Cinematography quiz 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
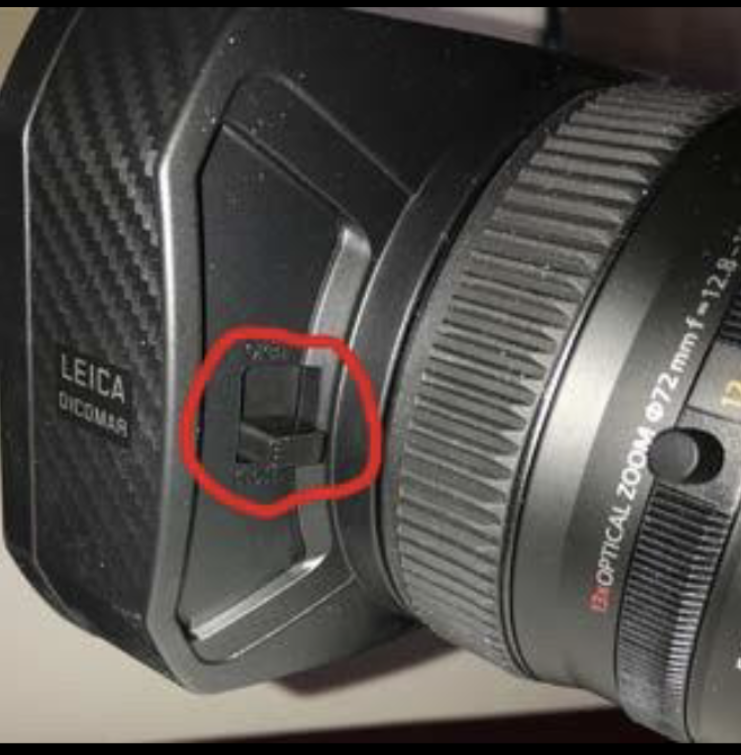
Lens cap switch

Battery Compartment Release switch
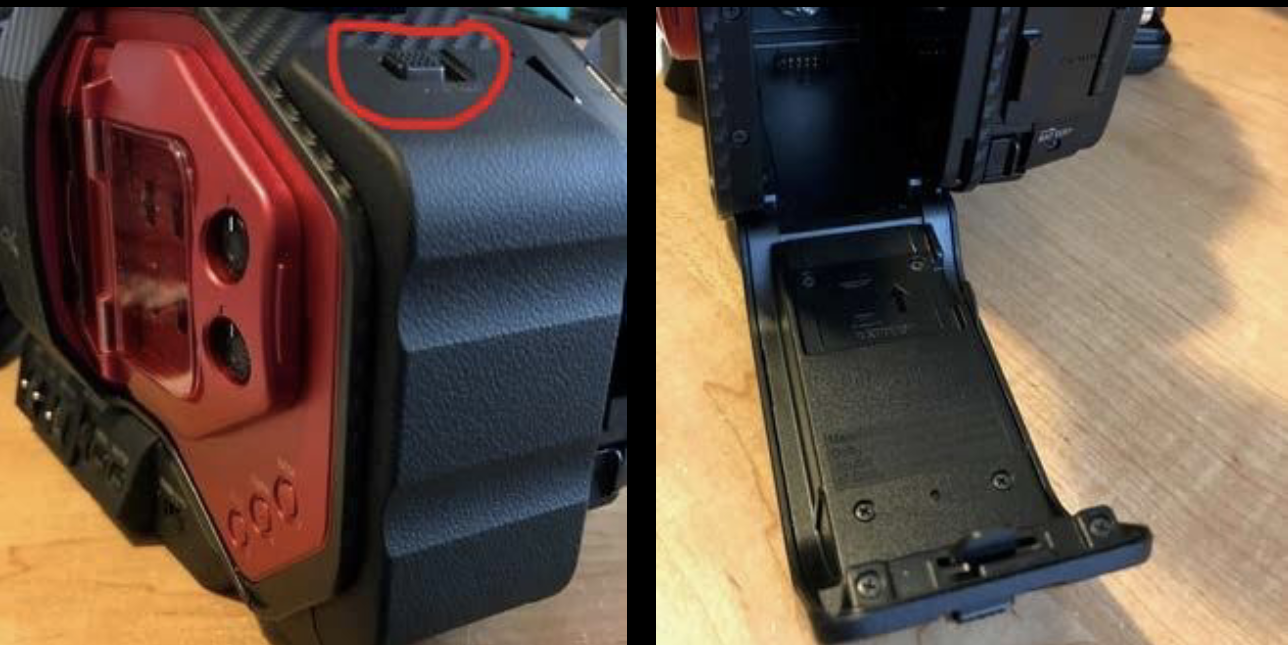

battery release switch
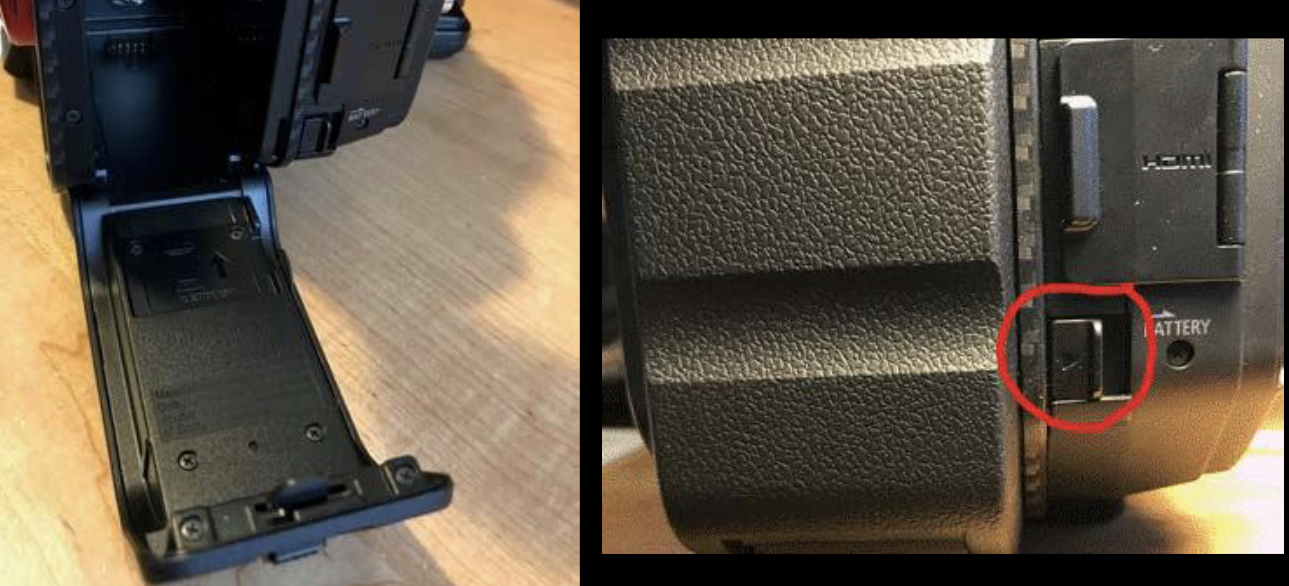

LCD Screen

Power Switch
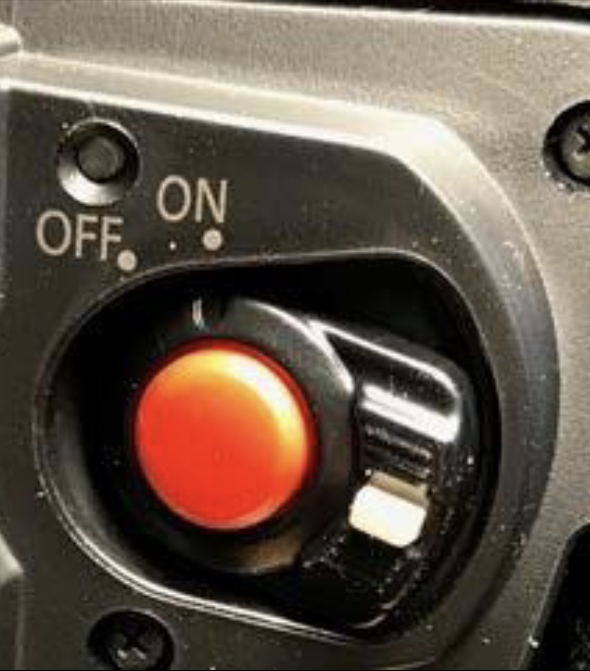

Media Card Slot

Focus
closest to to lens, thickest ring (Yellow ring)
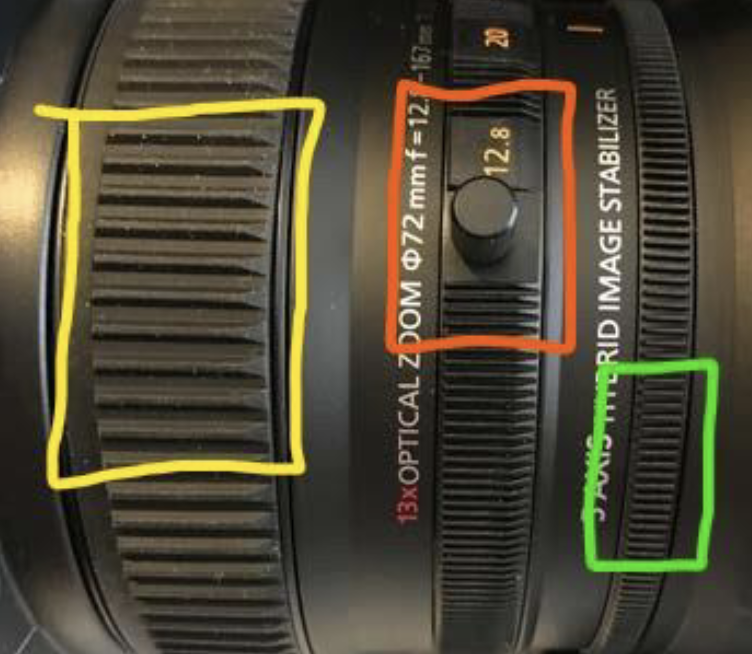

Zoom
middle, medium ring (Red ring)
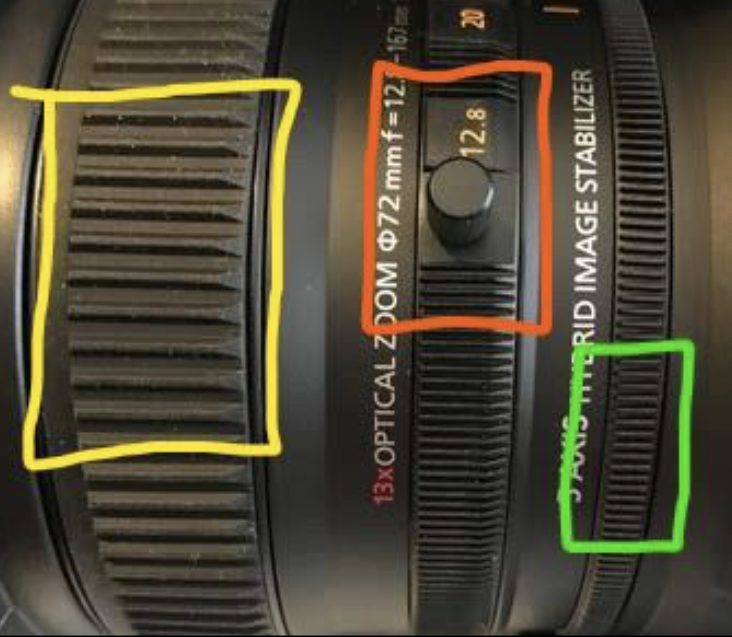
Iris Ring
furthest from lens, smallest ring (Green ring)
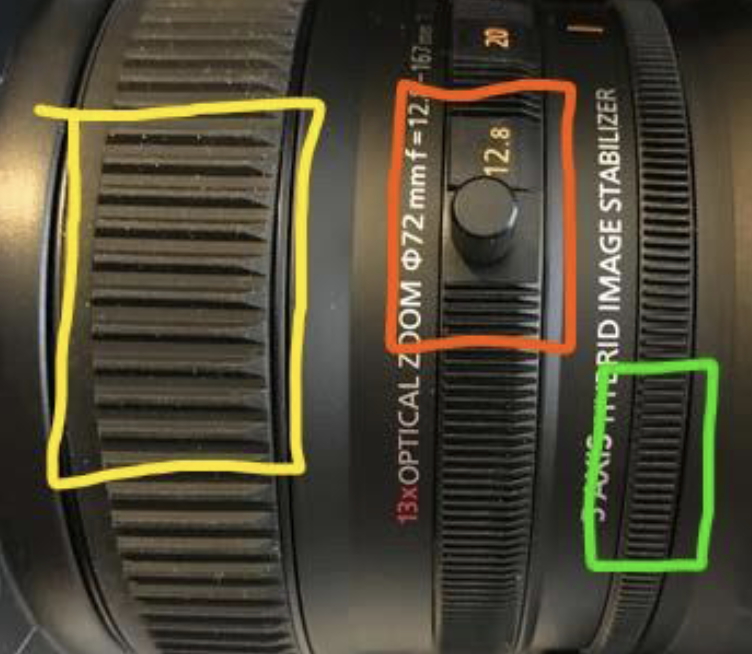

White Balance

Audio controls
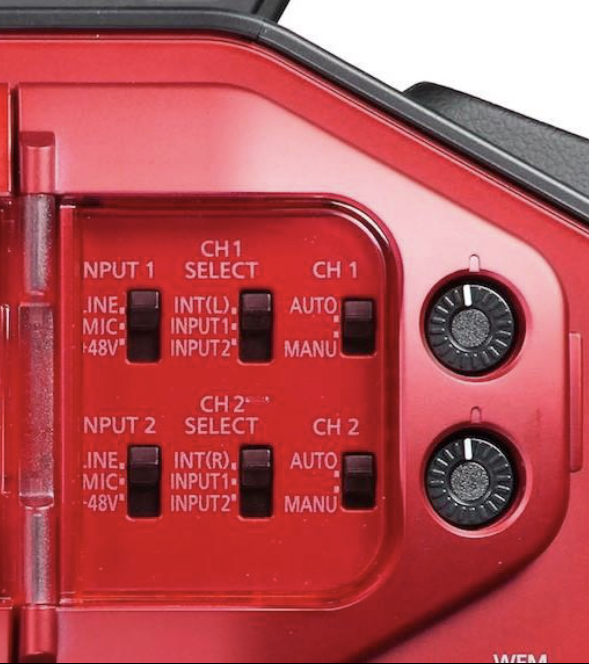

Playback button

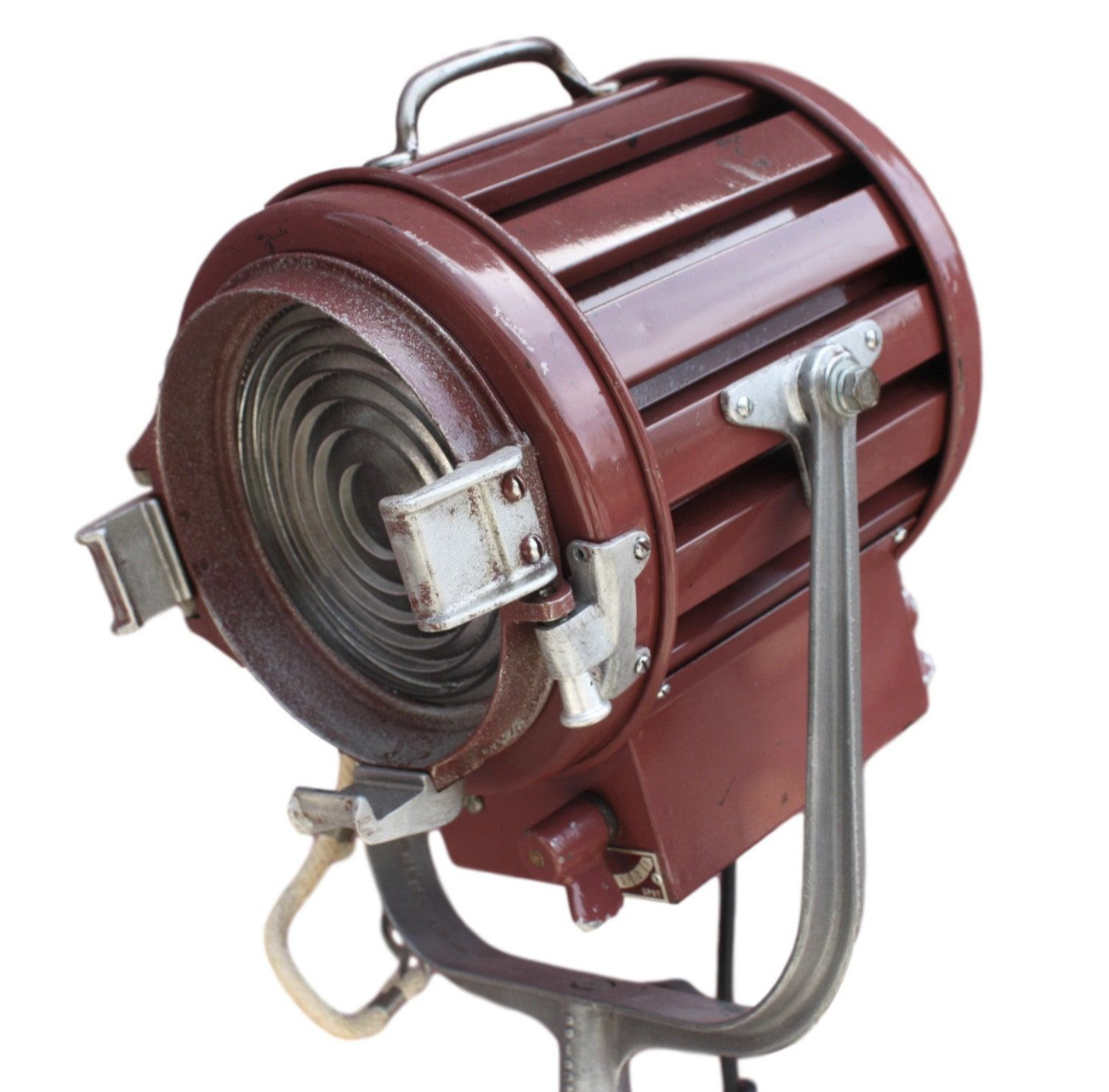
Fresnel light
Has a lens called a fresnel lens, the lens softens and directs light

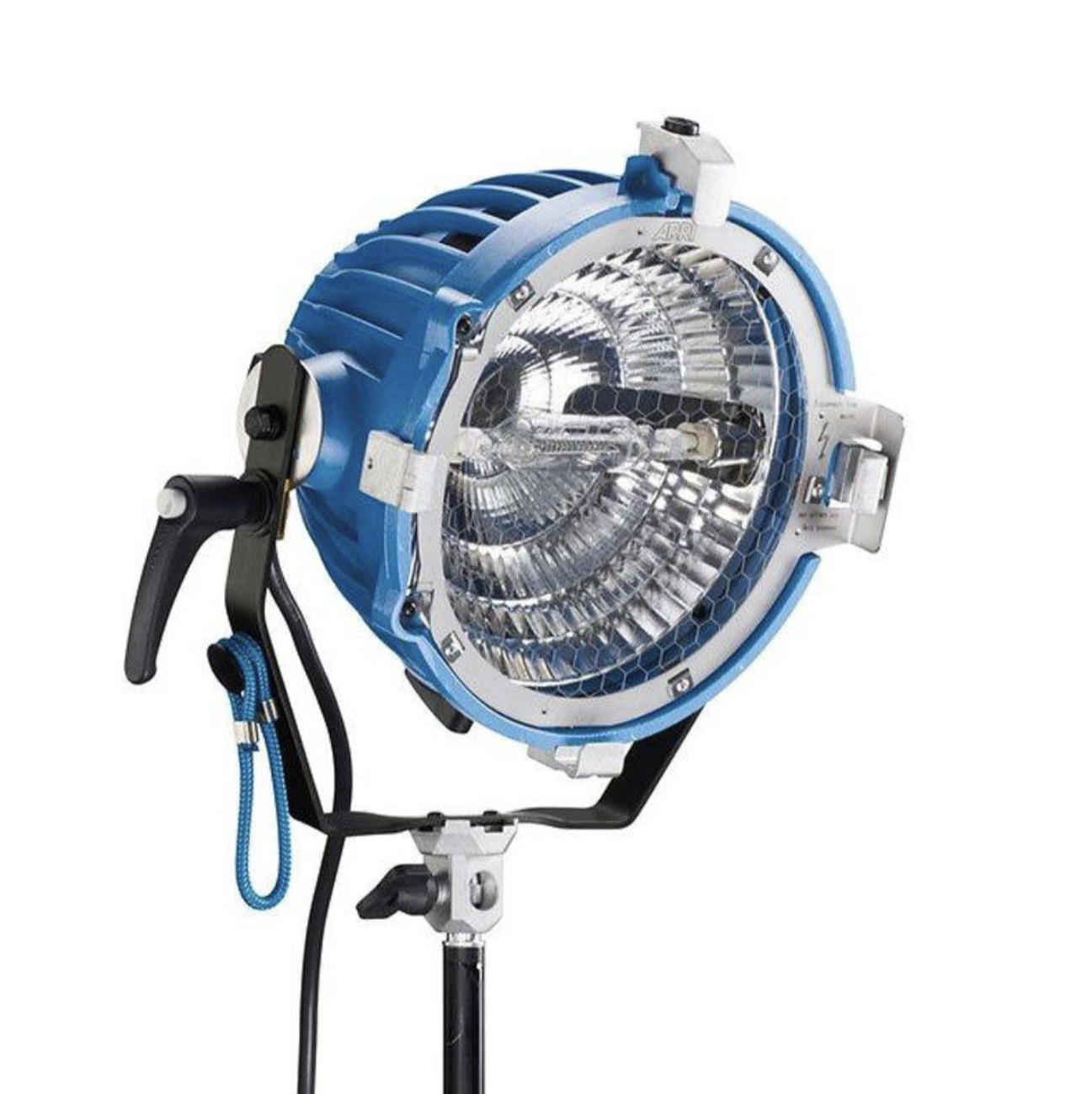
Open Face light
does not have a fresnel lens, the bulb is exposed. This provides a harder light

Amps = Watts / Volts
equation for amps
T-shape prongs
a 20 amp plug has these
Barndoors
Big Flaps attached to the front of the light that helps shape light

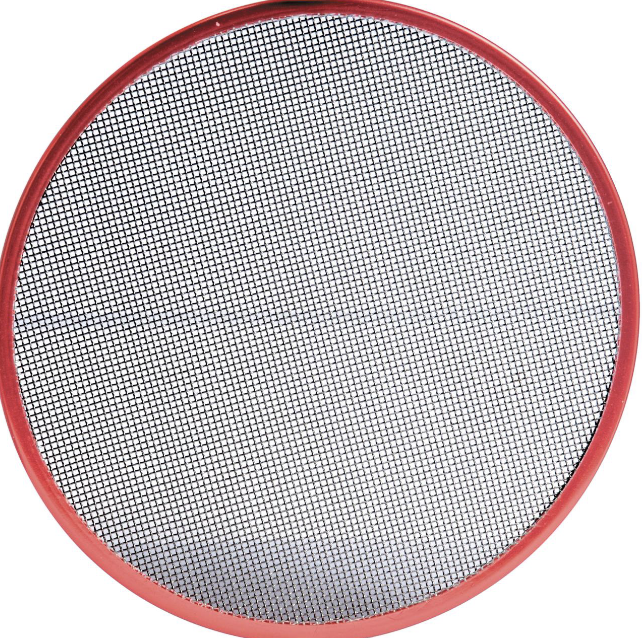
Full Double Scrim
reduces light by 50%

Full single scrim
reduces light by 25%

Half Double
Reduces one side of the beam by 50%
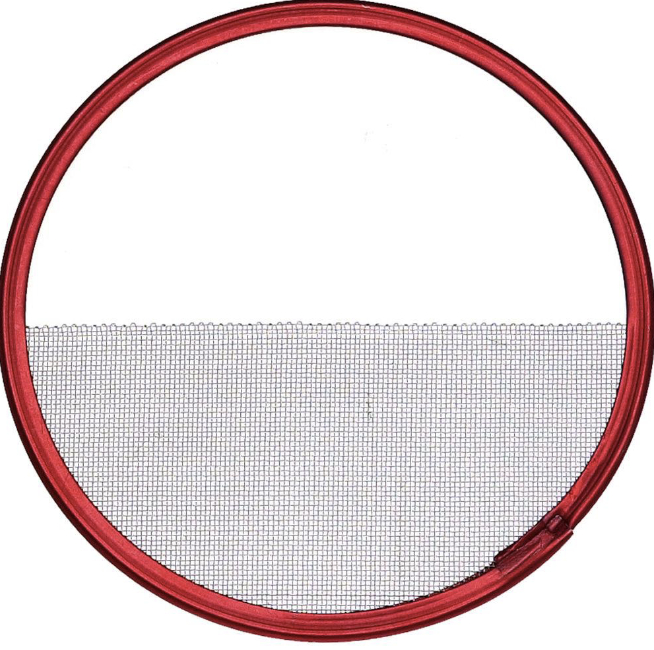
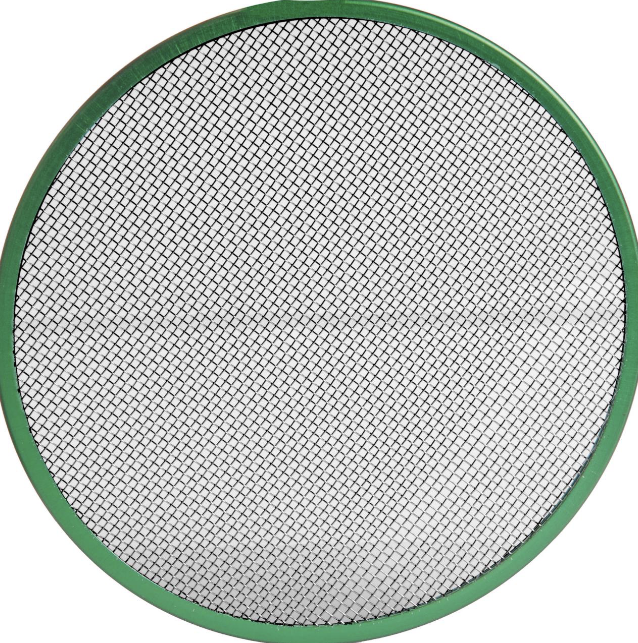
Half Single
Reduces one side of the beam by 25%
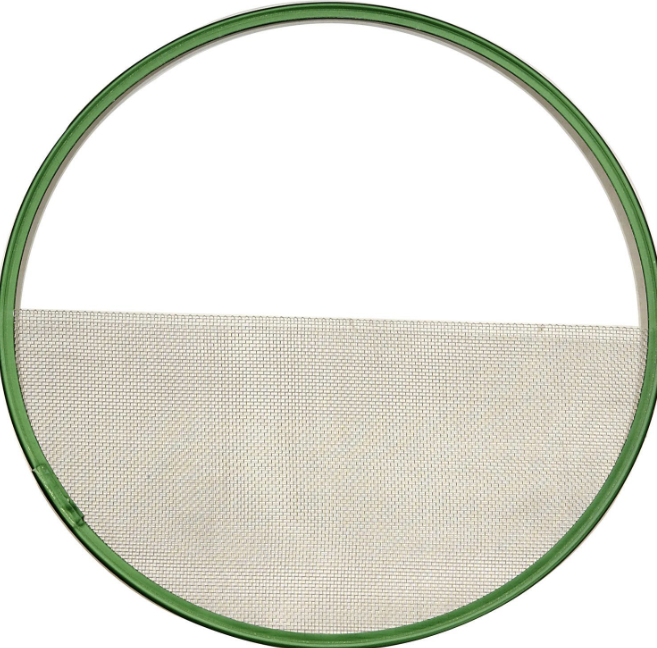

Grip
The department deals with the rigging for camera movement and lighting, setting up camera support, and building supports on set. Shapes the light placed by the electricians. their tools include sandbags, ladders, apple boxes, frames, stands, ect.
C-stand
single most versatile tool for grip. Used to mount things like flags, silks, or reflectors. You have to make sure to rig it to the right. it is made up of a head and arm

Solid flag/ floppy
made out of opaque material that fully stops light
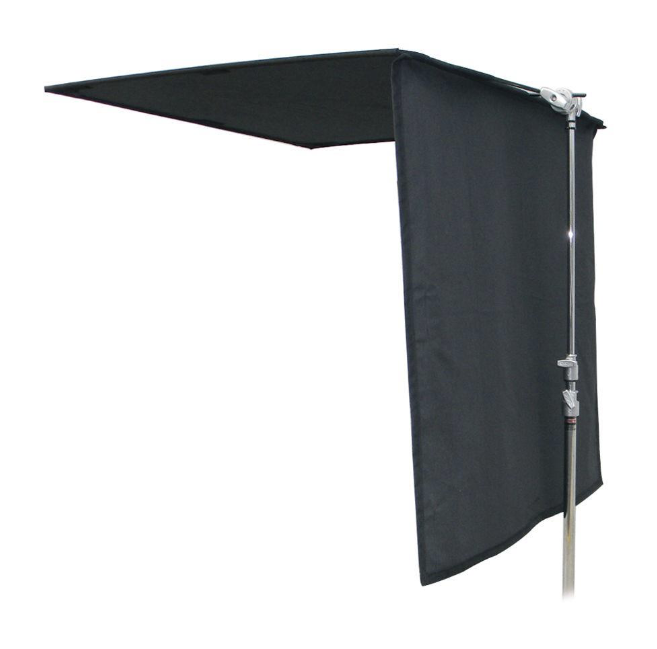

Flag
a panel that is mounted on a stand and used to block, shape, or manipulate light.
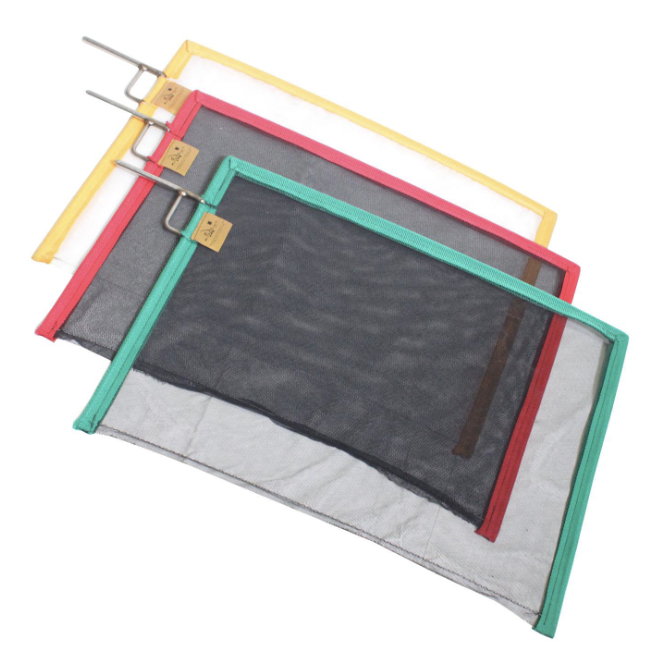

Double Flag
Flag used to block 50% of light

Single Flag (net)
Flag used to block 25% of light

Silk flag
used to diffuse light

Electric (the position)
Places the light for the Grip to shape
Gaffer
In charge of electric
best boy electric
position under gaffer in electric
electricians
position under best boy electric in electric
Key Grip
In charge of Grip
best boy grip
position under key grip
grips (Position)
position under best boy grip
Composition
arangement of the visual elements of a scene to tell a story and convey meaning
Frame
the edge of the visual picture. Has a x(width), y (height), and z axis (depth). It is generally a rectangle.
x axis
the width of a frame
y axis
the height of a frame
z axis
the depth of a frame. this is an imaginary axis created by illusion.
Aspect ratio
The ratio of the width and height of a frame.
depth via illusion
create by overlapping object and shading as well as object placement, size, value, focus, and linear perspective
Rule of thirds
If a frame is divided in three sections (vertically and horizontally), our eyes are drawn to the lines, especially the intersections of the vertical and horizontal lines
look room
For human subject, the area they are looking towards. Usually good to make sure the subject has enough space to look.
Lead room
Applied to frames in which a subject moves. It makes sure the subject has enough space to travel and isn’t fighting the frame.
Head Room
The space above the head of the person. The wider the shot, the more you can have. The tighter the shot the less you have.
extreme long shot
a wide shot usually used as an establishing shot. actors are so small they are not recognizable
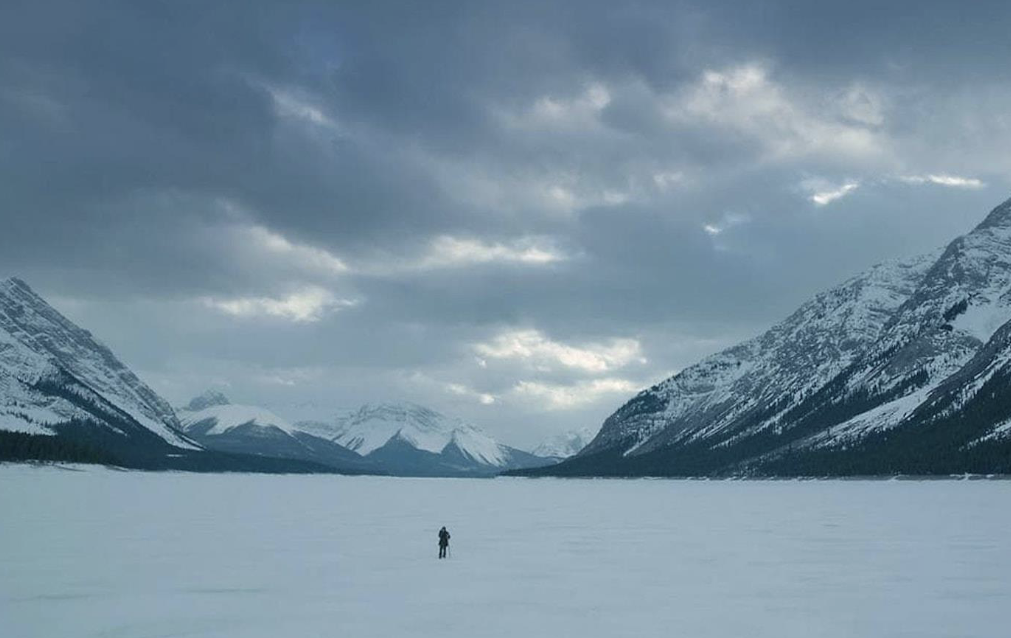

Long Shot
wide shot that contains the entire human frame with no cuts. The actors are recognizable
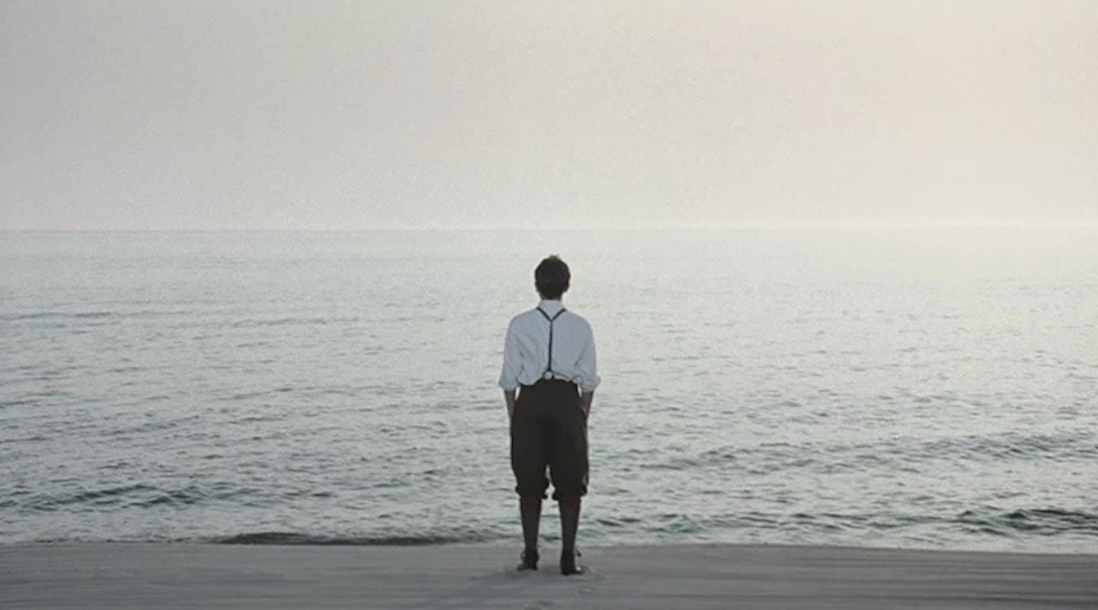

Medium long shot
contains the human figure from the knee up
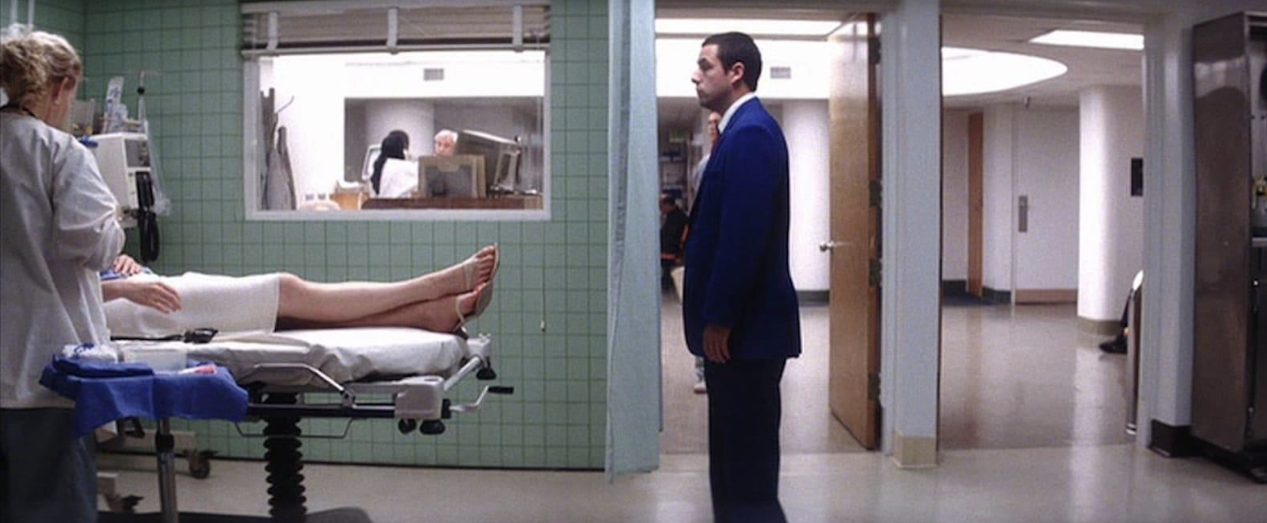

Cowboy shot
contains human figure from mid thigh up
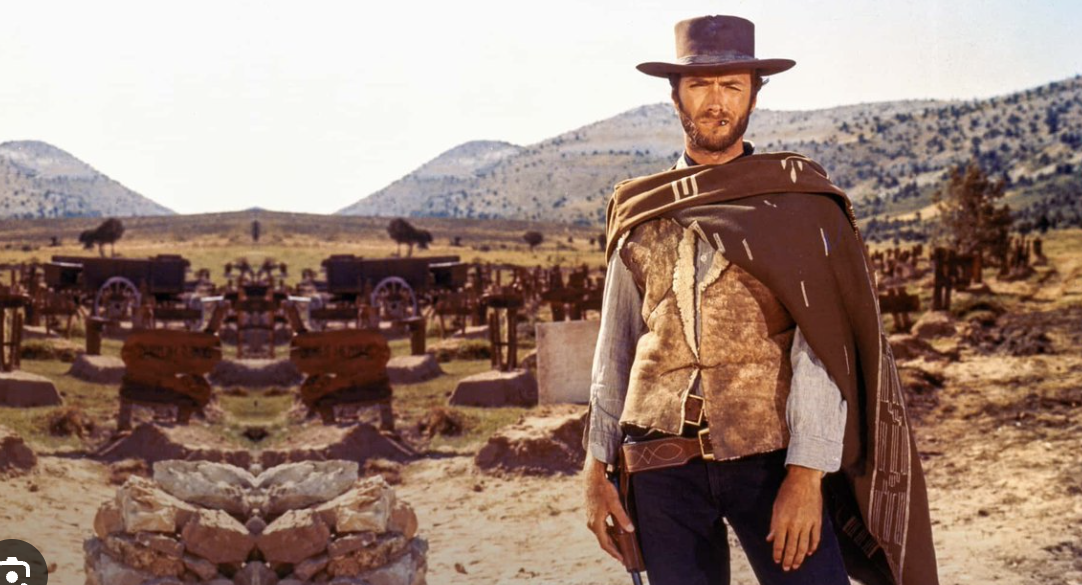

medium shot
contains a human figure from the waist up. often used to show 2 characters
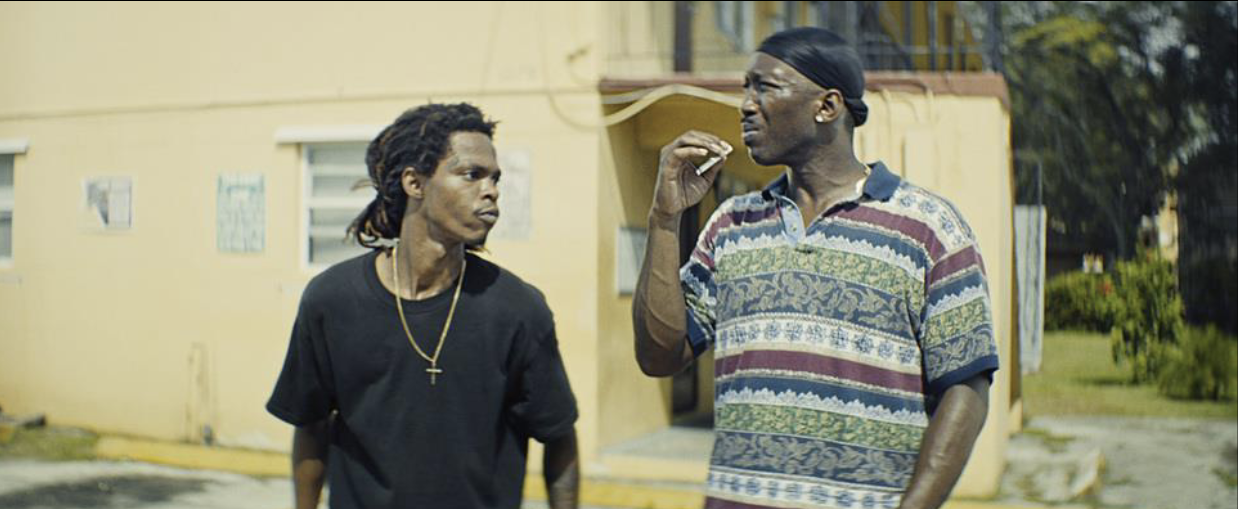

medium close up
a close up used to emphasize expression while still allowing you to see some of the actor’s body. chest up
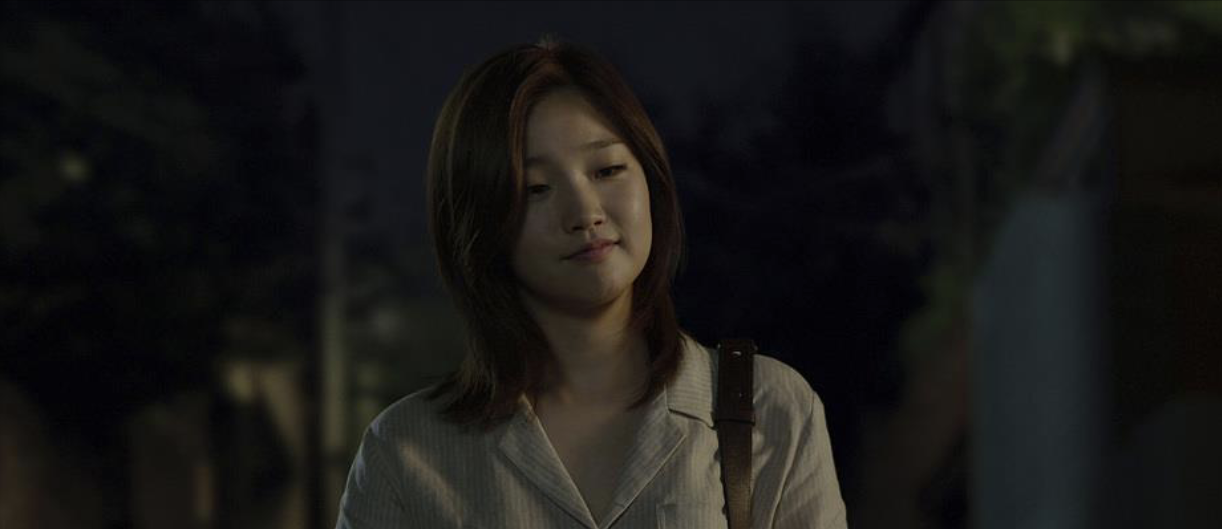

close up
When it is of a human figure, it is from slightly below the chin and up. It can also show a different part of the body or an objects. this is used to emphasize face, body parts, or inanimate objects
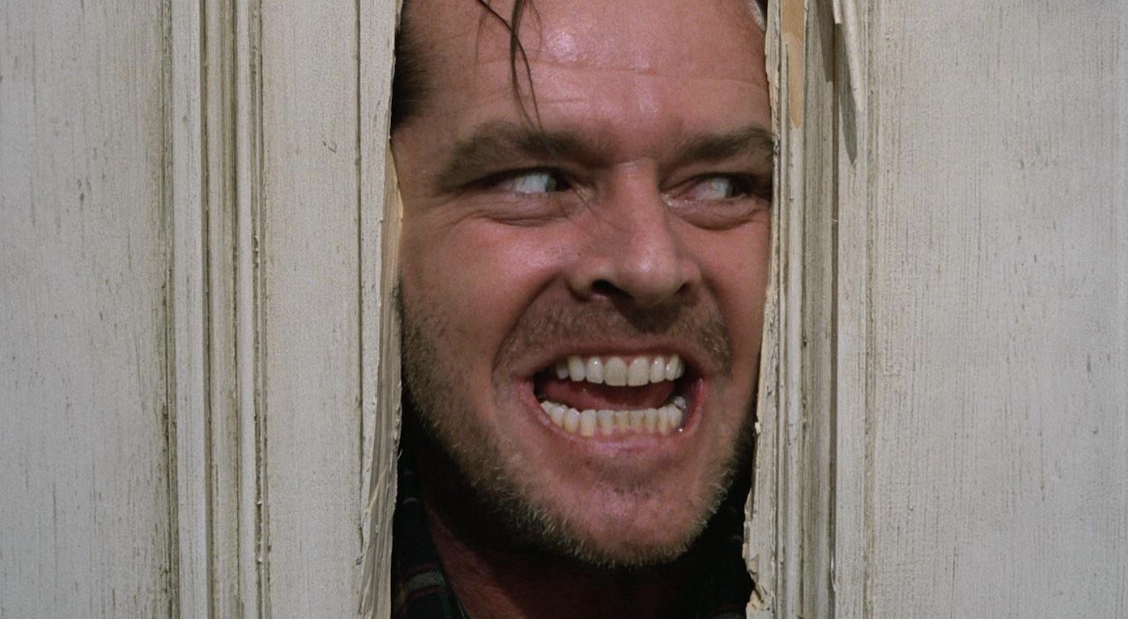

Extreme Close Up
Used to pick out specific details. Closer than a closeup and coveys details you might have missed otherwise
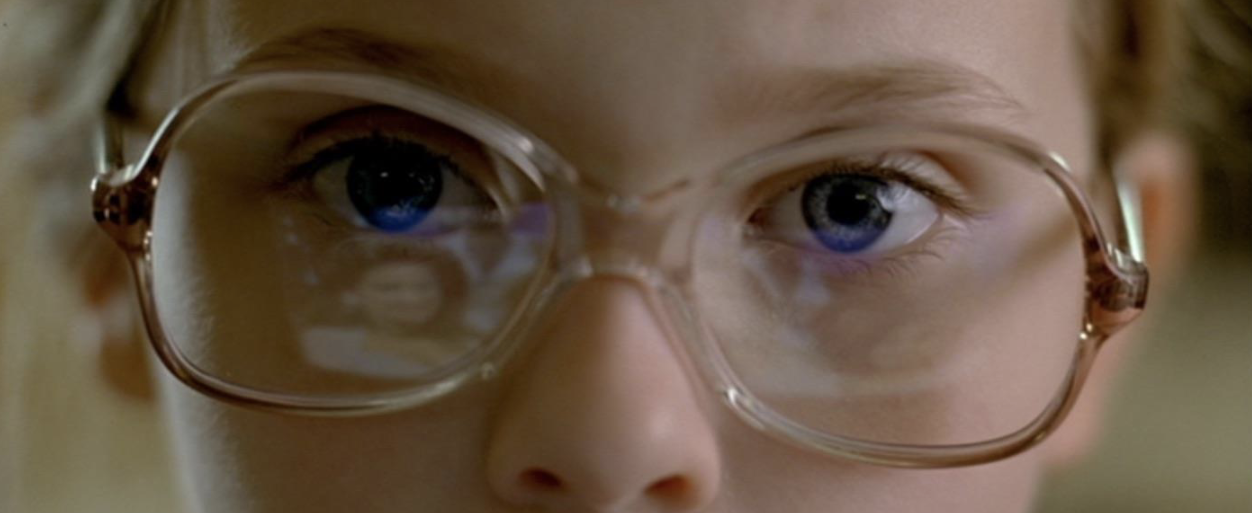

Insert Shot
Any tight shot (close up) used to emphasize an object or action

Master shot
The Widest shot in any scene that establishes geography, camera blocking, lighting, and blocking for the rest of the scene. this is normally shot first and covers as much of scene as possible so that if there is a problem the editor can always cut back to the master
2 shot
any shot with 2 actors. Usually shot as a medium shot of higher
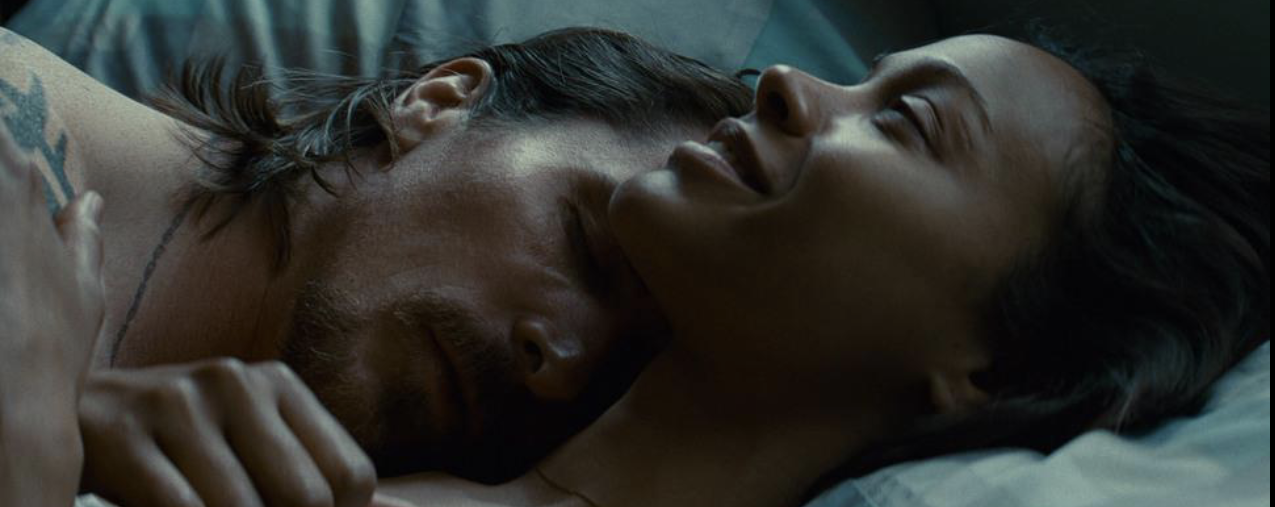

3 shot
any shot with 3 actors
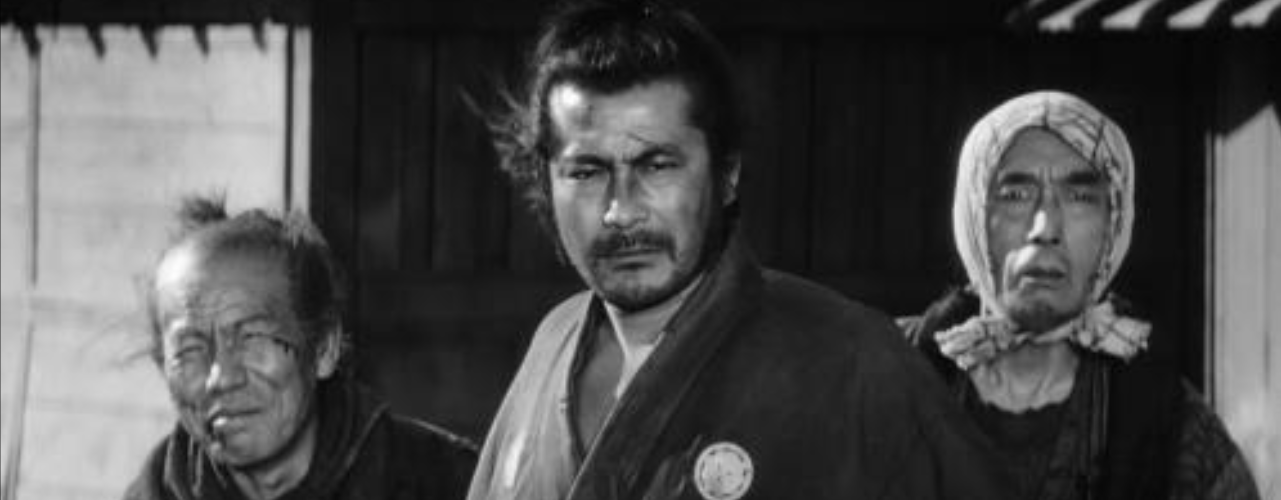

over the shoulder shot
shot where one or more charaters has their back to the camera

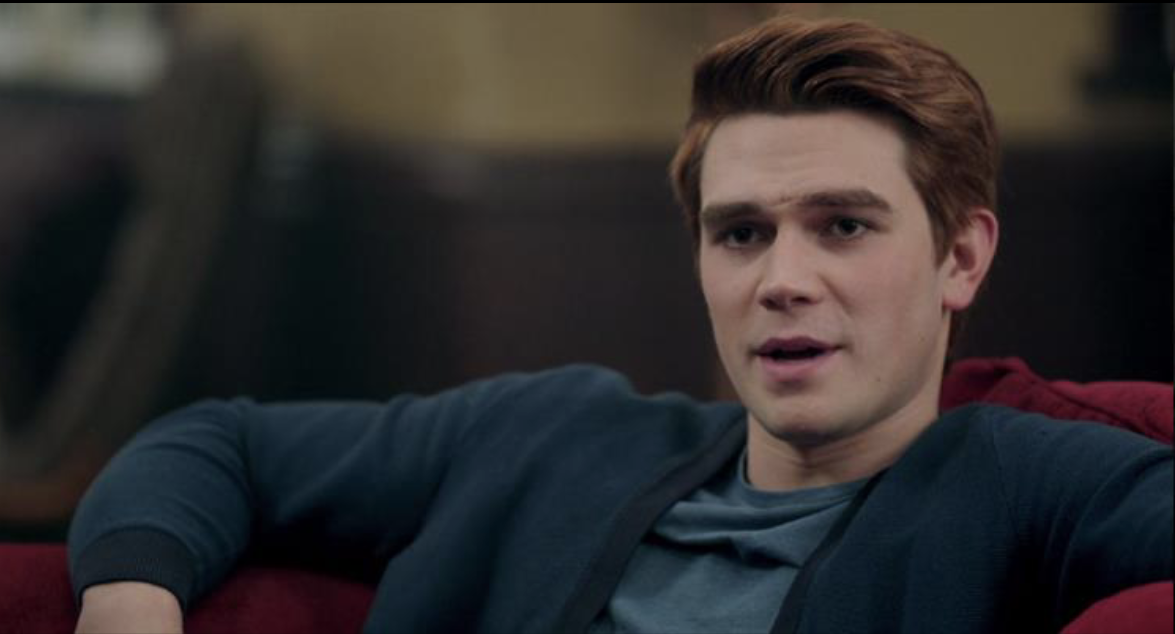
clean single
shot of one actor where no part of any other actor is showing

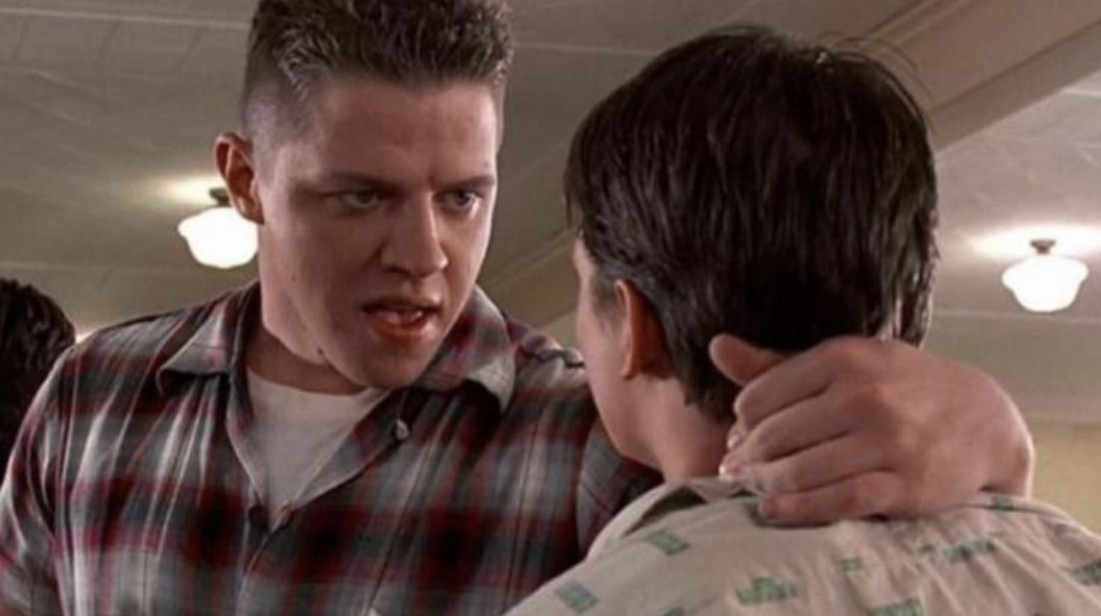
dirty single
shot of one actor where a part of another actor is showing. This can help orient the shot.
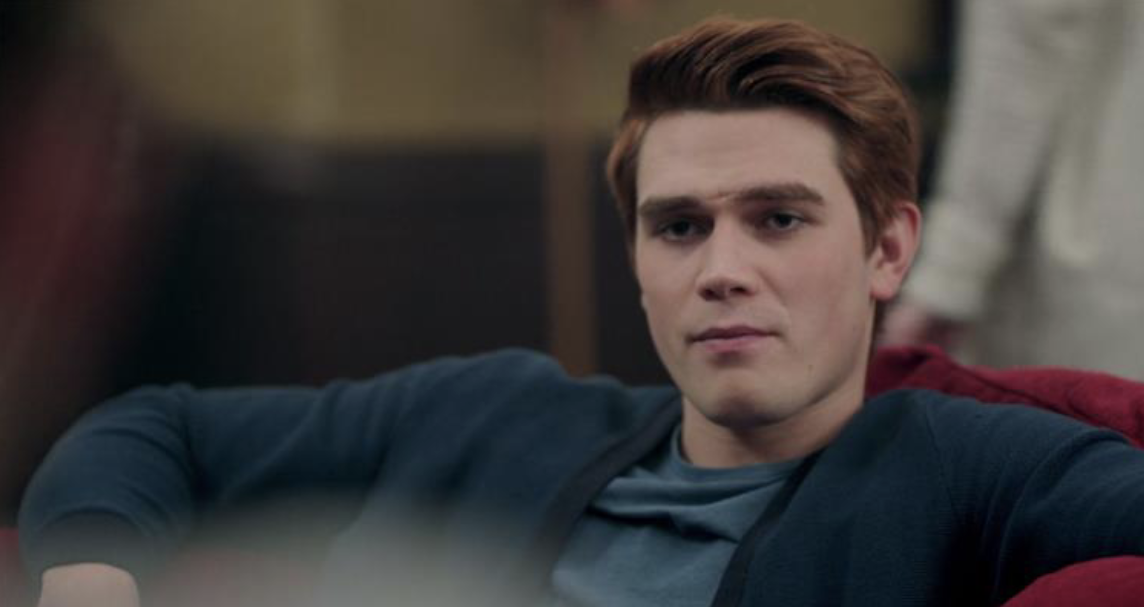

low angle
shot with the camera below the perceived eyeline
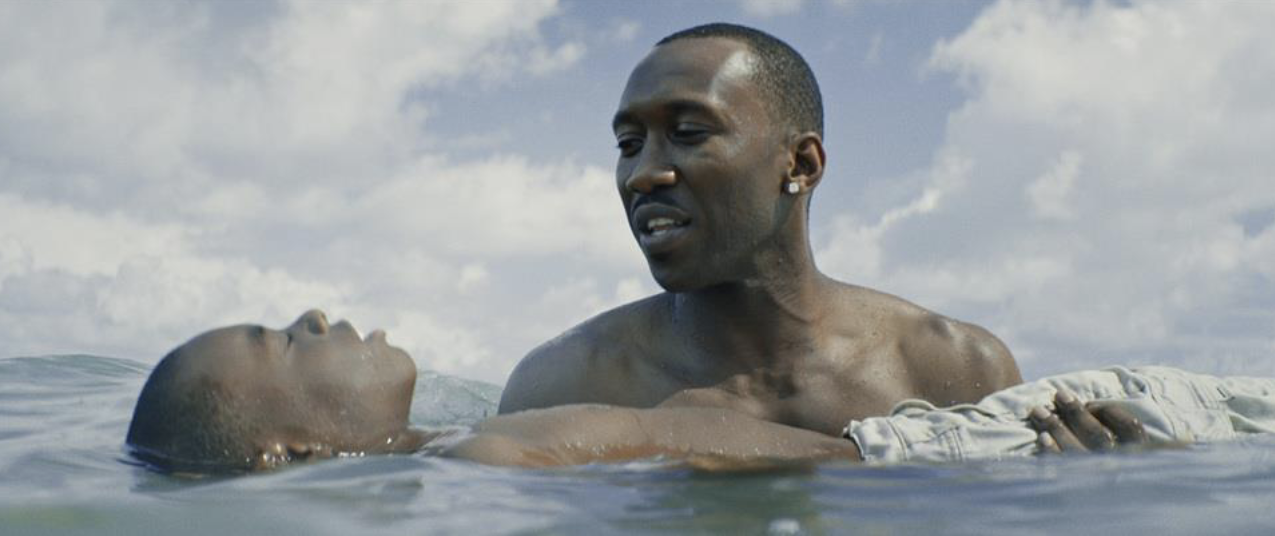

high angle
shot with camera above the perceived eyeline
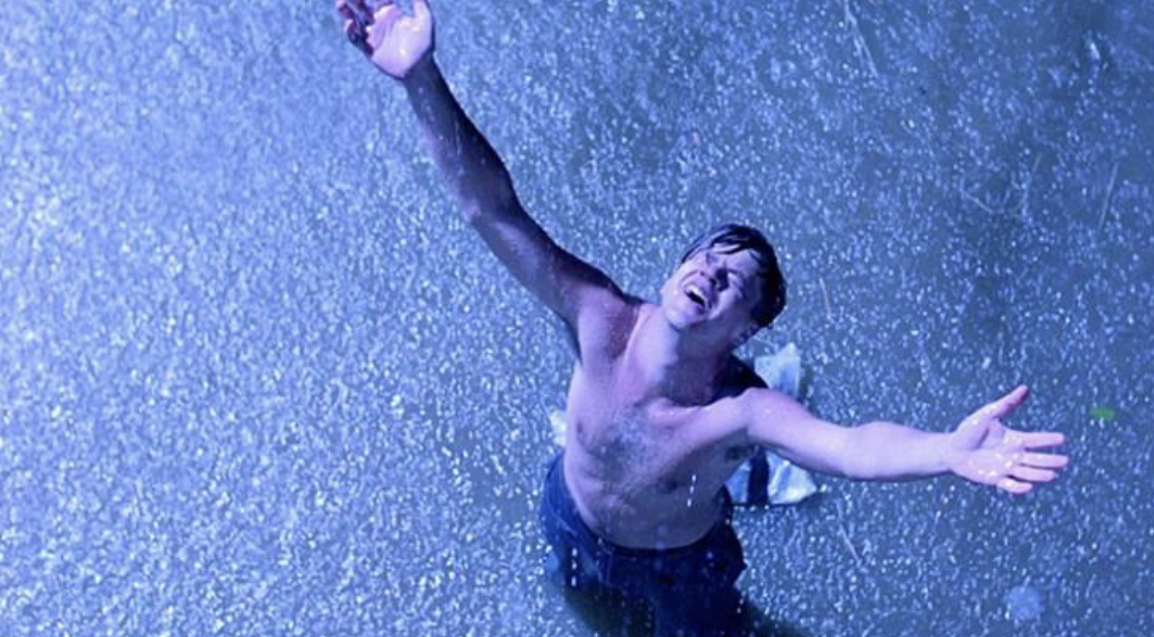

dutch angle
when the horizon is not level but rather canted to one side of the other. this is used to create dynamic composition
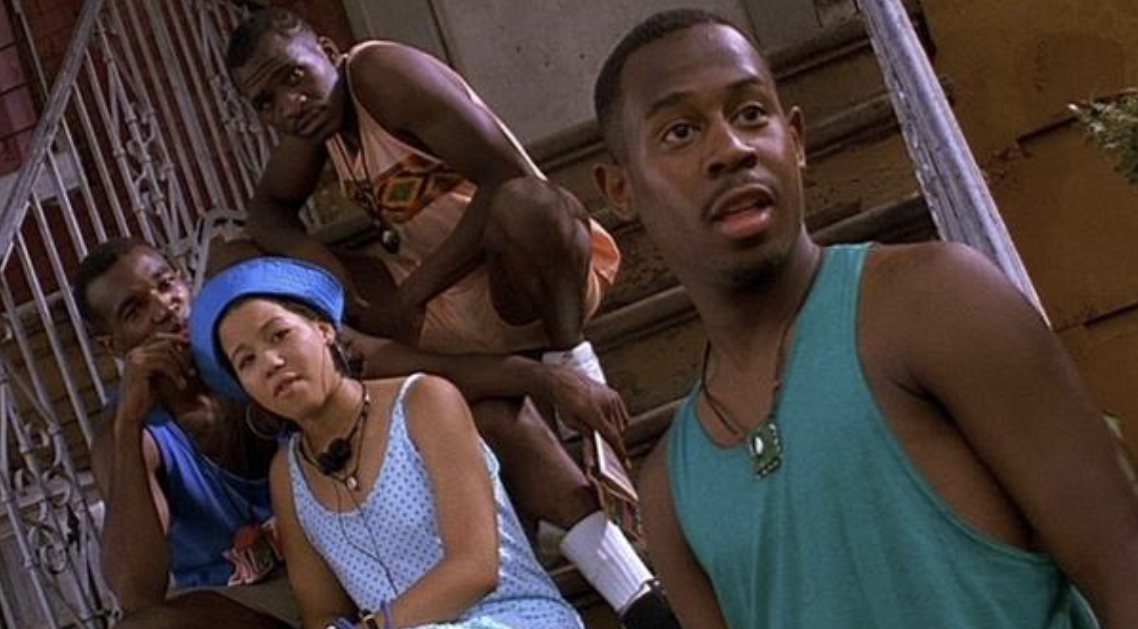

eyeline
The invisible/ virtual line that connects the gaze of characters looking at each other or an object. the camera must try to not cross the eyeline unless it is with a dolly.