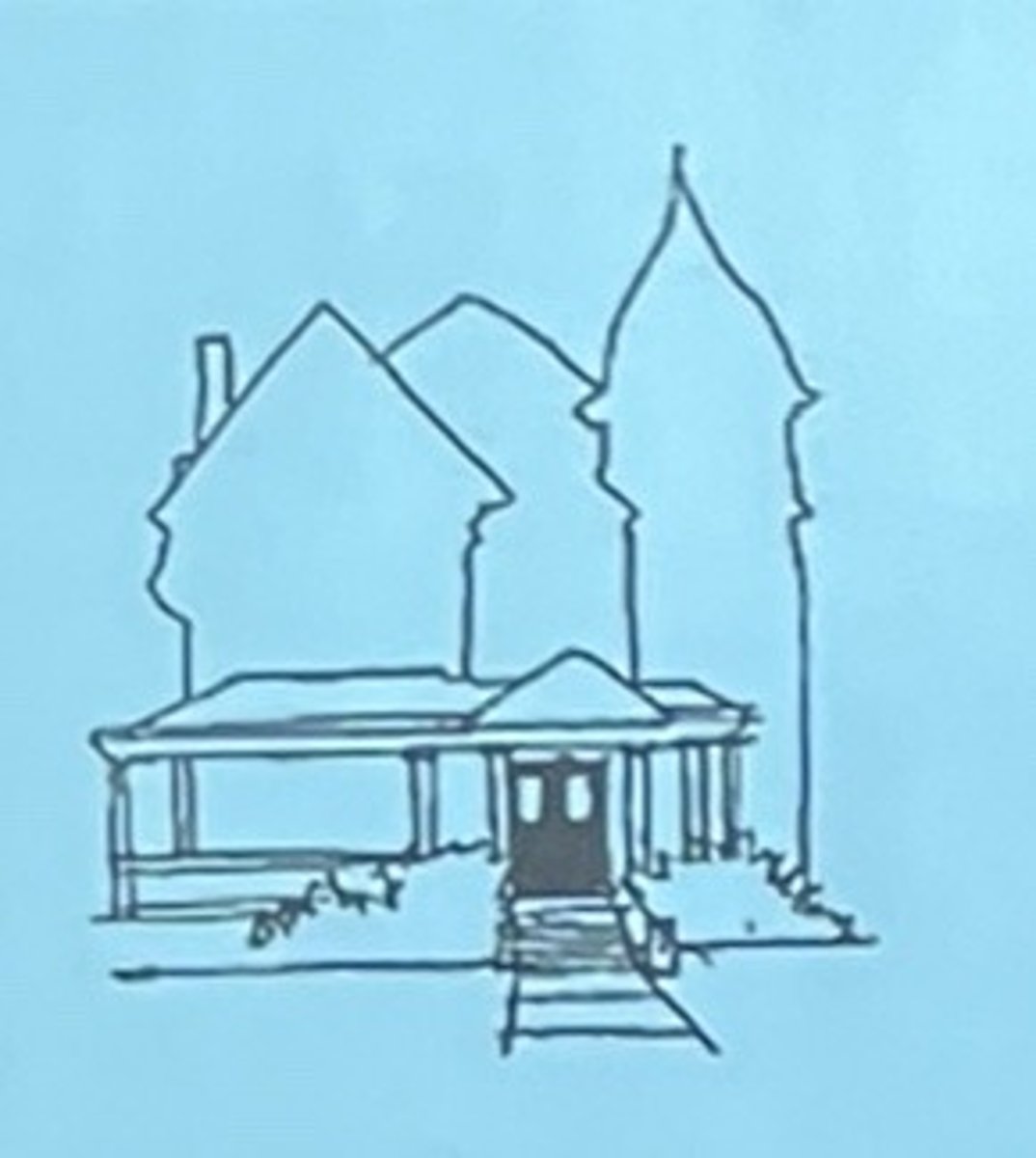

Example of a Symbolic Sketch

The relationship between solid and void creates ________________
architectural space
What is Symmetry?
designing one side of a space to mirror the opposite
What is Asymmetry?
architectural elements that are unevenly spaced in size, shape, and/or position
What is the Visual Scale?
the size or proportion a building element appears to have relative to other elements of known or assumed size
What is Proportion?
a quantified relationship among the parts of an element, as well as the relationship of that element to a whole
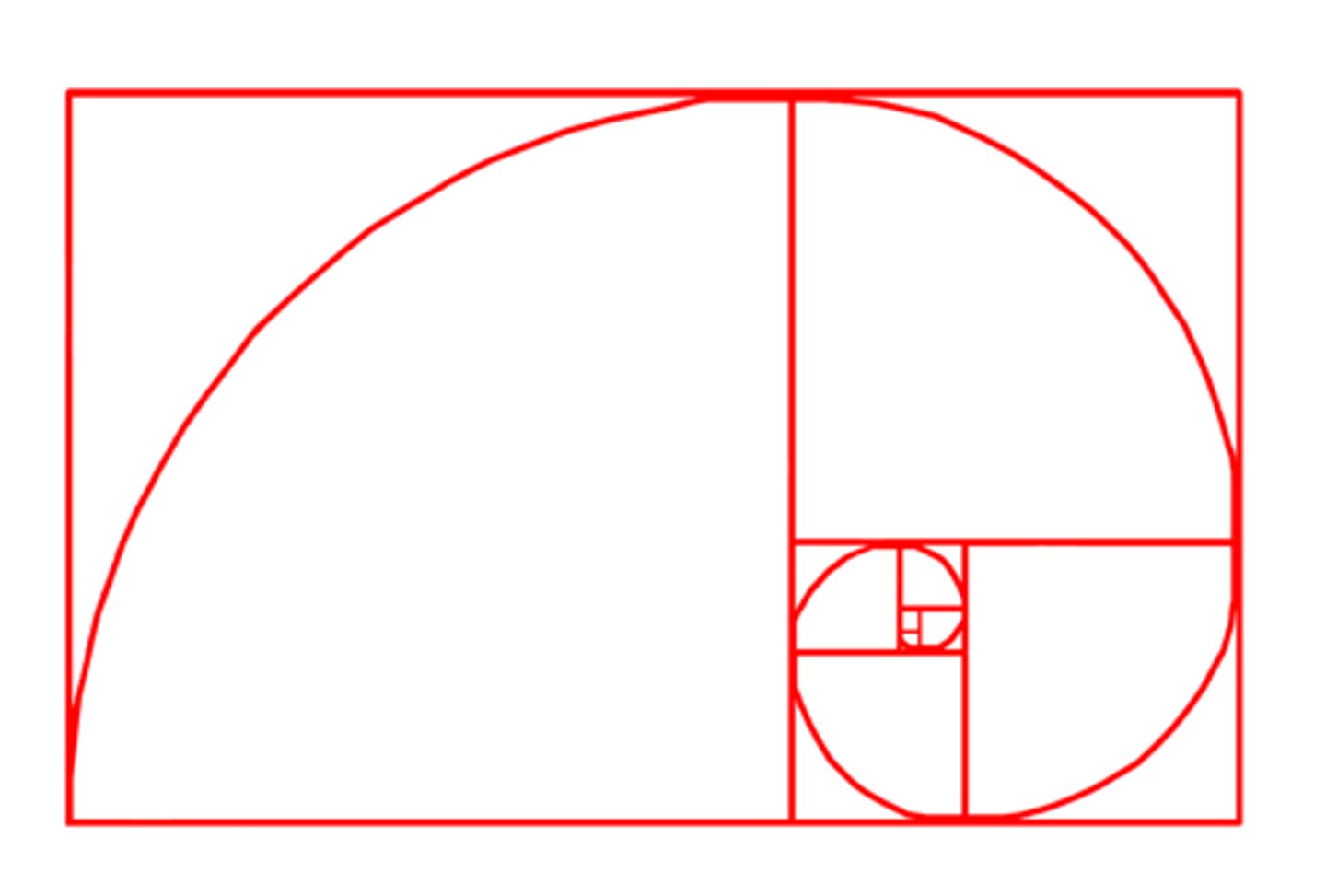
What is the Golden Section?
Known since the Greek mathematician Euclid, an irrational proportion with special mathematical and spatial relationships applicable to a wide variety of phenomena, including aesthetics, art, music, and nature:
“A line cut in such a way that the smaller section is to the greater as the greater is to the whole” approximately 8:5 or 1.6180340…
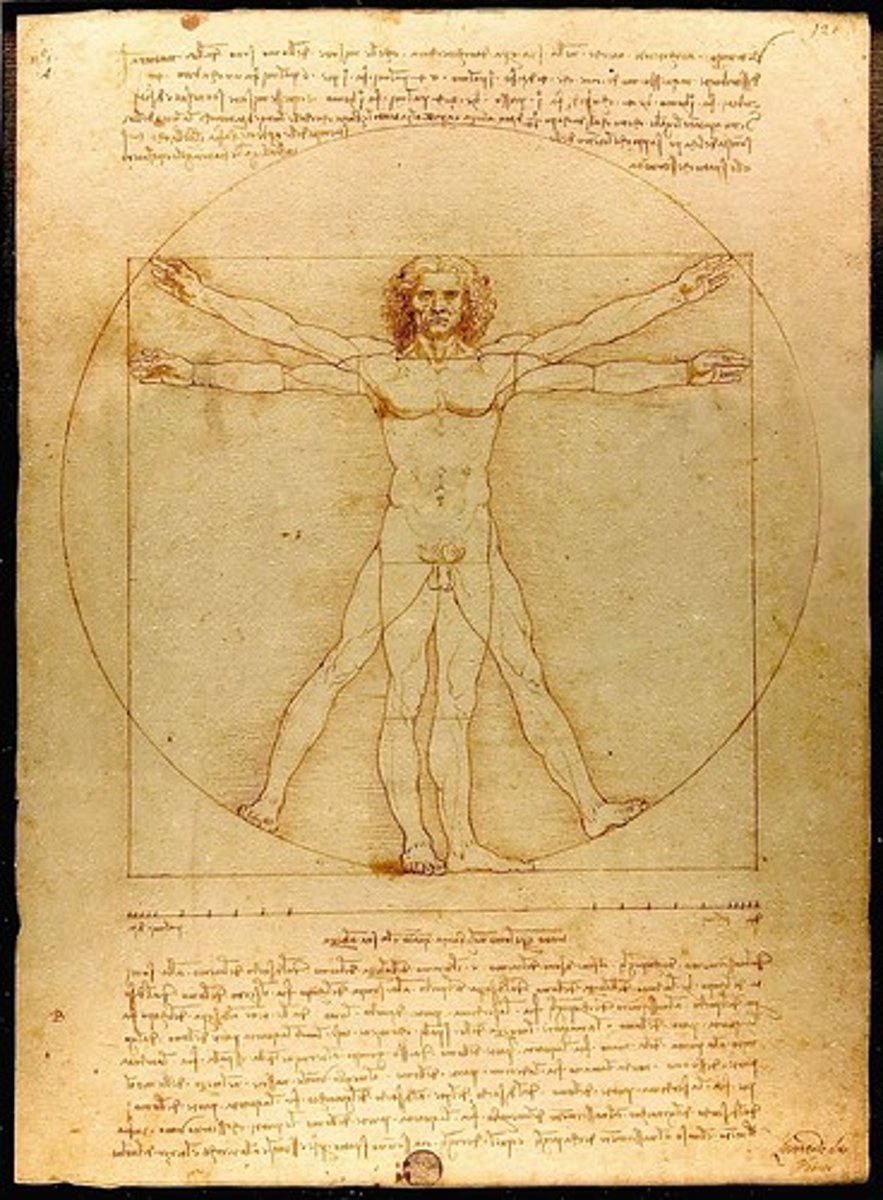
Who made the Drawing of the Body’s Balanced Proportions?
Leonardo da Vinci
What is Le Corbusier's Modular?
Le Corbusier created a series of harmonic numbers:
1. the average height of the human being
2. the height of a man with raised arms
What is Massing?
composing three-dimensional shapes or volumes into a building design
What is Style?
particular or distinctive form of artistic expression characteristic of a person, people, or period
What is a Shed Roof?
Slopes to one side
What is a Gable Roof?
Slopes to Two Sides
What is a Hipped Roof?
Sloping ends and sides that meet at a ridge
Used since the middle ages in Europe and Asia. Still widely used today
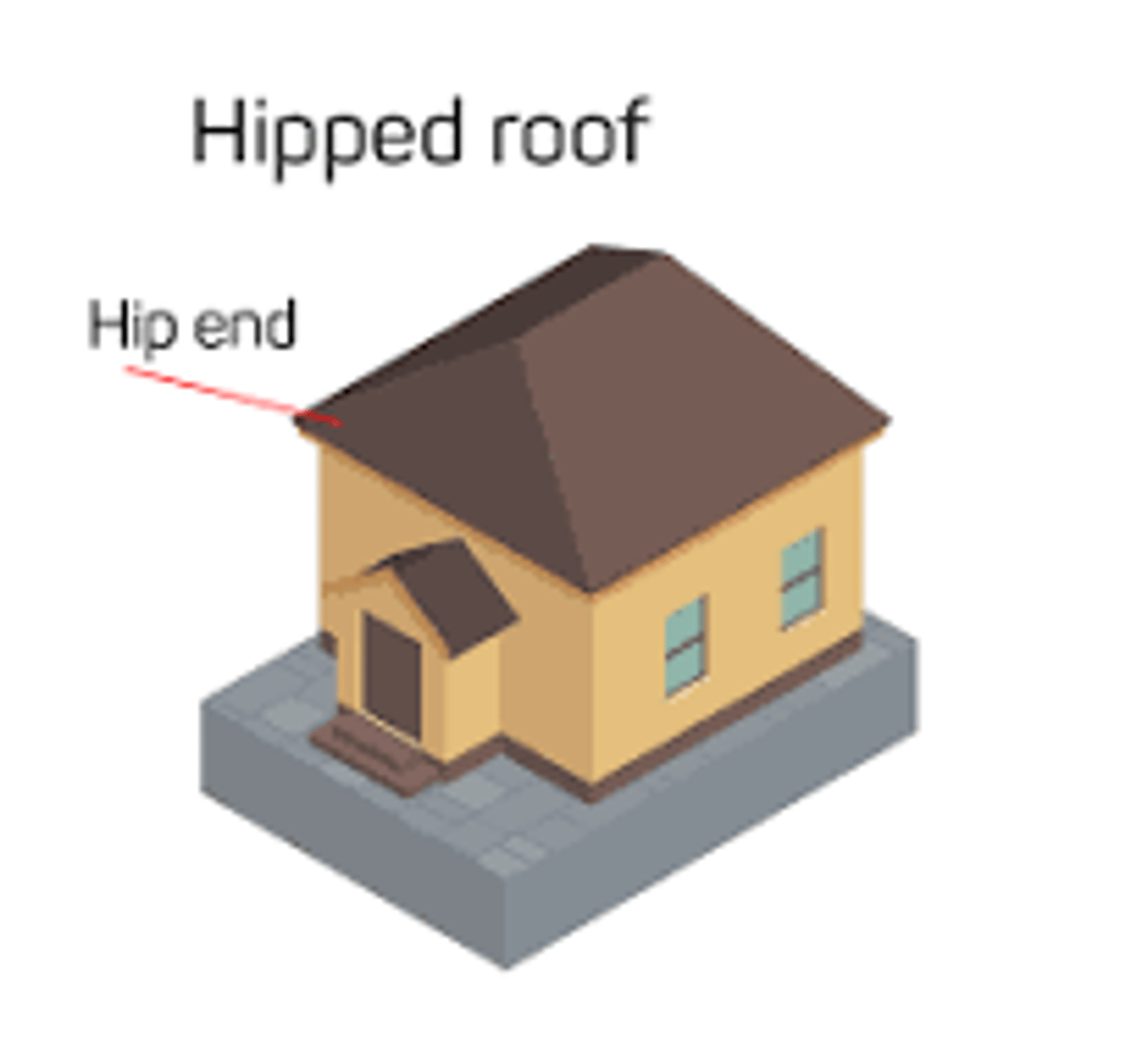
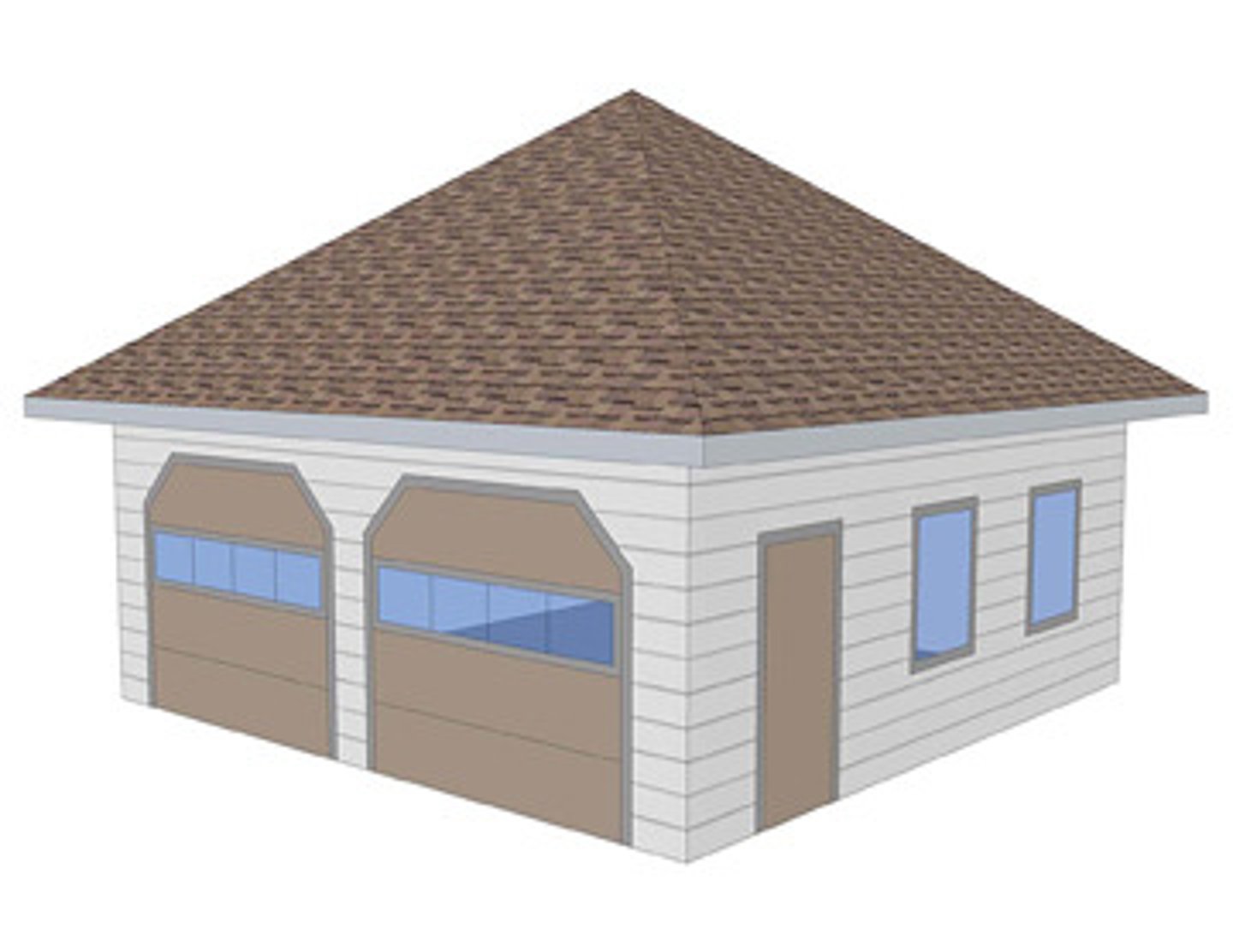
What is a Pavilion Roof?
Shaped like a pyramid and is used to cover a square structure
This roof form is used on almost every strip mall that has a clock tower

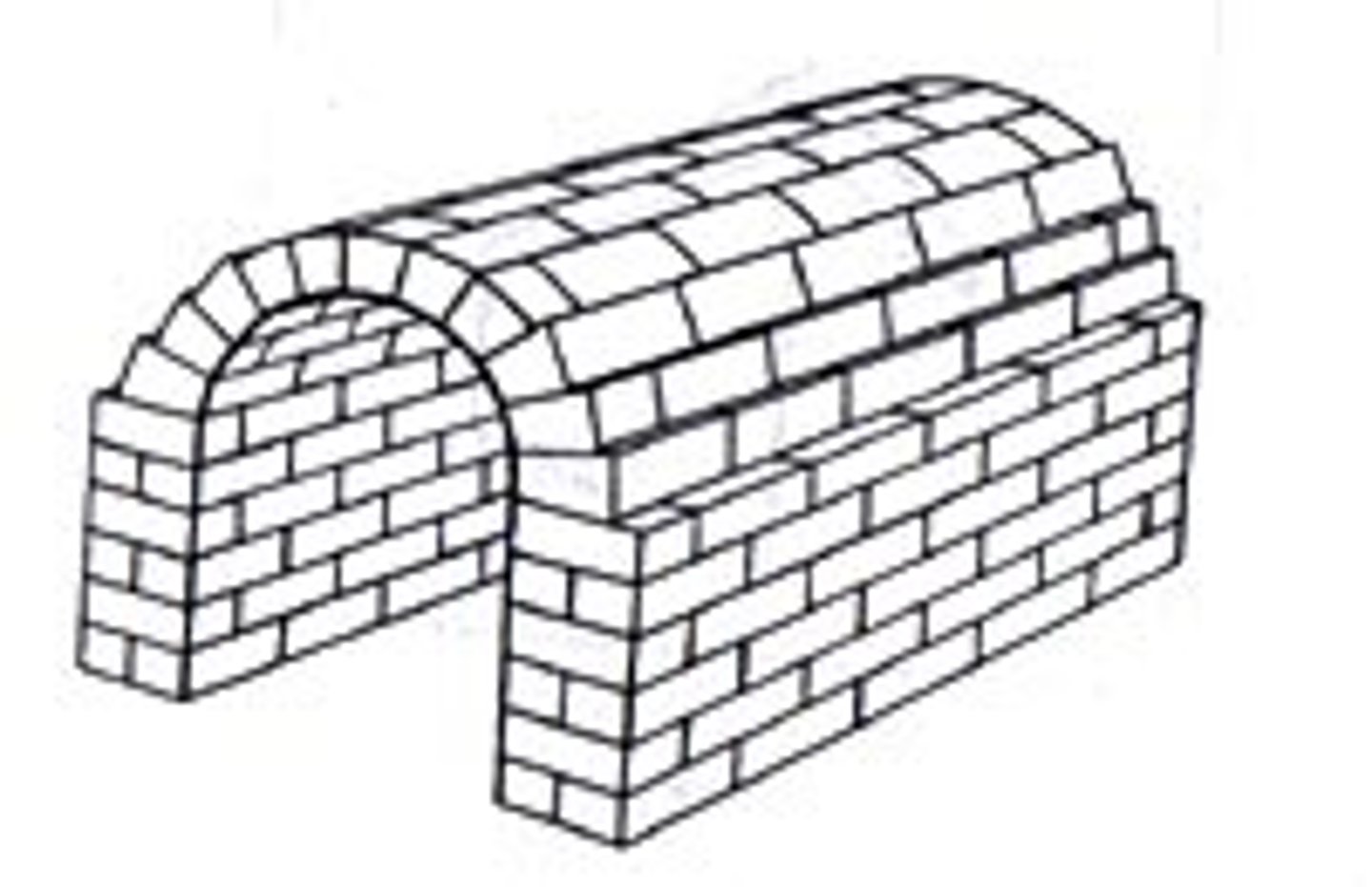
What is a Barrel Vault?
Semi-circular roof
First used by the Romans who built this form with brick or stone
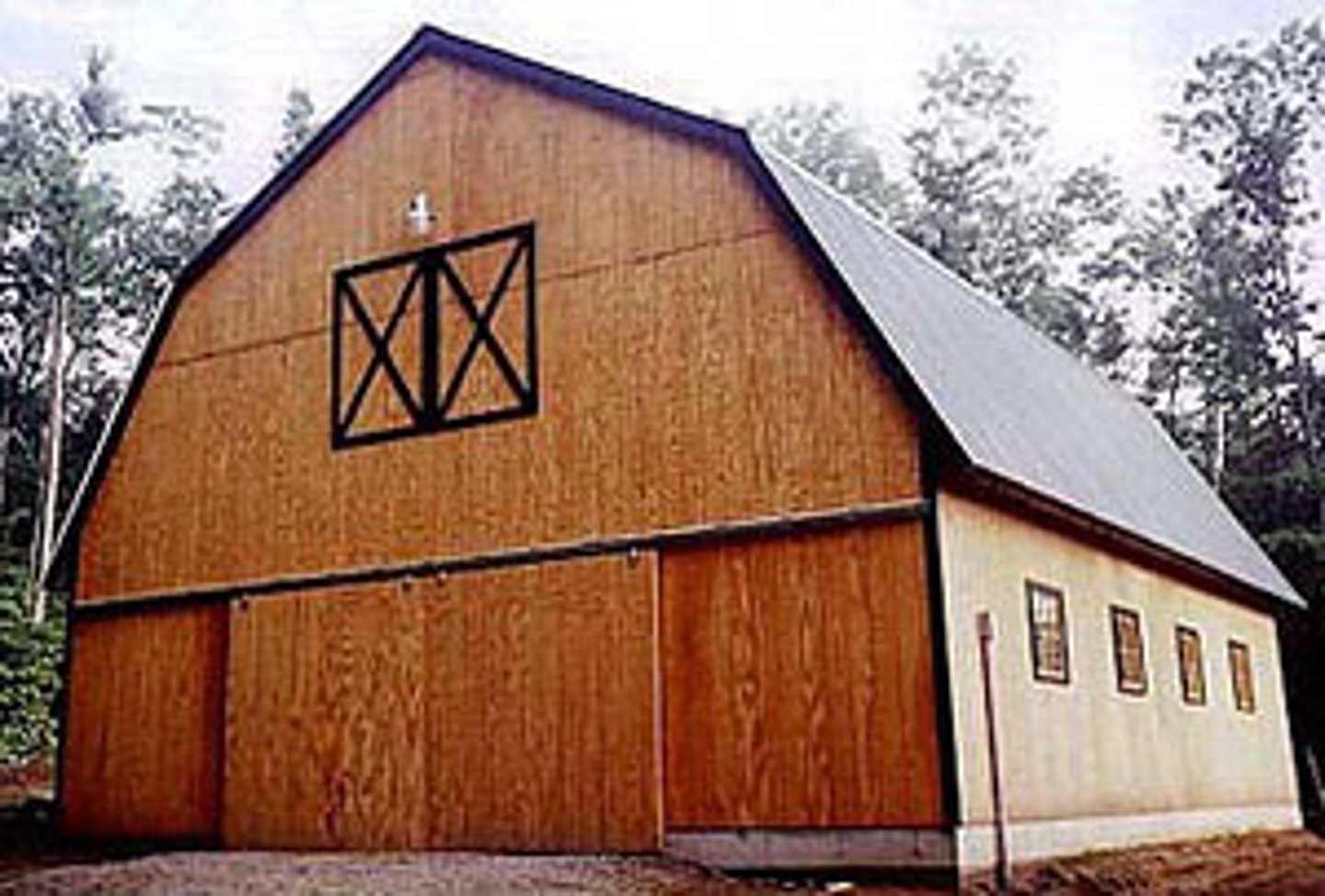
What is a Gambrel Roof?
The roof combines two different pitches
Widely used in American architecture in the 1700s. Creates more space on the top floor.

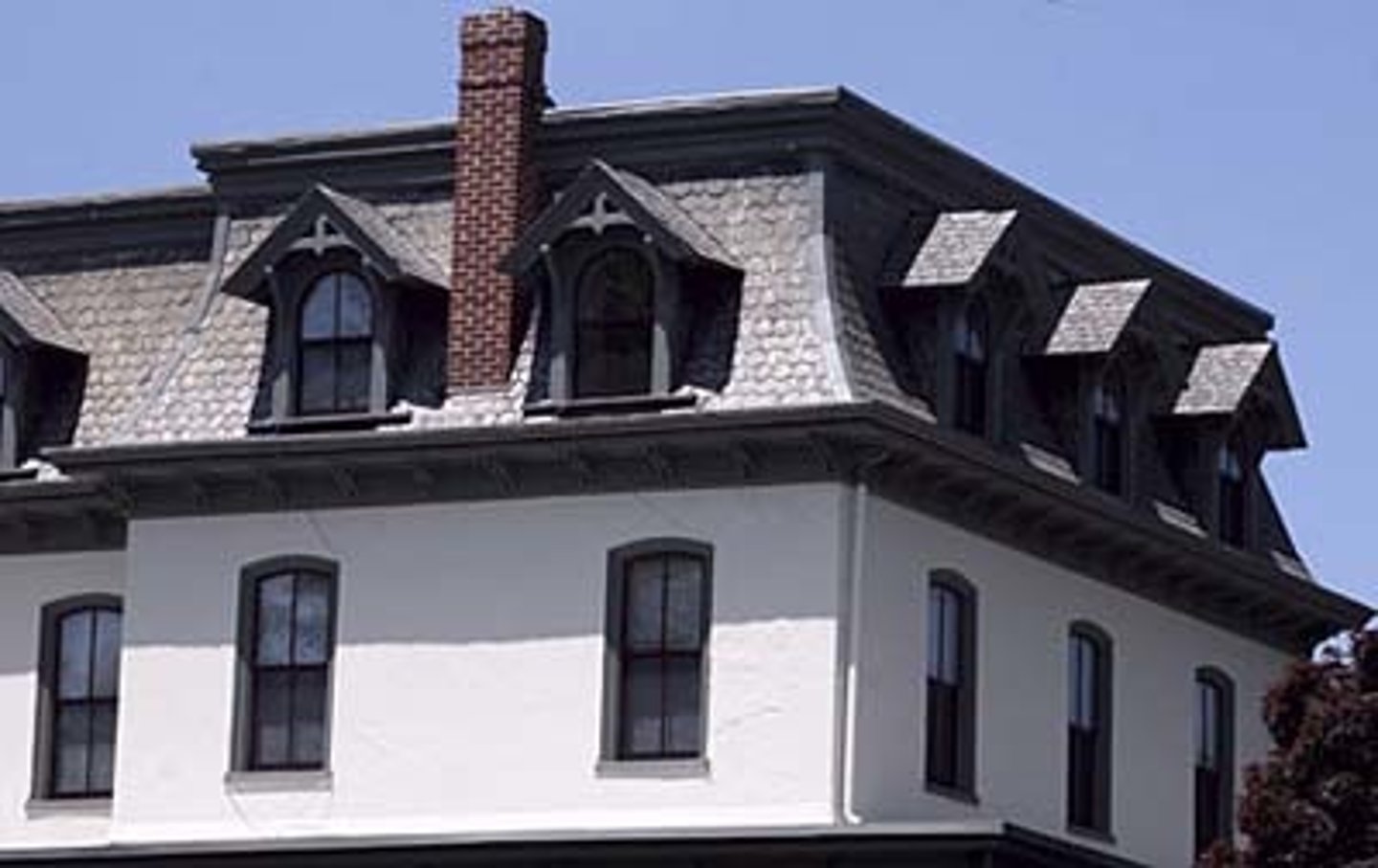
What is a Mansard Roof?
The roof combines two different pitches below the ridge. Named for French Architect Francois Mansard
Widely used by Paris architects in the 17th Century. Creates more space on the top floor

What is a Flat Roof?
- Made popular by European Architects of the 20th Century
- Widely used today
- Makes it possible to put a roof over a building that has a large plan
- Flat roofs are rarely actually flat - but have a very low slope

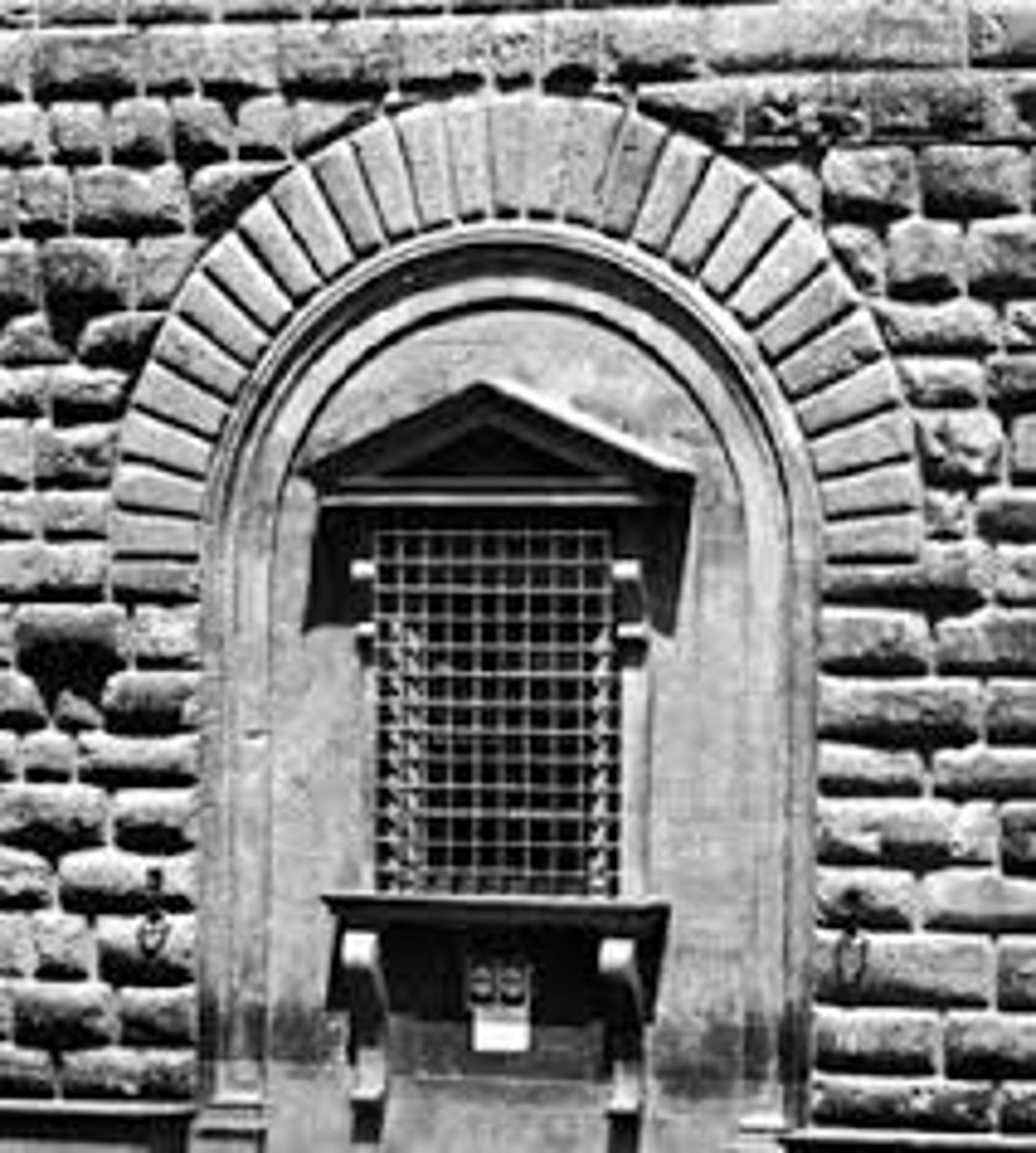
What is a Rusticated Wall?
Made of stone that is typically rough and raised off the wall surface
First used on the ground floors of Renaissance palaces to make them look impenetrable

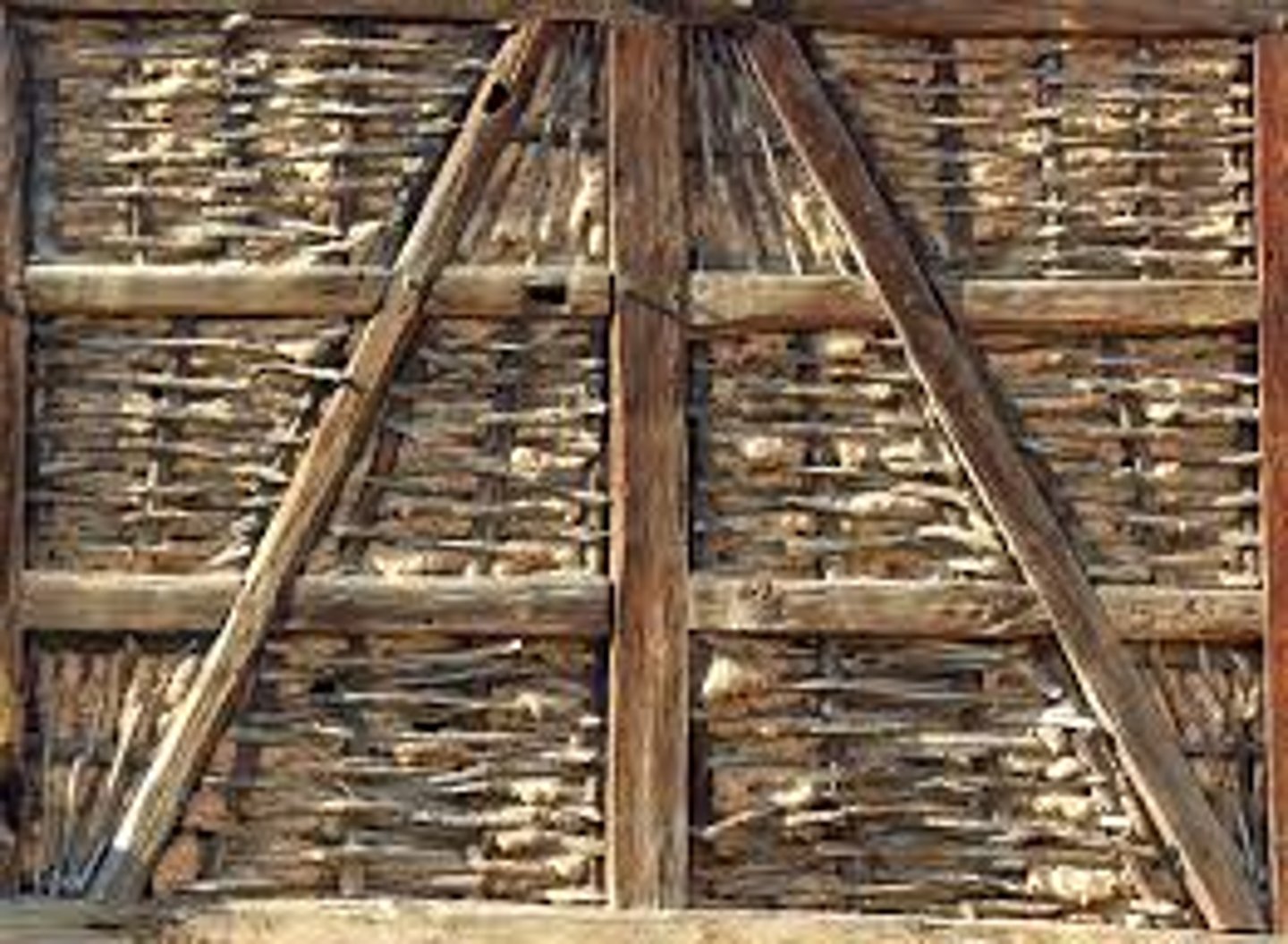
What is a Half-Timbered Wall?
Having a timber framework with the spaces filled with masonry or plaster
Common in 16th Century England. Associated with the Tudor Style

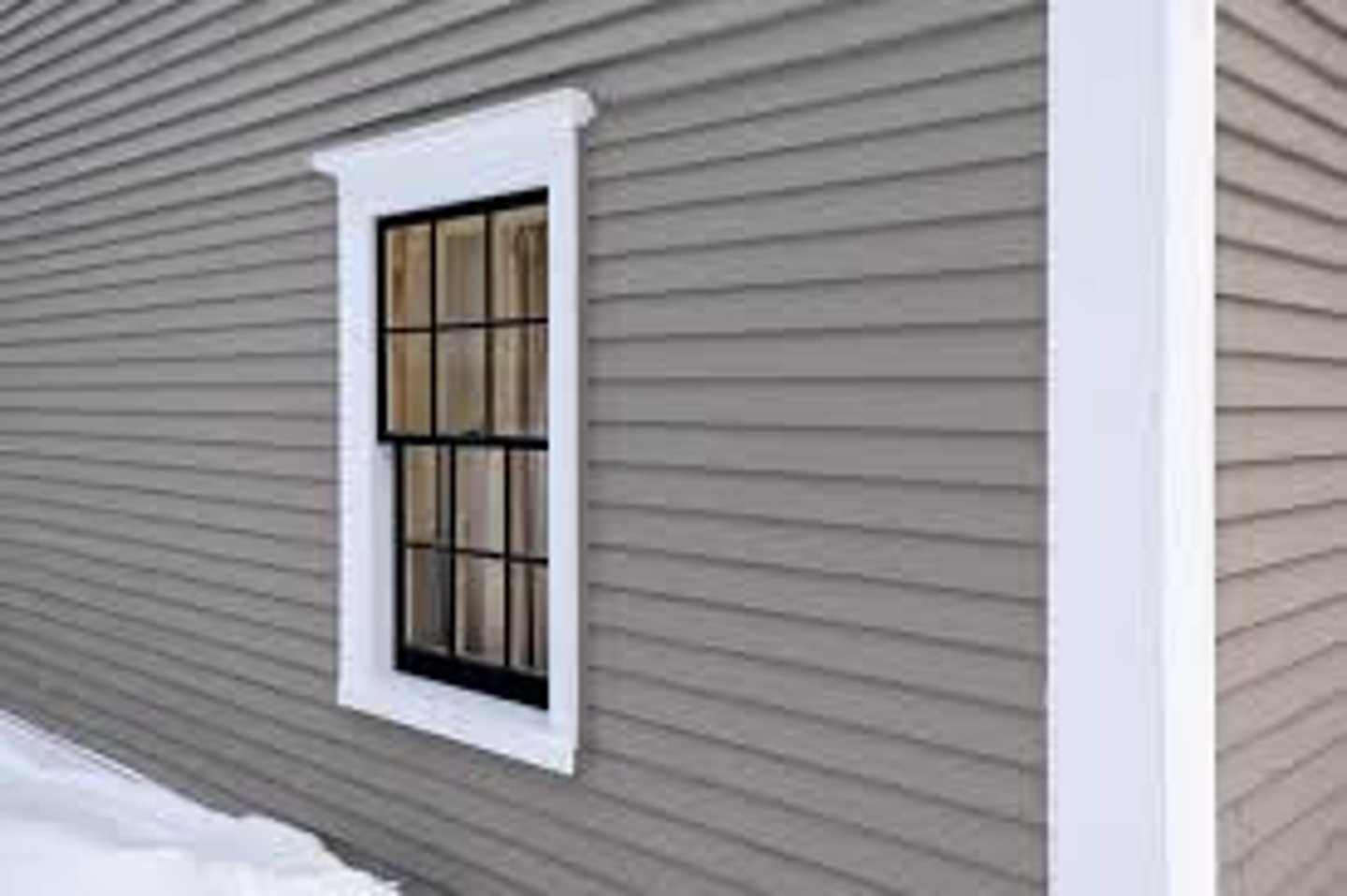
What is a Clapboard Siding Wall?
Wood siding laid horizontally
Common in the colonies 17th and 18th centuries and still common today. Associated with many styles found in the United States

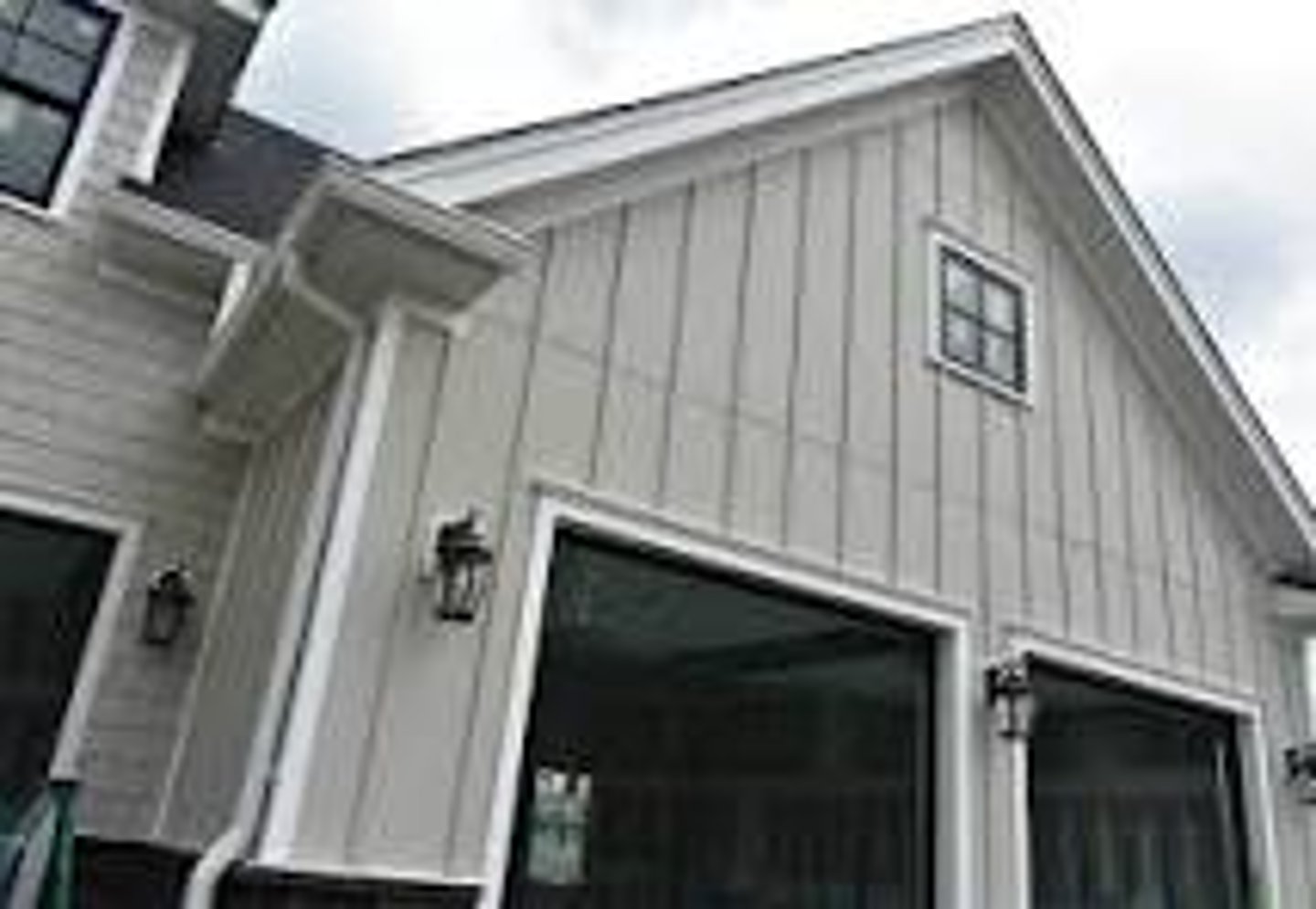
What is a Board and Batten Siding Wall?
Wood siding laid vertically consisting of wide boards and narrow battens
Often associated with the Victorian and Craftsman styles

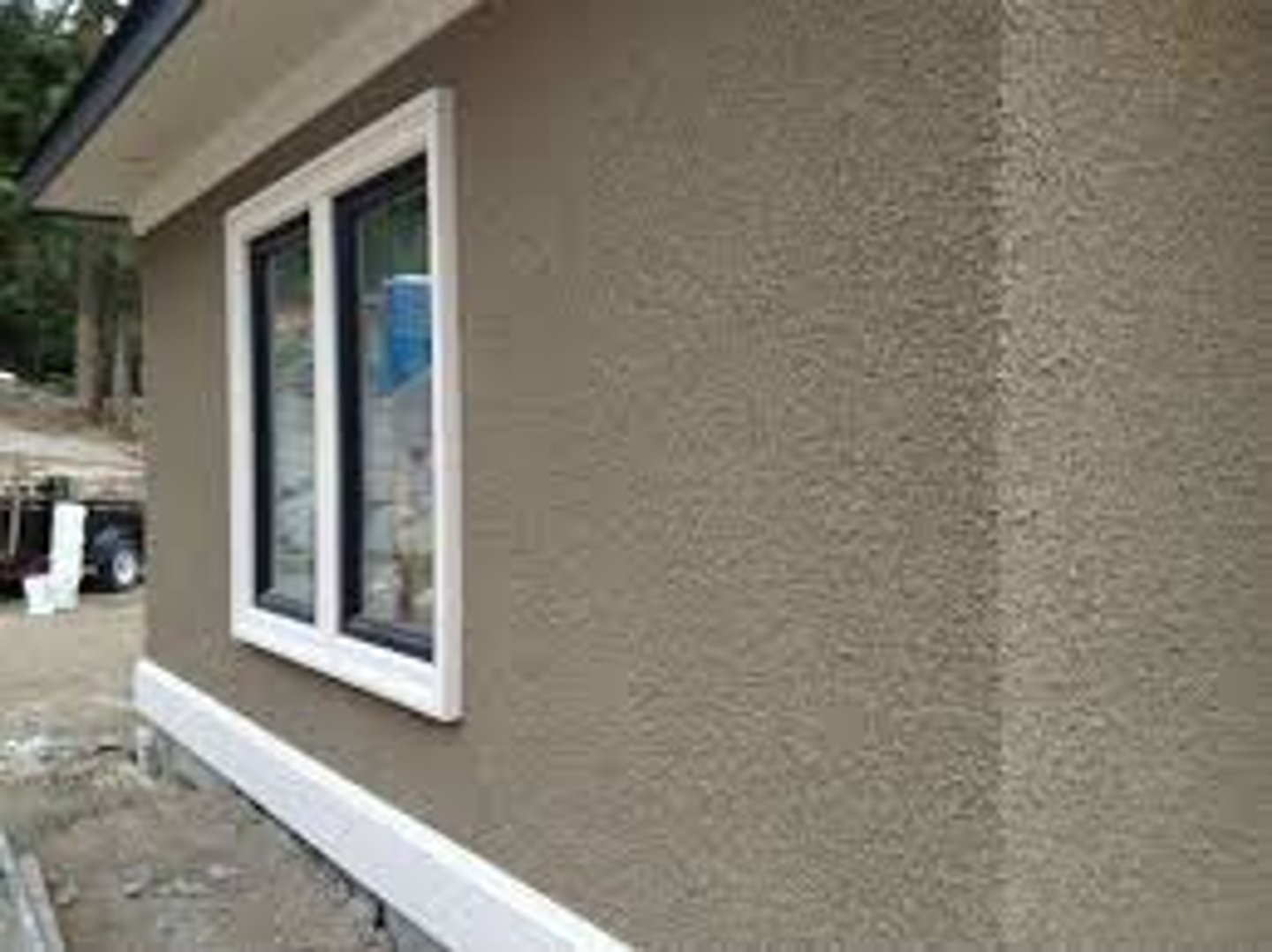
What is a Stucco Wall?
A course plaster composed of cement, sand and lime, mixed with water and used to cover exterior walls

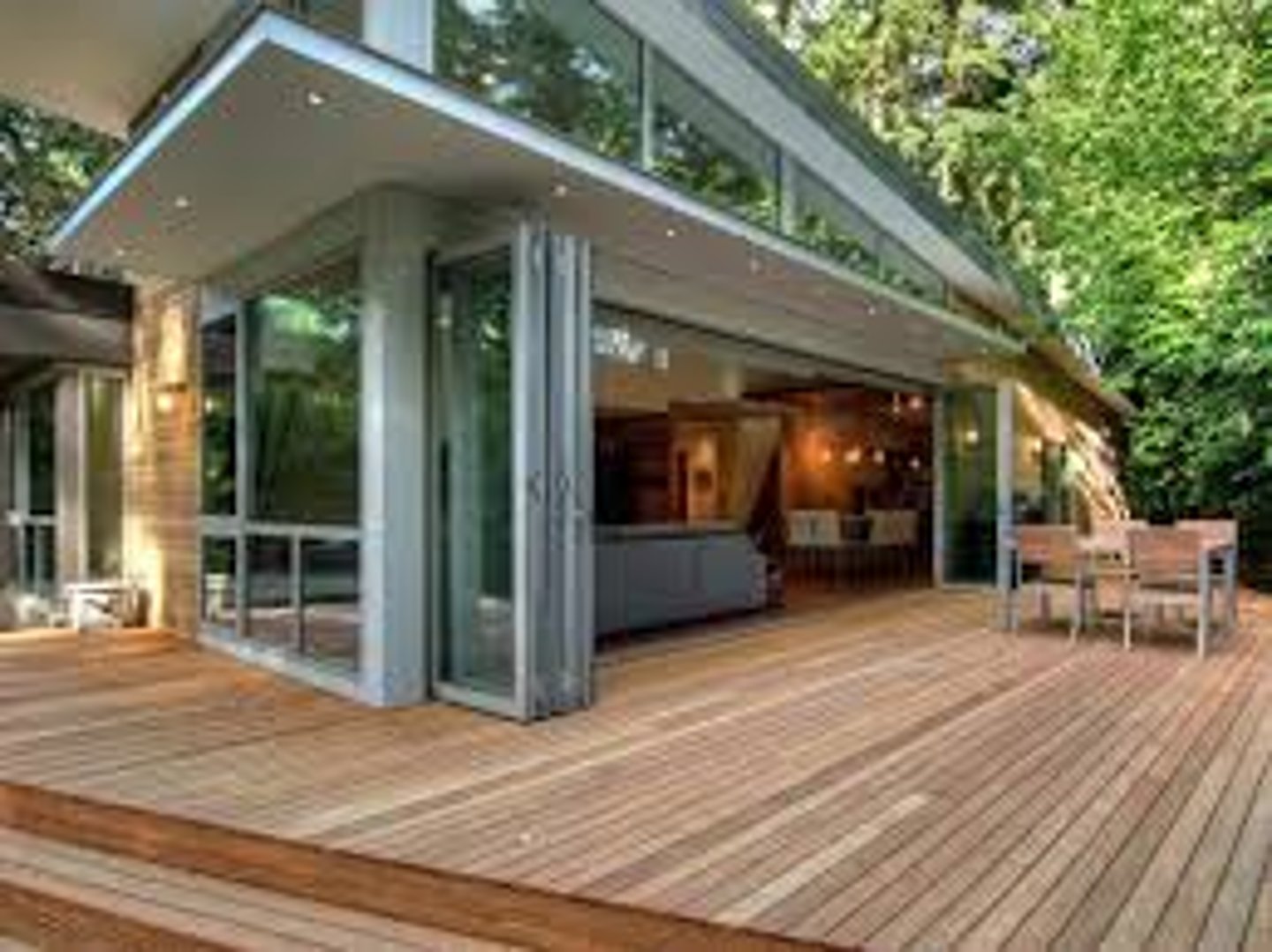
What is a Glass Wall?
- The ability to create large expanses of glass in a wall was made possible by the manufacturing improvements in the late 19th and early 20th century
- Except in the most technically sophisticated buildings, glass is not used in a structural way
- Curtain wall - a nonstructural frame and glass cladding system

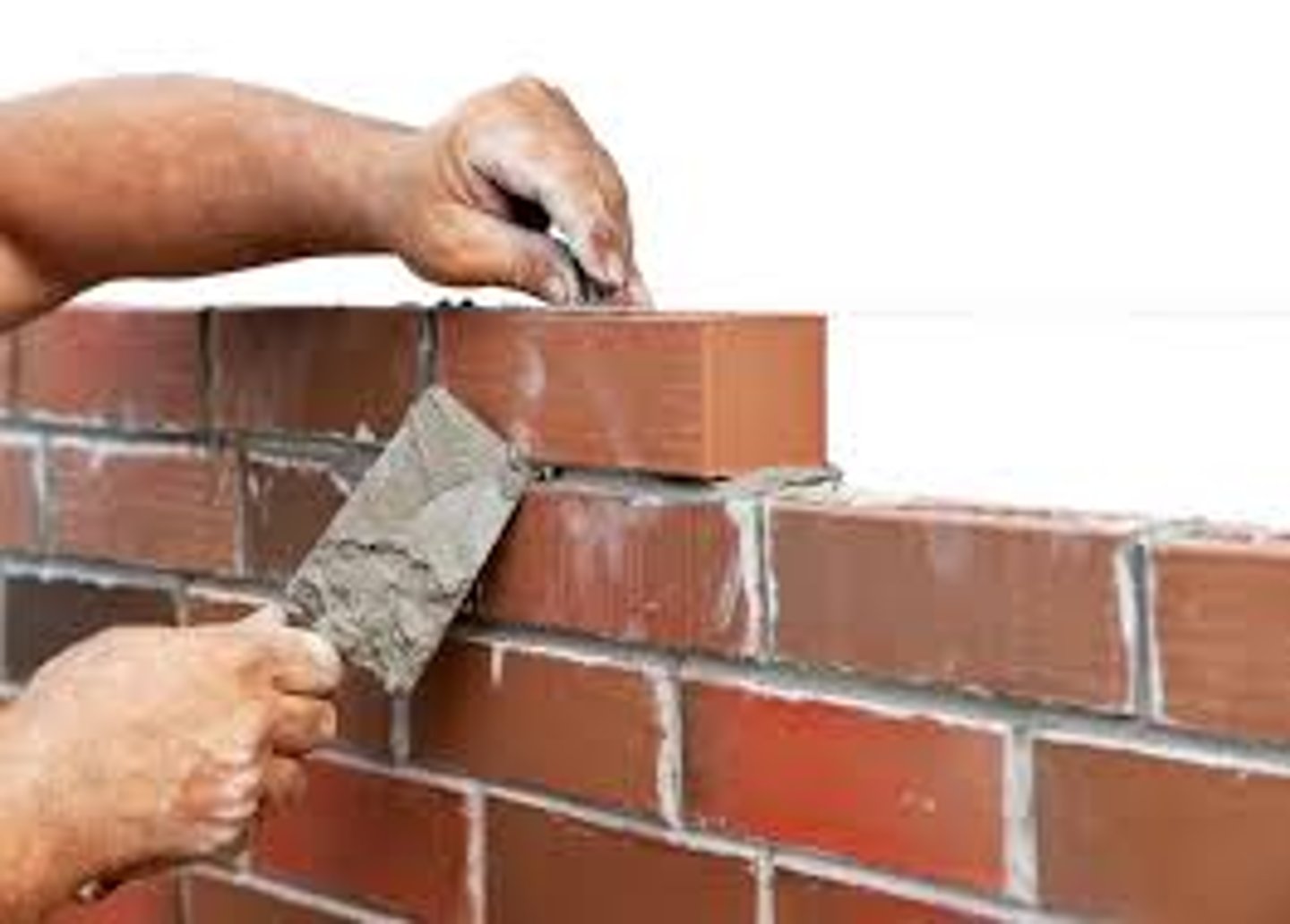
What is a Masonry Wall?
Brick / Stone / Concrete Block

What is a Concrete Wall?
Poured in place, pre-cast, and tilt up panels. You can design it however you want

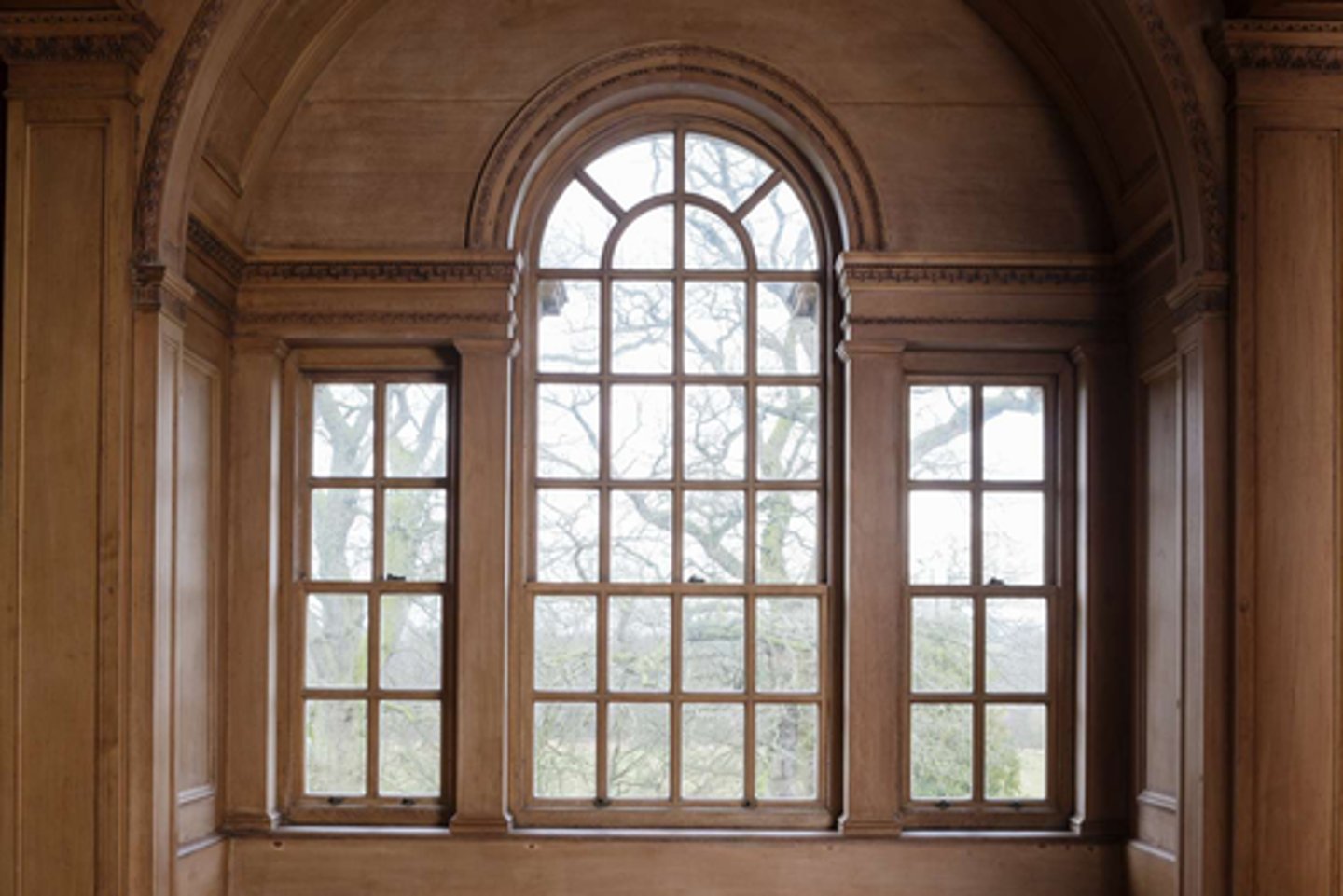
What is a Palladian Window?
A round-headed window flanked by two smaller windows

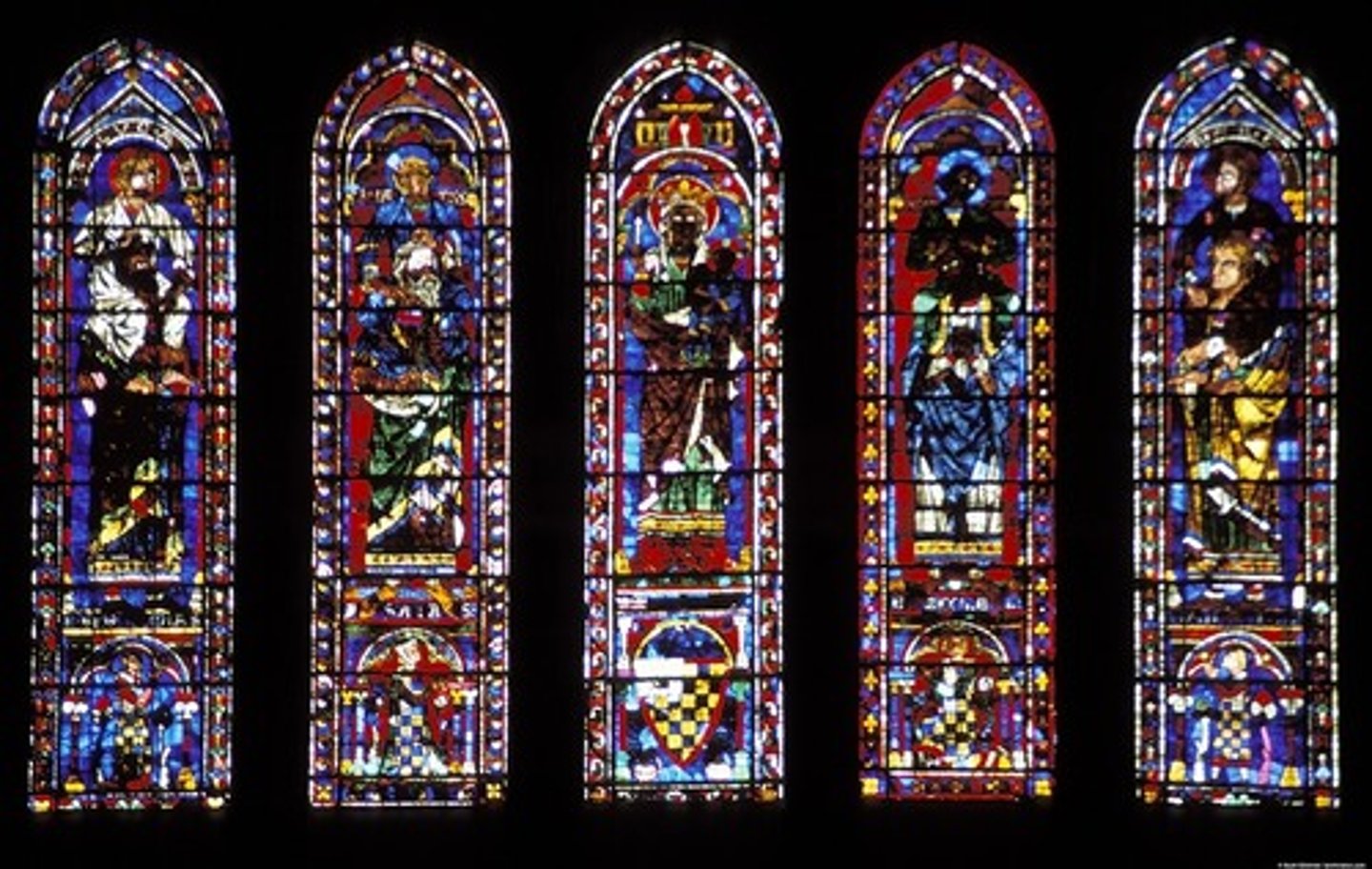
What is a Lancet Window?
Tracery - decorative stonework trefoil-cloverleaf shape with three foils quatrefoil-four foils. Popular in Gothic Structures

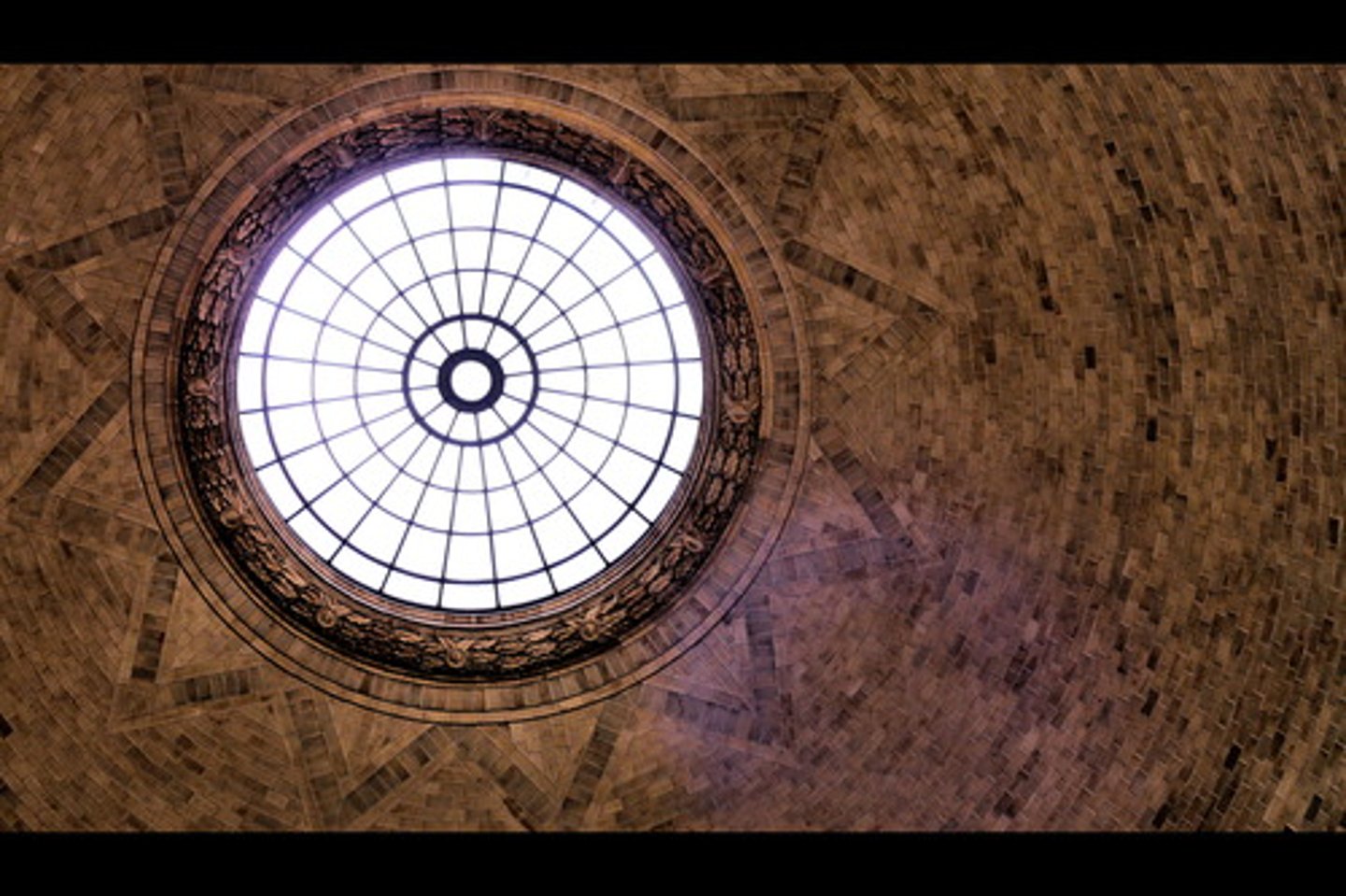
What is an Oxeye Window?
A comparatively small round or oval window used in a frieze or dormer

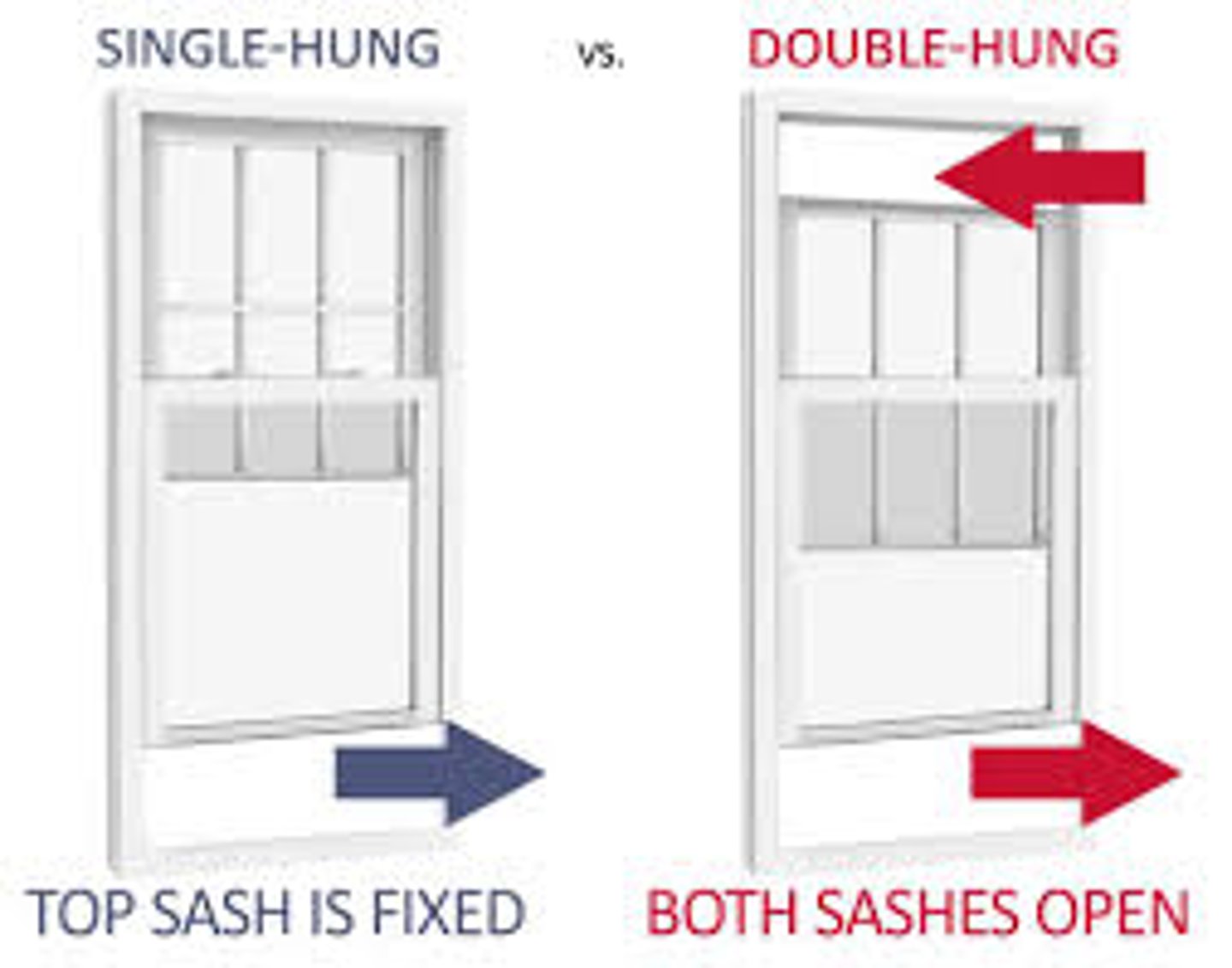
What is a Double Hung Window?
A window having two vertically hung sashes, each in separate tracks
Single hung window or triple hung window
1 over 1 / 6 over 6 / 12 over 12
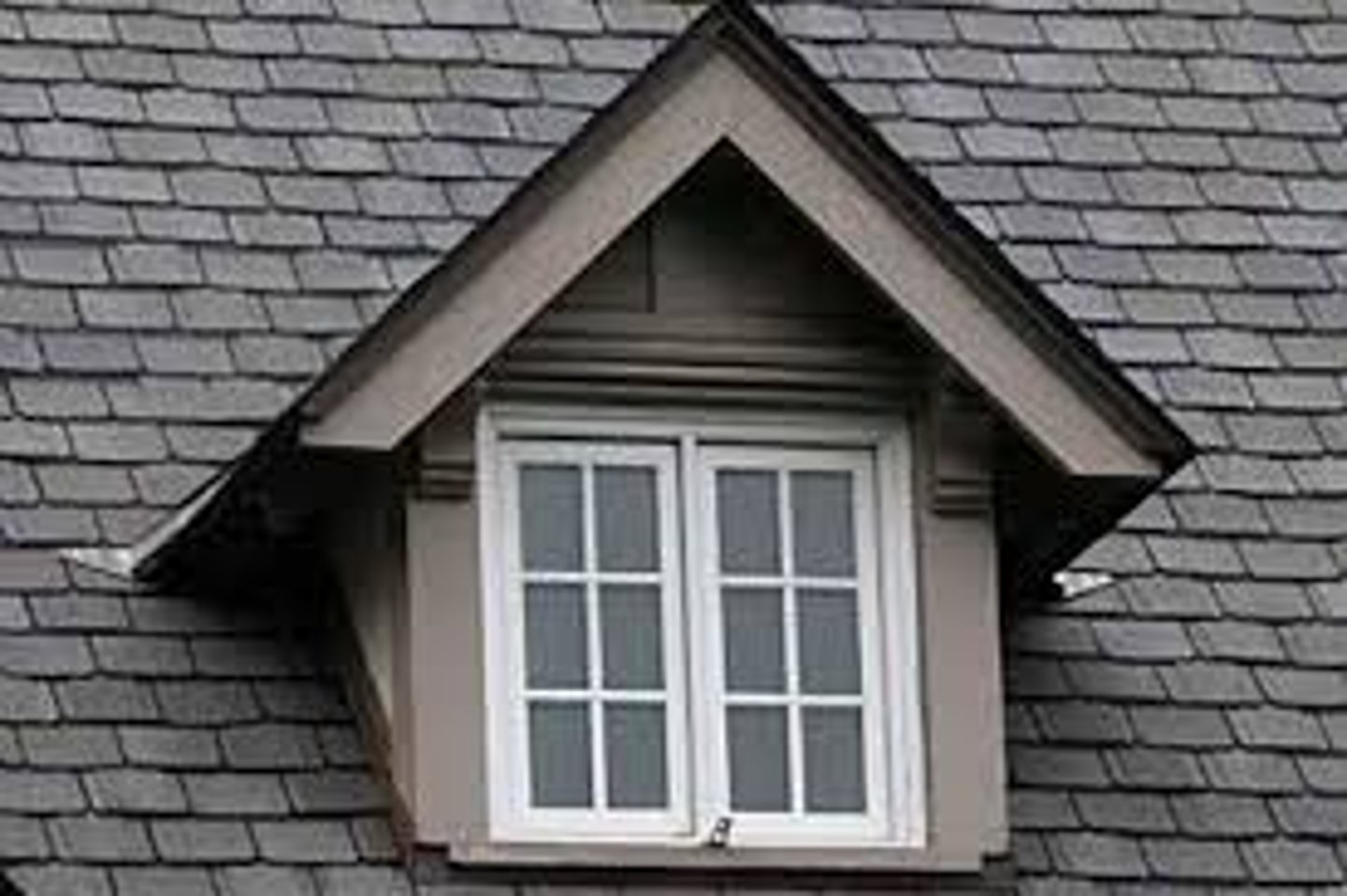
What is a Dormer Window?
A vertical window in a projection built out on a sloping roof

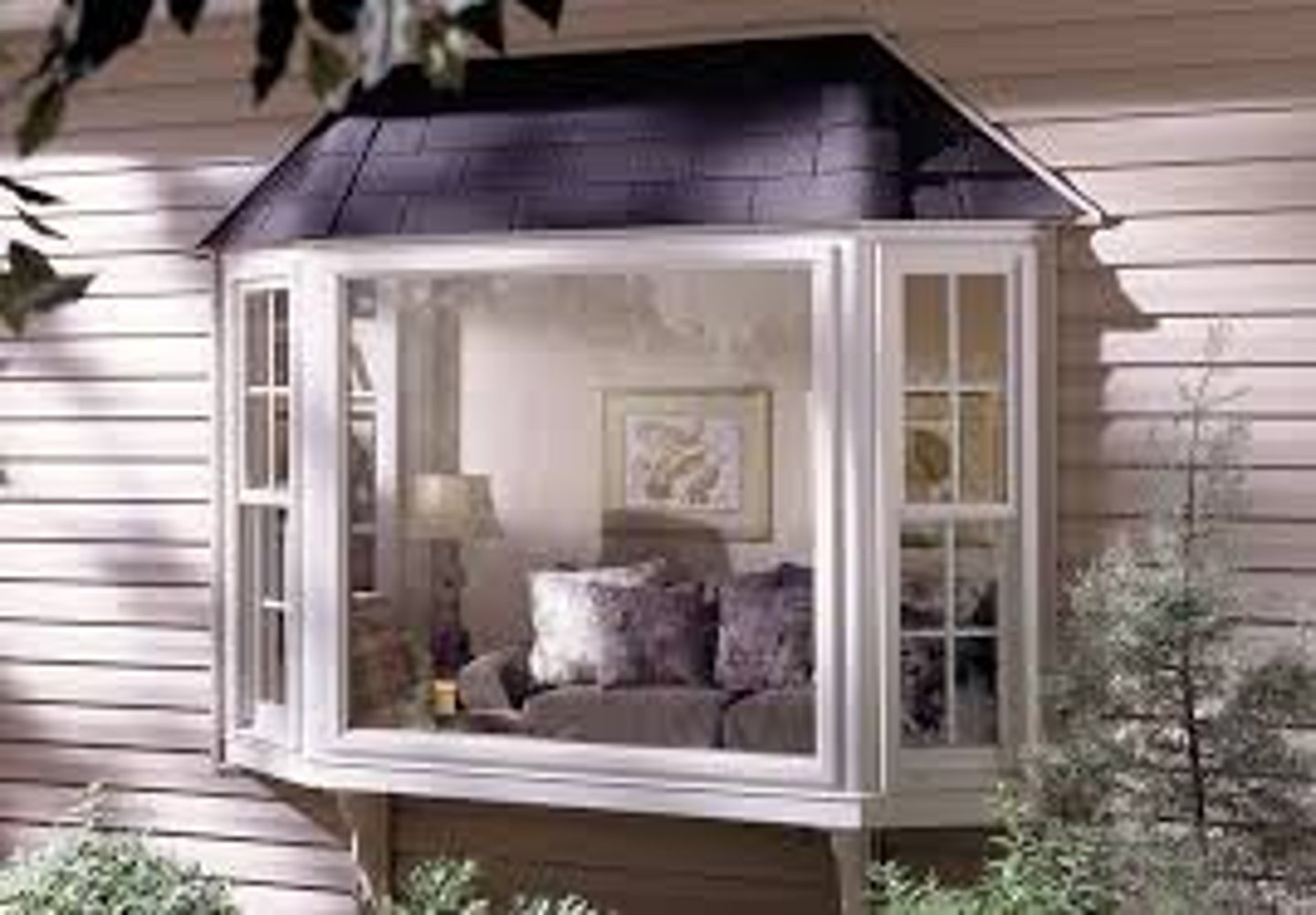
What is a Bay Window?
A window projecting from the surface of the wall to allow light from three sides
Oriel window- bay window supported by brackets
Bow window- curved bay window

What is a Ribbon Window?
Horizontal band of windows

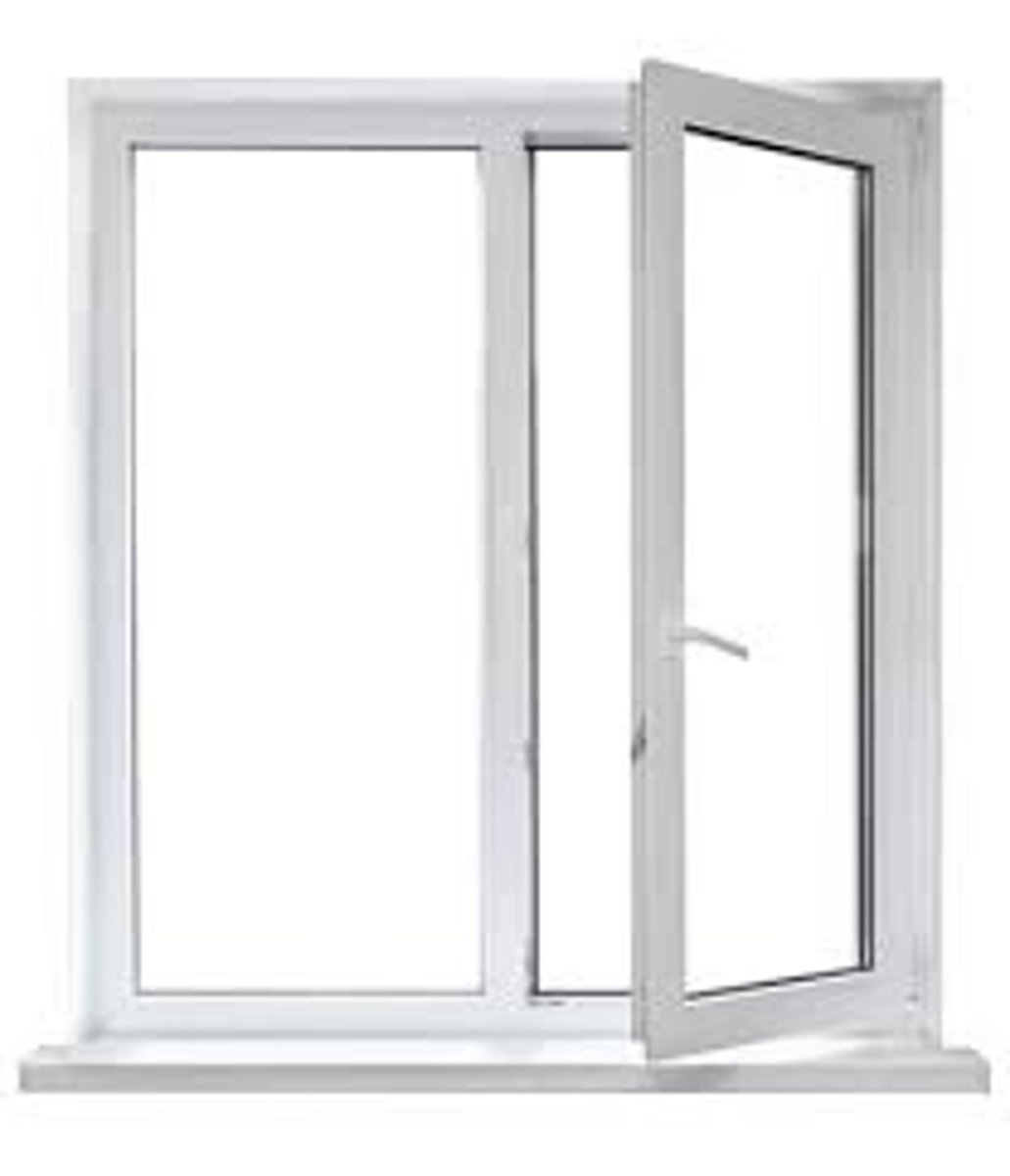
What is a Casement Window?
A window sash opening on hinges generally attached to the vertical side of the frame

What is a Transom Window?
Window above the transom of a doorway
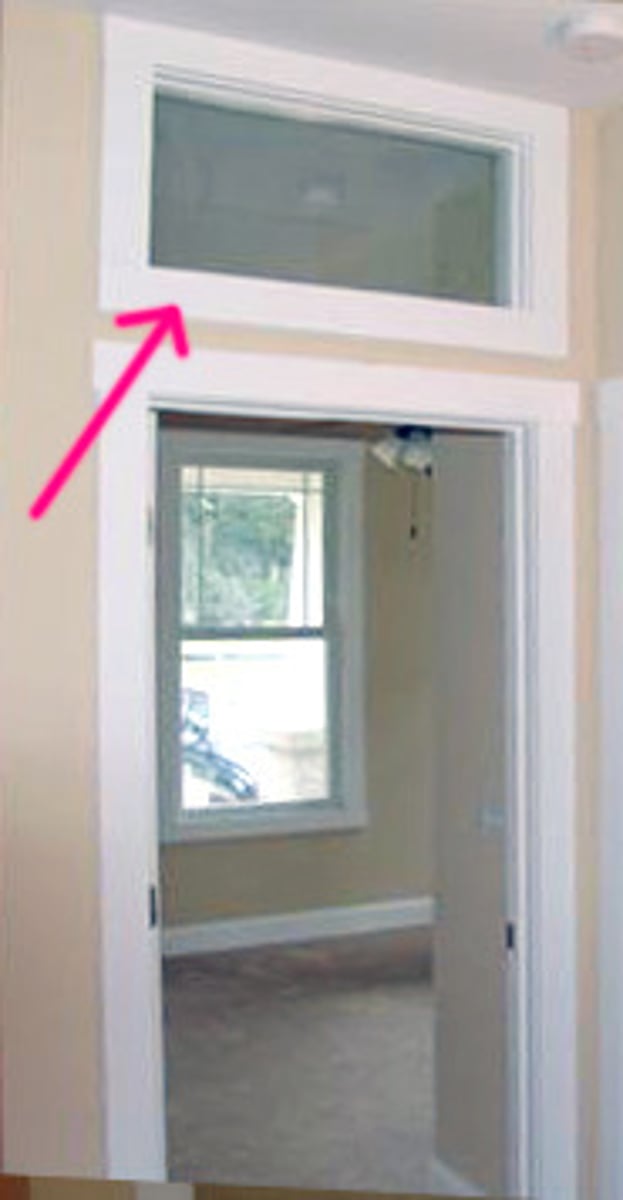

What is a Clerestory Window?
A portion of an interior rising above adjacent rooftops and having windows to admit daylight
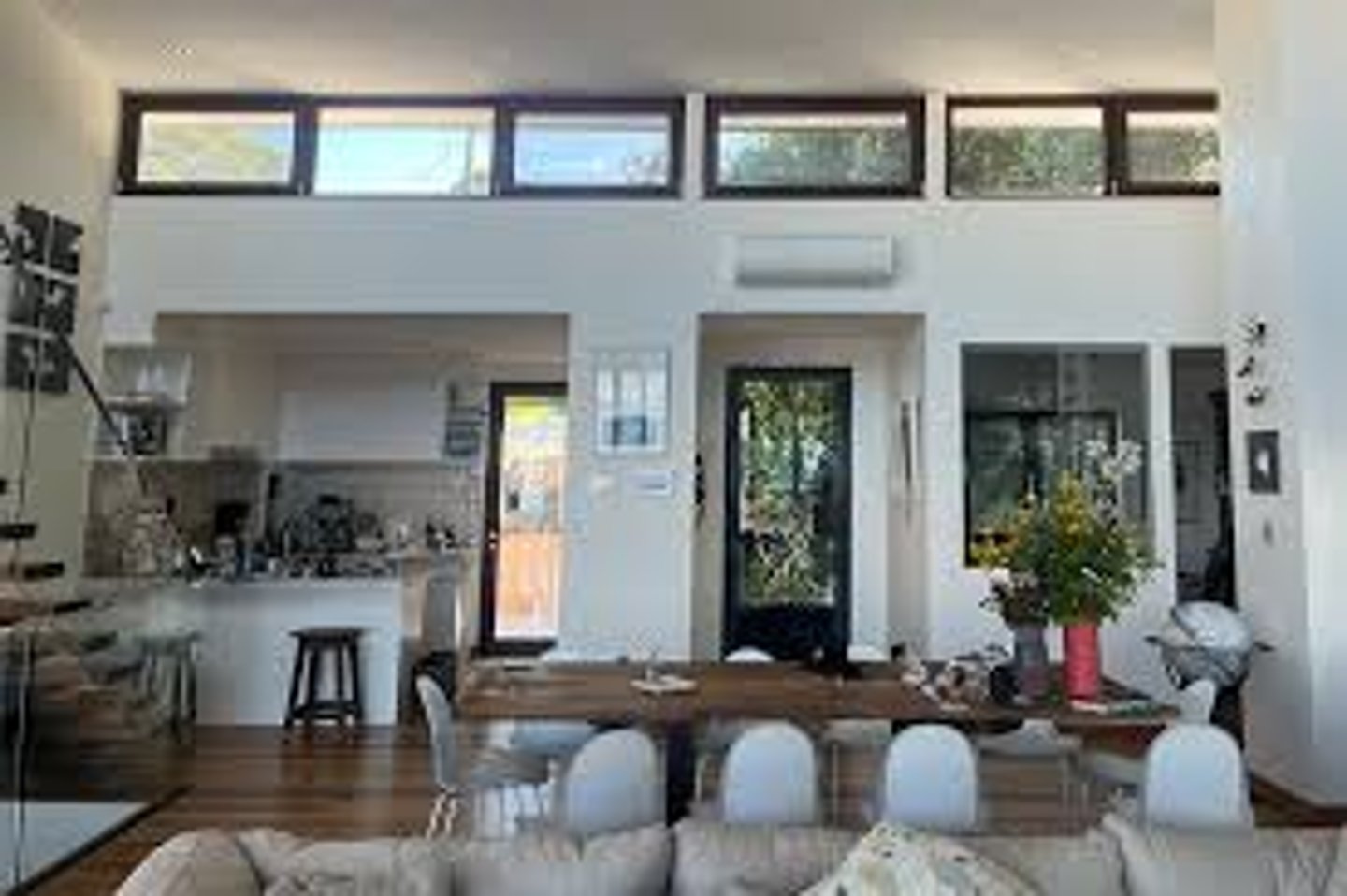

What is a Venetian Door?
A door opening, with a semicircular window (fanlight) above and flanked by vertical windows (sidelights)
Similar to a Palladian Window
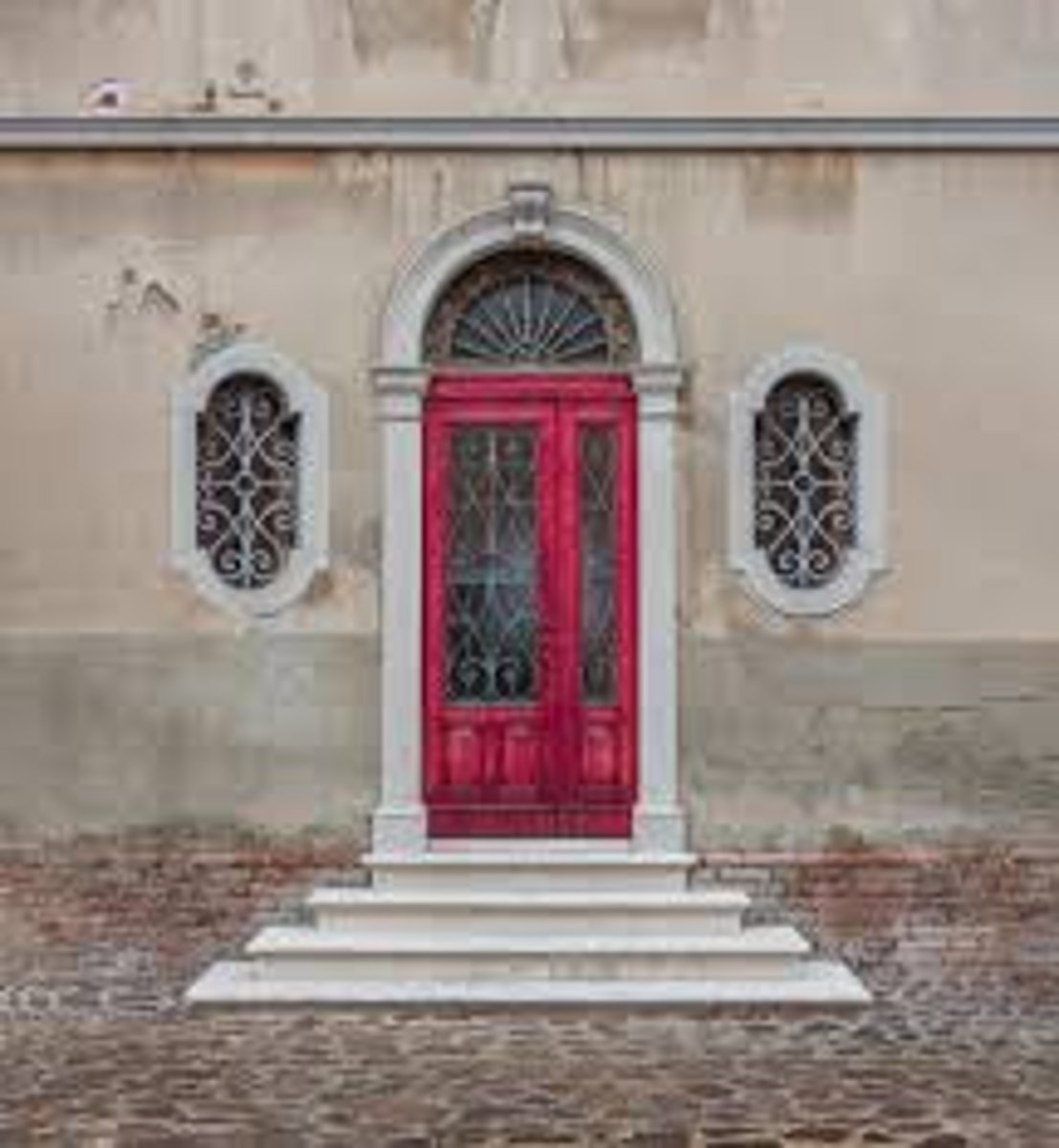

What is a French Door?
A door having rectangular glass panes extending throughout its length often hung in pairs
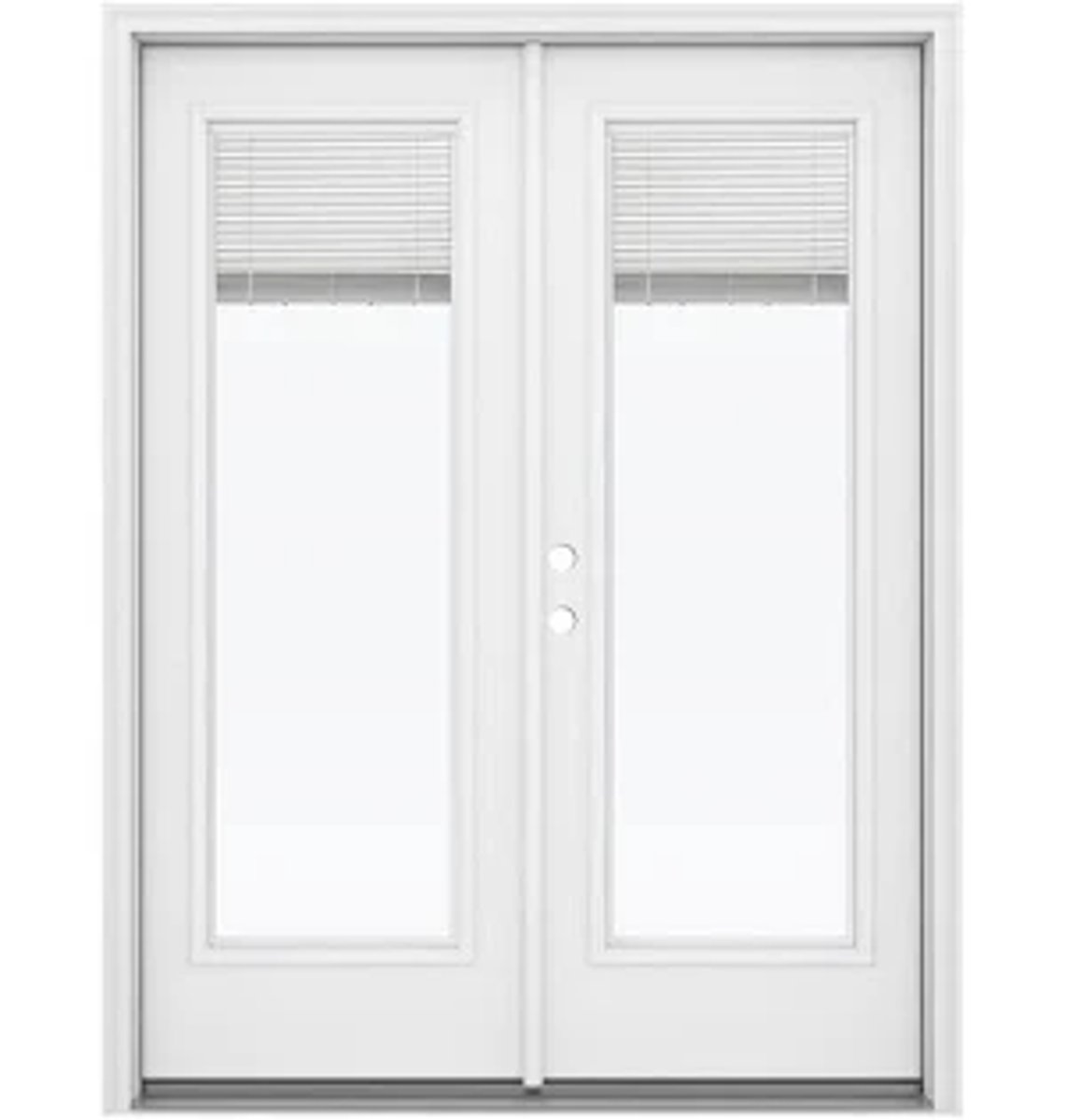

What is a Sliding Door?
A door that operates or moves by sliding on a rack
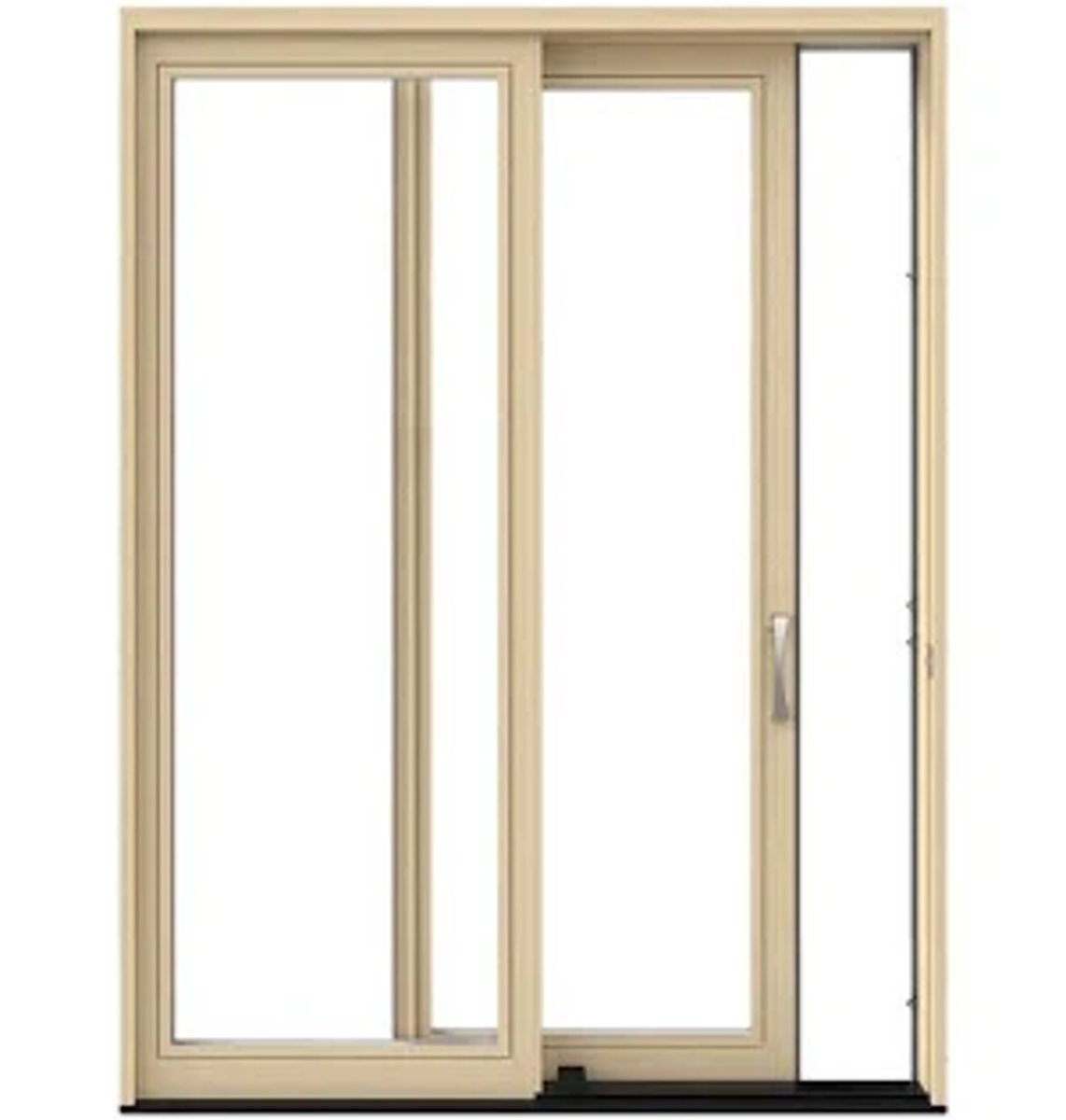

What is a Pedimented Doorway?
Pediment- a triangular shaped element historically made of stone. Modern pediments are imitated in a variety of materials
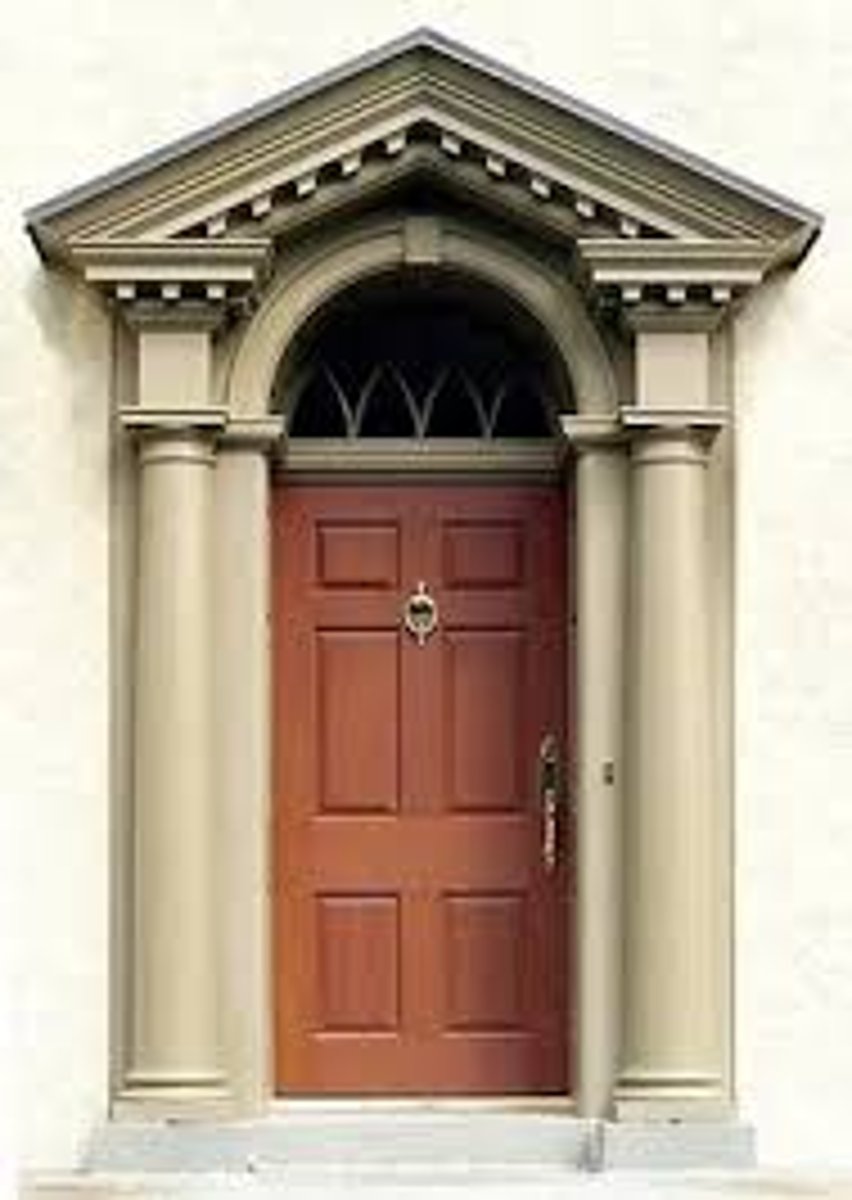

What is an Arched Doorway Associated With?
Associated with Romanesque and Gothic architecture

What is a Building Type?
An architectural form which has become accepted by society through repeated use
Examples of Building Types
1. Cathedral
2. Bank
3. Train Station
4. Palace
5. Castle
6. Skyscraper
7. Temple
8. Airport
9. Factory
What is the Building Program?
a client’s list of practical requirements for a design project
What three things are required for any architectural project?
1. Need
2. Land (site) - renovation vs new
3. Financing
What are the Steps Required to Become a Licensed Architect?
- 5 Year BARC (or 4+2 MARC or 3+ year MARC)
- Minimum 3 year internship (minimum weeks of exposure to various aspects of practice)
- Pass 6 part ARE 5.0 exam
What are the Basic Architectural Services to Earn the Fee?
- Schematic design: 15% of fee
- Design development: 25% of fee
- Construction Documents: 35% of fee
- Bidding and Contract negotiation: 5% of fee
- Construction phase: 20% of fee
What are the Three Basic Types of Drawings?
1. Orthographic
2. Axonometric
3. Perspective
What are Orthographic Drawings?
Depict and require measurements in two dimensions
Three Parts:
1. Plan
2. Section
3. Elevation
What are Axonometric Drawings?
- Axon + metron = "axis" "measure"
- Depict and require measurements in three dimensions
- "Paraline" = parallel lines in the object are depicted in drawings
- This is NOT how we perceive the world
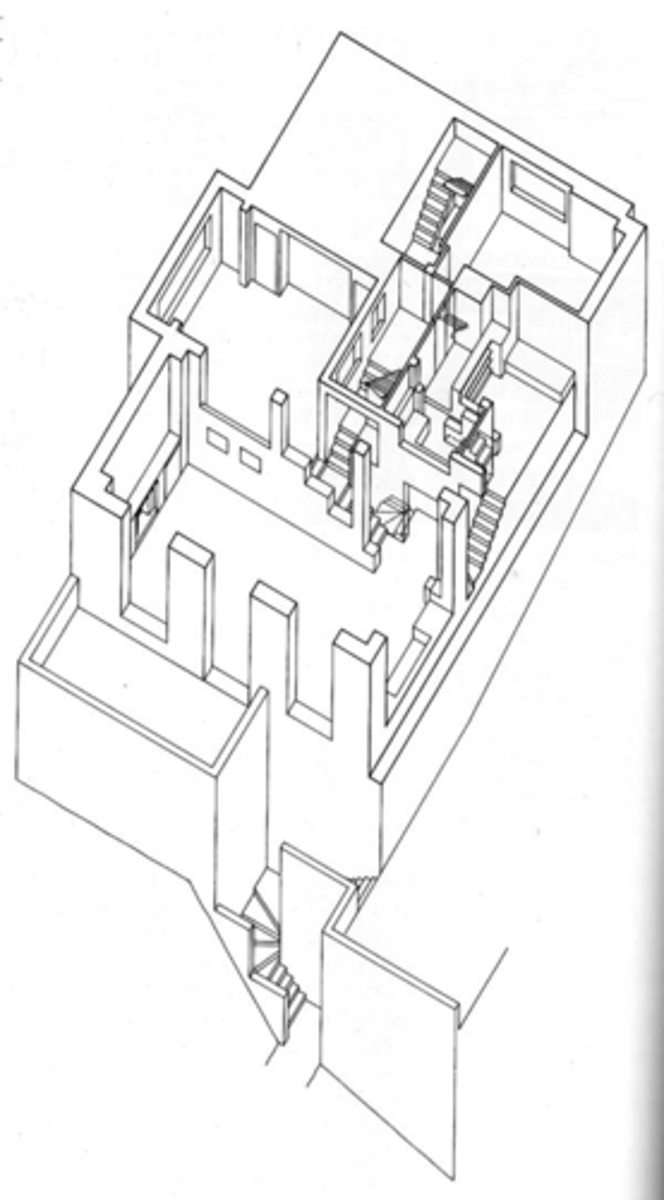
What are Perspective Drawings?
- Depict and require measurements in three dimensions (like axonometric drawings)
- "Foreshortening" = parallel lines in the object appear to recede in depth (unlike axonometric drawings)
- THIS IS HOW WE SEE IT, IT IS REALISTIC
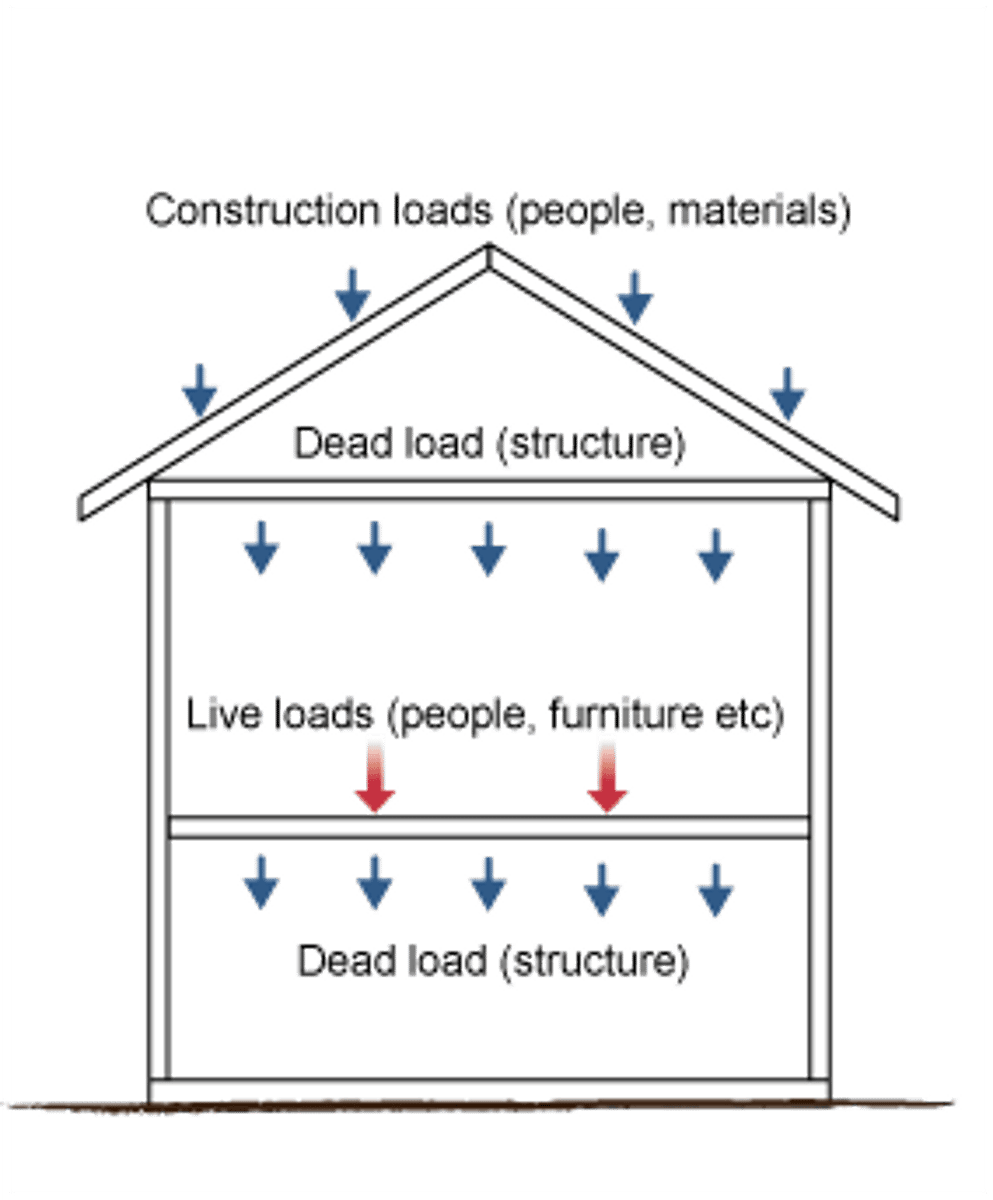
What are Live Loads?
forces from all the “movable” elements of a building (people, equipment, furniture, etc.)
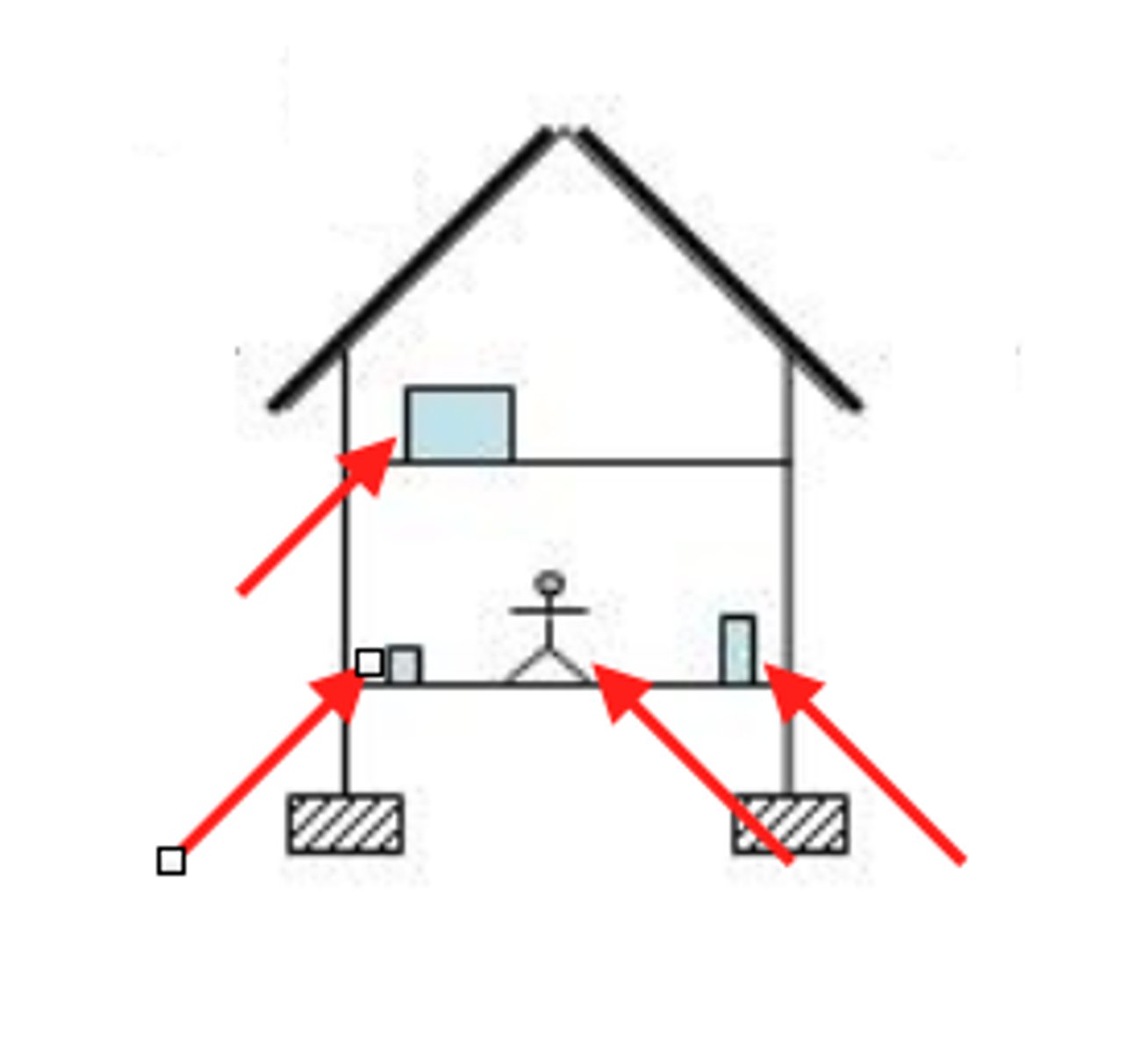
What are Dead Loads?
forces from all the “immovable” elements of a building (weight of building materials, walls, floors, built-ins, etc.)
Dynamic Loads are are applied ______
suddenly
Ex: wind, earthquakes, etc.
Static Loads are applied _______
slowly
Examples: stack of books on a table, weight of building weighing on ground, etc.
What are Stone Megaliths?
Big Rocks
Not used to make enclosure, but to mark location from great distances
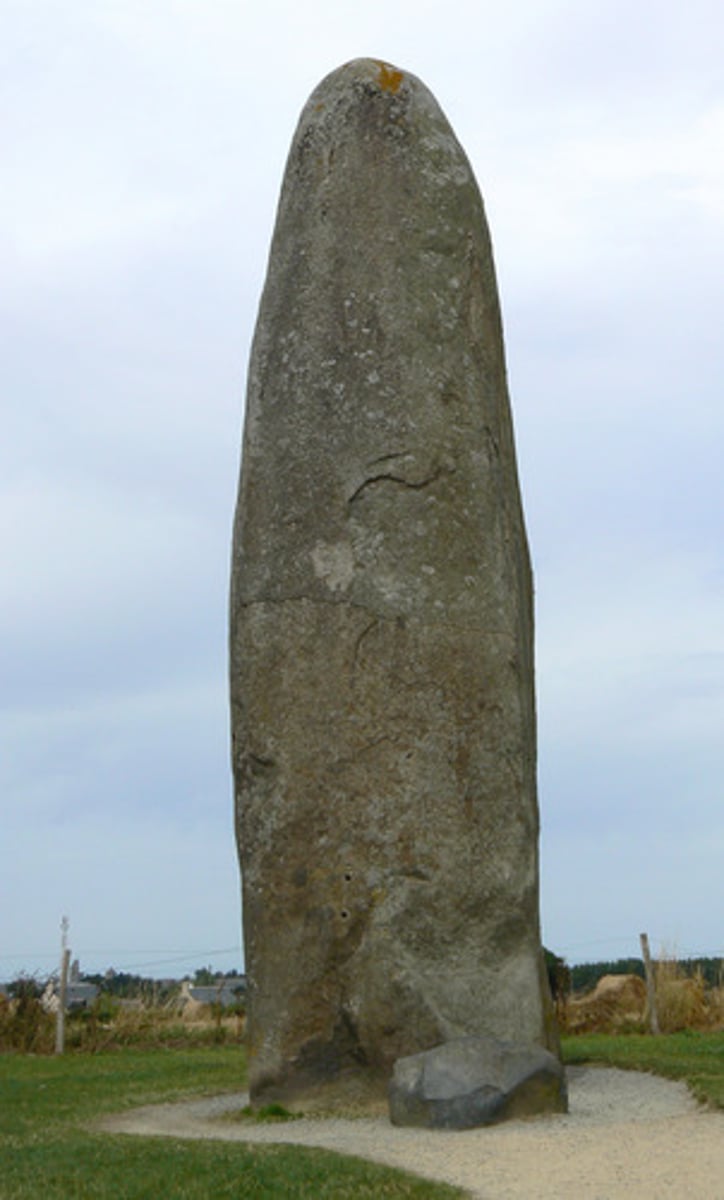
What is a Menhir?
A single stone standing upright

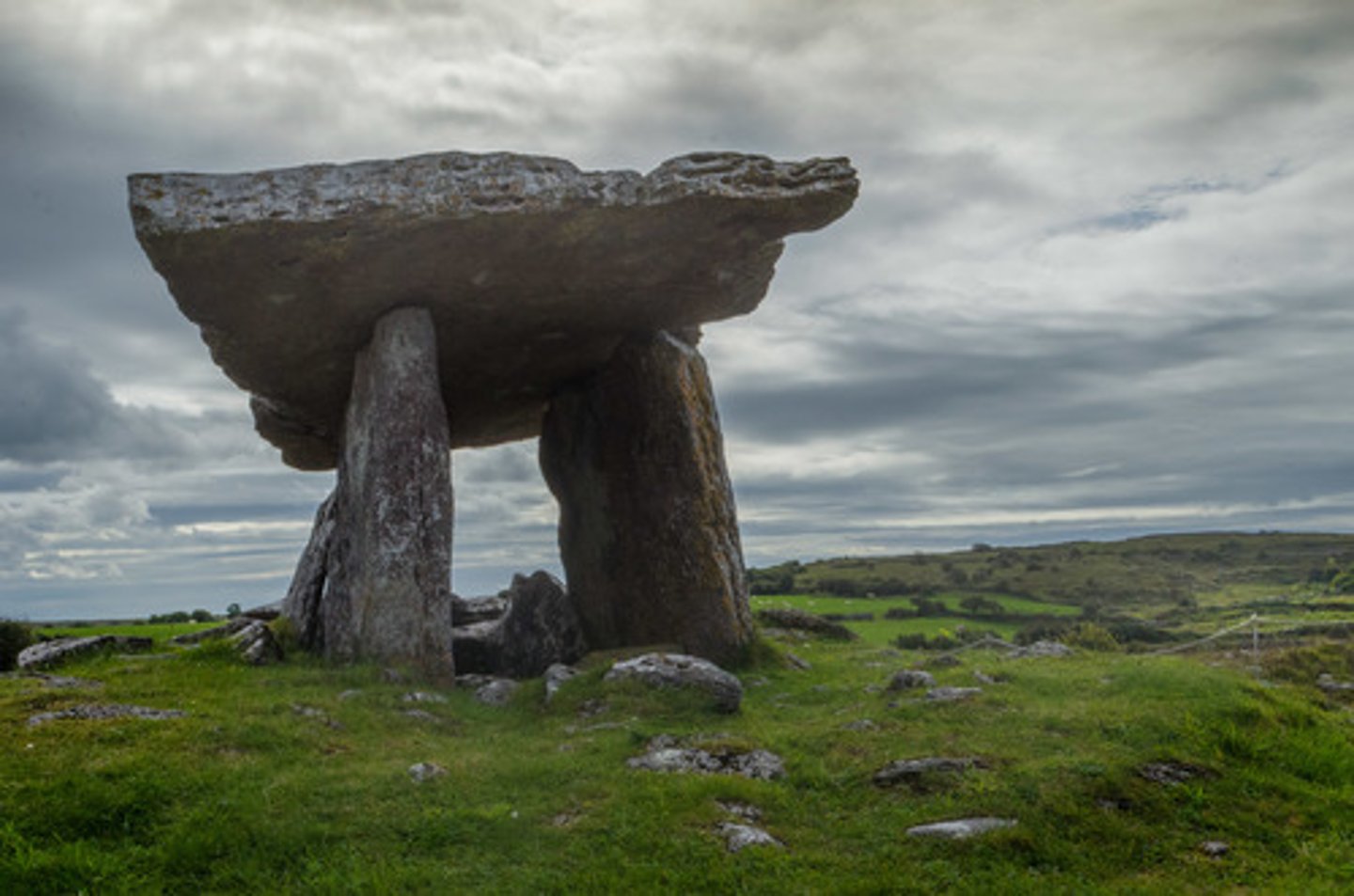
What is a Dolmen
Several stones supporting a stone slab

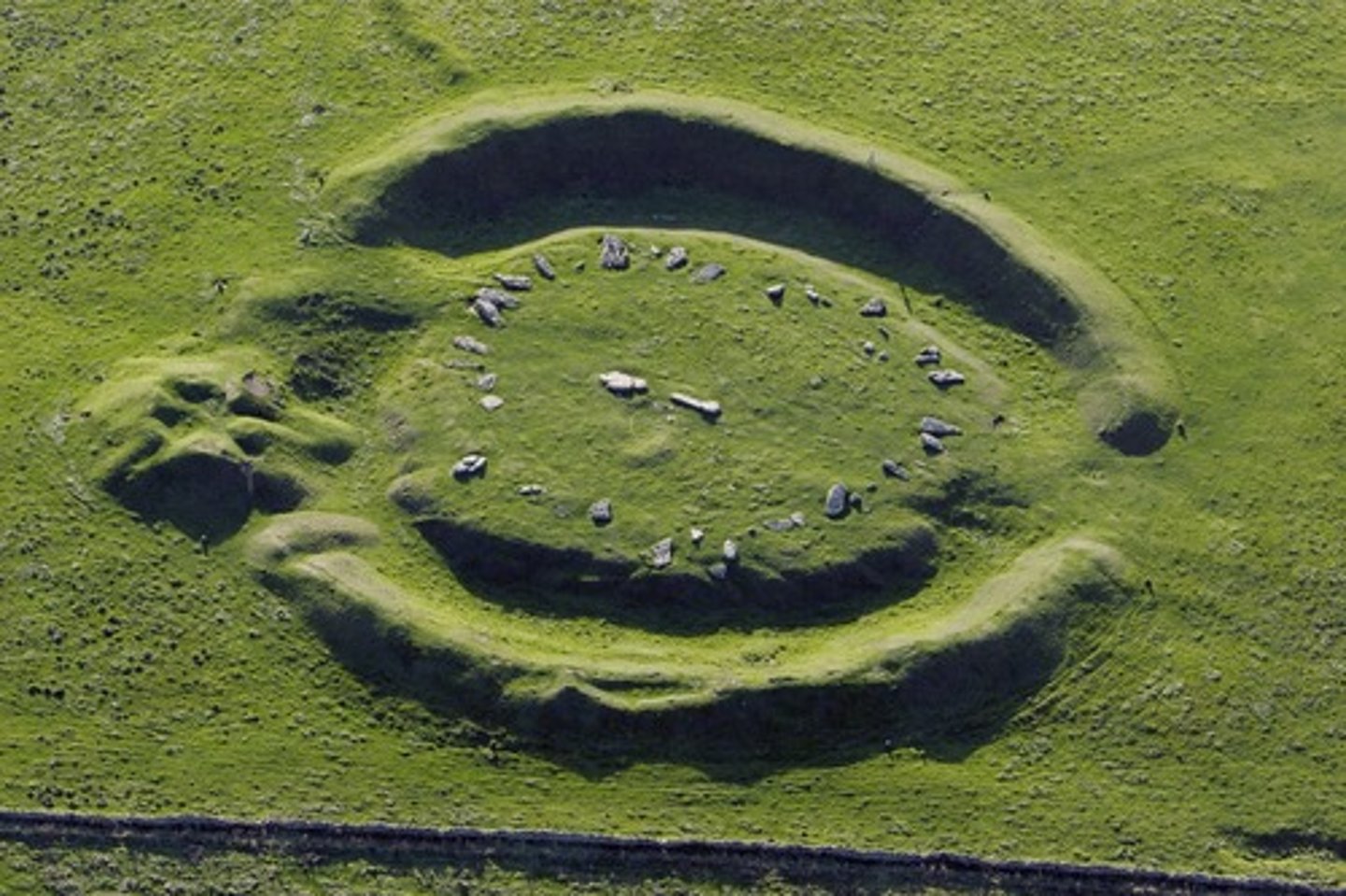
What are Henges?
Circular ditches around which some megalithic monuments are arranged (Stonehenge)

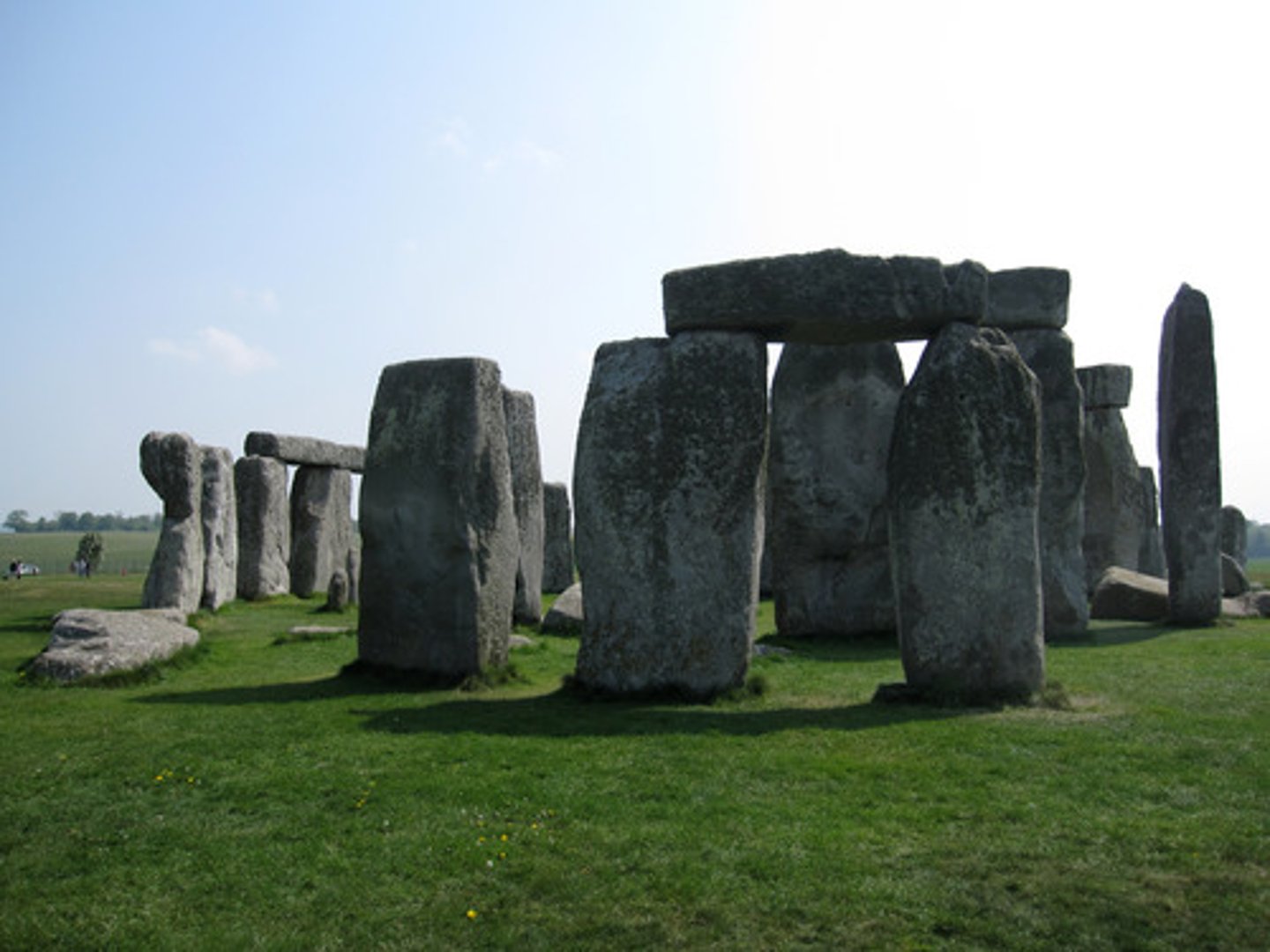
What is a Cromlech?
A circle of stones

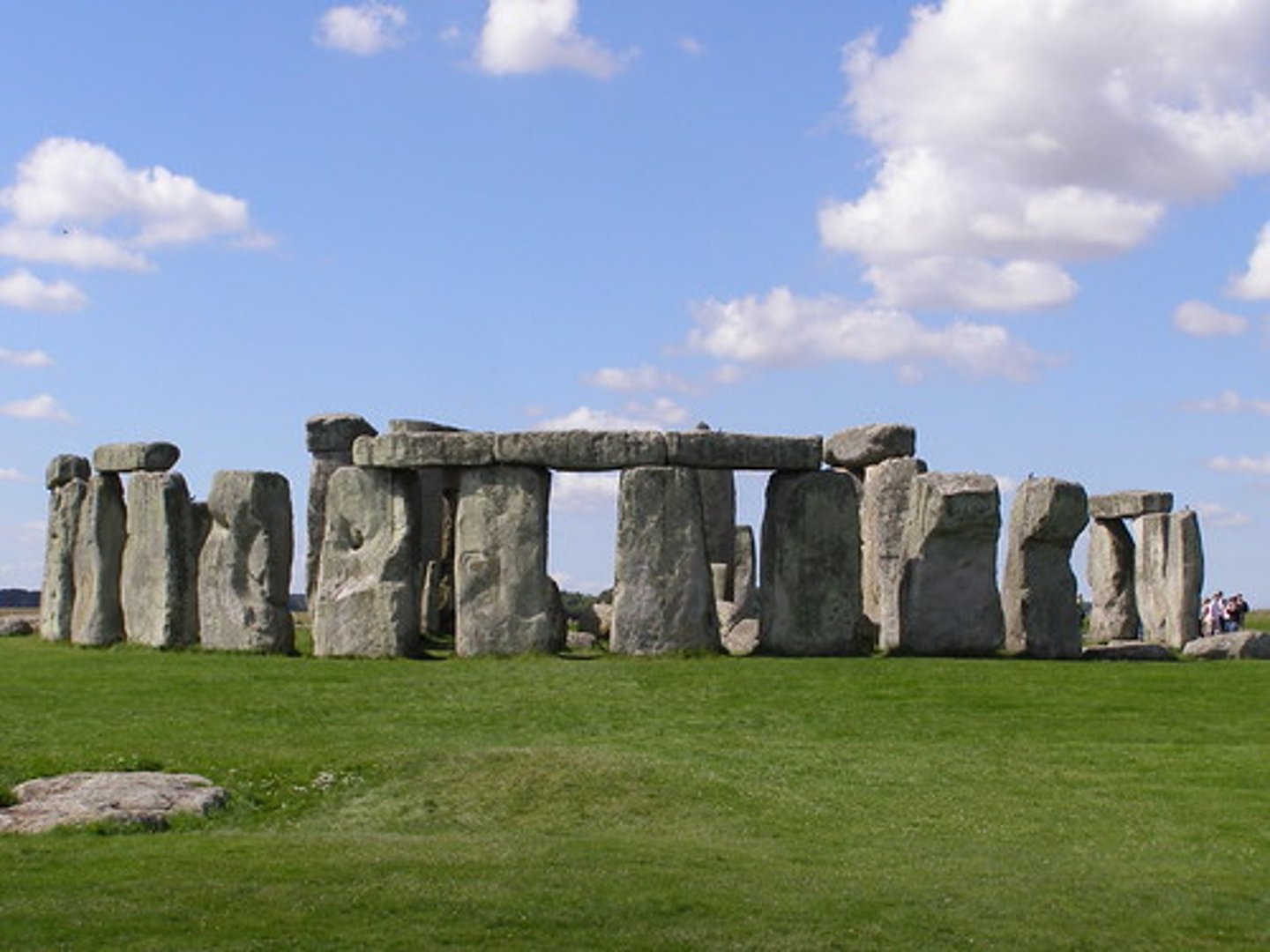
What is Stonehenge?
The oldest surviving structure in England are the stone circles around Stonehenge
Note: Menhir, Dolmen, Henge, and Cromlech
Trabeation - Post and Lintels

What are the Three Types of Pyramids?
1. Step Pyramid
2. Bent Pyramid
3. Straight-sided Pyramid
What is an Example of a Step Pyramid?
Saqqara: Doser's Step Pyramid
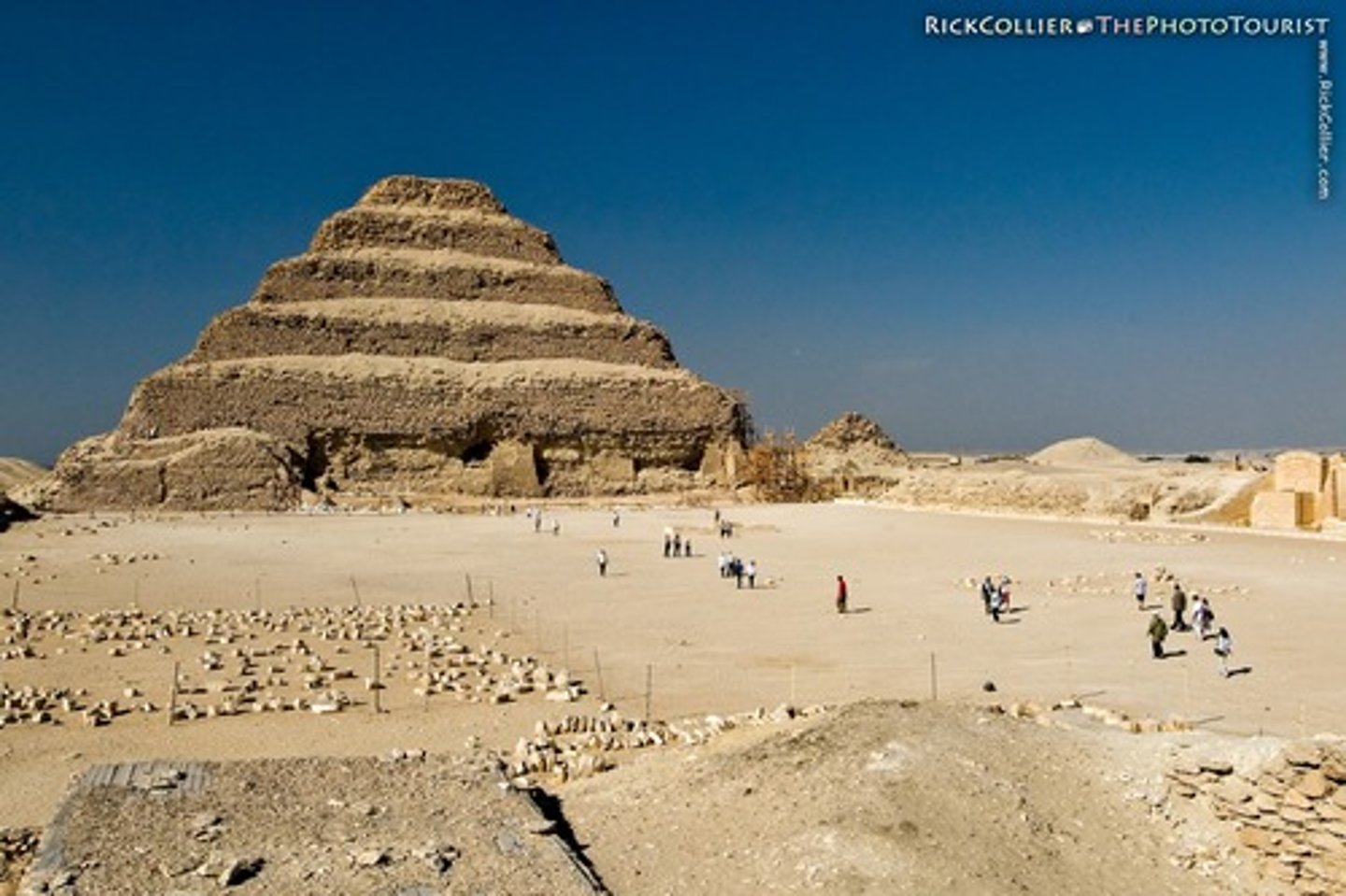

What is an Example of a Bent Pyramid?
Sneferu’s South Pyramid in Dahshur, Egypt
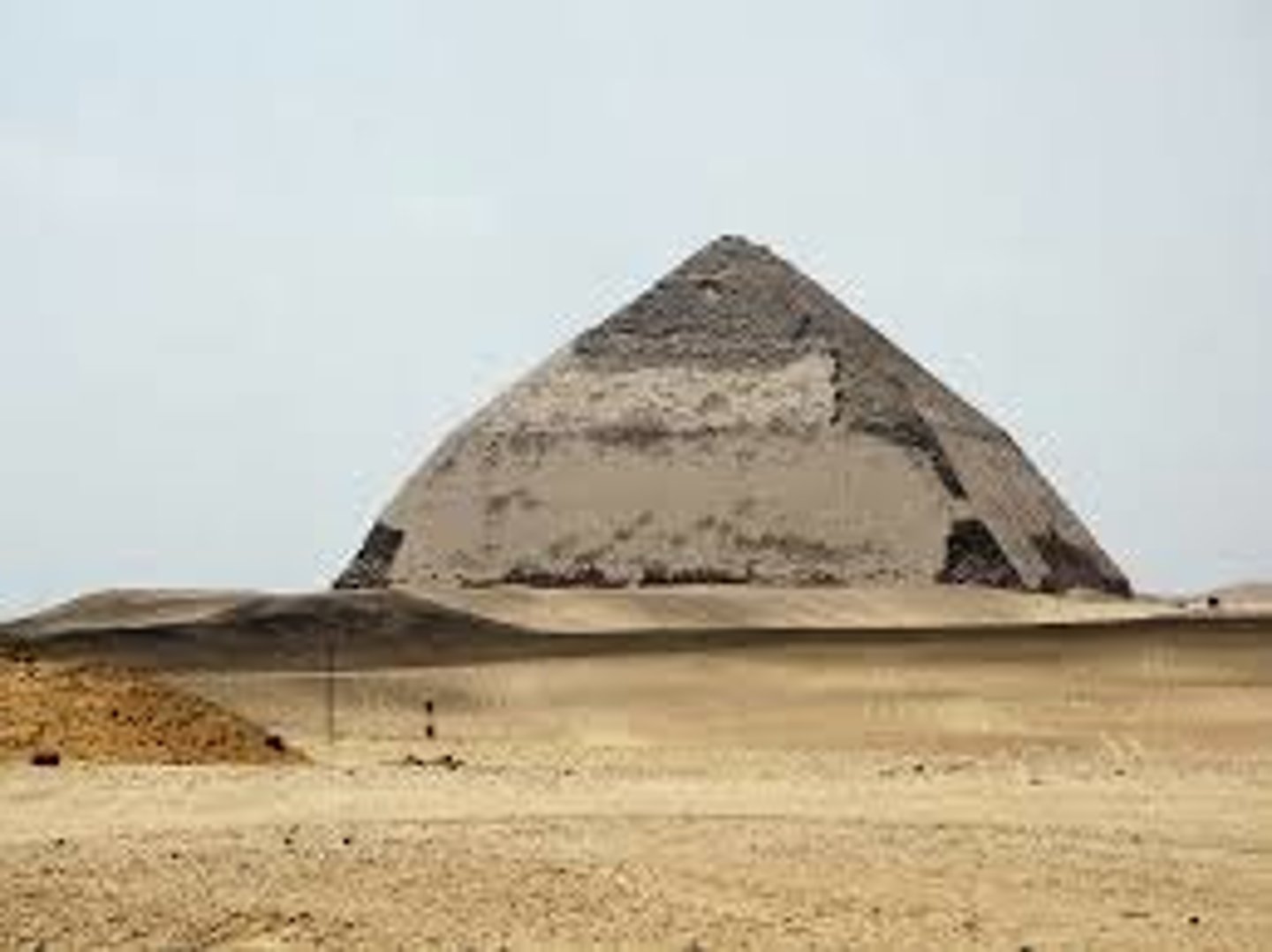

What is an Example of a Straight-Sided Pyramid?
Cheop’s Pyramid in Giza, Egypt
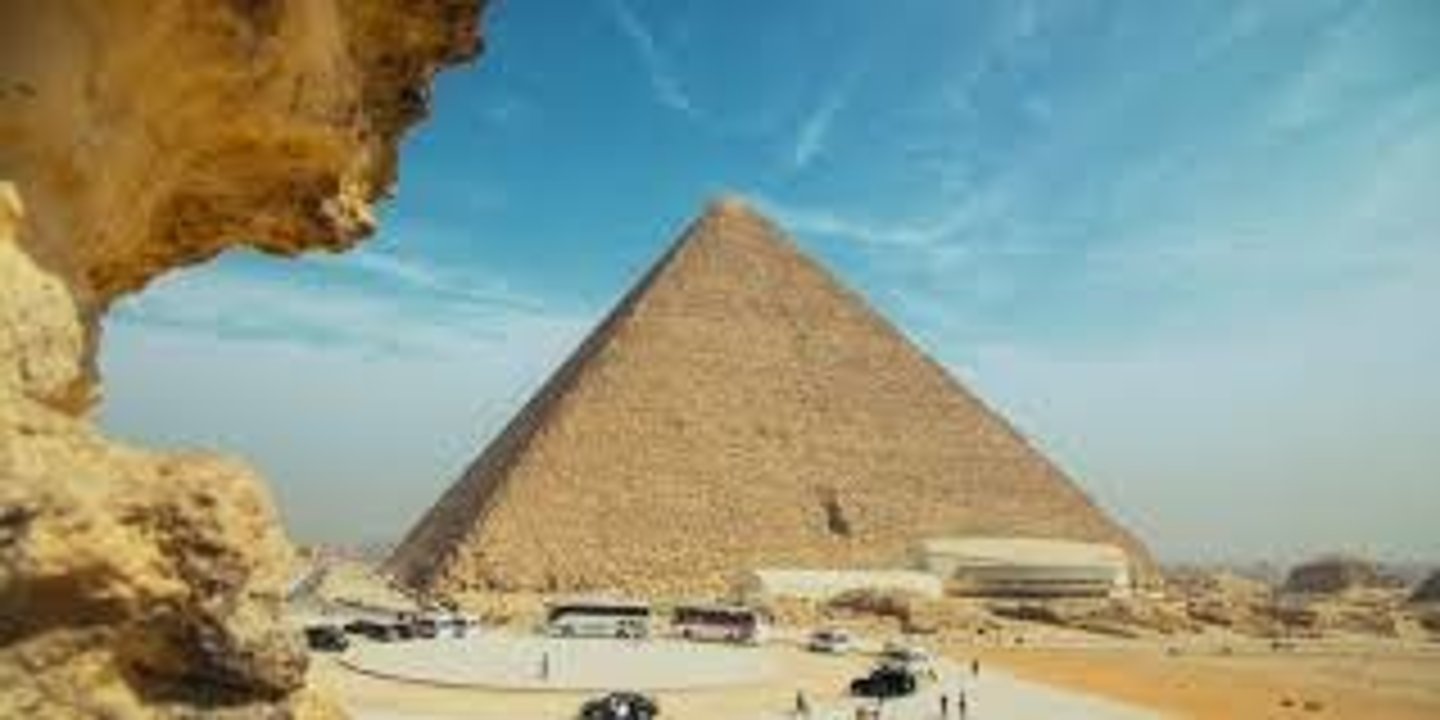

Who was the First Reported Architect?
Egyptian named Imhotep - "the one who comes in peace" who was born a commoner. Between 2,700 to 2,600 Zoser hired Imhotep to design and build his tomb. Imhotep “translated” traditional building materials of mud, wood, and reeds into stone. Imhotep was also an astronomer, magician, and a doctor. Later worshipped by the Egyptians as a god
The Temple at Karnac
Contains Papyrus bundles and bud columns
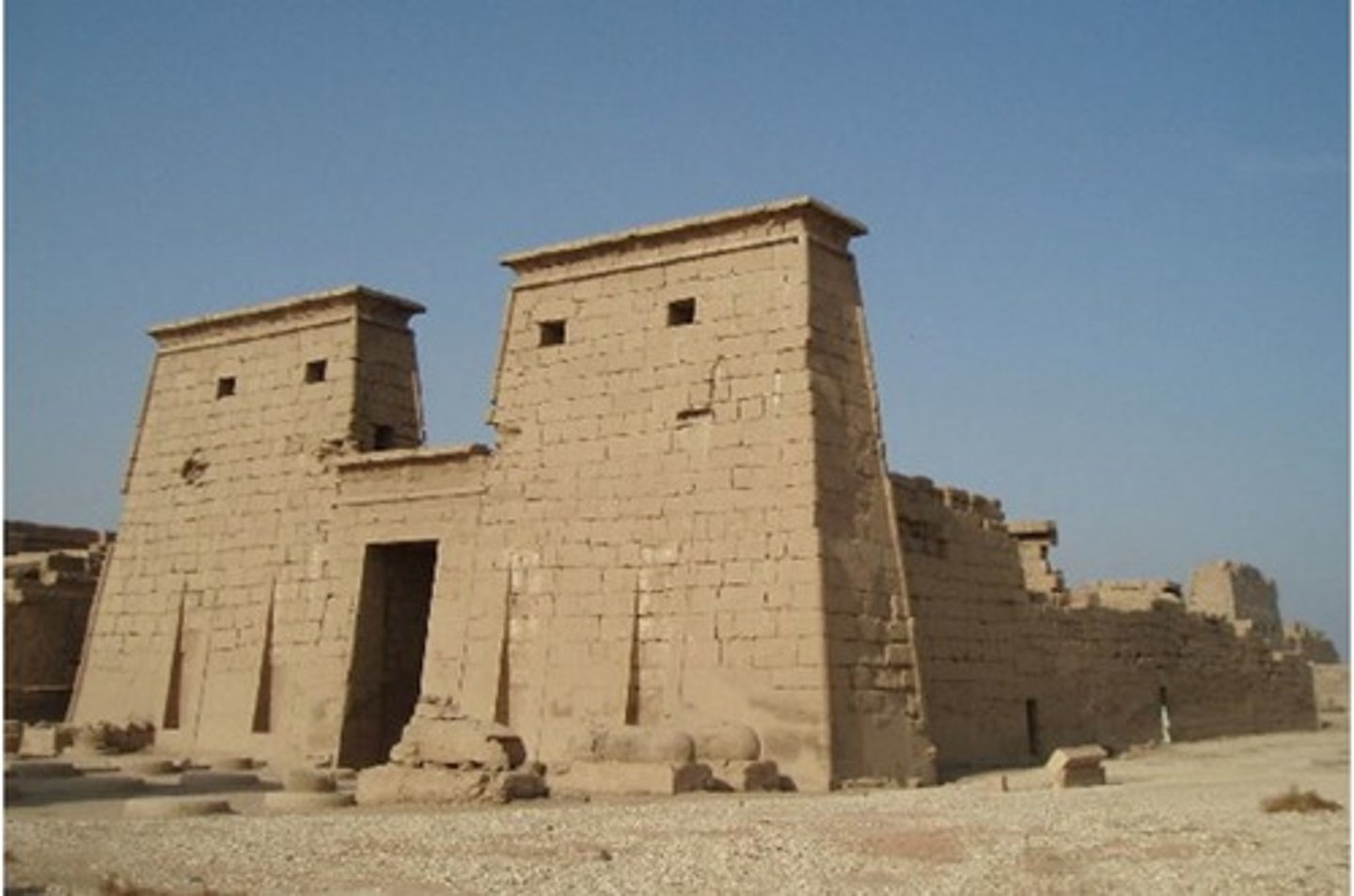

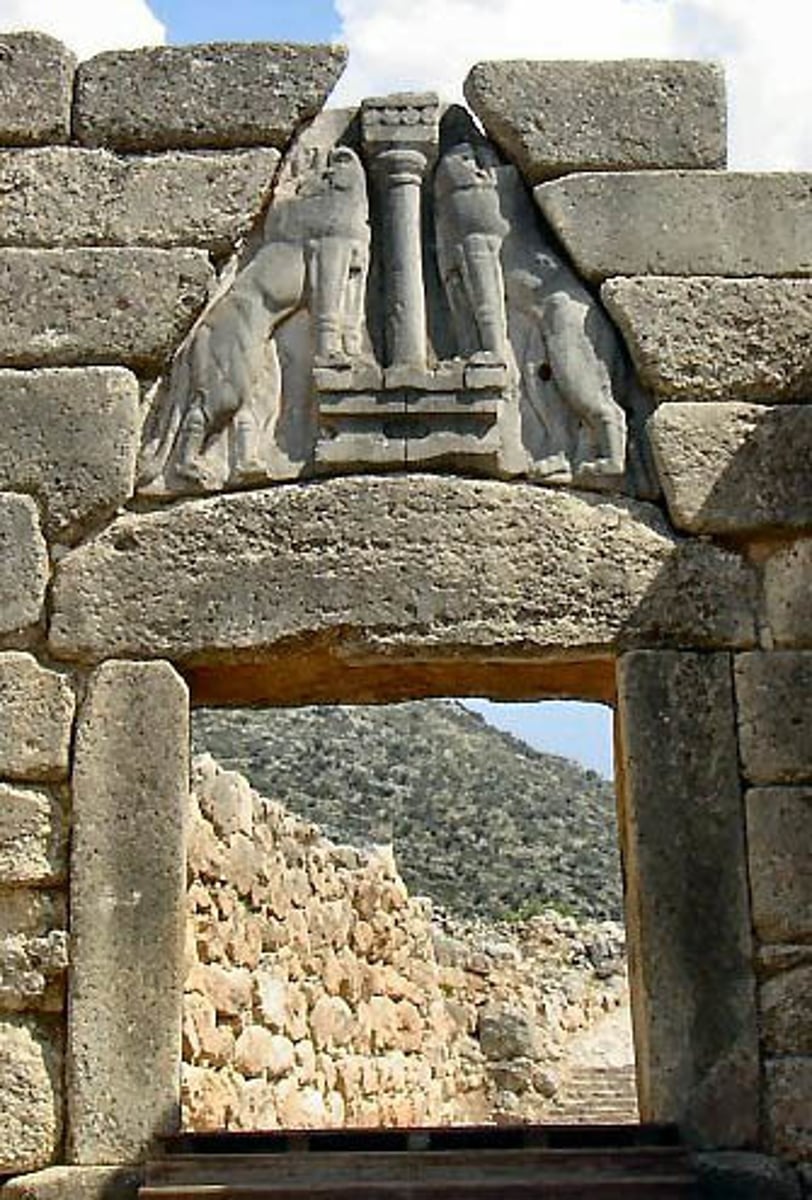
What is the Lion's Gate?
- Sense of structure that was an inheritance from Neolithic period (remember stonehenge)
- Lion element borrowed from Egypt, but now more organic
- Post and lintel
- Greeks will refine post and lintel, triangular relief

What are the Differences Between the Egyptians and the Greeks?
Egyptians believed in the afterlife with collective eternity where if the pharaoh lives forever, then so does the population. Brought effort to celebrate individual
Greeks believed there wasn't an afterlife and sought immortality through achievement where they will be remembered forever based on their record achievements. Excellence in deeds
Temples Housed _______
Gods
Why were Temples Made?
To impress non-Greeks. Made with vivid colors and are seen from great distances.
What are the Three Orders?
1. Doric
2. Ionic
3. Corinthian
What is the Doric Order?
- Oldest, simplest, most massive
- Columns placed close together, often no bases
- Plain capitals
- Entablatures have metopes and triglyphs
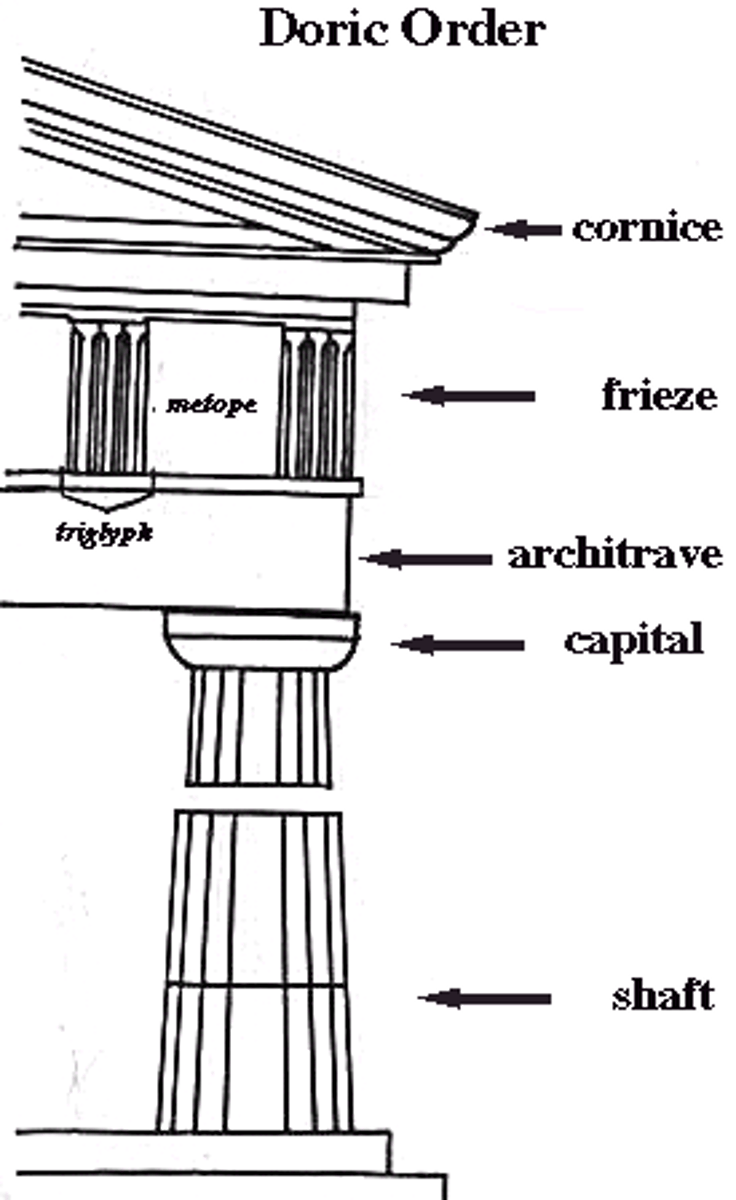
What is the Ionic Order?
- Developed in Ionian Islands
- Characterized as delicate order - “female”
- Contrasts with “male” Doric order
- Used for smaller buildings and interiors
- Easily recognized by Volutes on Capital (based on nautilus shells or animal horns)
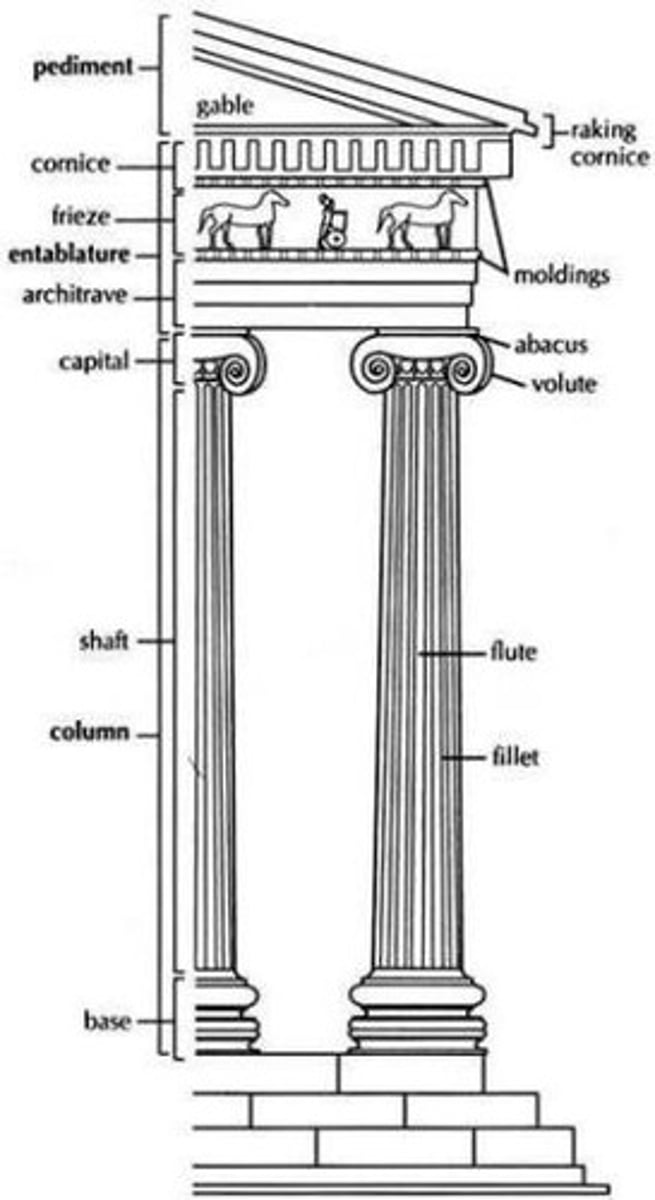
What is the Corinthian Order?
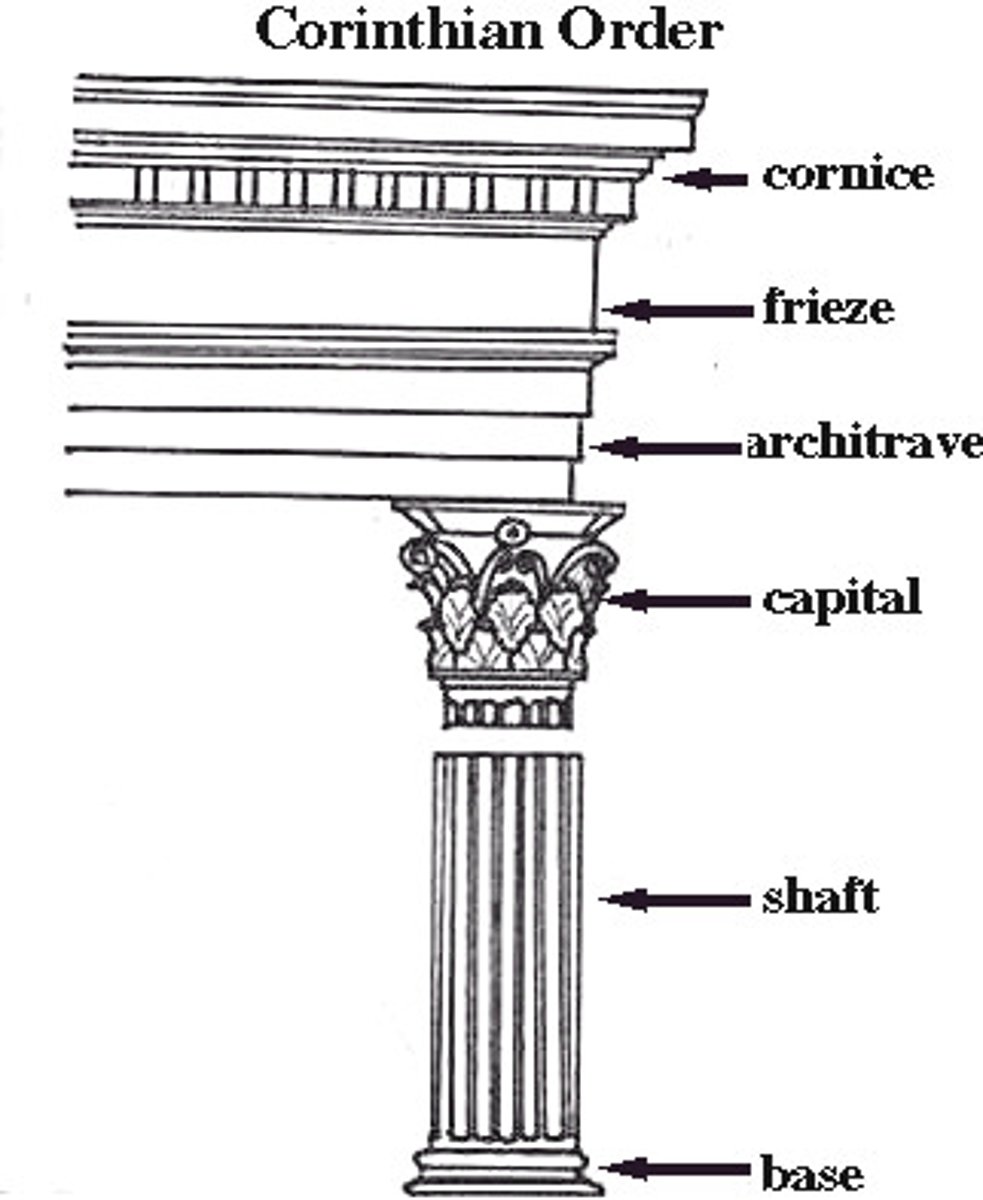
- Variation of Ionic Order
- Same as Ionic except a new type of Capital
- Capital is more ornate-acanthus leaves
- Often found on interiors
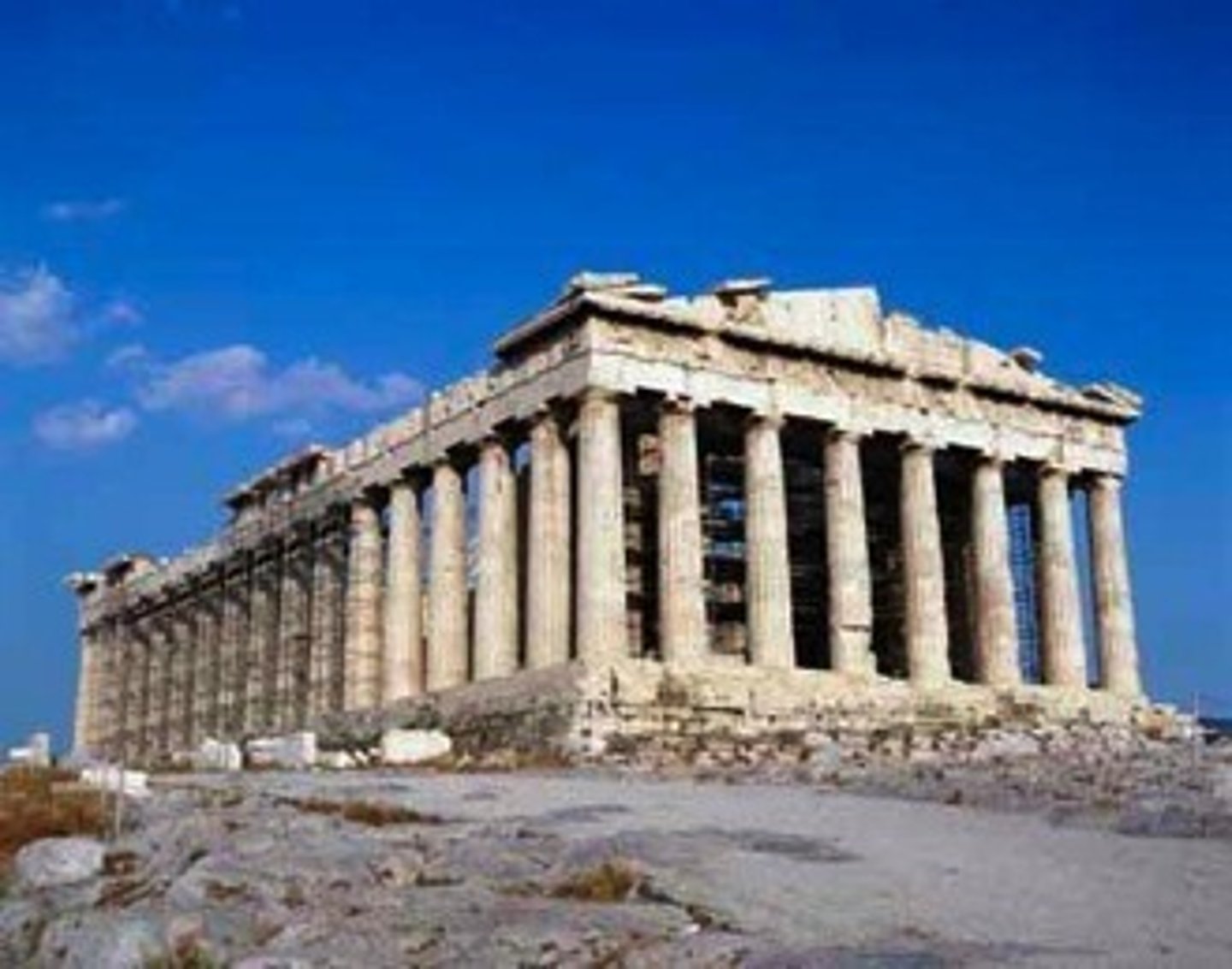
The Parthenon in Athens, Greece
Constructed between 448,432 BCE, the Parthenon is the perfection of the Doric Order and it is a supreme example of classical architecture

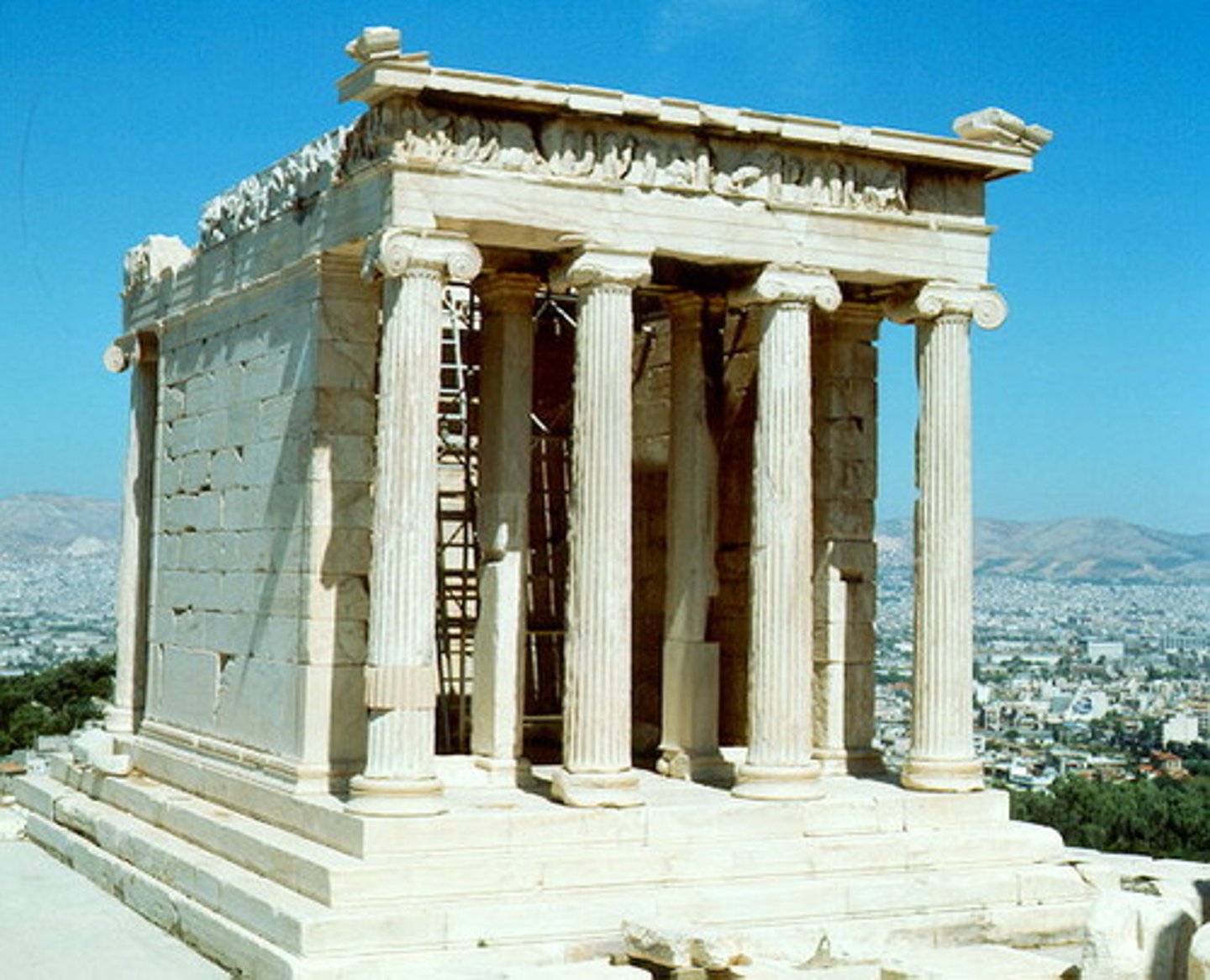
The Temple of Athena Nike is the Perfection of the _________ Order
Ionic

What is the Corinthian Order Usually Used for?
the interior of temples (Greeks)
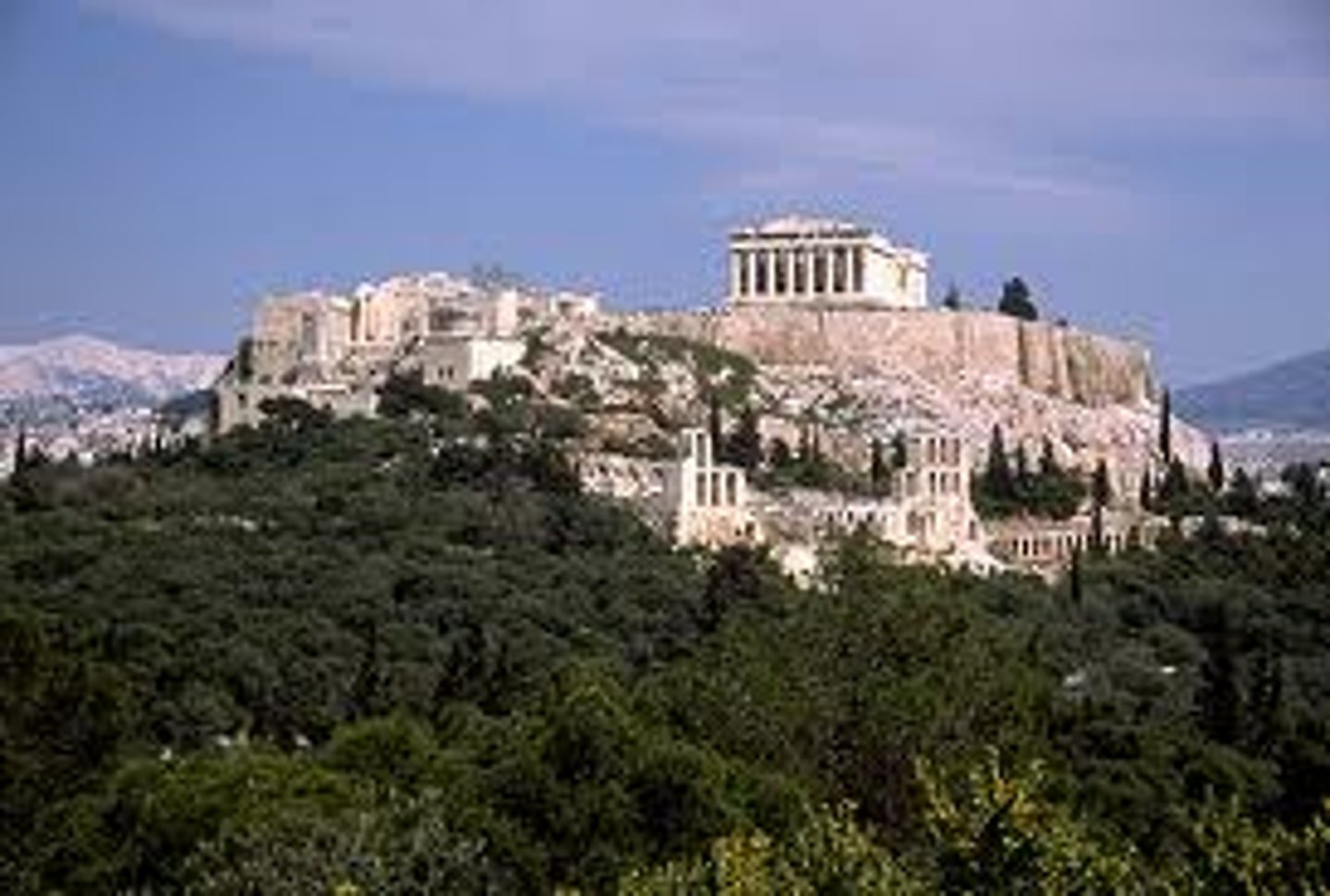
The Acropolis in Athens, Greece
Contains the Temple of Athena Nike and the Erechtheion

Who is Elgin Marbles?
Lord Elgin purchased marble from Turks. Made sculptures that are located in the British Museum in London
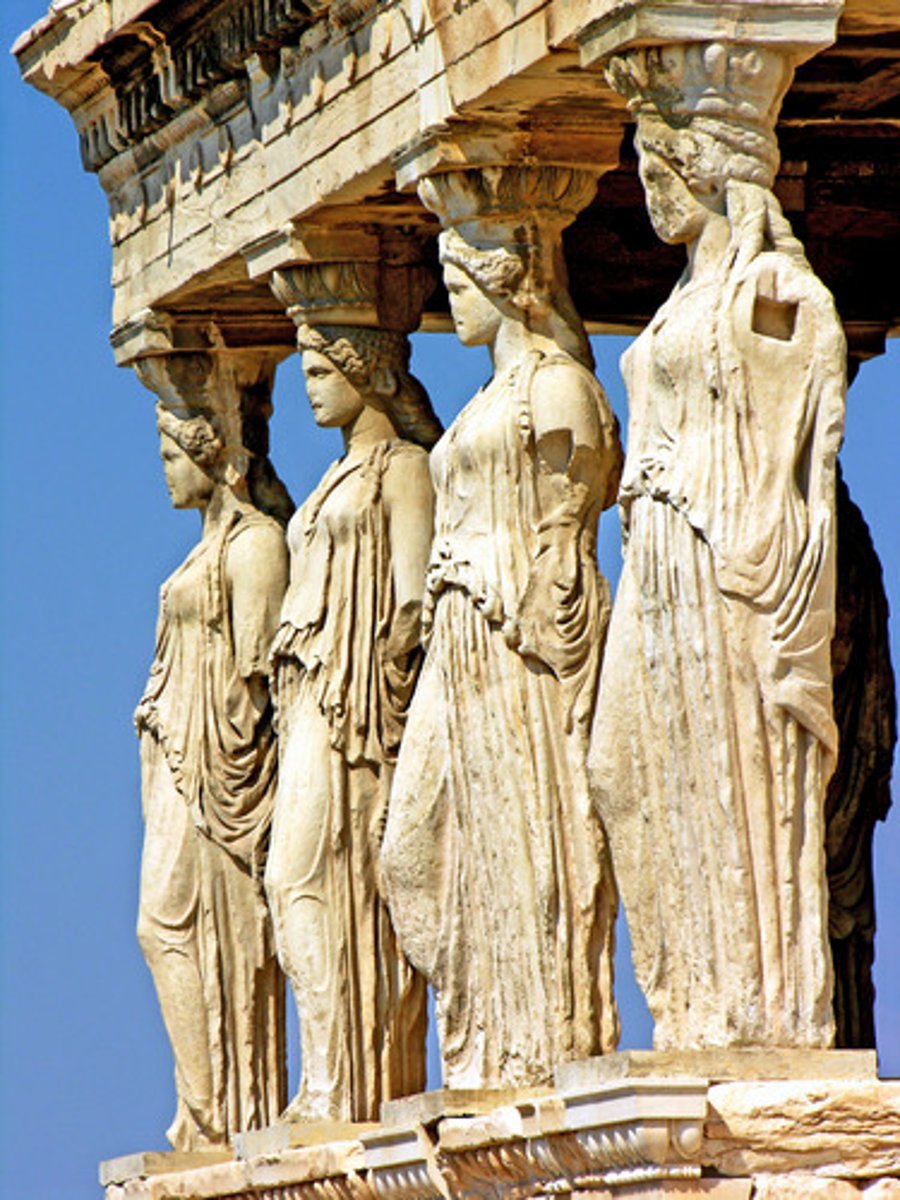
What are Caryatids?
A sculpted female figure used as a column
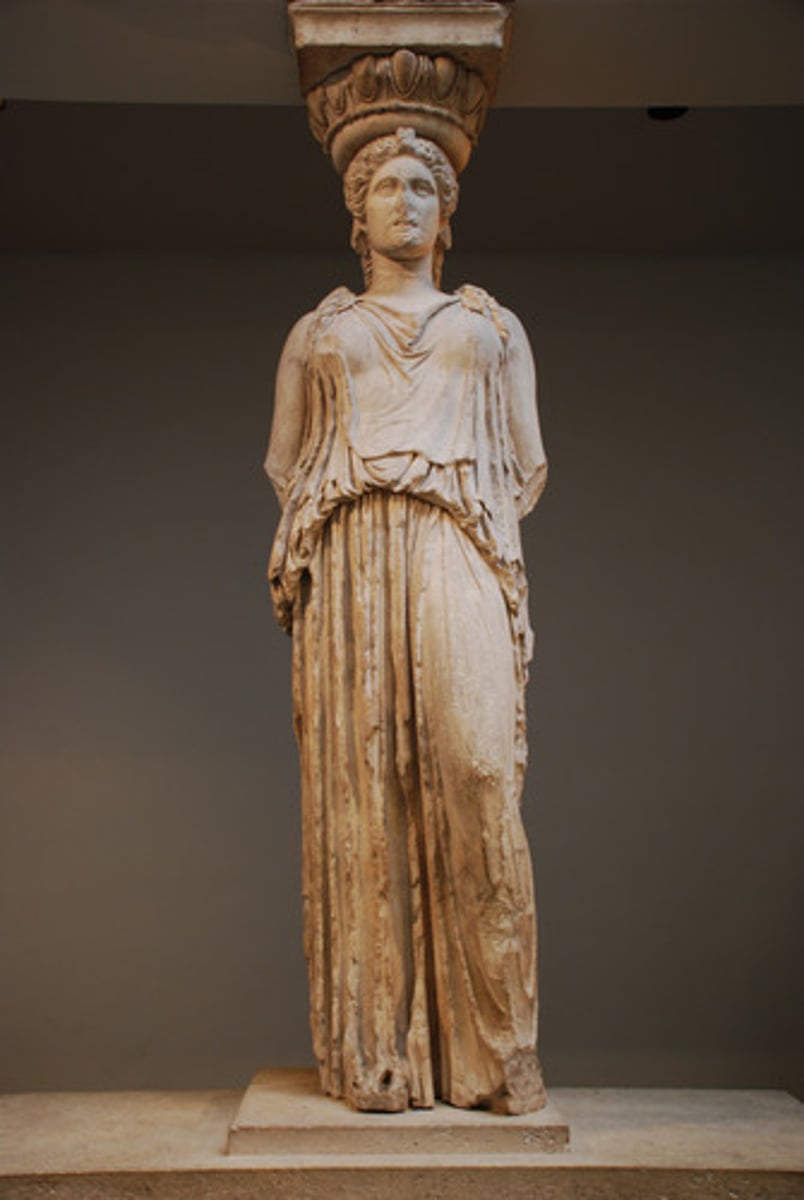

What is an Atlas?
A sculptured male figure used as a column

What's the Difference Between Greeks and Romans/Etruscans?
Greeks made in the landscape using balance, harmony, refinement of form, and without structural innovation. Greeks utilize Post and Beam.
Romans (Etruscans) conquered the Greeks and brought Classical architecture to Roman Empire where 20% of the world was under Roman rule. Made images in context and made innovations in construction and technology.
What is the Tuscan Order?
Unlike Doric, supports an entablature with no decoration. Used to create wooden temple with pitched roof

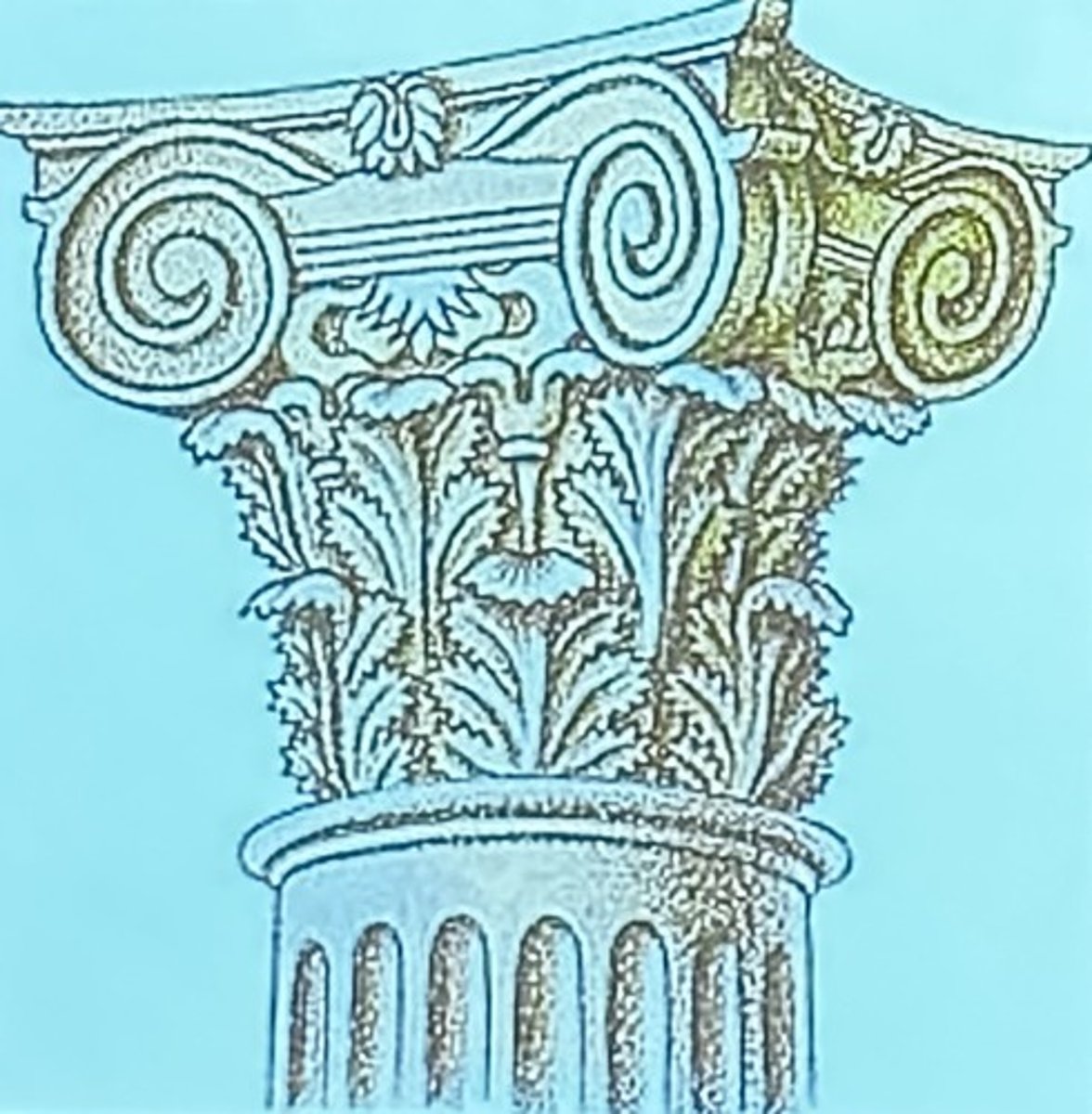
What is the Composite Order?
A Roman innovation that combines Ionic volutes with Conrinthian acanthus leaves

What were the Roman Structural Inventions?
- Concrete
- Barrel vault: extending arch along its depth
- Groin vault (intersecting two barrel vaults that opens a space in 4 directions. Used to create huge interiors such as gyms and bathes)
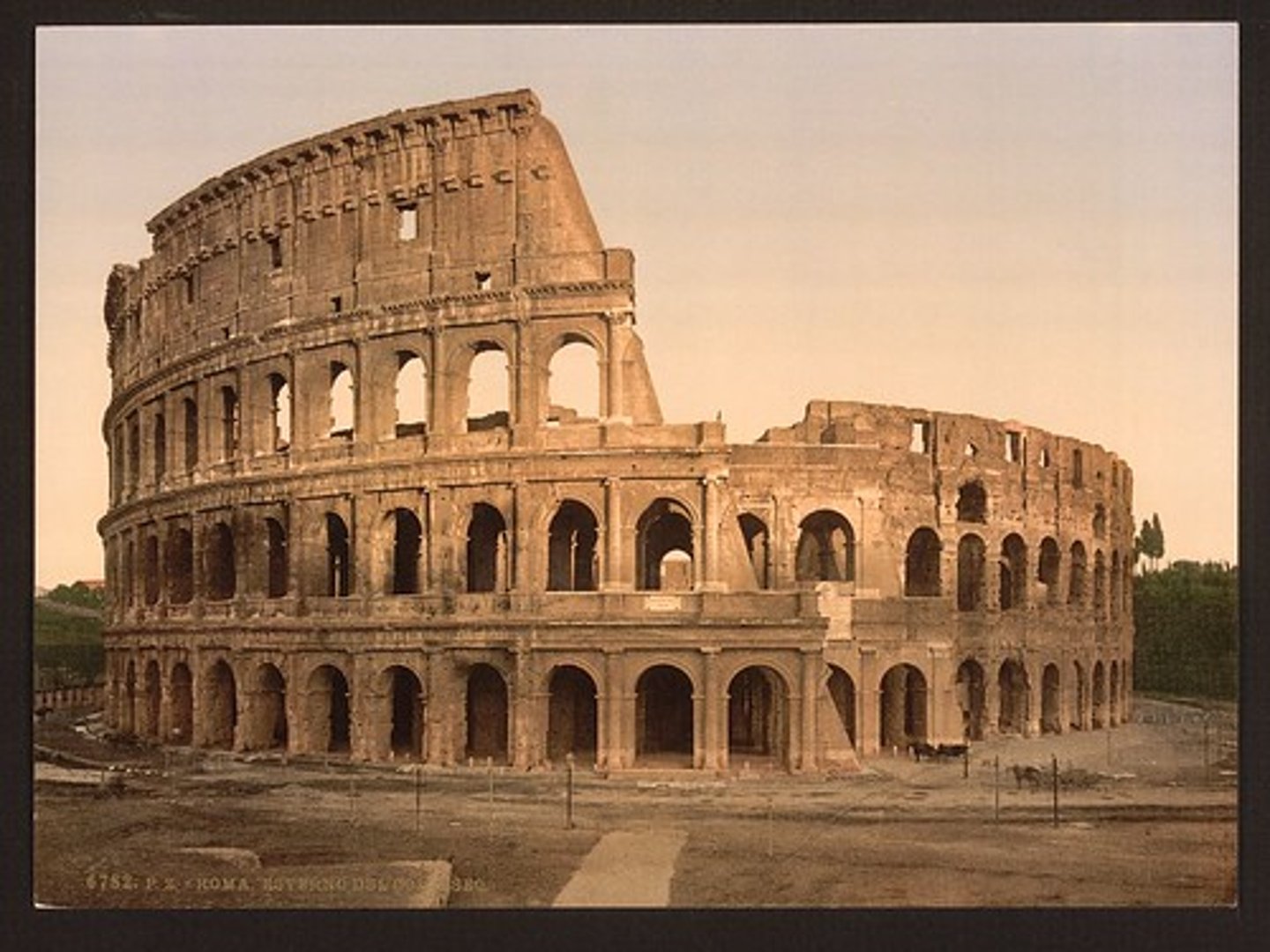
Coliseum in Rome
Completed around 80 ACE
Largest colosseum in Rome

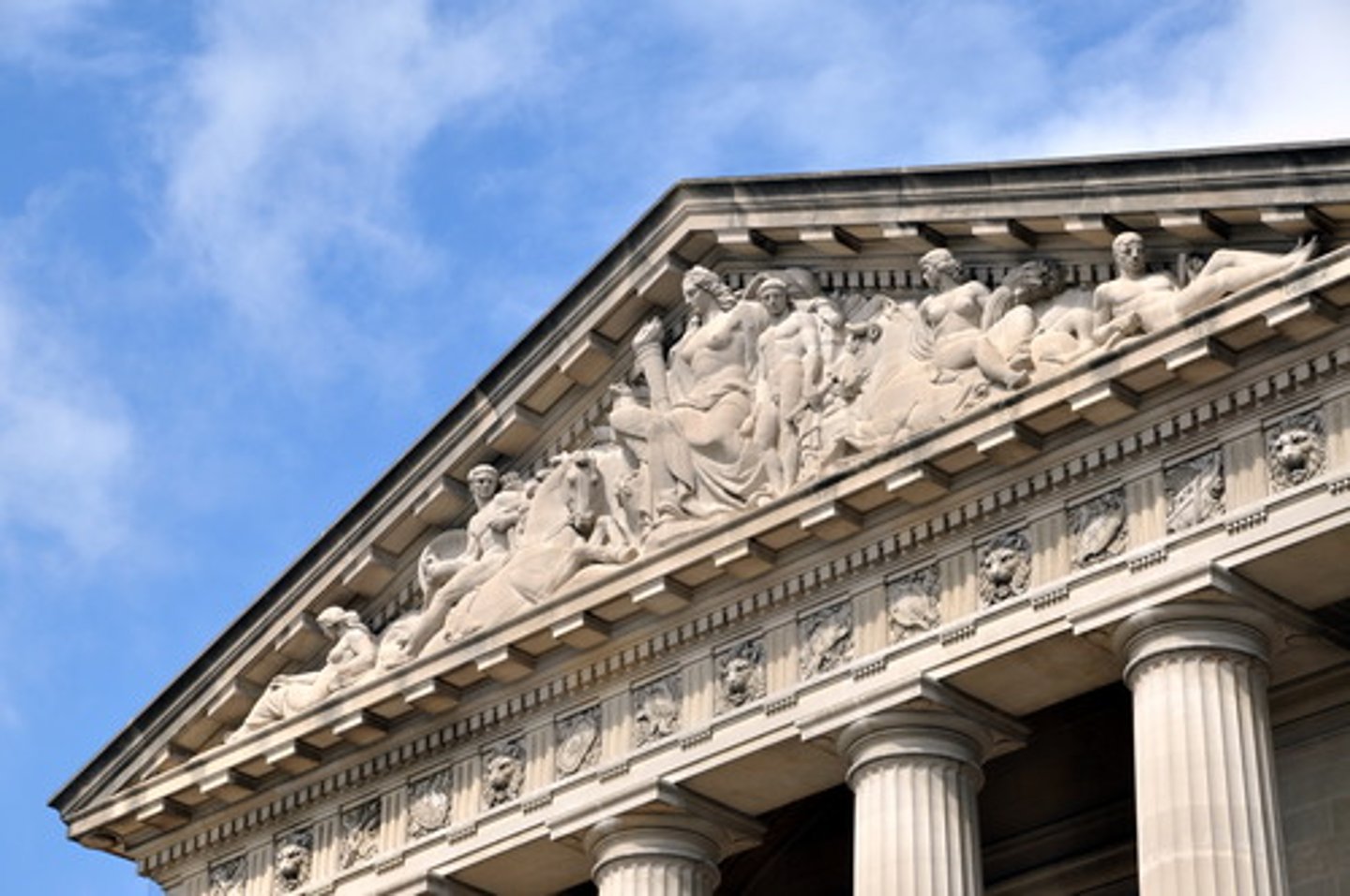
What is a Pediment?
A triangle shape over colonnade

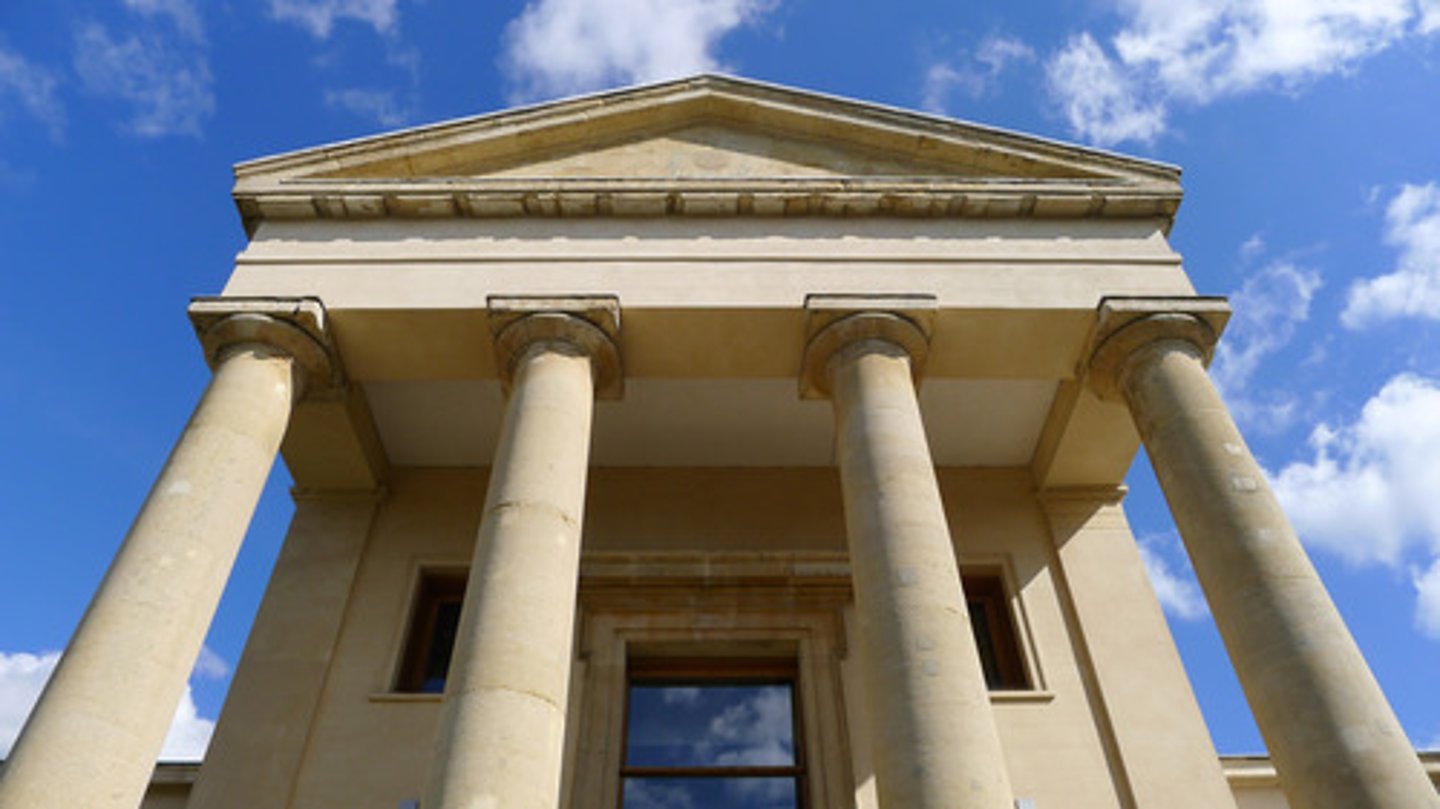
What is a Portico?
a colonnaded space forming an entrance or vestibule

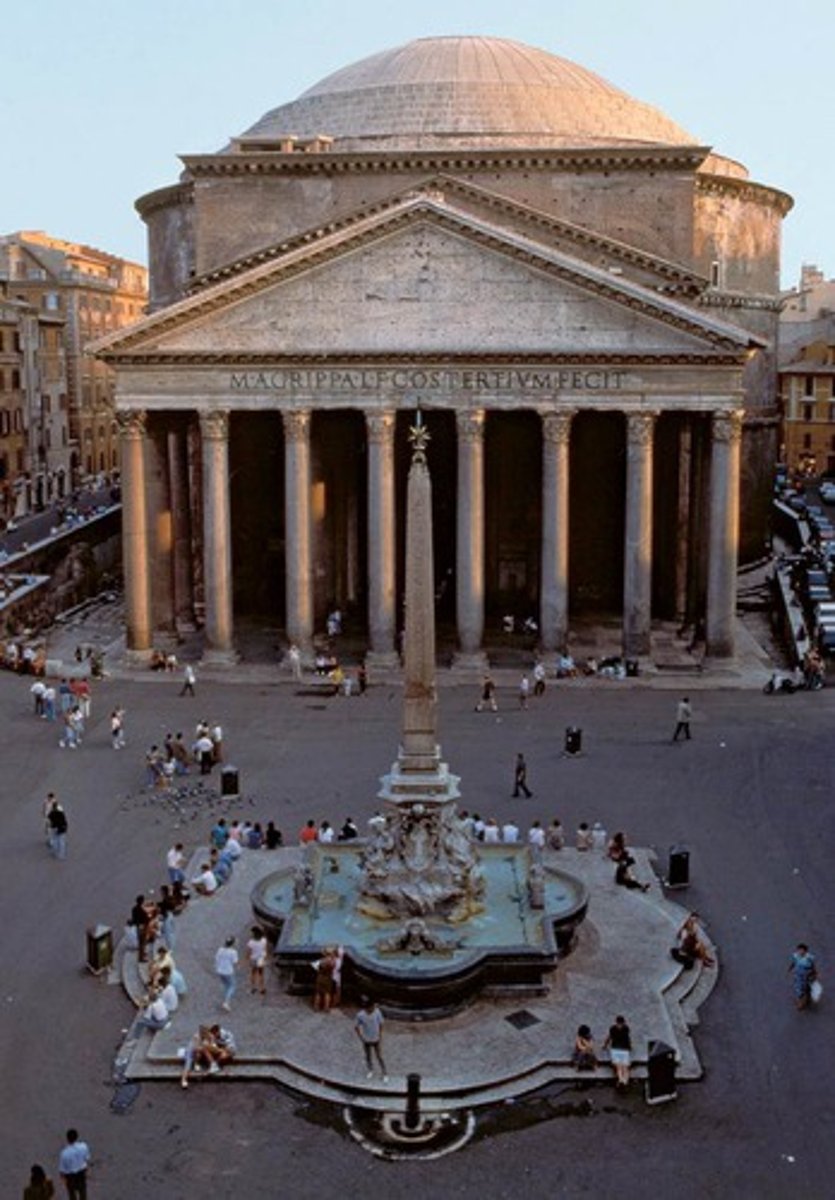
What is the Pantheon?
Designed by Hadrian and it utilizes pediments and porticos

Who is Constantine I (306-337 A.D.)?
Designed the Edict of Milan in 313 A.D.
Proclaimed tolerance of all religions - gave Christians authority to build churches
Early Christian Churches were Based on ____________
Timber-roofed Basilicas