WBC path
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
two ways to classificy white blood cells neoplastic
based on origin of tumor cells
based on location
ways to classify neoplastic proliferations of white cells: based on origin
pluripotent stem cell
myeloid stem cell/neoplasms: cells stay in blood
granulocytes/moncytes
platelet
erythocyte
Lymphoid stem cell/neoplasms: migrate to lymph nodes (blood and lymph nodes)
B cells
T cells
ways to calssificy neoplastic prolif: location
Luekemia
starts in bone marrow and blood (myeloid or lymphoid neoplasm)
spread to other places such as lymph nodes
Lymphoma
starts in lymph nodes (usually lymphocytes)
can spread ot other places including blood and bone marrow
Types of leukemias depend o
cell lineage
myeloid or lymphoid
rate of development →acute or chronic
acute leukemia
most immature cells or blasts
mutations that stop differentiations
promote uncontrolled proliferation
chronic leukemia
cells that are more mature (but not fully)
stop differenttiaons
promote uncontrolled proliferation
leukemias: symtpoms etc
starts in bone marrow usually
symp
anemia (low RBC)
thrombocytopenia (low platelets0
neutropenia
bone pain (increase pressure in bone marrow, leukemia cells take up too much space in marrow)
lymphoid leukemia symptoms also include
lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes)
more severe symptoms in acute or chronic
acute
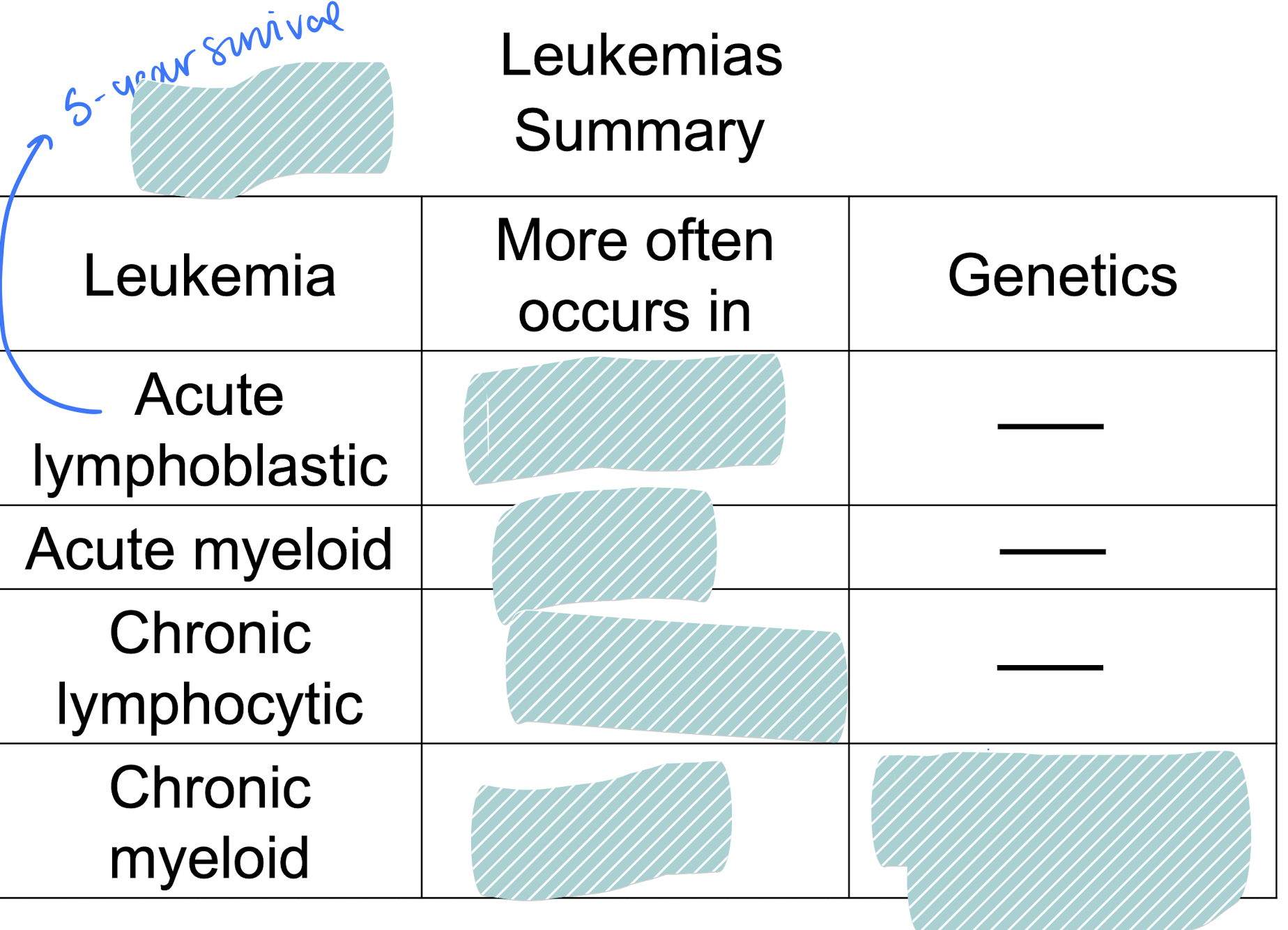
90%
children
adults
adults
adults: philadelphia chromosome
which has a genetic component?
chronic myeloid (philly chromosome)
piece of chromosome 9 and 22 break off and trade places
forms bcr-abl gene on 22
tyrosine kinase produced involved in cell transformation
lymphomas: start and symp and kind?
lymph node
lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes)
Hodgkin and non-Hodkin
Hodgkin lymphoma
neoplastic proliferation of atypical lymphoid cell: reed, originates from germinal center B cell
reed sternberg cell
large cells
abundant pale cytoplasm
bicnucleate (owels eye)
releease many cytokines and chemokines
surrounding reactive inflammatory cells (most cells in tumor)
neoplastic proliferation of
Non-hodgkin lymphoma
neoplastic proliferation of B cells, T cells, or rarely histiocytic cells (macrophages and dendritic)