Forces and motion
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
distance definition
total length between 2 points/
how much ground an object has covered during its motion
speed definition
total distance travelled per unit of time
displacement definition
the overall change in an objects position/
how far an object has travelled from its starting position in certain direction
velocity
rate of change of displacement of an object
acceleration
rate of change of velocity of an object
What is instantaneous speed/ velocity
Speed/ velocity of an object at any given point in time
What does curved line of s / t graph
accelerating - chaning v
How to find instantaneous velocity from distance- time graph:
Draw tangent at required time
Find grad
Displacement-Time graph characteristics:
Grad = velocity
Y-intercept = initial displacement
Diagonal straight line = constant v
Curved line = acceleration
Velocity- time graph characteristics:
Slope = acceleration
Y-intercept = initial velocity
Straight line = uniform acceleration
Curved line= non-uniform acceleration
Area under curve = displacement/ distance travelled
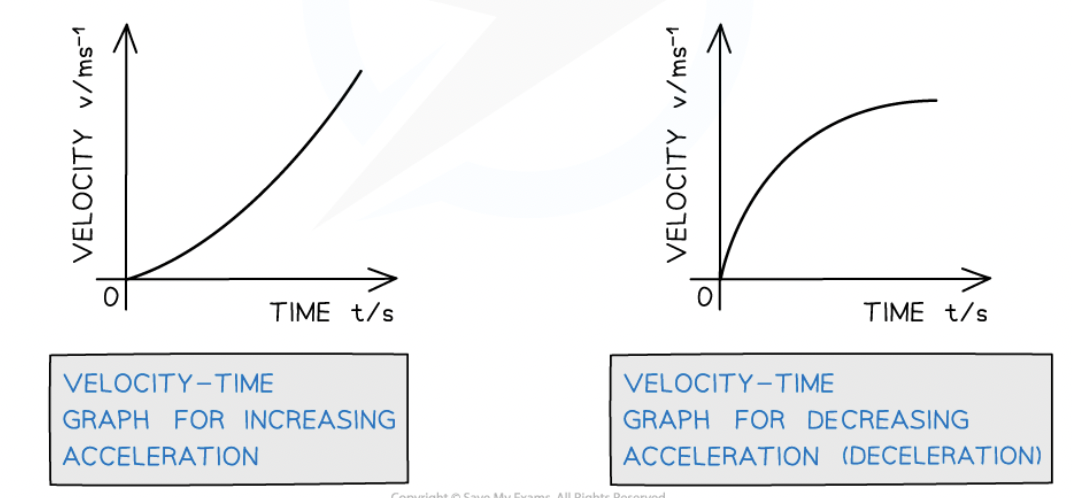
Acceleration-time graph:
Slope = meaningless
Horizontal line = constant acceleration
Area under curve = change in velocity
Acceleration of free fall, g, is defined as:
The acceleration of any object in response to the gravitational attraction between the earth and the object
Stopping distance consists of two parts:
Thinking distance
Braking distance
The stopping distance increases considerably with the ____ of a car
speed
The thinking distance ________ _______ with speed
increases proportionally
The braking distance increases at an even ____ rate with speed
faster
Thinking distance is defined as
The distance travelled by the vehicle from when the driver sees a problem and the brakes are applied
How to calculate thinking distance
Thinking distance = Initial speed × Reaction time
Braking distance is defined as:
The distance travelled by the vehicle after the driver has applied the brake
What is the braking distance of the vehicle is proportional to?
square of the initial speed of the car, u2
vehicle’s kinetic energy (½ mv2) must be dissipated by the brakes in order to come to a stop
Work done by brakes:
Work Done = Braking Force × Braking Distance = ½ mv2
Time of flight:
how long the projectile is in the air
Maximum height attained:
the height at which the projectile is momentarily at rest
Range:
the horizontal distance travelled by the projectile
when asked to calculate horizontal range of an oblique projectile vertical displacement is usually 0m
The only force acting on the projectile, after it has been released, is ____
gravity
If the resultant force is at an angle, it will change the ______ of the body
direction
SI units for Newtons
kg m s–2
What is free fall?
An object in free fall is falling solely under the influence of gravity
In the absence of air resistance, all bodies near the Earth fall with ___ ____ _______ regardless of their mass
the same acceleration
Weight is a _____
Mass is a _____
vector
scalar
Tension definition
The force experienced by a cable, rope, or string when pulled, hung, rotated or supported
Normal Contact Force/reation force:
The force arising when an object rests against another object acting at a 90° angle to the plane of contact
normally labelled as _ or _ on free body diagrams
N or R
What was normal force arise because of
newton’s 3rd law
What is upthrust:
+equation
The upward buoyancy force acting on an object when it is submerged or partially submerged object experiences in a fluid
Upthrust= (h2- h1)pgA
What is friction:
The force that arises when two surfaces are in contact with each other/ FORCE THAT OPPOSES MOTION
The magnitude of the drag force depends on several factors, including:
The speed of the object
The object’s shape and texture
The density of the fluid
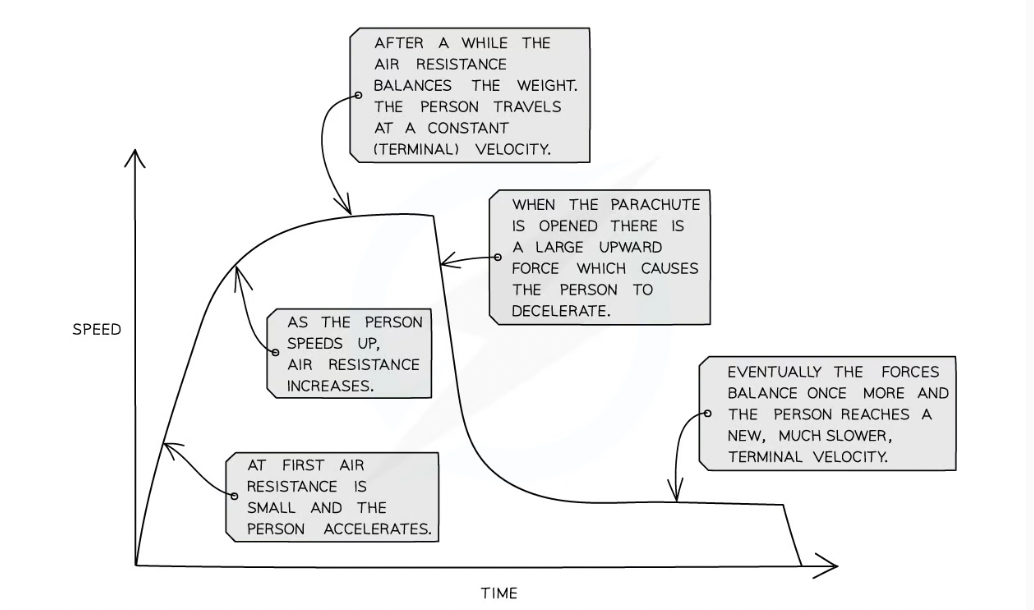
what is terminal velocity?
The drag force will increase until it is equal in magnitude to the weight of the object
This leads to the object reaching a steady speed, known as its terminal velocity
Opposing drag forces reduce the net force acting on an object and as a result, reduce the magnitude of the acceleration
What is it called when the drag force is equal to the gravitational pull on the body, and the body will no longer accelerate and will fall at a constant velocity
terminal velocity
V -T graph of parachutist
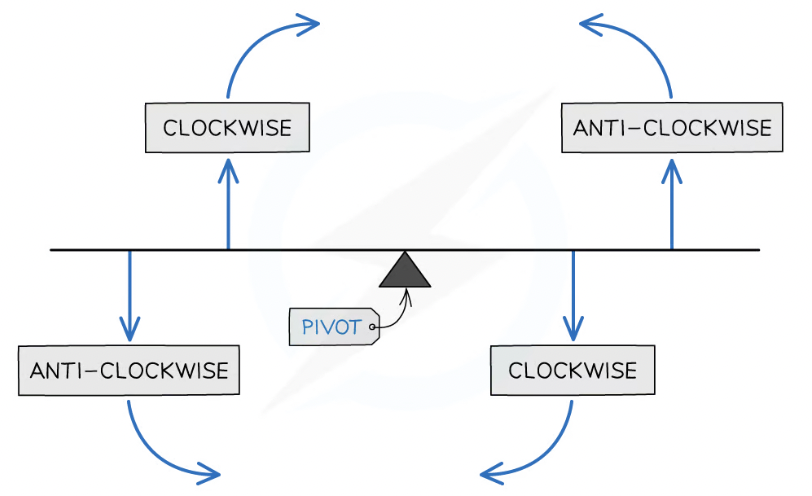
What is a moment?
turning effect of a force
/ force multiplied by the perpendicular distance between the line of action of the force and the turning point
Moment equation (given)
Moment (N m) = Force (N) × perpendicular distance from the pivot (m)
Principle of moments:
For a system to be in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about a point must be equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments (about the same point)
Uniform beam
weight will act as its centre of gravity
Moments diagrams
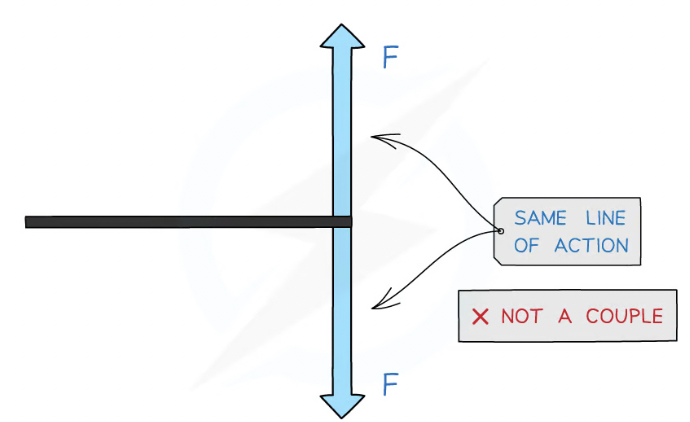
What is a couple
pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces (act on same plane) that acts to produce rotation only
A couple consists of a pair of forces that are:
Equal in magnitude
Opposite in direction
Perpendicular to the distance between them
What is the resultant force of couples and what does this mean
zero
according to newton’s 2nd law, object does not accelerate
Unlike moments of a single force, the moment of a couple doesn’t depend on a _____
pivot
The moment of a couple is equal to:
Force × Perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the forces
What is torque
moment of a couple
/ sum of the moments produced by each of the forces in a couple
Units of torque equation (given)
T=Fd
τ = torque (N m)
F = one of the forces (N)
d = perpendicular distance between the forces (m)
The forces given might not always be perpendicular to the distance between them
find the component of the force vector that is perpendicular by resolving the force vector.The forces that make up a couple cannot share the same line of action which is the line through the point at which the force is applied.
centre of mass of an object is
point at which the weight of the object may be considered to act
For symmetrical objects with uniform density, the centre of mass is located at the ___ ___ _____
point of symmetry
An object is stable when its centre of mass lies above its _____
base
stability
The wider base an object has, the lower its centre of mass and it is more stable
The narrower base an object has, the higher its centre of mass and the object is more likely to topple over if pushed
A system is in equilibrium when all the forces are balanced. This means:
There is no resultant force
There is no resultant torque
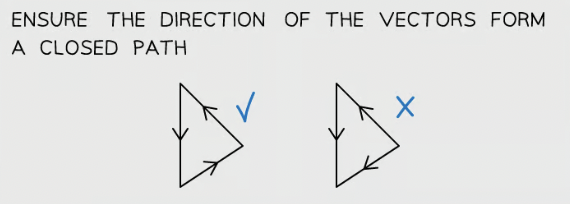
Coplanar forces can be represented by ____ ______
vector triangles
In equilibrium, coplanar forces are represented by ____ vector triangles
closed
equilibrium represented in diagram
1 Pa is the same as ___
1 N/m2
units of equation of hydrostatic pressure P=hpg
P= Pressure (pa)
h=change in height (m)
p= density (kgm-3)
g=acceleration due to gravity (ms-2)
Archimedes’ principle states:
+WHY
An object submerged in a fluid at rest has an upward buoyancy force (upthrust) equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
Upthrust= (h2-h1)pgA= Vpg = mg= W
The object sinks until
the weight of the fluid displaced is equal to its own weight
object floats when the magnitude of the upthrust equals the _____ of the object
weight
magnitude of upthrust can be calculated by(learn):
F=pgV
F= upthrust/ buoyancy force (N)
p=density of a fluid (kgm-3)
g=acceleration due to gravity (ms-2)
V= volume displaced (m3)
how is that equation devised
Since m = ρV, upthrust is equal to F = mg which is the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
total pressure=
atmospheric pressure + hydrostatic pressure
Atmospheric pressure (also known as barometric pressure) is equal to ______
101 325 Pa
Work is defined as
The amount of energy transferred when an external force causes an object to move over a certain distance
If the force is _____ to the direction of the object's displacement, the work done can be calculated using the equation: W = Fx
parallel
What units mean in W = Fx
W = work done (J)
F = average force applied (N)
x = displacement (m)
SI unit for energy
kg m2 s–2
1 Joule definition
The energy transferred to (or work done on) an object when a force of 1 N acts on that object parallel to its motion through a distance of 1 m
energy equations to learn

Transfer of energy = Work Done
Thermal (heat) is the work done on or by a system to transfer heat
E = mcΔT
m = mass (kg)
c = specific heat capacity (J kg-1 K-1)
ΔT = change in temperature (K or °C)
Elastic potential energy is the work done in stretching or compressing an object
E = ½ Fx = ½kx2
F = stretching or compressing force (N)
x = extension (or compression) (m)
k = force constant (N m-1)
Nuclear is the work done by nuclei during the processes of fusion and fission
E = Δmc2
Δm = mass defect (kg)
c = speed of light
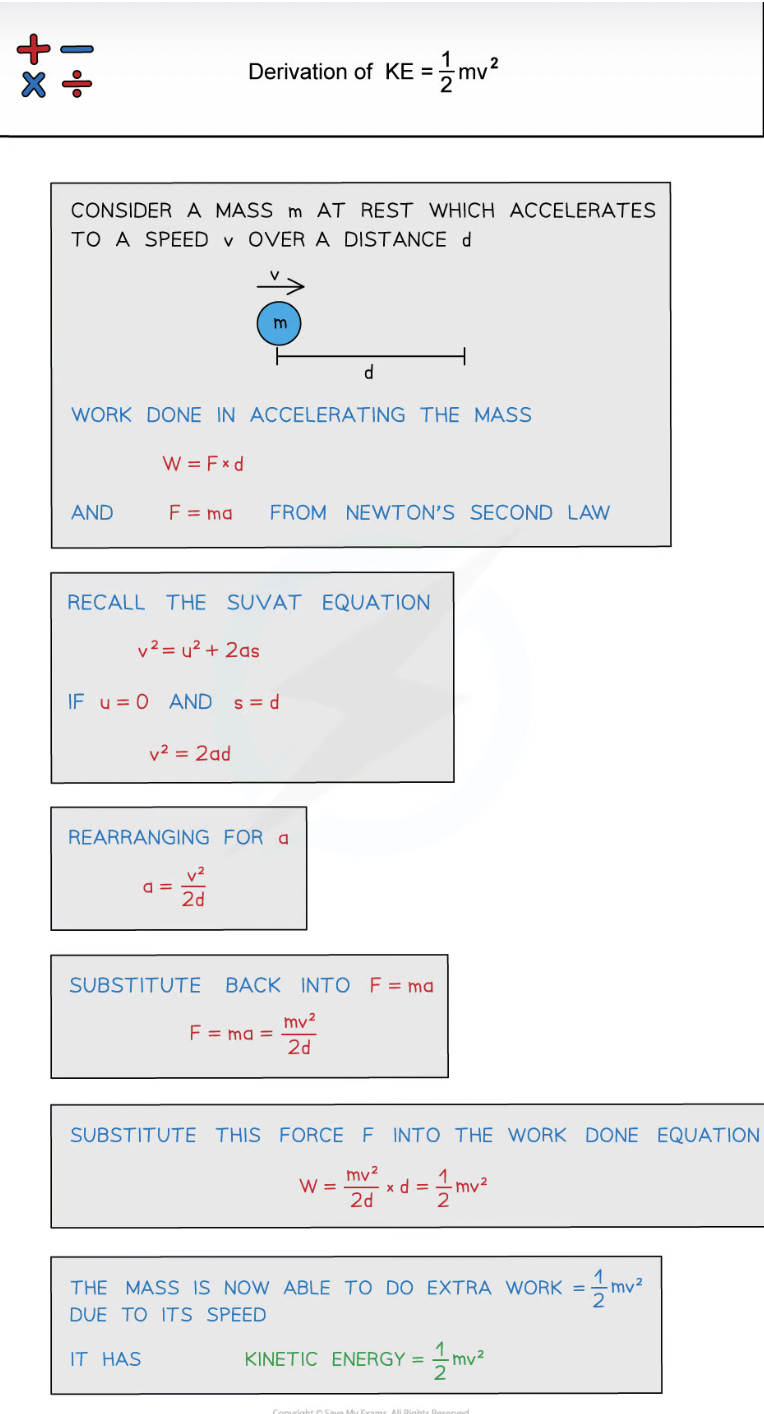
derivation of KE equation
derivation of GPE equation

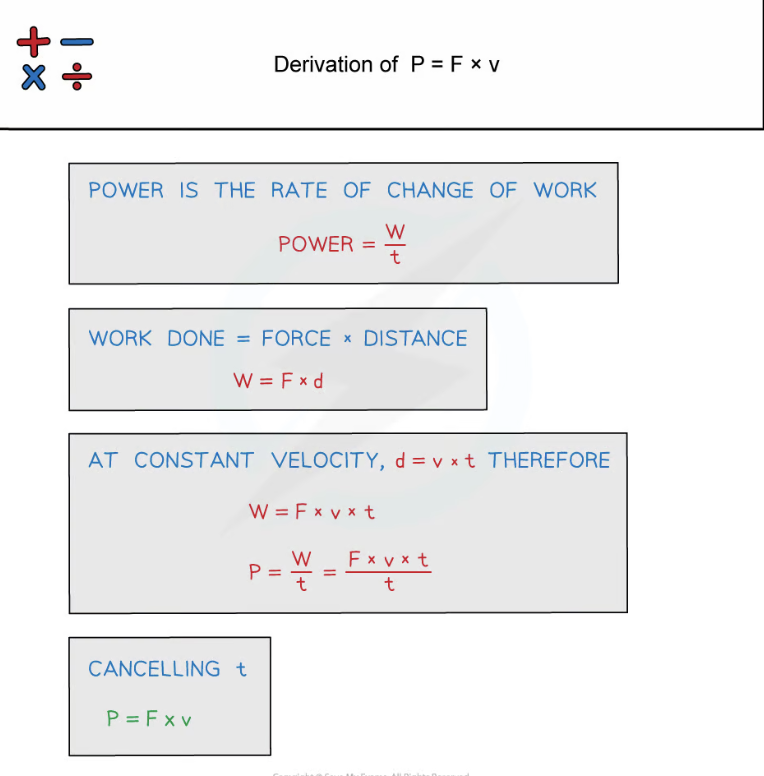
power of a machine is
rate at which it transfers energy or the work done per unit time
units of P=Fv (given)
P= power (W)
F= force (N)
v= velocity (ms-2)
When to use P=Fv
constant force moves a body at constant velocity. Power is required in order to produce an acceleration
The force must be applied in the same direction as the velocity
deriving P=Fv
Newton's First Law states:
A body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
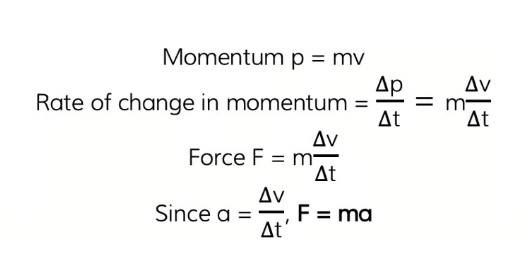
Newton's Second Law states:
The resultant force is equal to the rate of change in momentum. The change in momentum is in the same direction as the resultant force
What can newton’s 2nd law also be rewritten as:
F=ma (learn)
How if F=ma derived from the definition of momentum
Newton's Third Law states:
If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B will exert a force on body A of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction
Newton’s Third Law force pairs must act on two ___ objects
Newton’s Third Law force pairs must also be of the ____ ___e.g. gravitational or frictional
different
same type
Linear momentum (p) is defined as the product of mass and velocity: P=mv (given)
P= Momentum (kg ms-1)
m= mass (kg)
v= velocity (ms-1)
momentum is a _____
vector
Force is defined as
rate of change of momentum (final momentum minus the initial momentum) on a body
F= ▵p/▵t (given)
F= Force (N)
▵p= change in momentum (kg ms-1)
▵t= change in time (s)
How to find ▵p
▵p= pf -pb
change in momentum= final p - before p
what can average force be worked out from?
F=▵p/▵t
F=resultant force
How to find impulse equation:
force and momentum equation can be rearranged to find the impulse. cuz impulse, I, is equal to the change in momentum:
I = FΔt = Δp = mv – mu
unit for impulse
Ns