Complement & Cytokines
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1 - Lec 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
The complement system (aka complement cascade) is a part of the immune system that _________ the ability of antibodies & phagocytic cells to __________.
enhances
clear microbes/ damaged cells, promote inflammation, & attack pathogen cell membrane
What are the 4 big functions of the complement system?
Cell lysis → kill pathogens
Opsonization/ Phagocytosis → clearance of apoptotic cells/ debris, synaptic pruning
Regulation → inhibition of complement cascade
Others → promote cell differentiation/ recruitment, modulation of immune cell migration, regulation of B-cell function, leukocyte adhesion
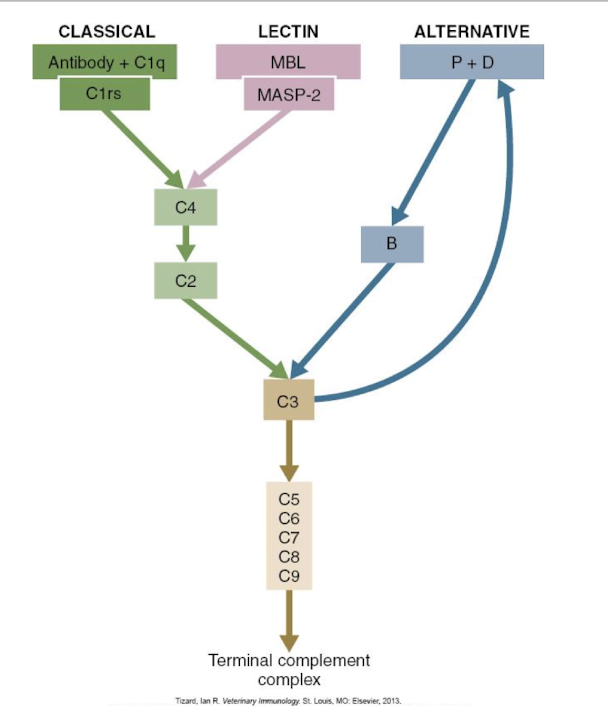
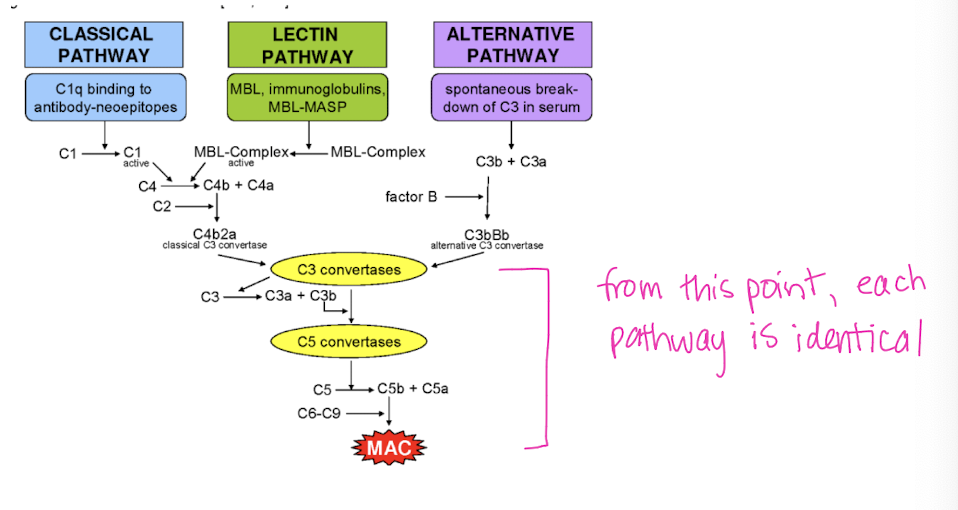
There are ______ pathways of complement activation.
3
All 3 complement activation pathways lead to _____ then the formation of _____________ and __________.
C3
membrane attack complex (MAC)
pathogen destruction
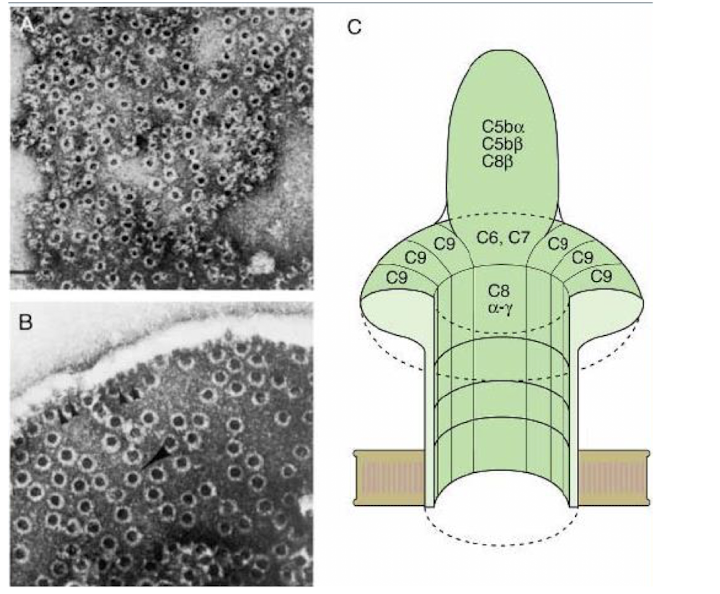
How does the membrane attack complex work?
a protein subunit embeds itself into the cell membrane of a pathogen causing ions to rush in/out
What is the overall goal of the membrane attack complex?
osmotic cell lysis
The classical complement activation pathway is part of ________ immunity, requires the presence of _______, and is activated after about _______ into an infection.
acquired (adaptive)
antibodies
5 days
The alternative & lectin complement activation pathways are part of _______ immunity, are triggered when _____________ in the blood, and response is seen ________.
innate
microbial cell walls meet complement proteins
immediately (no delays)
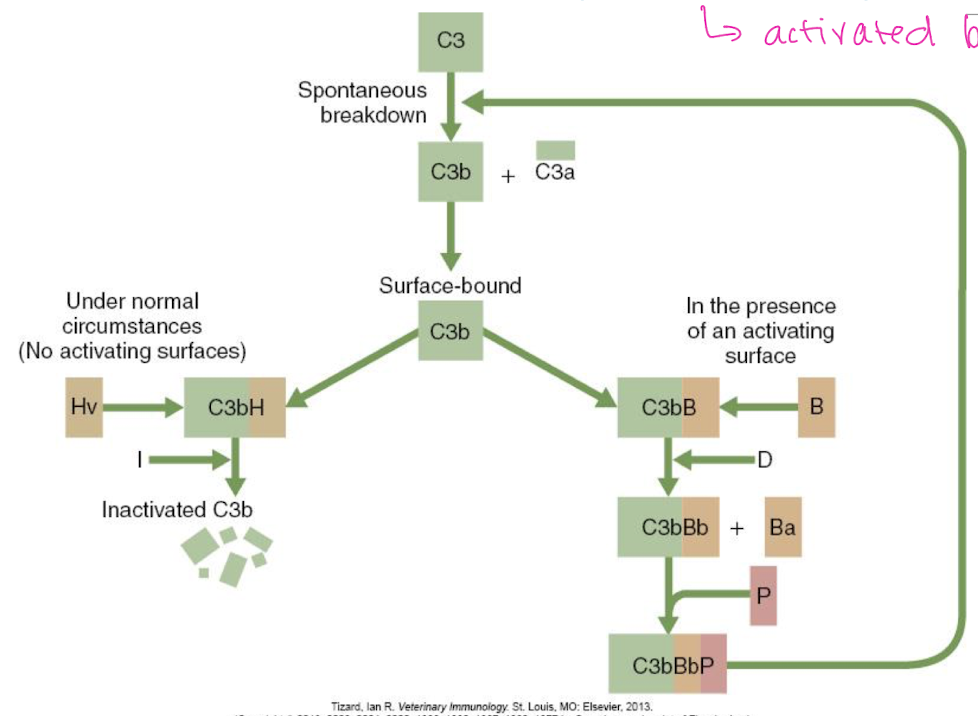
The alternative pathway is activated by the presence of a ______.
pathogen
What happens after the alternative pathway is activated by the presence of a pathogen?
C3b will bind to pathogenic surface → complement cascade ensues
If no pathogen is present, what happens to in the alternative pathway?
NO activating surfaces → cascade inhibited (under normal circumstances)
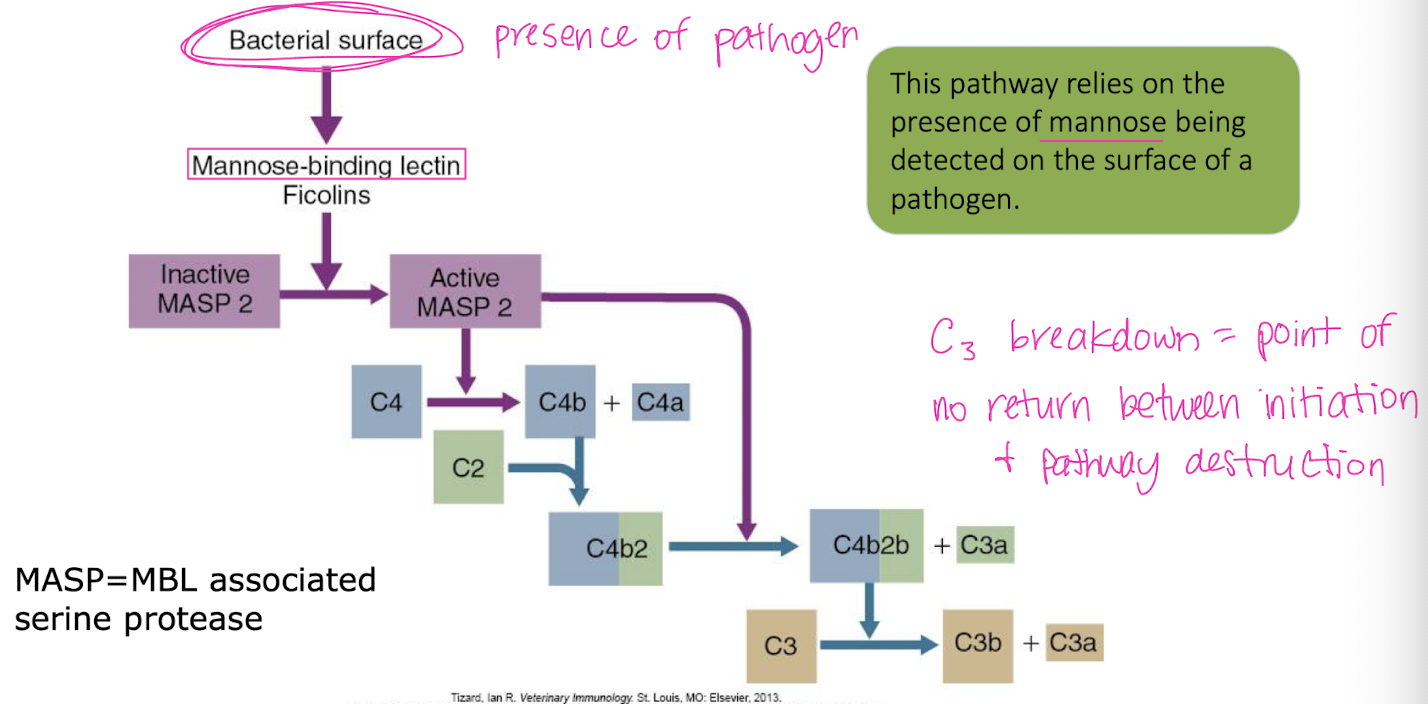
The lectin pathway relies on the presence of ______ being detected on the surface of a pathogen.
mannose
The classical pathway requires ________ antibodies to bind to the antigenic surface relatively __________.
at least 2
close together
Explain the classical pathway.
antibody binds to microorganism → exposes C’ binding site on antibody → C1 encounters bound antibody & crosslinks bt adjacent antibodies → C1 is activated & becomes an active protease → C1 cleaves C4
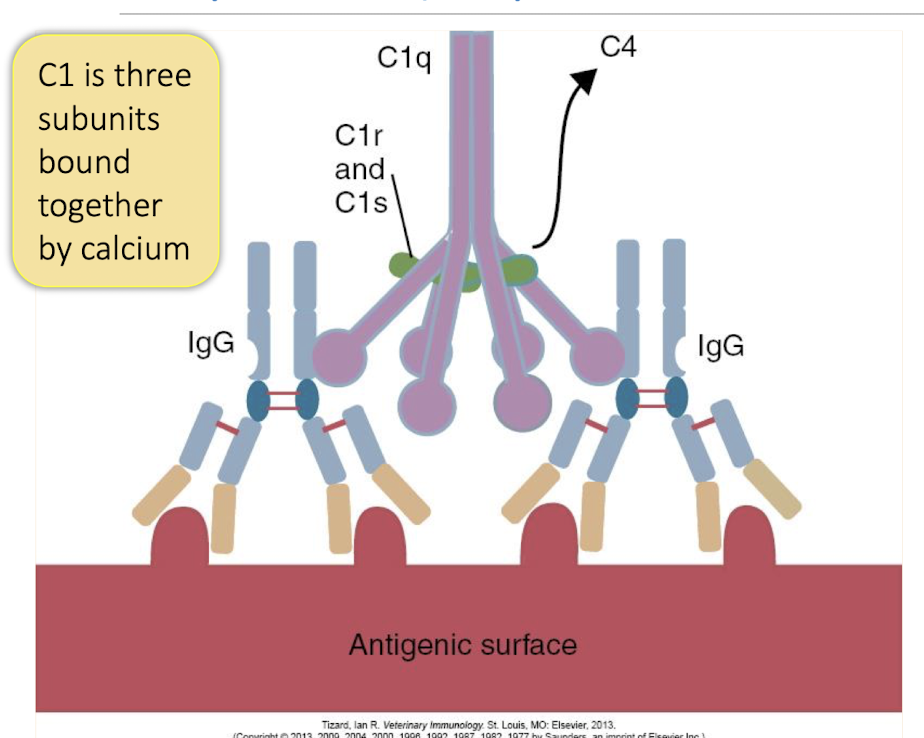
C1 is ______ bound together by Calcium.
3 subunits
Which antibody is more efficient in activating the classical pathway?
IgM → bigger + more binding sites
The differences in the 3 complement pathways involves the initial steps of activation leading to the formation of ________.
C3 convertase
During the complement cascade, each C component is ________ into smaller pieces a & b on the _______ surface.
cleaved
pathogen
The smaller _______ component is ________ & has other effects on the immune system and host body.
“a”
released
The larger ____ fragment _________ to the pathogen surface as part of the cascade.
b (“big bound b”)
remains bound
Exposure of the b fragment is __________ of the next complement protein (convertase).
required for activation
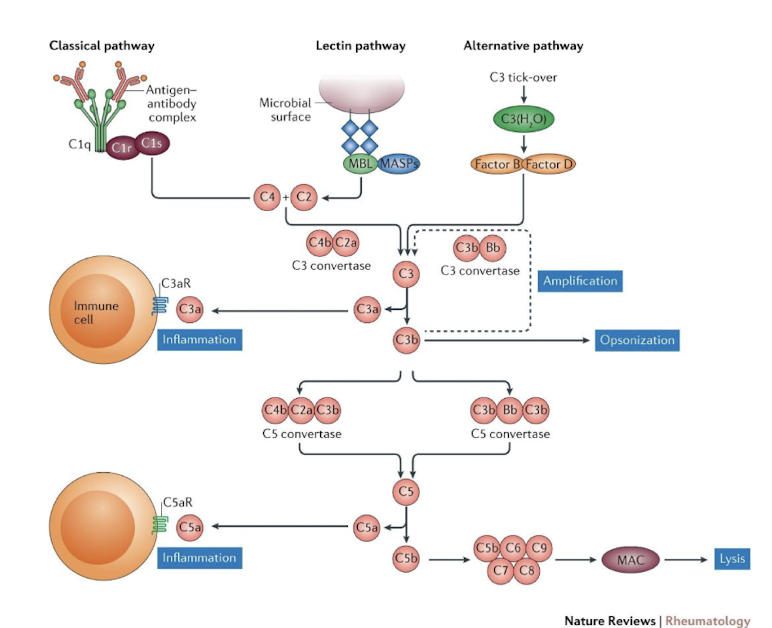
What happens during the amplification pathway?
C3 convertase activates C5
C6 & C7 rapidly bind to form a multimolecular complex that inserts on microbial cell wall
C8 binds & 12-18 C9 molecules polymerize to form a circle
Produces a hole in the pathogen surface
Pathogen killed by osmotic lysis
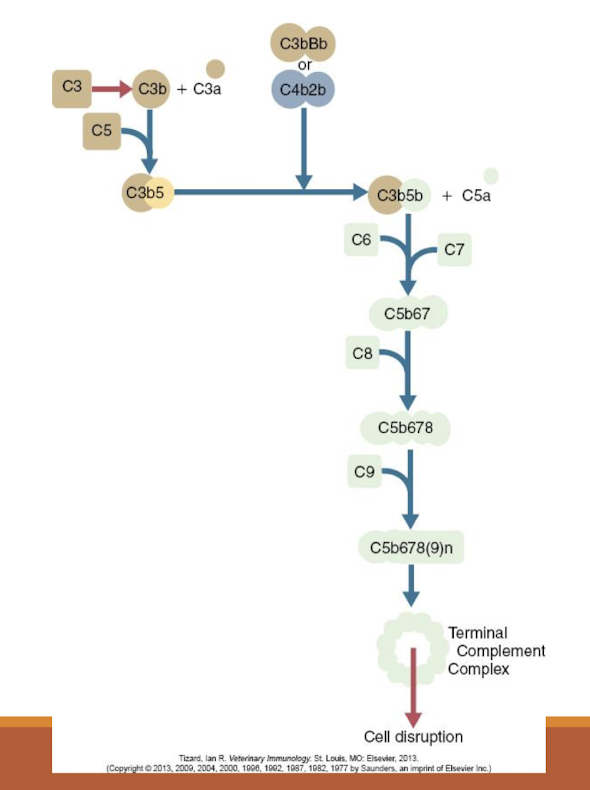
What is the major product of the amplificatio pathway?
membrane attack compound (MAC) = “nature’s hole-punch”
What biological consequence does the activation of C2a produce?
increased vascular permeability
What biological consequence does the activation of C3a produce?
anaphaylatoxin, mast cell degranulation
What biological consequence does the activation of C3b produce?
immune recognition & opsonization
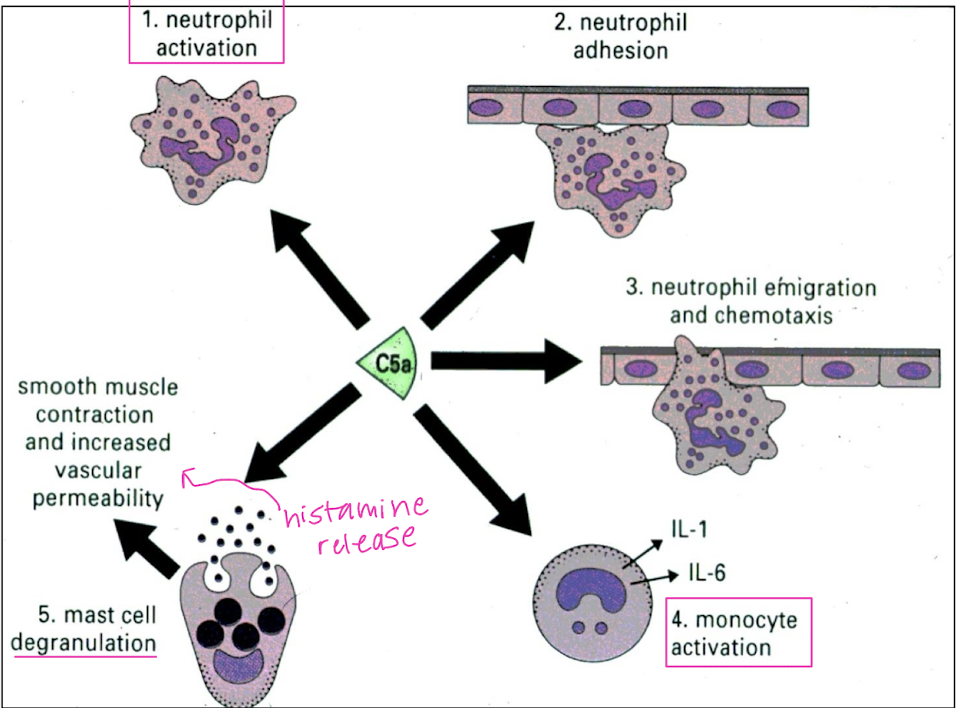
What biological consequence does the activation of C5a produce?
neutrophil chemotaxis, anaphylatoxin, lysosomal enzyme secretion, neutrophil activiation, increased vascular permeability, smooth muscle contraction
What biological consequence does the activation of C5b, C6, & C7 produce?
leukocyte chemotaxis
Biologic effects of C5a include:
Neutrophil activation
Neutrophil adhesion
Neutrophil emigration & chemotaxis
Monocyte activation
Mast cell degranulation = smooth muscle contraction & increased vascular permeability
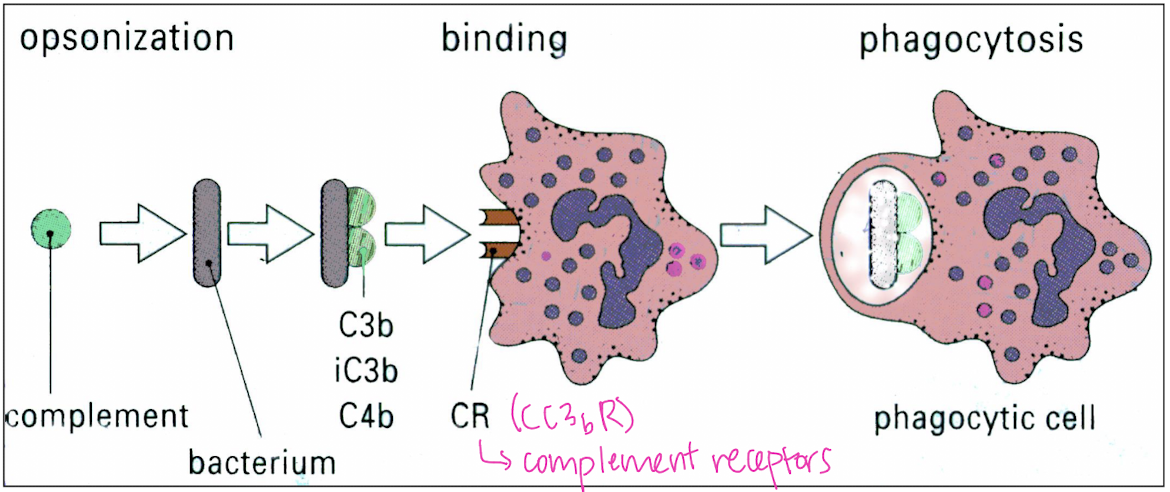
C3b is one of the most powerful _________.
opsonins
What is opsonization?
biological tagging of a bacterium/pathogen by a complement for phagocytosis
What is the overall summary of the complement system.
series of protein interactions that amplifies inflammatory response → works together with innate/ adaptive immune pathways
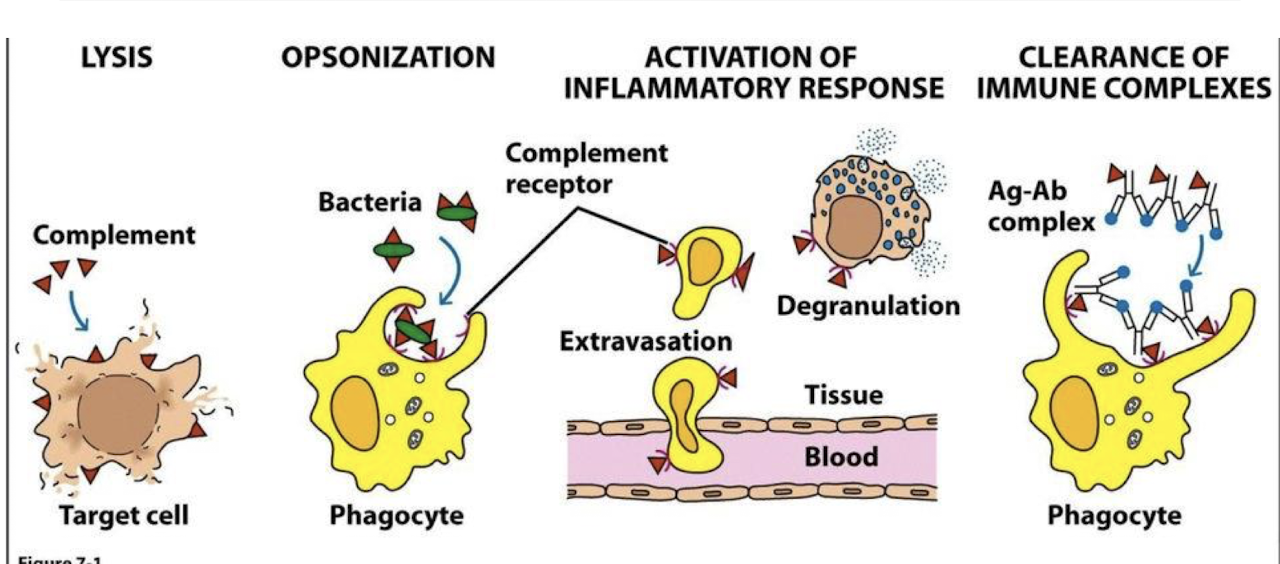
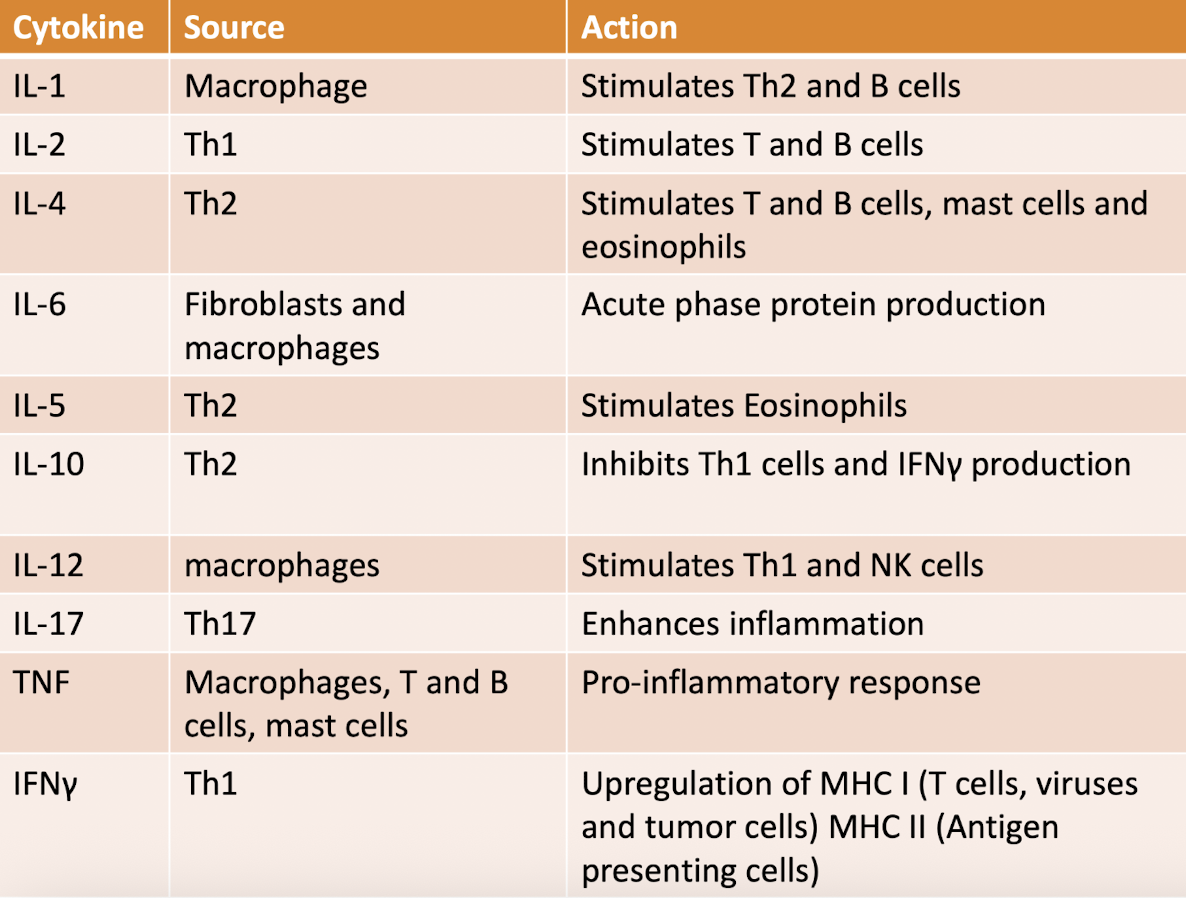
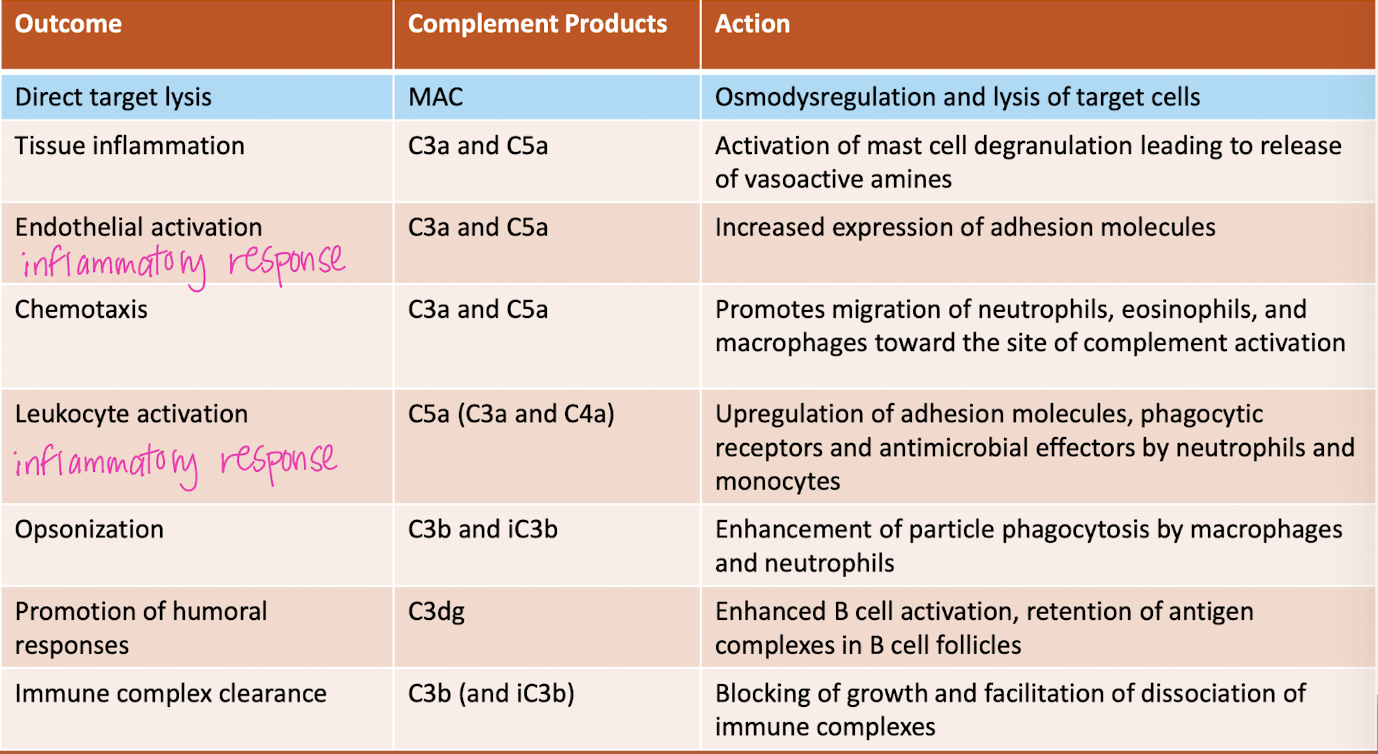
take a gander at this chart
Cytokines are master _______ of the immune response
regulators
What are some examples of cytokines?
interleukins, chemokines, TNF, interferons, monokines
Cytokines are ________ secreted by cells of the __________ to regulate the immune system.
proteins
immune system
T/F: Cytokines only affect a small number of cells/ organs.
FALSE - affect a wide variety of cells and organs
T/F: Cells rarely secrete only one cytokine at a time.
TRUE - groups may be synergistic or anatagonistic
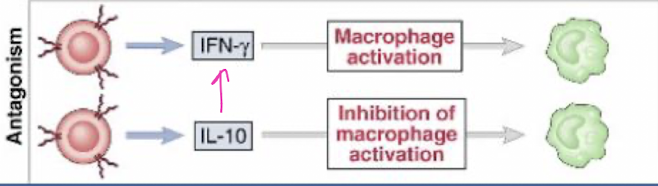
Without anatogonistic cytokines, ______ occurs.
pathology (immune-mediated arthritis)
What are the overall functions of cytokines?
inflammation, immune regulation, turmor surveillance, hematopoiesis, cell differentiation
Cytokines are produced by cells that are integral to _______ innate (natural) and acquired (adaptive) immune responses.
both
Cytokines are _________ as preformed molecules.
not stored → actively secreted
Secretion of cytokines is ______ and ______.
brief (pathology of COVID = sustained secretion of IL-6)
limited
Cytokines are ________ and ________ of immune and inflammatory responses.
mediators
regulators
Cytokines influence the ________ of other cytokines.
synthesis
Cytokine cascades can _________ or _________ the production of other cytokines. (+ or - regulatory mechanism)
enhance
suppress
Cytokines bind to ________ on target cells with _____ affinity.
specific receptors
high
Cellular responses to cytokines are generally _______ because they require _____ mRNA & protein synthesis.
slow (hours)
new
Pleiotrophic
an individual cytokine may be produced by many different cell types and act on many different cell types → cellular host efficiency
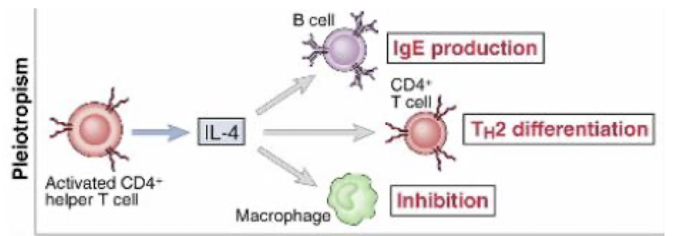
Redundancy
many cytokines have similar actions
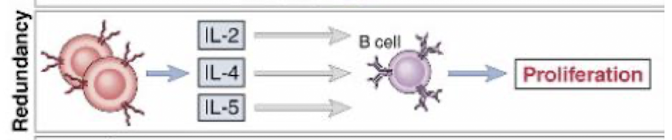
Synergism
working together
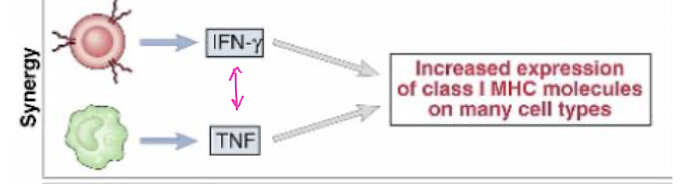
Anatagonism
working against each other
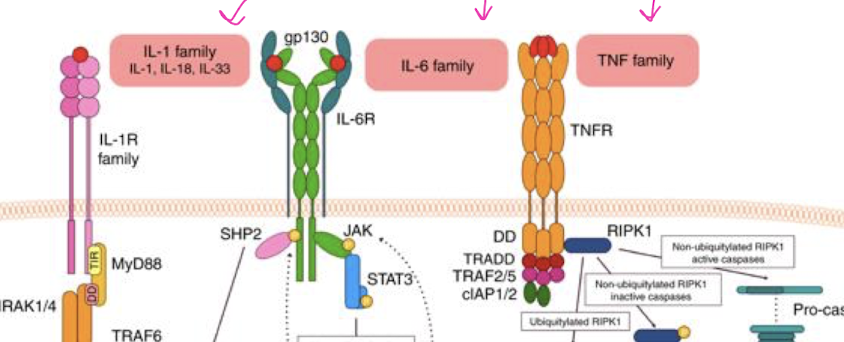
T/F: Many cytokine receptors have common subunits.
TRUE - grouped in families
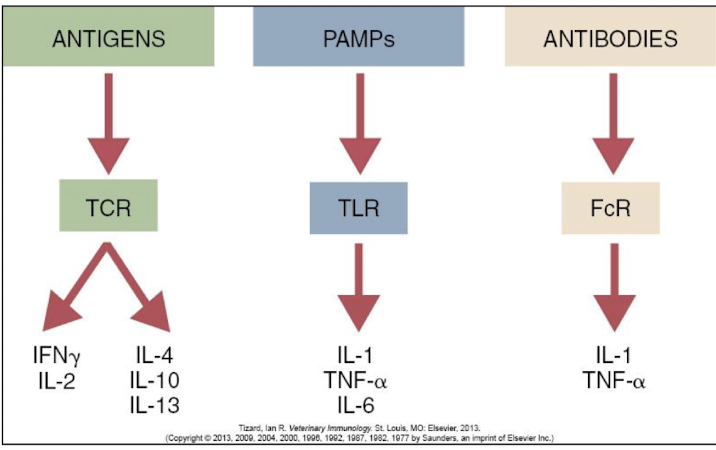
What are the 3 most important reactions that trigger cytokine release?
Antigens bind to their receptors on T & B cells
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) bind to TLR
Antibodies bind to Fc receptors (FcR)
What is the general function of Interleukin-2 (IL-2)?
promotes lymphocyte proliferation
one of the most generic cytokines
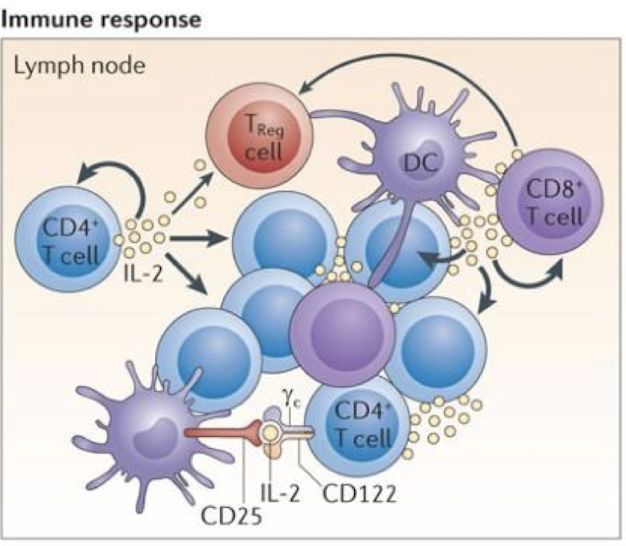
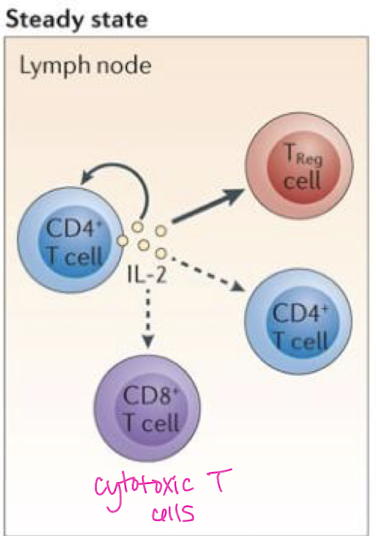
IL-2 is produced by which cell(s)?
CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells (cytotoxic), dendritic cells, & thymic cells → pleiotrophism
What is general function of Interleukin-12 (IL-12)?
activates T cell and NK cells → promotes Th1 pathway (pro-inflammatory)
Which cell(s) produce IL-12?
macrophages, dendritic cells, & neutrophils → pleiotrophism
IL-12 is _______ meaning it shares a common subunit with IL-23.
redundant → in host defense to many pathogens
What is IL-12 central role in cell mediated immunity?
stimulates T cells & NK cells which in turn secrete IFNγ → IFNγ further activates macrophages → collectively mediates macrophage activity & elicits a cell mediated response
Which cell(s) produce interferon gamma (IFNγ)?
Th1 cells and NK cells → pleiotrophism
IFNγ under goes ______ with TNF-α.
synergism → triggers inflammatory cell death, tissue damage, & mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection & cytokine shock syndromes
T/F: Cytokines work in isolation.
FALSE - do not work in isolation → many overlapping cytokine networks activated during an immune response
What is the importance of cytokine networks?
control reactions, keep immune responses in balance, & activate or down-regulate various cells
Cytokine summary chart
goal = enhance overall inflammatory response