histology - exam 1 review nucleus
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
The largest membrane-bound compartment in most cells. They contain DNA in the form of chromatin and RNA in the form of the nucleolus
Describe the nucleus
Neutrophil: Polymorphonuclear (PMN) = multishaped
Lymphocyte: Circular nucleus
Red Blood Cell: Anucleate (no nucleus)
Describe the nuclei of the neutrophil, lymphocyte, and red blood cell.

Euchromatin: lightly condensed DNA indicates that cells are metabolically active
What type of chromatin does the arrow indicate and what does it tell you about the properties of the cell?
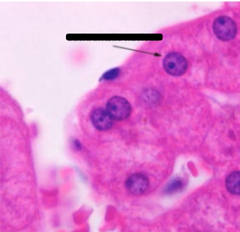
Heterochromatin: very condensed DNA indicates that the cells are metabolically inactive (cells that provide structure)
What type of chromatin does the arrow indicate and what does it tell you about the properties of the cell?
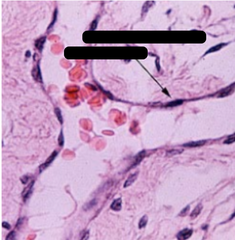
Barr body: It is made of the repressed X chromosome in the female's DNA
What is indicated by the green arrow & what is it made of?

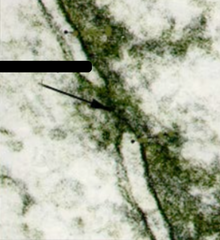
Nuclear envelope: It is made of two membranes
Black arrow: Nuclear pore
Name the major structure seen here, what it is made of & what is indicated by the black arrow?
Nucleolus: It is the site of ribosomal RNA synthesis and involved in protein synthesis
What does the black arrow indicate & what is its function?

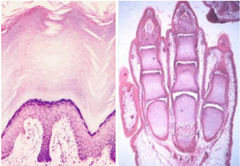
Apoptosis: This is controlled cell death which produces pynkonotic nuclei. These cell become squamous as the cells die.
What type of cell death is seen here?
Loosely Condensed Nuclei = Active cell
Non-Basophilic Cytoplasm = Not producing protein
Large Cell Size (Room for Mitochondria) = Involved in Transport
Green Arrow = Acidophilic rim = Absorption
Structure = Microvilli
Based on the form of this cell (black arrow) what can you determine about its function?

The structure increases the surface area to improve the rate of absorption. Note: This is an Electromicrograph
What does the structure of these cells tell you about their function?

Loosely Condensed Nuclei = Active cell
Nonbasophilic Cytoplasm = Not producing protein
Cuboidal/Columnar Cell shape = Secretory or Absorptive
Increased Basal Surface Area = Absorbing extracellular substances & excreting into a lumen
Based on the form of this cell (black arrow) what can you determine about its function?
It is composed of structural proteins to support & maintain the shape of the cell. It also assists in cell functions like cell division & muscle contraction.
Describe the cytoskeleton
Microfilaments: Specifically actin - found in most cells
Functions:
1. Contraction of muscle cells
2. Maintenance of cell structure
3. Movement of vesicles & organelles within the cell
4. Anchoring of membrane proteins
What is indicated by the blue arrow? Describe the function

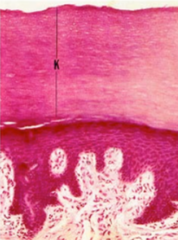
Intermediate filament: Keratin - found in the skin & forms the protective outer layer of the skin
What is indicated by "K"?
1. Neurofilaments - in neurons , helps to maintain cell shape and facilitate conduction
2. Nuclear Lamina - in nuclei, maintains nuclear structure
3. Desmin - in muscle cells, maintains structure of cells and connects internal structures to transmembrane proteins
4. Glial Fibrillary Acid Protein (GFAP) - in astrocytes, forms structural links between membrane & organelles
5. Vimentin - in mesodermal cells, connects intracellular structures
List the 5 other major classes of intermediate filaments and their function
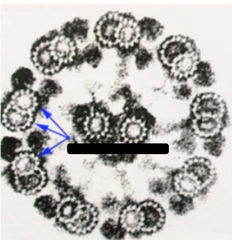
Microfilaments: Specifically microtubules (composed of tubulin)
Functions:
1. Maintenance of cell shape
2. Special movement of cilia
3. Movement of chromosomes during division
4. Intracellular transport
5. Cell elongation & movement
Identify the structures indicated by the blue arrows and list their function
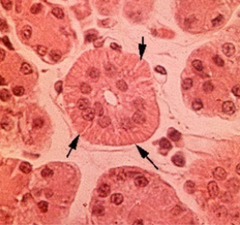
Secretory Granules which are membrane bound and are transported out of the cell via exocytosis
Identify what is indicated by the black arrows and explain how they are transported

Glycogen - A Non-membrane bound storage product which is converted to glucose during energy production
What is indicated by the purple arrows and what is its purpose?

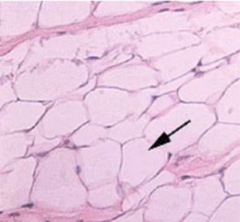
Adipocytes - made of lipid droplets which are non-membrane bound storage of fat droplets
What is indicated by the black arrow and what is it made of?
Pigment: Lipofuscin - Known as the "wear & tear" pigment and develops with aging. Found most commonly in liver, nerve, & heart muscle cells
What is indicated by the black arrows, how & where does it tend to develop?
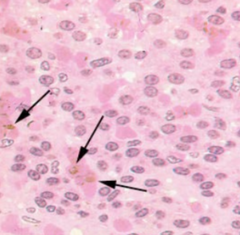
Pigment: Melanin - Found in the skin and protects again UV light. It gives humans and animals their characteristic skin & hair color
What is indicated by the black arrows, how & where does it tend to develop?
