Biology Lab Midterm (Section 40)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Dissecting Scope
View objects in 3D at low magnification
Compound Scope
View small objects at high magnification (<1000x)
phylogenetic tree
A diagram that shows the hypothesized evolutionary relationships among species
Monophyletic Group (Clade)
Group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
Paraphyletic Group
Group of organisms that includes a common ancestor but not all of its descendants
Polyphyletic Group
Group of organisms that includes groups of species with different ancestors
Divergent Evolution
Process of related species adapting differently to their environment and more diverse
Homology
Morphological and molecular traits that are derived from a common ancestor
Convergent evolution
When similar trait arises between species that do not share a recent common ancestor
Homoplasy
independently evolved but similar traits
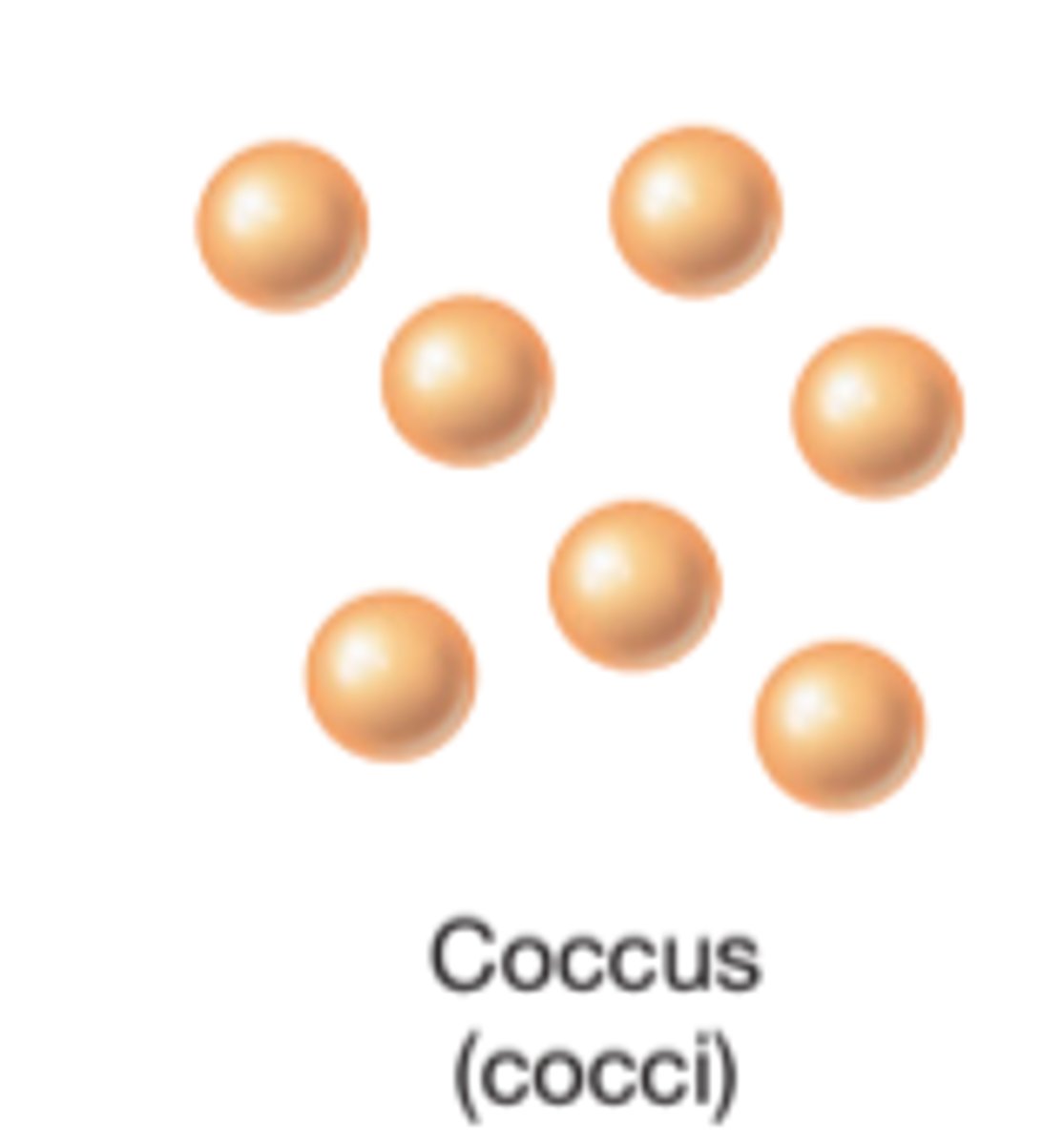
What shape is coccus bacteria?
Spherical
What shape is a coccobacillus bacteria?
short round rod
What shape is vibrio bacteria?
comma shaped

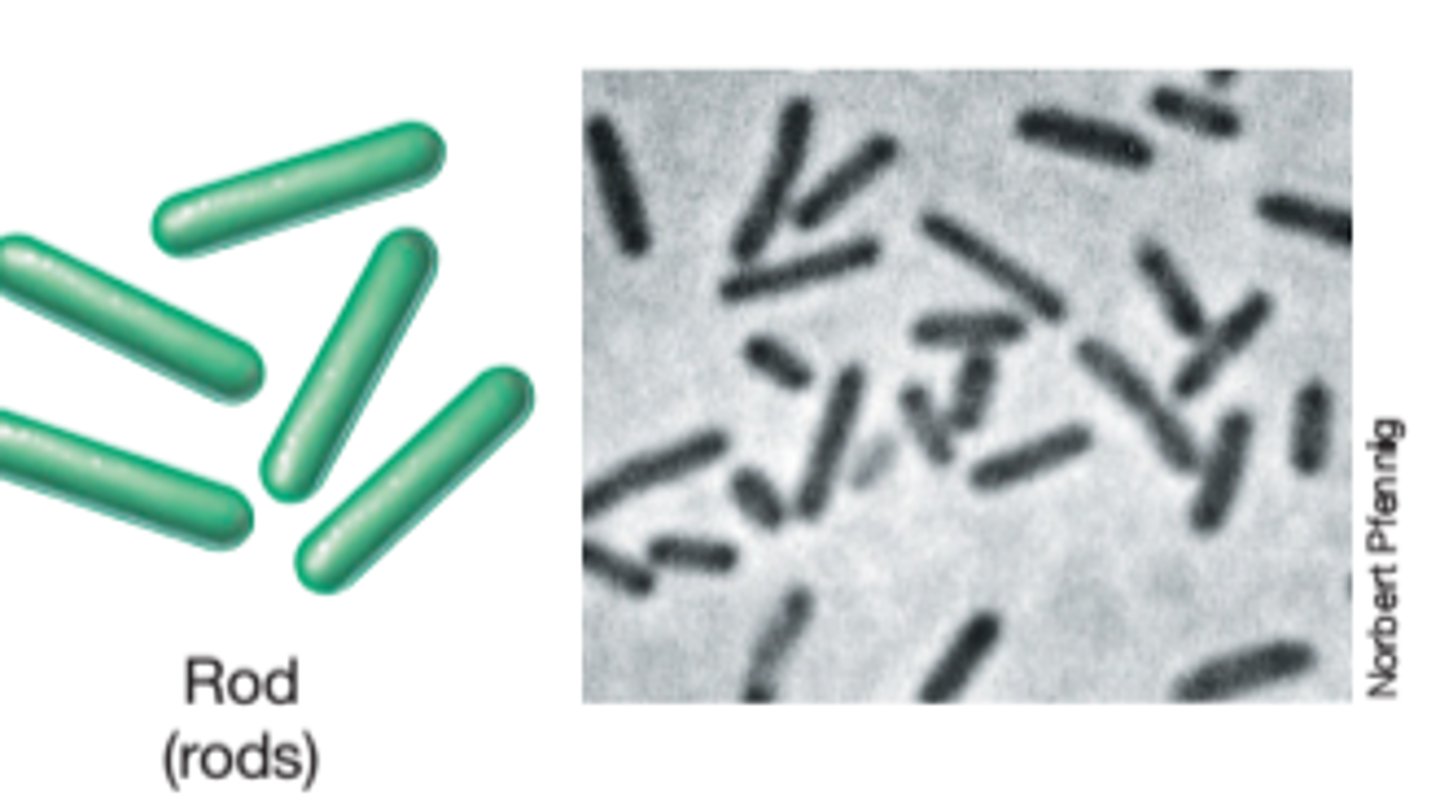
What shape is bacillus bacteria?
rod shaped
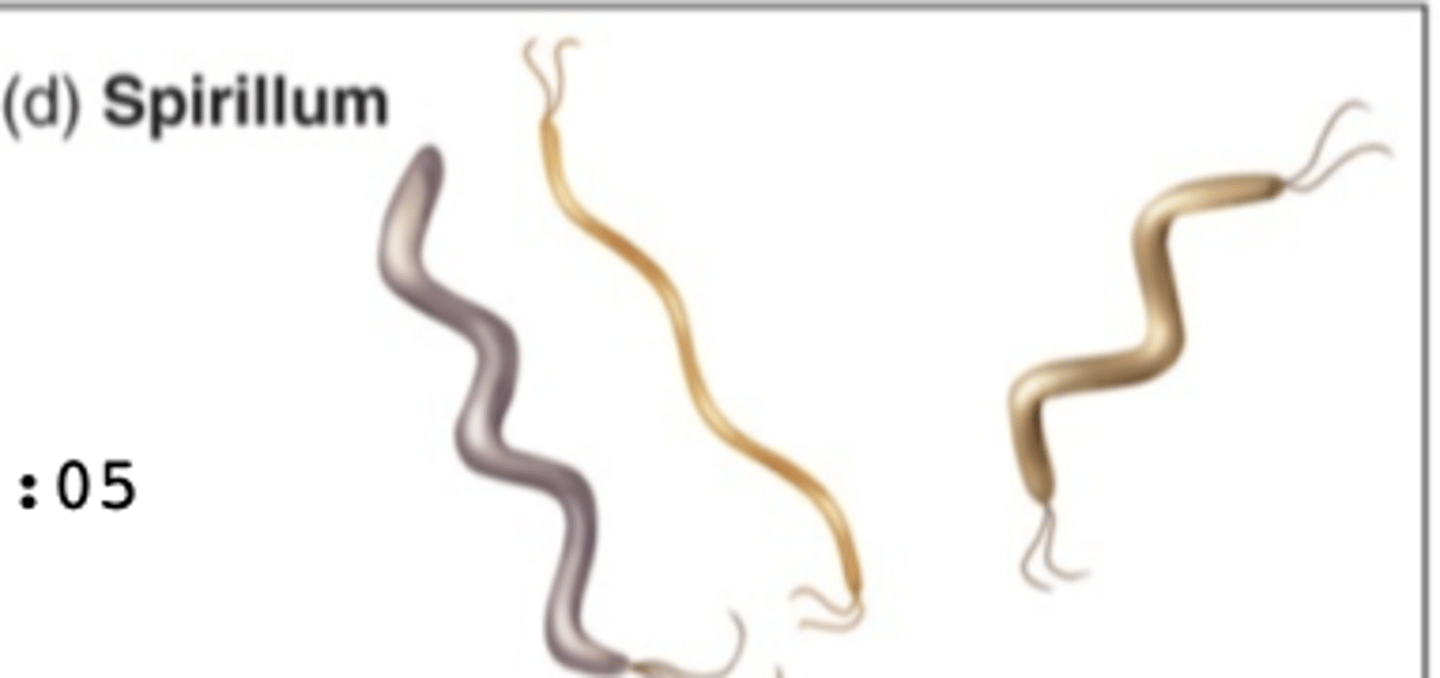
What shape is spirillum bacteria?
spiral shaped

What shape is a spirochete bacteria?
tightly coiled
What does an arrangement of diplococci look like?
Two balls
What does an arrangement of streptococci look like?
A comma shape with multiple balls
What does an arrangement of staphylococci look like?
A 2D pyramid of balls
What does an arrangement of sarcina look like?
A cube made up of four balls
Cyanobacteria pros ecologically
produce oxygen via photosynthesis, fix carbon dioxide and nitrogen out of the atmosphere, food source for invertebrates, indicators of water quality
Anabaena (Cyanobacteria)
Forms filamentous chains, found in freshwater, saltwater, hot springs, top-soil
The light colored ball on the chain is the heterocyst
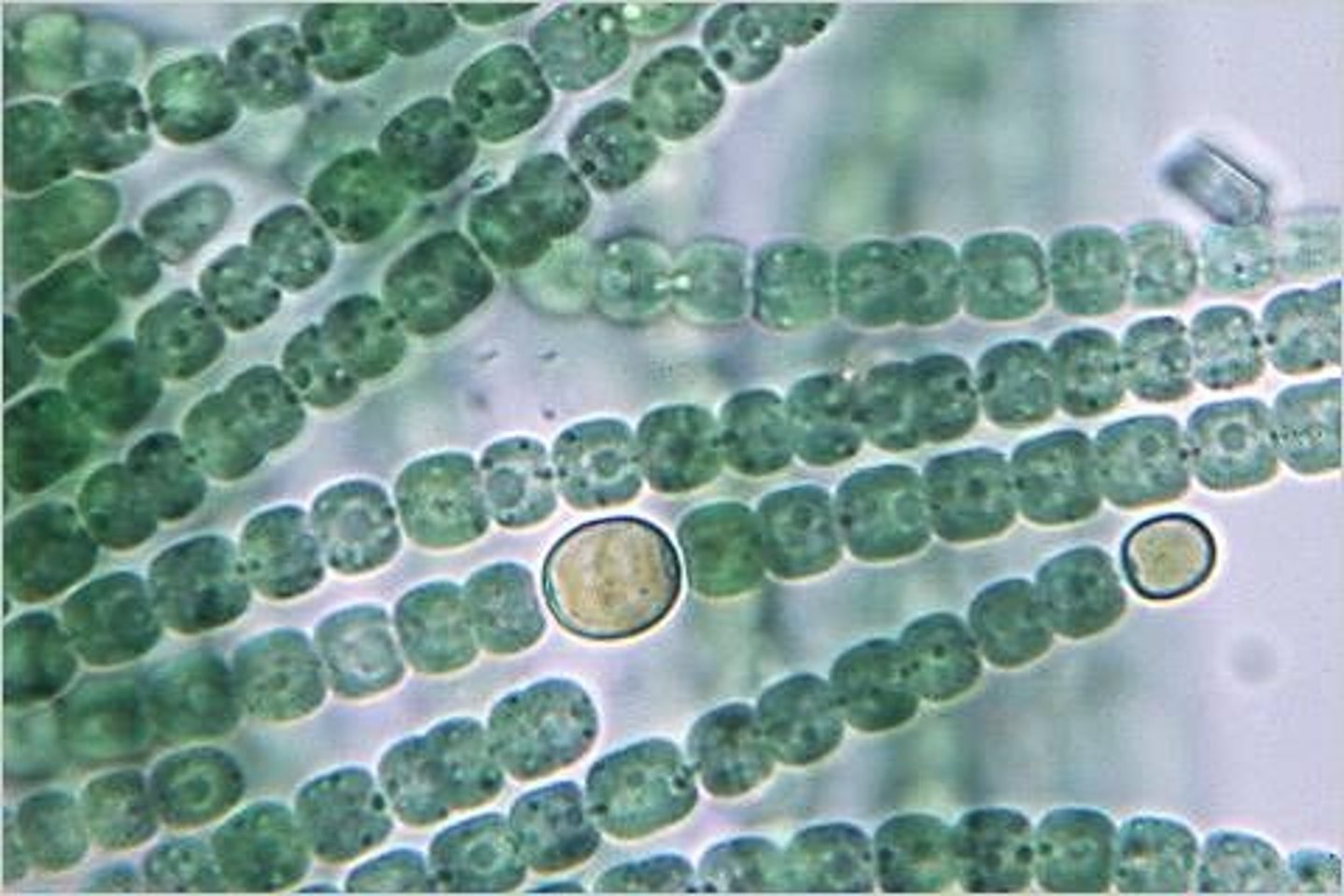
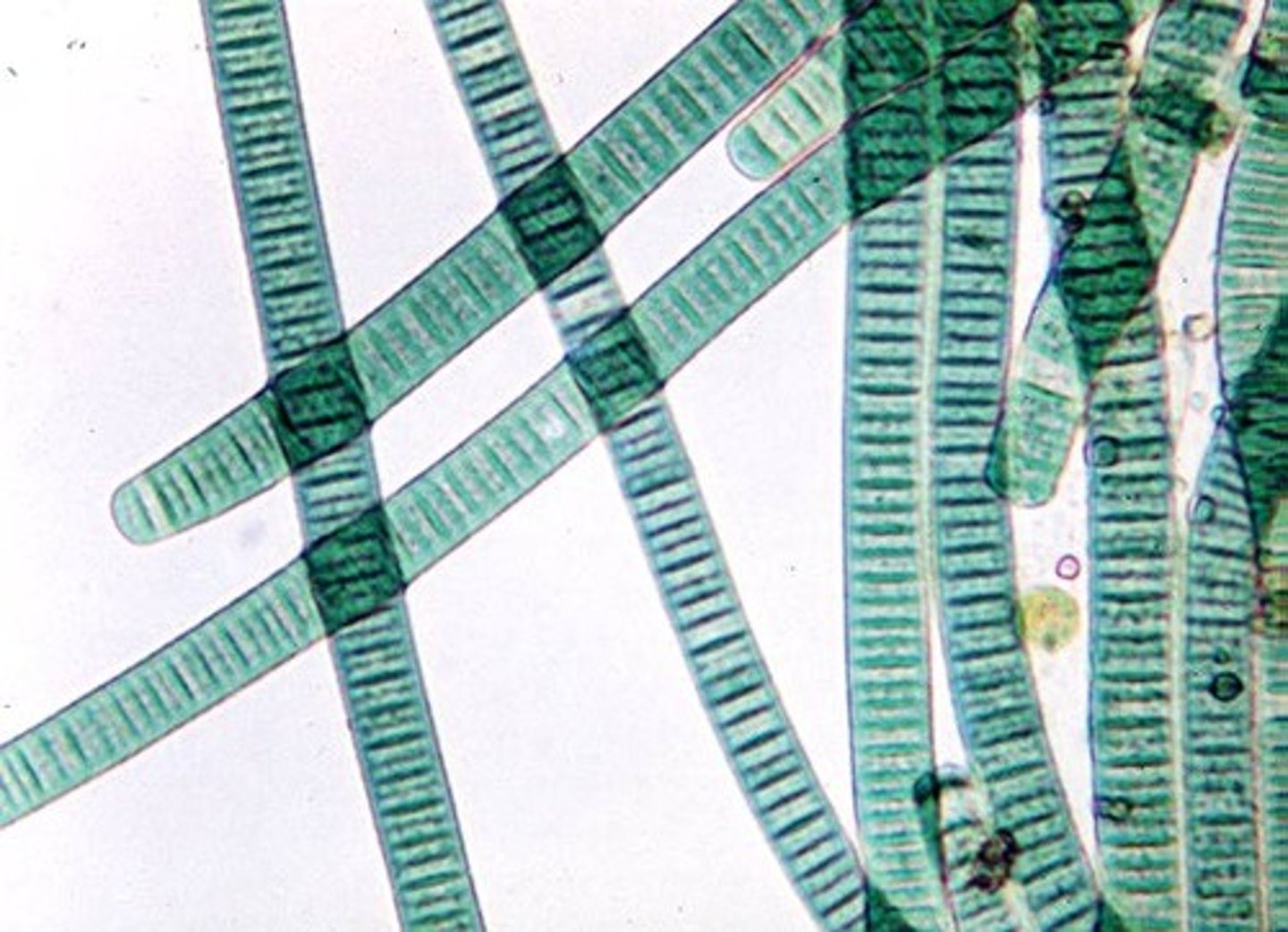
Oscillatoria (Cyanobacteria)
Colonies can slide back and forth against each other to orient to light source
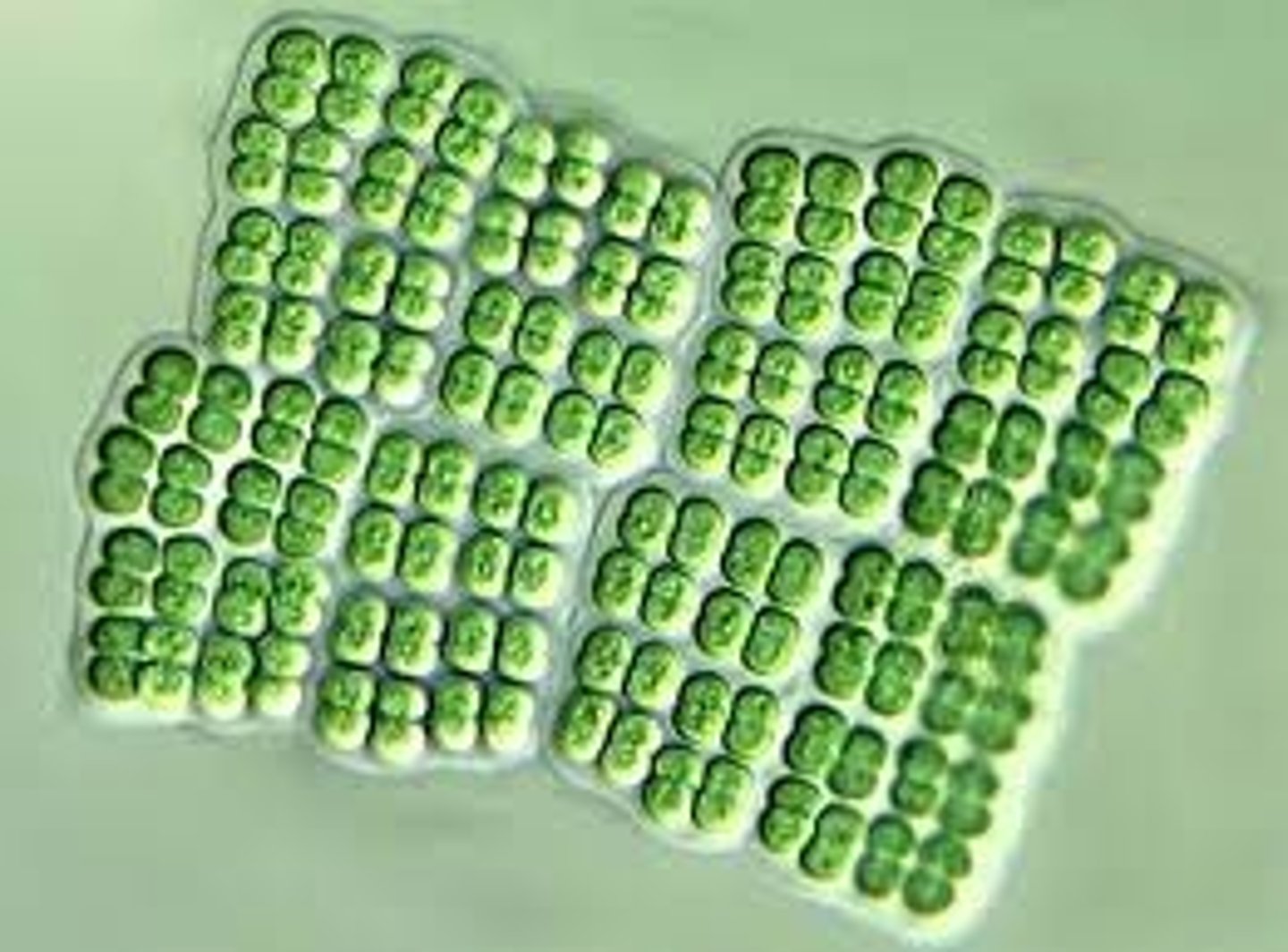
Merismopedia (Cyanobacteria)
Colonies form grid like sheets (result of cell division only occuring in two directions)
What does it mean if you make a gram stain experiment and the bacteria comes out purple?
Thick peptidoglycan layer traps crystal violet (Gram positive bacteria)
What does it mean if the bacteria comes out pink after a gram stain experiment?
Has a thin peptidoglycan layer so cannot retain the Crystal Violet (Gram negative bacteria)
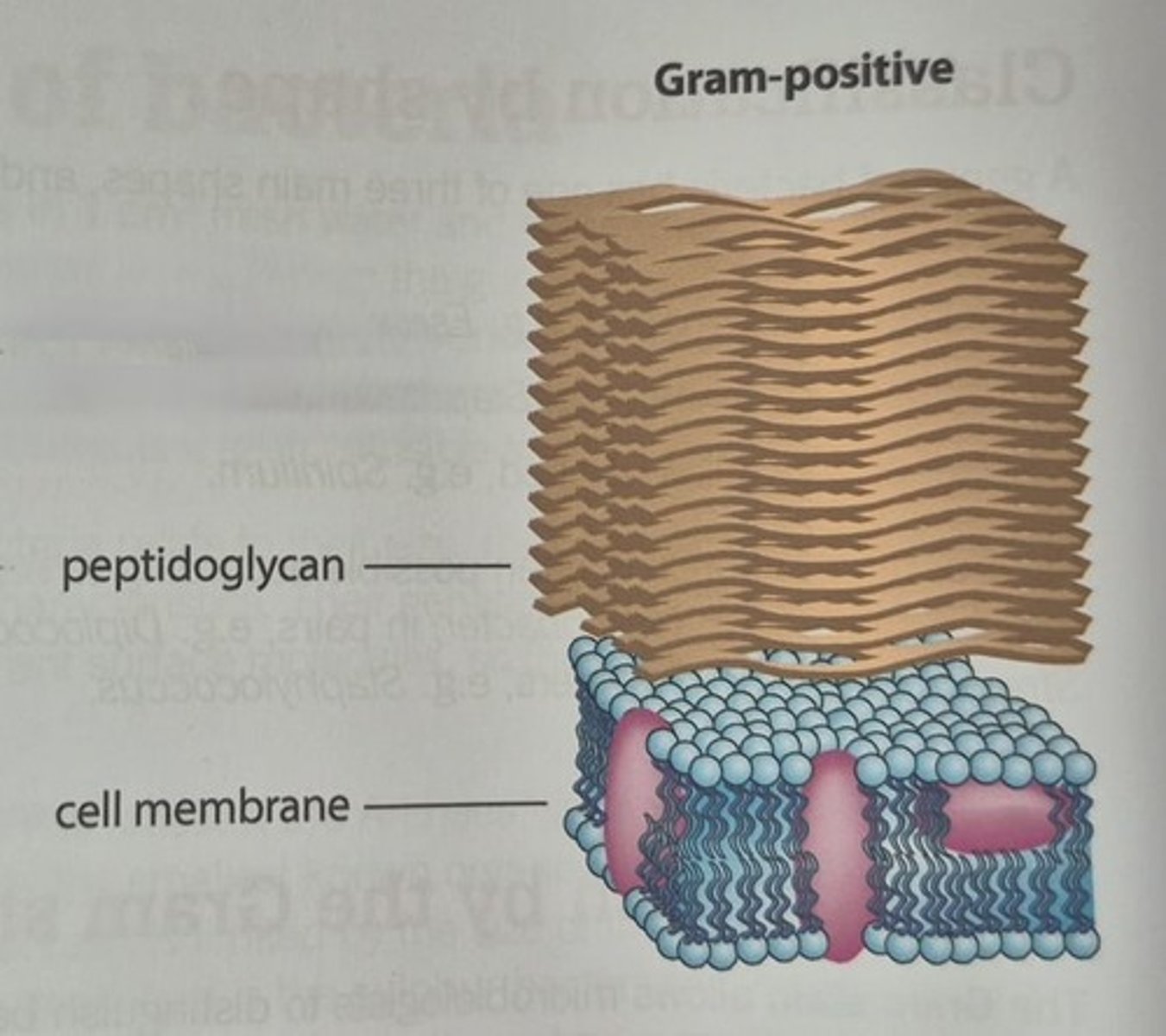
Structure of Gram positive bacteria
thick Peptidoglycan layer, periplasmic space, cytoplasmic membrane
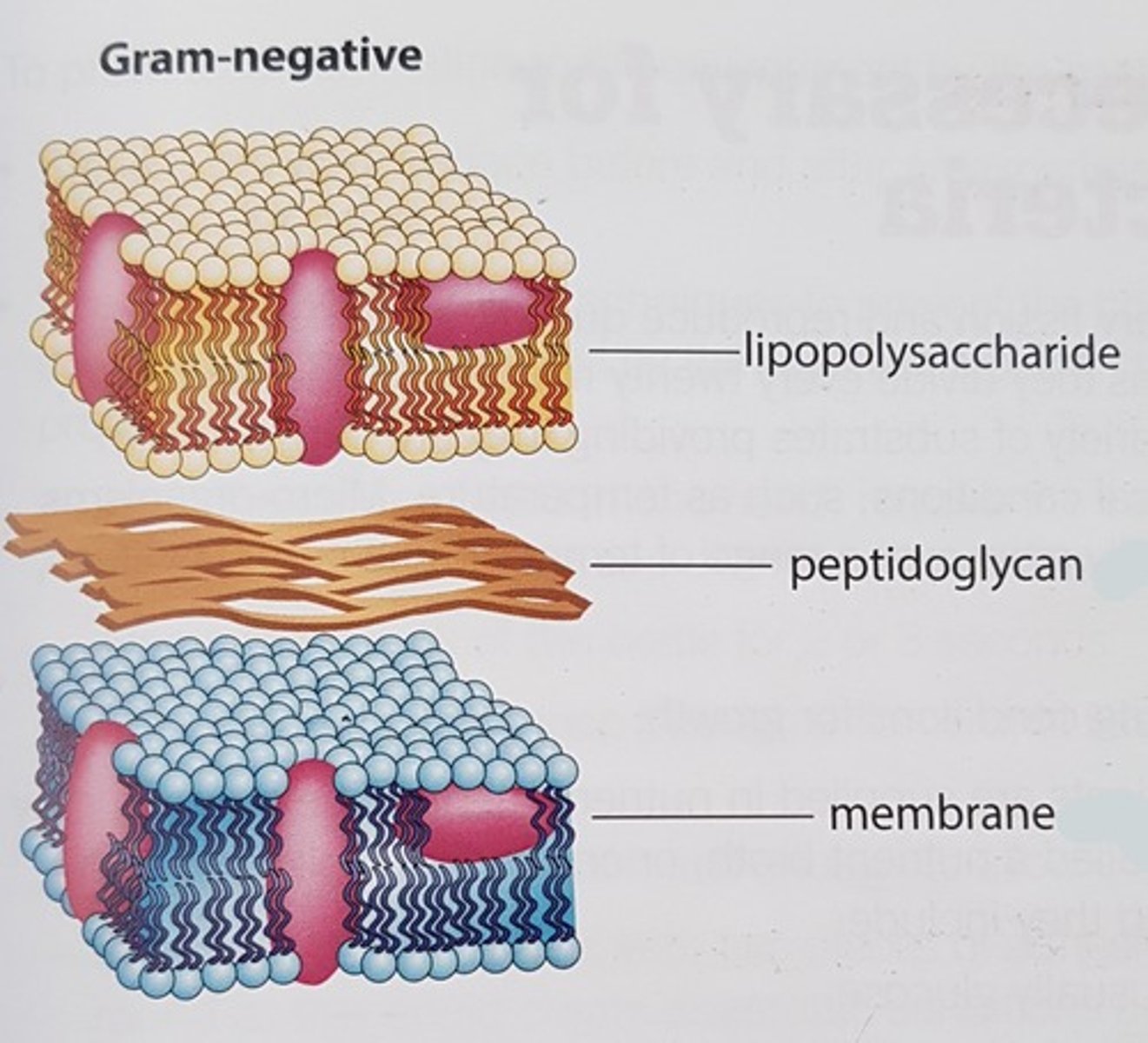
Structure of Gram negative bacteria
Outer membrane, thin peptidoglycan layer, periplasmic space, cytoplasmic membrane, contains lipopolysaccharides and porin
Steps for gram-stain procedure
Put bacteria on slide, stain with crystal violet, pour iodine treatment on slide, using 95% ethanol decolor the negative, counter stain using safranin (makes it pink)
Protists
eukaryotic organisms that are not classified as plants, animals, or fungi
Protists are a monophyletic group true or false
False, they do not all share a common ancestor
Supergroup Excavata
some members have an "excavated" groove on one side of the cell body, distinctive twin nuclei
examples: trypanosoma (found in blood), giardia (found in feces contaminated water)
What does SAR stand for?
Stramenopiles, Alveolates, Rhizarians
Clade Stramenopila (Stramenopiles)
straw like hairs help them swim more efficiently, includes diatoms, brown algae, giant seaweeds
Clade Alveolata
Contain sac-like vesicles called alveoli, dinoflagellates, stentor and paramecium
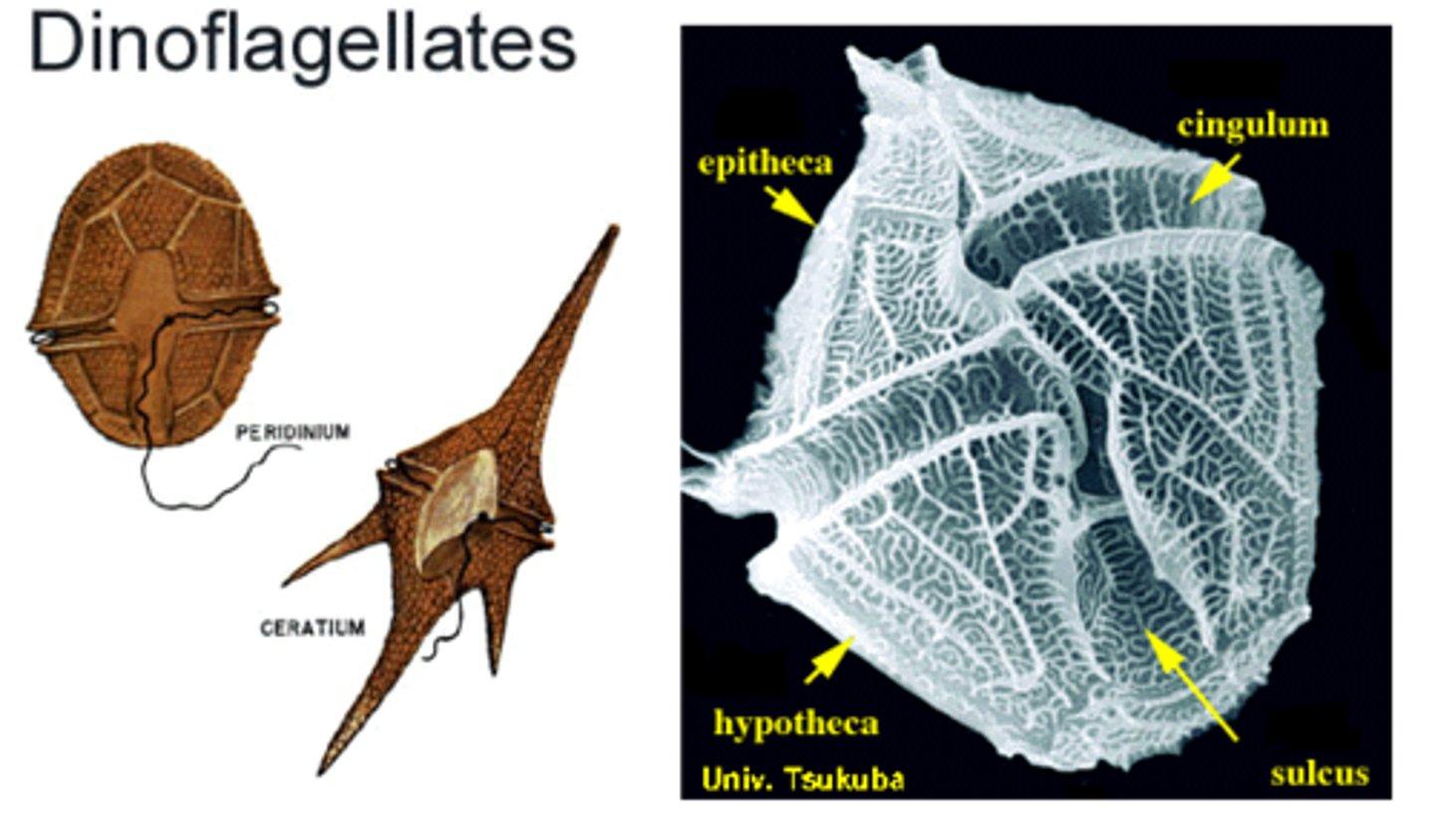
Dinoflagellates
Two perpendicular flagella, cause red tide and can be bioluminescent, most have cellulose plates
Clade Rhizaria
Planktonic marine eukaryotes, most are non-photosynthetic, form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic algae, have axopodia
Supergroup Archeplastida
Contains plastids which are photosynthetic organelles that originated from engulfed cyanobacteria
Supergroup Unikonta
includes: amoebas, non-amoeba protists, fungi, animals
Amoebozoans
A member of a clade of protists that includes amoebas and slime molds and is characterized by lobe-shaped pseudopodia.
slime molds
Funguslike protists that play key roles in recycling organic material, lack key fungi features
Haploid (n)
one set of chromosomes
diploid (2n)
two copies of each chromosome
Nonvascular plants (bryophytes)
liverworts, hornworts, mosses, lack roots, stems and leaves
Liverworts (Phylum Marchantiophyta)
Have flattened gametophytes with liver like lobes(gemmae cups)
no guard cells around pore
require lots of water
also undergo asexual reproduction
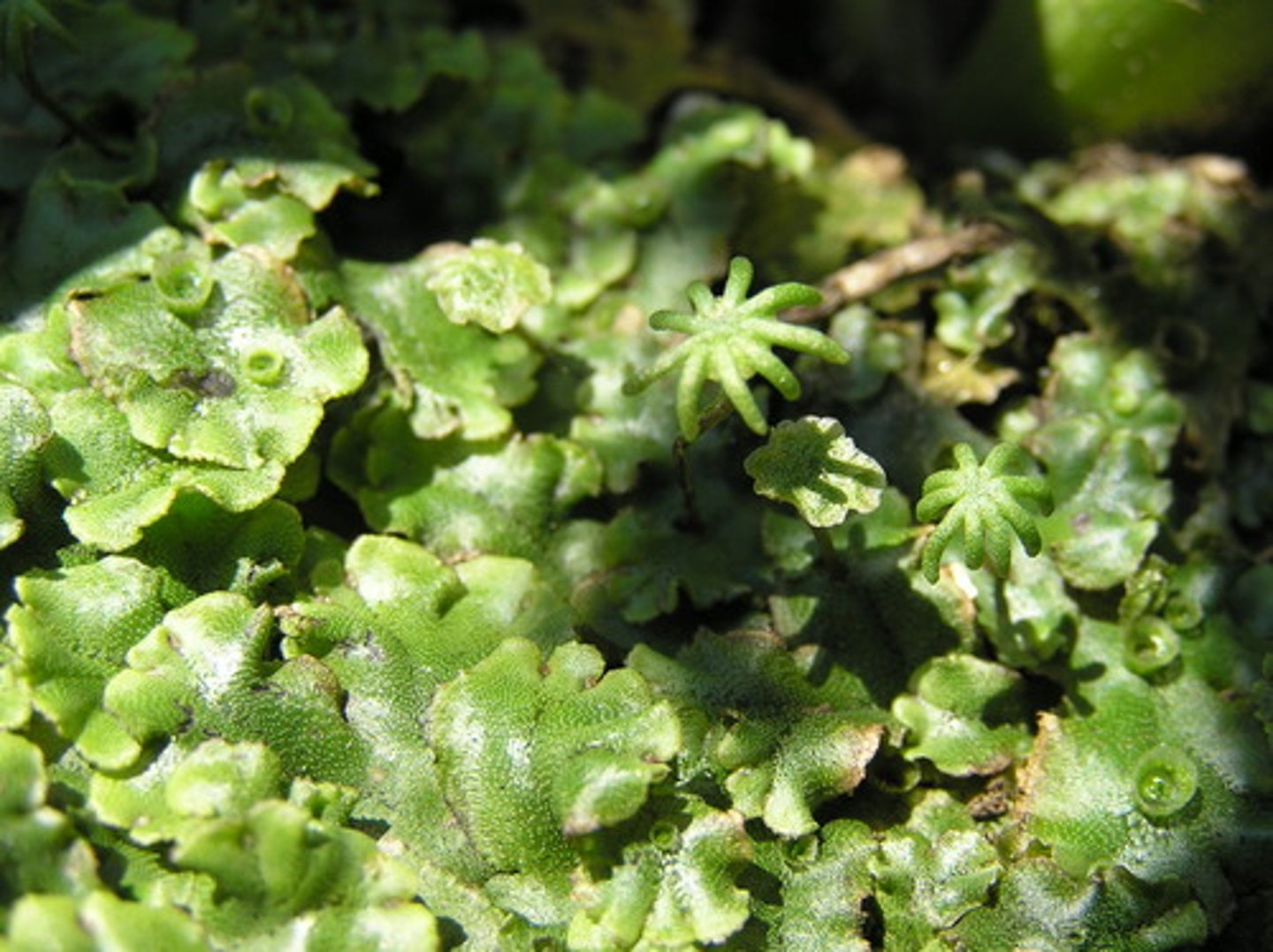

Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta)
-mainly gametophytes
-blades of leaves usually one cell thick
-sporophytes turn brownish red when they are ready to release spores
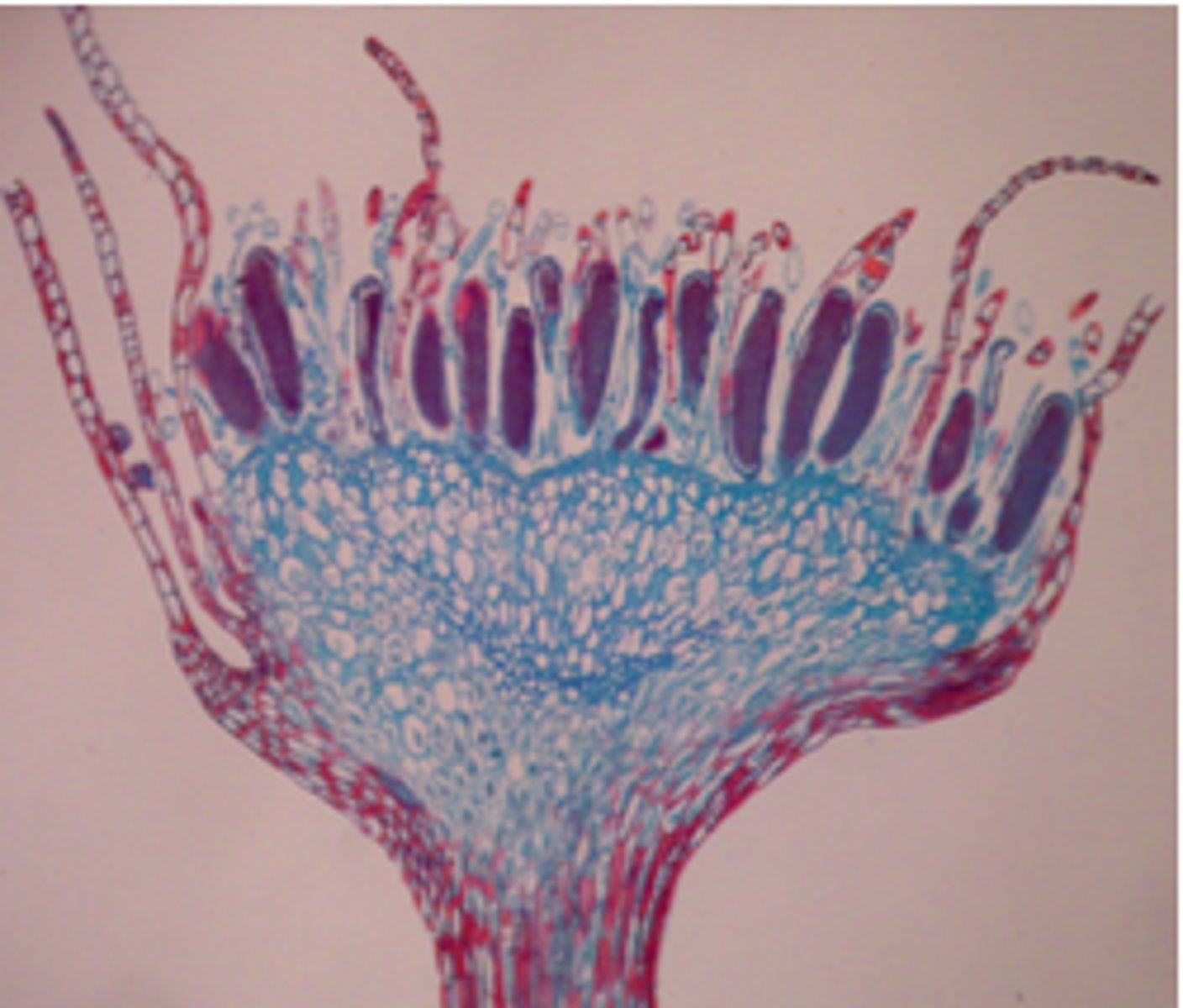
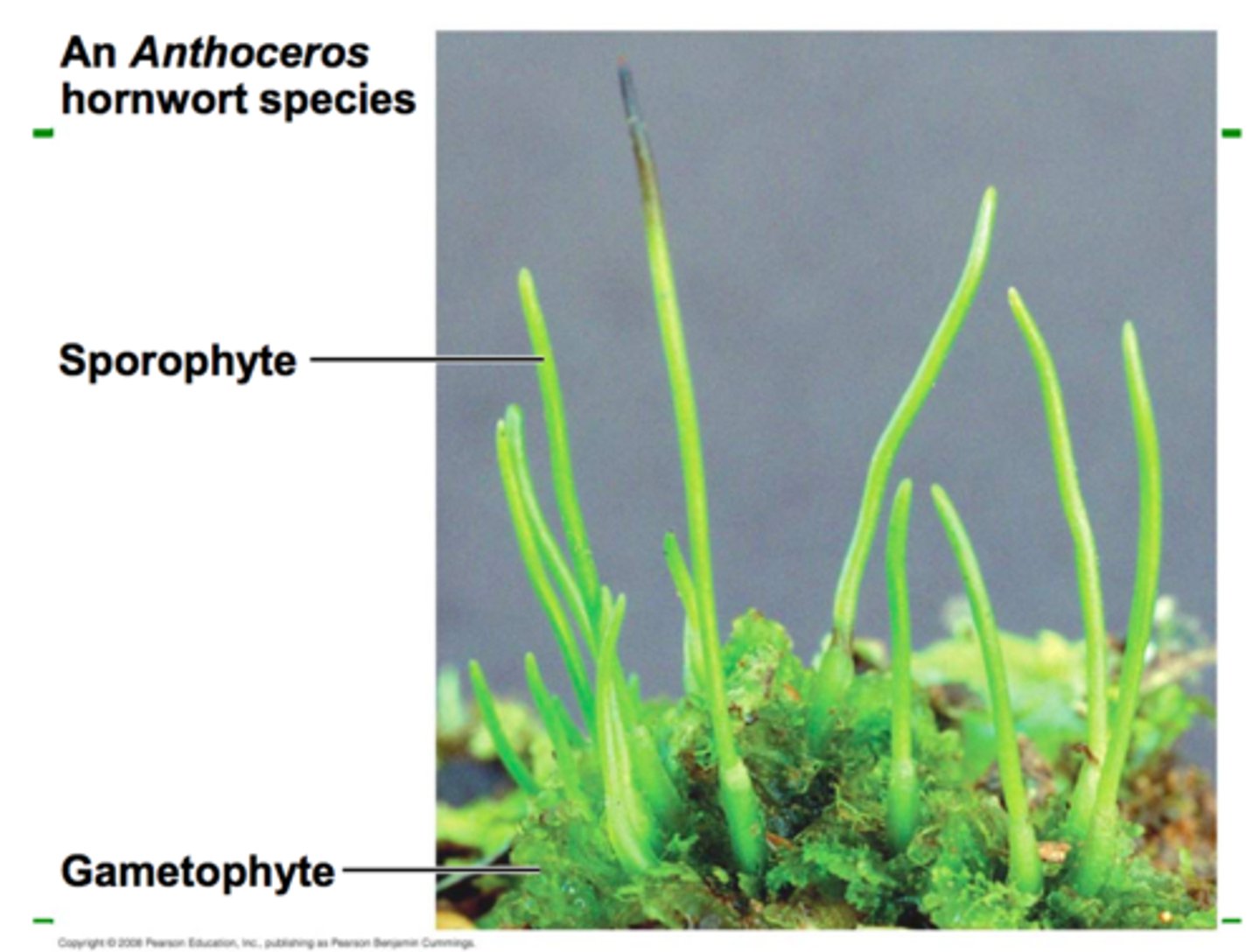
Hornworts (Phylum Anthocerophyta)
-long, tapered sporophyte
-lacks seta and consists of only a sporangium
-colonize open moist soils because of symbiotic relationship with cyanobacteria
-gametophytes grown horizontally
seedless vascular plants
- Have vascular tissues
- Uses spores instead of seeds
- Example: phylum monilophyta, phylum lycophyta,
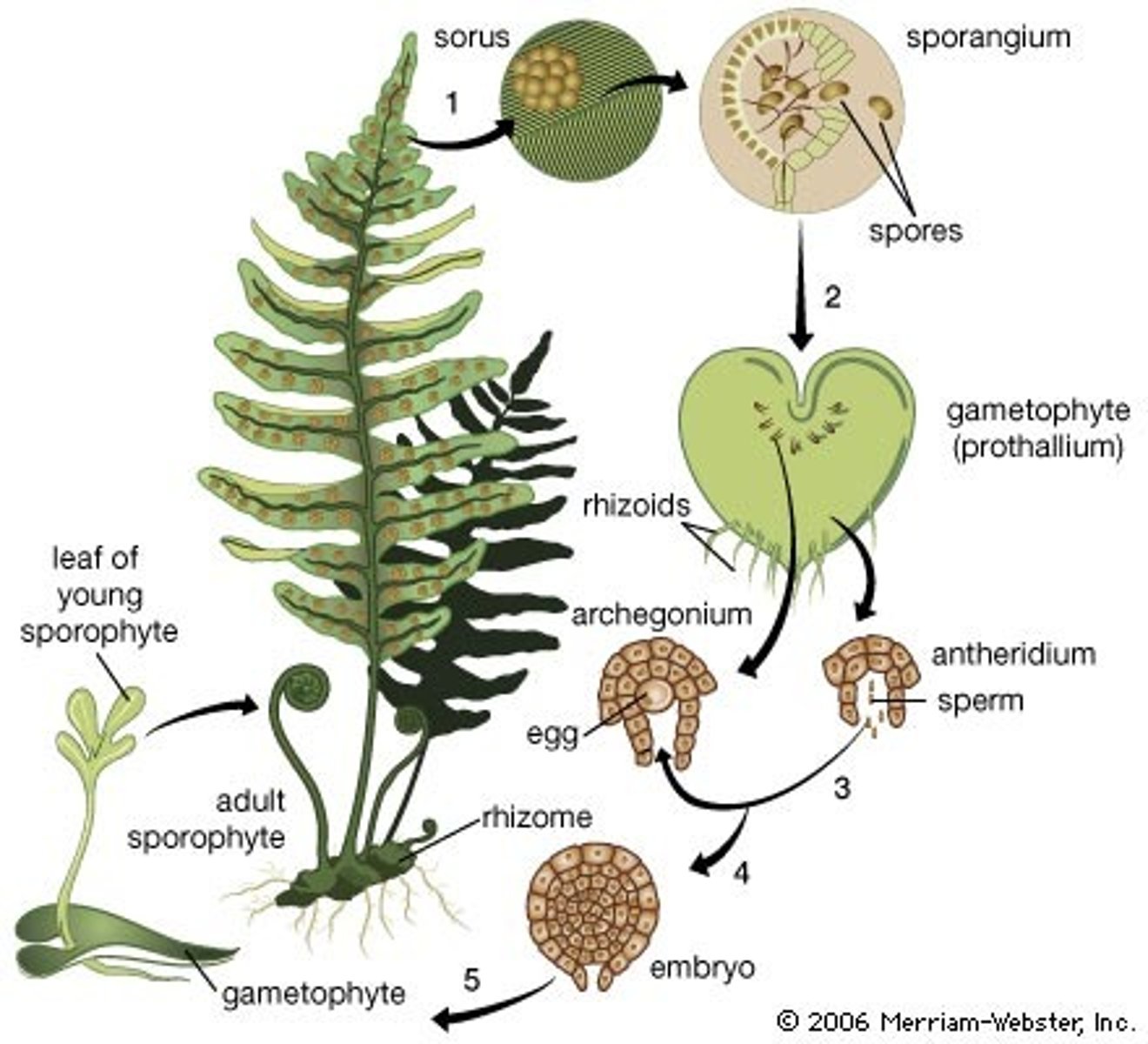
Phylum Monilophyta (Ferns)
•Most common seedless vascular plants (> 12,000 species),
•Leaves are called fronds, and grow from fiddleheads,
•Homosporous.
Horsetails (Equisetum)
- jointed hollow stems with tiny leaves
- strobili
- stem covered in silica
- approximately 15 species
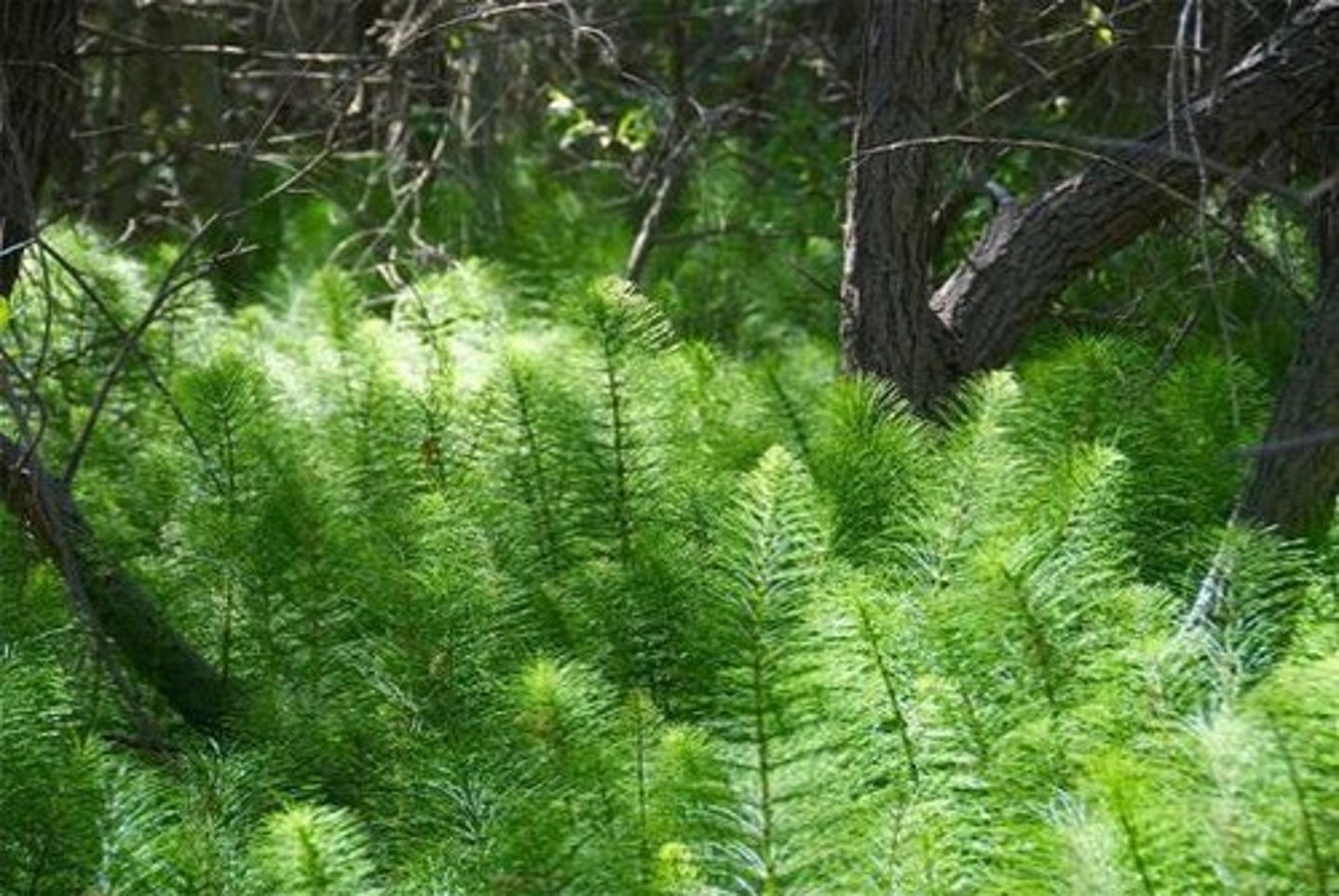

Phylum Lycophyta
club mosses (lycopodium), spike mosses(selaginella), quillworts
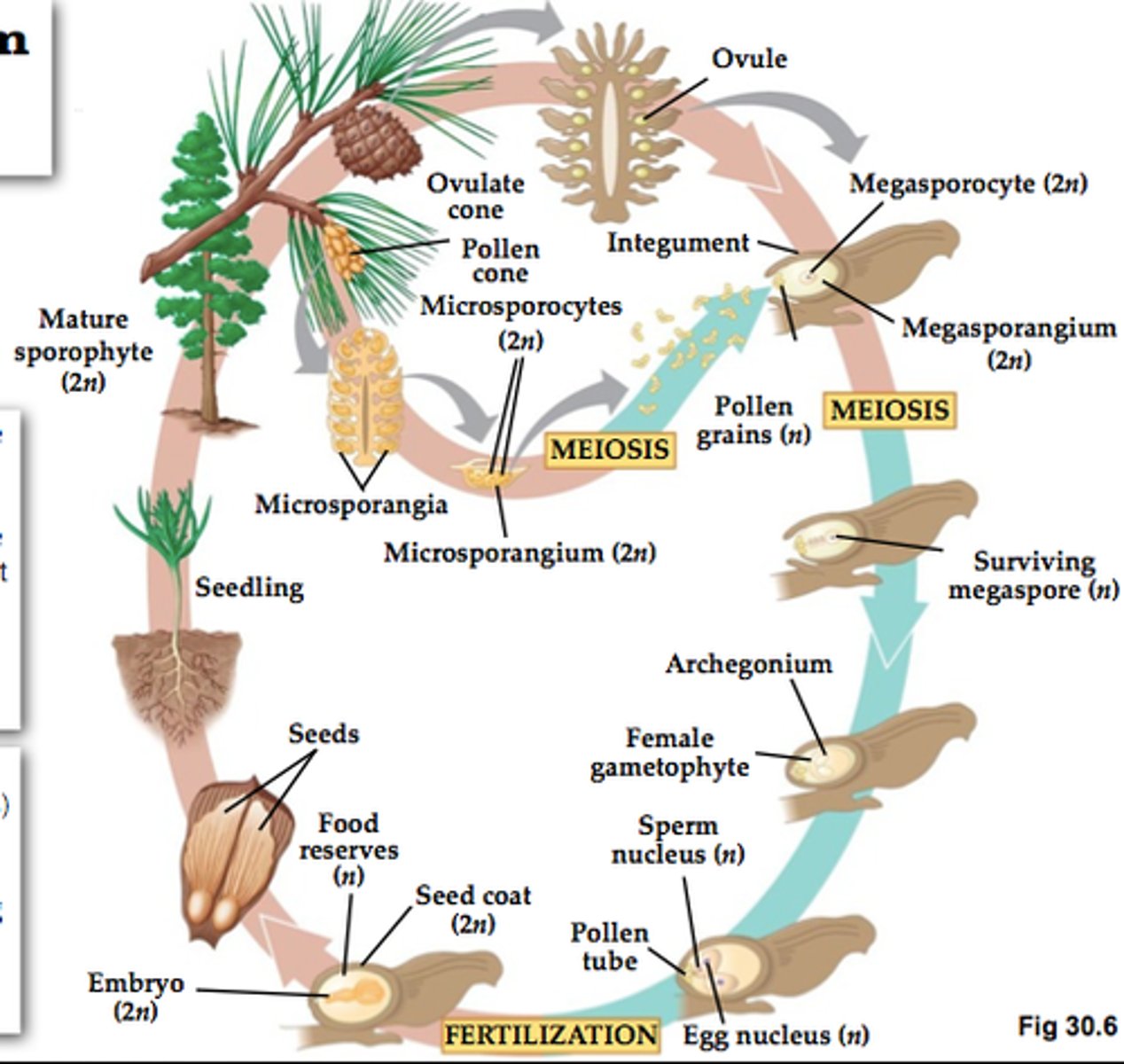
Gymnosperms
Produce seeds found on cones
- seed bearing vascular plant
Angiosperms
Produce seeds enclosed within a fruit
- seed bearing vascular plant
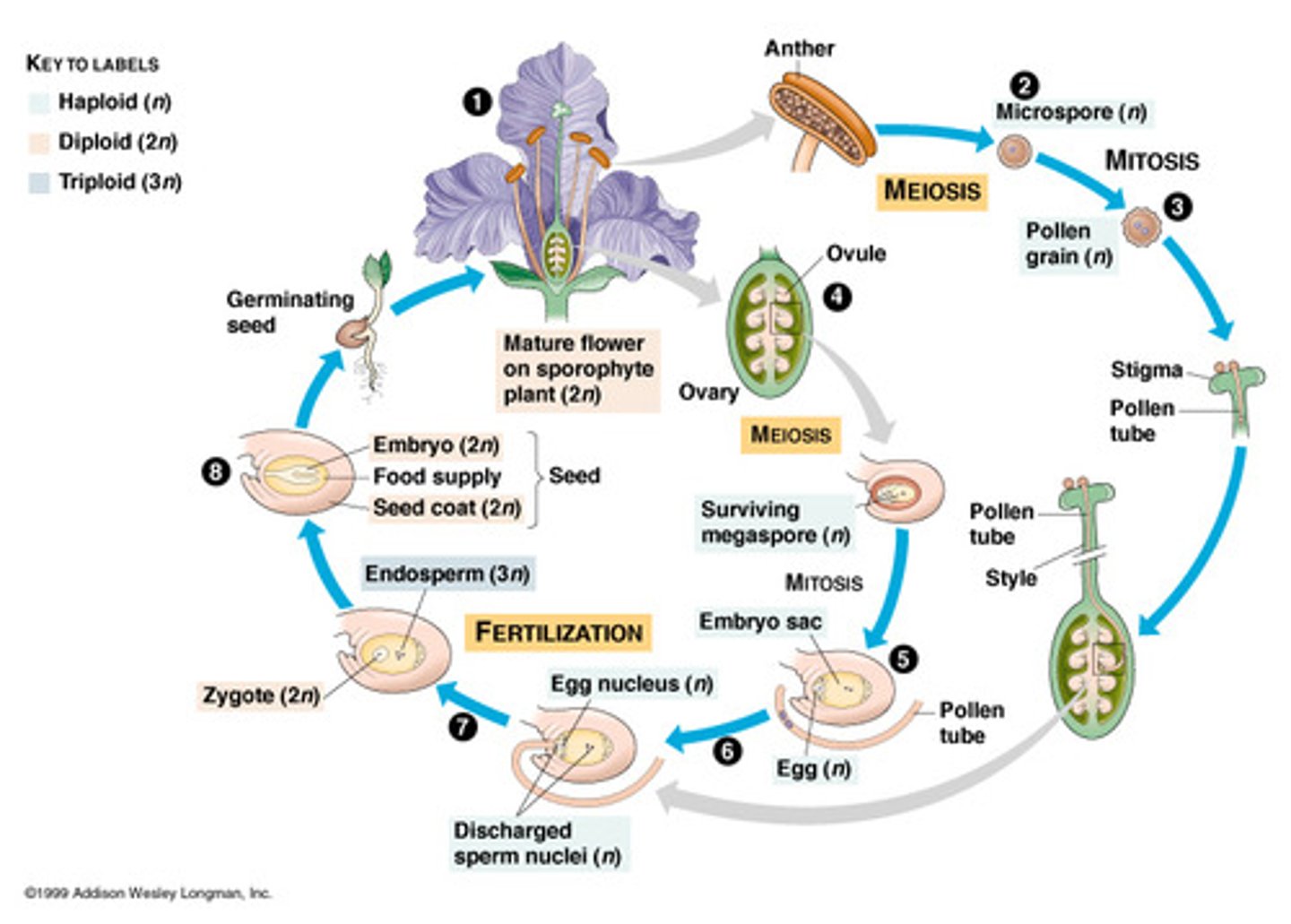
Heterosporous
produce two kinds of spores
Pollen contains which gender of gametophyte?
Male (sperm cells) which are carried from plant to plant
Seeds contain which gender of gametophyte?
Female, they form when the gametophyte has been fertilized
Monoecious plants
Single plant with male and female parts, produces both pollen and cones
dioecious plants
have separate male and female plants