Lecture 8: historical returns, expected return, variance, standard deviation
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
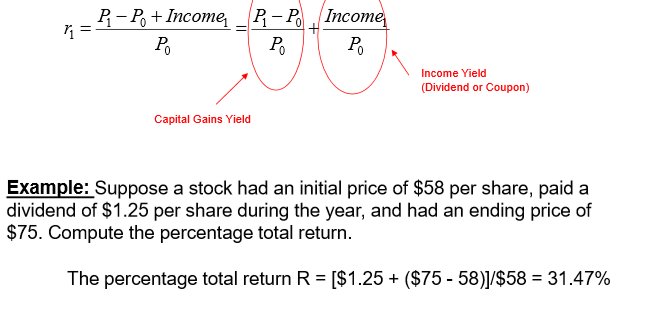
What is a historical return (HPR)?
The formula used to calculate the percentage return for a single period
What are the 4 types of assets?
Cash → short term, risk-free, liquid
Bonds → risk of interest rate, not default, longer maturity than cash
Large stocks → risk of default, debtholders paid first then equity holders
Small stocks → ownership of shares in publicly held small corporations
What is the market cap?
Market cap = number of shares x price
What kind of treasuries are more riskier than others?
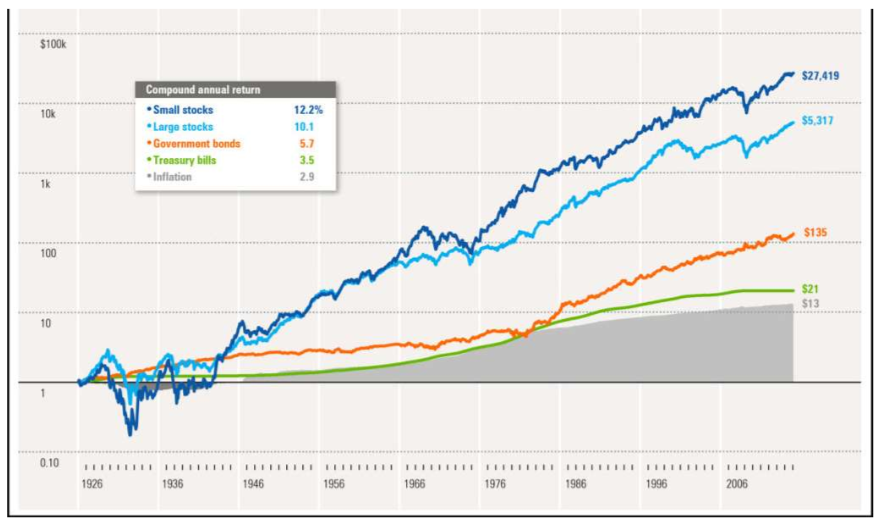
Small stocks most risky → more returns
Large stocks
Government bonds
treasury bills
What is variance and standard deviation?
The spread of a return → measure of how the return may deviate from its average (mean) value
standard deviation represents the spread of a normal distribution

What is the formula for variance?
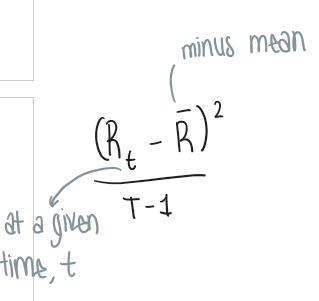
What is the formula for the average return (the mean)?
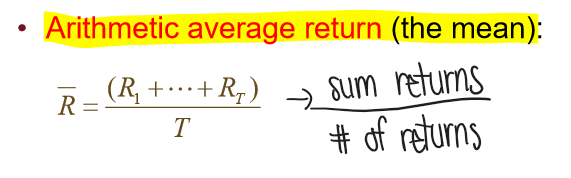
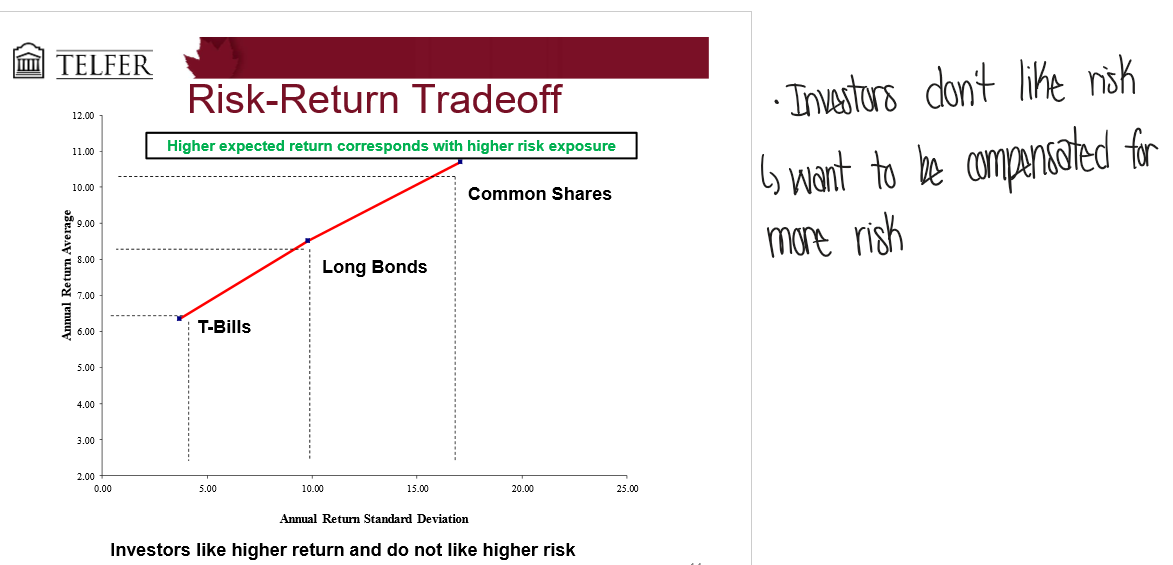
Why would investors buy more risky securities?
Investors don’t like risk
want to be compensated for risk
more compensation in exchange for higher risk (risk premium)
Risk premium = average (return - risk free rate)
What is the coefficient of variation (CV)?
Standard deviation / expected return
measure risk/unit of return
Why do we care about historical returns?
Historical data is a good predictor of future returns
past data to forecast the future
historical average return to estimate expected future return
historical standard deviation to estimate future standard deviation
What are some issues with historical data?
Issues with the sample → you can get different mean, standard deviation, variance depending on the period of sample used
need a lot of data (long sample period)
single stocks can be biased
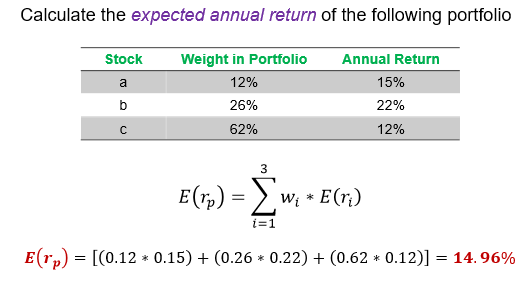
What is the formula for expected returns and risk?
What are portfolio measures? (positive & negative weights)
Portfolio: combination of securities
Positive weight: buy security
Negative weight: sell security
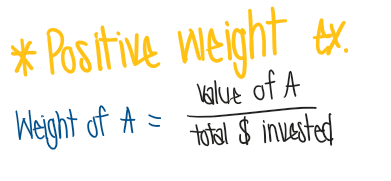
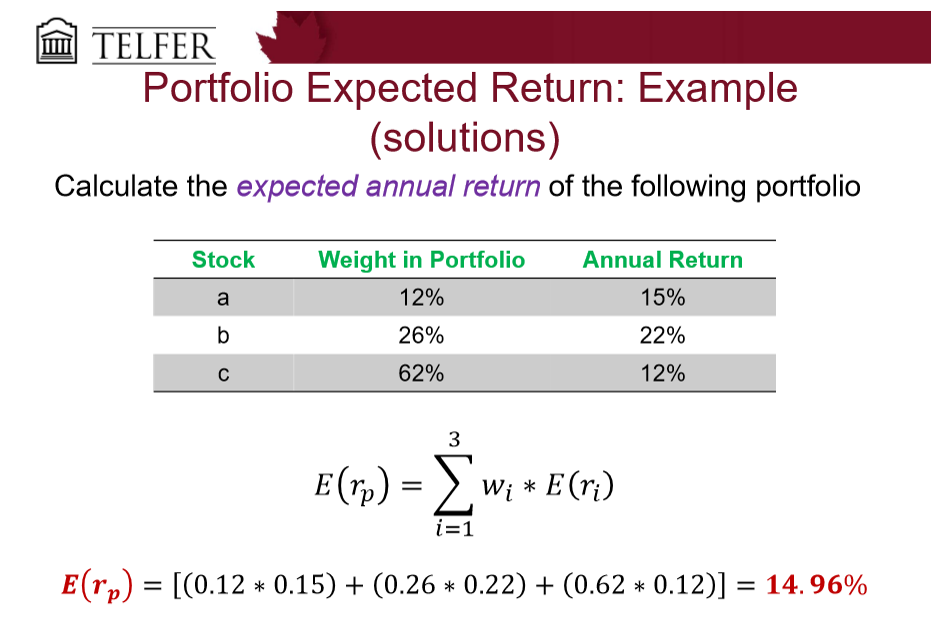
What is the portfolio expected return?
portfolio weight 1 x annual return 1 + portfolio weight 2 x annual return 2