Fundamentals Exam 03-08-2024
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
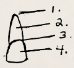
Name of 1.
apex
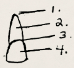
Name of 2.
root
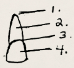
Name of 3.
neck/cervix
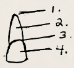
Name of 4.
incisal
List the four tissues of the tooth.
pulp
cementum
dentin
enamel
Pulp:
soft, center of tooth, containing nerves, and blood vessels
Cementum:
hardest part of our body, protects root, and serves as an anchor to the periodontal ligament
Dentin:
hard,supports structure of enamel, yellow hued
Enamel:
hard, insulating barrier, protecting tooth from chemical, physical, and thermal forces
List the surrounding supportive structures of the tooth.
periodontal ligament
alveolar bone
cementum
gingiva
Periodontal Ligament/PDL:
connects cementum to alveolar bone, protects vessels and nerves from masticatory forces
Alveolar Bone:
structure that holds and surround the roots
Gingiva:
tissue of the upper and lower jaw, surrounding, and protecting the base of the teeth
List the three types of oral mucosa.
lining
masticatory
soft
Lining Mucosa:
soft, more delicate tissue
Masticatory Mucosa:
hard, tough tissue
Soft Mucosa:
soft tissue
What are the different parts of the tongue?
dorsum
ventral
lingual frenum
What type of mucosa is the dorsum made of?
masticatory
What type of mucosa is the ventral made of?
lining
What type of mucosa is the lingual frenum made of?
lining
List the soft tissue landmarks of the oral cavity.
Upper lip, buccal frenum, rugae, max. tuberosity, lower lip, lingual frenum, uvula, retromolar area, upper labial frenum, stensen's duct, dorsum, lower labial frenum, soft palate, gag reflex, pillars of fauces, palatine tonsils
Define dentition.
All of the natural teeth in the mouth
How is the mouth divided for the purpose of identification?
using the terms Maxillary and Mandibular
How is the dentition divided into quadrants?
using the terms UR, UL, LR, LL
How is the dentition divided into quadrants?
using the terms Anterior and Posterior
List the three periods of dentition.
Primary
Mixed
Permanent
Primary dentition:
first set of teeth to erupt, known as decidous teeth
Mixed dentition:
both primary and permanent teeth present
Permanent dentiton:
final set of teeth to erupt, known as succedaneous teeth
How is the Permanent Dentition identified?
#’s 1-32
How is the Primary Dentition identified?
letters A-T
What types of teeth are in the anterior section?
incisors and canines
What types of teeth are in the posterior section?
molars and premolars
How many roots do Molars have?
max.-3
mand.-2
How many roots do Premolars have?
1
How many roots do Incisors have?
1
How many roots do Canines have?
1
List the surfaces of the teeh.
buccal , lingual , occlusal , mesial , distal
Describe buccal surface.
faces cheek
Describe lingual surface.
faces tongue
Describe occlusal surface.
where occlusion meets, used for chewing/grinding
Describe mesial surface.
towards midline
Describe distal surface.
facing away from midline
Identify the concepts surrounding the management of the dental chart.
___
List the situations in which a medical alert is placed inside the patient’s chart.
severe latex allergy, allergies to antibiotics, prophylactic antibiotic trt./premed, pacemaker, defibrillator, mitral valve prolapse
For the purposes of hard tissue charting, what are the two types of tooth diagrams found in dental charts?
periodontal tissue charting and hard tissue charting
What colors are used in hard tissue charting?
red, blue
When is the color red used in hard tissue charting?
needs attention
When is the color blue used in hard tissue charting?
existing condition
Class I cavity:
OL, OB
Class II cavity:
MO, DO, MOD
Class III cavity:
M, D
Class IV cavity :
MI, DI, MID
Class V cavity:
Ling., B, F, Lab.
Class VI cavity:
I, O
How many locations per tooth are identified in periodontal charting?
6 (3 facial and 3 lingual)
What is a study model used for?
pt. educational purposes, accurate replication
What is another name for study model?
diagnostic cast
What is the name of the body’s process of adding new bone?
osteoblasts
What is the name of the body’s process of eliminating bone or hard tissue?
osteoclasts
What is the difference between the anatomical crown and the clinical crown?
one shows entire tooth including root, while the other does not
Anatomical Crown:
part of the tooth covered by the enamel
Clinical Crown:
portion of the crown that is visible in the mouth
Define occlusion.
the way the teeth come together in their functional position, the bite
Define centric occlusion.
position of max. and mand. arches that produces proper occlusion
Define functional occlusion.
when max. and mand. connects when functioning during day-to-day tasks (ex.talking)
What is the term meaning without teeth?
edentulous
Which instrument is used by a dentist to detect decay?
explorer
How many classifications of mobility are there?
1-3
What is the ideal classification of mobility?
1
What is the least desirable classification of mobility?
3
On which tooth is the Cusp of Carabelli found?
Max. 1st molars
List the various anatomical features of teeth.
cusp, ridge, incisal ridge, incisal edge, cingulum, fossa, groove, fissure, pit
What is the name of the area where adjacent teeth physically touch?
contact point
What is the term for the widest point on the crown of a tooth?
height of contour
What is the term for the junction of two tooth surfaces?
line angle
What is the term for the junction of three tooth surfaces?
point angle
What are the names for the horizontal third divisions of the crown of the tooth?
incisal, middle, cervical
What is the term that means below the gums?
subgingival
What is the term that means above the gums?
surpagingival
What is the name of the hole that a tooth is anchored in?
alveolar socket
Define eruption.
process of the movement of teeth entering and becoming visible in mouth for normal working position
Define impaction.
not erupted into the mouth due to being blocked by position, tissue, bone, or another tooth
Name examples of fixed prosthodontics.
bridge, crown, inlay, onlay, veneer, pontic, abutment
Bridge:
cast rest. that replaces missing teeth (fixed)
Crown:
cast rest. covering the anatomical crown (fixed)
Inlay:
cast rest. made to restore a class II prep. (fixed)
Onlay:
cast rest. made to cover occlusal, one or more cusps, & proximal surfaces of a post. tooth (fixed)
Veneer:
layer of tooth-colored material that is bonded or cem. to the prepared fac. surface of a tooth (fixed)
Pontic:
artificial tooth in a br. that replaces a natural missing tooth (fixed)
Abutment:
either a tooth or an implant that supports a fixed br. , covering the pts. teeth (fixed)
Name examples of removable prosthodontics.
full denture, partial denture
Full Denture:
prosthesis that replaces all teeth in one arch (removable)
Partial Denture:
prosthesis that replaces several teeth with the same arch (removable)
List the parts of a Tofflemire/matrix band setup.
tofflemire retainer, matrix band, wedge
Restorative Dentistry:
to bring back natural appearance of a tooth
What is an example of Restorative Dentistry?
amalgam, palladium, alloy, gold materials used
Esthetic Dentistry:
recreating the tooth to an artistically pleasing and attractive appearance
What is an example of Esthetic Dentistry?
ceramic, porcelain, composite, veneers used