NUTR 202 - Module 6: Proteins
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
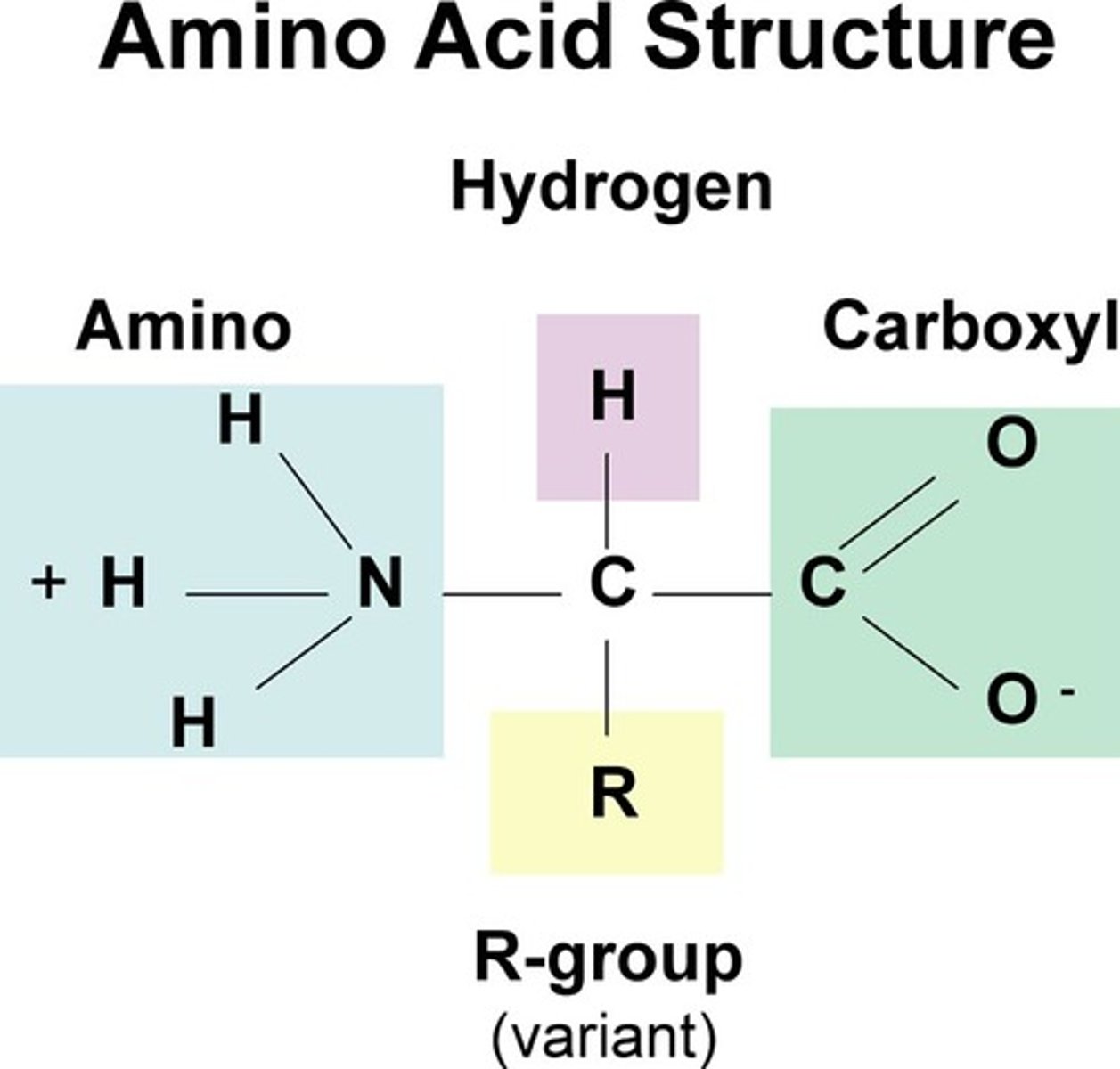
Amino Acid Structure
A Central Carbon connected to an acid group (carboxyl), a hydrogen group, an amino group, and a R group
Transamination
Transfer of amine group from one molecule to another to create amino acid
How are amino acids linked?
Peptide Bonds through Dehydration Synthesis
How can a protein's structure be altered?
Heat, acid, enzymes, agitation, alcohol, an electrical charge, and salting
What happens if a protein loses its shape?
It can no longer function and is said to have Denatured
Why are proteins important for blood vessels?
Proteins maintain an optimal balance between the fluids inside and outside cells in blood vessels
Albumin
Protein in Blood; Maintains the proper amount of water in the blood through osmosis
Edema
Fluid accumulation due to low blood albumin
Antigens
Foreign substances that trigger the attack of antibodies in the immune response.
How do proteins protect our immune system?
They are present in our skin and also give mucus the consistency it has to trap invaders
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
They lower the activation energy required
Hormones are made of what?
Lipids like Estrogen and Proteins like Insulin
How do proteins help with transporting substances?
Things like the Sodium-Potassium pump, Retinol-binding proteins that transport Vitamin A, etc.
Is protein ideal for energy?
No; Protein as energy is a last resource
Protein Turnover
The degradation and synthesis of protein
Protein Synthesis
Requires presence of essential amino acids in adequate amounts
Limiting Amino Acid
Present in lowest amount relative to body's needs
Protein Breakdown/Degradation
Free amino acids become apart of the amino acid pool
Deamination
Amino group converted to Urea
Nitrogen Balance
Nitrogen Consumed vs. Nitrogen Excreted; Protein Intake
Complete Proteins or High Quality Proteins
Provide all essential amino acids in amounts needed by the body so that they can be used to make the nonessential amino acids
Ex. Animal Proteins, Soy, and Quinoa
Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score
Value assigned to proteins that accounts for protein quality and digestibility; Based on a scale of 0-100
Incomplete Proteins
Do not contain all essential amino acids
Ex. Legumes, Grains, Vegetables
Complementary Proteins
Amino acid contents combined provide all essential amino acids
Ex. Rice and Beans
Health Benefits associated with Soy Consumption
Protection against certain cancers and CVD disease, and prevention of bone loss
RDA For Protein
0.8g per kg of body weight
AMDR For Protein
10%-35%
Health Benefits of Vegetarianism
Lowered risk of heart disease and rates of obesity
Concerns of Vegetariansim
Vitamin Defiency especially in B12
Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM)
Inadequate Protein Intake; Most common nutrient deficiency in hospital and nursing home populations in the United States and the most lethal form of malnutrition
Who is at the greatest risk for PEM?
Infants and Young Children
Marasmus
A condition of starvation characterized by emaciation, or skeletal appearance; Caused by inadequate protein and calorie intake
Kwashiorkor
Characterized by swollen appearance, especially the abdomen; Caused by low protein intake and altered gut bacterial populations
What can excess protein intake cause?
Increased risk of certain types of cancer, kidney disease, and heart disease