Microeconomics
5.0(5)Studied by 323 people
Card Sorting
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:26 AM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
What is the basic economic problem?
Unlimited wants with finite resources
2
New cards
What are the three fundamental questions?
1. What to produce
2. How to produce
3. For whom to produce
3
New cards
Opportunity Cost
The next best alternative forgone.
This arises since there is a cost/ sacrifice of one product when a choice is made.
This arises since there is a cost/ sacrifice of one product when a choice is made.
4
New cards
What does a PPC represent?
The maximum production combinations of two goods when goods are fully employed.
5
New cards
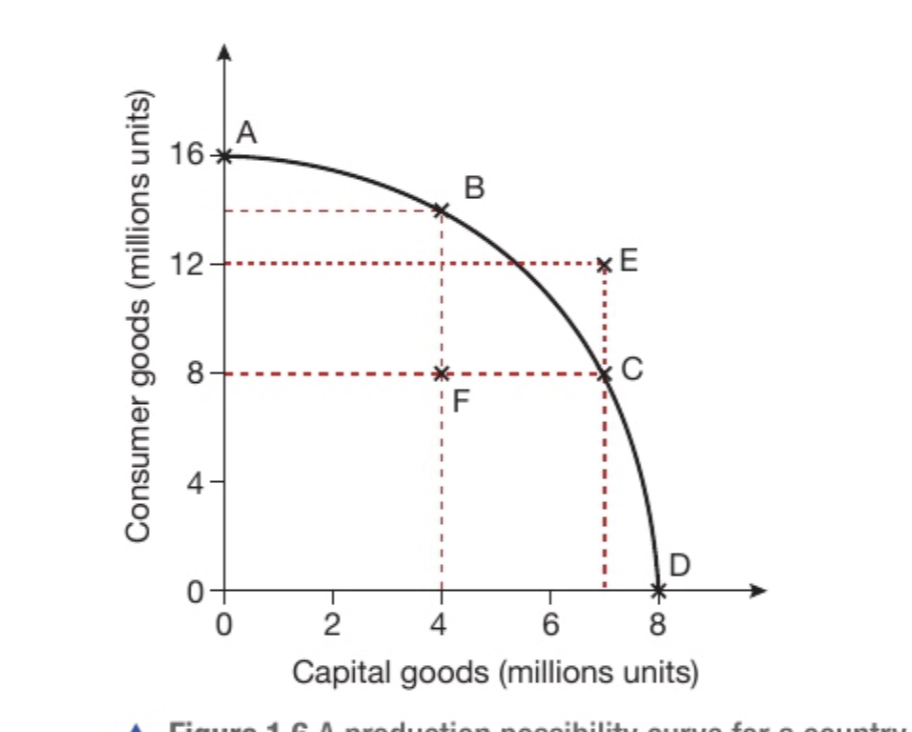
What is occuring at point E?
E is an impossible combination. This point lies outside the PPC so this country does not have the resources to produce at point E.
6
New cards
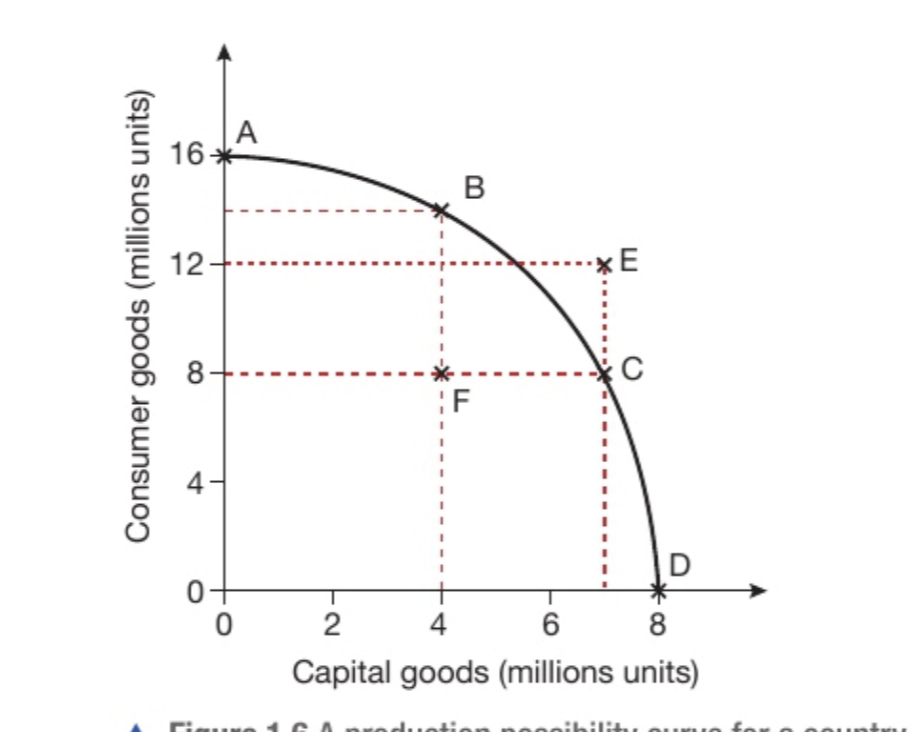
What is occurring at point F?
8 million consumer goods and 4 million capital goods. However this combination is inside the PPC which shows that resources are underemployed in this country.
7
New cards
What can cause a shift in the PPC?
When the production of goods increases in general this is knows as economic growth. (economic growth = increases level of output by the nation)
8
New cards
How does new technology cause economic growth?
New technology benefits businesses since it is much faster and more accurate making it more reliable in production. This will eventually lead to more output.
9
New cards
How does improved efficiency cause economic growth?
More efficient methods of production will increase productivity. Increased productivity will lead to more output with fewer resources or in less time.
10
New cards
How does education and training cause economic growth?
This raises the proportion of educated workers. Educated workers can more easily carry out tasks.
11
New cards
How do new resources cause economic growth?
new resources enable you to produce more
* increased production leads to an outward shift in the PPC
* increased production leads to an outward shift in the PPC
12
New cards
What do consumers tend to maxmise?
Their benefit (whatever gives them the most satisfaction)
* best quality for same price
* cheapest price for same quality
* best quality for same price
* cheapest price for same quality
13
New cards
What to businesses tend to maximise?
Their profit (best financial results)
* always set highest possible price
* cheapest raw materials for same quality
* always set highest possible price
* cheapest raw materials for same quality
14
New cards
What might cause a consumer to not always maximise their benefit?
1. difficulty calculating benefit
2. developing buying habits (brand loyalty)
1. irrationality develops overtime as someone buys a product habitually
3. influence and trends
4. limited information
15
New cards
What might cause a business to not always maximise their profit?
1. alternative business objectives (customer care)
2. operating as charities
3. social enterprise to improve wellbeing
4. limited information
16
New cards
What kind of relationship do demand and price have?
inverse relationship
17
New cards
What happens to demand curve when price changes
There is a movement along the curve
18
New cards
What happens to the demand curve when a non price factor affects it?
There is a shift in demand
19
New cards
What factors can shift demand?
“PASIFIC”
P-population
A-advertising
S- substitutes (the price of)
I- income
F- fashion
I- interest rates
C- complements (the price of)
P-population
A-advertising
S- substitutes (the price of)
I- income
F- fashion
I- interest rates
C- complements (the price of)
20
New cards
Will increased advertising shift demand to the right? Why?
Yes. Demand increases with more advertising. This is since it increases awareness and influence to buy this product.
21
New cards
Will increased income shift demand to the right? Why?
Yes if it is a normal good. This is when disposable income rises, and demand for goods will rise. Income rising will decrease demand for inferior goods.
22
New cards
Will increased fashion/tastes (for a good) shift demand to the right? Why?
Buying season for something being more favourable and trend for a good or service increasing will lead to increased demand for it. This is influenced by social change.
23
New cards
Will increased price of a subsitute shift demand to the right? Why?
The increased price of a substitute will shift demand to the right since consumers will maximise benefits and opt for a better price for a similar quality good.
24
New cards
Will increased price of a compliment shift demand to the right? Why
Increased price of a complement will shift demand to the left since some goods are purchased together. When two goods are used together, increasing price of a complement will decrease the demand of the original good or service.
25
New cards
Will increased population shift demand to the right? Why
Yes when there are more people, more people want goods and services so this will shift demand to the right?
26
New cards
What is the relationship between supply and price?
A proportionate relationship.
* when price goes up so does supply
* when price goes up so does supply
27
New cards
What happens to supple curve when price changes
A movement along the curve
28
New cards
What happens to the supply curve when a non-price factor changes?
A shift in the curve
29
New cards
What non price factors will affect supply?
“PINTSWC”
P-Productivity
I-Indirect tax
N-Number of firms
T-Technology
S-Subsidies
W-Weather
C-Cost of production
P-Productivity
I-Indirect tax
N-Number of firms
T-Technology
S-Subsidies
W-Weather
C-Cost of production
30
New cards
What is the effect of indirect tax on supply?
Indirect taxes are levied on spending and goods or services. When indirected tax is imposed supply will decrease and shift to the left.
* can be imposed on producers if their production methods harm the environment
* can be imposed on producers if their production methods harm the environment
31
New cards
What is the effect of subsidies on supply?
A subsidy is when the government give money to a business in form of a grant.
* can encourage production of a particular product
* Subsidising=increased supply
* can encourage production of a particular product
* Subsidising=increased supply
32
New cards
What is the effect of changing technology on supply?
New technology and advancement can help production by being more efficient. This will reduce cost of production or increase yield. This will increase supply.
33
New cards
What is the effect of weather on supply?
When conditions are good: Increased supply
In the event of natural disaster or bad conditions seasonally: Decreased supply
In the event of natural disaster or bad conditions seasonally: Decreased supply
34
New cards
What is equilibrium price?
Price at which supply and demand are equal
35
New cards
What is total revenue?
Total revenue is the amount of money generated from the sale of goods (price x quantity sold)
36
New cards
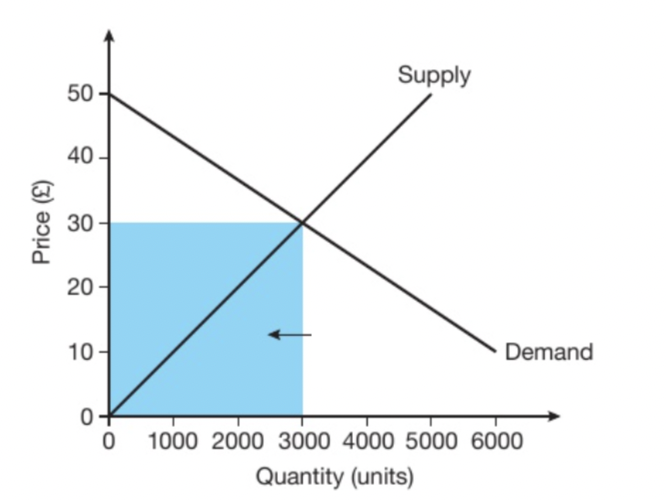
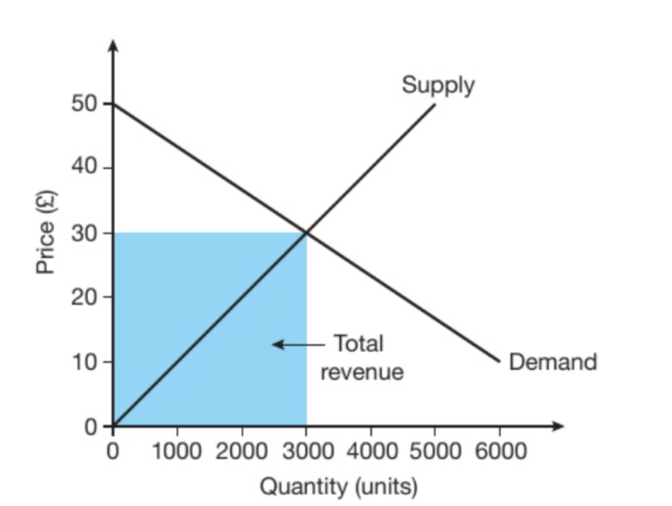
What does this blue box represent?
Total revenue
37
New cards
What will a shift in demand do to the equilibrium?
If demand increases then the price will rise. If the demand curve shifts to the right (D2), P AND Q will rise (p1-p2 and q1-q2)
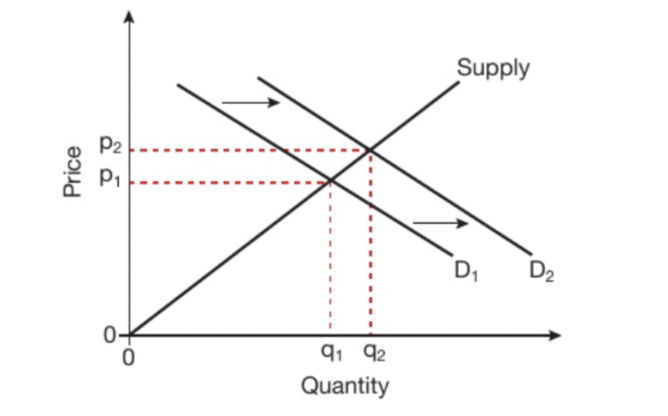
38
New cards
What will a shift in supply do to the equilibrium?
When supply increases the price of equilibrium will decrease. If supple curve shifts to the right (S2), P AND Q will fall ( p1-p2 and q1-q2)
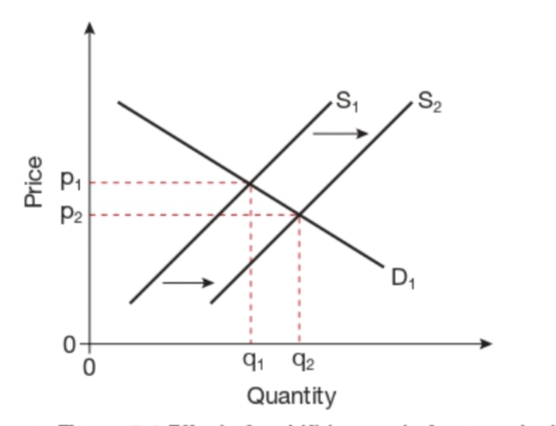
39
New cards
What is excess demand?
Where demand for a good will exceed supply leading to a shortage. This exists when price is set below equilibrium price.
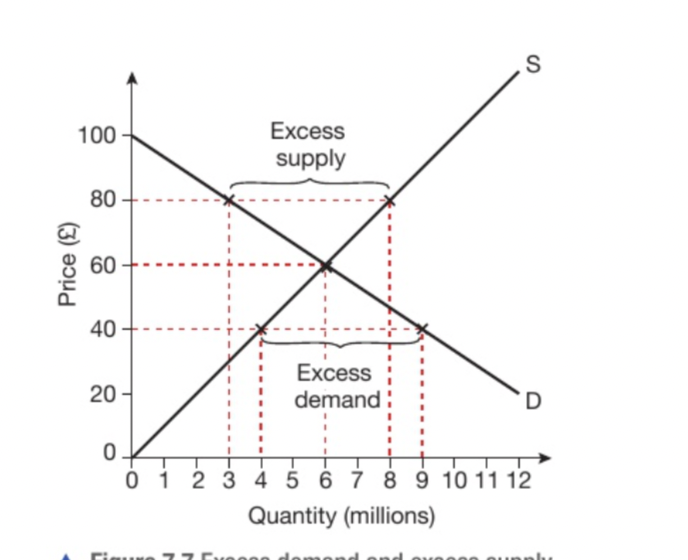
40
New cards
What is excess supply?
Where supply for a good will exceed demand leading to unsold goods. This exists when price is set abve equilibrium price
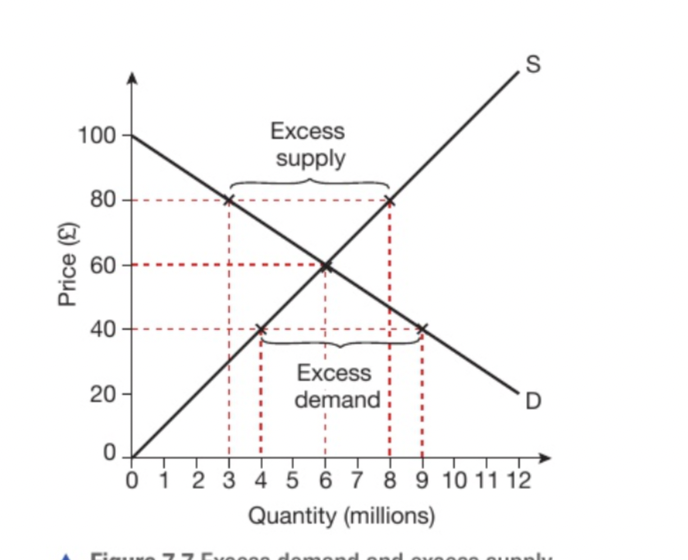
41
New cards
What is the formula to calculate price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand = Percentage change in quantity demanded/Percentage change in price
* minus signs signify that the demand falls but elasticity is only based on the number
* minus signs signify that the demand falls but elasticity is only based on the number
42
New cards
Define PED and PES
* Price elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price
* Price elasticity of supply is the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price
* Price elasticity of supply is the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price
43
New cards
Define elastic demand
elastic demand is when a change in price results in a proportionately larger change in quantity demanded due to more responsiveness.
44
New cards
Define inelastic demand
inelastic demand is when a change in price results in a proportionately smaller change in quantity demanded due to lower responsiveness.
45
New cards
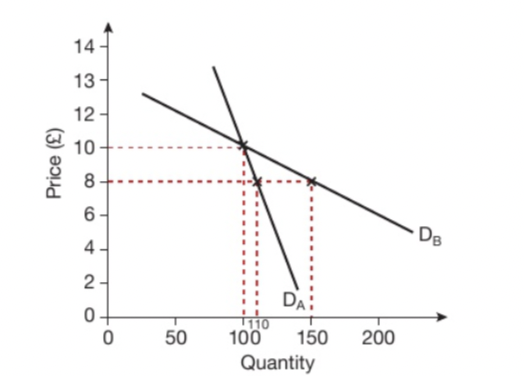
Which of the two graphs is elastic and which is inelastic?
graph dA is inelastic and graph dB is elastic
46
New cards
What are the numerical values of elasticity?
>1 = elastic
1=unitary
1=unitary
47
New cards
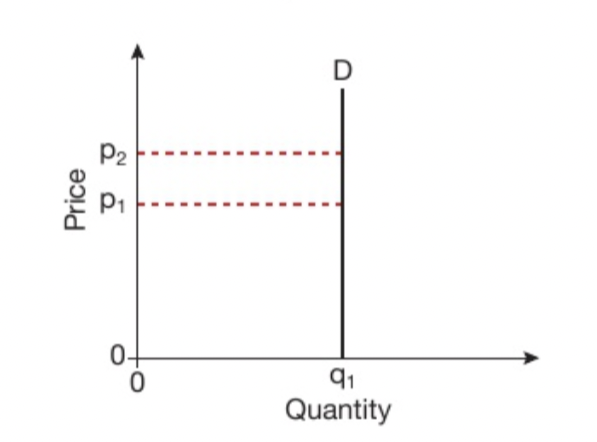
What is this the graph for?
perfectly inelastic(0)
48
New cards
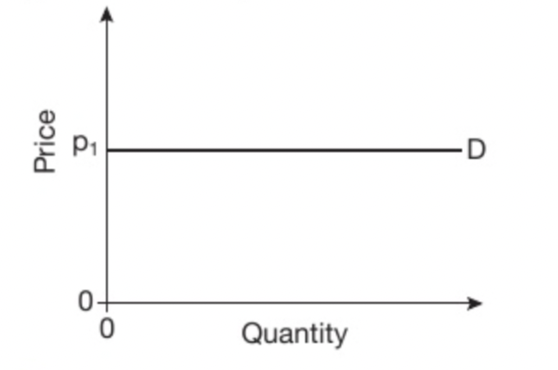
What is this the graph for?
perfectly elastic(∞)
49
New cards
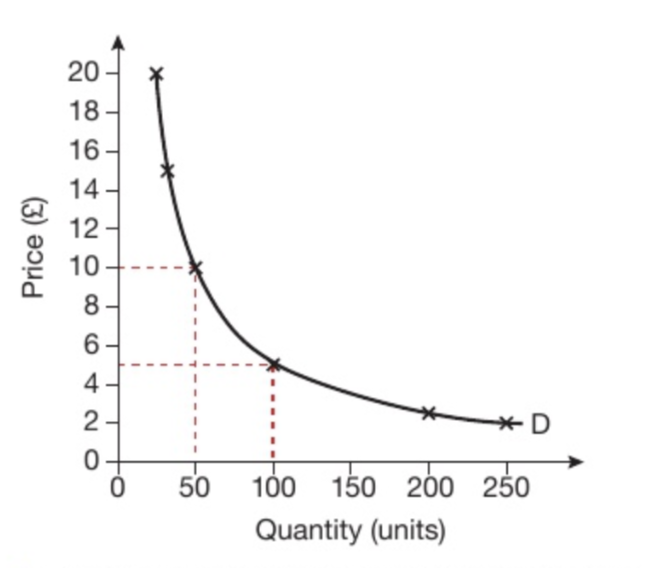
What is this the graph for?
unitary price elastic demand. This is a special case where revenue is always constant no matter the change in price.
50
New cards
What factors affect PED?
“PLANTS”
P-Proportion of income-more spent is more elastic
L-Luxury vs necessity
A-Addictive good-habitual buying means it becomes inelastic
N-No. of uses
T-Time period
S-Substitute availability
P-Proportion of income-more spent is more elastic
L-Luxury vs necessity
A-Addictive good-habitual buying means it becomes inelastic
N-No. of uses
T-Time period
S-Substitute availability
51
New cards
What are the factors that influence PES?
STEMPS
S- spare capacity
T- Time
E- Ease of Entry
M- Mobility of FOPS
P- production speed
S- stock
S- spare capacity
T- Time
E- Ease of Entry
M- Mobility of FOPS
P- production speed
S- stock
52
New cards
What is fixed cost?
Costs which do not vary with output (e.g. rent)
53
New cards
What is variable cost?
Costs that vary based on output (e.g. labour, raw material, fuel)
54
New cards
What is total cost + diagram?
Total fixed cost + Total variable Cost
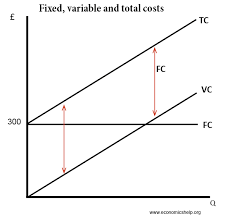
55
New cards
What is total revenue?
The amount a firm receives from selling its output.
Total revenue = price x quantity
Total revenue = price x quantity
56
New cards
What is profit and loss?
Total revenue-total cost = profit
\
When this number is positive it is profit
When this number is negative it is loss
\
When this number is positive it is profit
When this number is negative it is loss
57
New cards
What is average cost?
The average cost is the total cost of production divided by output (Cost of producing a single unit of a good or service)
58
New cards
Define economies of scale
As firms grow larger average costs begin to fall
59
New cards
What are the 6 internal economies of scale?
“Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies”
R-Risk Bearing
F-Financial
M-Managerial
T-Technical
M-Marketing
P-Purchasing
R-Risk Bearing
F-Financial
M-Managerial
T-Technical
M-Marketing
P-Purchasing
60
New cards
Explain risk-bearing economies of scale
Large firms may have a wider range of products and sell into wider varieties of markets. This reduces risk of business.
61
New cards
Explain financial economies of scale
As firms grow larger they can access money more cheaply and with a wider variety of sources.
Large firms also have to ability to negotiate with banks for lower interest rates
Large firms also have to ability to negotiate with banks for lower interest rates
62
New cards
Explain managerial economies of scale
As firms expand they can afford specialist managers. This will improve efficiency as managers will work specifically with smaller sectors of the firm allowing them to oversee weaknesses.
63
New cards
Explain marketing economies of scale
Larger firms can afford to pay fixed marketing costs as they can be spread over more units of output. (e.g. they can run their own delivery service so the cost of paying a distributor is reduced)
64
New cards
Explain technical economies of scale
Larger firms can invest more in machinery making them more efficient. Larger companies may also use capital more regularly so they are making better use of their capital. This means AC will fall overtime.
65
New cards
Explain purchasing economies of scale
As firms grow larger and they buy in larger quantities they can get cheaper rates.
* an example is bulk buying discounts
* an example is bulk buying discounts
66
New cards
Define external economies of scale
cost benefits that all firms within an industry can experience when the industry expands
67
New cards
What are the four external economies of scale?
“SACI”
S-skilled labour
A-access to suppliers
C-cooperation with other bussinesses
I-infrastructure
S-skilled labour
A-access to suppliers
C-cooperation with other bussinesses
I-infrastructure
68
New cards
Explain how skilled labour is an external economy of scale
When industry is concentrated in one area there will be a high amount of labour with work experience and training. As a result training cost is lowered and local schools may provide vocational courses.
69
New cards
Explain how infrastructure is an external economy of scale
When industry is concentrated in one area this will lead to facilities being accommodating for this industry (e.g. roads, railways, buildings)
70
New cards
Explain how access to suppliers is an external economy of scale
Established industry encourages suppliers to set up close by. This means all firms will benefit from increased accessibility to suppliers.
71
New cards
Explain how similar businesses in an area is an external economy of scale
When similar firms are near each other this leads to cooperation between them to increase benefit mutually. (e.g. sharing costs to reduce AC and cooperate on R n D
72
New cards
Define diseconomies of scale
Average costs will begin to rise when a firm grows too large
73
New cards
What are the diseconomies of scale?
“Bob Calls Linda Darling”
B- beuracracy
C-communication issues
L-lack of control
D-distance between senior and junior staff
B- beuracracy
C-communication issues
L-lack of control
D-distance between senior and junior staff
74
New cards
How is bureaucracy a diseconomy of scale?
Bureaucracy is when businesses use large numbers of departments and officials. If businesses grow too large they often become too bureaucratic so excessive amounts of time are spent making decisions which slow down movement in the firm. This also makes communication channels too long. When resources are overused in admin, AC will rise.
75
New cards
How is communication problems a diseconomy of scale?
When companies grow they may become MNC’s and this means that workers between company may have cultural and language barriers. Time differences also make organization challenging.
76
New cards
How is lack of control a diseconomy of scale?
Large businesses are difficult to control and coordinate so this will require more supervision which raises AC
77
New cards
How is distance between senior and junior staff a diseconomy of scale?
When a firm grows too big, relations may worsen as there may be too many layers of supervision between senior and junior staff. This leads to less acknowledgement of staff needs and leads to demotivation of workers.
78
New cards
What is competition?
Competition is the rivalry between firms when trying to sell goods for a particular market.
79
New cards
What are features of a competitive market?
* low barriers to entry-easy to enter the market
* products sold are homogeneous or close substitutes
* many buyers and sellers
* price takers-no firm can generally change price
* lots of accurate information about the products
* products sold are homogeneous or close substitutes
* many buyers and sellers
* price takers-no firm can generally change price
* lots of accurate information about the products
80
New cards
How do firms change and respond to competition?
COMPETITION LIMITS A FIRMS PROFIT:
* firms prefer dominating the market since competition creates pressure to be more efficient and innnovation.
* firms will try to keep: costs as low as possible, good customer service, low prices
* firms will also try to use product differentiation to make themselves seem better than rivals
\
* firms prefer dominating the market since competition creates pressure to be more efficient and innnovation.
* firms will try to keep: costs as low as possible, good customer service, low prices
* firms will also try to use product differentiation to make themselves seem better than rivals
\
81
New cards
How do consumers change and respond to competition?
The advantages of competitive markets to a consumer are: lower prices, better quality goods, and more choice.
82
New cards
Is competition good or bad for the economy?
* competition ensure resources are allocated efficiently
* efficiency and innovation will increase
* this increases overall standard of living
* efficiency and innovation will increase
* this increases overall standard of living
83
New cards
What are the advantages of being a small firm?
* cater to niche markets
* flexibility-adapt to change as minimal decision makers
* personal service
* lower wage costs- do not belong to trade unions and pay can be restricted
* better communication
* innovation-due to competitve pressure
* flexibility-adapt to change as minimal decision makers
* personal service
* lower wage costs- do not belong to trade unions and pay can be restricted
* better communication
* innovation-due to competitve pressure
84
New cards
What are the disadvantages of being a small firm?
* Higher costs- small firms don’t benefit from EOS
* Lack of finance-limited resources and limited finance as they are considered riskier
* Difficult to attract staff
* Vulnerability-small firms have more difficulty surviving
* Lack of finance-limited resources and limited finance as they are considered riskier
* Difficult to attract staff
* Vulnerability-small firms have more difficulty surviving
85
New cards
What are the advantages of being a large firm?
* economies of scale
* large scale contracts
* market domination
* large scale contracts
* market domination
86
New cards
What are the disadvantages of being a large firm?
* Diseconomes of scale
* Motivation
* Motivation
87
New cards
What can change and influence the size of a firm?
* government regulation
* access to finance
* economies of scale
* desire to spread risk
* desire to take over competitors
* access to finance
* economies of scale
* desire to spread risk
* desire to take over competitors
88
New cards
Why do firms stay small?
* size of market
* nature of the market
* catering to niche markets
* diseconomies of scale
* nature of the market
* catering to niche markets
* diseconomies of scale
89
New cards
What is a monopoly
When one firm dominates the market
25% or more of the market
25% or more of the market
90
New cards
What are 4 key features about a monopoly?
* one business dominates the market
* unique product
* price-maker
* high barriers to entry
* unique product
* price-maker
* high barriers to entry
91
New cards
What are the main barriers to entry?
* high start up cost
* legal barriers
* patents- license to grant permission to be the sole producer of a product
* marketing budgets
* technology (specific to market)
* legal barriers
* patents- license to grant permission to be the sole producer of a product
* marketing budgets
* technology (specific to market)
92
New cards
What are the advantages to being a monopoly?
* efficiency
* innovation
* economies of scale
* innovation
* economies of scale
93
New cards
What are the disadvantages to being a monopoly?
* higher price
* restricted choice
* limited innovation- no incentive to innovate products
* inefficiency- no incentive to keep costs down
* restricted choice
* limited innovation- no incentive to innovate products
* inefficiency- no incentive to keep costs down
94
New cards
What is an oligopoly?
A market dominated by a few large firms
95
New cards
What are features of an oligopoly?
* few firms
* large firms dominate-highly influential and set price
* different products-substitutes but some differentiation and aimed at different market segments
* barriers to entry-discouraged entry by investment in brands
* collusion-restricts competition or price fixing
* non-price competition-avoid price wars through competing in advertisement, branding etc.
* price competition-price is usually the same for long periods of time to avoid price wars.
* large firms dominate-highly influential and set price
* different products-substitutes but some differentiation and aimed at different market segments
* barriers to entry-discouraged entry by investment in brands
* collusion-restricts competition or price fixing
* non-price competition-avoid price wars through competing in advertisement, branding etc.
* price competition-price is usually the same for long periods of time to avoid price wars.
96
New cards
Advantages of an oligopoly
* provides consumer with some choice
* non price competition leads to good quality goods and services
* EOS allows firms to benefit from AC and this allows for lower prices
* large firms have resources to invest in R n D → leading to investment
* Price wars are avoided so generally there is price stability
* non price competition leads to good quality goods and services
* EOS allows firms to benefit from AC and this allows for lower prices
* large firms have resources to invest in R n D → leading to investment
* Price wars are avoided so generally there is price stability
97
New cards
Disadvantages of an oligopoly
* price fixing and collusion
* price fixing can lead to extremely high prices
* if a market is shared out geographically there will be a lack of choice
* cartel
* price fixing can lead to extremely high prices
* if a market is shared out geographically there will be a lack of choice
* cartel
98
New cards
What is a cartel?
where a group of firms or countries join together and agree on pricing or output level of the market
99
New cards
What is the wage rate?
The price of labour
100
New cards
What factors affect the demand for labour?
* derived demand
* availability of substitutes- replacement with capital
* productivity of labour
* other employment costs
* availability of substitutes- replacement with capital
* productivity of labour
* other employment costs