Biology (External Revision)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Biodiversity,
Refers to how many different species work together in an ecosystem.
Biotic factors
living organisms
abiotic factors
physical environment
species richness
the number of species present in an ecosystem
relative species abundance
the number of individuals present for each species in an ecosystem
percentage cover
the percentage of the quadrat that a species takes up
percentage frequency
the percentage of quadrats in which a species appears
Simpson’s diversity index
the combined ratio of individuals in each species to the total individuals in an ecosystem – a quantitative measure of biodiversity
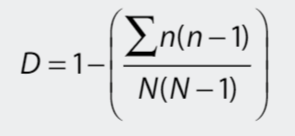
temporal scale
the time period over which an ecosystem is studied
spatial scale
how much area a studied ecosystem covers
Limiting factor
Environmental conditions (abiotic, could also be a biotic condition) that restrict how well an organism can survive and thrive in a location
clade
A group comprising all of the descendants of a particular ancestor organism
symbiosis
The relationship in which at least one species benefits from the interaction.
parasitism
one benefits, the other is harmed
commensalism
one benefits, the other is unaffected
mutualism
both benefit
photosynthetic efficiency
how well a producer converts light energy into the chemical energy of carbohydrates
autotroph (producer)
an organism that can produce its own organic compounds from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide
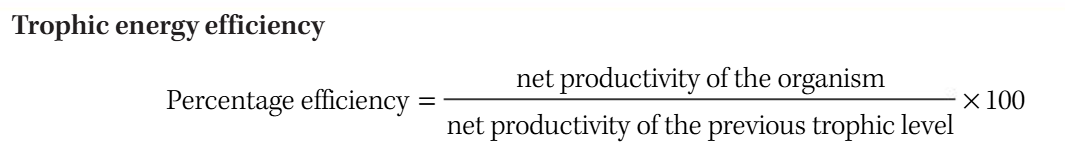
Energy Loss
10% of the energy at one trophic level is passed on to the next level with the rest (90%) being transformed by metabolism into heat energy and lost to the surroundings orbody waste
Calculating energy efficiency
ecological niche
the role and space that an organism fills in an ecosystem, including all its interactions with the biotic and abiotic factors of its environment
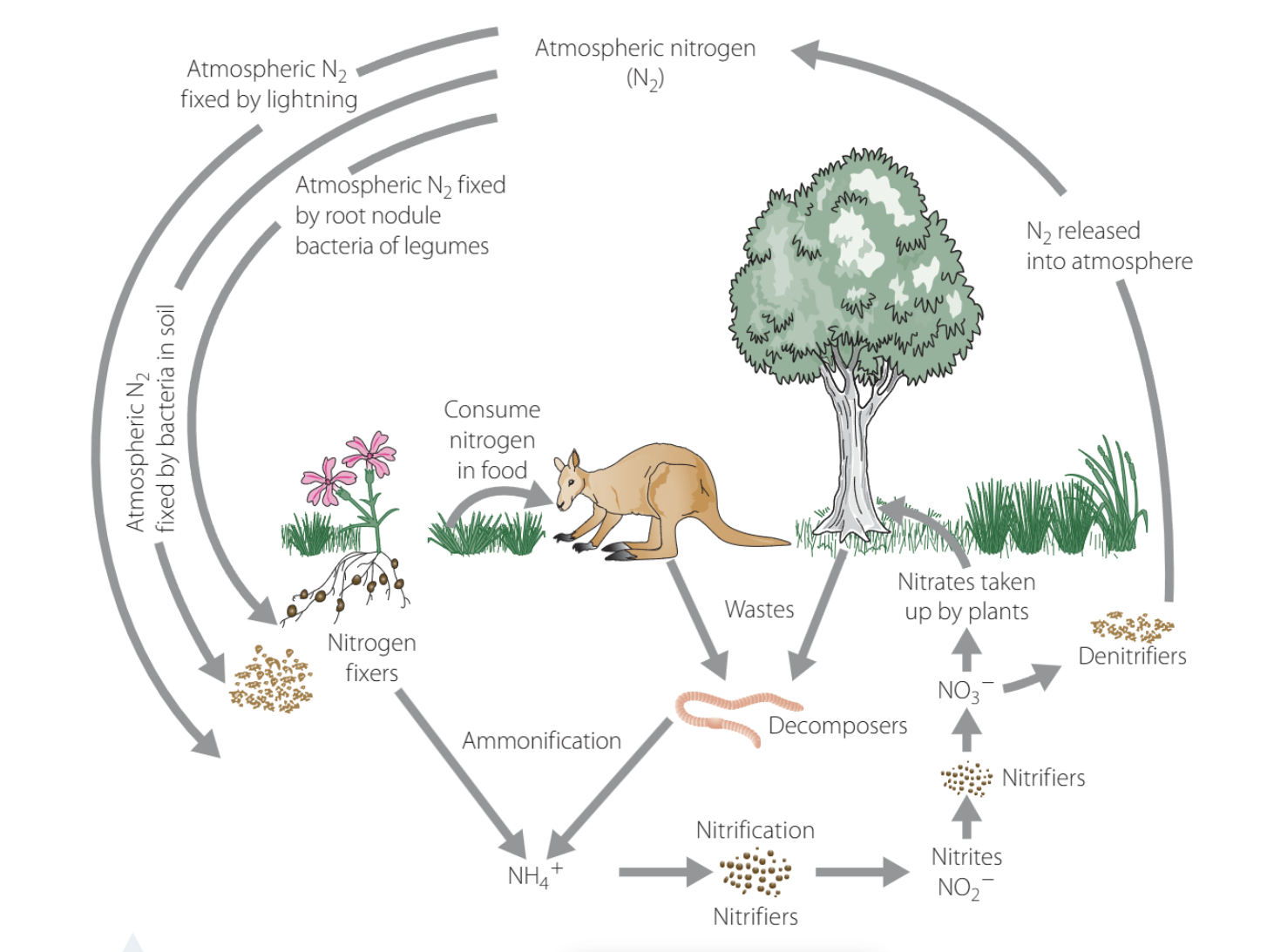
Nitrogen Cycle
N₂ (gas) in the atmosphere → NH₄⁺ (ammonium) by nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
NH₄⁺ → NO₂⁻ (nitrite) → NO₃⁻ (nitrate) by nitrifying bacteria.
NO₃⁻ → N₂ (gas) again by denitrifying bacteria.
Resource Partitioning
The creative use of space and time that reduces competition between species and allows many unique ecological niches to exist in the same area
Fundamental niche
The full potential range of conditions and resources a species can use.
Realized niche
The actual range a species occupies due to competition and other limits.
Competitive exclusion principle
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in an ecosystem. And if so, they will compete with each other in the overlapping areas until one out-competes the other and the other retreats.
keystone species
A species that has a major impact on its ecosystem, keeping it balanced and diverse.
carrying capacity
the maximum population size of a species that can be supported in a given environment.
Population growth rate
Question: Calculate the growth rate of a population of 1000 individuals where, every year, 100 individuals are born, 65 individuals immigrate into the population, 37 individuals die and 25 individuals emigrate to another population.
Answer: 103

Lincoln Index

Random distribution
Organisms are scattered irregularly; one’s location doesn’t affect others. Common in plants.
Uniform distribution
Organisms are evenly spaced; one’s location affects how close others can be. Seen in animals with territories.
Clumped distribution
Organisms group together in patches; often due to social behavior or favorable conditions.
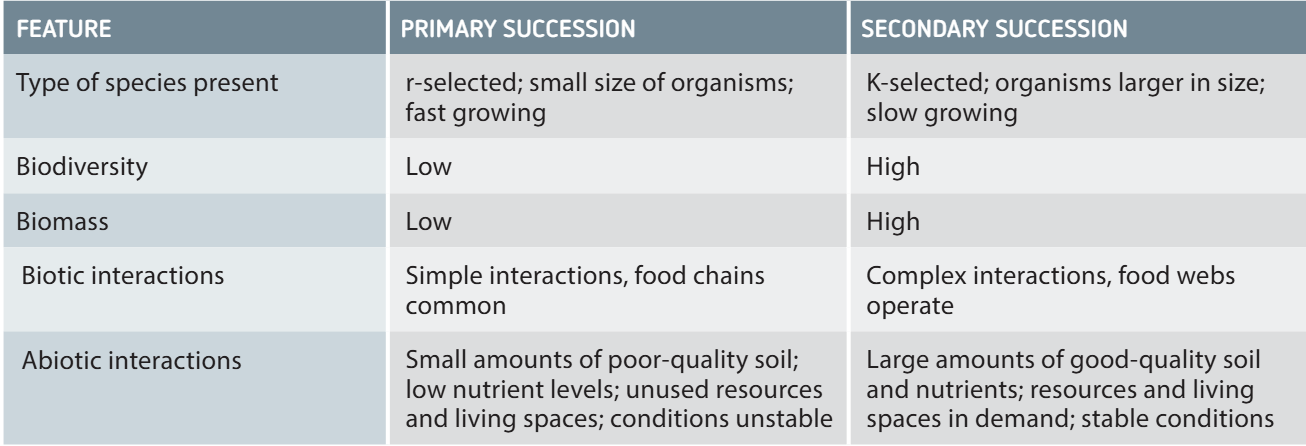
What is Primary succession and its steps:
Colonisation of plants on a barren land, resulted from a catastrophic event (i.e, tsunamis volcanic eruptions)
Pioneer species (like lichens) break down rock with its acid, forming cracks in the rock allowing mosses to grow and start forming soil.
Small plants (grasses, ferns) grow once soil develops → followed by shrubs and trees.
Over a long time, a stable climax community (e.g., forest) forms.
r-selected
small size and fast growing organisms found during primary succession
K-selected
organisms larger in size and slow growing found during secondary succession
What is Secondary succession and its steps:
Occurs in areas where soil already exists but vegetation has been removed (e.g., after fire, farming, floods, or human intervention).
Plants regrow faster than in primary succession due to fertile soli and stable conditions → grasses → shrubs → trees → eventual climax community.
climax community
the end-point in a community succession where the community has become relatively stable, e.g. old-growth forests and rainforests
Features of Primary and Secondary succession
habitat fragmentation
the process by which areas of a habitat are lost, resulting in a large continuous habitat being broken up into smaller, more isolated habitats