NU 125 Mental Health Nursing: Mood Disorders + Depression
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Mood
pervasive and sustained emotion that has major influences on a person's perception of the world
Affect
external, observable emotional reaction associated with an experience
Mood continuum
Range of emotional states from depression to mania
Normal emotional states
Sad, euthymia, happy
Euthymia
normal range of moods and emotions
There are many different ________ of depression.
types
Dysthymia
a form of depression that is not severe enough to be diagnosed as major depression
Substance/medication induced depression
Depressed mood and physiological affects due to direct use of a substance or medication
Depression occurs due to..
a combination of genetics, biochemical, and psychosocial experiences
Depression is more common in..
women
Risk factors for depression
Genetics
Prior depressive episodes
Lack of social supports
Stressful life events
Multiple medical problems
Substance use
Depression can occur..
from childhood to the elderly
Depression ranges from..
transient to severe
DSM 5: Major Depression
Depressed mood or anhedonia with impairment in function for at least 2 weeks and at least 5 of the listed symptoms
Symptoms of Major Depression
1. Decrease or increased in appetite
2. Psychomotor agitation or slowing
3. Insomnia or hypersomnia
4. Fatigue or anergia
5. Feelings of worthlessness, excessive guilt
6. Decreased concentration or decisiveness
7. Suicidal ideation
Anhedonia
inability to feel pleasure
Common neurotransmitter disturbances with depression
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Areas of the Brain Impacted by depression
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Hypothalamus
Limbic structures
Frontal cortex
Medications for Depression
SSris/SNRis
What do SSRIs and SNRIs do?
Increase serotonin and or norepinephrine
When assessing symptoms of depression, the nurse should assess what 4 areas?
Affective
Cognitive
Behavioral
Physiological
Affective
despair, feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, sadness, anger, anhedonia, anxiety
Cognitive
delusional, confusion, indecisiveness, decreased concentration, self-deprecating, thoughts of self-harm, suicidal ideations
Behavioral
tearfulness, social isolation, anger outbursts, self-harm
Physiological
decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, psychomotor slowing, psychomotor agitation
Levels of Depression
Transient
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Transient depression
normal, "the blues"
Affective symptoms of transient depression
"the blues"
Cognitive symptoms of transient depression
some difficulty getting mind off one's disappointment
Behavioral symptoms of transient depression
some crying
Physiological symptoms of transient depression
feeling tired and listless
Mild depression
less severe symptoms, but can last for years
Affective symptoms of mild depression
Anger and anxiety
Cognitive symptoms of mild depression
preoccupied with loss
Behavioral symptoms of mild depression
tearful, age-related regression
Physiological symptoms of mild depression
insomnia, anorexia, pain sensations, headaches
Moderate depression
dysthymic disorder persistent depressive disorder
Affective symptoms of moderate depression
helpless, powerless
Behavioral symptoms of moderate depression
slowed physical movements, slumped posture, limited verbalization
Cognitive symptoms of moderate depression
slowed thinking processes, difficulty with concentration
Physiological symptoms of moderate depression
anorexia, overeating, sleep disturbance, or headaches
Severe depression
major depressive disorder and bipolar depression
Affective symptoms of severe depression
feelings of total despair, worthlessness, flat affect, and anger
Behavioral symptoms of severe depression
psychomotor retardation, curled-up position, absence of communication, and social isolation
Cognitive symptoms of severe depression
presents of psychosis, prevalent delusional thinking, delusions of persecution and somatic delusions, confusion, suicidal thoughts
Physiological symptoms of severe depression
general slow down of the body
Most Effective Treatment Modality for Depression
Antidepressants paired with talk therapy
Other treatment
Antidepressants
Light box therapy
Talk therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
Electroconvulsant Therapy (ECT)
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)
How long do antidepressants take to work?
2-6 weeks for mood changes
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
antidepressant medications that block the enzyme monoamine oxidase
What do MAOIs result in?
elevated levels of norepinephrine
Why are MAOIs not a first-line treatment?
risk of hypertensive crisis and other fatal side effects
Risk of hypertensive crisis due to increased epinephrine levels in blood is associated with..
foods high in tyramine
Foods high in tyramine
cheese, soy sause, pepperoni, salami, processed meats, bananas, wine, bear, nuts
phenelzine (Nardil)
MAOI antidepressant
MAOIs also have many..
drug-drug interactions that can lead to hypertensive crisis, such as some decongestants
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA)
antidepressants that prevent the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin and require medical clearance before starting
Why is medical clearance needed with TCAs?
EKG changes
What should be noted with TCAs?
Overdose is very dangerous
Discontinue SLOWLY
Assess serum levels to assess toxicity
Narrow window of safety
Side effects of TCAs
anticholinergic effects, orthostatic hypotension, lowered seizure threshold
Anticholinergic effects
dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention
nortriptyline (Pamelor)
tricyclic antidepressant
Selective Serotonin and Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI and SNRI)
front line and most widely used antidepressants that inhibit reuptake of serotonin at the pre-synaptic neuron, increasing levels
Side effects of SSRI and SNRI
GI disturbances and sexual disturbances, and should not be stopped abruptly
Can SSRIs and SNRI be used for other disorders?
yes
fluoxetine (Prozac)
SSRI
escitalopram (Lexapro)
SSRI
citalopram (Celexa)
SSRI
Serotonin Syndrome
potentially life-threatening condition from excess serotonin with symptoms that range from mild to severe
SHIVERS mnemonic for serotonin syndrome
Shivering
Hyperreflexia and myoclonus
Incr. temp
Vital signs instability
Encephalopathy
Restlessness
Sweating
Examples of contraindications for Serotonin Syndrome
SSRI
St. John's Wort
Tryptophan
MAOI
Agents that stimulate the release of seratonin, such as ectasy
Serotonin syndrome explains why..
one should never take 2 SSRIs at once
Black Box Warning
on all antidepressants and warns for increased risk of suicidality in children, adolescents, and adults with major depressive disorder
Electroconvulsant Therapy (ECT)
treatment that induces a grand mal seizure and is performed in the PACU under general anesthesia
What is ECT effective for?
depression and mania
When is ECT considered?
after trials of antidepressants are ineffective or pregnancy
What is prioritized immediately after treatment?
post-operative nursing care, such as airway, vitals, LOC
Typical ECT course is _______ treatments.
12
Risk of ECT
short term memory loss, especially in combination with medications such as Lithium
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS)
use of high frequency and low frequency to stimulate prefrontal cortex done in 40 minute sessions, 3-5 times a week for 4-6 weeks
Is anesthesia required for RTMS?
no
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
type of talk therapy that addresses perceptions and negative thoughts and focuses on the client's thoughts that impact behaviors
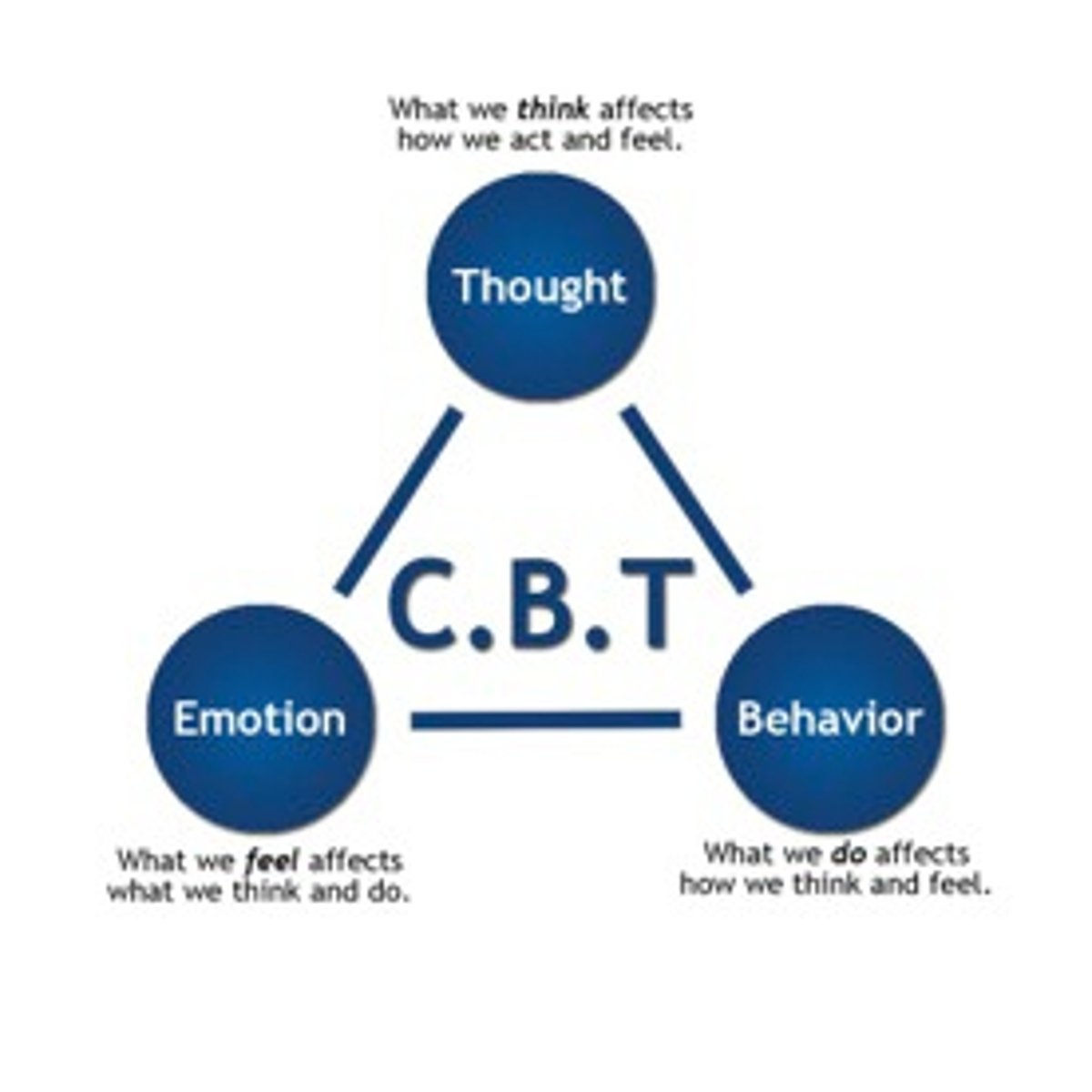
CBT can be used for..
many disorders
When assessing a patient for depression, the nurse should prioritize ..
safety and screen for suicide or homicidal ideation
Behaviors/Cues the Nurse may Look for
General presentation
Mood
Affect
Thought Content
Thought process
Perceptions
Behaviors
Sleep pattern
Functional status
Screening tools for Depression
Hamilton Depression Rating Scale
Nursing Interventions for Depression
Maintain client safety with suicide precautions
Management of the illness
Client and family education
Maintaining Client Safety
Remove access to lethal means
Address all needs and implications
Teach and educate about coping and symptoms
Facilitate access to support
Management of illness
treatment of symptoms and use of medications
Client and family education
Relapse prevention
Recovery process
Develop a crisis plan
Intended outcome for depressed patients
The patient will not harm self while hospitalized