Week 6: Proteins, Translation & Mutations
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PAL 6: 5b, 6a
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
The unfolding of a protein by heat or chemical treatment is referred to as:
A) hydrolysis
B) depolymerization
C) disaggregation
D) uncoupling
E) denaturation
E) denaturation
The smaller sub-structures such as a helices and B sheets within a single polypeptide chain are referred to as:
A) secondary
B) primary
C) quaternary
D) tertiary
A) secondary
Proteins that prevent inappropriate folding of newly synthesized proteins are called:
A) synthetases
B) chaperones
C) enzymes
D) polymerases ribosomes
B) chaperones
T/F: Most proteins retain metabolic activity when denatured.
False
The interactions between amino acids are major factors in determining the shape of a protein. These interactions can be affected by the environment surrounding a protein.
Which factor would have an effect on the shape of a protein?
A) the temperature of the environment
B) the pH of the environment
C) whether the other molecules in the environment are predominantly hydrophilic or hydrophobic
D) the concentrations of ions present in the environment
E) All of these choices are correct.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Which step occurs in the E site of the ribosome during translation?
A) None of the other answer options is correct.
B) An incoming charged tRNA binds to this site.
C) The tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide moves to this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
D) An uncharged tRNA is ejected from this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
D) An uncharged tRNA is ejected from this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
Which step occurs in the P site of the ribosome during translation?
A) The tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide moves to this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
B) An uncharged tRNA is ejected from this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
C) An incoming charged tRNA binds to this site.
D) None of the other answer options is correct.
A) The tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide moves to this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
Which step occurs in the A site of the ribosome during translation?
A) The tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide moves to this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
B) An incoming charged tRNA binds to this site.
C) None of the other answer options is correct.
D) An uncharged tRNA is ejected from this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
B) An incoming charged tRNA binds to this site.
When a charged tRNA is about to bind to the vacant A site of a ribosome, where is the growing polypeptide?
A) in the E site
B) in the A site
C) in the P site
D) The polypeptide is equally likely to be in any of the three sites.
C) in the P site
Binding sites for tRNA are located in:
A) the large ribosomal subunit.
B) neither ribosomal subunit.
C) both ribosomal subunits.
D) the small ribosomal subunit.
A) the large ribosomal subunit.
Assuming A-U and G-C pairing between the anticodon and the codon, what anticodon in tRNAMet would pair with the codon 5'-AUG-3'?
A) 5'-ATG-3'
B) 5'-GUA-3'
C) 5'-AUG-3'
D) 5'-CAU-3'
E) 5'-UAC-3'
D) 5'-CAU-3'
Ribosomes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are:
A) identical in structure and translate using the same genetic code
B) similar in structure and translate using different genetic codes.
C) similar in structure and translate using the same genetic code.
D) identical in structure but translate using different genetic codes.
C) similar in structure and translate using the same genetic code.
T/F: In a protein-coding region of DNA, a mutation that replaces a single nucleotide for another doesn't necessarily change the original amino acid encoded by that region.
True
T/F: Protein families contain proteins with identical primary structures, but differing secondary and tertiary structures.
False
In a population of organisms, selection is the process by which:
A) Chaperones progressively fold the respective domains of a protein.
B) Cells choose which genes to express in a given circumstance.
C) A protein is selected to either be maintained or denatured.
D) RNA levels are regulated to avoid saturating ribosomes in the ER.
E) Beneficial and harmful random mutations are retained or eliminated.
E) Beneficial and harmful random mutations are retained or eliminated.
An area of a polypeptide that bends in a particular way, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule, is a folding:
A) segment.
B) domain.
C) region.
D) exon.
E) lariat.
B) domain.
T/F: Insertion of one nucleotide into a gene cannot lead to a frameshift mutation.
False
T/F: Any DNA damage is considered to be a mutation, even if it is immediately corrected by the action of DNA polymerase.
False
A point mutation that causes an amino acid replacement is called a:
A) synonymous (silent) mutation.
B) nonsense mutation.
C) nonsynonymous (missense) mutation.
C) nonsynonymous (missense) mutation.
A point mutation that results in the early termination of translation is a:
A) nonsynonymous (missense) mutation.
B) synonymous (silent) mutation.
C) nonsense mutation.
C) nonsense mutation.
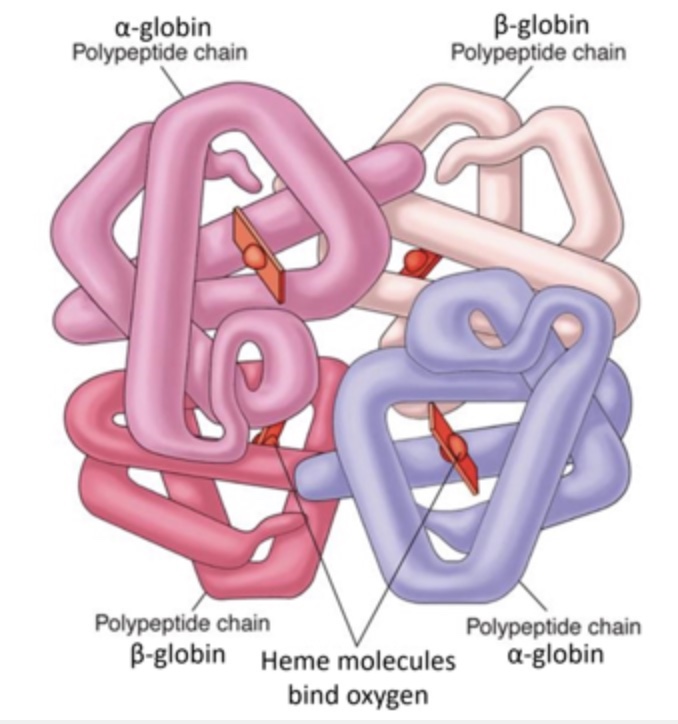
Hemoglobin is a protein found in the cytosol of red blood cells. In humans, it is coded for by two different genes: HBA and HBB. The HBA gene encodes a protein subunit called alpha-globin and the HBB gene encodes a protein subunit called beta-globin. Each of these subunits binds a heme molecule that binds oxygen. A diagram of human hemoglobin is shown below. Use this information to determine whether each of the following statement is true or false.
T/F: Individual alpha-helices found in hemoglobin are stabilized by ionic bonds.
False
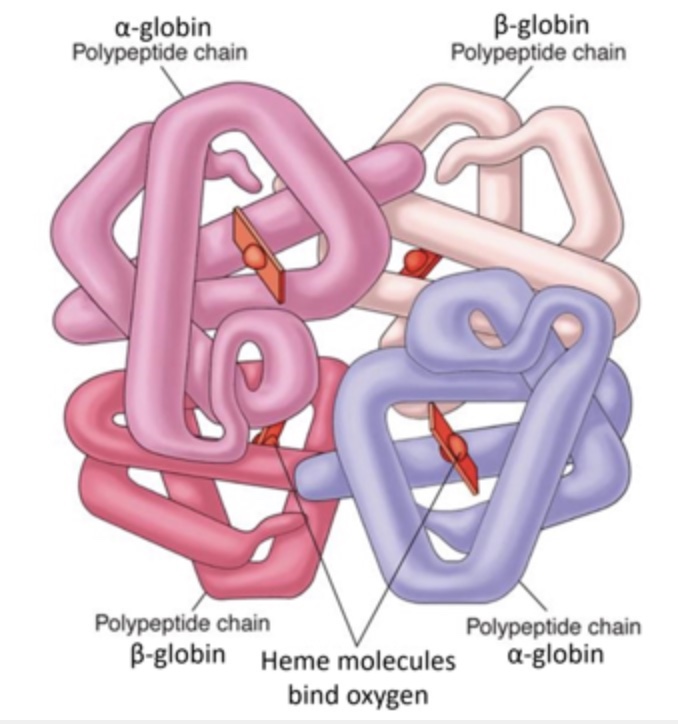
Hemoglobin is a protein found in the cytosol of red blood cells. In humans, it is coded for by two different genes: HBA and HBB. The HBA gene encodes a protein subunit called alpha-globin and the HBB gene encodes a protein subunit called beta-globin. Each of these subunits binds a heme molecule that binds oxygen. A diagram of human hemoglobin is shown below. Use this information to determine whether each of the following statement is true or false.
T/F: An individual alpha-globin polypeptide chain has quaternary structure.
False
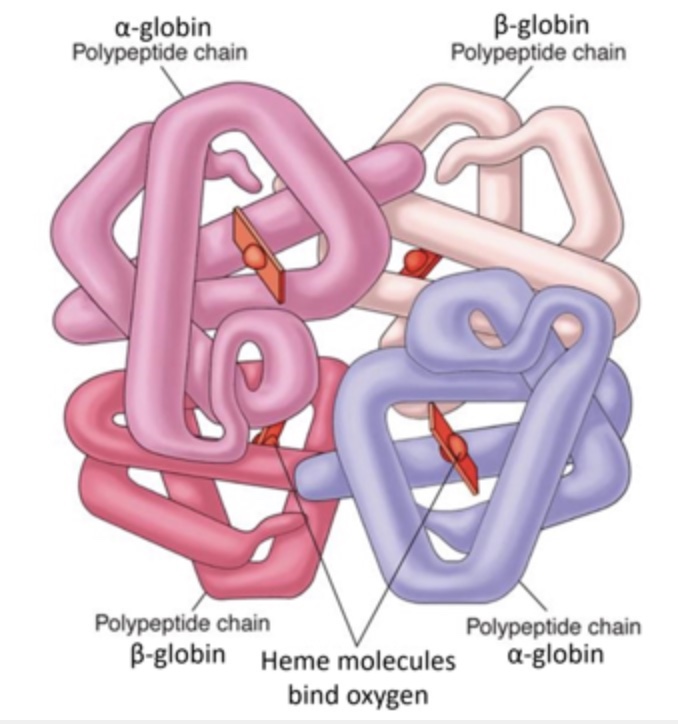
Hemoglobin is a protein found in the cytosol of red blood cells. In humans, it is coded for by two different genes: HBA and HBB. The HBA gene encodes a protein subunit called alpha-globin and the HBB gene encodes a protein subunit called beta-globin. Each of these subunits binds a heme molecule that binds oxygen. A diagram of human hemoglobin is shown below. Use this information to determine whether each of the following statement is true or false.
T/F: A DNA mutation that affects the primary structure of the beta-globin protein subunit would also affect the primary structure of the alpha-globin subunit.
False
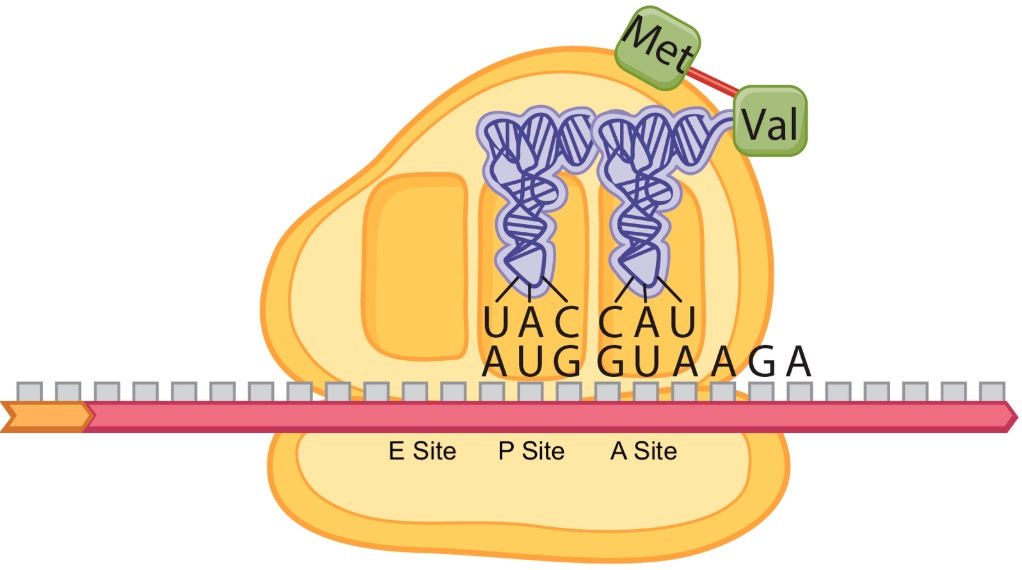
The figure above depicts one stage in the process of translation in a eukaryote. The next amino acid after valine (Val) will be ____________, and it will be associated with a tRNA with the anticodon ____________.
A) Serine, 3'-AGA-5'
B) Serine, 3'-UCU-5'
C) Arginine, 3'-AGA-5'
D) Arginine, 3'-UCU-5'
D) Arginine, 3'-UCU-5'
If the RNA transcript 5′‑UACAAAAUGCUGGGUUCG‑3′ is translated codon by codon from one end to the other, which of the polypeptides would correspond to this part of the mRNA?
A) NH2- Arg-Thr-Gln-His-Phe-Val -COOH
B) NH2‑ Met‑Phe‑Tyr‑Asp‑Pro‑Ser ‑COOH
C) NH2- Tyr-Lys-Met-Leu-Gly-Ser -COOH
D) NH2- Ala-Trp-Val-Val-Lys-His -COOH
C) NH2- Tyr-Lys-Met-Leu-Gly-Ser -COOH
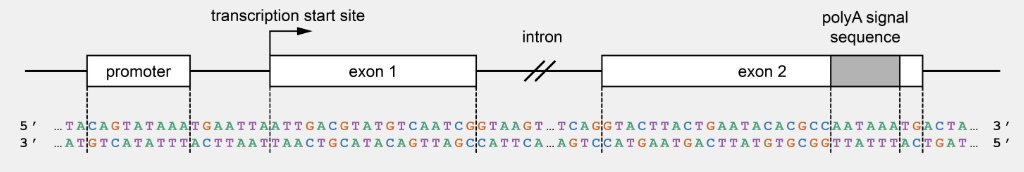
The diagram below shows an imaginary eukaryotic gene containing two exons. A portion of the intron is not shown to save space.
The same sequence is typed out below. You are permitted to copy/paste this sequence into a text editor on your computer to work on it during the PAL. (Tip: use a monospace font like Courier New to line up the letters properly.) The promoter is highlighted in yellow, and the exons are highlighted in blue. The poly(A) signal sequence is bolded.
Exon nucleotides are numbered beginning at the transcription start site (+1), and they do not include the nucleotides in the intron. Exon 1's first nucleotide is nucleotide 1, and exon 2's first nucleotide is nucleotide 19. Use this information to answer the following questions.
The product of this gene contains how many amino acids?
6
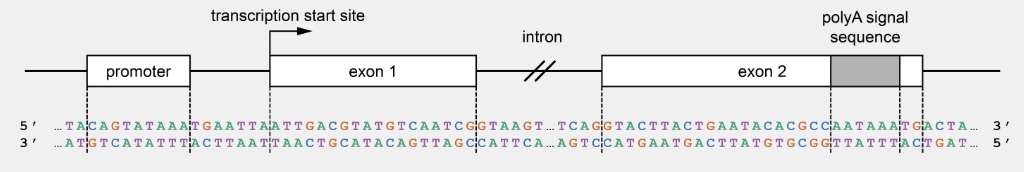
What amino acid does the third codon of this gene's open reading frame encode?
Isoleucine (Ile)
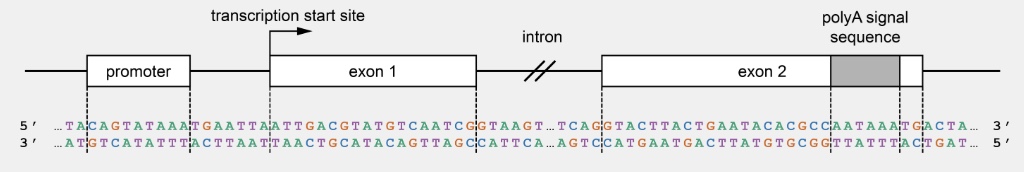
T/F: Changing nucleotide 17 from C to A would result in no change in the amino acid sequence.
True

T/F: Changing nucleotide 13 from C to A would result in a truncated (shortened) polypeptide.
True

The diagram below shows a gene with four exons. The reading frame that encodes the protein is shaded and begins in exon 1 and ends in exon 3. Use this diagram to determine whether each of the following statements is true or false.
T/F: The start codon is in exon 1.
True

The diagram below shows a gene with four exons. The reading frame that encodes the protein is shaded and begins in exon 1 and ends in exon 3. Use this diagram to determine whether each of the following statements is true or false.
T/F: The stop codon is in exon 4.
False

T/F: The polyA signal sequence is in exon 4.
True

T/F: A frameshift mutation could occur in exon 4.
False
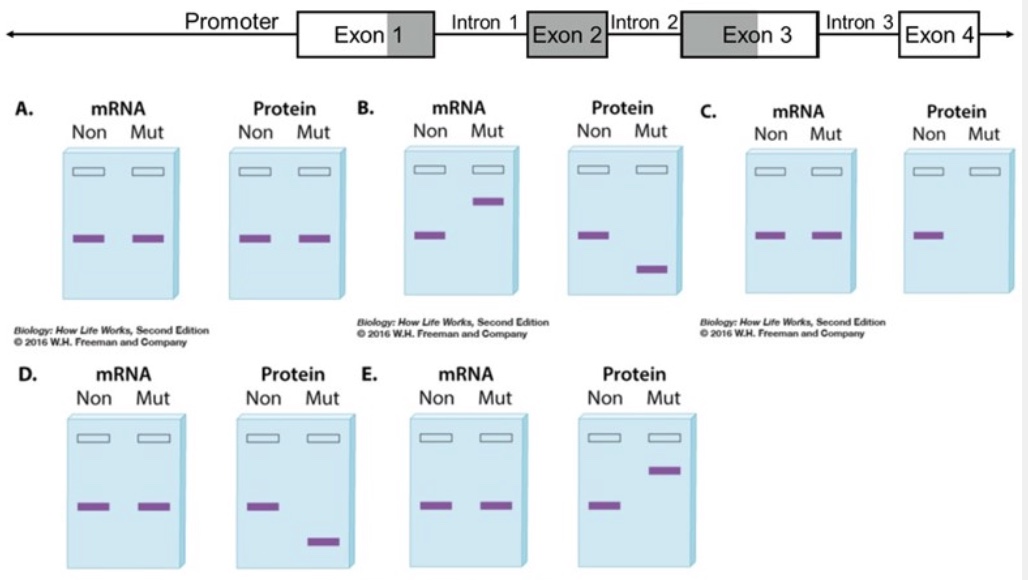
The diagram below shows a gene with four exons. The reading frame that encodes the protein is shaded and begins in exon 1 and ends in exon 3. The questions below describe different mutations. Determine which pair of mRNA and protein gels (A-E) you would most likely observe as a consequence of the mutation. On each gel, "Non" is the nonmutant version of the mRNA/protein and "Mut" is the mutated version of the mRNA/protein.
Note: All mRNAs in the gels represent mature mRNAs.
Gel pair that could result from the denaturation of ribosomes within the cell:
C
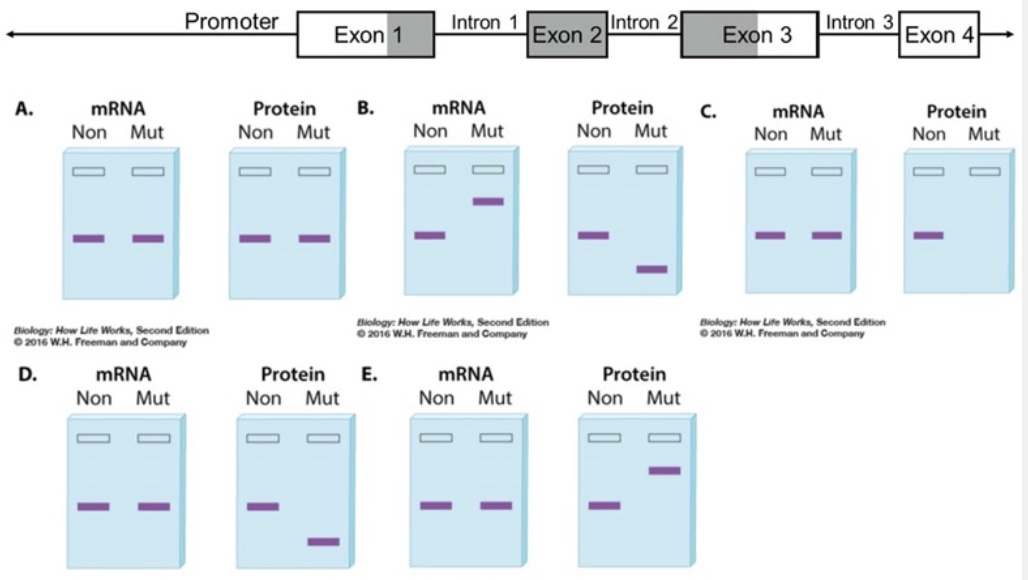
Gel pair that could result from a silent mutation in exon 2:
A
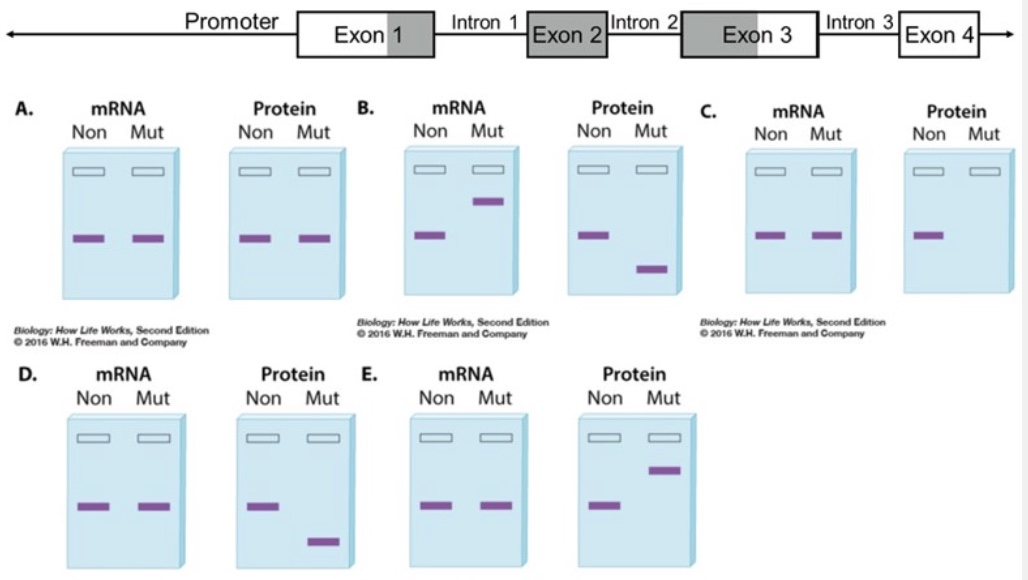
Gel pair that could result from a missense mutation in exon 3:
A