Lecture 12: Population Genetics and Exercise 10 Genes in Populations
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Population
These are a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area, (potentially) interbreed, produce fertile offspring, and share the same gene pool
Population genetics
study of heredity and variation in a population
Gene pool
All copies of every type of allele at every locus in all members of the population
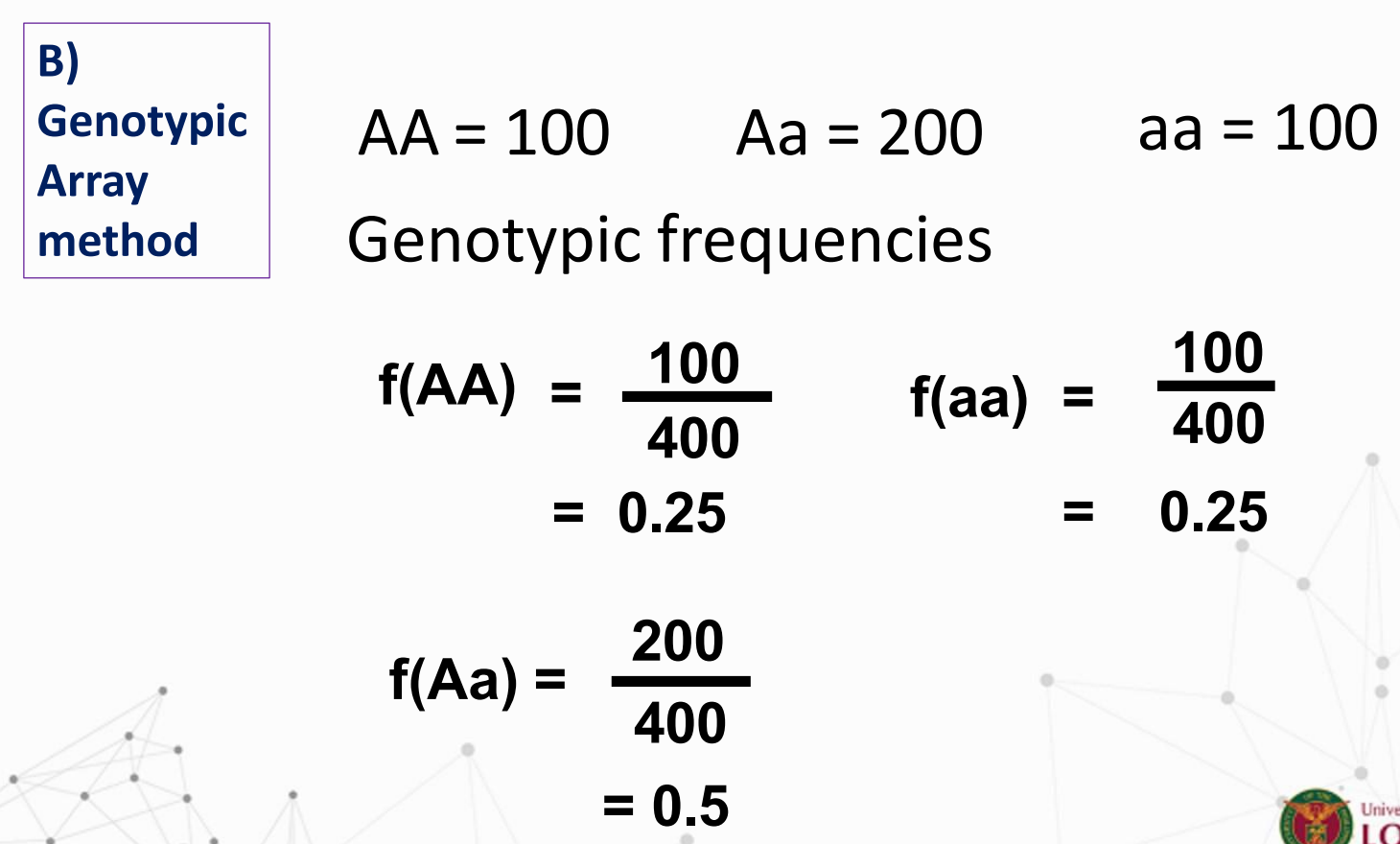
Genotype frequencies
The relative proportion of a specific genotype for a gene to all genotypes for that gene in the population
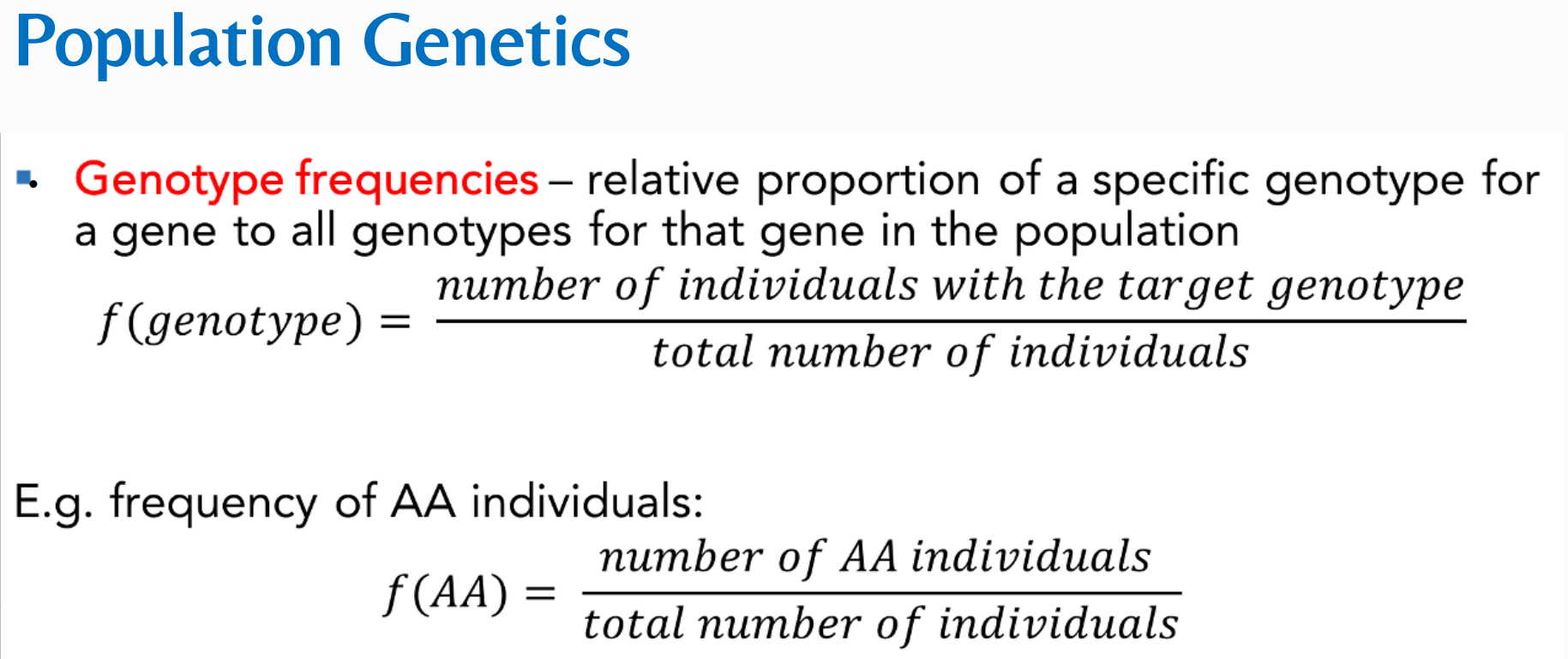
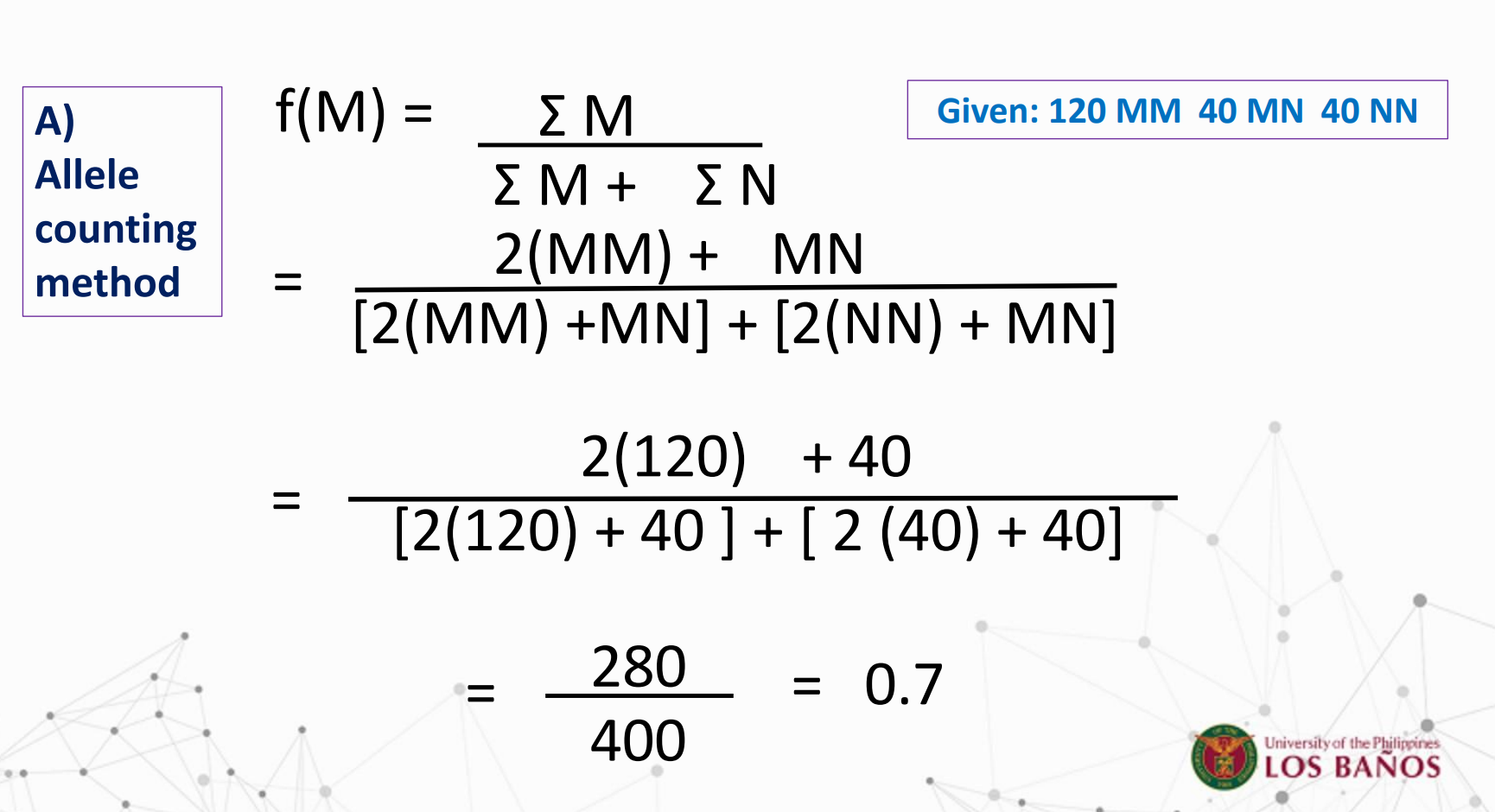
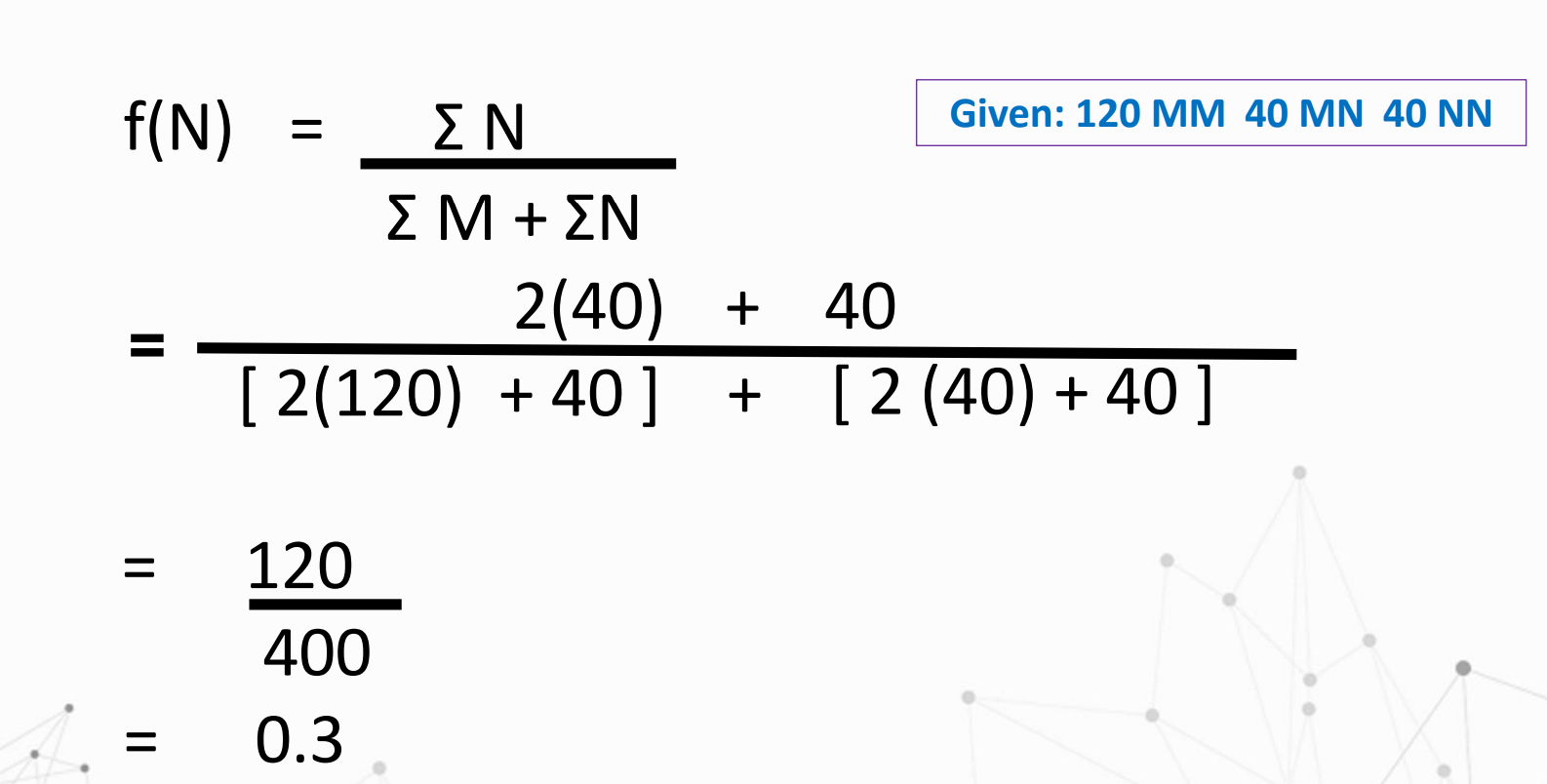
What is the formula for Genotype frequencies?

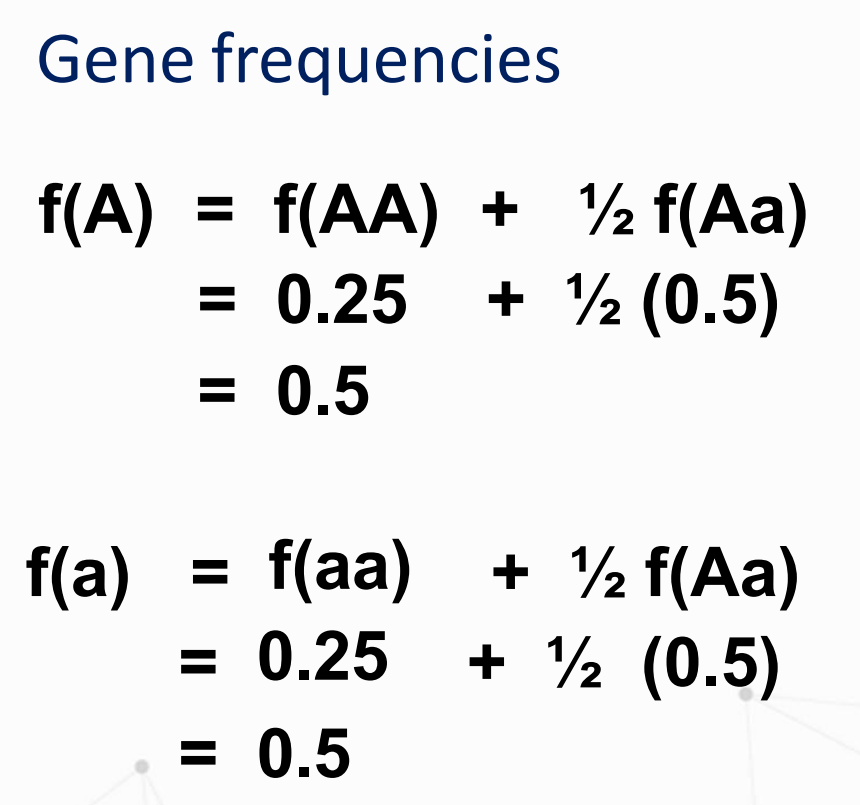
The relative proportion of an allele of a gene to all alleles of that gene in the population

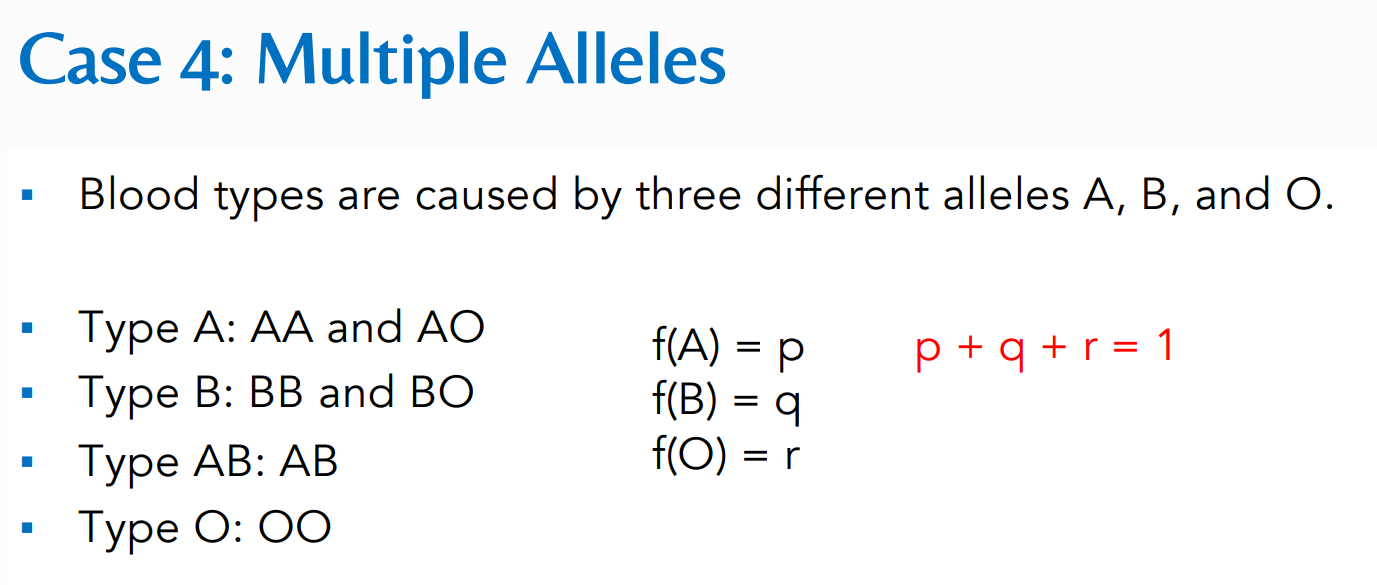
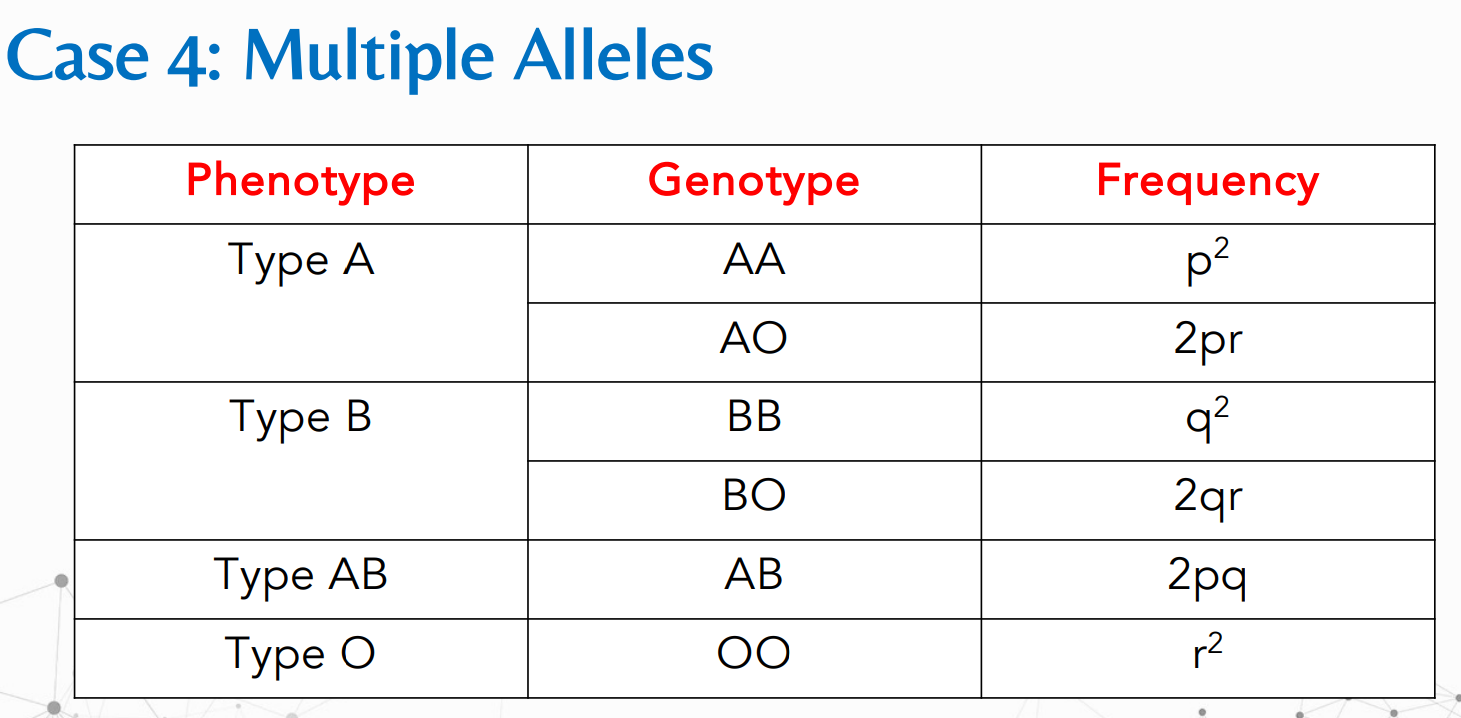
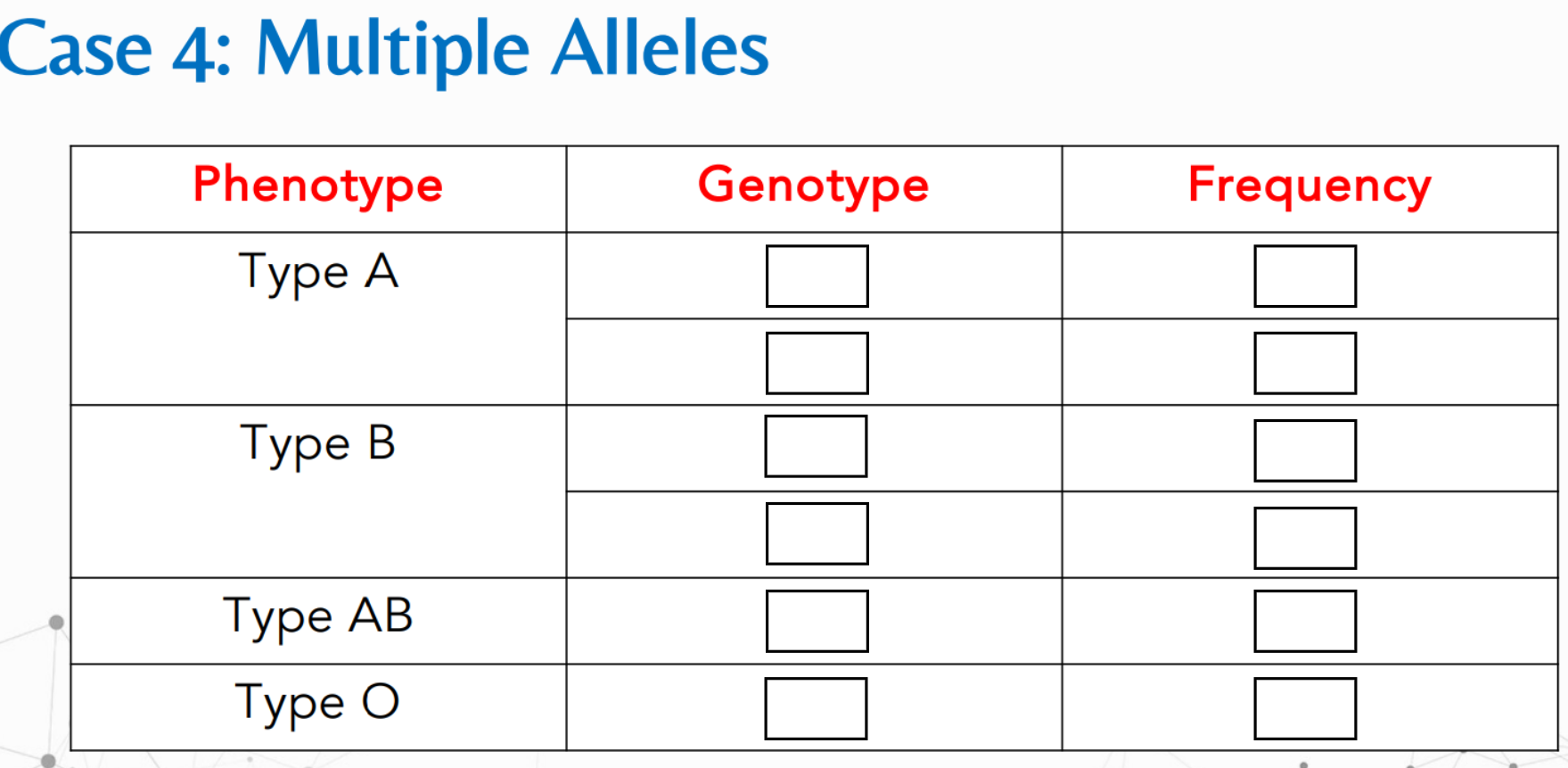
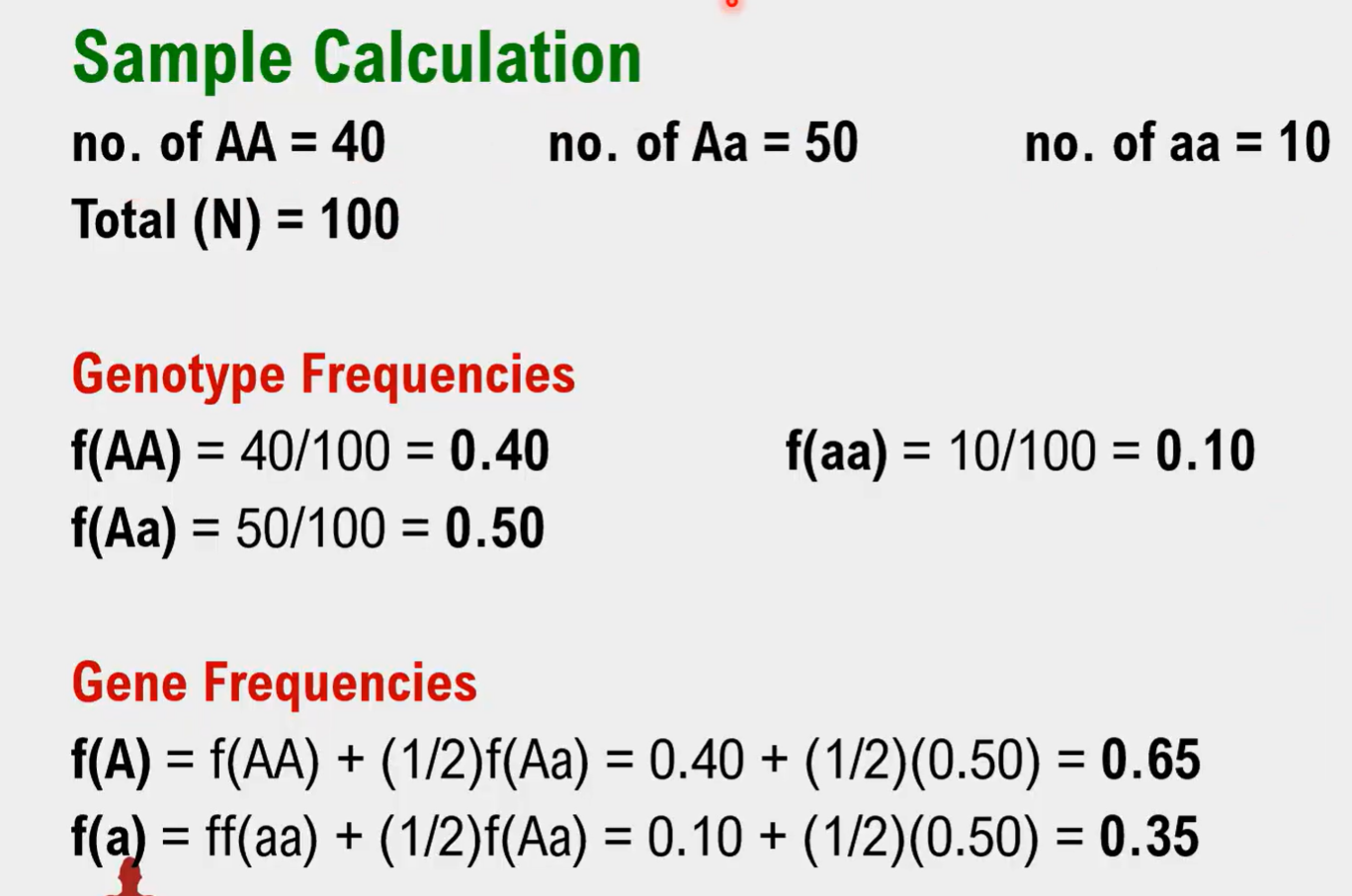
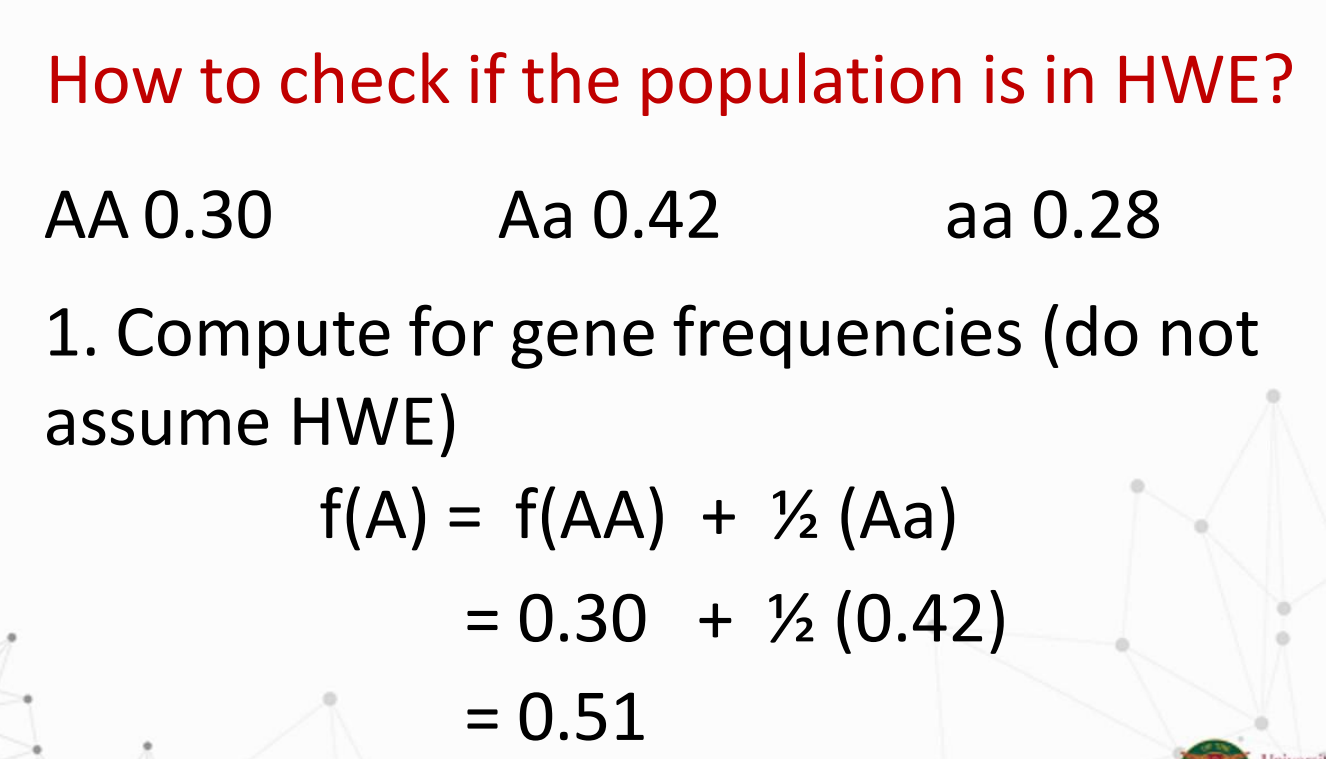
What is the formula for:

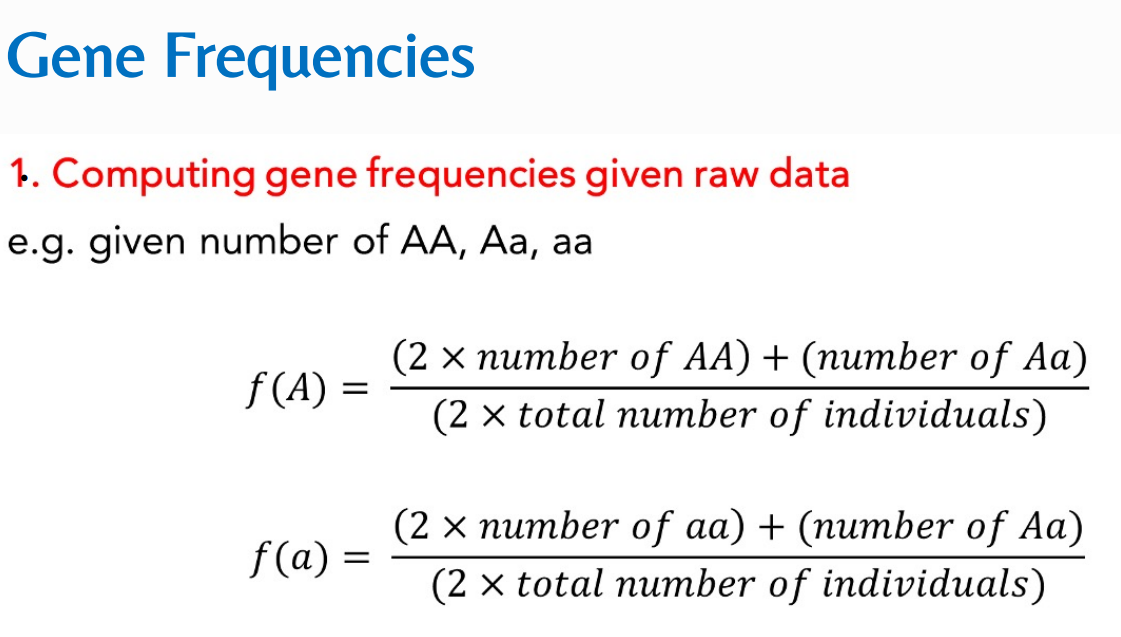

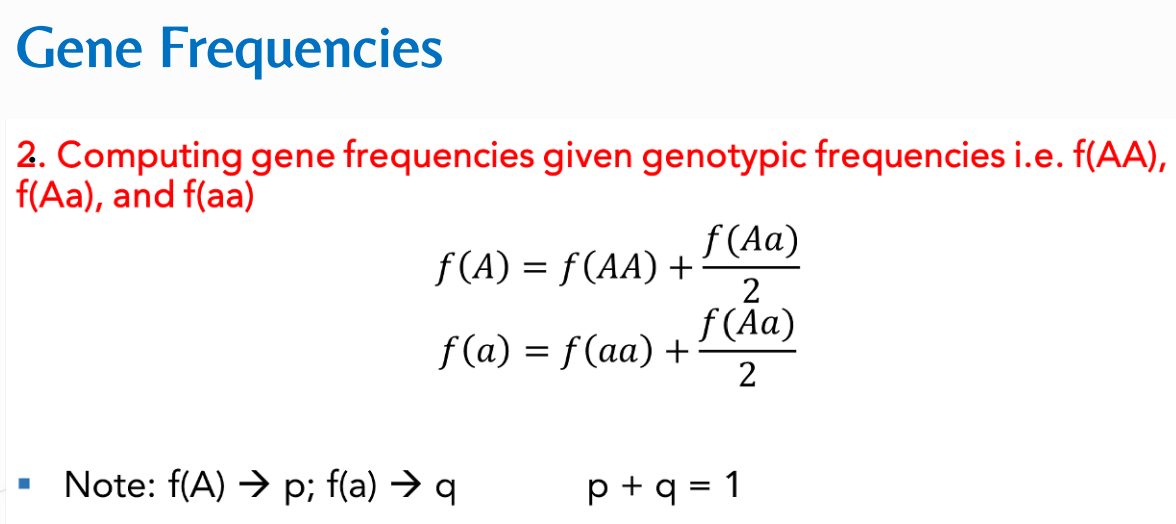

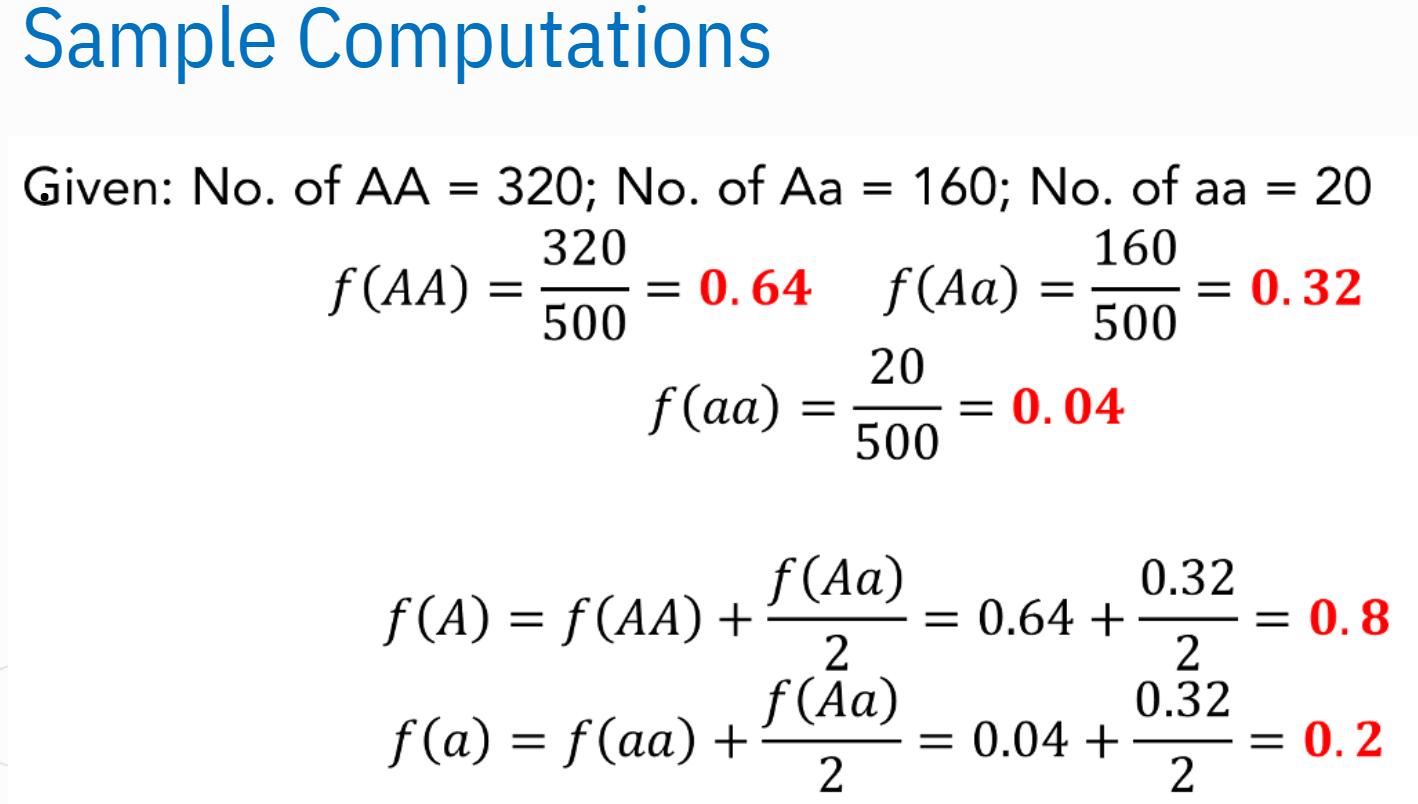
Solve for f(A) and f(a)

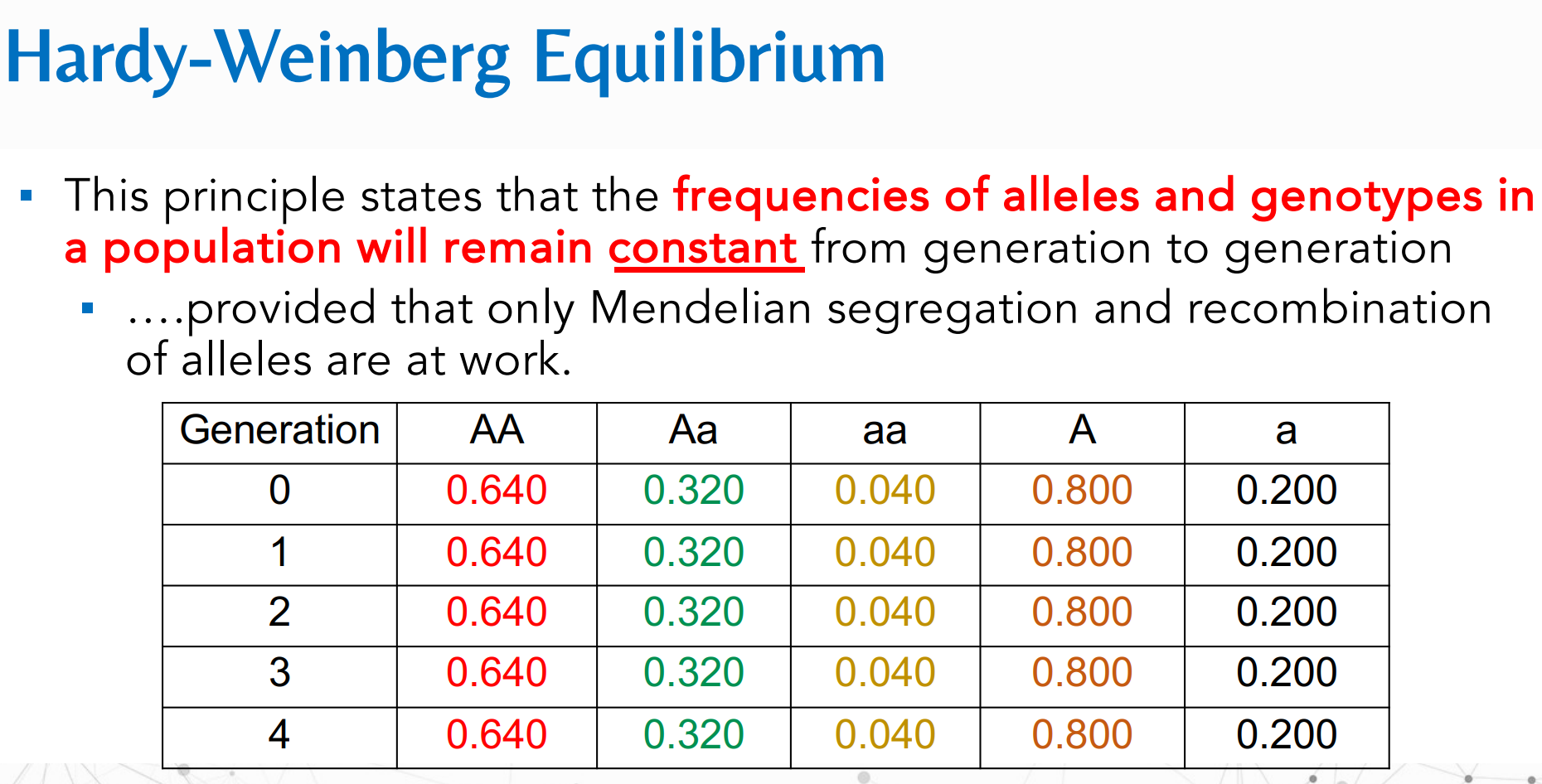
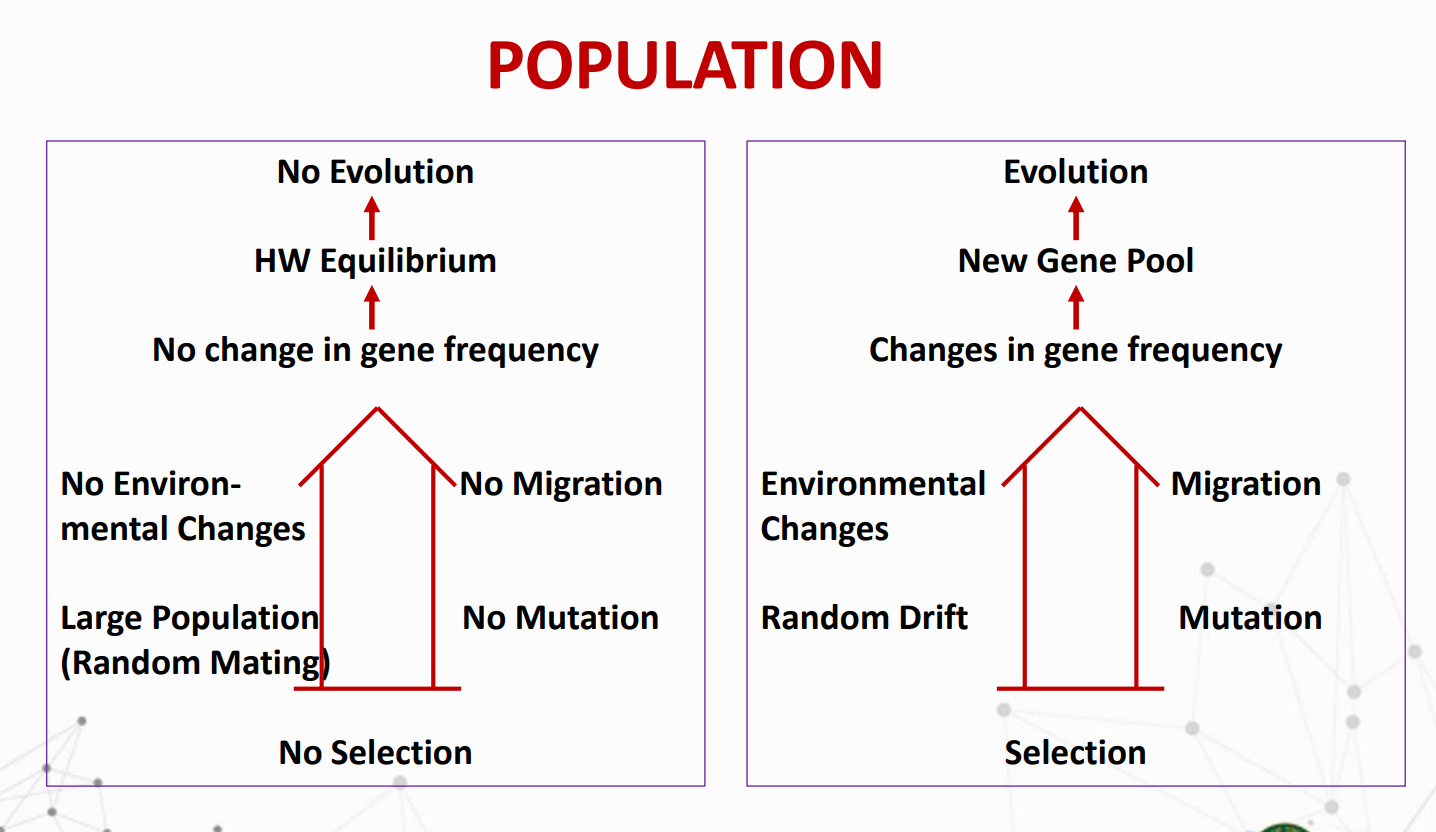
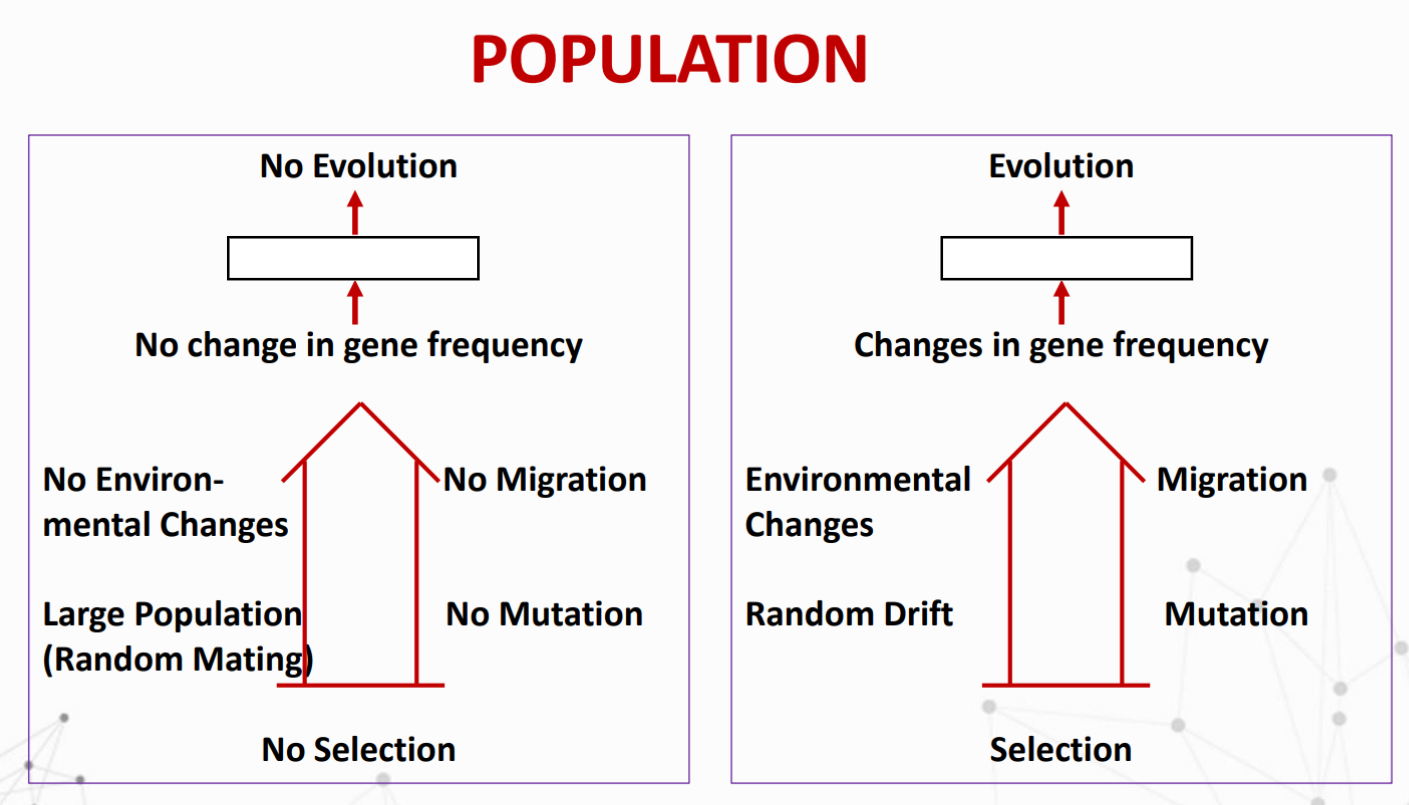
This principle states that the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population will remain constant from generation to generation, provided that only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles are at work.
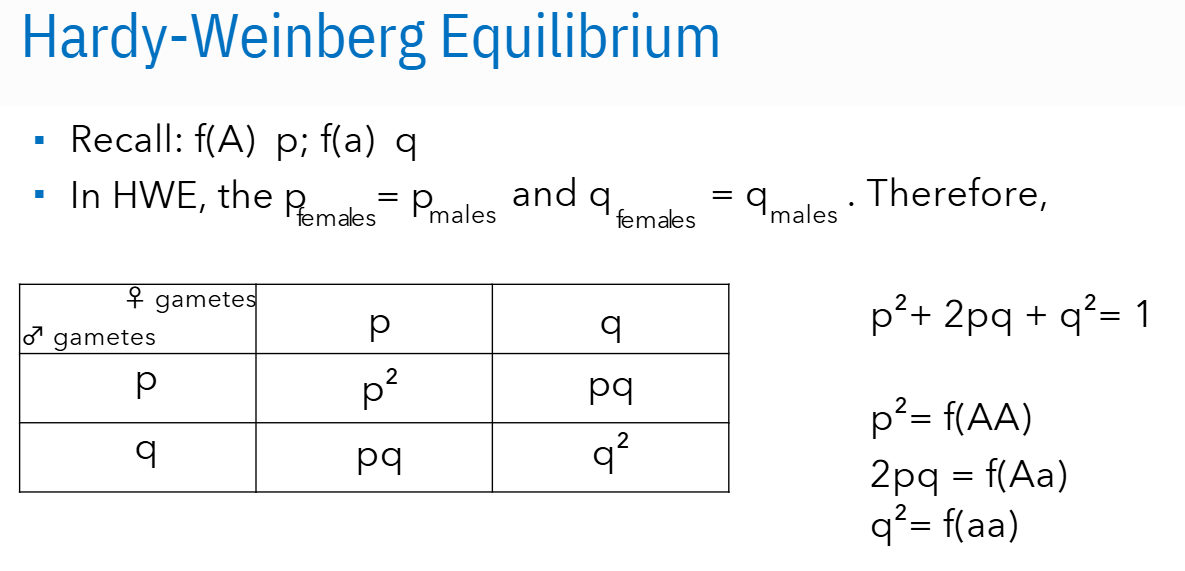
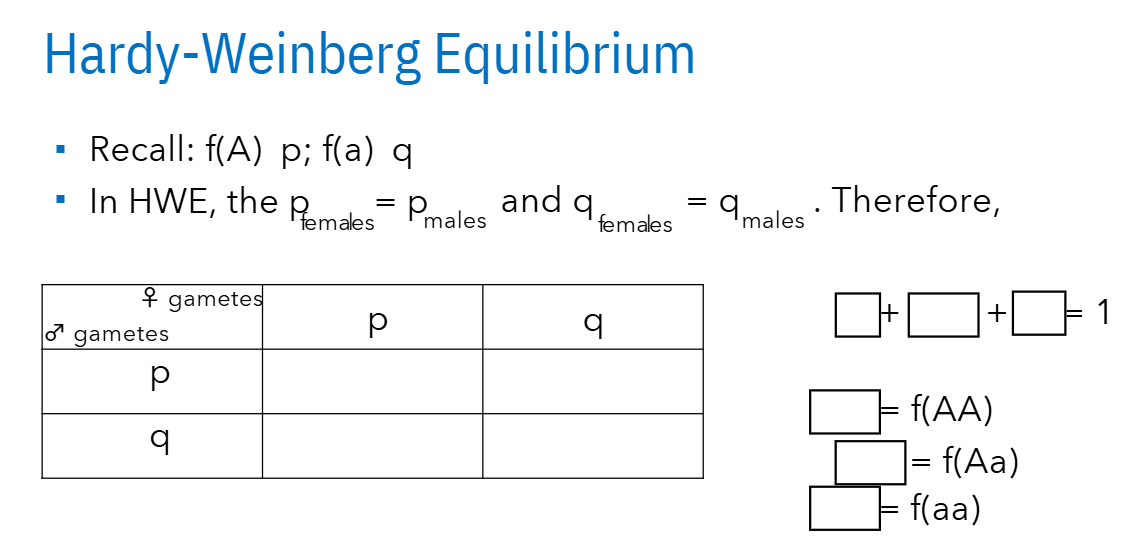

What are the Conditions for Hardy-Weinberg Eq.?










Look for genotype and gene frequencies.

Population Genetics
It is concerned with heredity in groups of individuals or population and how the genetic constitution changes from generation to generation
Population Genetics
It studies the genetic constitution of population and predicts the fate of a gene in a population

What determines an Effective population size?
Gene frequency
It is the relative proportion of the different alleles of a gene in a population



Gene pool
It is the sum total of genes in the reproductive gametes of the population
It is also know as the gametic pool
Gene pool
Here Samples are drawn at random and we must include the gametes that will form the zygote for the next generation
Godfrey H. Hardy (Mathematician)
Wilhelm Weinberg (Physician)
In 1908 they independently derived the equations for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
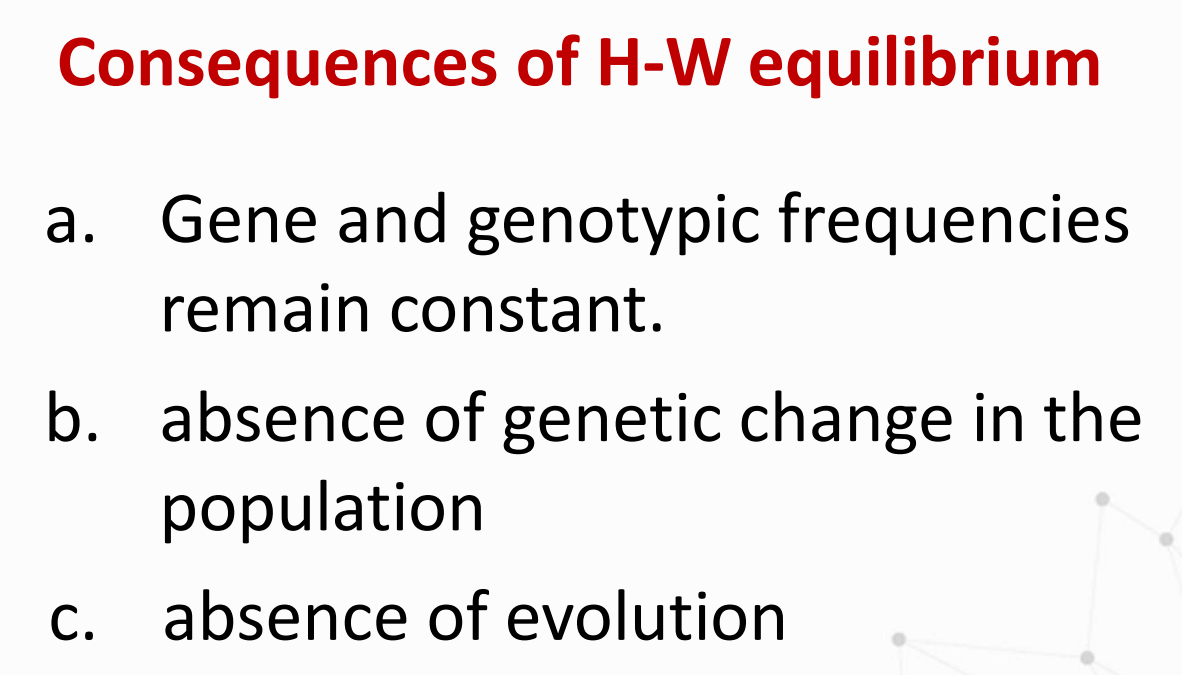
What are the Consequences of H-W equilibrium


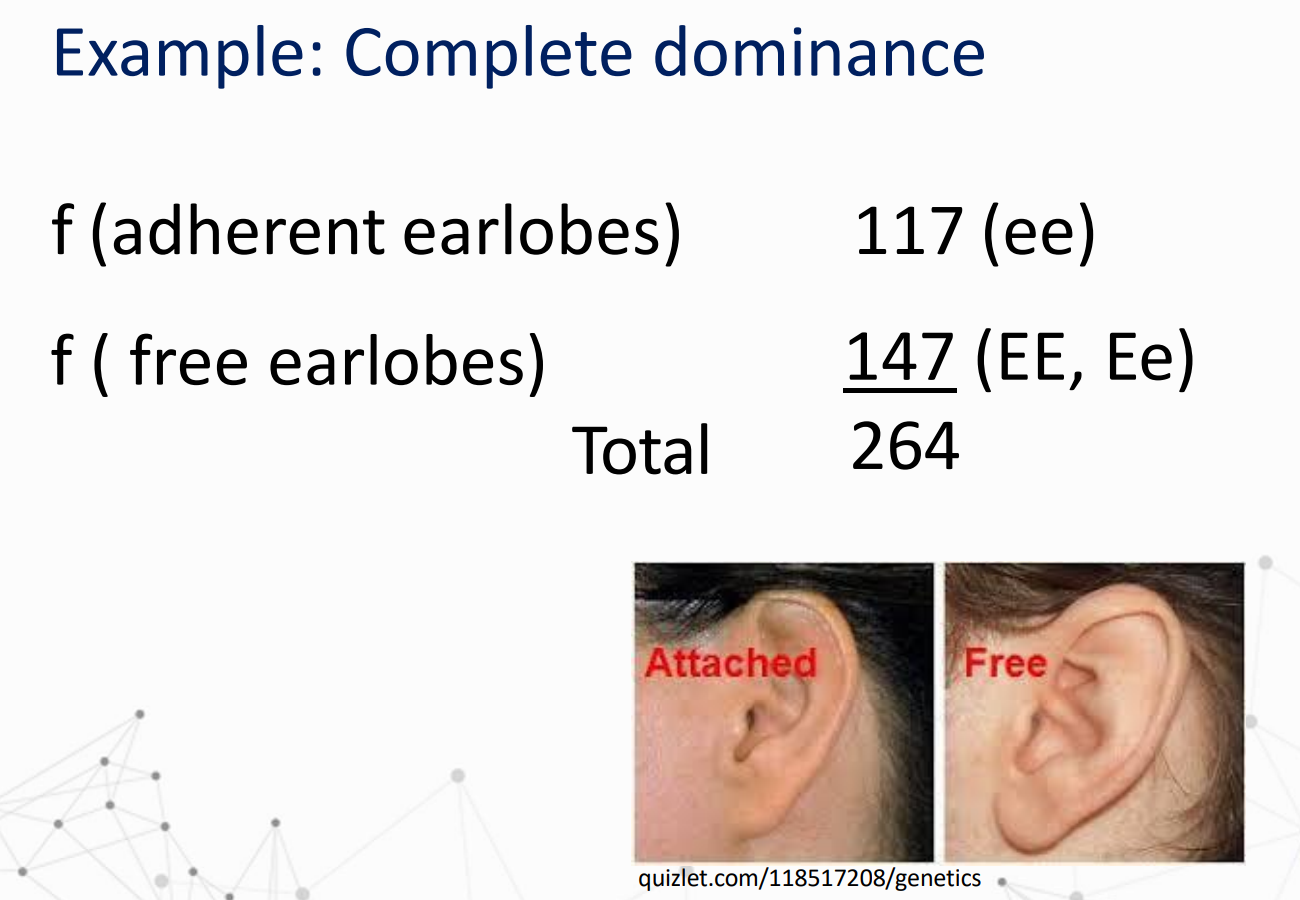
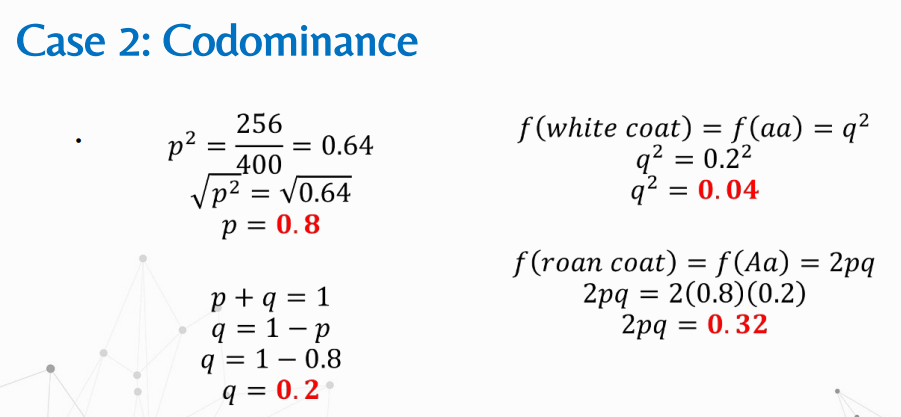
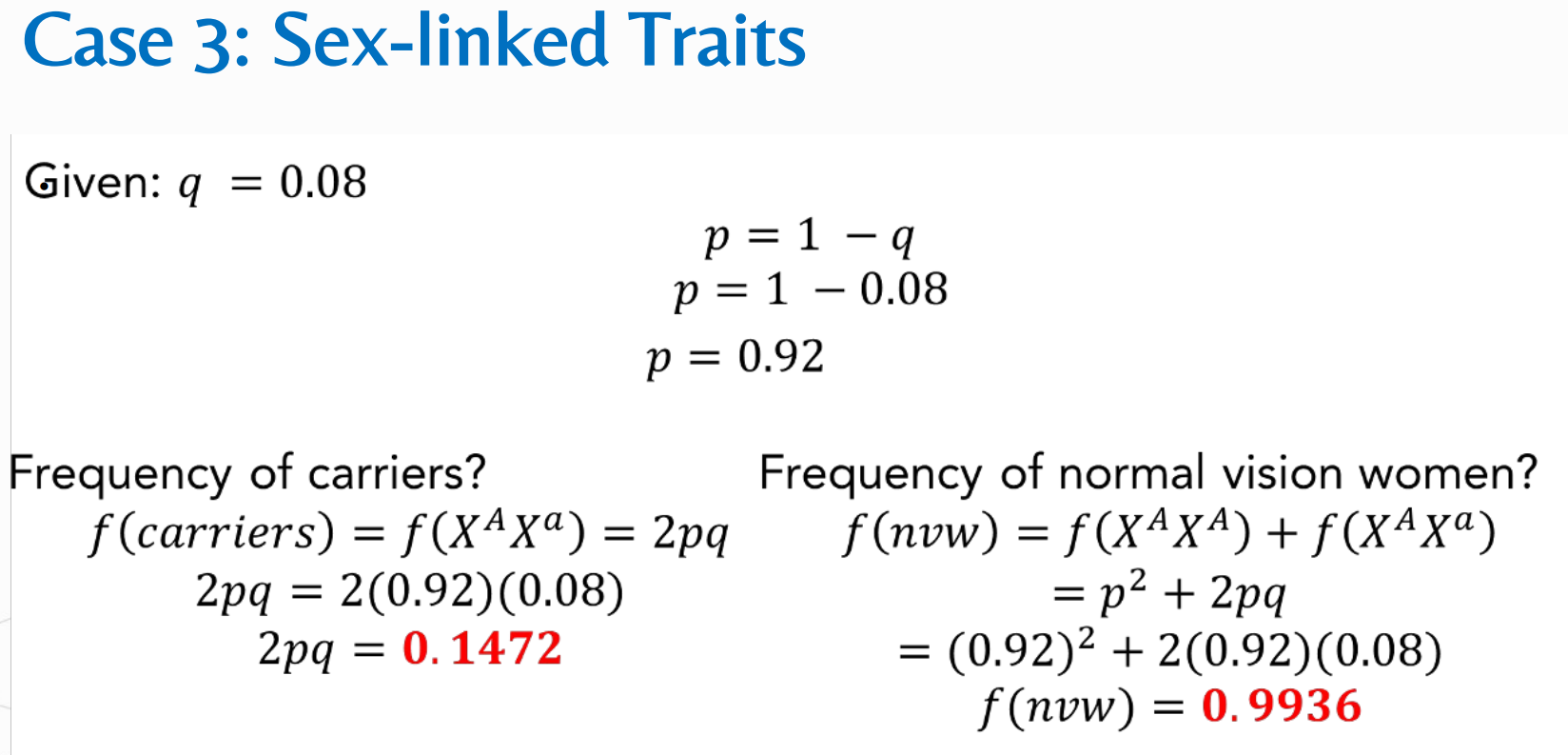
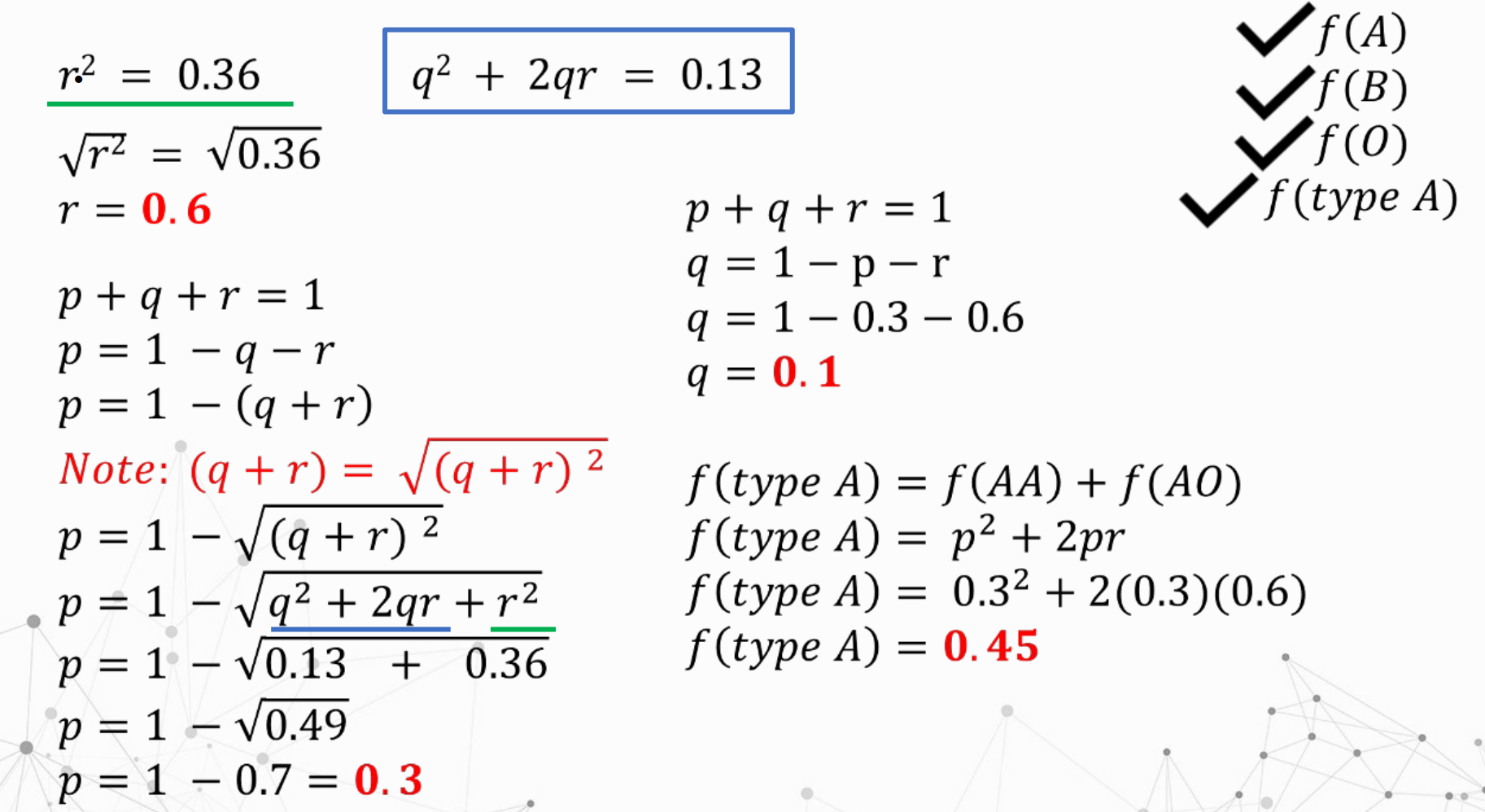
Given:
Solve for genotypic frequencies of EE, Ee, and ee
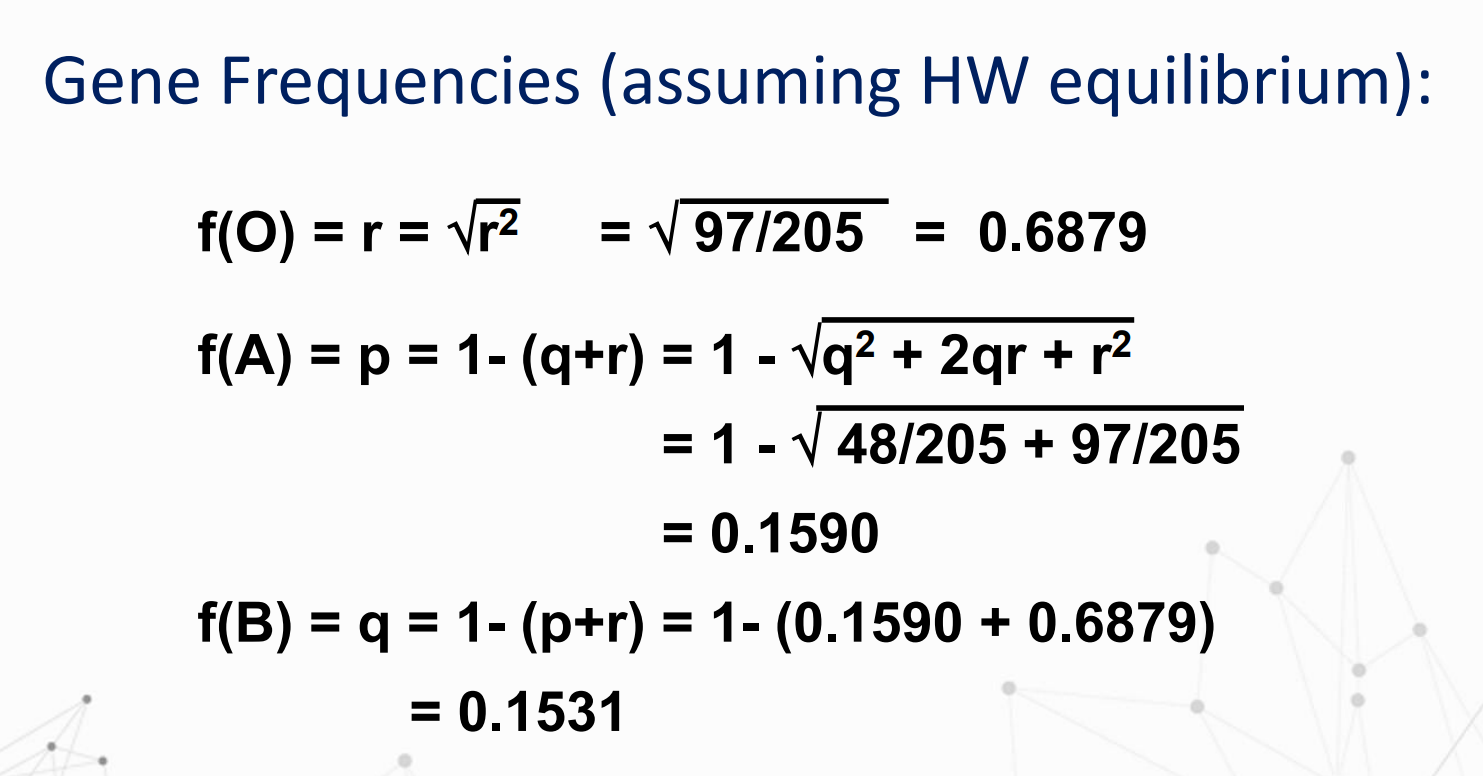
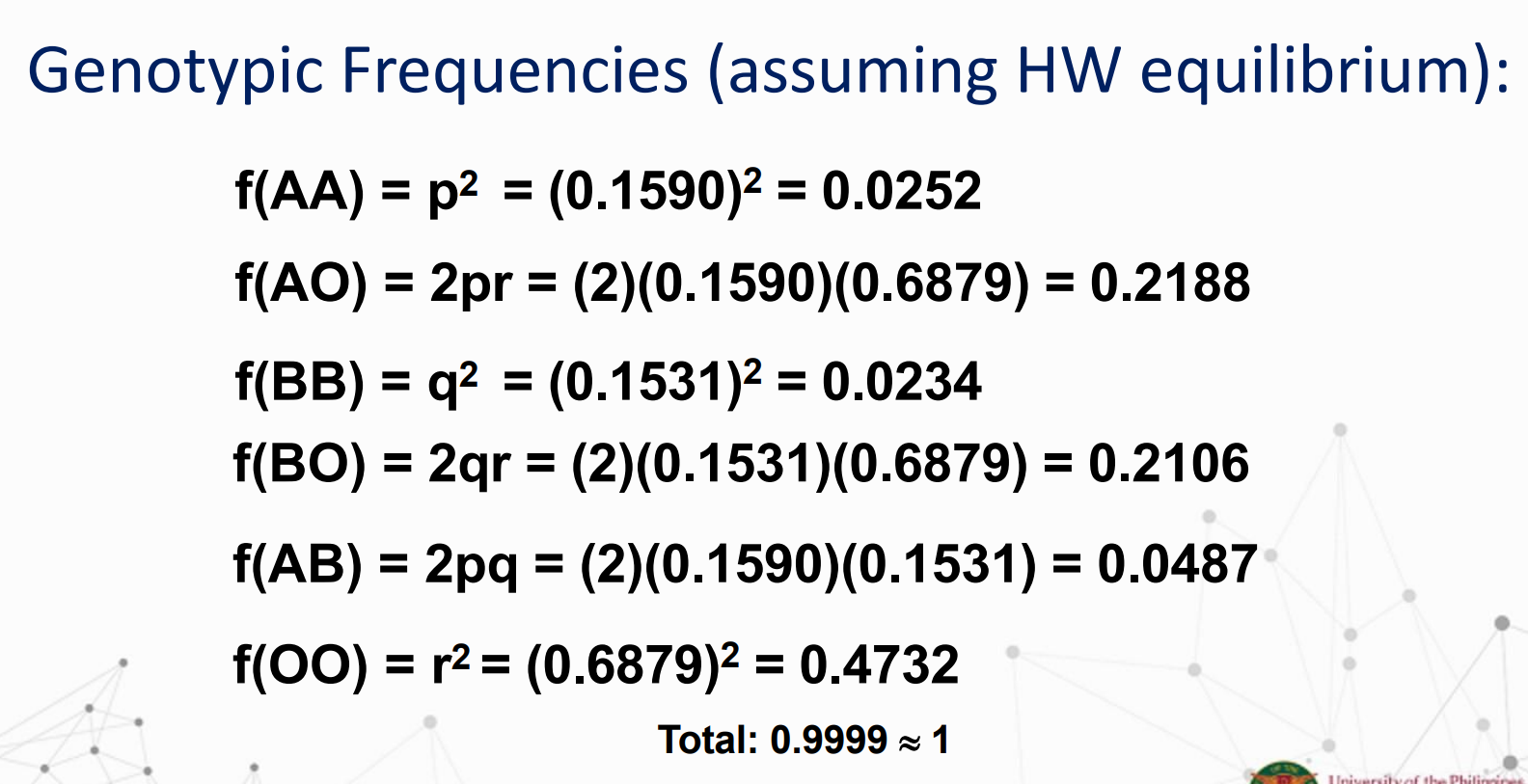

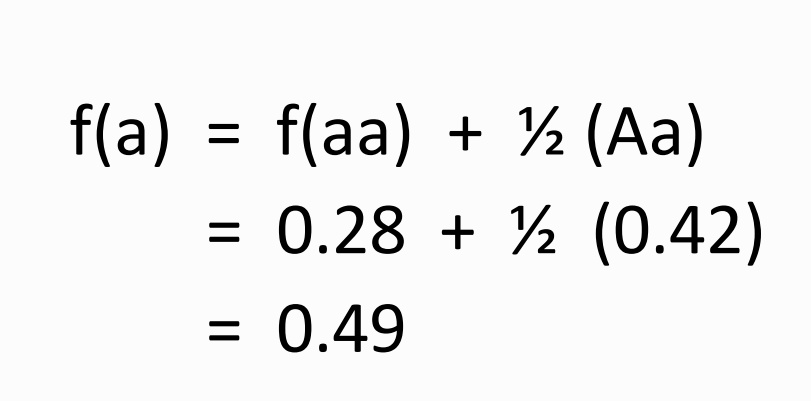



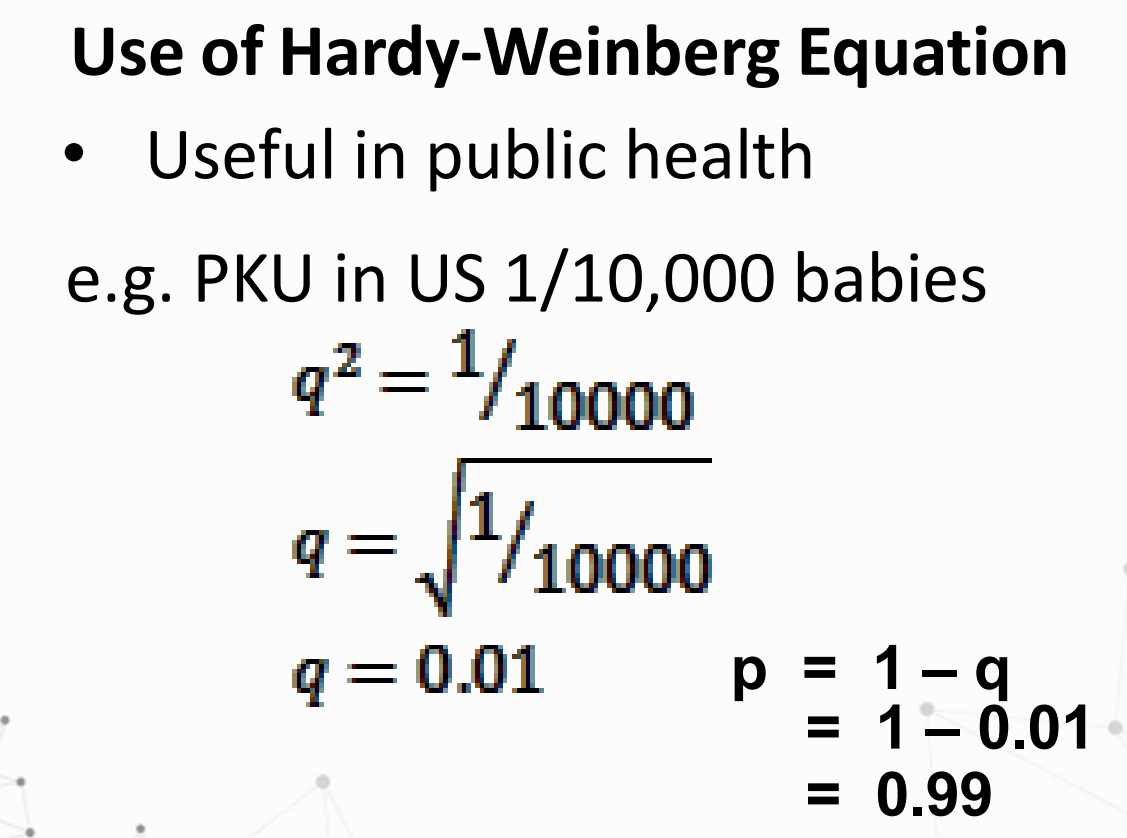

Compute for the frequency of carriers.

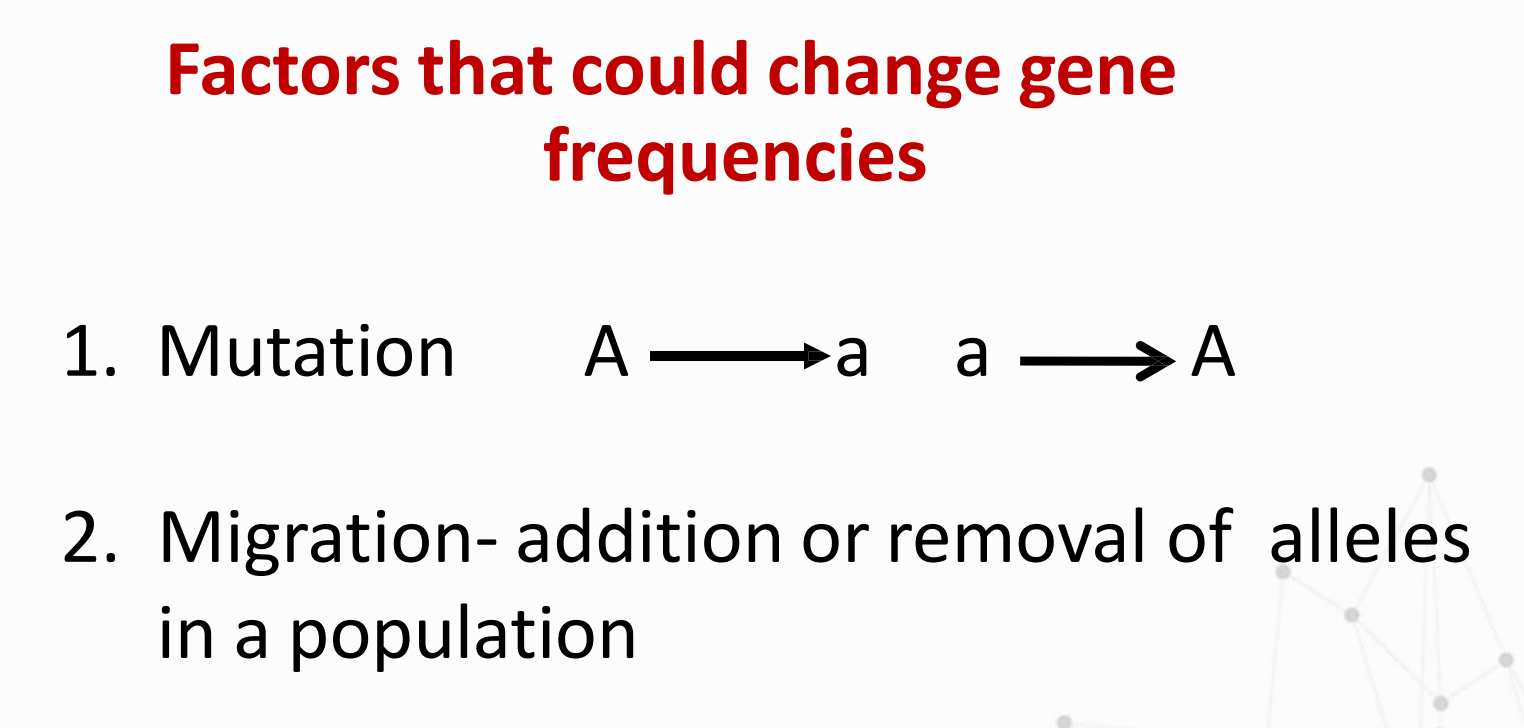

What are the Factors that could change gene frequencies?
Mutation
Factor that could change gene frequencies in which:

Migration
Factor that could change gene frequencies in which:
addition or removal of alleles in a population
Selection
Factor that could change gene frequencies in which:
considers reproductive advantage or disadvantage of a particular genotype
Random genetic drift
Factor that could change gene frequencies in which:
change in allele frequency is due to sampling error
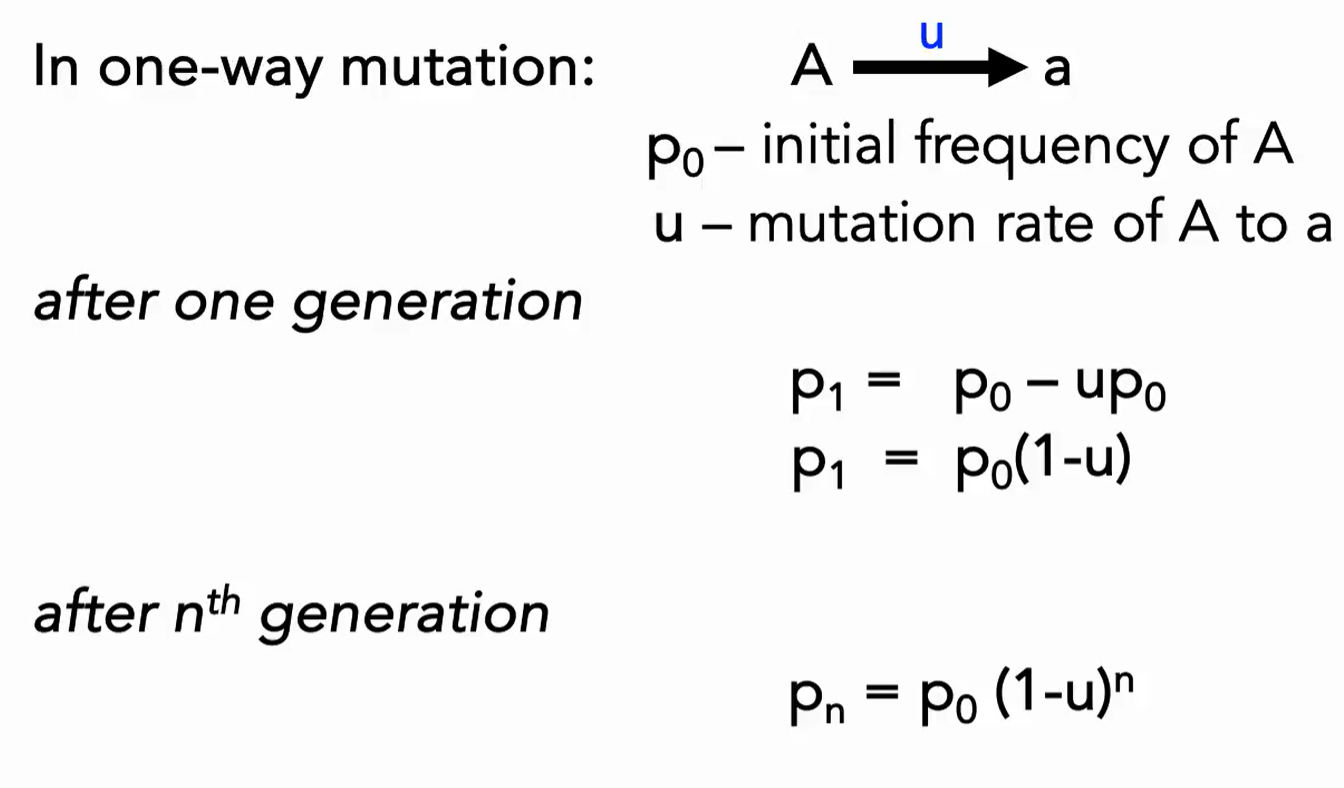
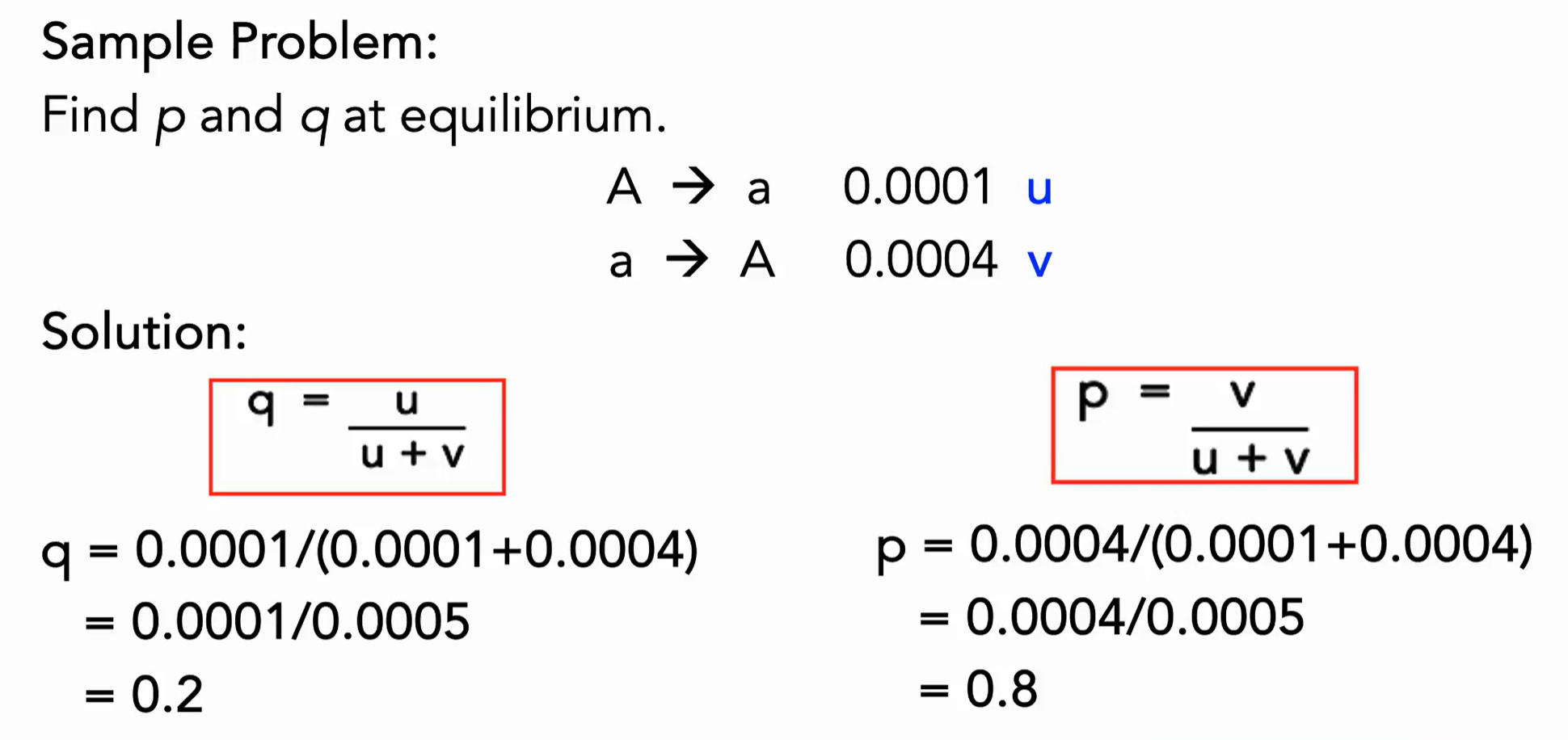
What is the formula for a one way recurrent mutation after nth generation?
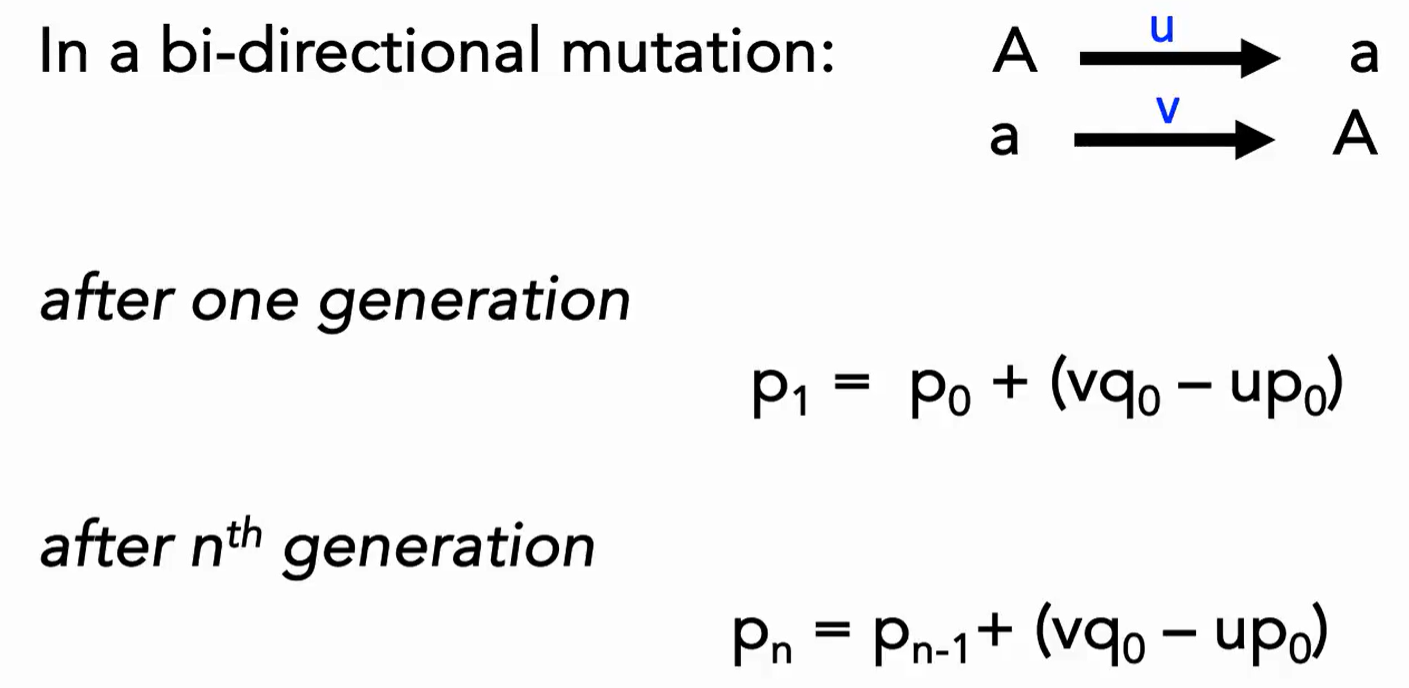
What is the formula for bi-directional mutation after nth generation?

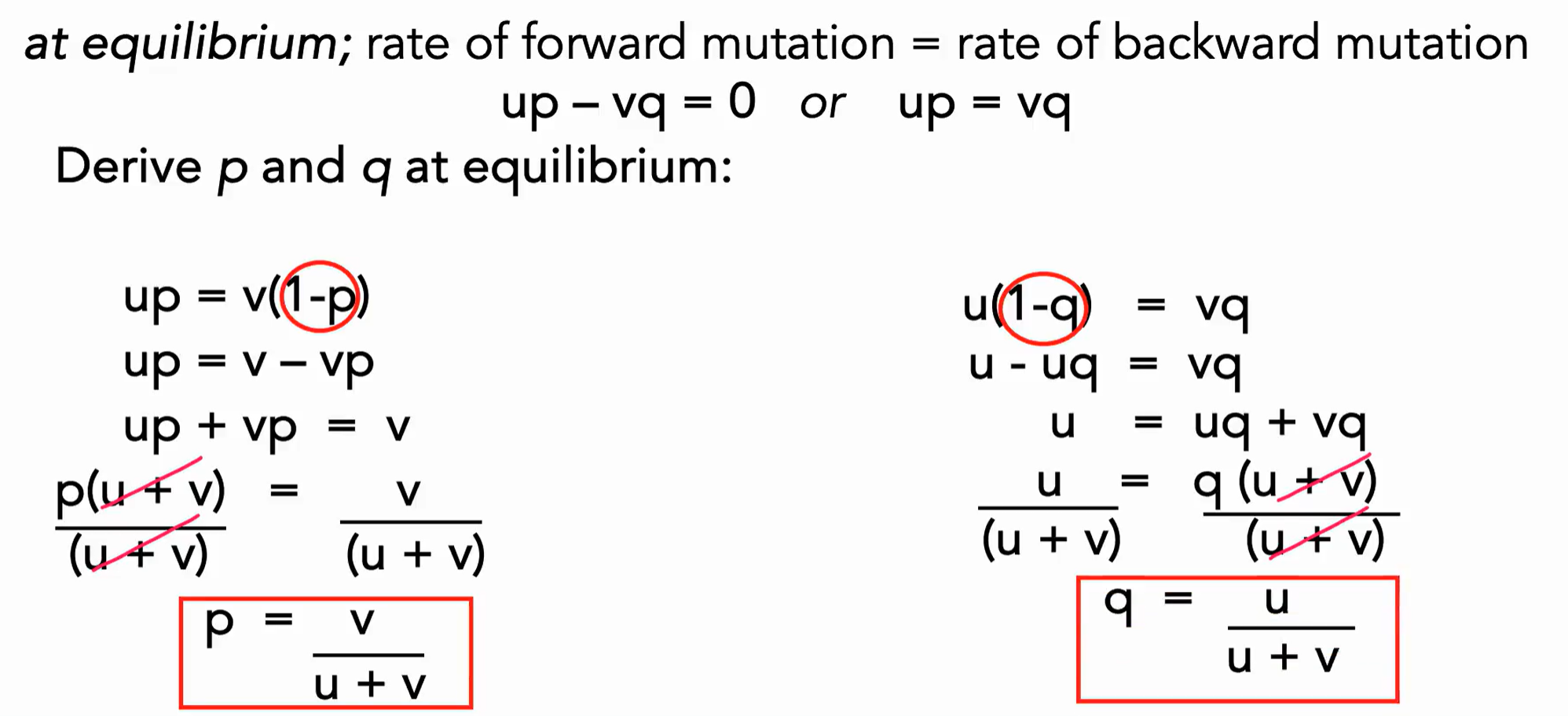
What is the formula for p and q at equilibrium after bi-directional mutation?
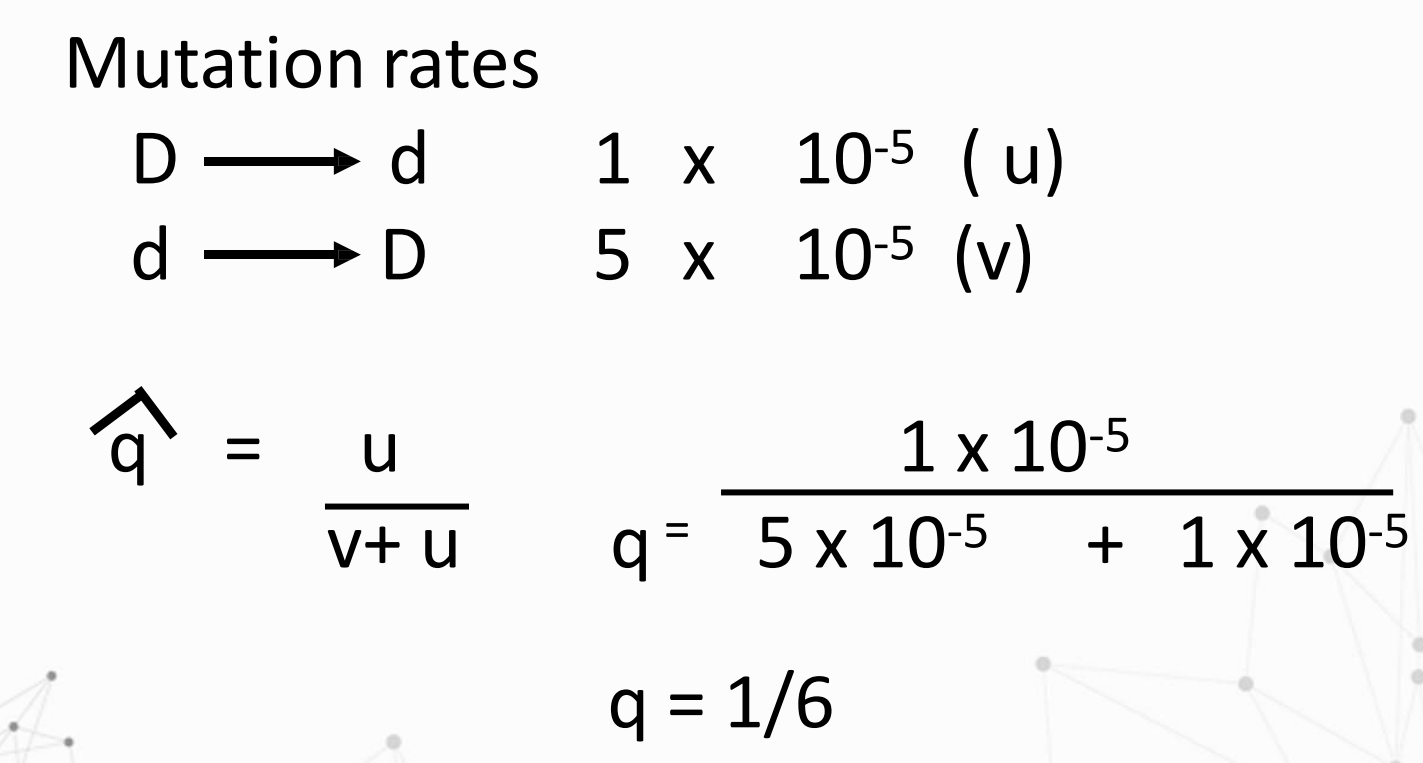
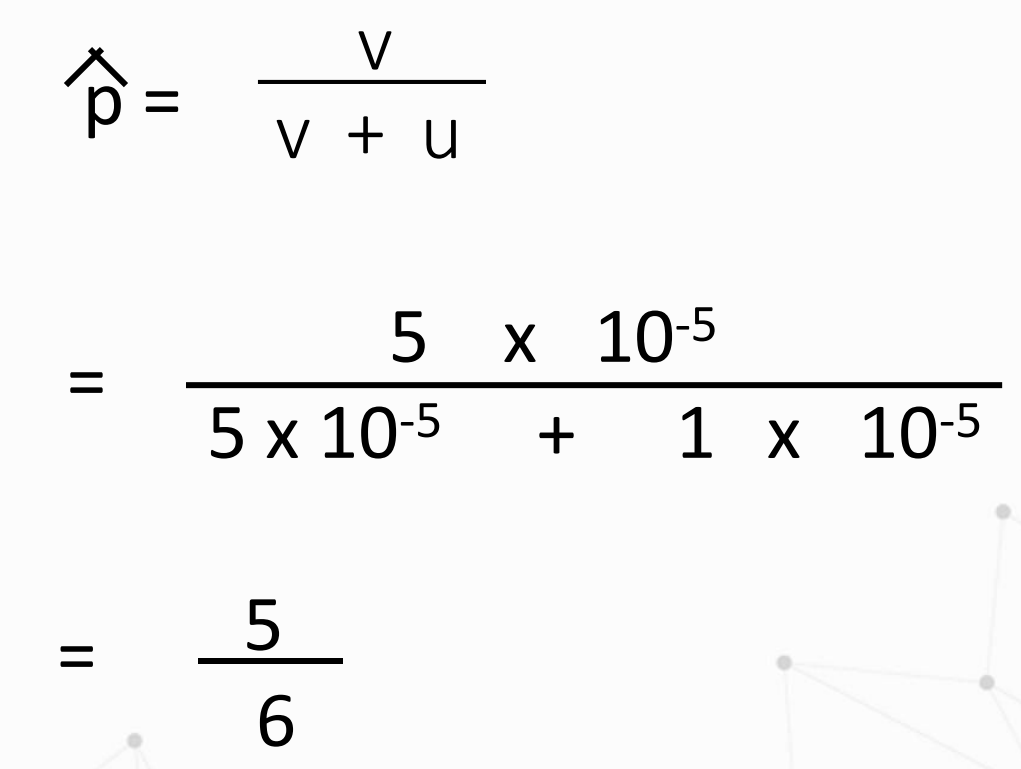
Solve for q and p.
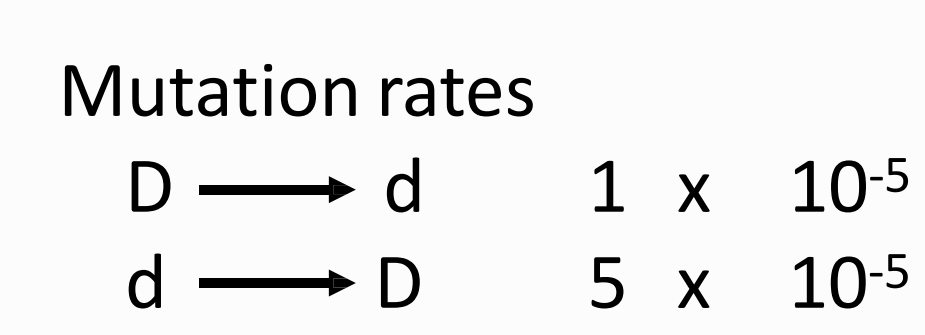

Selection
When Genotypes differ in their capacity for survival and reproduction.
Selection
- guiding force in evolution
- real test of mutation
Mutation; selection
_________ proposes while __________ disposes
relative fitness
It is the reproductive success of one phenotype as opposed to alternative phenotype
Selection pressure
It is the force acting upon a phenotype to reduce its fitness or adaptive value
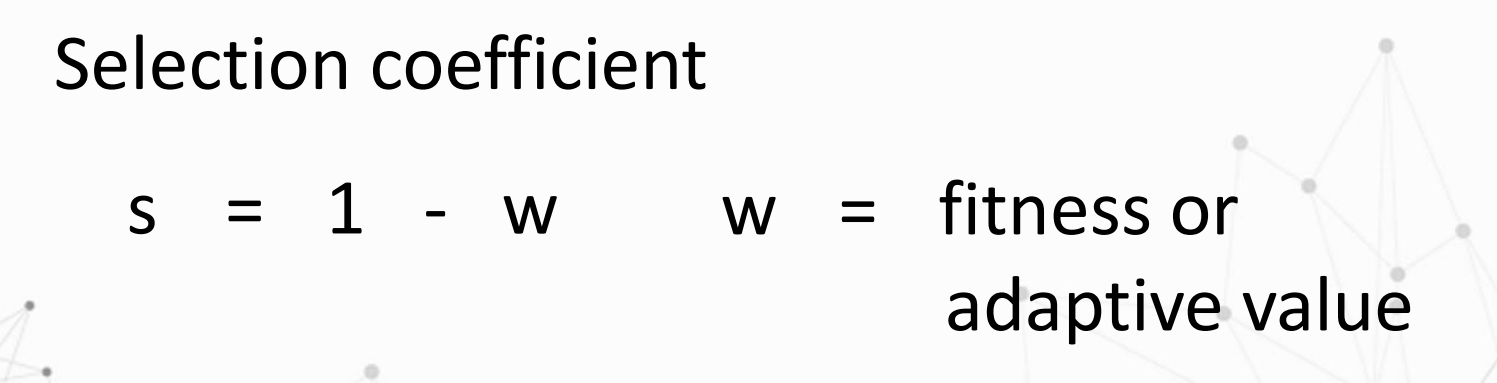
Selection coefficient formula
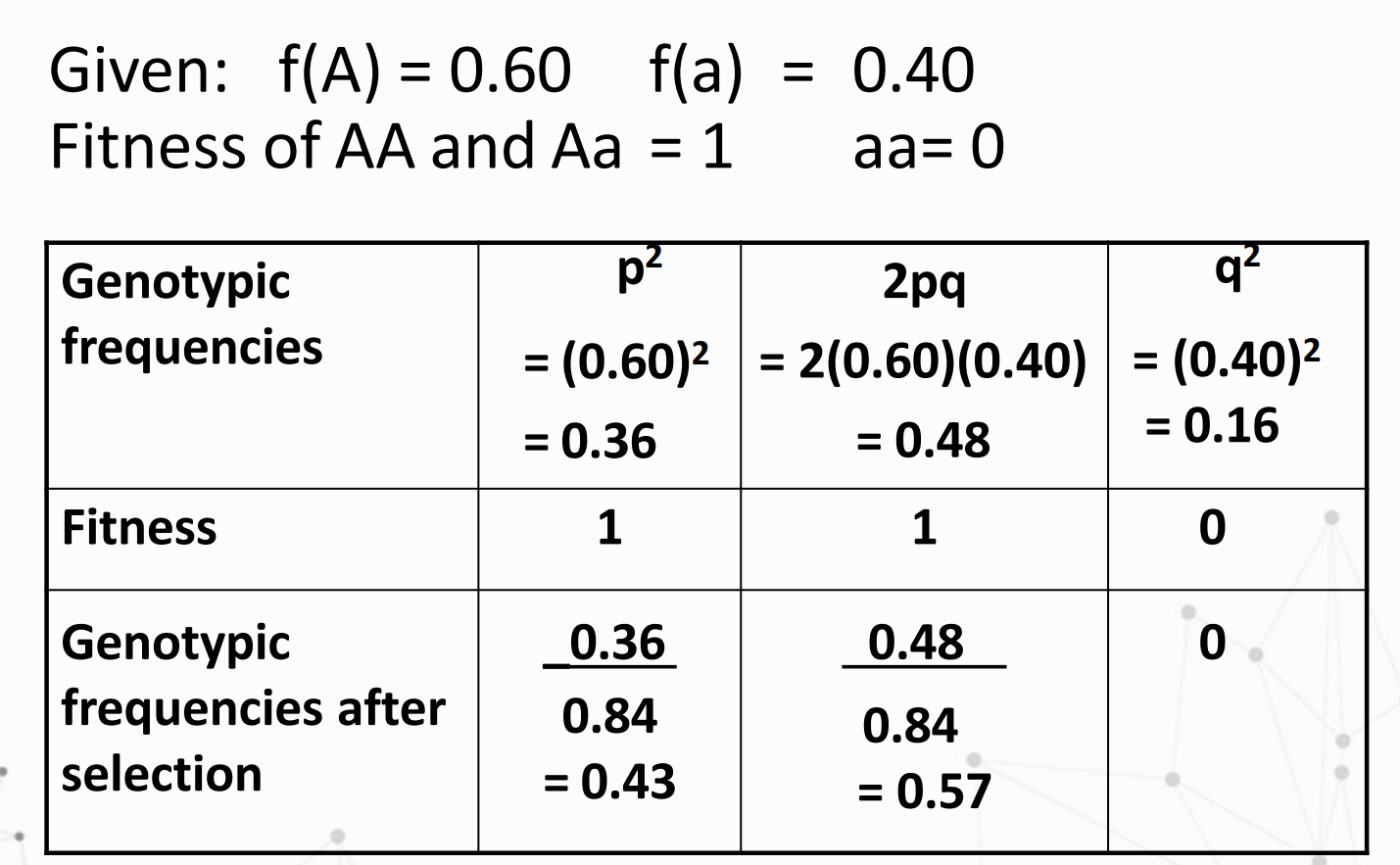


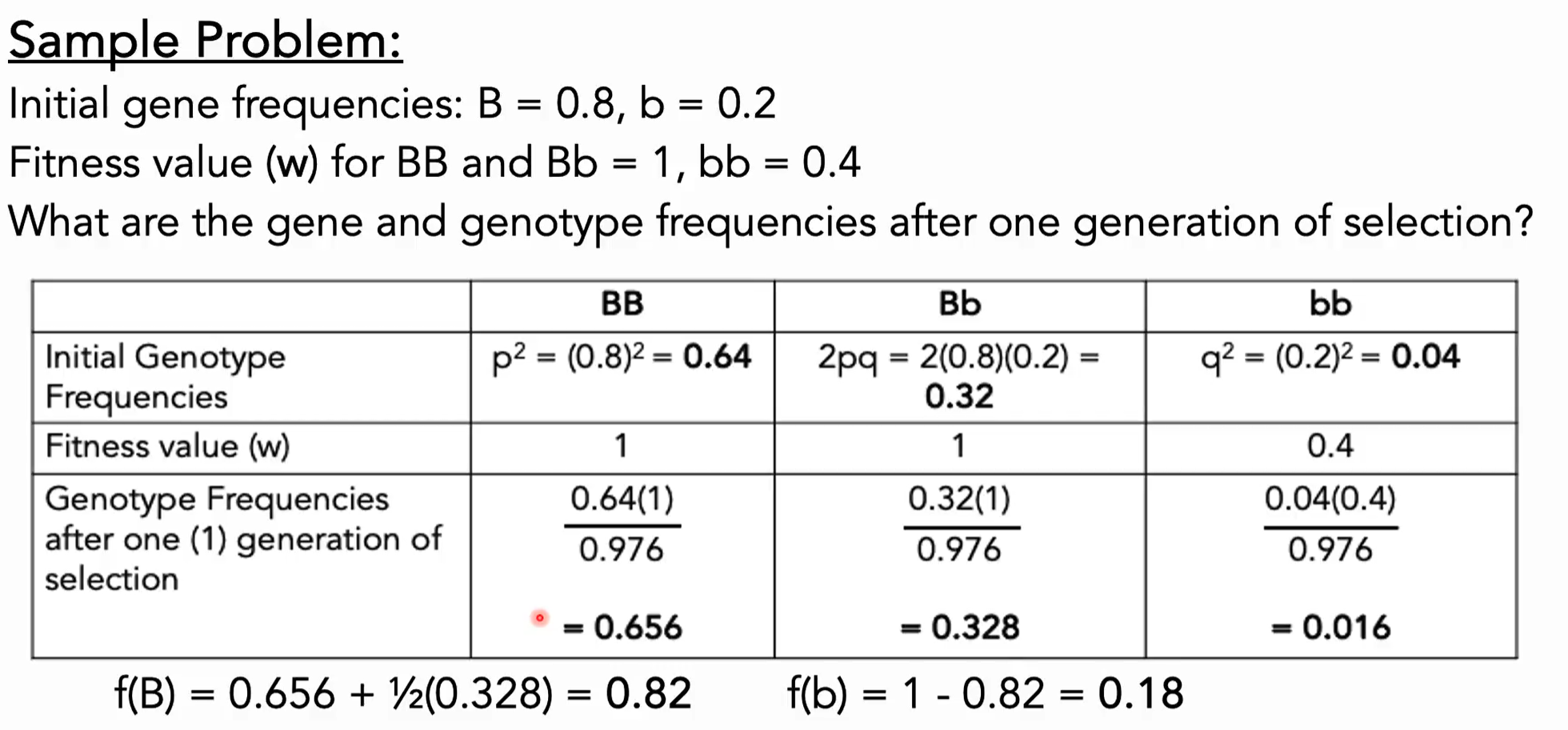
Given:
Solve for the Gene frequencies after selection



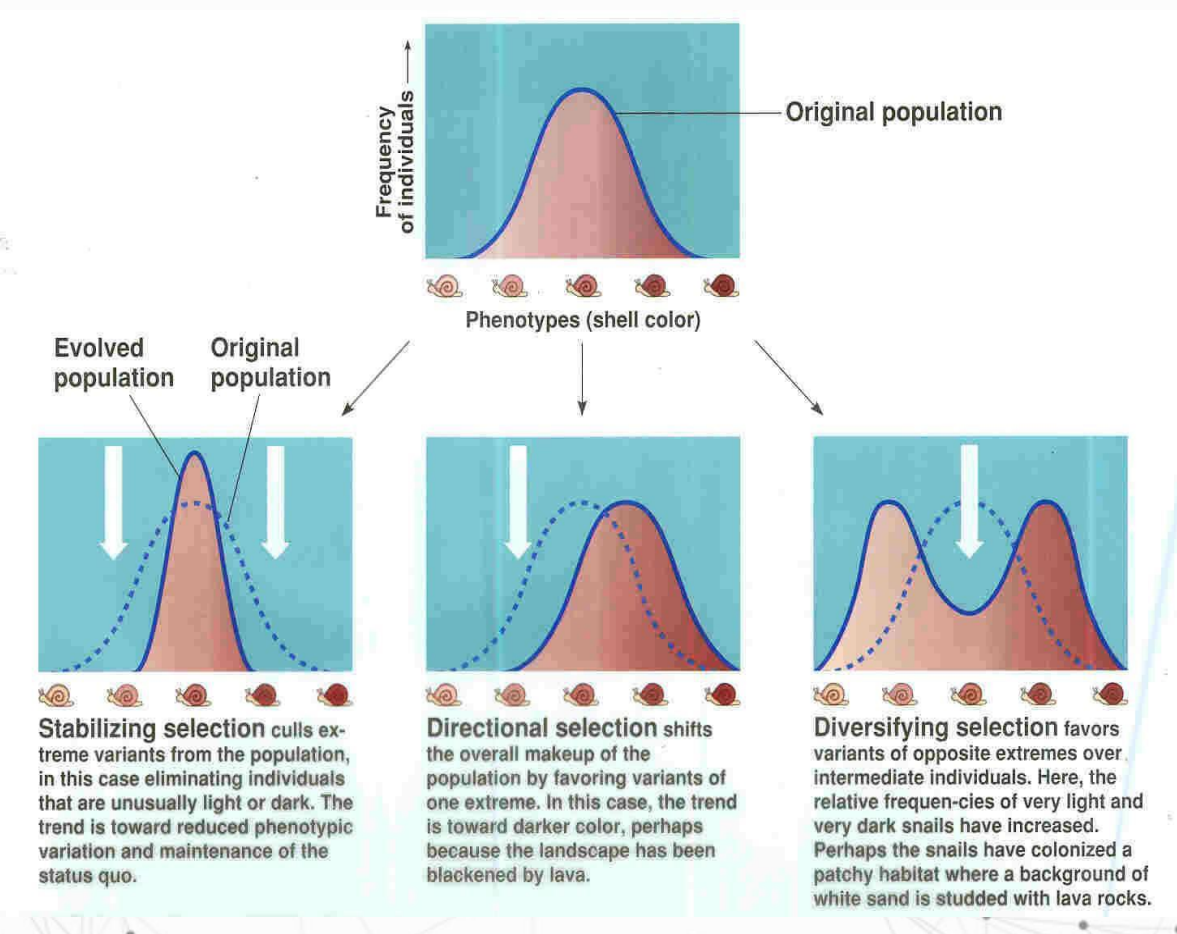
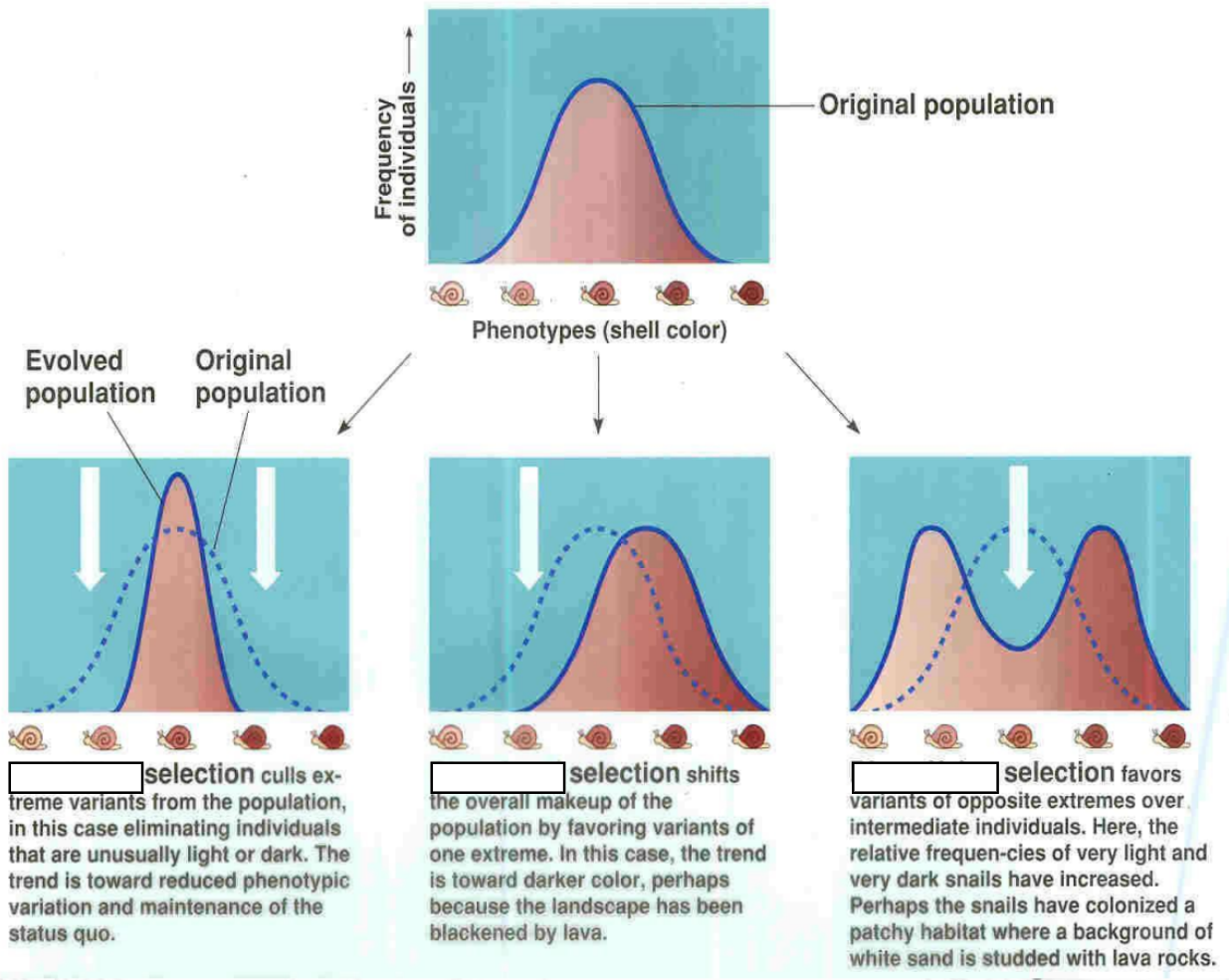
What are the Modes of Selection?
Stabilizing
Modes of Selection
phenotypic extremes are eliminated
Stabilizing
Modes of Selection
The phenotypes close to the mean are preserved by the populations that are environmentally well adapted.
Directional
Modes of Selection
one extreme is favored
Disruptive or diversifying
Modes of Selection
both extremes are selected for
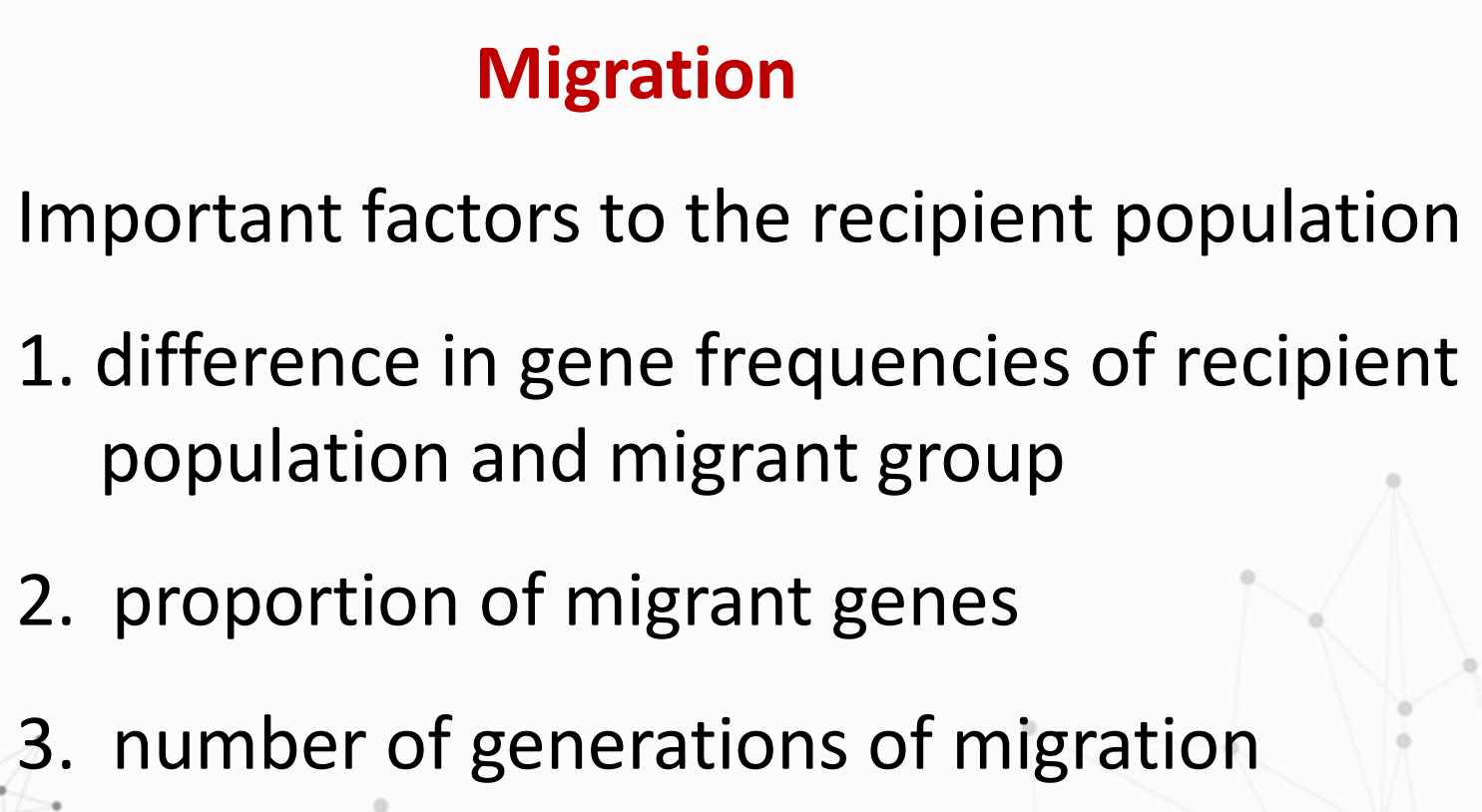
Migration
What are the Important factors to the recipient population?

m = proportion of the migrants to the mixed population, so
(migrants)/(migrants + recipient)
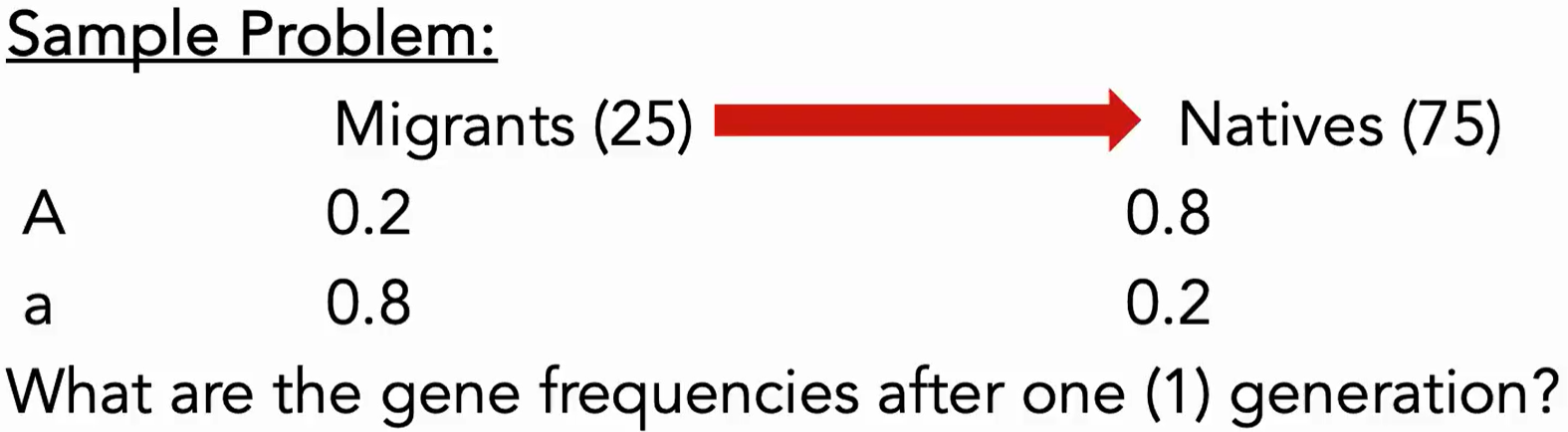
What is the migration formula?


Find q1 and p1.
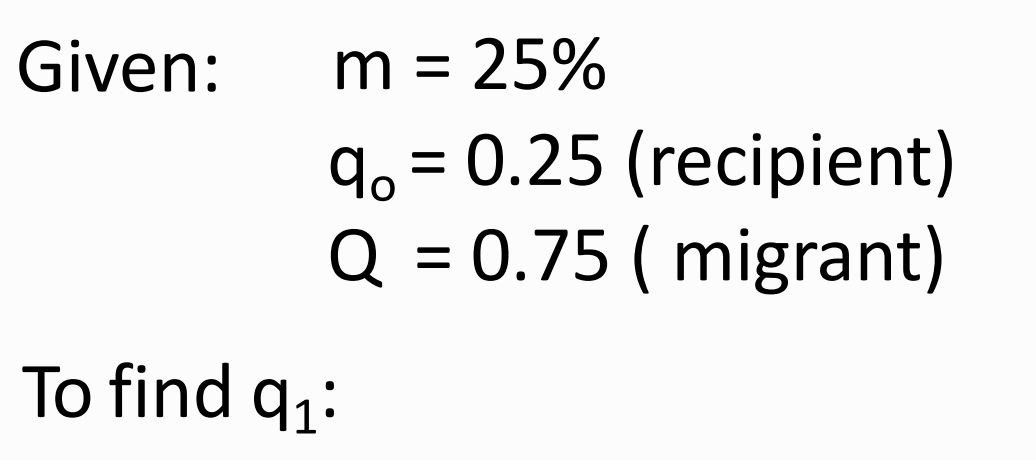
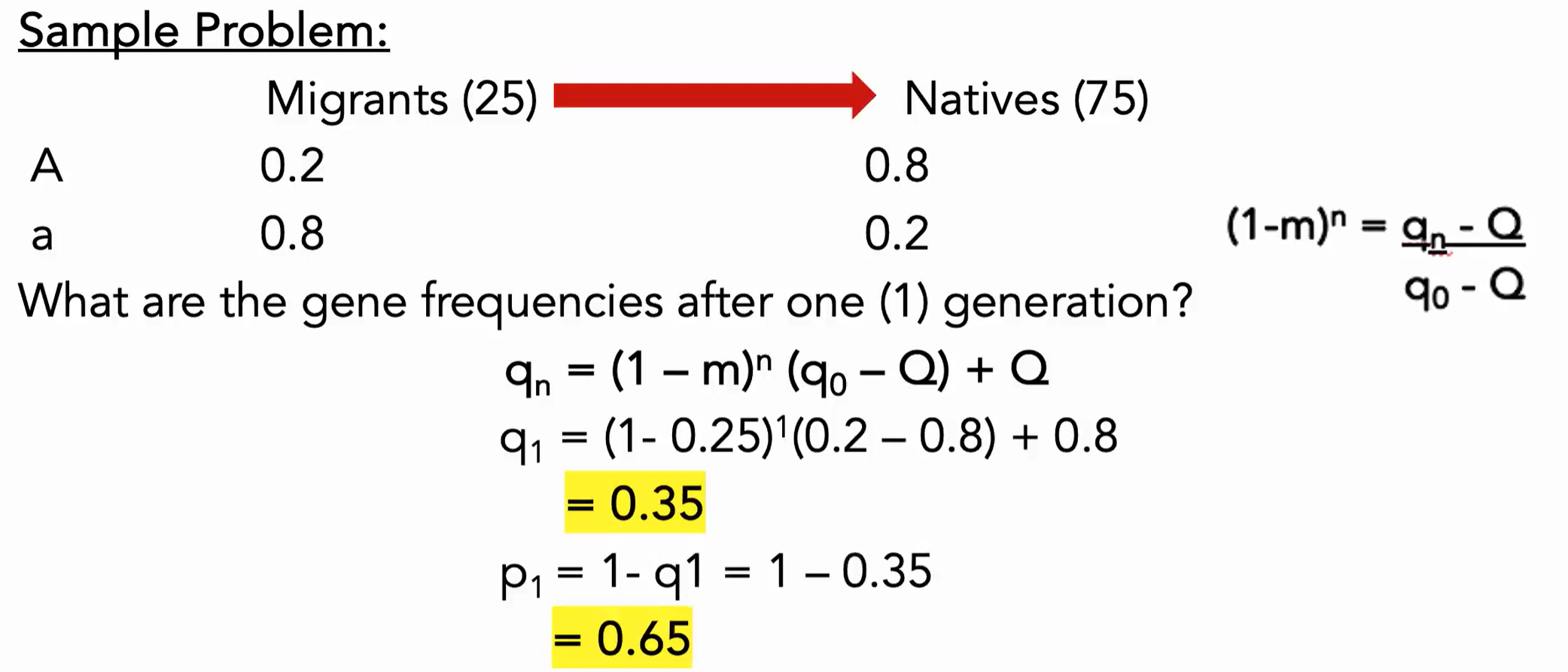
m = (25)/(25+75)
Random genetic drift
It is the random change in allelic frequency due to sampling error
Random genetic drift
Its change is in random direction and is dependent on population size
Random genetic drift
- causes homozygosity
- loss of genetic diversity
significant
negligible
- for small population, Random genetic drift is ___________
- for large population, Random genetic drift is ___________
If a small number of individuals migrate into a new location, they become founder of a new population.
- founder effect
- proposed by Mayr (1952)
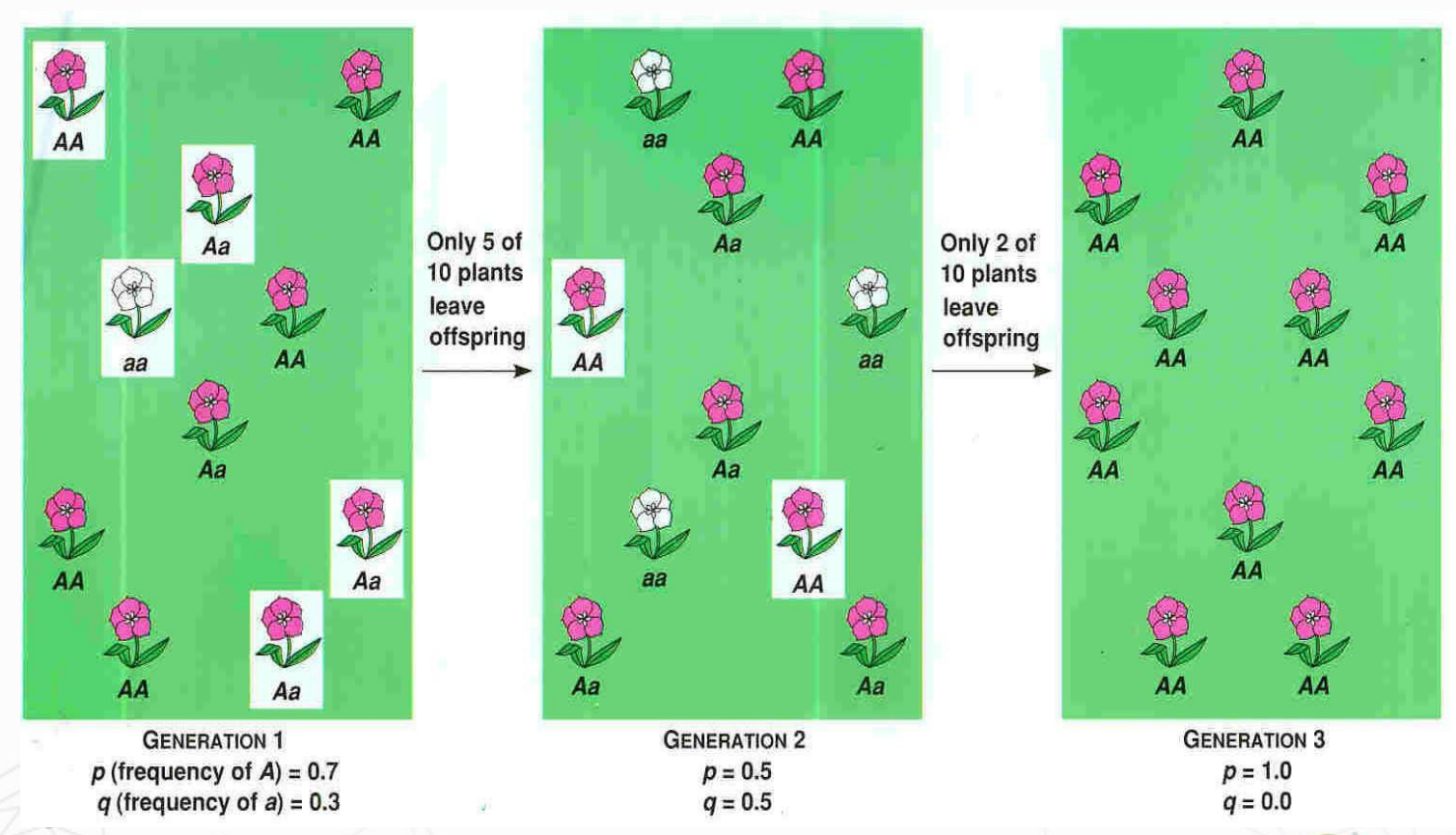
If a small number of individuals migrate into a new location, they become __________ of a new population.
- _____________
- proposed by _______ (1952)
FOUNDER EFFECT


FOUNDER EFFECT


Inbreeding
mating between individuals with common ancestry
Consequences of inbreeding
1. genetic uniformity
2. reduced vigor
3. reduced viability
4. reduced fertility
What are the Consequences of inbreeding?
1. genetic _________
2. reduced _________
3. reduced _________
4. reduced _________
inbreeding depression
It is the appearance of deleterious phenotypes
inbreeding coefficient (F)
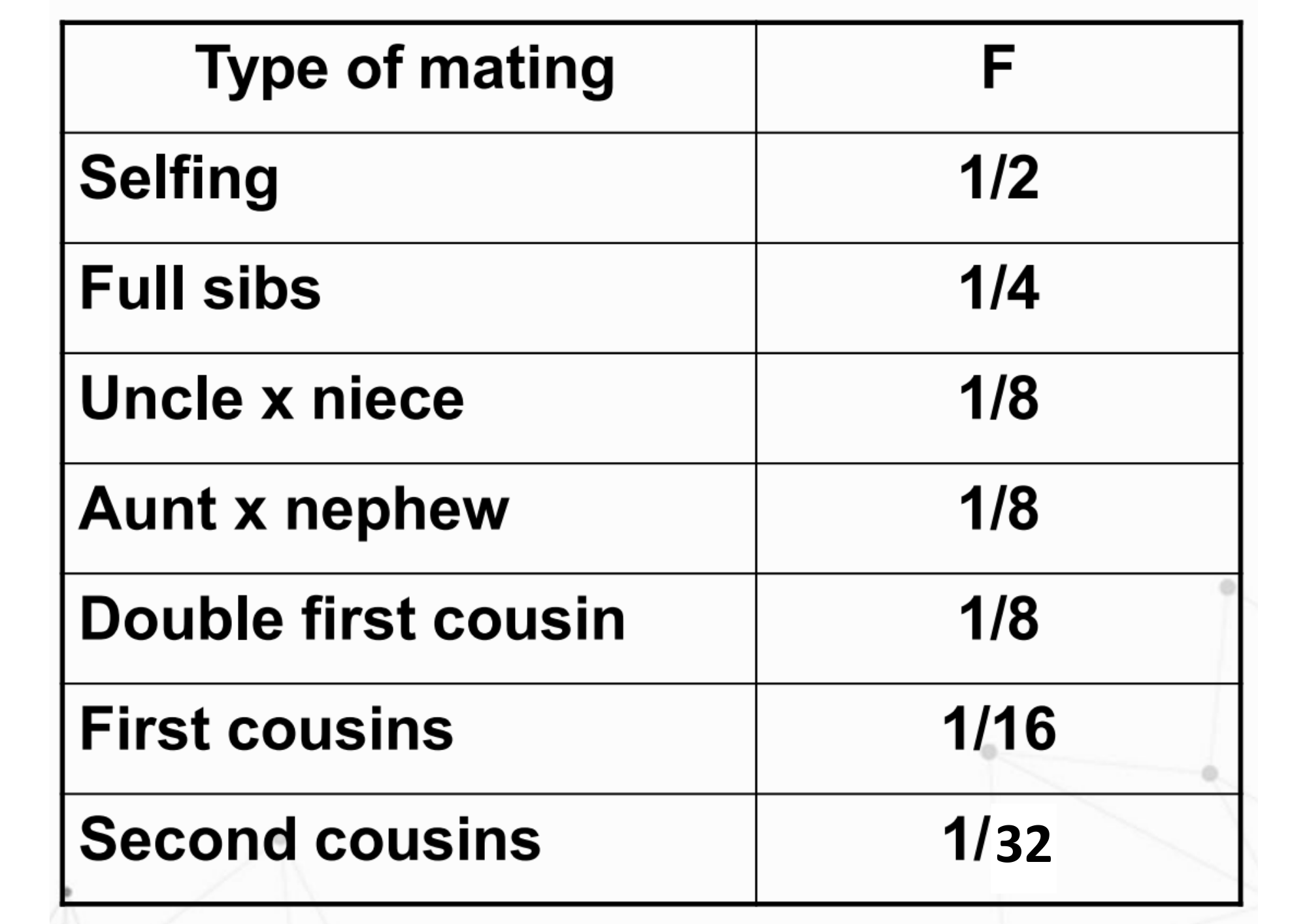
It is the probability that any two alleles at a locus are alike by descent

Divergence within a population occurs due to the ff:
Race
These are genetically distinct populations of the same species that differ in the relative frequency of some genes

Race is a consequence of:
False

Race is an irreversible process.
T or F

It is a group of interbreeding natural population that is reproductively isolated and share a common gene pool

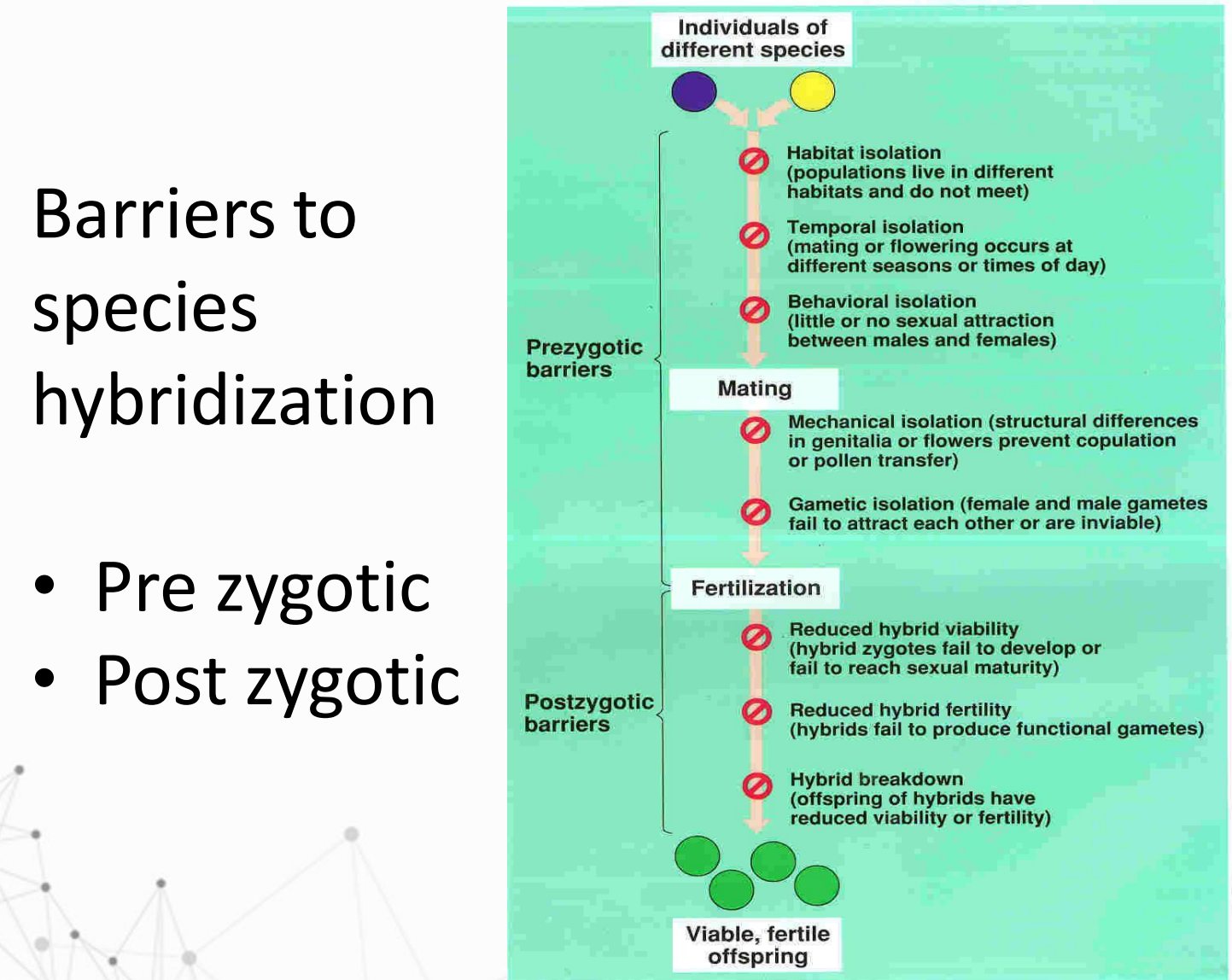
Speciation can occur if there is:
Allopatric speciation
These are species that inhabit separate geographic reg
Sympatric speciation
These are species that inhabit at least in part the same ge