zotc 119 ppt 5 hamster, guinea pig, and rabbit
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
free of all organisms including those normally found in the gut
germ free or axenic
contain 1 or few non-pathogenic microorganisms
gnotobiotic or defined flora
contain specifically defined microorganisms
specific pathogen free (SPF)
colonized with diverse and largely undefined microbiome
conventional
housing/caging
safe - no sharp edges or protrusions
meet the minimum space requirement
meet the basic physical, physiological and behavioral needs of the animals
provide enrichment
accounts for social needs
facilitate feeding and waste removal
material for good housing/caging
durable, non-toxic, corrosion resistant
withstand cleaning and disinfection
most commonly used and durable material for housing
stainless steel
transparent, autoclavable, durable
autoclaving temp: 120°C
max temp of sterilization: 138°C
cannot be autoclaved with soiled litter
Polycarbonate (PC)
transparent, autoclavable, durable
lifetime: 3x longer, higher cost
autoclaving temp: 134°C
max temp of sterilization: 165°C
can be autoclaved with soiled litter
Polysulfonate (PSU)
cons of PSU over PC
3x longer lifetime, can be autoclaved with soiled litter
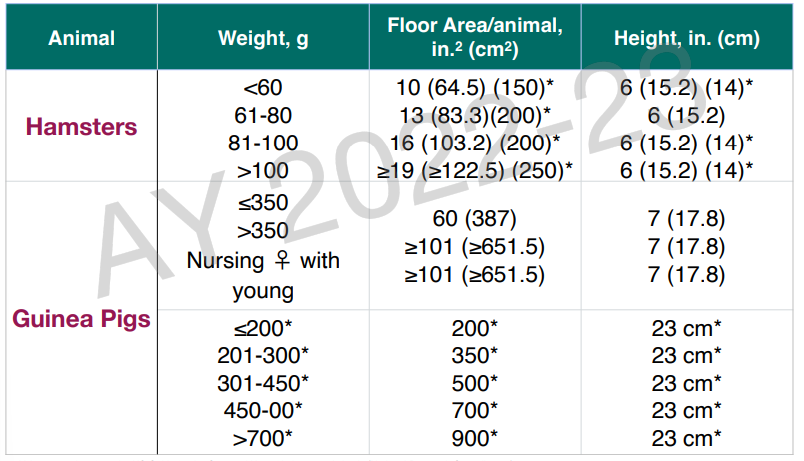
cage size/ space requirement for hamsters and guinea pigs
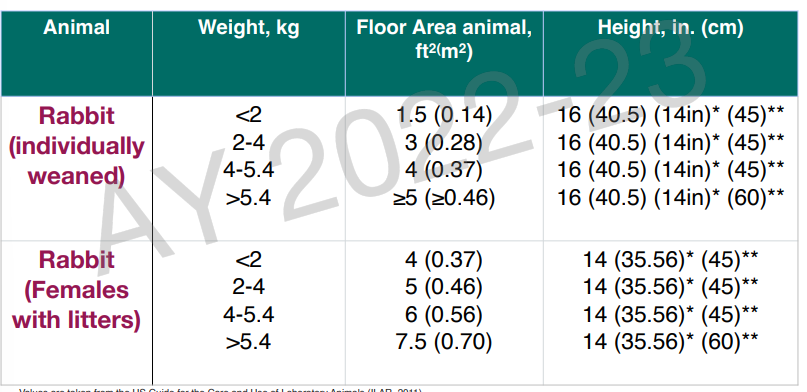
cage size/ space requirement for rabbit individually weaned and females with litters

shoebox cage type

suspended cage type

metabolic cages

individually-ventilated cages

integrated cage type

self-contained removable cage type

modular cage type

group housing
floor area for weaning to 7 weeks old
800 cm² floor area/animal
floor area for 7 to 10 weeks old
1200 cm² floor area/animal
for tops and walls
solid or mesh
allow proper ventilation and observation
flooring must be
solid, perforated, slatted and wire grids
slip-resistant
appropriate spacing and size of holes and slats (0.5-0.7 in)
beddings must be
allow species-specific behavior
facilitates thermoregulation
provides comfort
low potential toxicity
free of dust, microbial organisms or parasitic contamination
absorbs urine and feces
smell should not alter species-specific behavior
may be in direct contact with the animals or in the bottom of the cage
type of beddings
paper pellets
shredded paper
straw pellets
straw
sawdust
wood shavings
adv and disadv of sawdust/softwood shavings
adv - cheap, absorbent, eco-friendly
disadv - pine and cedar oils can cause hepatic problems. dust can cause respiratory problems
adv and disadv of paper pellets
adv - dust-free, eco-friendly, absorbent
disadv - soiled easily, expensive, ingestion problems
adv and disadv of paper shreddings
adv - absorbent, less dust, eco-friendly
disadv - soiled easily, more expensive than sawdust’shavings, ingestion problems
adv and disadv of pelleted straw
adv - comfortable, safe when ingested, dust-free, absorbent
disadv - expensive, ingestion problems
adv and disadv of straw
adv - readily available in large quantities, cheap
disadv - sharp edge can cause injury, soiled easily

J-type feeder, 3-4 inches off the floor

rubber stopper

slipper tubes

plastic bottles
nameplate holder
enhance well-being by providing animals with sensory and motor stimulation thus promoting species-specific behaviour and psychological well-being
influence animal phenotype and experimental outcome
enrichment
physical enrichment
enclosure complexity, nesting material, sensory enrichment, nutritional enrichment
social enrichment
contact vs non-contact (group caging, harem mixed groups)
sensory enrichment
soft background sound to mask loud noises
enrichment for hamster
fruits and vegetables
sunflower seeds
cardboard house
cardboard tunnel
nesting, nesting cup
cyclone chew
crawl ball

what should be avoided for guinea pig housing
solitary
>2 males
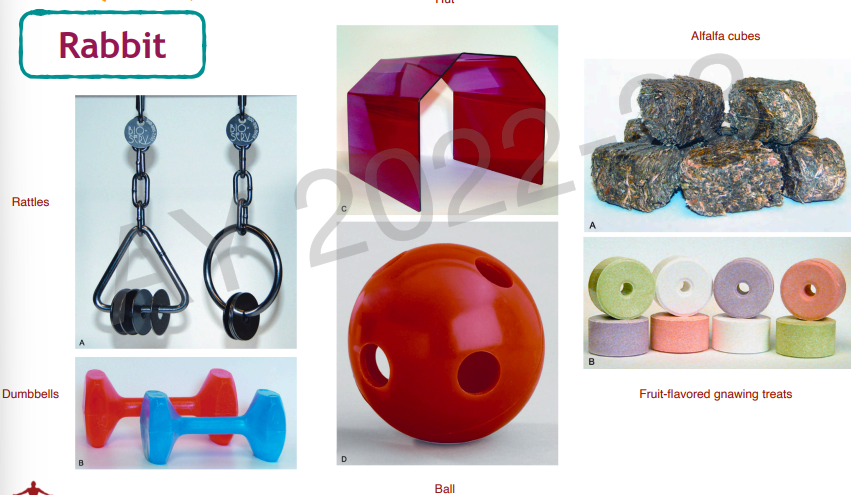
enrichment for rabbit
rattles
dumbbells
ball
hut
alfalfa cubes
fruit-flavored gnawing treats

microenvironment vs macroenvironment
micro - high temp, humidity, and gases of particulate matter
macro - high lighting
refers to the ambient air temperature. measured by thermometer freely exposed to the air but shielded from radiation and moisture
generally should be set below the animals’ LCT
dry-bulb temperature
metabolic heat production = evaporative heat loss mechanism
lower and upper critical temperatures (LCT & UCT)
thermoneutral zone (TNZ)
blank
Blank
bbbb
Bbbb
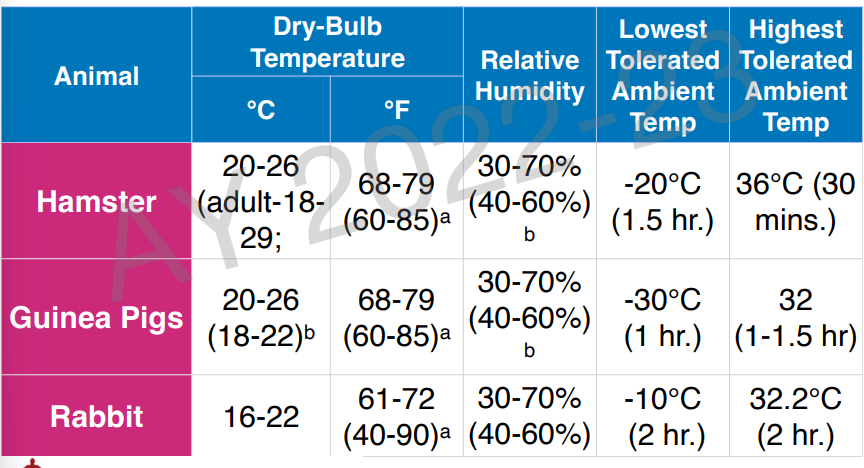
recommended dry-bulb macroenvironmental temperature and humidity
factors affecting temperature and humidity
house design
construction materials
enrichment devices - shelters and nesting materials
filter tops
animal-related factors - age, BW, sex
type and frequency of contact bedding changes
fresh air changes per hour
10-15 (ILAR< 2011)
15-20 (European Commission, 2007)
recommended room air supply should be
100% fresh air with no recirculation
recycled air should be filtered ___
85--95% with efficient filters to remove airborne particles
factors affecting ventilation
room dimensions
type of primary enclosure
enrichment devices - shelters and nesting materials
animal-related factors - age, BW, sex
type and frequency of contact bedding changes
odor control, allergen control and particle generation
T/F:
Natural lighting from external windows are recommended as source of light
FALSE. NOT recommended
factors affecting illumination
pigmentation of the animal,
body temp
hormonal status
age, species, sex, stock/strain
aspects to consider for illumination/lighting
photo-intensity
photoperiod
spectral composition
recommended photo-intensity
130-325 lux (12-30 ft candles)
if the photo-intensity is >325 lux, it will lead to
phototoxic retinopathy
affects vaginal opening, ovarian and uterine weights, estrus cycle length and pre-weaning mortality
measured in Lux
photo-intensity
animals with ____ are more susceptible of photo-intensity
non-pigmented iris
illumination of 1 meter sq. surface that is 1 meter away from a single candle
Lux
day length or the period of daily illumination received by the animal
critical regulator of reproductive behavior
photoperiod
photoperiod for hamster, guinea pig, rabbit (L - light, D - dark)
hamster: 12hr L:12hr D
14hr L: 10hr D
guinea pigs: 12hr L: 12 hr D
14hr L: 10hr D
rabbit: 12hr L: 12hr D
16hr L: 8hr D
nocturnal; brief periods of activity during daytime
hamsters
nocturnal; wild type are crepuscular
rabbits (wild rabbits - crepuscular)
no distinct circadian rhythm; active > 20 hours/day if house singly; wild guinea pigs are crepuscular
guinea pigs
wavelength of the light should stimulate the natural wavelength of the sunlight
spectral quality
incandescent light source
red ~700 nm
fluorescent light source
violet ~400 nm
quartz halogen light source
red ~600-900 nm
light emitting diodes
ultraviolet-infrared ~365-880 nm
wavelength for h, gp, r
300-2000 nm (450-700 nm)
factors affecting illumination
light intensity and wavelength
animals’ exposure to light
animal pigmentation
circadian rhythm
animal-related factors - strain, size, body temp, age, sex
hormonal status
noise a hamster can detect?
<85 dB
noise a guinea pig can detect?
0.1-40kHz (0.2-2kHz @ 97dB)
0.32-50kHz @ 60dB
4-28kHz @ 10 dB
noise a rabbit can detect?
0.075-50 kHz (2-9kHz)
<85
rabbits’ constant exposure to white noise leads to
increase in size of adrenal gland
optimum condition for audiogenic seizure production
10-20kHz @90-120 dB
standard diets in most laboratory facilities
produced from natural ingredients
pelleted
closed formulas/propriety
chow diets
combination of natural ingredients,
pure nutrients and ingredients of varying degrees of refinement
may not be pelleted
open formulas
purified or semi-purified diets
softer composition
provide greater availability of nutrients
increase wastage
high production cost
extruded diets
feeding regimen of the 3
h and gp - ad libitum
r - once or twice a day for adult (90-120 g sid)
crude protein, crude fiber and fat of the 3
Extensive calcification of the soft tissues, rickets (broadened cartilage plates and hypoplasia of incisors
calcium and vit D
Reproductive disorders i.e. fetal resorption, abortion, stillbirths & hydrocephalus, poor growth, eye abnormalities
vit A
Muscular dystrophy, abortion, stillbirths, neonatal death, testicular degeneration
vit E and selenium
Poor skin, poor hair coat, weight loss, stiffness, swollen joints, paralysis, poor bone and tooth development
vit C
Tremor, imbalance
B1 thiamine
Corneal vascularization
B2 riboflavin
Anemia, diarrhea
niacin
Anemia, diarrhea
B6 Pyridoxine
Anorexia, weight loss, intestinal hemorrhage, abortion
Pantothenic acid
more water should be provided on
growers, lactating, pregnant, fed with high fiber diet

chemical waste pail

radioactive solid waste container

radioactive liquid waste container

risk group 2 biologically contaminated solids
biohazard waste pail

biologically contaminated solids only
biohazard bag

needles, syringes, lancets, blades, etc
sharps containers