Neuroeducation & Metacognition
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Educational Neuroscience
Interdisciplinary research field that seeks to translate research findings on neural mechanisms of learning to educational practice & policy
Routes From Neuroscience to Education
Direct: brain as biological learning machine & sstudying the optimal condition for learning processes
Indirect: The neuroscience underlying mental processes that facilitate learning
Brain & Behaviour/Performance
Visible Results: Learning outcomes (behavioural performance)
Processes Leading to that Result: Psychological & physiological adaptation through NP
Underlying Source & Potential: Evolution, Genetics, Epigenetics, Nature & Nurture
Challenges in Applying Educational Neuroscience in Educational Systems
Measurement: education outcomes are complex/multifaceted
Validity: lab results do not always transfer to the real world (classroom)
Communication: Lack of effective channels between neuroscientists and educators
Neuromyths: misinformation & misuse of neuroscientice information
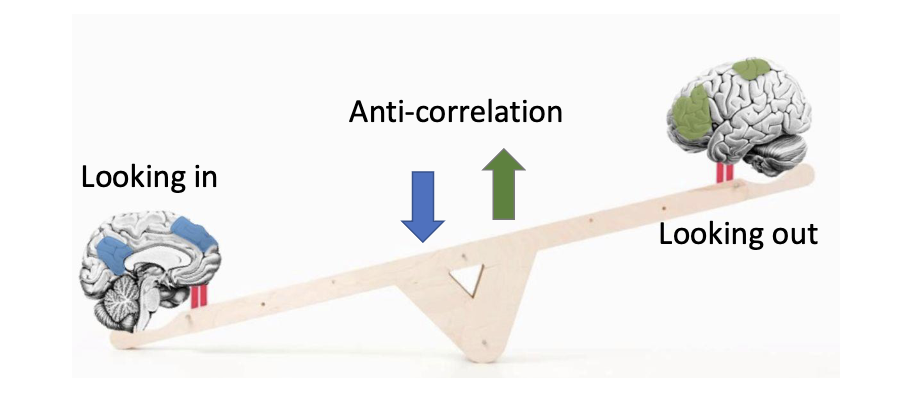
Default Mode Network
Neurocognitive network that is preferentially activated when we mind-wander
Heavily involved in self reflection & social cognition
Intrinsic Processing
Executive Control Network
Task/stimulus driven network
Heavily involved in executive functioning
Extrinsic Processing
Metacognition
Ability to monitor and control cognitive processes
Positively correlated with academic performances
Metacognitive Judgement
Neural basis of introspective judgements about one’s own cognition
Meta-Control
Neural basis of higher-order functions that monitor & control lower cognitive processes as they happen
Executive functions are considered meta-control
Online Metacognition
Happens in the present
On. Meta-Knowledge: Awareness of our cognitive processes while we are actively engaged in task
On. Meta-Control: Ability to regulate cognitive processes during active engagement in a task
Offline Metacognition
About the past or future
Of. Meta-Knowledge: Awareness of cognitive processes during active engagement in a task
Of. Meta-Control: Ability to regulate out cognitive processes during offline activites
Metacognition Over Time
Meta-knowledge emerges around 5 y/o
Meta-control at 8
Meta knowledge & meta control develop into adolescence
Metacognition Over Time (p2)
Believed to be domain-dependent at first, transitions to be domain-independent due to accumulating knowledge and experience and domain-connections
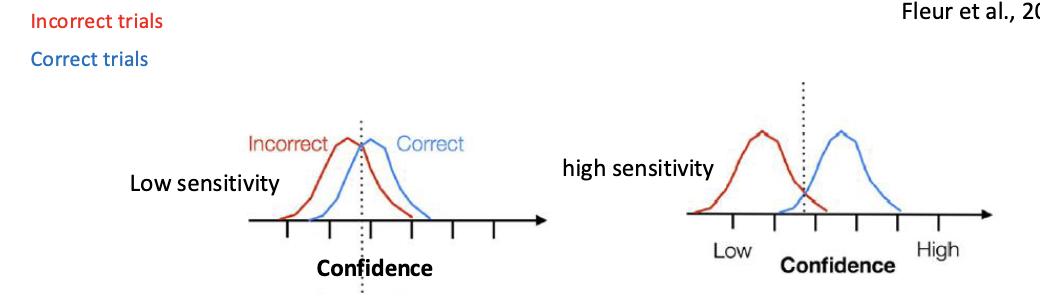
Metacognitive Judgement Sensitivity
Assessment of meta-knowledge based on confidence vs accuracy
Larger distance between curves = higher sensitivity
+confidence and +correctness WITH -confidence and -correctness = high metacognitive sensitivity
Mind Wandering & Metacognition
No! MW is part of cognitive processing
Creative generation is a part of spontaneous thought, creative evaluation is achieved through metacognition
Creativity, Metacognition, and Spontaneous Thought Processes
Generating Ideas: online MC is inhibited to allow spontaneous thought (DMN) during generative phase
Evaluating Ideas: MC and DMN are co-activated to identify fruitful outcomes from the generation phase and direct thinking towards subsequent generation phases
Metacognitive Awareness Inventory
Widely used gauge of metacognition
Declarative Knowledge
Knowing myself as a learner
Understanding the task
Awareness of learning strategies
Procedural Knowledge
Knowing how to use learning strategies
Conditional Knowledge
Understanding when and why to use specific strategies