Principles of Ecology Chapter 18Which ingredient is not required in the process of carbon fixation to occur? Multiple choice question. PAR incorrect O2 Reason: Oxygen interferes with this process and makes it less effective than it otherwise would be. CO2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Which ingredient is not required in the process of carbon fixation to occur?
PAR
O2
CO2
O2
Which of the following is not one of the uses of forest biomass?
It is food for herbivores.
It is broken down into organic soil matter.
It is used as an energy source for photosynthesis.
It is food for detritivores.
It is used as an energy source for photosynthesis.
When studying ecosystems, Arthur Tansley realized the importance of considering organisms and their environment as a(n) blank system.
integrated
Which statement best fits the definition of primary production over some period of time?
production of new inorganic matter by autotrophs
production of new organic matter by autotrophs
production of new biomass by the heterotrophs
production of new organic matter by autotrophs
Secondary production is the rate of blank produced by heterotrophic consumers.
biomass
Select the statement that best describes the process of carbon fixation.
PAR converts CO2 into sugar and other biomass.
CO2 and O2 are converted into sugar and biomass.
PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) converts O2 into sugar and other biomass.
PAR converts CO2 into sugar and other biomass.
Which organism would directly use the biomass produced by forest vegetation?
oak tree
rabbit
Hyena
fox
rabbit
When determining an organism's trophic level, what group is used as the start of the transfer of energy?
detritivores
primary producers
secondary consumers
primary consumers
primary producers
An ecosystem is a biological community and all of the blank.
biotic factors influencing it
relationships they have with other communities
living organisms within it
abiotic factors influencing it
abiotic factors influencing it
In which trophic level are the carnivores that feed upon herbivores placed?
first
second
third
fourth
third
The production of new organic matter, or biomass, by autotrophs in an ecosystem per unit area or volume during some period of time is known as blank
primary production
Identify the two key variables that are highly correlated with variation in terrestrial primary production.
moisture
temperature
soil pH
biodiversity of producers
moisture
temperature
The rate of biomass production by heterotrophic consumers is known as blank production.
secondary
Annual actual evapotranspiration (AET) is reported in what way?
millimeters of water evaporated and transpired per year
liters of water collected as runoff
liters of water stored per square meter of producers
grams of water stored per square meter
millimeters of water evaporated and transpired per year
Which variable helps explain the difference in terrestrial primary productivity within the same ecosystem?
elevation
levels of rainfall
soil fertility
temperature levels
soil fertility
What is the definition of a trophic level?
an organism's position within a food web
the amount of biomass generated by the autotrophs
the role an organism plays within the ecosystem
an organism's position within a food web
Which statement describes Liebig's (1840) Law of the Minimum?
All producers require a minimum amount of rainfall for growth.
Multiple nutrients control primary productivity.
A single nutrient controls primary productivity.
A single nutrient controls primary productivity.
In what trophic level are detritivores placed?
first
second
third
fourth
second
Identify the maximum increase in net primary productivity at the Shaver and Chapin study sites.
8%
23%
150%
300%
300%
Which environmental conditions would most likely produce the highest primary productivity?
warm and dry
warm and moist
acidic and wet
temperate and moist
warm and moist
What is annual actual evapotranspiration (AET)?
the total amount of water that evaporates and transpires during the course of a year
the total amount of water that is collected and retained by the producer's base during the course of a year
the total amount of water that transpires through the producer's base in a year
the total amount of water that evaporates and transpires during the course of a year
Which nutrient was determined to be a limiting factor in the biomass of phytoplankton?
total potassium
total iron
total phosphorus
available sulfur
total phosphorus
Which two soil nutrients play the greatest role in determining terrestrial primary productivity?
sodium
phosphorus
nitrogen
calcium
phosphorus
nitrogen
Which nutrient combination increased the phytoplankton biomass the most in the Experimental Lake Area study?
iron and carbon
sucrose and nitrate
sucrose, nitrate, and carbon
carbon, nitrate, and phosphate
carbon, nitrate, and phosphate
Liebig's Law of the Minimum helped scientists gain which perspective about primary productivity?
Rainfall levels will affect the rates of primary production.
Variation in soil fertility can affect the rates of primary production.
The same nutrient always limits primary productivity.
Variation in soil fertility can affect the rates of primary production.
Identify the minimum increase in net primary production at the Shaver and Chapin Alaska tundra study sites.
2%
23%
35%
300%
23%
The nutrient that is most often the limiting factor for marine ecosystems is blank
nitrogen
In addition to species diversity, what other facets are considered components of biological diversity?
Multiple select question.
climatic diversity
physiological diversity
ecosystem diversity
genetic diversity
elemental diversity
physiological diversity
ecosystem diversity
genetic diversity
What is the correct relationship between total phosphorus and plankton biomass when conditions are otherwise good for plankton growth?
Low total phosphorus is correlated with high phytoplankton biomass.
High total phosphorus is correlated with high phytoplankton biomass.
High total phosphorus is correlated with low phytoplankton biomass.
High total phosphorus is correlated with high phytoplankton biomass.
A collection of plants with similar physiological and anatomical characteristics that influence their seasonality, resources requirements, and life histories is known as a(n) blank.
carbon fixation lineage
primary production troop
evolutionary NPP cluster
plant functional group
plant functional group
Which nutrients produce an increase in phytoplankton biomass in the Experimental Lake Area study area?
carbon
nitrate
sucrose
potassium
carbon
nitrate
sucrose
The primary production of a large lake has been increasing over time; a likely cause is blank the lake.
a drop in the average ambient air temperature above
an increase in the diversity of primary producers in
a decrease in the amount of runoff into the lake
the recent localized extinction of algae species from
an increase in the diversity of primary producers in
In which aquatic ecosystem is nitrogen the limiting nutrient for phytoplankton biomass?
marine
streams
Lake Victoria
Lake Michigan
marine
Species, genetic, physiological, anatomical, functional, and ecosystem diversity all are components of blank diversity.
bio
Which organism would most likely cause a trophic cascade?
field mouse
beech tree
grey wolf
rabbit
grey wolf
A plant functional group consists of plants with similar blank that influence their seasonality, resource requirements, and life histories.
geographic distributions
pollinators
physiological and anatomical characteristics
root structures in the same soil type
physiological and anatomical characteristics
Which abiotic factors stimulate plant production in a grassland ecosystem?
rainfall levels
carbon availability
soil fertility
types of grazing animals
rainfall levels
soil fertility
As the number of algal species increases in a lake, you would expect blank in primary production
no net change in
a decrease
an increase
strong fluctuations in
an increase
What mechanisms underly compensatory growth?
a decrease in water availability
a reduction in self-shading
lower rates of respiration
an increase in soil pH
a reduction in self-shading
lower rates of respiration
Which of the following factors are bottom-up controls of ecosystems?
physical factors
type of predators
chemical factors
physical factors
chemical factors
What happens to sunlight as it shines upon a forest?
Some is reflected from the forest canopy.
All of it is reflected by chlorophyll.
Some is converted into heat energy.
All of it is absorbed by chlorophyll.
Some is reflected from the forest canopy.
Some is converted into heat energy.
What are the effects of a trophic cascade?
a change in the prey abundance
a change in the productivity of a population
a change in the biomass
a depletion of soil nutrients
a change in the prey abundance
a change in the productivity of a population
a change in the biomass
Trophic dynamics is the transfer of energy from one part of an ecosystem to blank.
another part of it
another part of the electromagnetic spectrum
the bottom trophic level
another ecosystem
another part of it
Which influences on grassland ecosystems are produced by grazing mammals? (More than one answer may be correct)
plant production
temperature
soil fertility
plant production
soil fertility
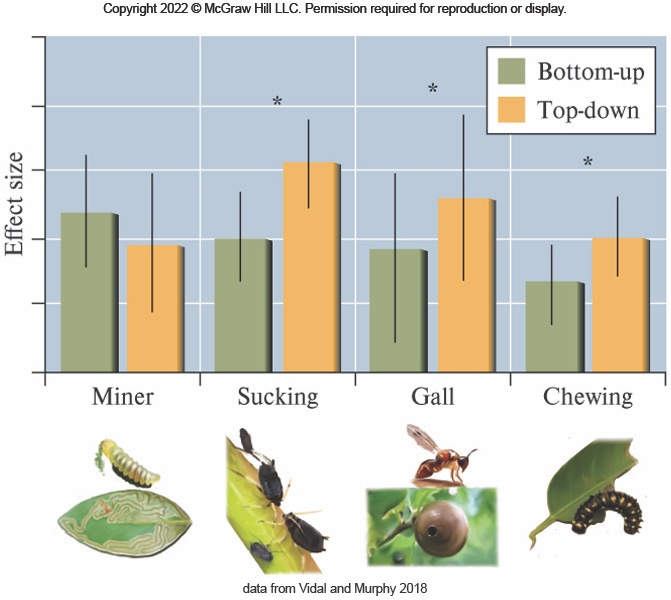
The results of a meta-analysis of tri-trophic studies about controls on the trophic structure showed that blank.
both top-down and bottom-up effects were important
there were no cases where bottom-up effects were more important than top-down effects
sucking insects were not influenced by top-down effects
top-down effects were more important for most of the animal groups studied
both top-down and bottom-up effects were important
top-down effects were more important for most of the animal groups studied
What event would cause plants to undergo compensatory growth?
a decrease in atmospheric pressure
grazing by herbivores
an increase in the soil pH
an increase in the rainfall levels
grazing by herbivores
As primary production increases, the abundance of organisms blank.
only increases at the level of predators
increases at all trophic levels
only increases at the primary level
is largely unaffected
increases at all trophic levels
Identify the bottom-up control.
average temperature
biodiversity of decomposers
type of predators
average temperature
What are the various forms of energy for consumers in a salt marsh?
inorganic solutes
detritus
phytoplankton
upland plants
detritus
phytoplankton
upland plants
What plant structure is responsible for absorbing solar energy?
bark on the trunk
mitochondria in surface leaf cells
starch in the leaves
chlorophyll in the leaves
chlorophyll in the leaves
When studying trophic dynamics, what is the key component that is being discussed?
nutrient levels
biodiversity of predators
transfer of energy
transfer of energy
The results of a meta-analysis of tri-trophic studies (including three tropic levels) about controls on the trophic structure discovered that in most cases blank.
bottom-up and top-down effects were equally important
bottom-up effects were significantly stronger
top-down effects were significantly stronger
top-down effects were significantly stronger
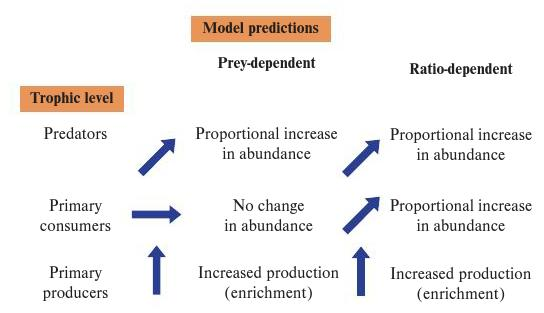
Which of the following statements is true regarding the models displayed in the figure? Experimental and observational studies indicate blank.
both models are equally supported
greater support for the ratio-dependent model
both models need to be rejected
greater support of the prey-dependent model
greater support for the ratio-dependent model
What is the main source of energy at the bottom trophic level of the salt marsh ecosystem?
zooplankton
detritus of salt marsh grass
phytoplankton
crabs
detritus of salt marsh grass