runestone academy ap csp unit 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:27 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
procedural abstraction
organizing and encapsulating algorithms in named procedures that can then be invoked by name
2
New cards
parameter
\-input variable for a procedure
\-allows procedures to be generalized
\-enables procedures to be reused with a range of arguments (input values)
\-allows procedures to be generalized
\-enables procedures to be reused with a range of arguments (input values)

3
New cards
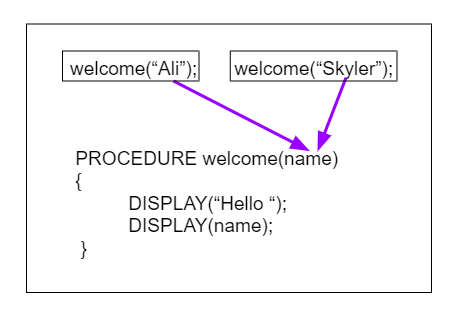
argument
specifies the value of a parameter when a procedure is called
4
New cards
function
procedure that returns a result

5
New cards
sequential (linear) search
\-algorithm that checks every element in a list from the start to the end to find the searched-for item
\-running time grows proportional to a __linear__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = N\]
\-running time grows proportional to a __linear__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = N\]
![\-algorithm that checks every element in a list from the start to the end to find the searched-for item
\-running time grows proportional to a __linear__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = N\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a45d7e4090ad4c2eaa50af2510c338ef.jpeg)
6
New cards
binary search
\-algorithm that repeatedly divides a sorted list to narrow in on the searched-for item
\-starts at the middle to eliminate half of the data
\-running time grows proportional to a __logarithmic__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = log N\]
\-starts at the middle to eliminate half of the data
\-running time grows proportional to a __logarithmic__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = log N\]
![\-algorithm that repeatedly divides a sorted list to narrow in on the searched-for item
\-starts at the middle to eliminate half of the data
\-running time grows proportional to a __logarithmic__ curve as N grows larger \[f(N) = log N\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/93ac68721de5498a86f5aa9d25c24077.jpeg)
7
New cards
sorting algorithm
algorithm that puts a list in numerical or alphabetical order
8
New cards
comparison sort
algorithm that repeatedly compares 2 elements
9
New cards
radix (base) sort
algorithm that sorts numbers by their digits, placing them in each of their respective buckets
10
New cards
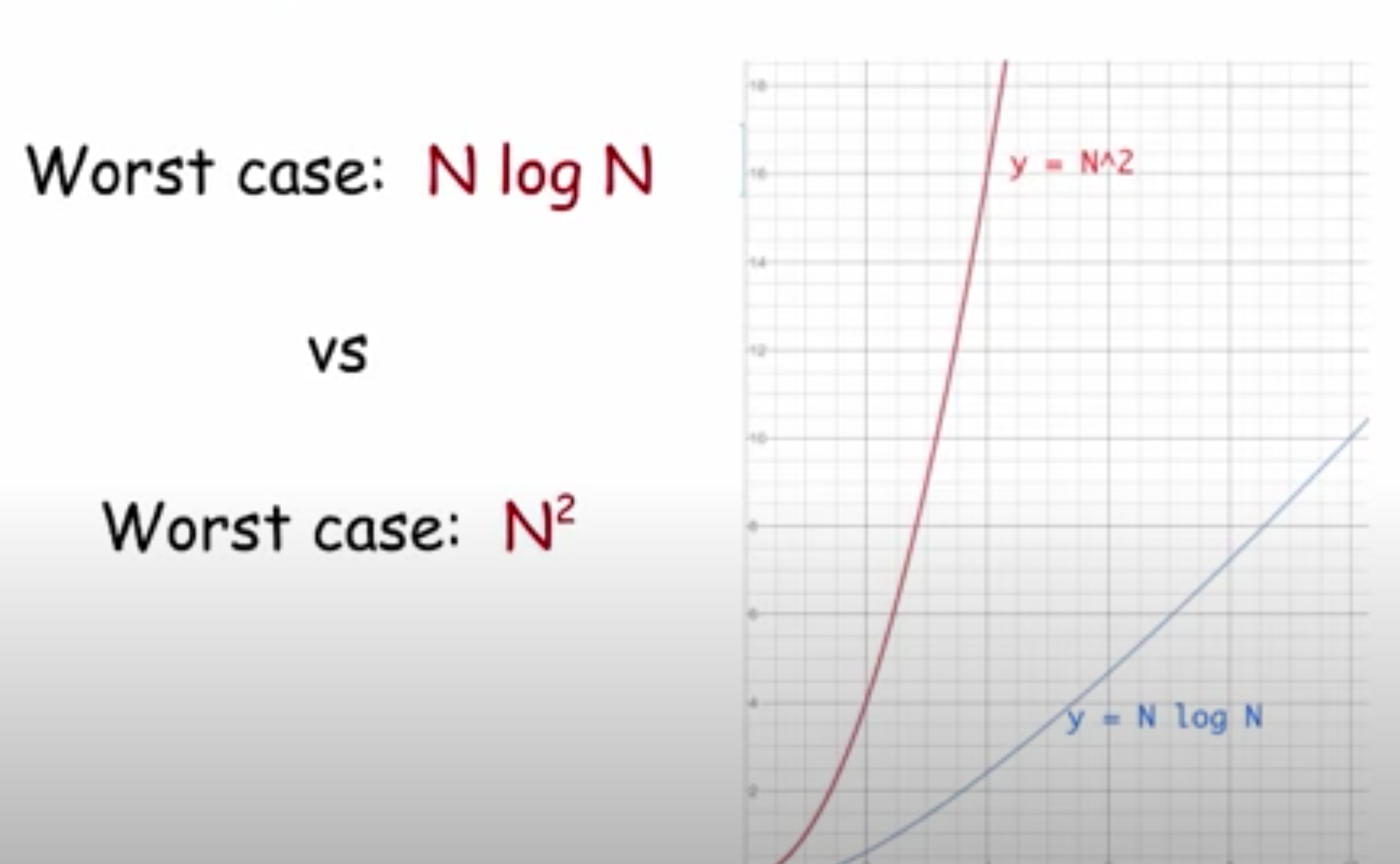
bubble sort
\-algorithm in which the highest value “bubbles” to the top after each pass
\-running time grows proportional to a __quadratic/squared__ curve as N grows larger (N^2)
\-running time grows proportional to a __quadratic/squared__ curve as N grows larger (N^2)
11
New cards
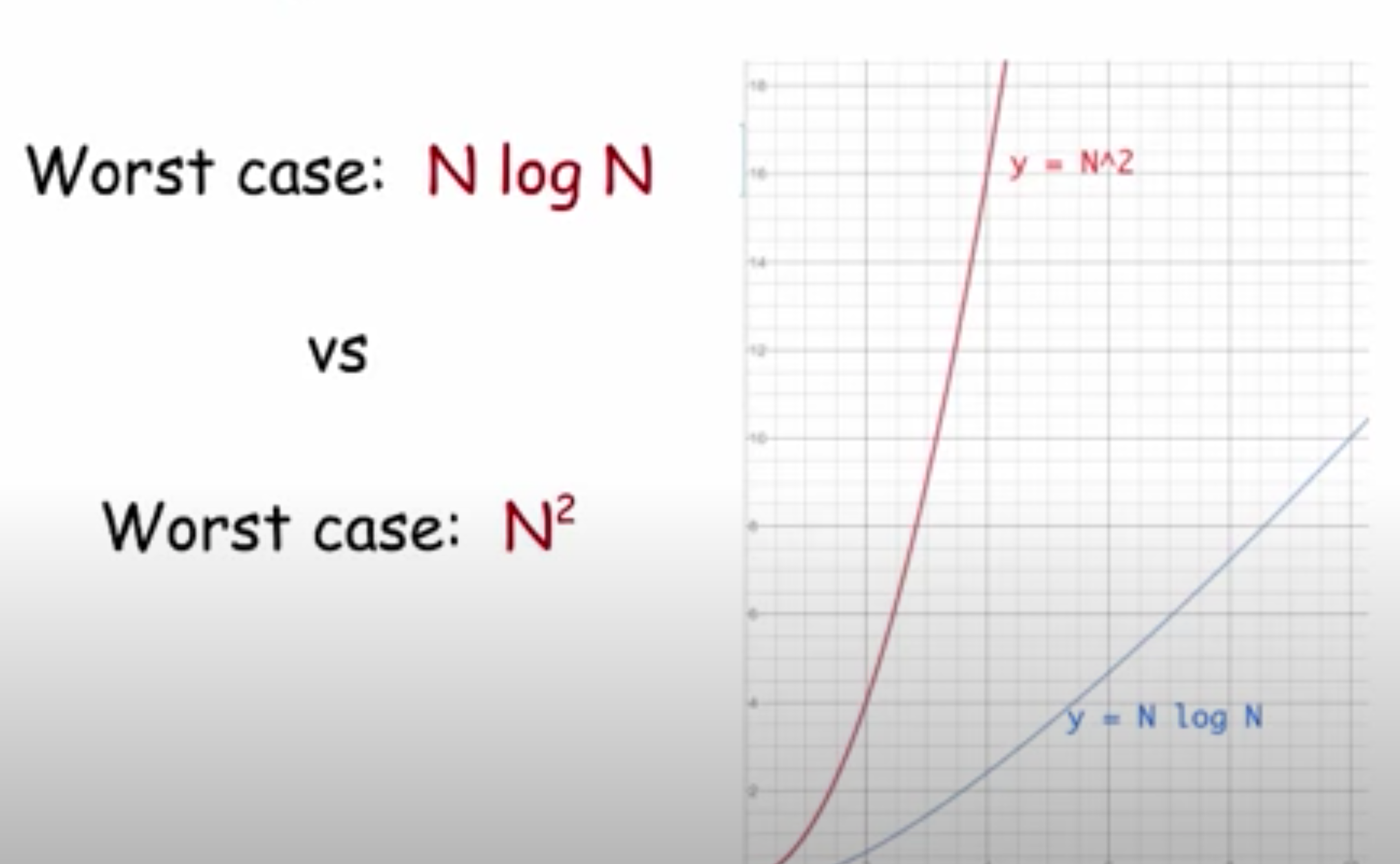
merge sort
\-algorithm in which sorted piles are continuously made & merged together until there is 1 complete pile
\-running time grows proportional to an __N log N__ curve as N grows larger
\-uses more memory
\-running time grows proportional to an __N log N__ curve as N grows larger
\-uses more memory
12
New cards
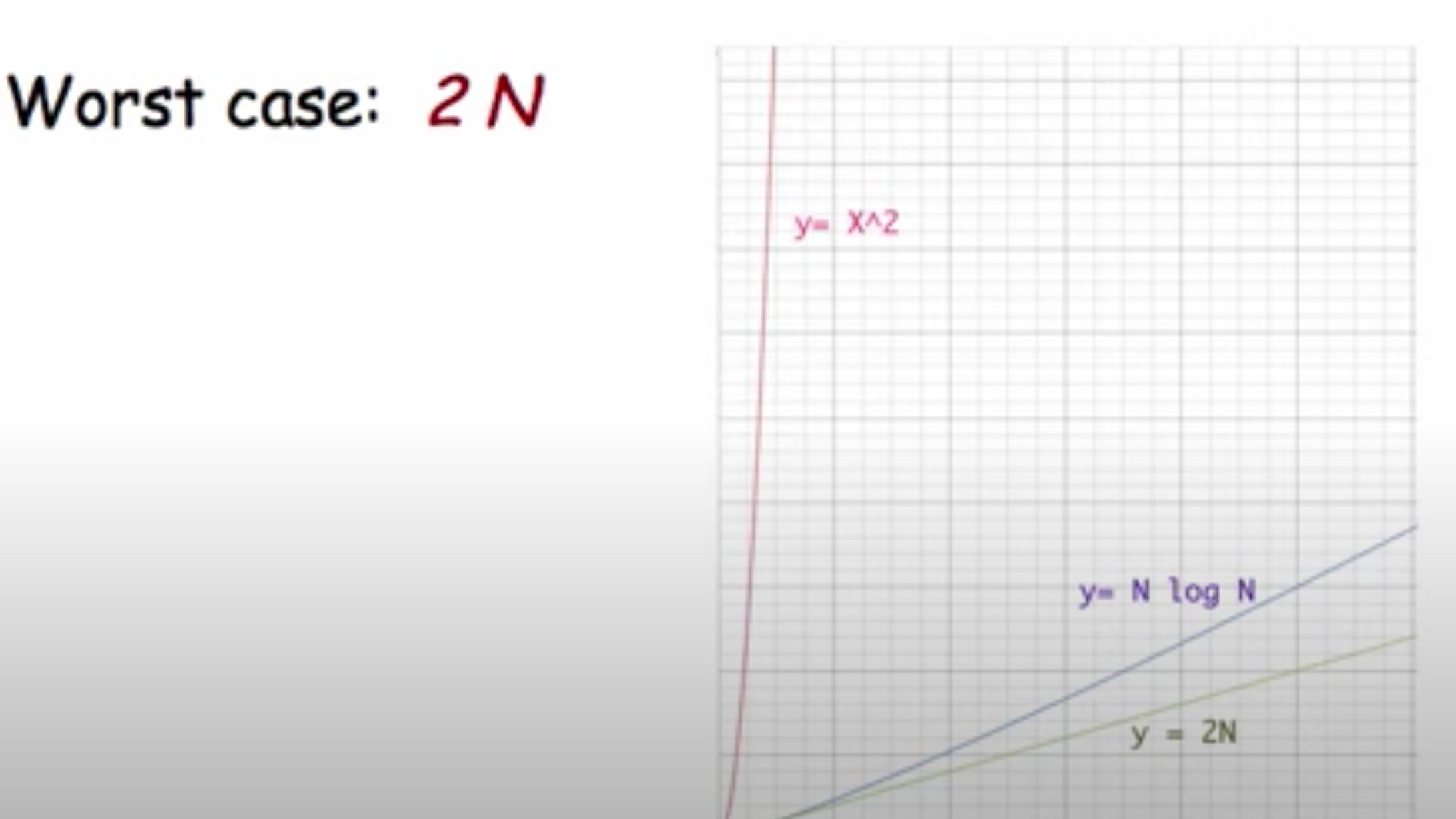
bucket sort
\-algorithm that uses each element’s value to place it into its appropriate bucket
\-running time grows proportional to a __2N__ curve as N grows larger
\-uses more memory for the buckets
\-running time grows proportional to a __2N__ curve as N grows larger
\-uses more memory for the buckets
13
New cards
index
number or position of an element in a list
14
New cards
parallel lists
\-2 or more lists that are setup to correspond based on the index location of the data in the lists
\-allows the data in the lists to be processed
\-allows the data in the lists to be processed
15
New cards
list traversal
loops used to visit every single item in a list
16
New cards
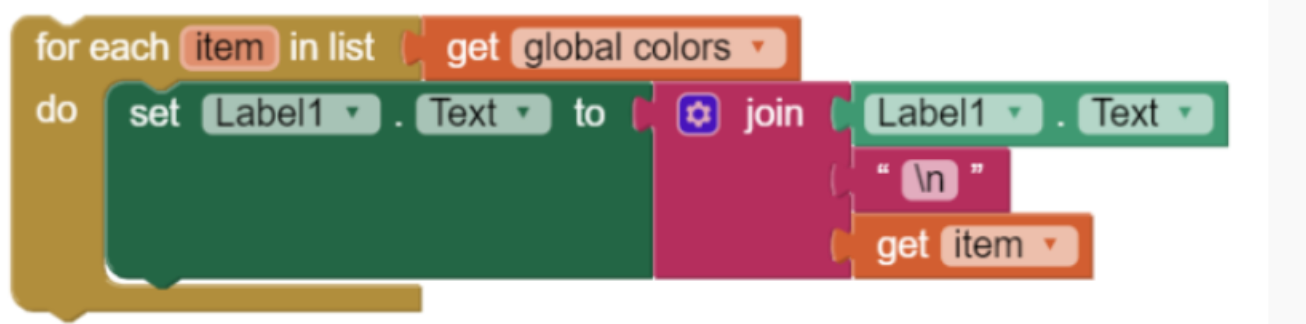
for each item in aList
\-variable item is assigned the value of each element of aList sequentially
\-code in block of statements is executed once for each assignment of item.
\-code in block of statements is executed once for each assignment of item.
17
New cards
insert
adds a value into a list at index i, moving down all other items at & after i in the list.
18
New cards
length
evaluates to the number of elements in a given list
19
New cards
append
adds a value to the end of a list
20
New cards
remove
removes item at index i, moving up all items after the ith item
21
New cards
efficiency
how well an algorithm uses time & memory/space resources (CPU & RAM) for a given input (N)
22
New cards
correctness
whether or not an algorithm contains errors
23
New cards
clarity
how well an algorithm is expressed
24
New cards
worst case analysis
maximum number of guesses required to find or not find the target
25
New cards
reasonable time
\-polynomial time (N^2, 3, 4, etc.)
\-constant time
\-linear time
\-square time
\-cube time
\-constant time
\-linear time
\-square time
\-cube time
26
New cards
unreasonable time
\-exponential time
\-factorial time
\-factorial time
27
New cards
intractable problem
\-Problem that is impossible to solve within a reasonable amount of time
\-Algorithmic solutions are too inefficient/slow to solve it when its inputs grow large (requires exponential time/space to run)
\-Can be used as protection in cryptography & password protection
\-Algorithmic solutions are too inefficient/slow to solve it when its inputs grow large (requires exponential time/space to run)
\-Can be used as protection in cryptography & password protection
28
New cards
heuristic algorithm
\-Algorithm that finds an approximate solution for a hard problem
\-Helpful for finding a solution to an intractable problem in reasonable time
\-Produces a fast & often correct solution, but it cannot be proven optimal
\-Helpful for finding a solution to an intractable problem in reasonable time
\-Produces a fast & often correct solution, but it cannot be proven optimal
29
New cards
decidable (decision) problem
problem in which an algorithm can be constructed to answer “yes” or “no” for all inputs
30
New cards
undecidable problem
\-problem in which no algorithm can be constructed that will always lead to a correct yes or no answer
31
New cards
Halting problem
\-Undecidable problem of whether a computer program will halt (produce an answer) or loop on a given input
\-Given an arbitrary (chance) computer program with an arbitrary input, decide whether it has an infinite loop
\-Undecidable problem proven by Alan Turing in the 1930’s
\-Given an arbitrary (chance) computer program with an arbitrary input, decide whether it has an infinite loop
\-Undecidable problem proven by Alan Turing in the 1930’s
32
New cards
optimization problem
problem with the goal of finding the best (optimal) solution among many
33
New cards
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
Given a list of cities & the distances between them, find the shortest path visiting each city once & returning to the start
34
New cards
dictionary attack
looks up the user’s password in a dictionary
35
New cards
brute force attack/search
\-tries every possible password
\-If there are M different letters & symbols used for a password, then for a password of length N, guessing it would take M^N guesses
\-If there are M different letters & symbols used for a password, then for a password of length N, guessing it would take M^N guesses
36
New cards
sequential computing
\-computational model in which operations are performed one at a time on a processor or computer
\-takes as long as the sum of all of its steps
\-takes as long as the sum of all of its steps
37
New cards
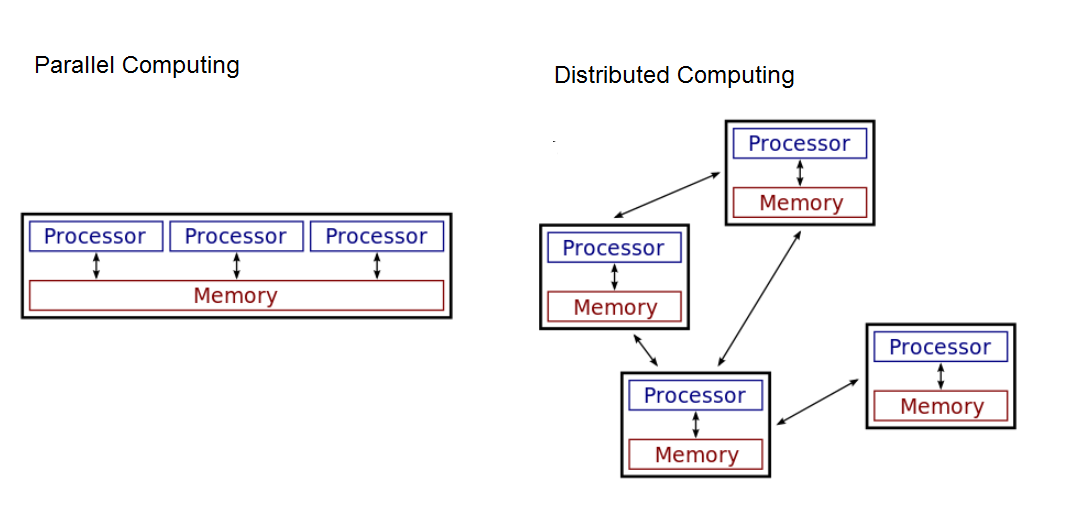
parallel computing
\-Computational model in which a problem or program is broken into smaller sequential operations that are performed in parallel
\-Usually on a computer with multiple processors
\-Takes as long as its sequential tasks (i.e. splitting up a deck of cards into 4 stacks) plus the longest of its parallel tasks (i.e. finding a card in parallel)
\-At some point, adding parallel portions will no longer meaningfully increase efficiency
\-Usually on a computer with multiple processors
\-Takes as long as its sequential tasks (i.e. splitting up a deck of cards into 4 stacks) plus the longest of its parallel tasks (i.e. finding a card in parallel)
\-At some point, adding parallel portions will no longer meaningfully increase efficiency
38
New cards
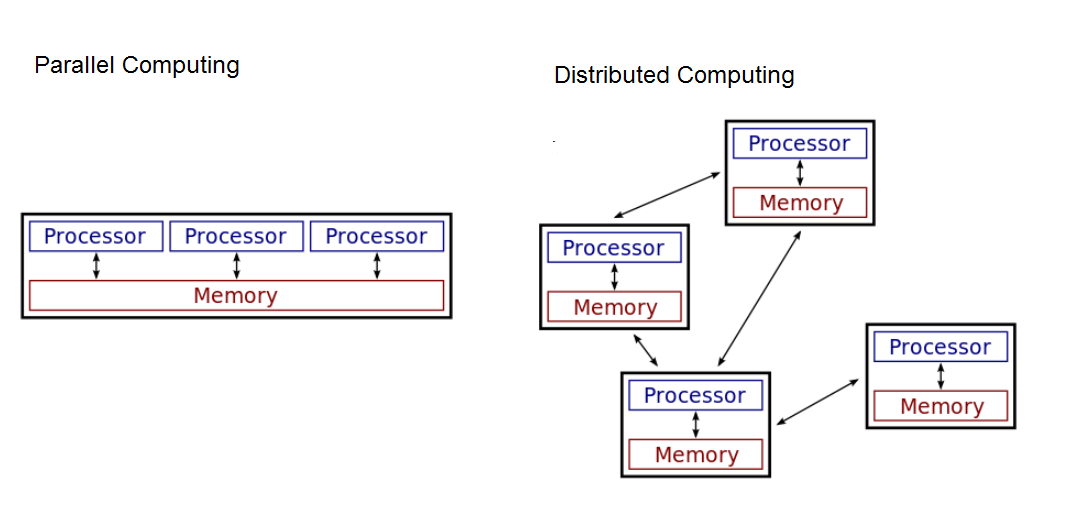
distributed computing
\-Computational model in which multiple networked computers are used to run a program
\-Allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer (required processing time/storage needs)
\-Allows problems to be solved quicker than on a single computer.
\-Allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer (required processing time/storage needs)
\-Allows problems to be solved quicker than on a single computer.
39
New cards
speedup
\-Measured in the time it took to complete the task sequentially divided by the time it took to complete the task in parallel (parallel solutions)
40
New cards
syntax error
a character or string __incorrectly__ placed in the syntax of a sequence of characters, causing failure in execution
41
New cards
semantic error
bug in a program that causes it to operate incorrectly, producing unintended/undesired output
42
New cards
search engine
\-useful for efficiently finding information
\-can record & maintain a history of searches made by users
\-can use search history to suggest websites or targeted marketing.
\-can record & maintain a history of searches made by users
\-can use search history to suggest websites or targeted marketing.
43
New cards
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
\-Seeks to improve how particular web pages rank within major search engines, intending to increase traffic to them
\-Tweaks their algorithms in order to see through disguises (fake legitimate results)
\-Tweaks their algorithms in order to see through disguises (fake legitimate results)
44
New cards
relevance
search engine’s job to provide results that match the intent of the query.
45
New cards
recall
\-The finding of all relevant documents
\-Total recall is unachievable, but it is unimportant
\-Degree of relevance always trumps level of recall, as users want to find a few good results, not all possible results.
\-Total recall is unachievable, but it is unimportant
\-Degree of relevance always trumps level of recall, as users want to find a few good results, not all possible results.
46
New cards
PageRank (Google)
\-measure of the “importance” of each page that takes into account the external references to it
\-A page is judged more important if a lot of important pages link to it
\-A page is judged more important if a lot of important pages link to it
47
New cards
cloaking
\-the deception of users/the presentation of different content to search engines than as displayed to users
48
New cards
CAPTCHA
\-type of challenge-response test used in computing to determine whether the user is human
\-purpose of preventing spam/bot raiding
\-purpose of preventing spam/bot raiding
49
New cards
spider (web crawler)
\-Software that crawls around the Web
\-Retrieves HTML text to index the information it contains
\-Creates Internet traffic, imposing a load on the web server
\-Retrieves HTML text to index the information it contains
\-Creates Internet traffic, imposing a load on the web server
50
New cards
bot
program that endlessly performs some intrinsically repetitive task, often an information-gathering task.
51
New cards
visit
the downloading of a copy of every web page a spider visits
52
New cards
cache
\-The retainment of a copy after it has been indexed
\-Can still be accessed even if the original document has been deleted
\-Makes it possible for people to have information that no longer exists/a version older than the updated information.
\-Can still be accessed even if the original document has been deleted
\-Makes it possible for people to have information that no longer exists/a version older than the updated information.
53
New cards
Logo
\-programming language invented in the 1960s by Seymour Papert
\-used to draw simple and complex geometric shapes.
\-used to draw simple and complex geometric shapes.