photoelectric effect extended
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What was the new way of thinking about energy, shown by Einstein and Planck?
Energy is quantised - only certain levels of energy are allowed. Planck said the energy could only be in multiples of a basic amount: Planck’s constant
How do conduction electrons in a metal move?
They move about at random, similar to molecules in a gas
what is the average kinetic energy of a conduction electron?
The average KE of a conduction electron depends on the temperature of the metal.
What is the work function of a metal?
The minimum energy needed by a conduction electron to escape from the metal surface when the metal is at zero potential
what happens to the kinetic energy of a conduction electron when it absorbs a photon?
It’s KE increases by an amount equal to the energy of the photon.
What happens if the energy of the photon exceeds the work function of the metal?
The electron can leave the metal
What happens if the electron does not leave the metal?
The energy of the photon has not exceeded the work function, so the KE of the conduction electron increases by an equal amount to the energy of the photon (as normal), however it collides repeatedly with other electrons and positive ions, and it quickly loses its extra KE.
Diagram of a vacuum photocell
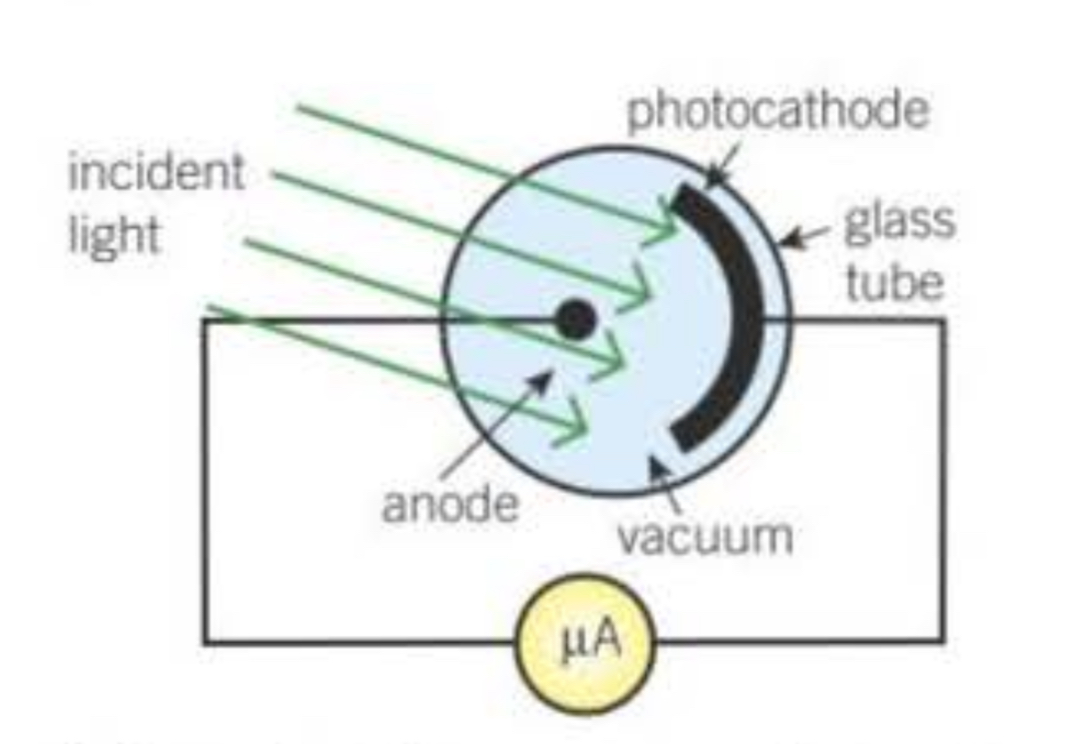
In a vacuum photocell, what happens when light of a frequency greater than the threshold frequency for the metal is directed at the photocathode?
Electrons are emitted from the cathode and are attracted to the anode. The microammeter in the circuit can be used to measure the photoelectric current.
What is the photoelectric current in a vacuum photocell proportional to?
The number of electrons per second that transfer from the cathode to the anode
How can you calculate the number of photoelectrons per second that transfer from the cathode to anode in a vacuum photocell?
I/e
Where I is the photoelectric current, and e is the charge of the electron.
Explain why photoelectric current is also proportional to the intensity of the light incident to the cathode
The light intensity is a measure of the energy per second carried by the incident light, which is proportional to the number of photons per second incident on the cathode. Because each photoelectron must have absorbed one photon to escape from the metal surface, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second (the photoelectric current) is therefore proportional to the intensity of the incident light
What is light intensity a measure of?
The energy per second carried by the incident light
What does the intensity of the incident light not affect and why?
It does not affect the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron because no matter how intense the incident light is, the energy gained by a photoelectron is due to the absorption of a single photon only.
What is the equation of the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
Eₖ = hf - work function
What is a vacuum photocell used for?
It can measure the maximum KE of photoelectrons emitted for a given frequency of light
Using a vacuum photocell, if the measurements for different frequencies are plotted as a graph of maximum kinetic energies against frequency, what is the shape of the graph?
Linear
Using a vacuum photocell, if the measurements for different frequencies are plotted as a graph of maximum kinetic energies against frequency, what is the x-intercept?
The threshold frequency
Using a vacuum photocell, if the measurements for different frequencies are plotted as a graph of maximum kinetic energies against frequency, what is the y-intercept?
The work function * -1
Using a vacuum photocell, if the measurements for different frequencies are plotted as a graph of maximum kinetic energies against frequency, what is the gradient of the graph?
Planck’s constant
Diagram of the graph
