Into 0.0.0
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Define economic growth?
An increase in the value of a country’s production
Define inflation
A sustained increased in the general level of prices
Define unemployment
When workers are willing and able to work but cannot find a job
Define “the balance of trade”
The difference between the value of exports and the value of imports
What are the 7 macroeconomic objectives?
A high rate of national income growth
A low rate of inflation
A low rate of unemployment
A beneficial trade situation
Protection of the environment
An acceptable level of inequality
A sustainable level of government
What are the 4 ways to judge macroeconomic performance?
Set macroeconomic objective - what a country wants
Set macroeconomic targets - the number that would indicate #1 being achieved
Look at macroeconomic statistics to see if #2 is being achieved
If not, use macroeconomic policies to try and solve the problem
What are the 3 targets for the UK’s performance?
GDP annual growth of 2%
Inflation 2% (but between 1% and 3% is fine)
Unemployment (approximately) 4%
What is the current state of the UK’s performance?
GDP annual growth of3.2% - not good
Inflation 3.8% - not good
Unemployment 4.7% - okay
What is one way of improving balance of trade?
establishing relations with emerging economies and countries with natural resource.
What are some key things that impact the size of an economy?
Land - natural resources, geology (location - how much land is available to be used for production)
Capital (technology)
Labour force
Enterprise
Government policy
What is income?
Payment for factors of production
What are the main factors of production?
labour - wage
land - rent
capital
enterprise - dividends
What are dividends?
Share of profits
Dividends are a percentage of a company's earnings paid to its shareholders as their share of the profits.
What is the circular flow of income?
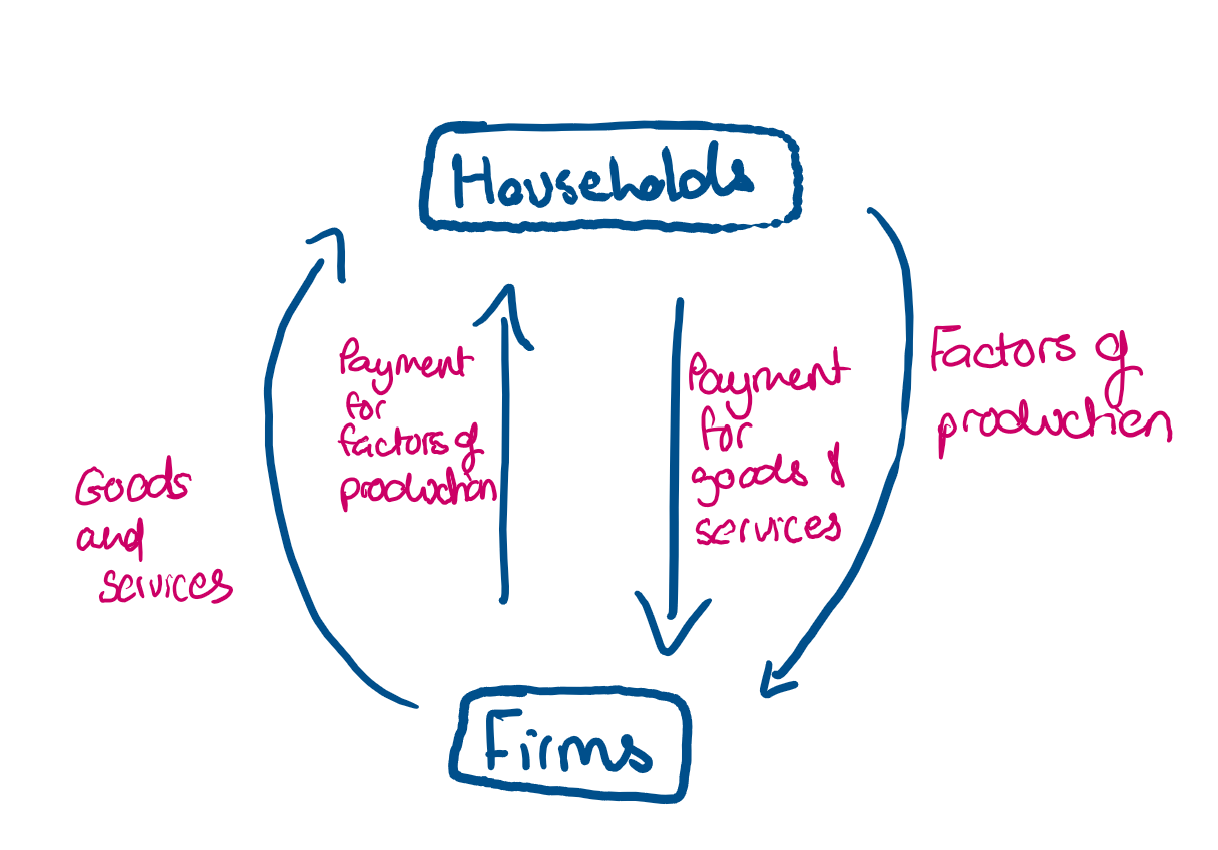
What are the 4 factors of production?
enterprise
capital (goods and services)
land
labour
Give 3 examples of income?
wage (mostly through labour)
rent (land)
dividends (enterprise)
What are the 2 agents in the circular flow of income?
firms
households
What are the ways income flows in and out of the economy?
investment - loans from a bank for firms to buy capital
Savings
Imports
Exports
Gov spending
Taxes
What are injections?
Money which comes into the circular flow of income
What are withdrawals/ leakages?
money going up out of the circular flow of income
Give some examples of injections
IGE
Investment (I)
Gov spending (G)
Exports (X)
give some examples of withdrawals
STI
Savings (S)
Taxes (T)
Imports (M)
What should the relationship be between injections and withdrawals
We way more injections than withdrawals as this will help the economy to grow