Geography #14-15 : Fieldwork
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is fieldwork?
When you go out and collect data yourself to find out the answer to a geographical question.
What is the order of a field world investigation?
Make aim and hypothesis.
Plan methods & field trip.
Complete field work
Present Results
Write analysis & conclusion of results
What is an aim?
The purpose of your whole piece of field work.
What is the aim of a rivers piece of field work?
To investigate how a rivers width, depth, and velocity changes as it moves downstream from the source.
What is a hypothesis?
A statement that is made at the start of a piece of field work that you intend to test.
What is the hypothesis of a rivers piece of field work?
The width, depth, and velocity of a river will increase as you move down stream from the source.
Why do you have to choose a method of data?
To help decide whether your hypothesis is correct/ can be accepted.
If you were to investigate whether a rivers width, depth, and velocity changes as it moves downstream from the source, you would need to..
Measure the rivers width, depth, and velocity.
What are the 3 types of sampling methods?
Systematic, Random, and Stratified Sampling
What is systematic sampling?
Using a regular interval or pattern.
What is random sampling?
Selecting sample points or people by using random numbers to avoid bias.
What is an example of systematic sampling?
Like asking a questionnaire to every 7th person or sampling ever 10 metres along a line.
What is an example of random sampling?
Getting all the people in an area on a list from 1-99 and then use the random number table to select which people you would give a questionnaire to.
What is stratified sampling?
A method where the population or area being studied is divided into groups (strata) based on a certain characteristic, and then samples are taken proportionally from each group.
Its something advisable to ensure different groups or types of people are represented in your sample at the same proportions as they exist in real life.
What is an example of stratified sampling?
If 30% of a town is young, 40% are working age, and 30% eldery you would sample 3 young people, 4 working age, and 3 Eldery people.
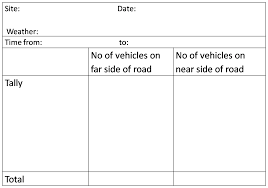
To record your data, a recording sheet is used. What must a recording sheet have?
A title, headings for date & day, time, and location, ensuring spaces next to each, tally's as they are the best option for counts, enough space for each site/sample you’ll visit and other factors such as weather if revelant.

When designing a questionnaire, your questions should be…
Essential to the Investigation, Quick & Easy to Answer, Polite Intro & Thank You, Short, Simple & Numbered, and Mainly closed with the set responses with tick boxes.
Why is a pilot questionnaire essential?
To irony out any mistakes. You send to people to find you whether it is easy to answer, worded confusingly, or had any mistakes.
What is something you DON’T ask people on a questionnaire?
Their sex or age, as it can embarassing for some.
What are two advantages of primary research?
The method of the collection is known & It is up-to-date.
What are two disadvantages of primary research?
It’s time-consuming to collect & Specialist equipment/resources may be required.
What are two advantages of secondary research?
It can be easy and quick to access & low-cost or free
What are two disadvantages of secondary research?
Data may be biased & out of date.
What is primary data?
When you go out in the field and collect data yourself.
What is secondary data?
Data that has already been collected or complied by somebody else.
What are some examples of primary data collection methods?
Field Sketches, Traffic Count, People Count, Questionnaire data, River data, Video/audio recordings, Photographs, Interview information.
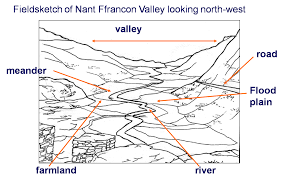
How do you draw a field sketch?
Draw the horizon and foreground first, then add in important features.
Label the features.
Add a title of the location.
What is the purpose of traffic count?
To show how busy a certain road is.
How is traffic count done?
You count the number of vehicles passing you for a set amount of time.
One road could be done at different times in the same day to see when peak traffic occurs, or several traffic counts can be done in different roads to compare how busy they are and should be done at the same time of day.
What is the purpose of the people count?
To show how busy/popular an area is.
How is a people count done?
By counting the number of people passing you at a set point in an area.
In one area in the same day, at different times to see when peak visitors occur.
Several people counts in different areas at the same time to compare how busy they are.
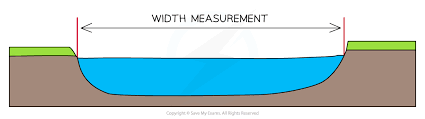
How to take an accurate measurement of a river width?
Take a tape measure and two poles (sticks)
Place one pole on each bank.
Stretch the tape measure from bank to bank touching the poles.
It should be kept as taut as possible to be accurate and ensure reliablility.
Record the width in metres.
What is essential when measuring the depth of a river?
It should be measured at regular intervals across the width, ensuring a full picture of the changes in the whole channel depth is recorded and allowing a mean depth to be calculated.
How do you measure a river depth?
Leave the width tape measure in place.
Put a meter rule in the water, ever 1 meter, until it just touches the bed of the river.
Measure depth from the bed to the measuring tape, getting the full depth of the bank.
Repeat this every metre across the river width.
What is river velocity?
The speed at which the river flows along it in a given time frame.
Where should velocity be recorded in a river?
Velocity should be recorded at three positions: towards the left bank, centre, and towards the right bank.
What are the 2 methods of measuring the velocity of a river?
Digitally with a flow meter and Manually using a float, tape measurer and a stop watch.
How do you measure river velocity using a flow meter?
You use a small propeller which you place just under the surface of the water, which then a small digital reads out giving the velocity of the river.
How do you measure the velocity of a river manually?
Measure out 10 metres down the river’s course using the tape measurer.
One person stands at the upstream part of the tape measure with a float.
One person stands at the downstream part of the tape measure with stopwatch.
A person with a stop watch tells the upstream person to release the float and begins timing it (in seconds). They stop timing when it reaches the end of the measured section.
Write down the result.
Repeat the experiment 4 more times if possible. Once you have your timings, work out the average time the float took to travel 10 metres with the velocity formula.
How many times should the float measurement be repeated?
At least 4 more times if possible. By averaging several different reading a better result can by obtained. It is also a good idea to take the timings at several locations ACROSS at the site you have chosen and take an average, as sometimes velocity is different in the middle of the channel compared to the sides.
What is the formula for river velocity?
Distance Travelled/Time Taken in metres per second.
How do you measure the size and shape of river bed load?
Systematically sample pebbles at each site by doing the following every metre across the channel:
Reach down with your index finger extended and select the first pebble it touches.
Grip the length of the longest avis on this pebble using the callipers and remove the pebble, leaving the gap still between the calliper grips.
Measure this gap with a ruler.
Next, repeat this for the width of the pebble and assess its roundness using a roundness index chart.
Continue this process for every metre, selecting more than one pebble if necessary.
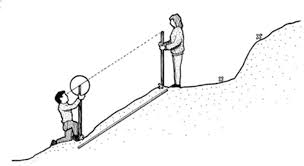
How do you measure beach gradient and complete a beach profile?
The required equipment includes a clinometer, a tape measure, and two ranging poles.
1) Person A stands at the shoreline.
2) Person B stands a measured distance from Person A up the beach.
3) Person A uses the clinometer on a ranging pole at the bottom of the slope.
4) Person B holds a second ranging pole at the top.
5) Person A lines up the clinometer with Persons B ranging pole and reads the slope angle.
6) Uphill angles are positive (+) and downhill angles are negative (-).
What is the theory when it comes to measuring the shape and size of beach material?
The material found on a beach varies in size and type as you move further away from the shoreline. The smallest material is deposited near the water and larger material is found nearer to the cliffs at the back of the beach.
How do we measure the size and shape of beach material?
Tape measure is placed from shoreline to back of beach to form a transect line.
Every 2 metres a square quadrat is placed down.
The dominant material, such as fine sand, medium sand, coarse sand, shingle, pebbles inside the quadrat is recorded.
This is repeated at all several sites to take an average.
How do we measure the movement of beach material/the speed and direction of long shore drift?
Measure out 10 metres along the coastline with a tape measure
2) Place a float into water in the breakwater zone at the start point.
3) Observe and time the object’s movement across the pre-set distance.
4) Note the direction the float moves
5) Repeat 5 times to get an average.
6) Note down the direction the float was moving, and then work out the velocity in metres per second, using the formula.
What is the formula for calculating the velocity of longshore drift?
Distance/Average Time
Why use ranging poles to measure beach gradient?
Helps in studying the shape of a beach section to compare it with other areas. The profile shows the shape from the shoreline to the back shore.
What is analysis?
Where you look at data and explain what it shows you.
When writing a conclusion, you should always do the following..
State what your hypothesis was.
State whether your hypothesis was rejected or accepted.
State why that is using evidence from your analysis.
Give an overall statement about what your investigation discovered.
Why do we pilot?
They research, test, and refine methods, instruments, and protocols before larger implementation. They identify potential issues, optimize data collection, and ensure practility.
What is the purpose of reconnaissance in research?
To visually assess the study area and gain a firsthand understanding of its features.
How does reconnaissance aid in data interpretation?
It helps researchers interpret data collected during main fieldwork by providing context about the terrain and vegetation.
What potential issues can reconnaissance identify?
It identifies obstacles or limitations such as accessibility issues or conflicts with local communities.
How can reconnaissance refine the research plan?
Information gathered can improve efficiency and data quality.
How does reconnaissance benefit relationships with local communities?
It builds relationships, facilitating better collaboration during fieldwork.
Why is it important to revisit (recoissance)?
To get a general view of the area, safety reasons, know which equipment is needed, and know if the area will satisfy your research.
What are some risks when it comes to fieldwork??
Tide times, Weather conditions, Slippery rocks, Polluted water, Working in an unfamiliar place, Misuse of equipment
How do we know if the data is accurate & reliable?
It depends on the quality of the equipment and the skills of the geographers taking the measurement. If the equipment is faulty or the geographers make a mistake, results may be inaccurate.
How do we know if the data is reliable?
It depends on the size of a sample/number of times you repeated the method to ensure your results were not a one off.
How could the investigation be improved if it was done again?
Making a sample size larger increasing reliability. Repeating a method at a different time of day or year to compare results. Improving accuracy by using digital equipment.
What are some aims of a rivers channel investigation?
To investigate the changes in velocity & the changes in the channel cross profile with increasing distance from the source.
What are three reasons that a river channel investigation may not achieve their aim?
Unpractical aim, Unsuitable sites, inaccurate data
What sampling methods would be appropriate to use in a river channel investigation?
Systematic as measuring at regular intervals ensures that no parts of the river are missed and it reduces bias.
Random as using a random number generator ensures all sites have an equal chance of being picked, thus no bias.
What equipment is used for river investigation?
25+ meter tape, 1-metre rule, Clipboard & Pencil, Camera, Float or Flow Meter, Stop Watch.
What are some risks related to river fieldwork?
Weather conditions, Slippery Rocks, Polluted Water, Working In An Unfamiliar Places, Misuse of Equipment
What are some examples of quantitative data?
Channel measurements & Sediment Measurements
What are some examples of qualitative data?
Field Sketches & Photographs
What is a quadrat?
A square frame used in geography and biology fieldwork to collect data on the distribution, frequency, or abundance of plants and small animals within a sample area.