Dermatology Lecture 3 Acne, Rosacea... (Sandy)
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
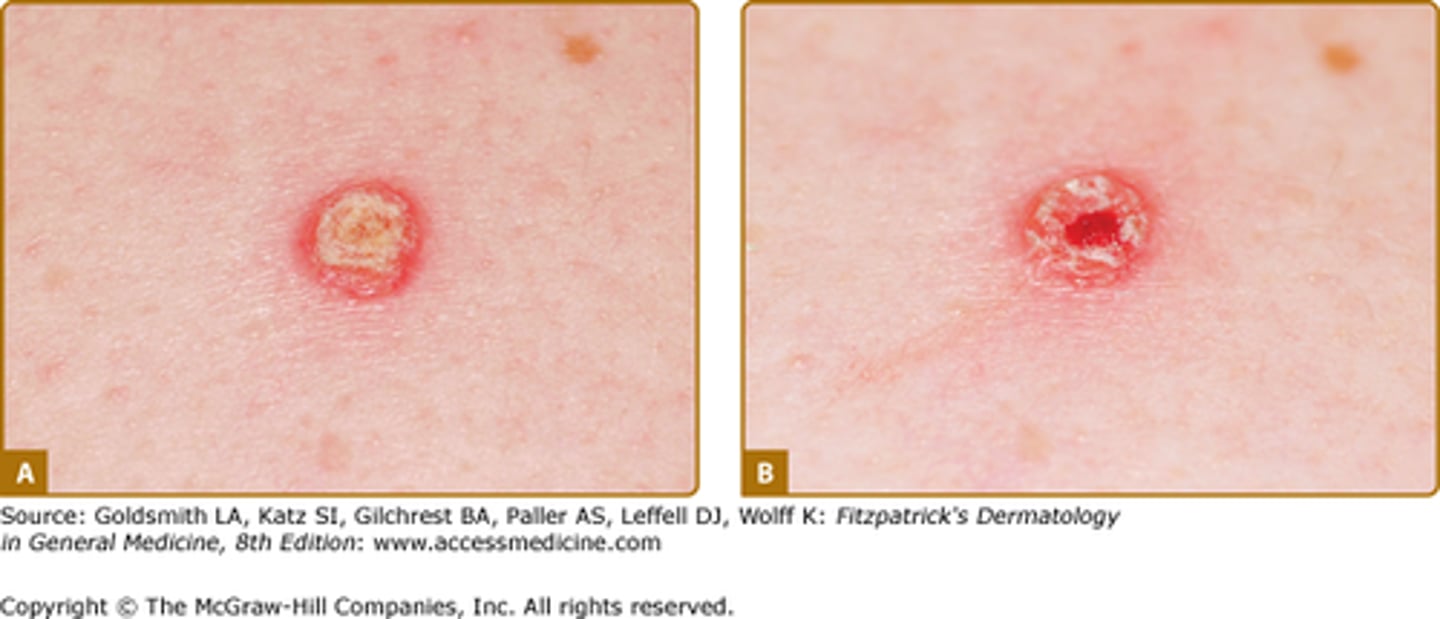
Pin-point bleeding when scale is removed
Auspitz sign
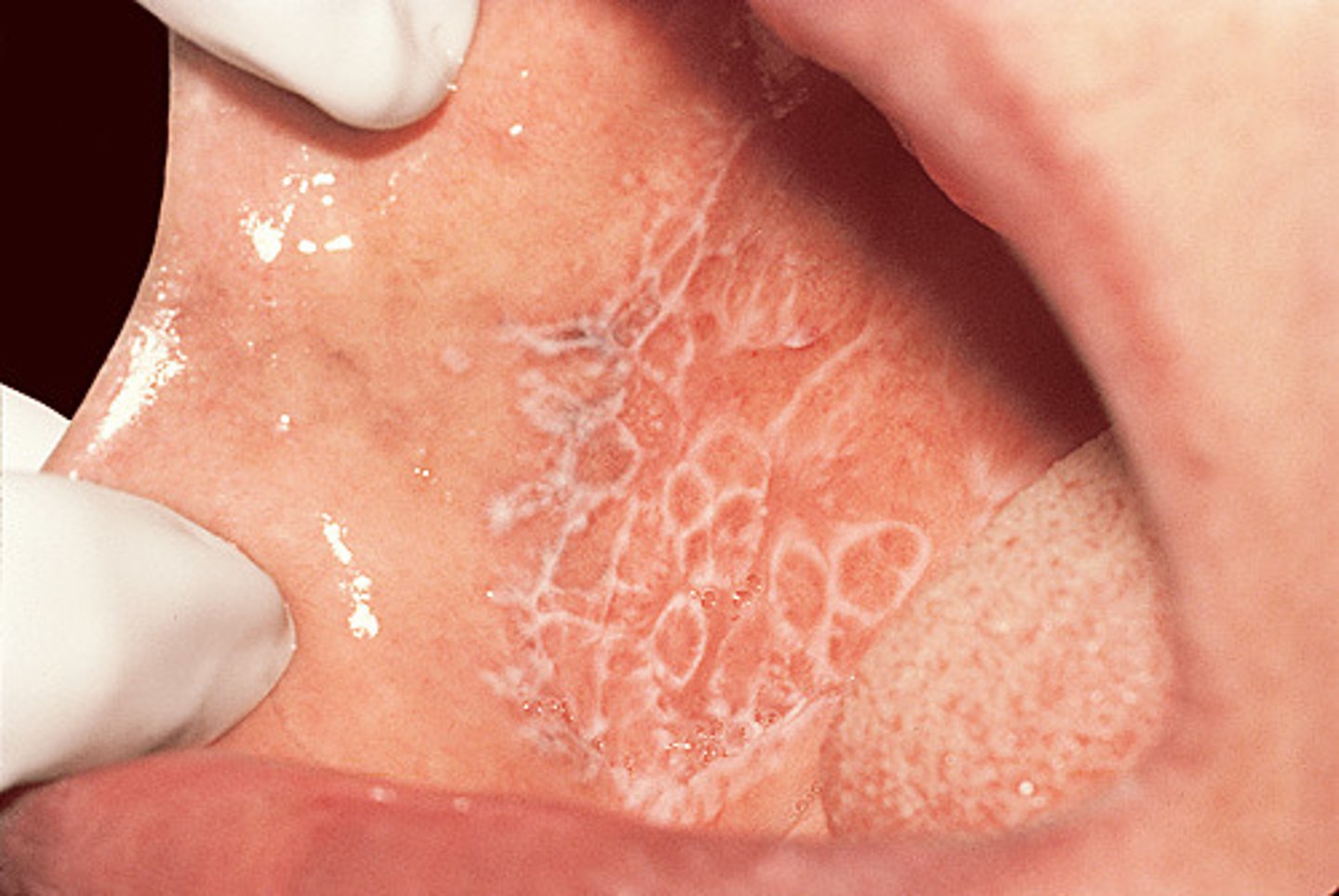
White or gray streaks on the surface of a
lesion
Wickhams straie
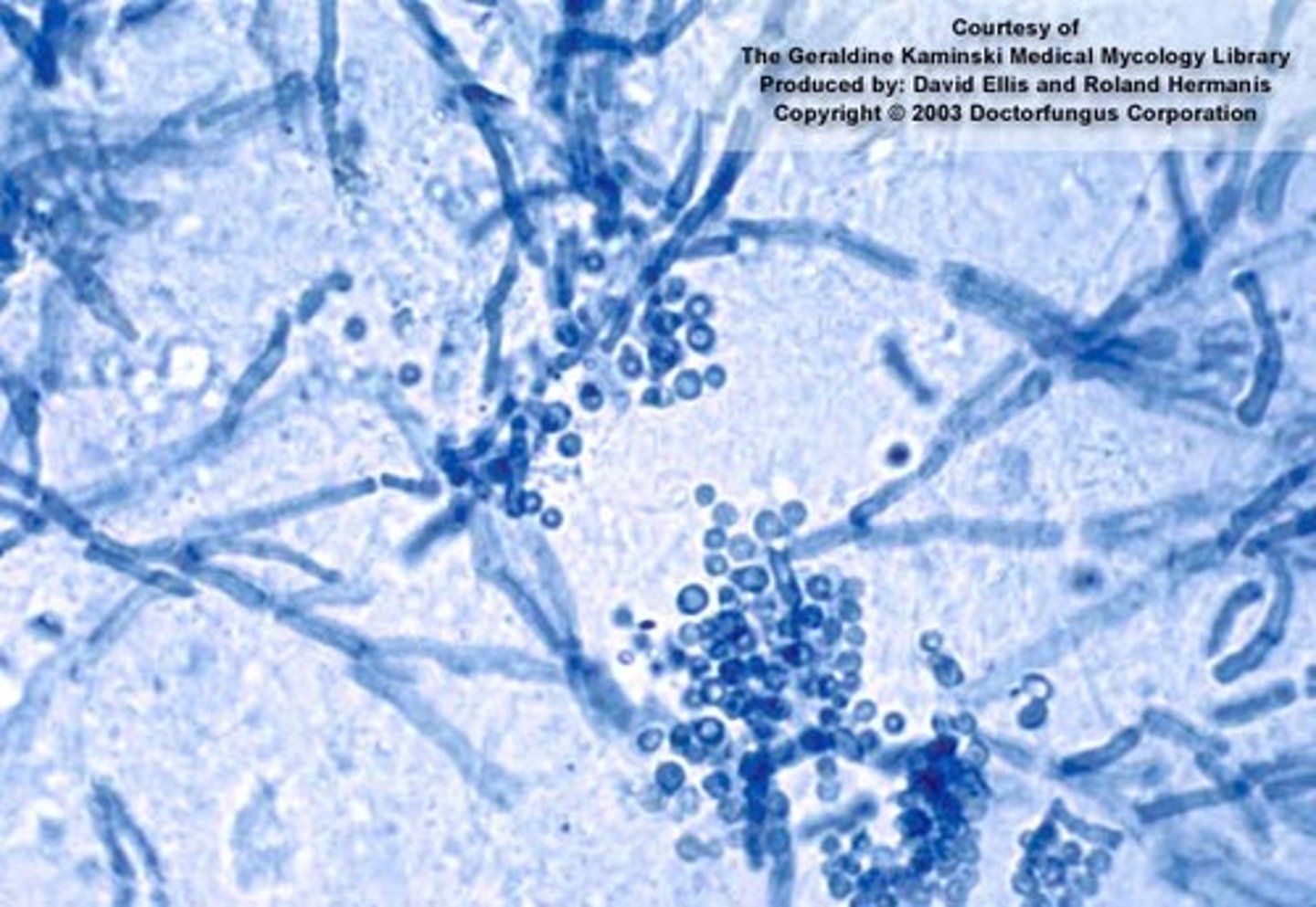
An inflammation that causes scaling and itching of the upper layers of the skin or scalp. Essentially dandruff
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis most commonly occurs on areas with increased ____ activity
Sebaceous gland activity
Face at eyebrows, nasolabial folds, posterior ear, scalp, groin, genitalia
Erythematous plaques with fine white scaling. Sometimes with a yellow greasy appearance.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The etiology of Seborrheic dermatitis is complex but it is potentially due to a lipophilic yeast called?
Malassezia Furfur
Seborrheic dermatitis increased in _____ and _______ pt
HIV; Parkinsons
A skin condition in infants in which the scalp develops patches of yellow, crusty scales. Seborrheic dermatitis in infants
Cradle cap
How do you tx Seborrheic dermatitis located on the scalp?
1. Topical Shampoos: Antifungal (Ketoconazole, Ciclopirox)
2. Selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione, T Gel/tar shampoos
Ketokonazole shampoo is extremely useful for patients with _____
Seborrheic dermatitis
How do you tx Seborrheic dermatitis on the face?
1. Topical antifungal cream (Ketoconazole, Ciclopirox, Clotrimazole)
2. May add a low potency (hydrocortisone) topical steroid 3-5 days for flare PRN
How do you tx Seborrheic dermatitis on the eyelids (blepharitis)?
baby shampoo one to
two times a day
What is an appropriate topical for children and infants with seborrheic dermatitis and cradle cap?
Baby/olive oil (or other emollient) then baby shampoo and use a soft bristled brush
Chronic inherited uncontrolled inflammatory disease that can be gradual in onset or sudden. The inflammation causes hyperkeratinization and dysregulation of
immune function (overactive T Cells).
Psoriasis
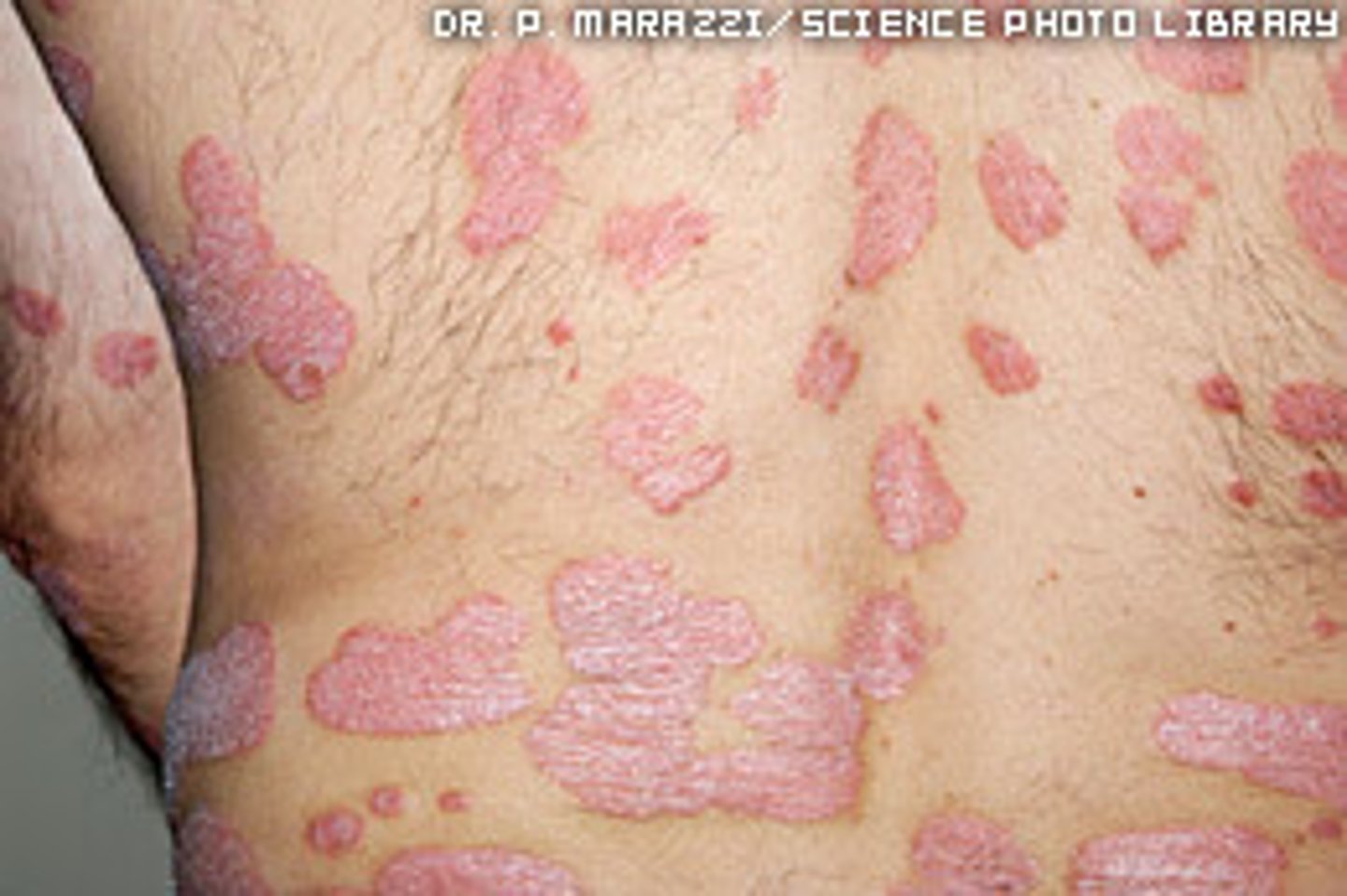
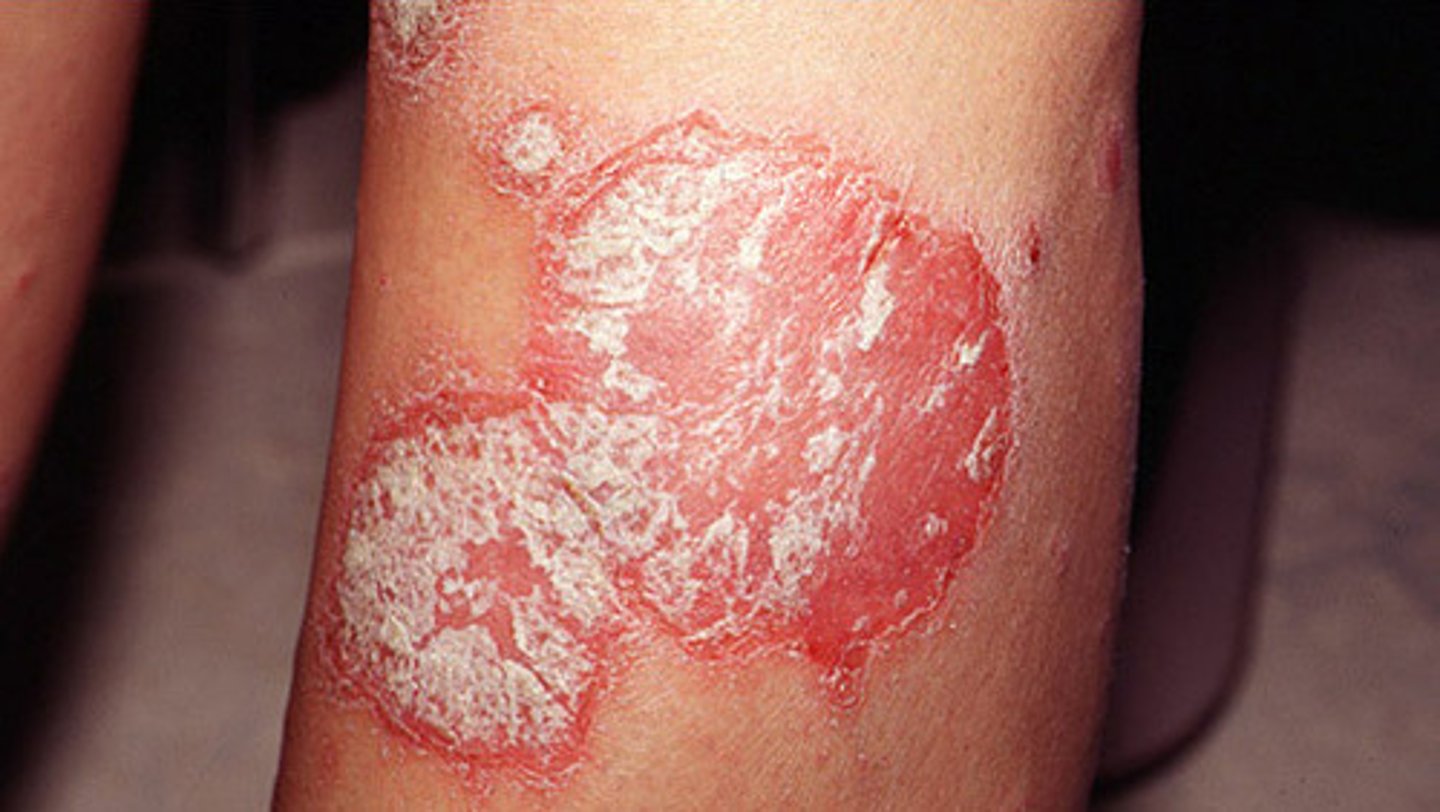
Well demarcated, circumscribed, erythematous, dry, silver scaly papules and plaques with variable size. MC on extensor surfaces, scalp and nails with oil spots and pitting. What's the diagonsis ?
Psoriasis
Chronic hereditary skin condition producing red lesions covered with silvery scales
Psoriasis
What is the MC type of psoriasis?
Plaque psoriasis
Positive _____ sign and _____ phenomenon present in psoriasis
Auspitz; Koebner
Even though the etiology of psoriasis is unclear some triggers include?
1. Stress
2. Medications*
3. Trauma (koebner phenomenon)
4. strep infxns
5. genetics
What medications can trigger psoriasis?
1. Beta-Blockers*
2. Antimalarials*
3. Lithium, terabinafine, CCBs,
The initial treatment of psoriasis and eczema is ____
Topical steroids
Injectable biologic considered standard in psoriasis treatment
Humira
What is the branching point/fork in the road for the treatment of eczema and psoriasis?
Initially, treat both with topical steroids. If no response, then you need to biopsy to determine eczema or psoriasis. If eczema, PO steroids. If psoriasis, biologics
What class of medications cannot be used in psoriasis patients, because they can cause a severe explosion of lesions?
PO steroids
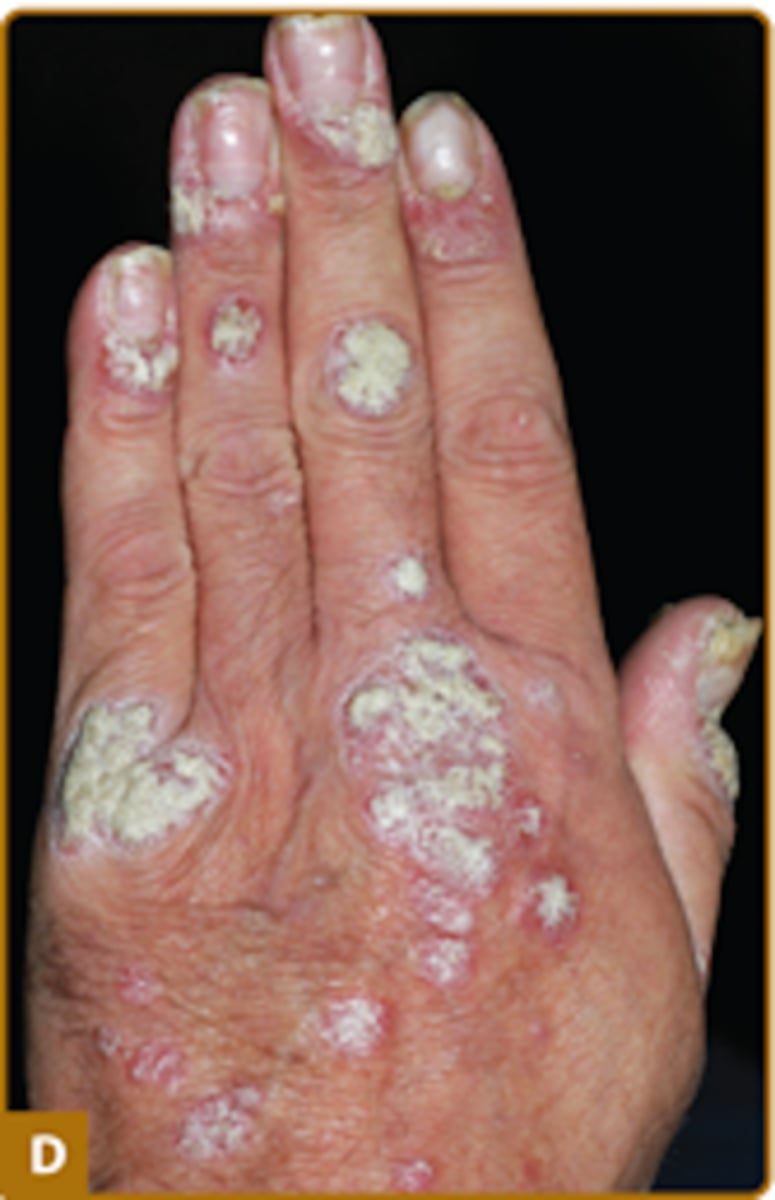
The most common type of psoriasis, characterized by erythematous plaques with silvery white scale that have distinct borders. Found on scalp, elbows, knees, back and buttock. Nails present with oil spots and pitting.
Plaque psoriasis
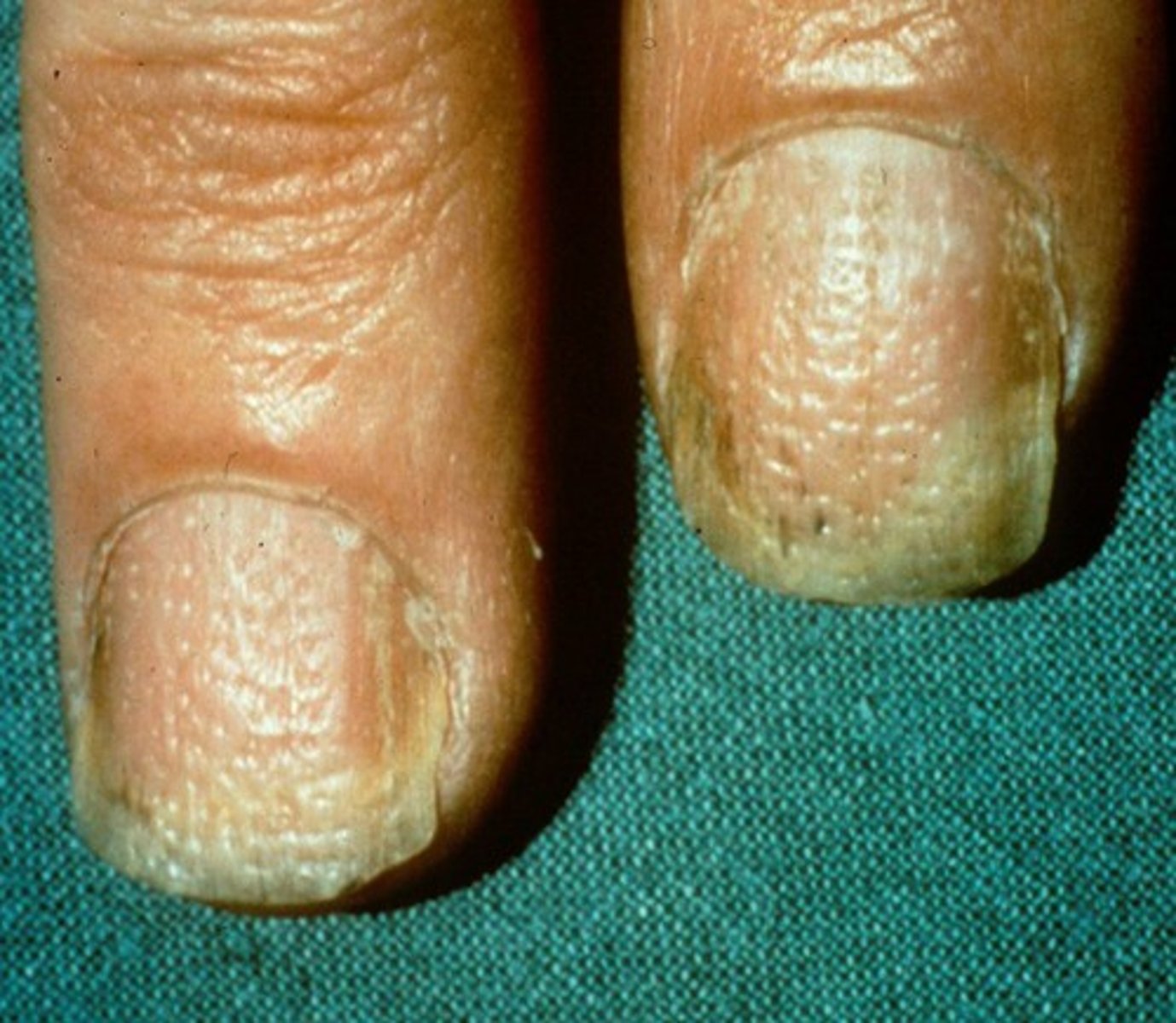
Nails with pitting and oil spots is pathognomonic for ____
Plaque psoriasis
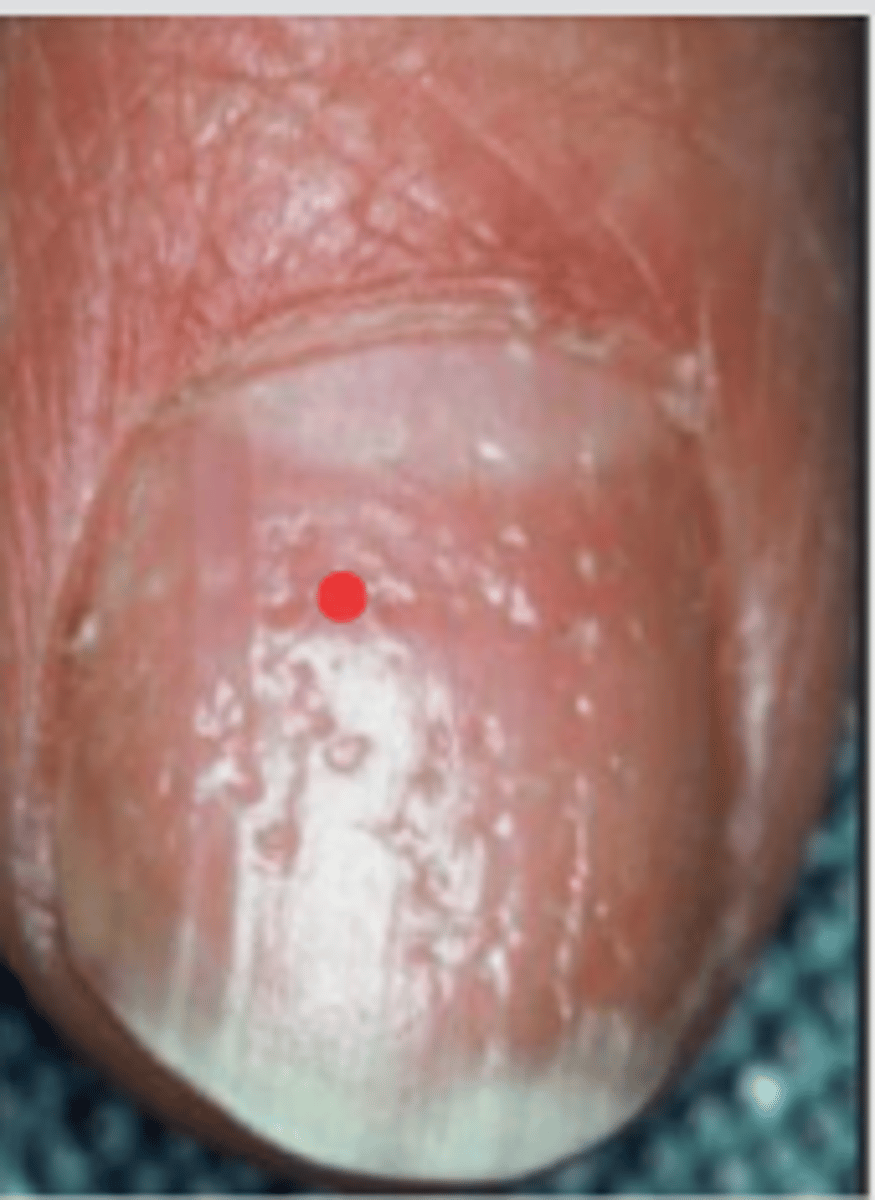
What can you expect to see on the nails of a patient with plaque psoriasis?
Nails with pitting and oil spots
What areas of the body would you expect to find plaque psoriasis?
Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, buttocks
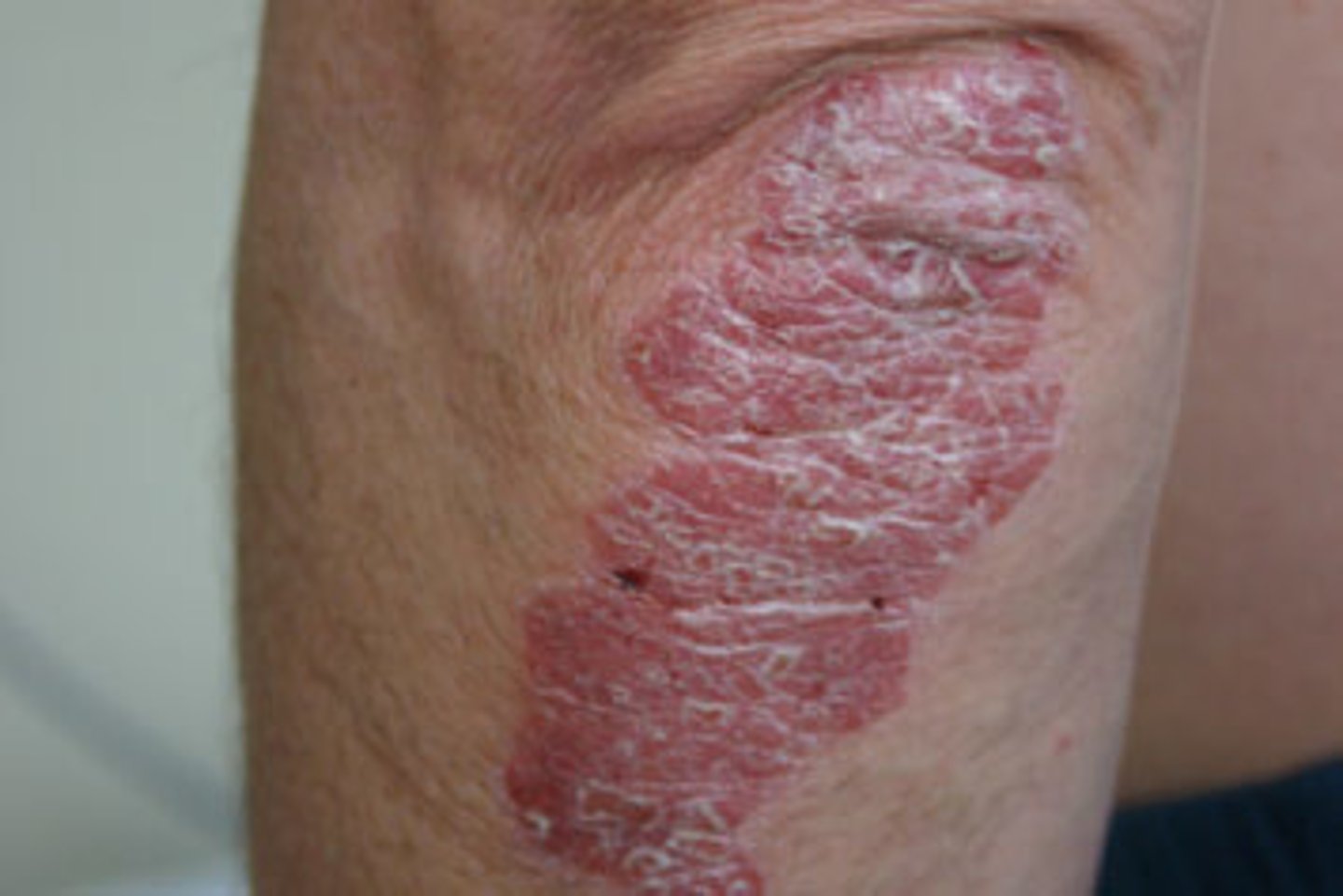
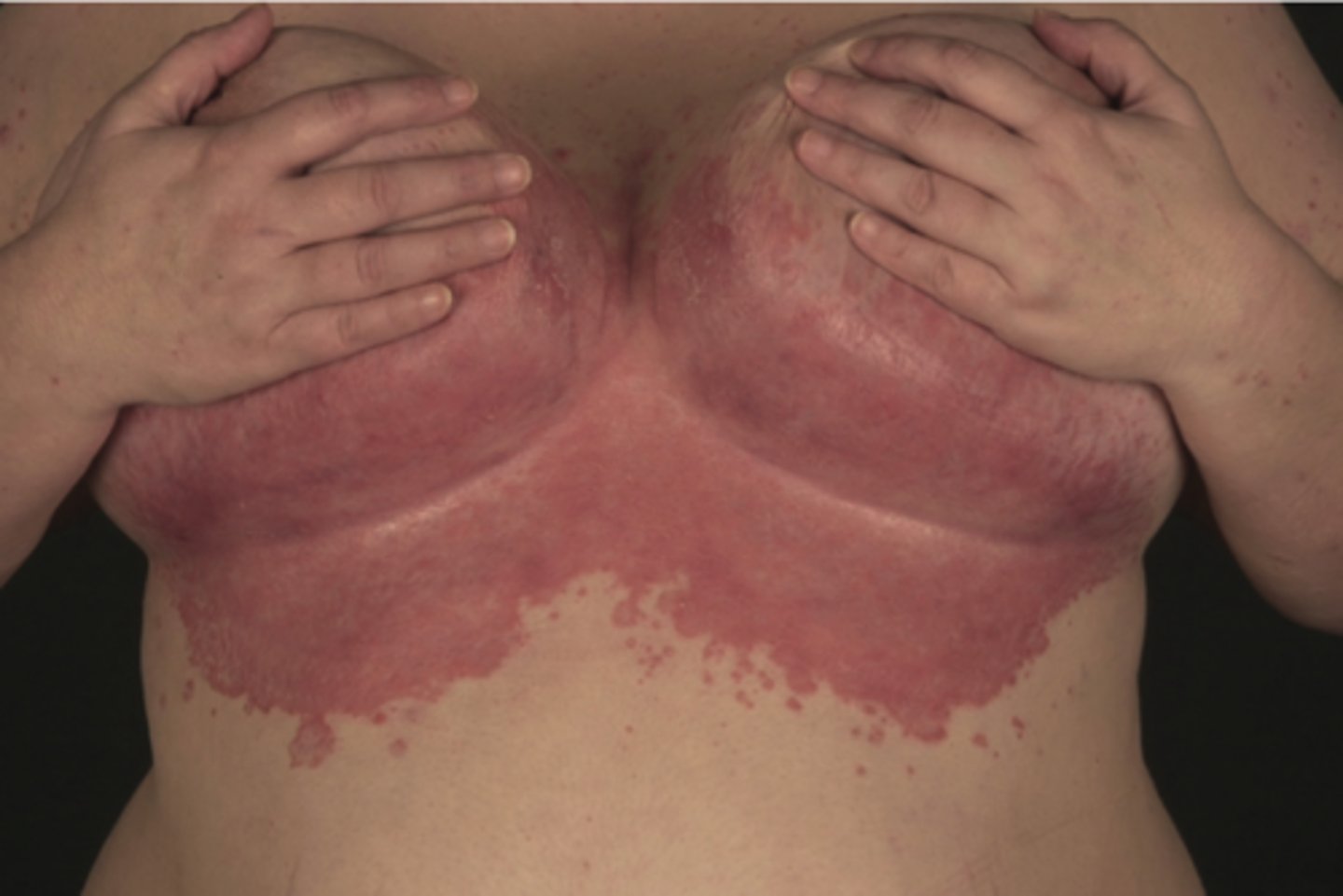
Psoriasis which occurs in the folds and recesses like the axilla and groin. Appears smooth shiny erythematous plaques with minimal scaling
Inverse psoriasis
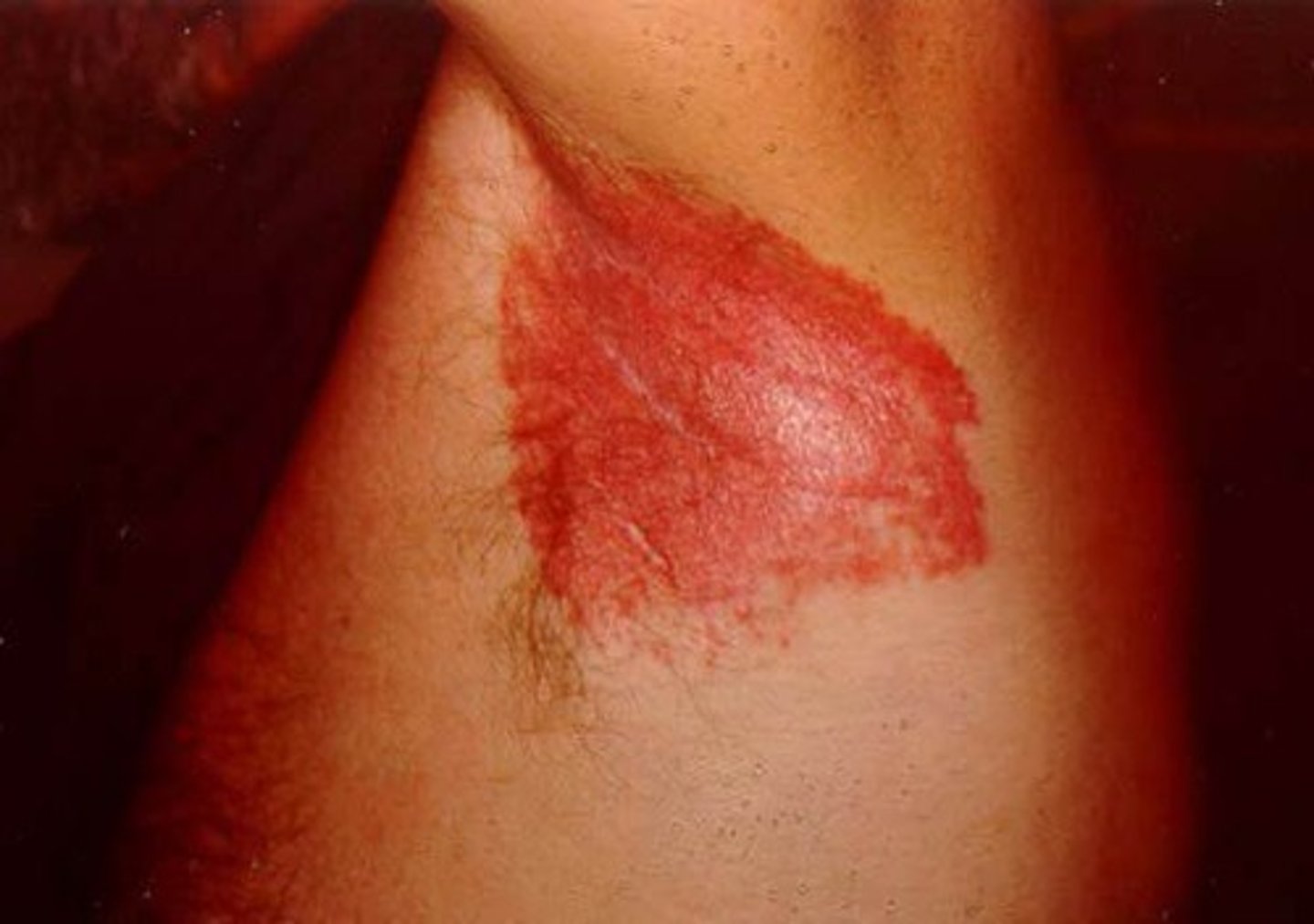
What areas of the body would you expect to find inverse psoriasis?
axillae, groin, inframammary folds
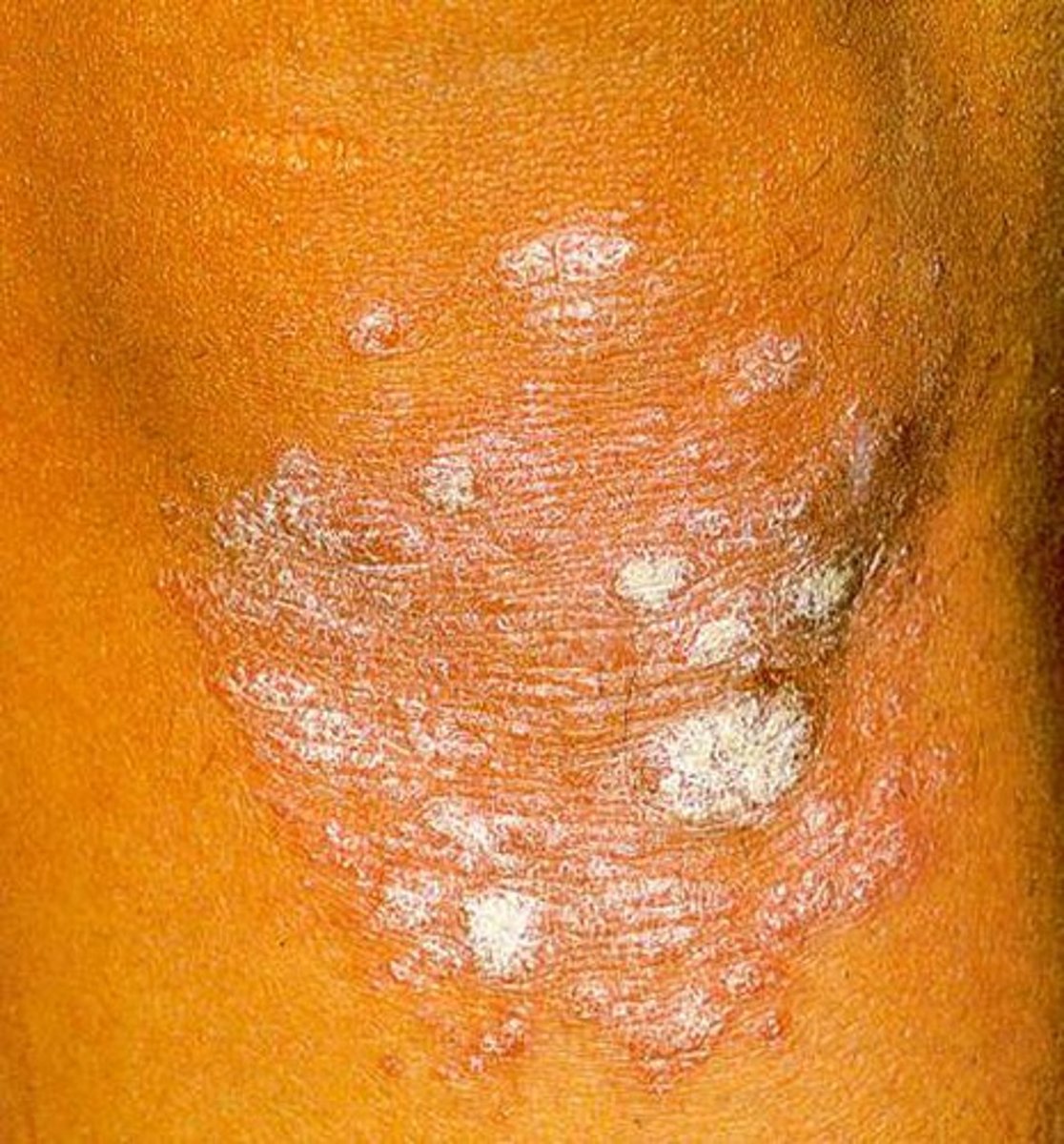
Psoriasis which present abruptly as drop-like discrete papules and plaques with fine scale (<1 cm usually), MC located on the trunk.
Guttate psoriasis
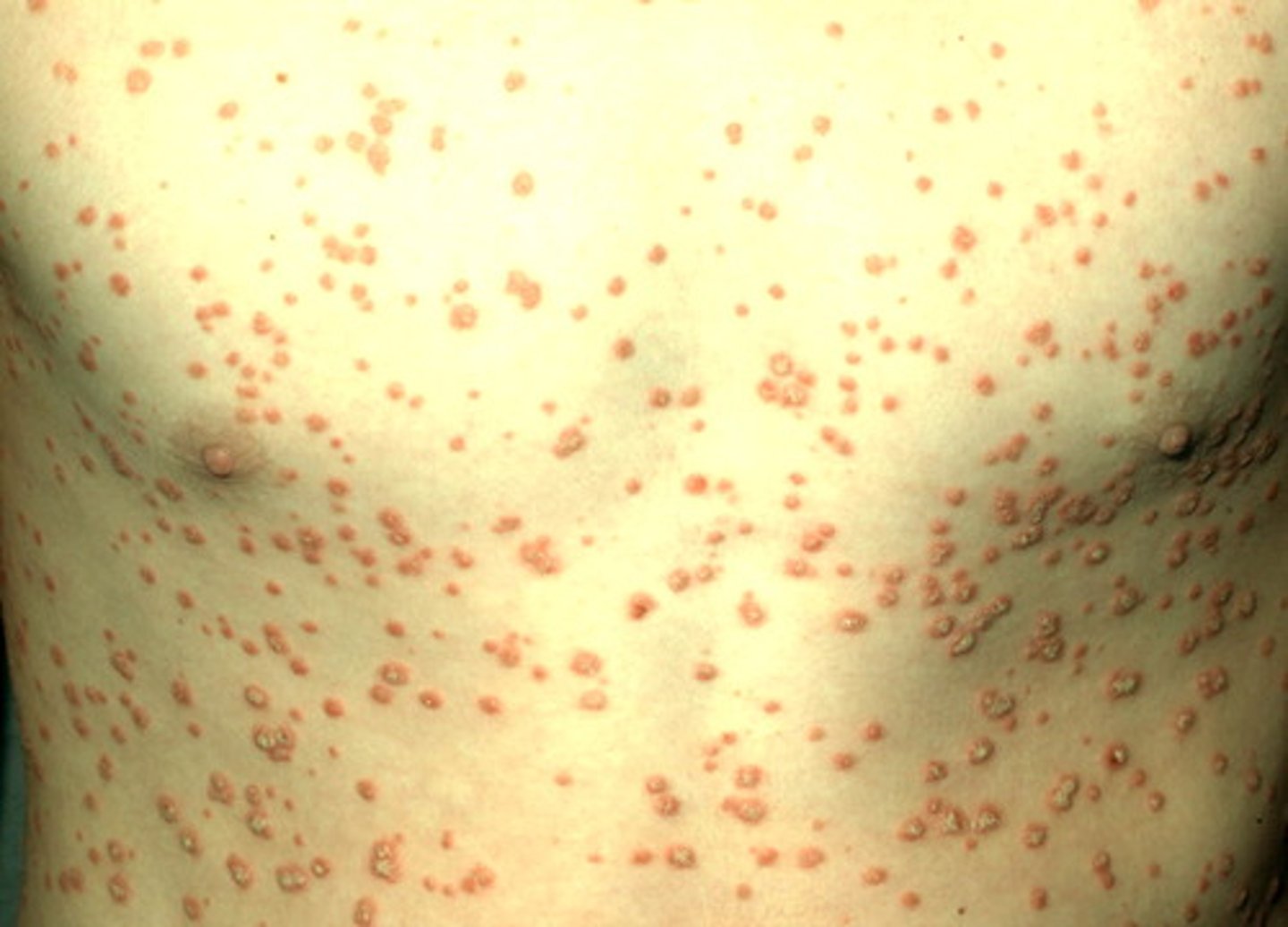
Guttate psoriasis is commonly induced after what type of infection?
streptococcal infection
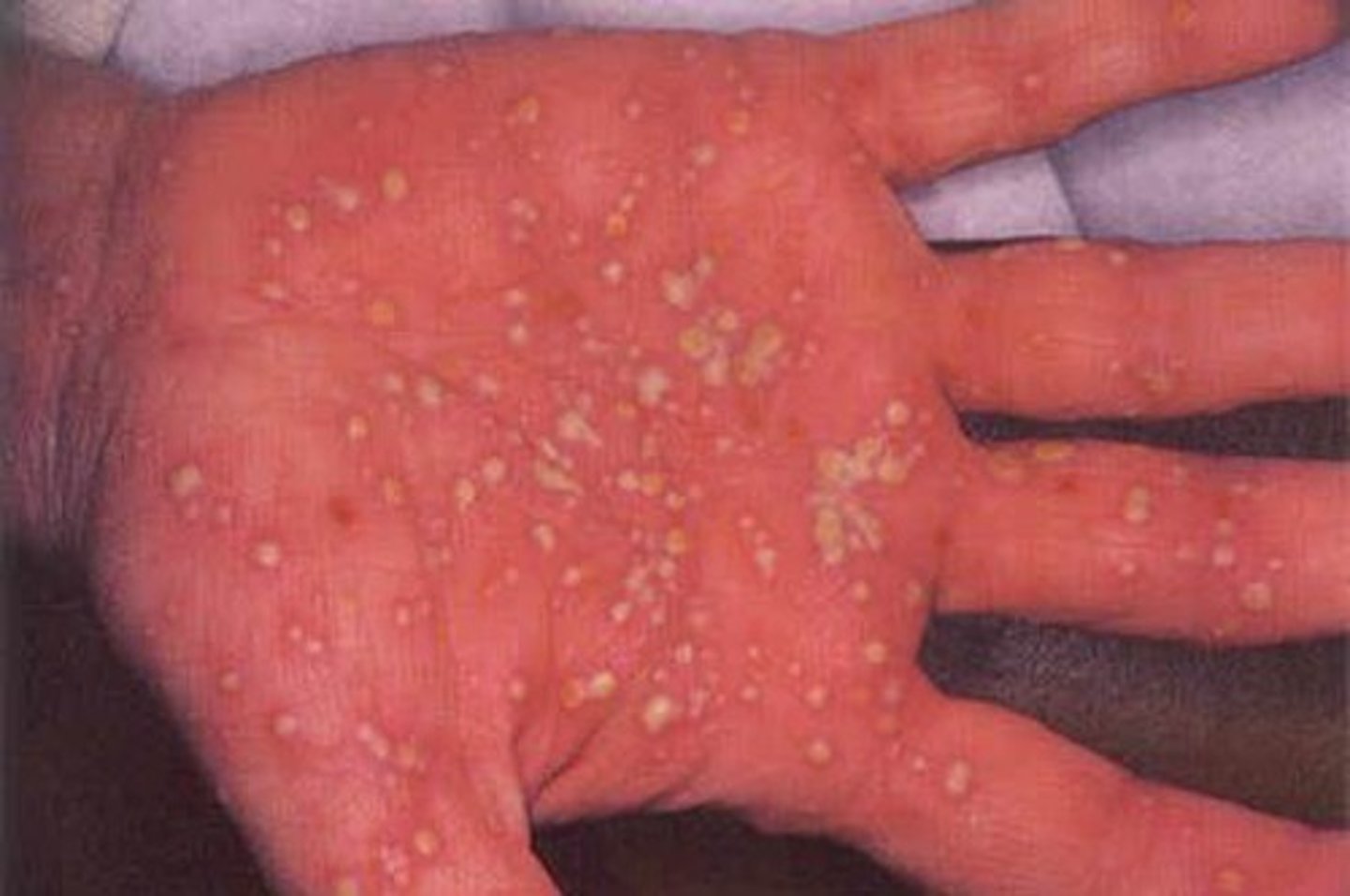
Psoriasis with erythematous plaques with pustules mostly on the hands and feet
Pustular psoriasis
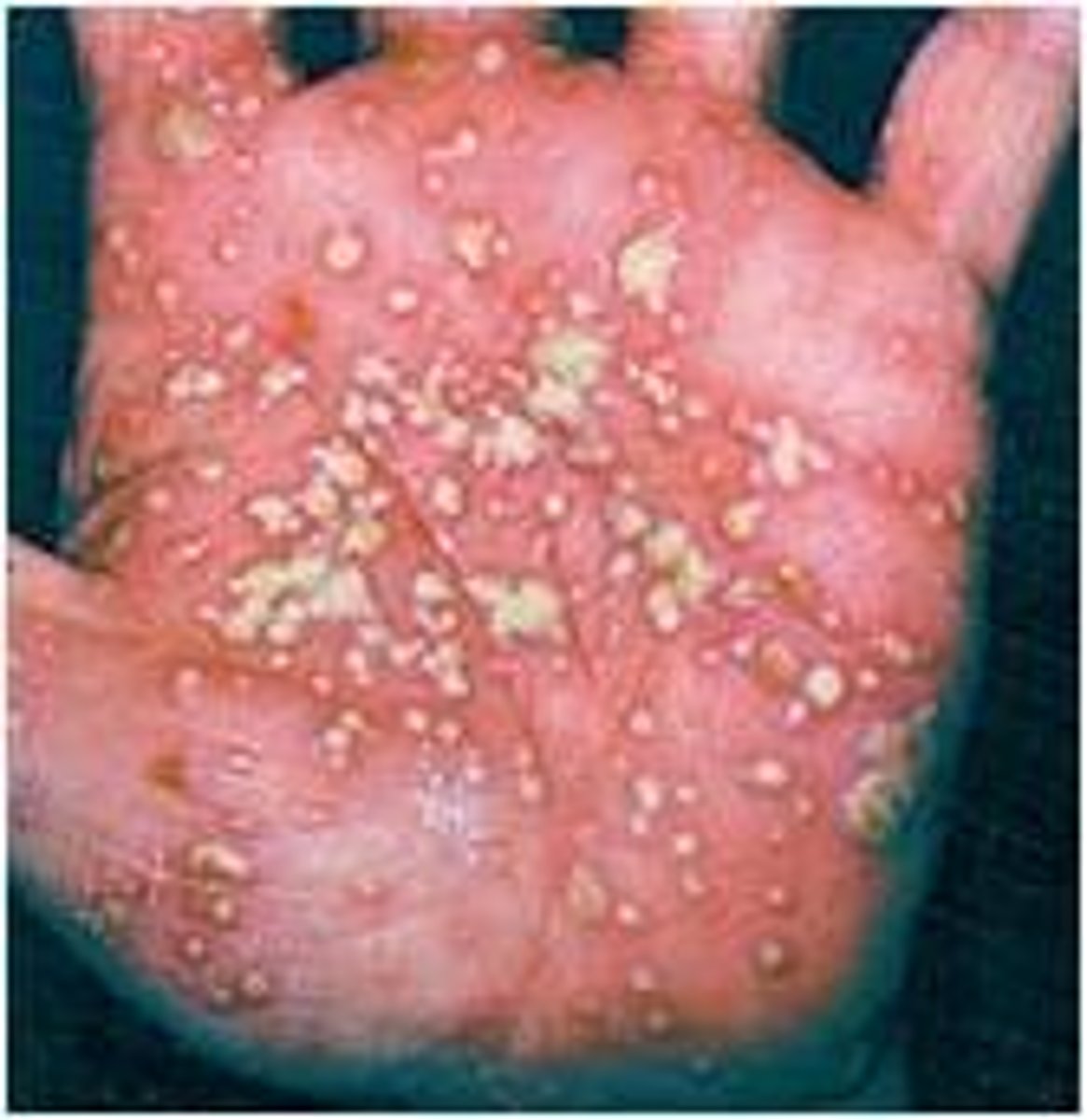
What areas of the body would you expect to find pustular psoriasis?
Hands and feet
Psoriasis that is uncommon but severe typically requiring hospitalization. Patient is ill, potentially fatal. Characterized by diffuse erythema, scaling and shedding of the skin on all or most of the body surface.
Erythrodermic psoriasis
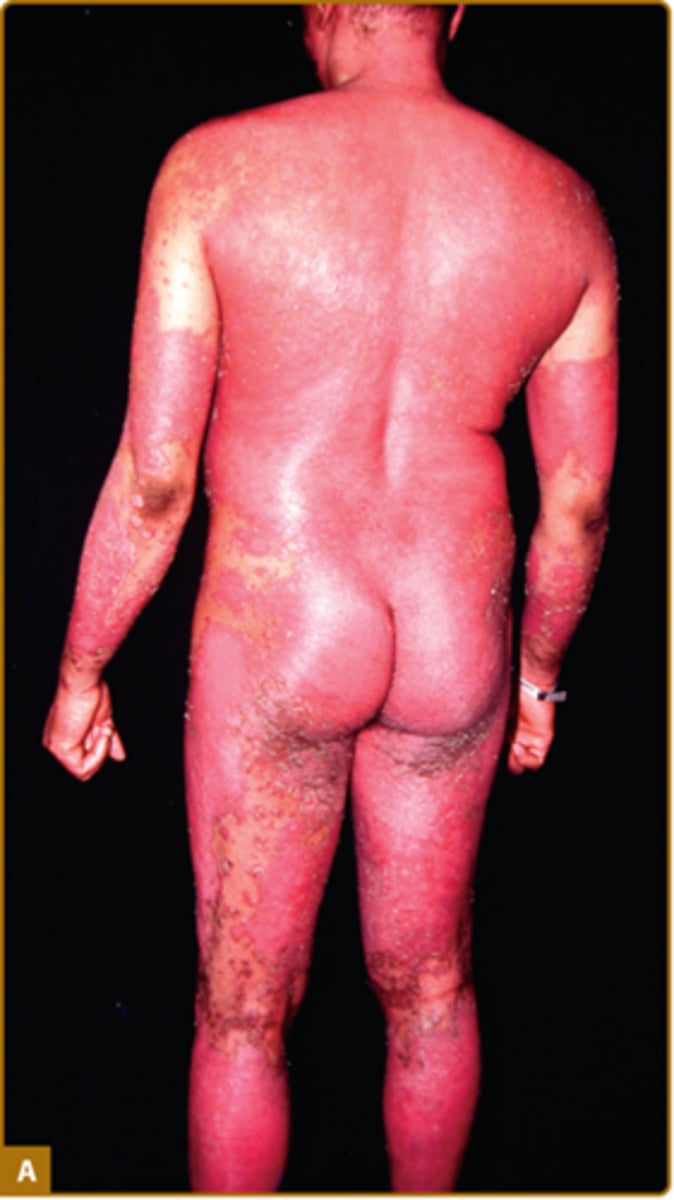
What is one of the only times you will give PO steroids to a patient with psoriasis?
For erythrodermic psoriasis while you are waiting for biologics to kick in
An inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis of the skin that cause asymmetrical DIP joint damage with yellow thickened nails. This is known to have a "pencil in cup deformity"
Psoriatic arthritis
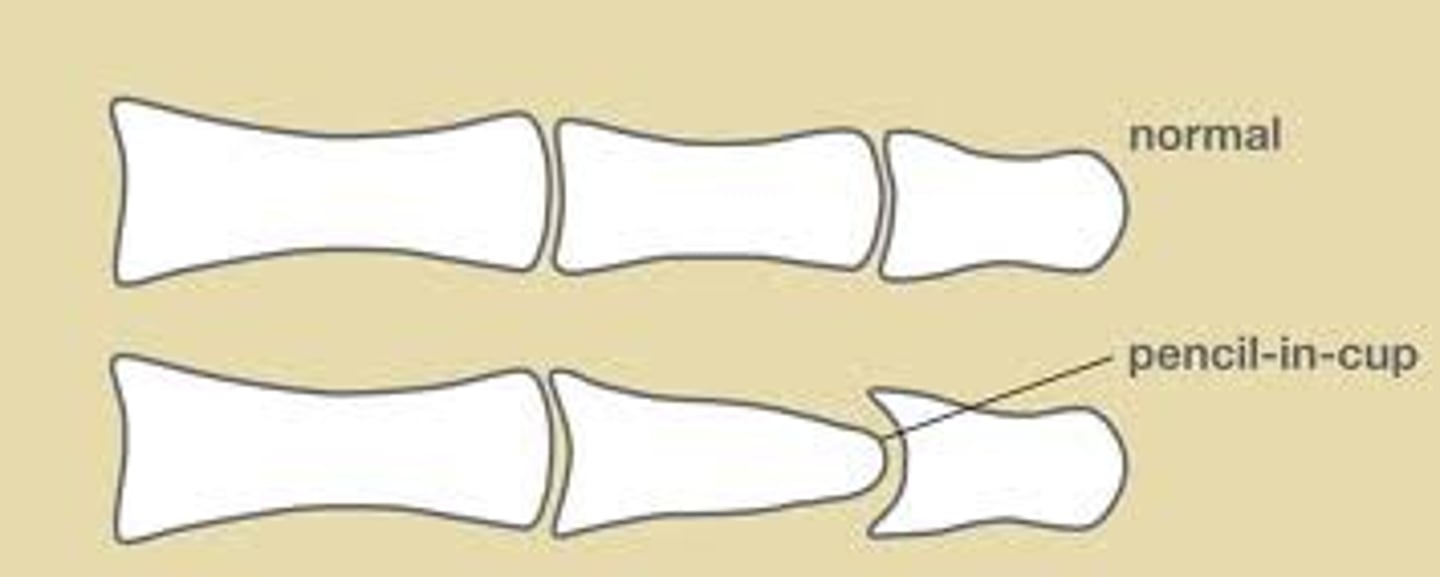
What is the first line therapy for psoriasis?
1. Topical steroids (Taclonex) with..
2. Vitamin D (Calcipotriene/Dovonex)
Calcipotriene and Dovonex are ____ analogs used in the treatment of psoriasis
Vitamin D
This can be used for the tx of thick plaques associated with psoriasis that can also be used in combination with steroids too (Duobrii).
Topical Retinoids (tazarotene)
For moderate to severe psoriasis, ________ can be used to decrease inflammation.
phototherapy (UVB)
Immunosuppressant that inhibits DNA synthesis and proliferation of lymphoid tissue. Used in patients with severe psoriasis
Methotrexate
Insurance companies will not cover the biologics unless the patient has failed ____ treatment for psoriasis
Methotrexate (MTX)
tx for severe psoriasis
COMB
Cyclosporine
Oral retinoids
Methotrexate
Biologics
What immunosuppressant can be used to front load a psoriasis patient while waiting for Humira to kick in?
Cyclosporine
How long does it take for Adalimumab (Humira) to kick in?
2 weeks-4 months
What other TNF biologics can be used for the tx of severe psoriasis ?
1. Etanercept (Enbrel)
2. iInfliximab (Remicade)
3. Certolizumab pegol
4. adalimumab
What is the symptom triad for reactive arthritis?
1. Urethritis
2. Conjunctivitis
3. Arthritis (and skin manifestations)
*** Can't pee, Can't See, Can't Climb a tree***
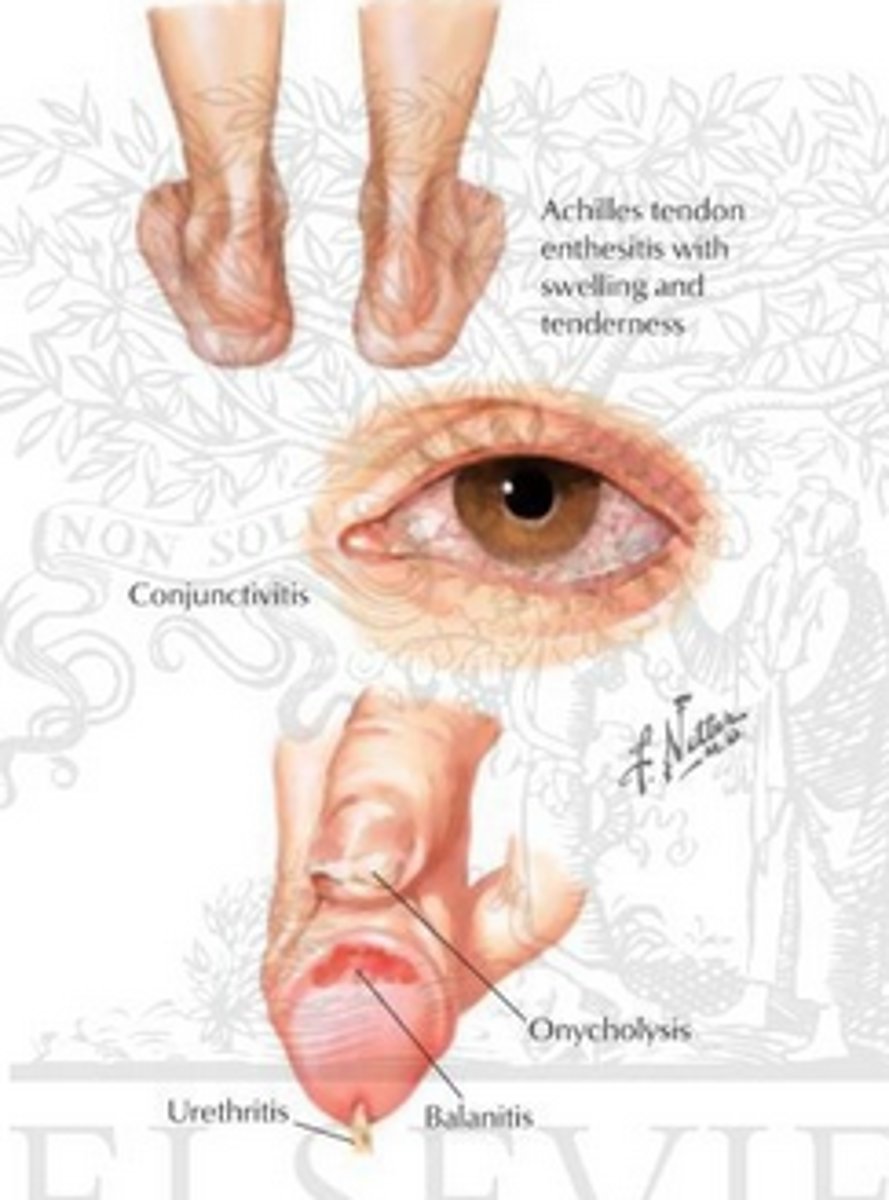
Where is reactive arthritis MC seen?
genitals, palms, soles
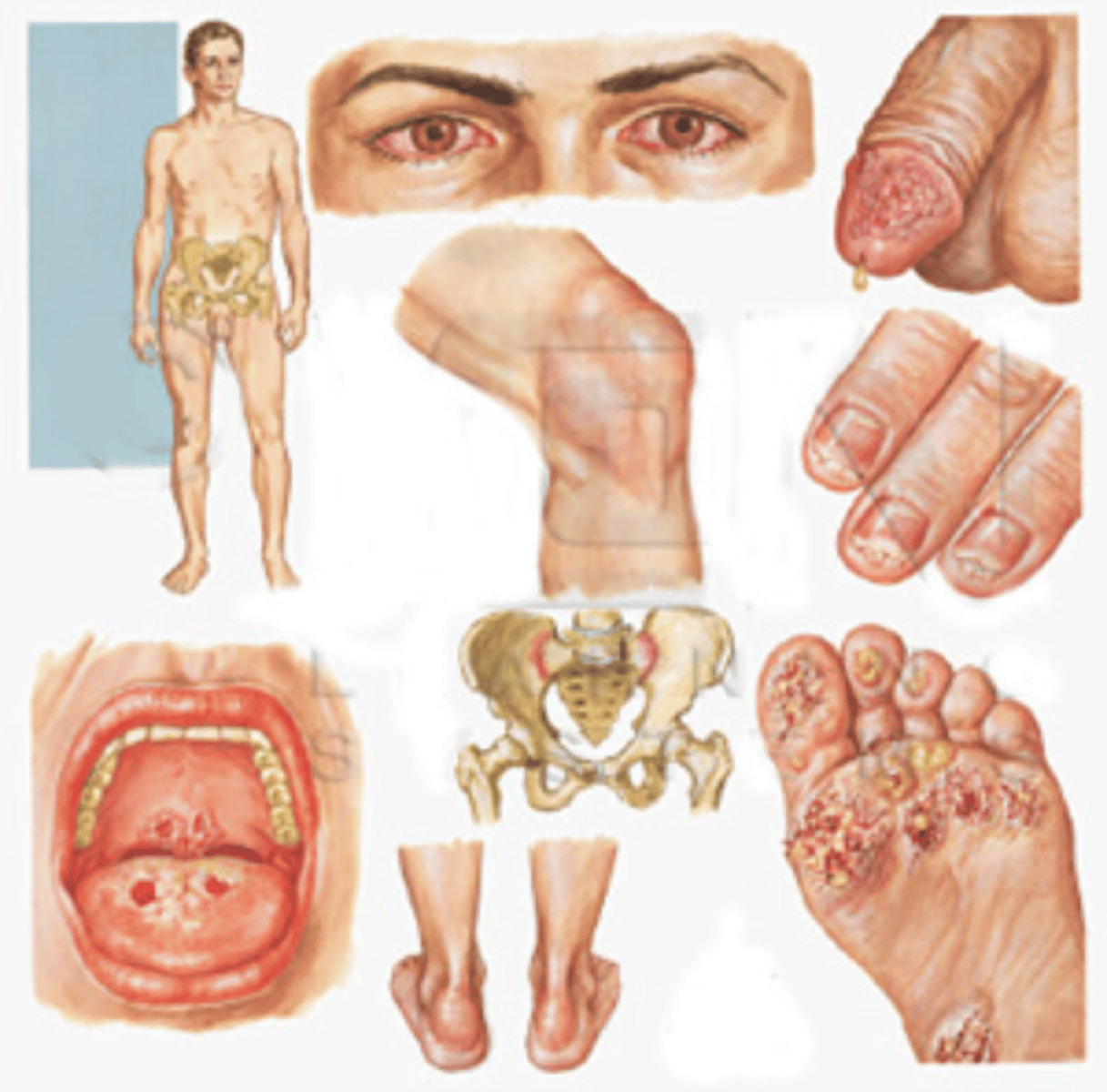
Initially small guttate, hyperkeratotic, crusted or pustular lesions
Reactive arthritis
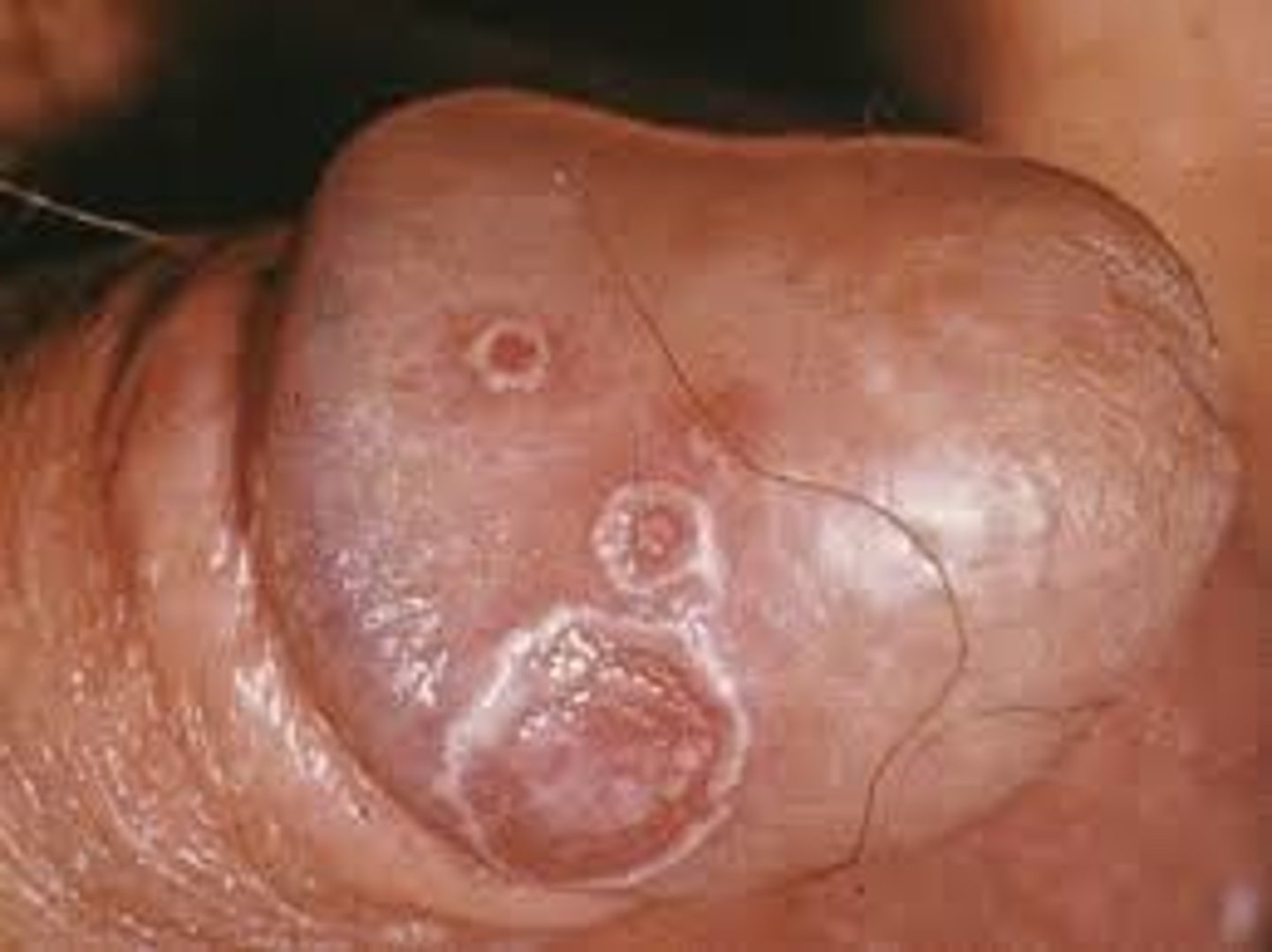
Erythematous painless lesions with small shallow ulcers located on the Glans penis associated with reactive arthritis
Balanitis circinata (25%)
Lesions that become hyperkeratotic and thick with crust seen on soles in reactive arthritis
Keratoderma Blennorrhagicum (10%)
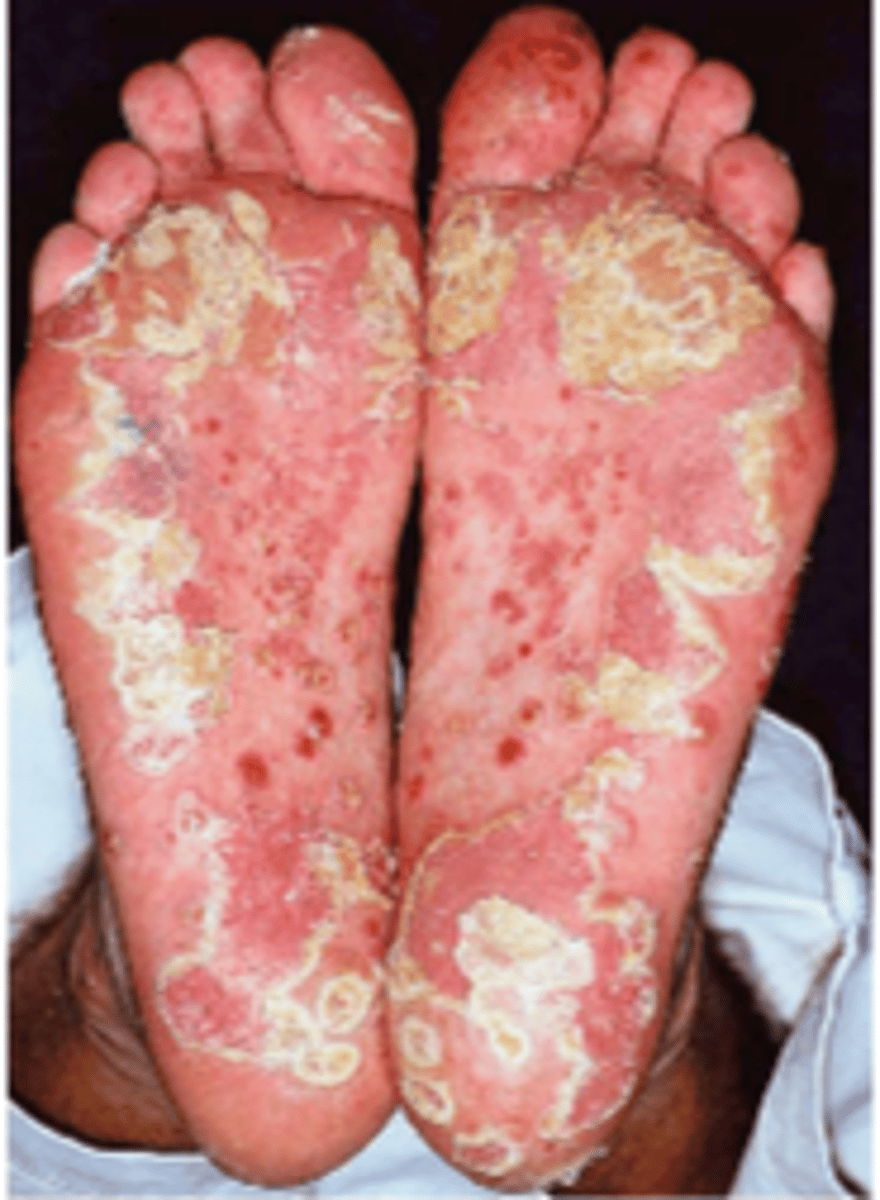
When does reactive arthritis occur?
After urethritis or diarrheal illness in genetically susceptible (after STD)
Reactive arthritis, typically triggered by dysentery or urethritis in genetically susceptible individuals (HLA-B27+)
Reiter's Syndrome
Conjunctivitis, urethritis and arthritis occurring after an infection
1. What is the genetic susceptibility for Reiter's syndrome?
2. Who does it MC affect?
1. HLA-B27
2. Males (90%)
What is the tx for reactive arthritis?
1. Tx Underyling condition
2. 1% hydrocortisone cream BID for genital erosions
3. Topical steriods of keratoderma blennorrhagicum
The causes of pityriasis rosea is unknown but its most likely a response to a virus, which one?
HHV-6 and HHV-7 (not contagious)
Mild inflammatory exanthem. Typically, on TRUNK & Proximal extremities and is seen in spring & fall
Pityriasis Rosea
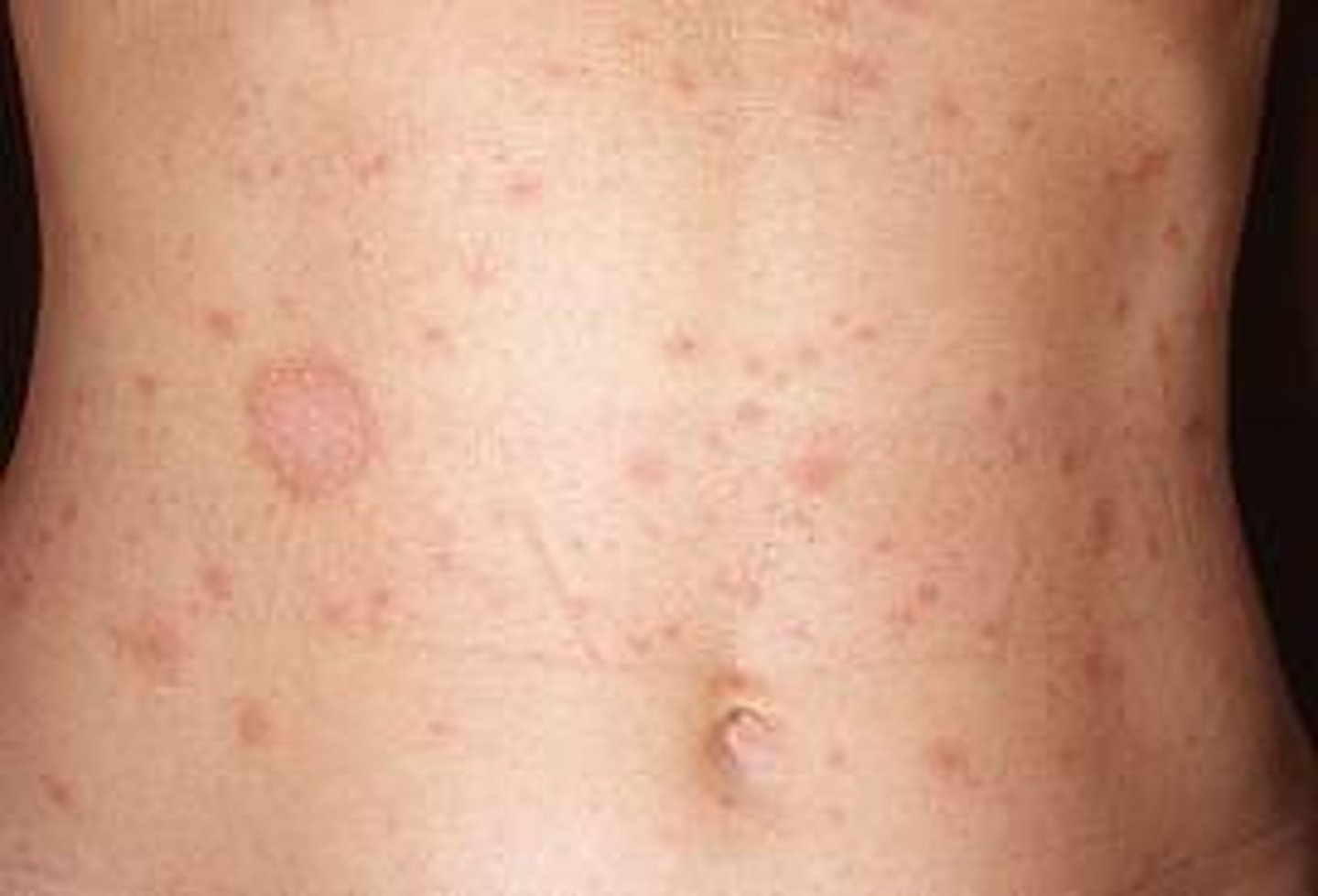
Who MC gets pityriasis rosea?
females b/w 15-40 (older children and young adults)
Discrete salmon colored oval or circinate thin papules and plaques with fine crinkled dry
epidermis. Desquamation leaves a central collarette of scale. This describes what type of rash?
Pityriasis Rosea
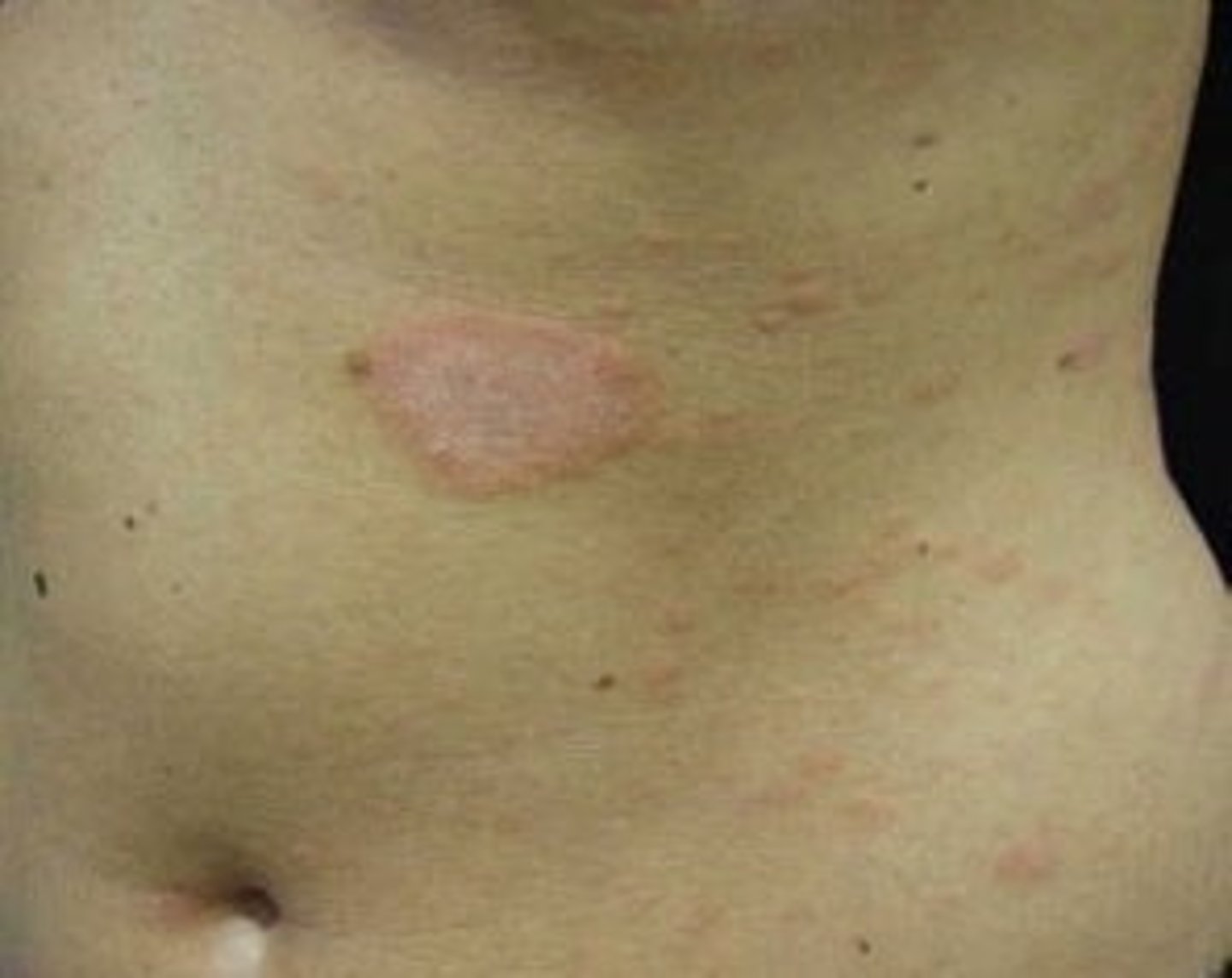
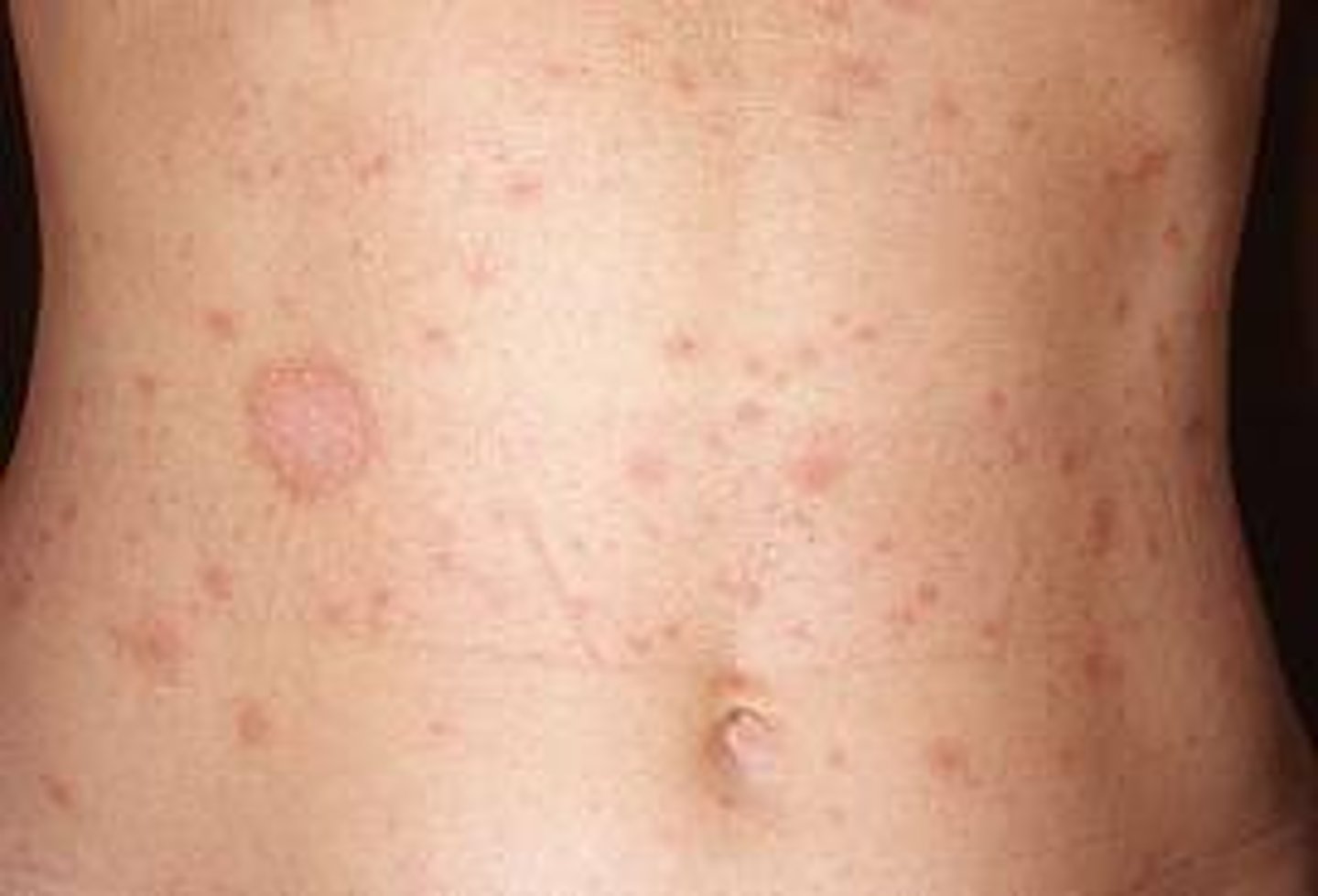
In Pityriasis Rosea, this is the first to appear on the skin.
HERALD PATCH (bigger than other
lesions)
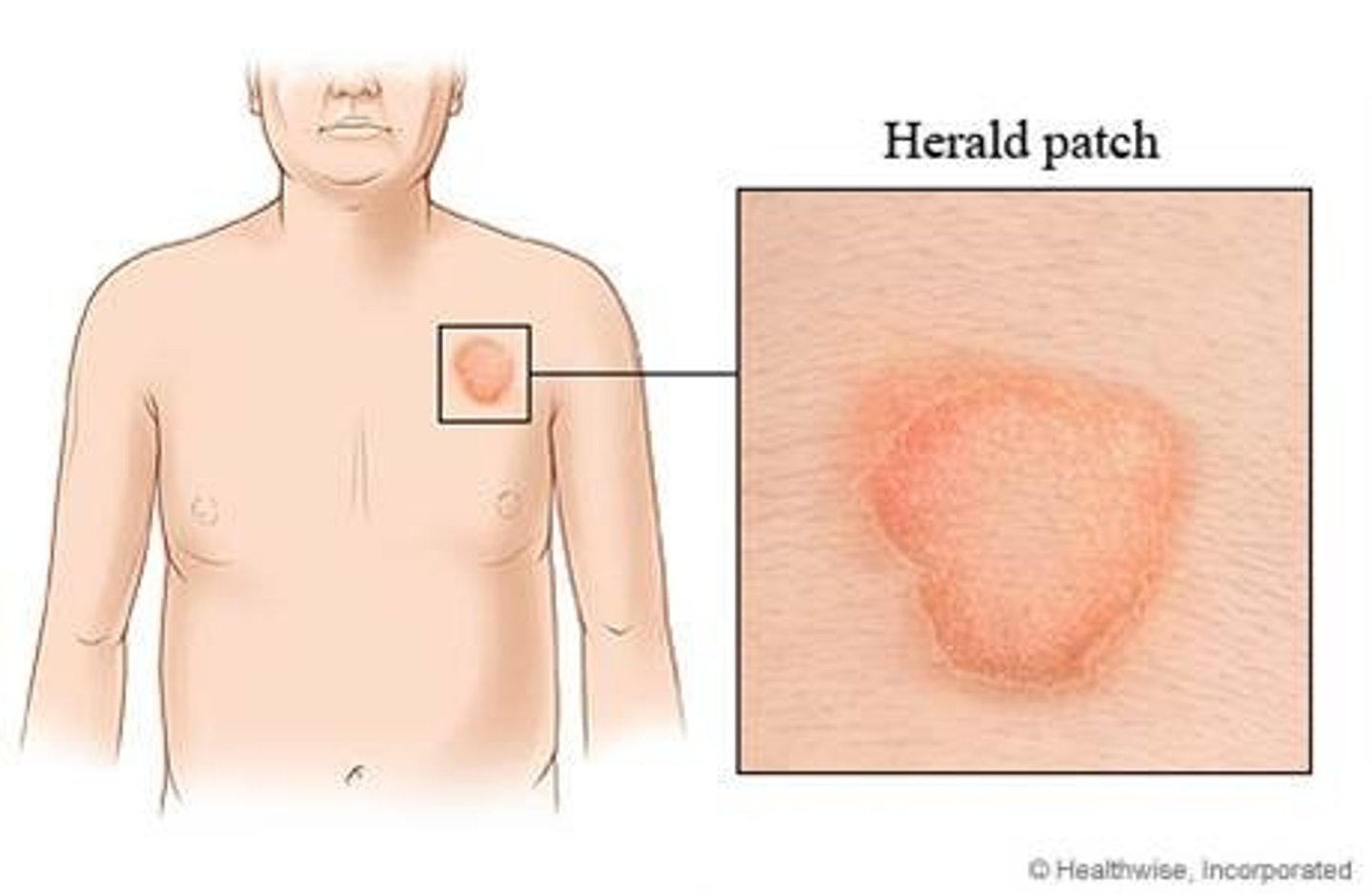
Which skin infection is associated with a Herald patch?
Pityriasis rosea
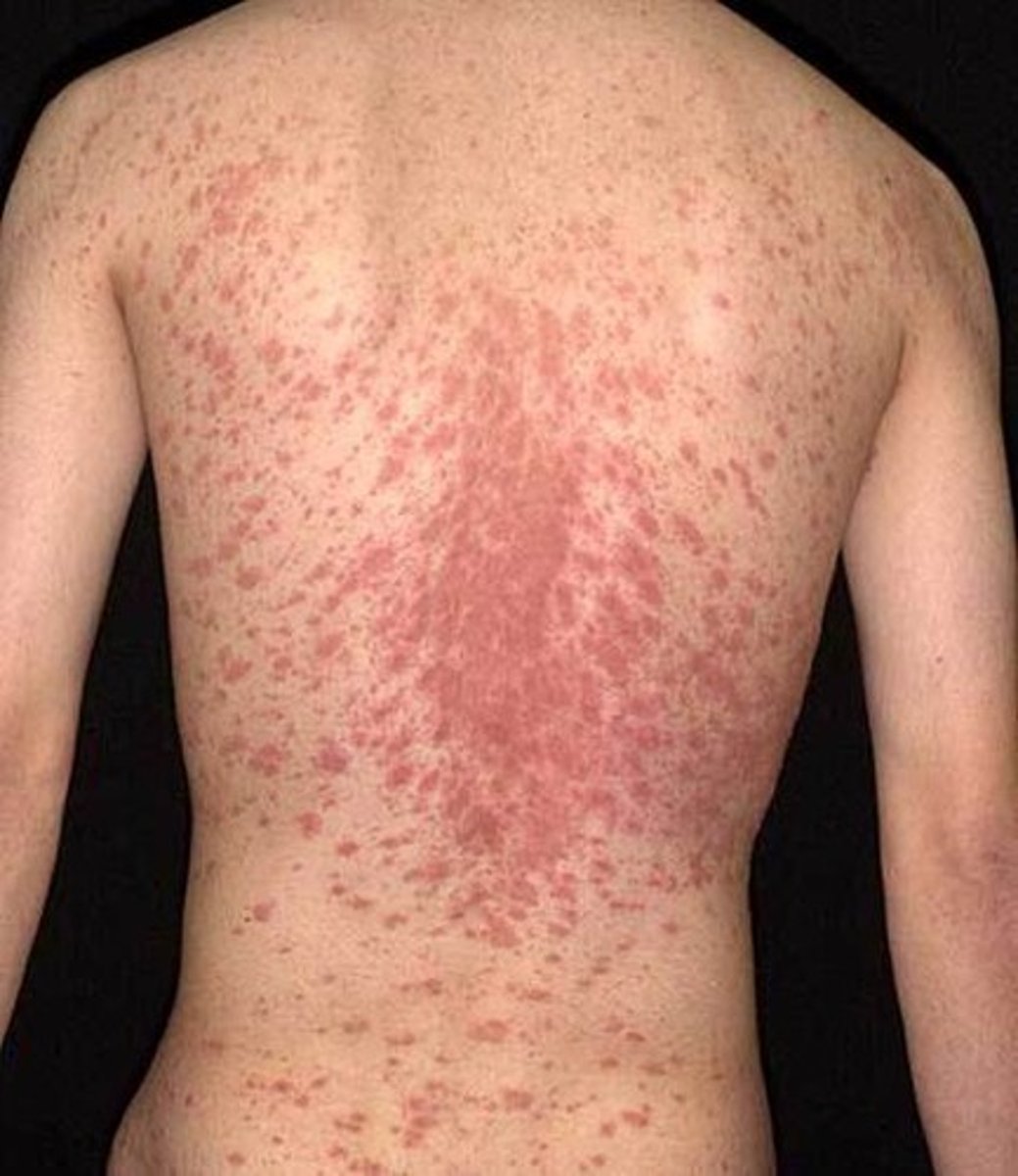
In pityriasis rosea, after the first week, the rest of the lesions appear is what type of pattern?
CHRISTMAS TREE PATTERN
In the last ______ weeks with pityriasis rosea it will spontaneously resolve.
Last 3-8 weeks
Before the patient develops the pityriasis rosea rash, what will they present with?
may have URI symptoms
What is the tx for pityriasis rosea ?
1. None needed unless symptomatic, self-limited 3-8 weeks
2. Topical steroid if pruritic
3. Emollients for dryness or irritation
Inflammatory skin condition, characterized by an itchy, non-infectious rash on the arms and legs. It consists of small, many-sided, flat-topped and purple papules/plaques.
Lichen planus
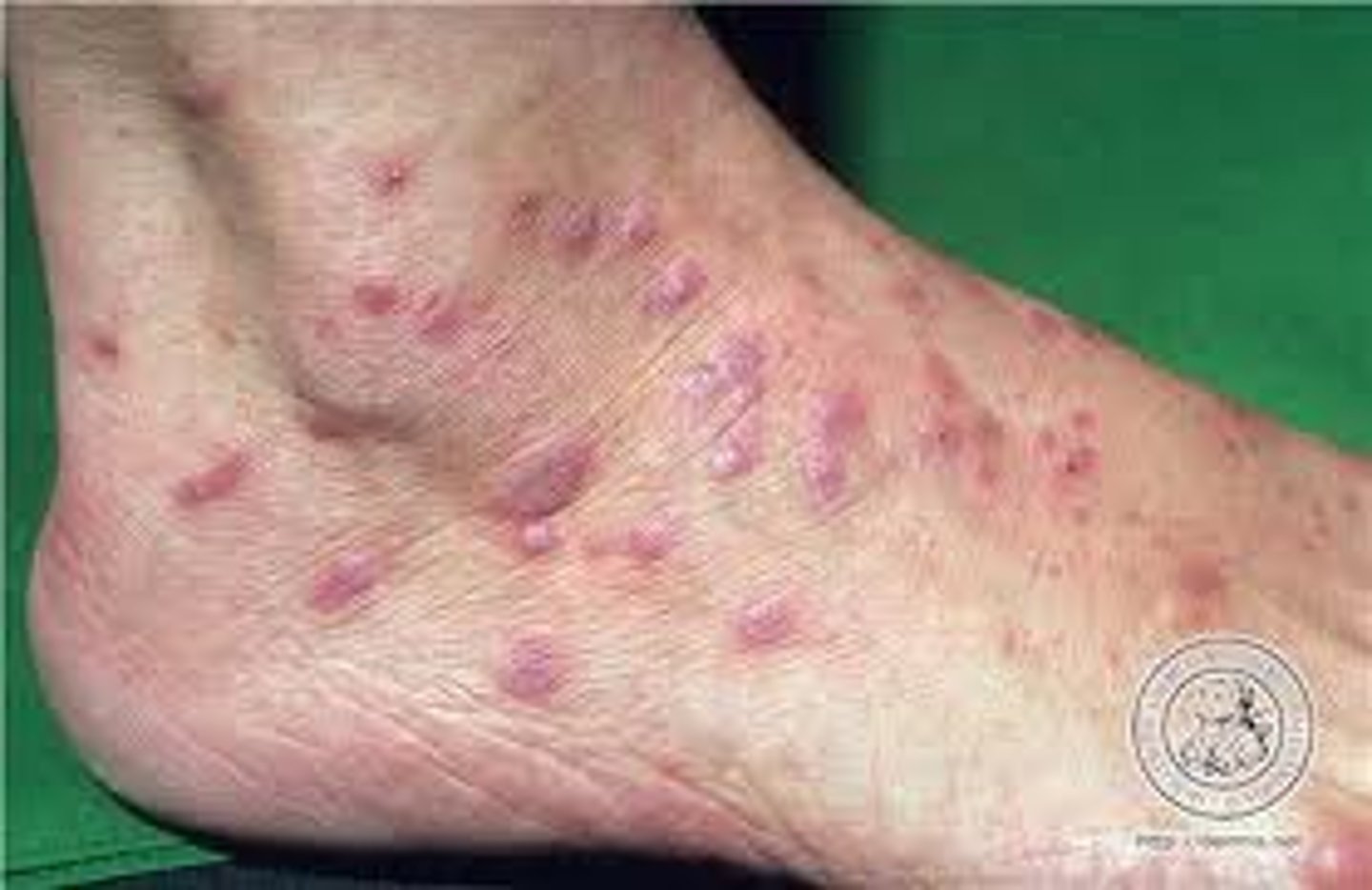
What are the 5 Ps associated with Lichen Planus?
1. Pruritus**
2. Purple (violaceous)
3. Polygonal
4. Planar
5. Papule or Plaques
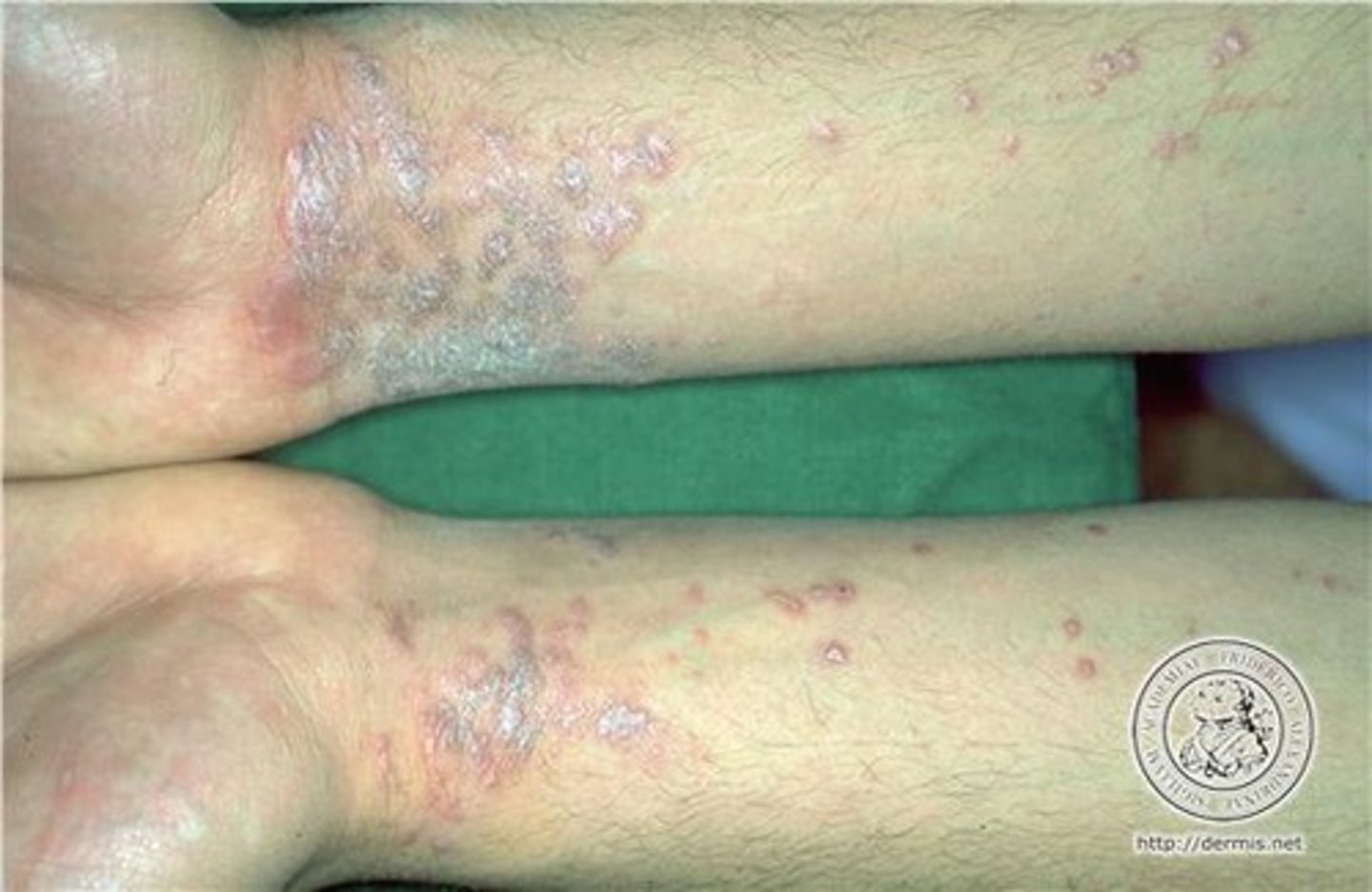
Where is Lichen Planus MC located?
1. flexor wrists and ankles (MC)
2. trunk, medial thighs, shins
3. dorsal hands, glans penis, mucous membranes, and hair follicle
Lichen planus has been a reported complication of what viral disease?
Hepatitis C (need screening)
If you diagnose a patient with Lichen planus, what serum levels might you want to check?
HepC
White lines on the surface of the lesions of Lichen planus
Wickham striae
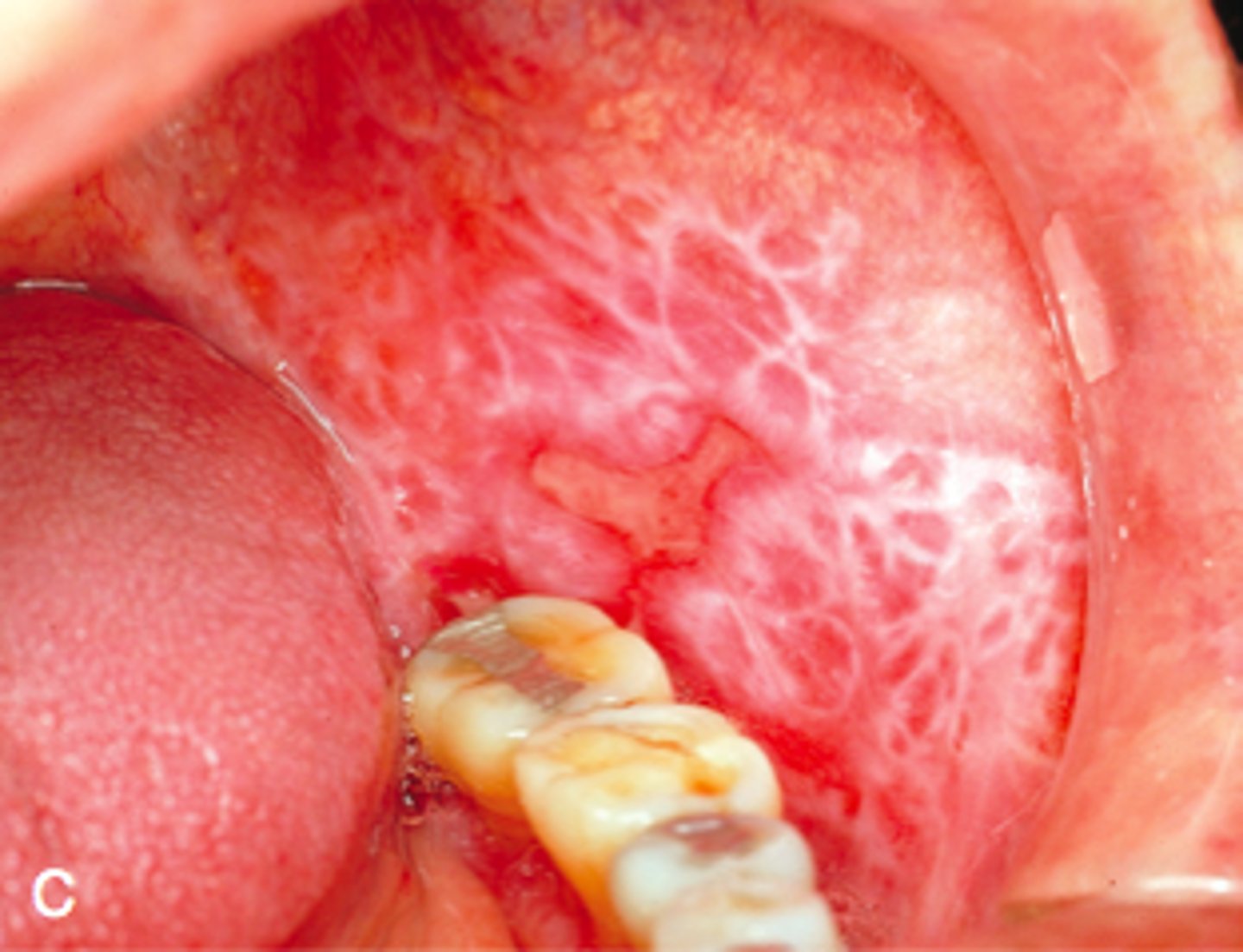
Wickham striae are diagnostic for what condition?
Lichen planus
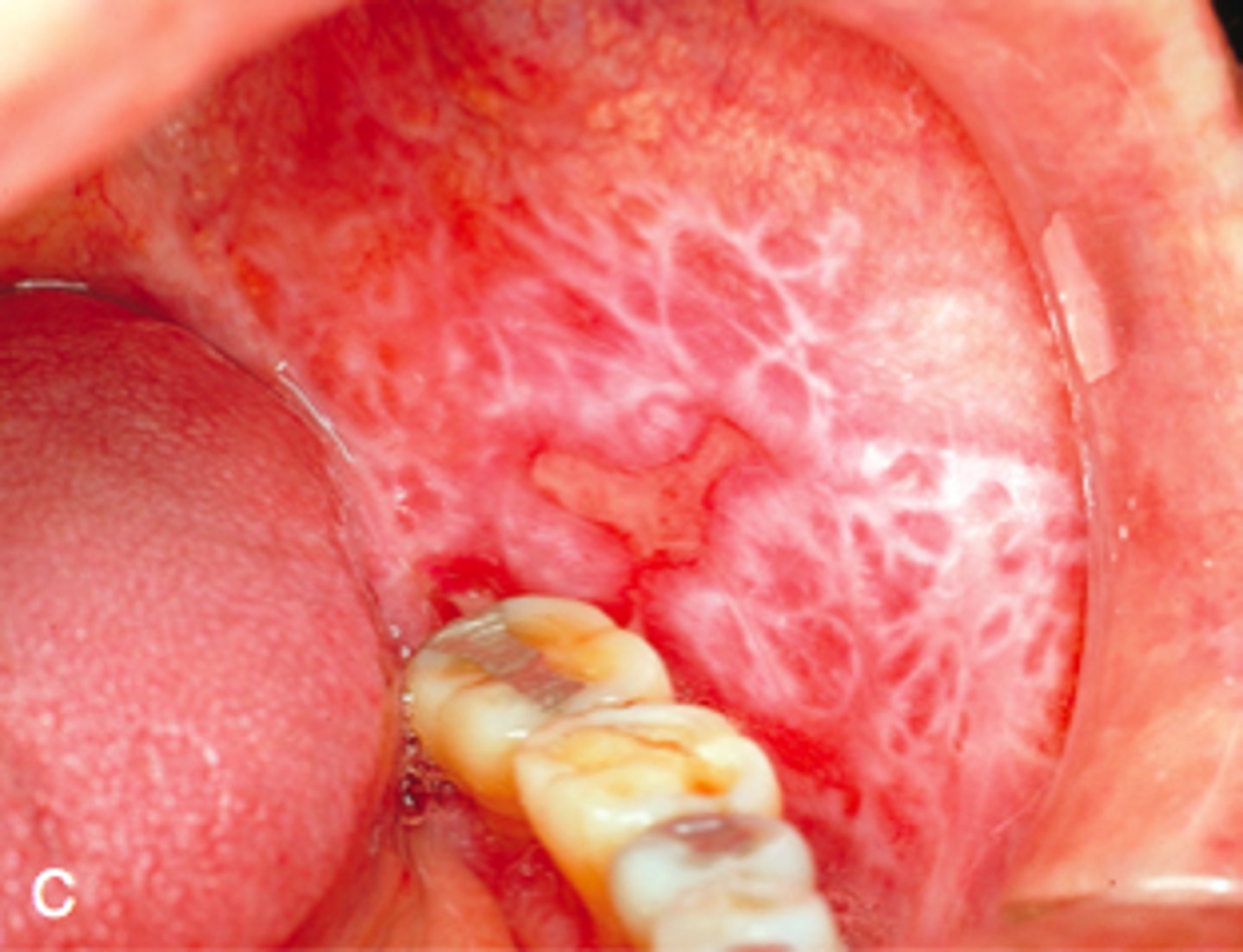
1. What is the most common pattern of lichen planus?
2. Second most common?
1. MC is localized
2. Second MC is hypertrophic
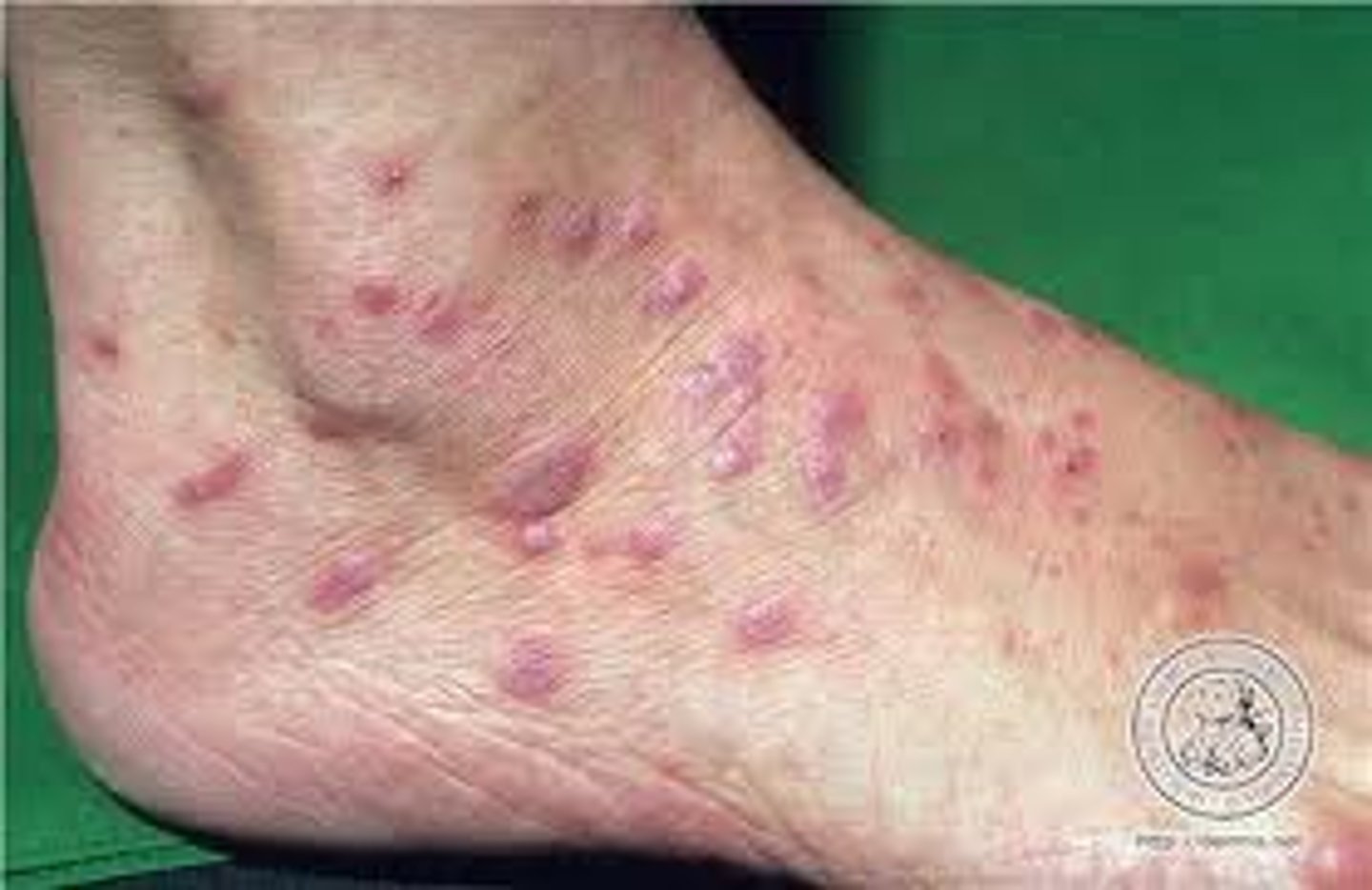
Lichen Planus with small lesions, caused by koebnerization. Follows Blaschko lines
linear lichen planus
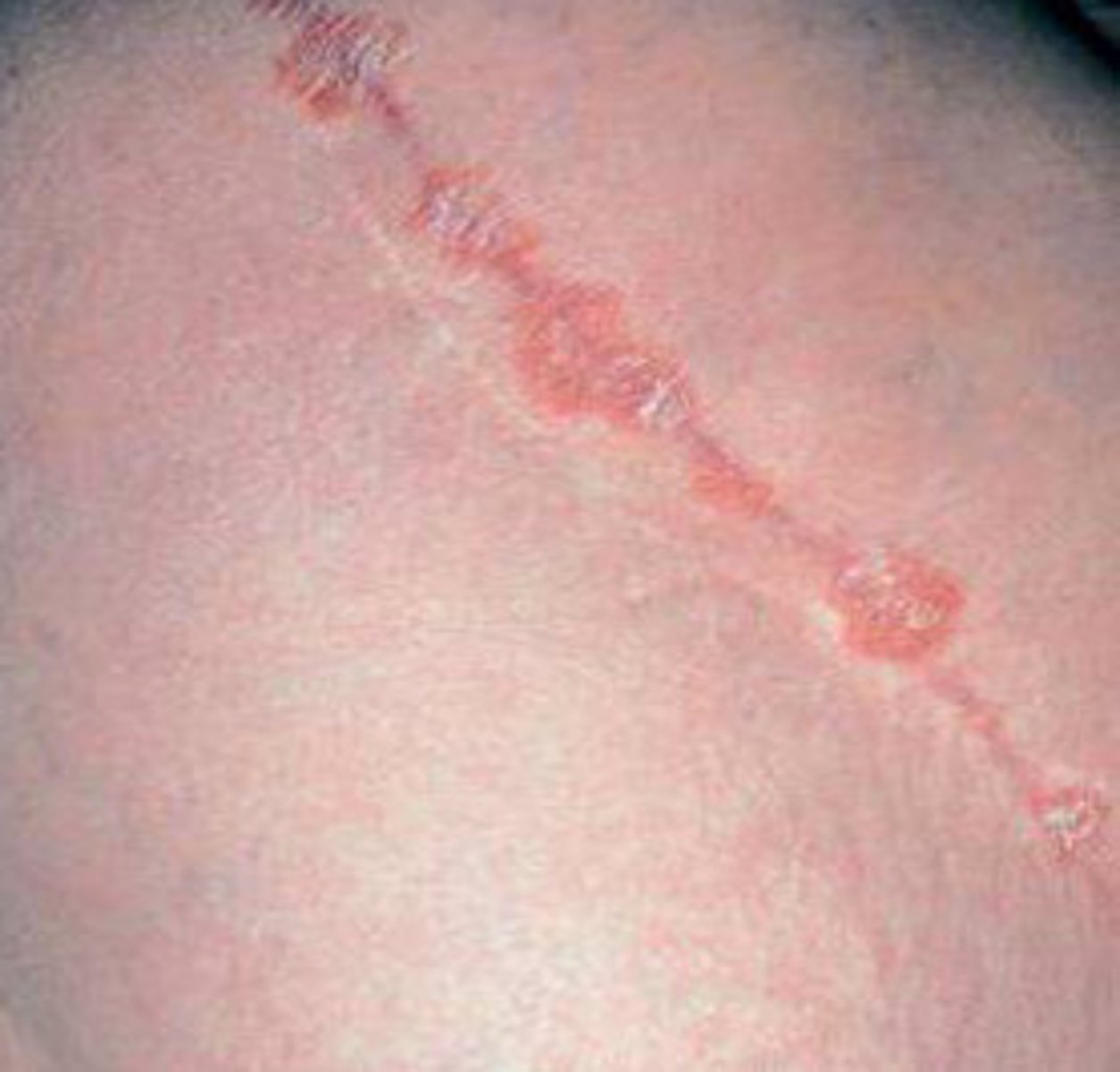
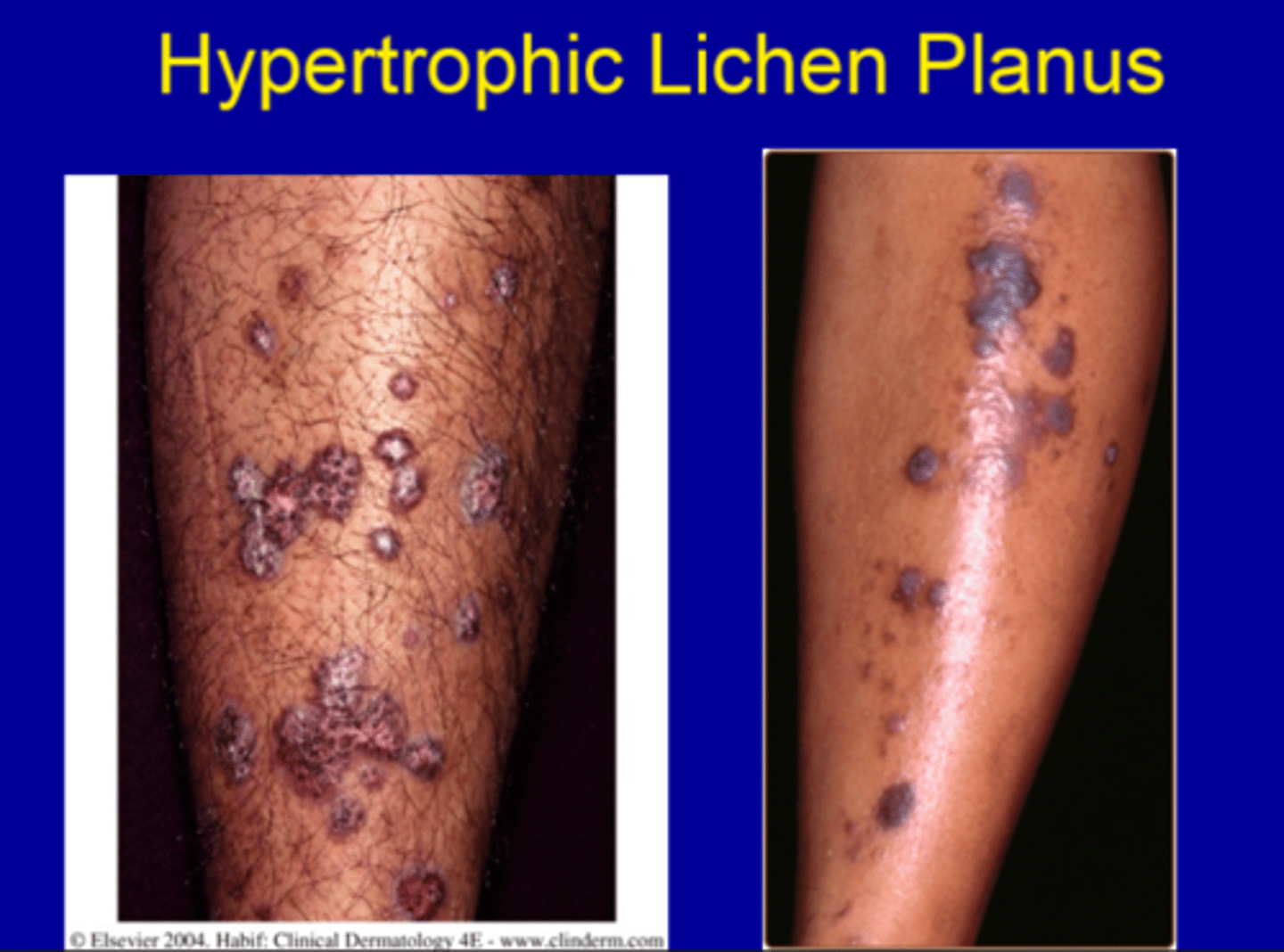
Pattern of lichen planus described as larger thickened, reddish-brown plaques, most often on the lower legs , MC the shins.
Hypertrophic lichen planus
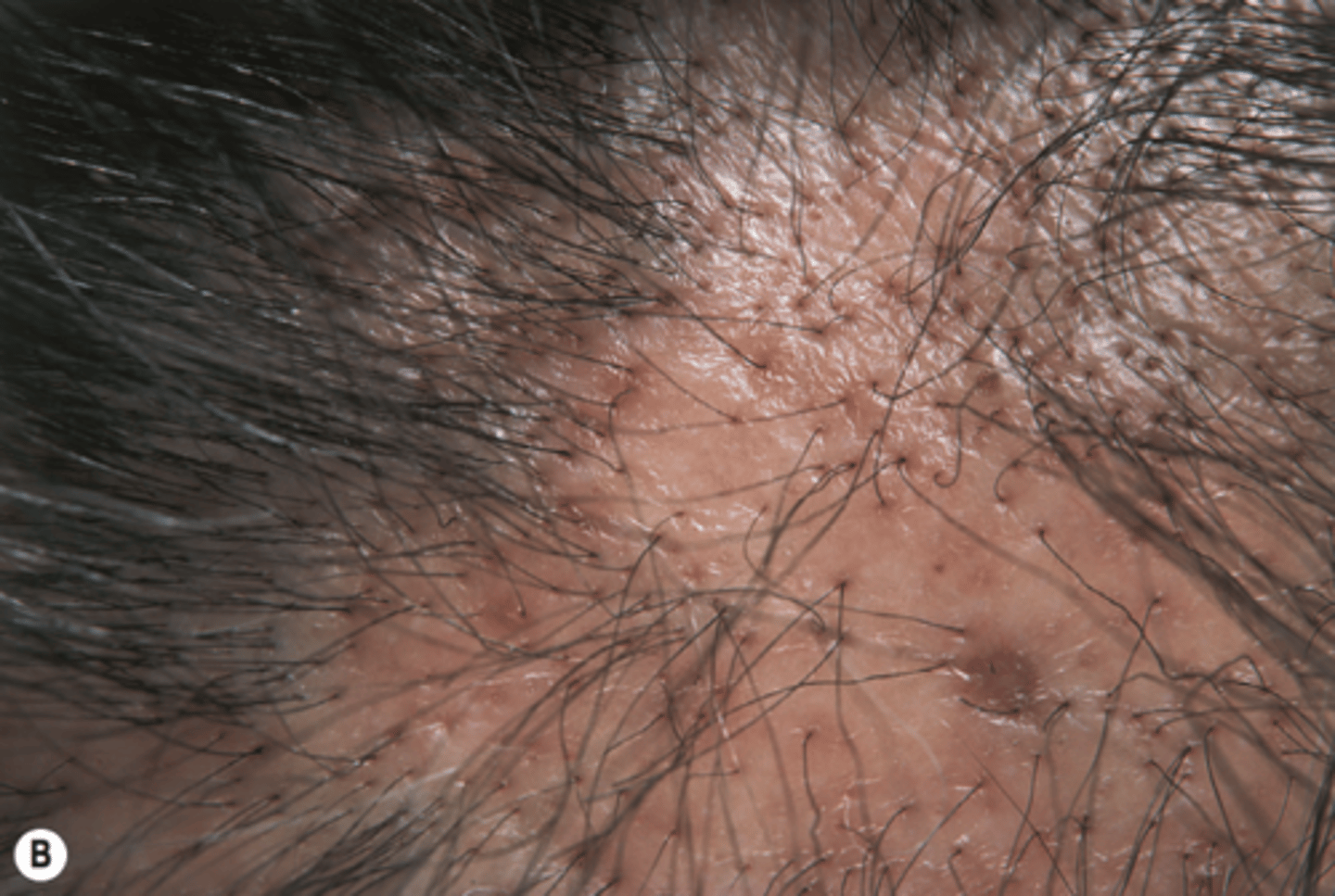
Lichen planus that affects the scalp involving perifollicular erythema and hyperkeratosis of the hair follicles, causing scarring alopecia.
Lichenplano pilaris (follicular)
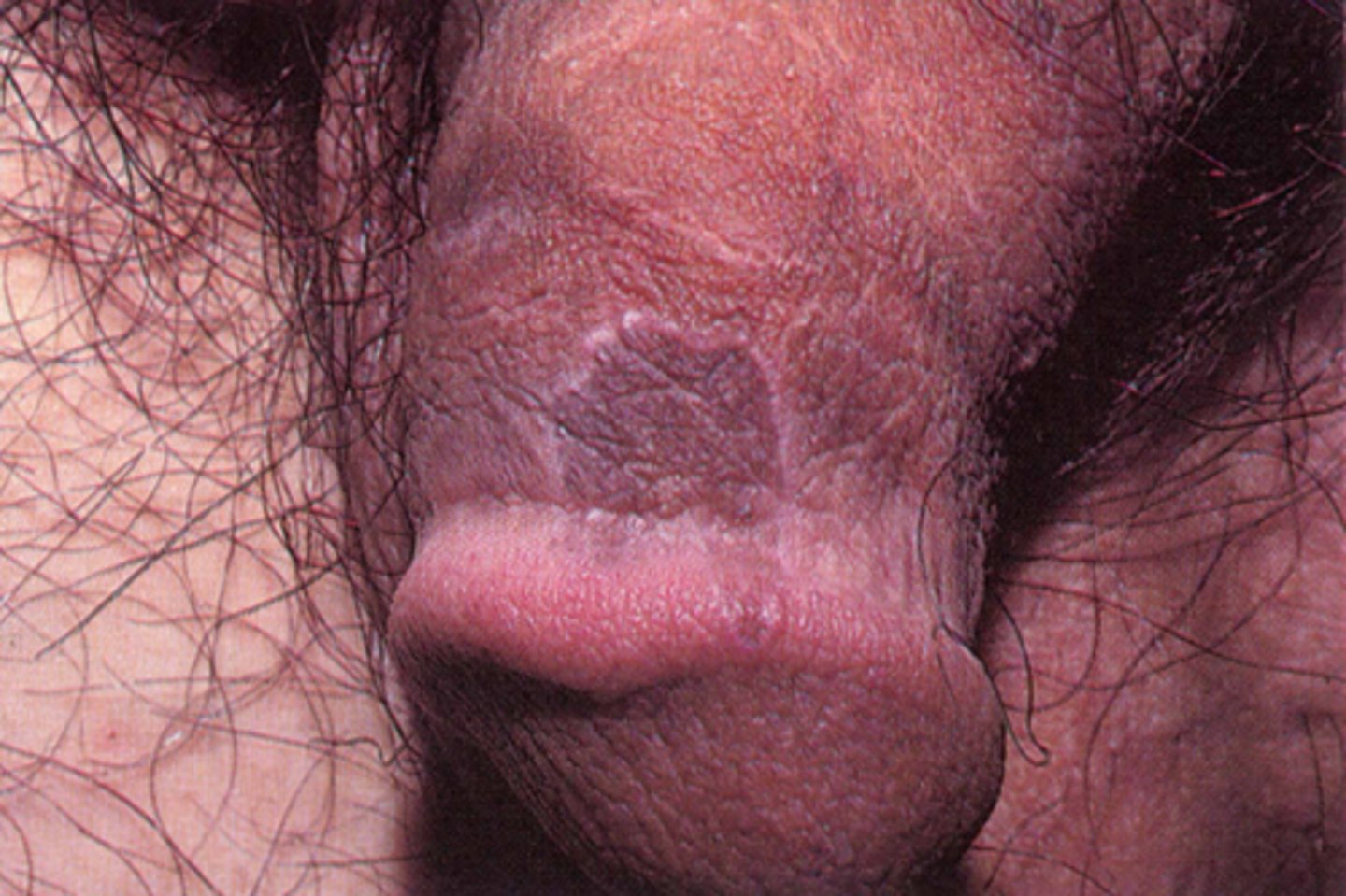
Lichen plus that MC affects the penis/scrotum, axilla and groin. Presents with small papules in ring or coalesce. Possible involution
of flat topped papules. ~1cm in size.
Annular lichen planus
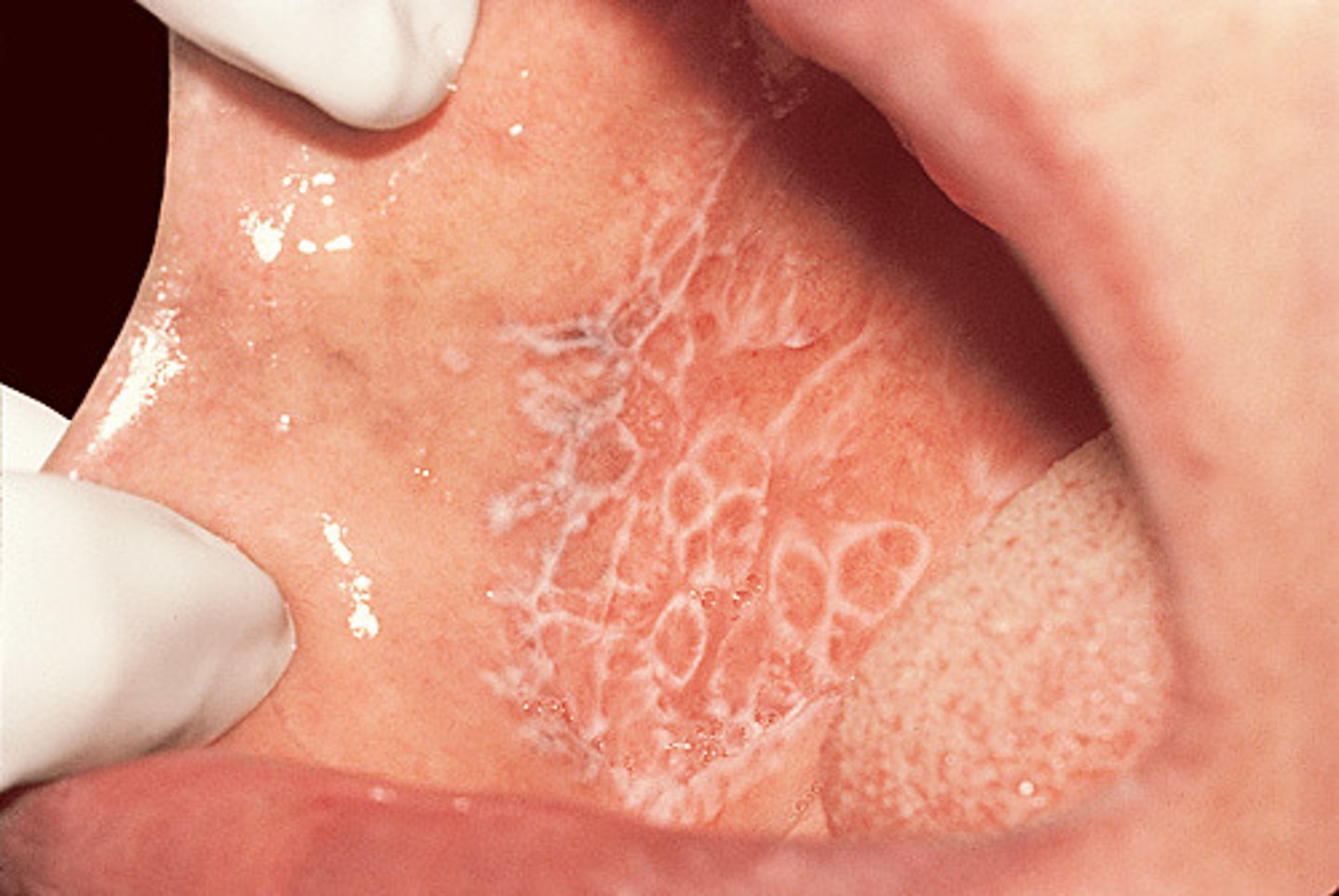
Chronic Lichen Planus that affects the mucus membranes. The most common is oral mucosa that presents with wickhams straie (Reticular), atrophic, or erosive lesions that are B/L and symmetric. Can lead to malignant transformation into SCC.
Mucosal Lichen Planus
What is the first line treatment for Lichen planus?
Topical Steroid
(Class depends on area but typically Class I (superpotent) cream or ointment with occlusion)
How do you tx the oral lesions in lichen planus?
superpotent steriods in Orabase or gel
What is the second line tx for Lichen planus?
1. ILK injections
2. Phototherapy (UVA +/- psoralen or UVB)
3. Systemic steroids
Inflammatory skin condition most commonly affecting the genitals or perianal area MC. May be a result of Koebner phenomenon. Initially starts as small, smooth white polygonal, flat-topped papules or plaques. Papules then coalesce to form atrophic smooth, white wrinkled patches.
Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus
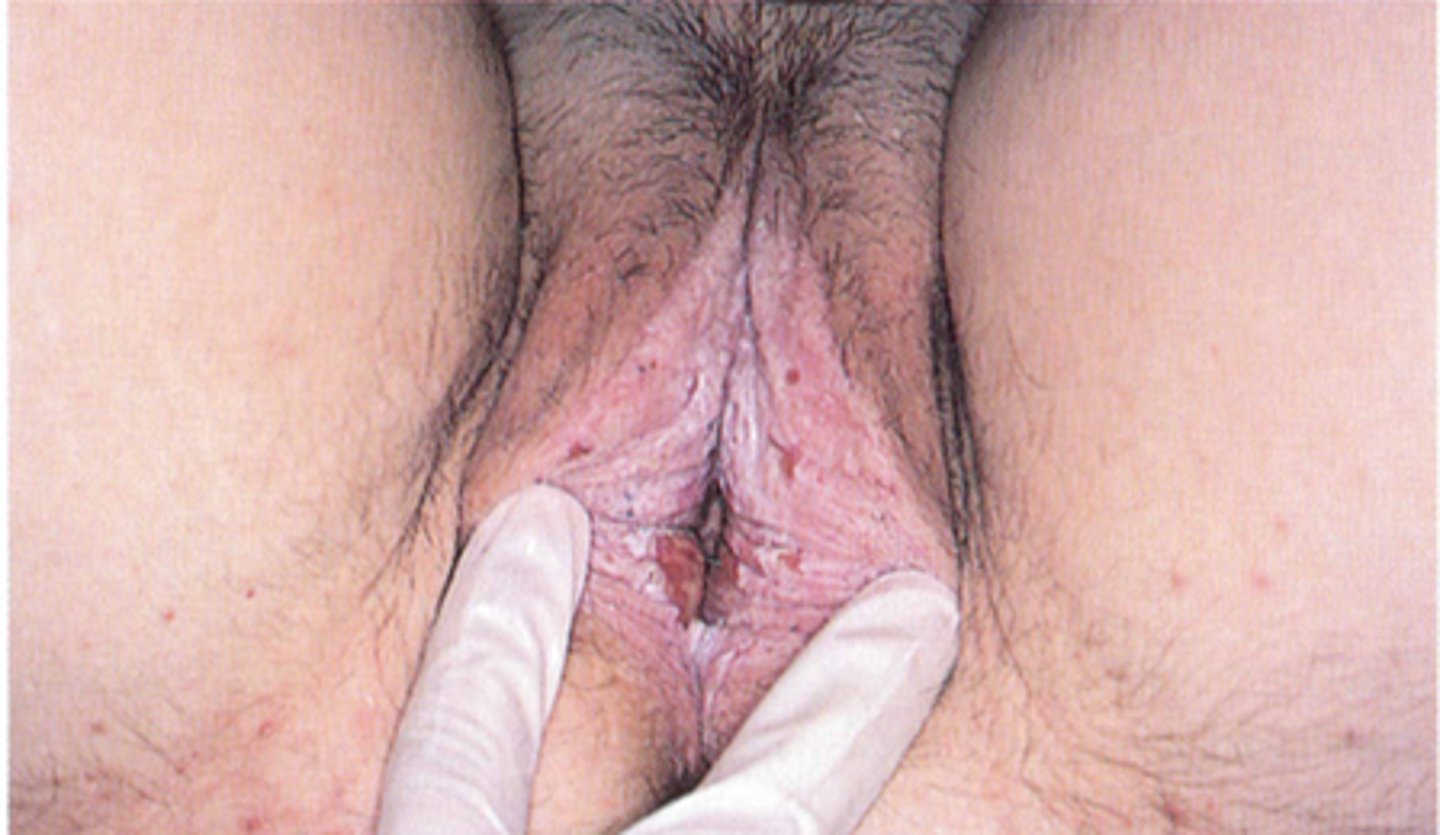
In women Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus causes
Obliteration of normal anatomic structures.
Which part of the body is most commonly affected by Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus in females? What type of pattern does this look like?
Vulva and perianal area in "Figure 8 pattern"
In females, what is the MC involvement for Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus?
mucosal involvement
Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus present in men is MC in?
Uncircumcised men
Patients with Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus have a 3% chance of developing _____
Squamous cell carcinoma
How do you tx female with Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus ?
GYN Referral
1. First line: Topical Steroids (superpotent) ointment usually
preferred one time a day for 6-12 weeks
2. 2nd line: Topical tacrolimus, PUVA, ILK, cryotherapy
How do you tx males with Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus ?
Circumcision (75-100% curative)
• Topical steroids
Chronic inflammatory condition of the sebaceous follicles that can be located on the Face, chest, back and upper extremities.
Acne Vulgaris (AV)
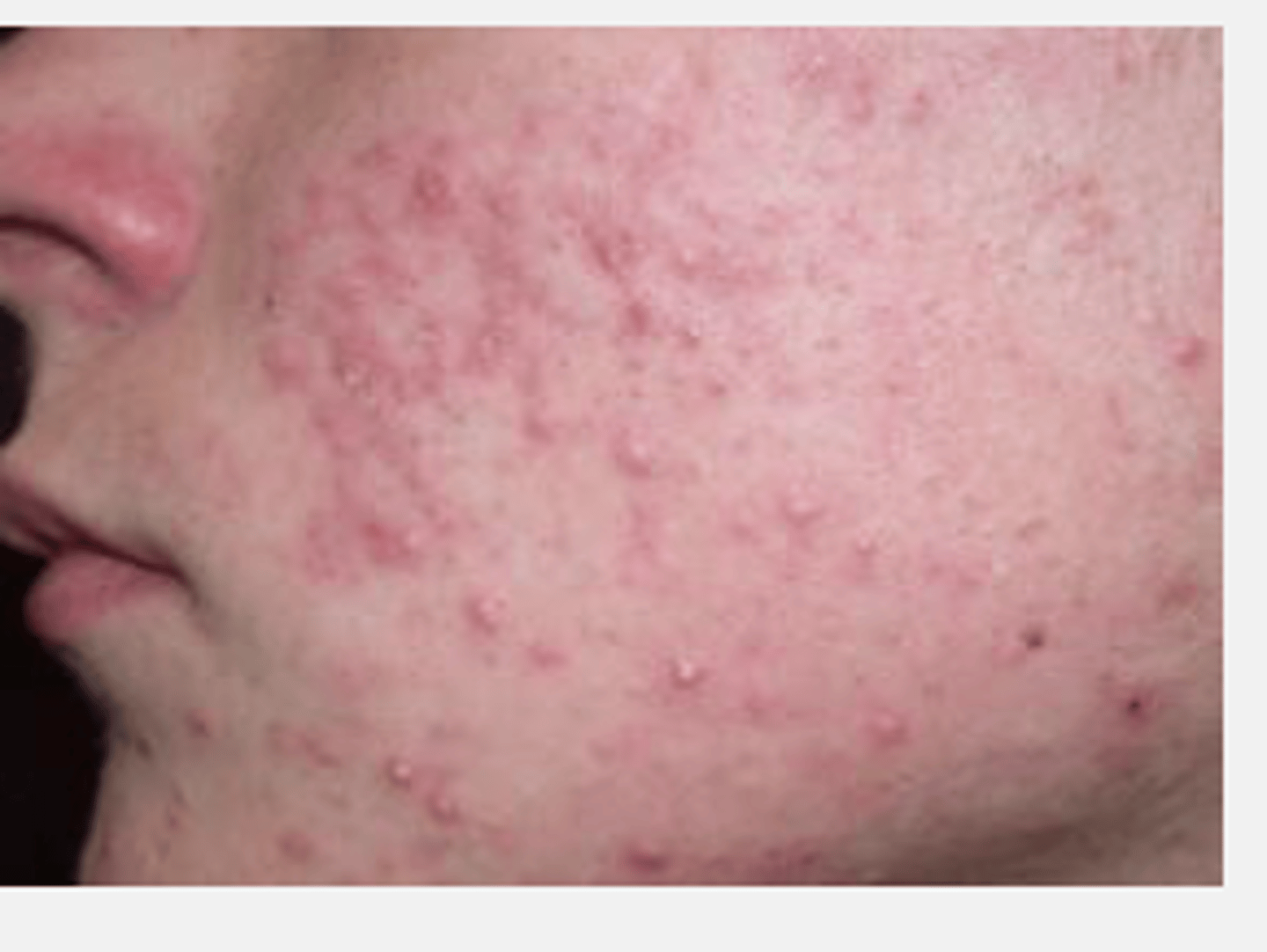
The acne lesions are noninflammatory primary lesions that can be characterized as open/closed
Comedones
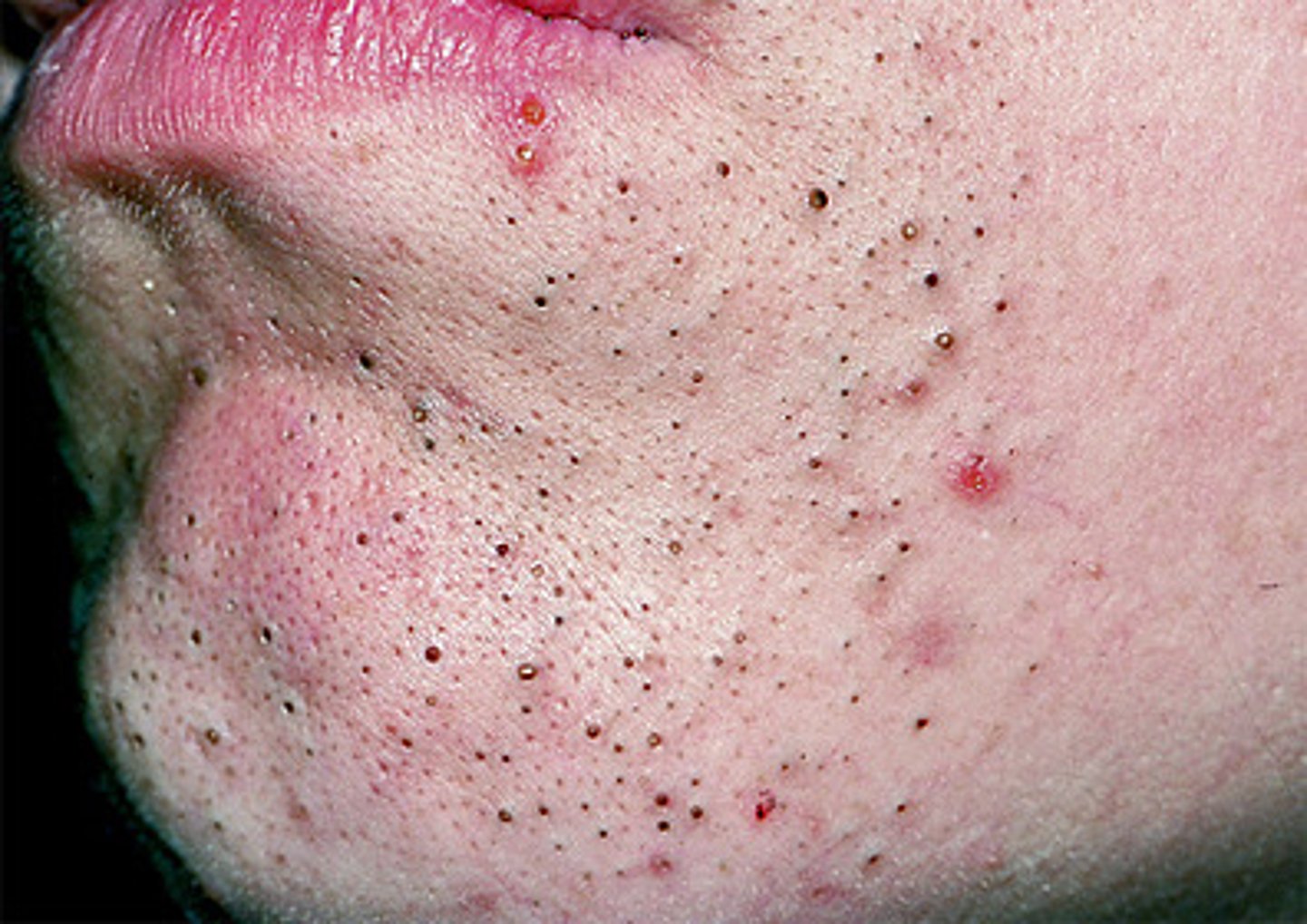
These comedones are flat or slightly elevated papule with central dilation and blackened keratin
Open comedones (blackheads)
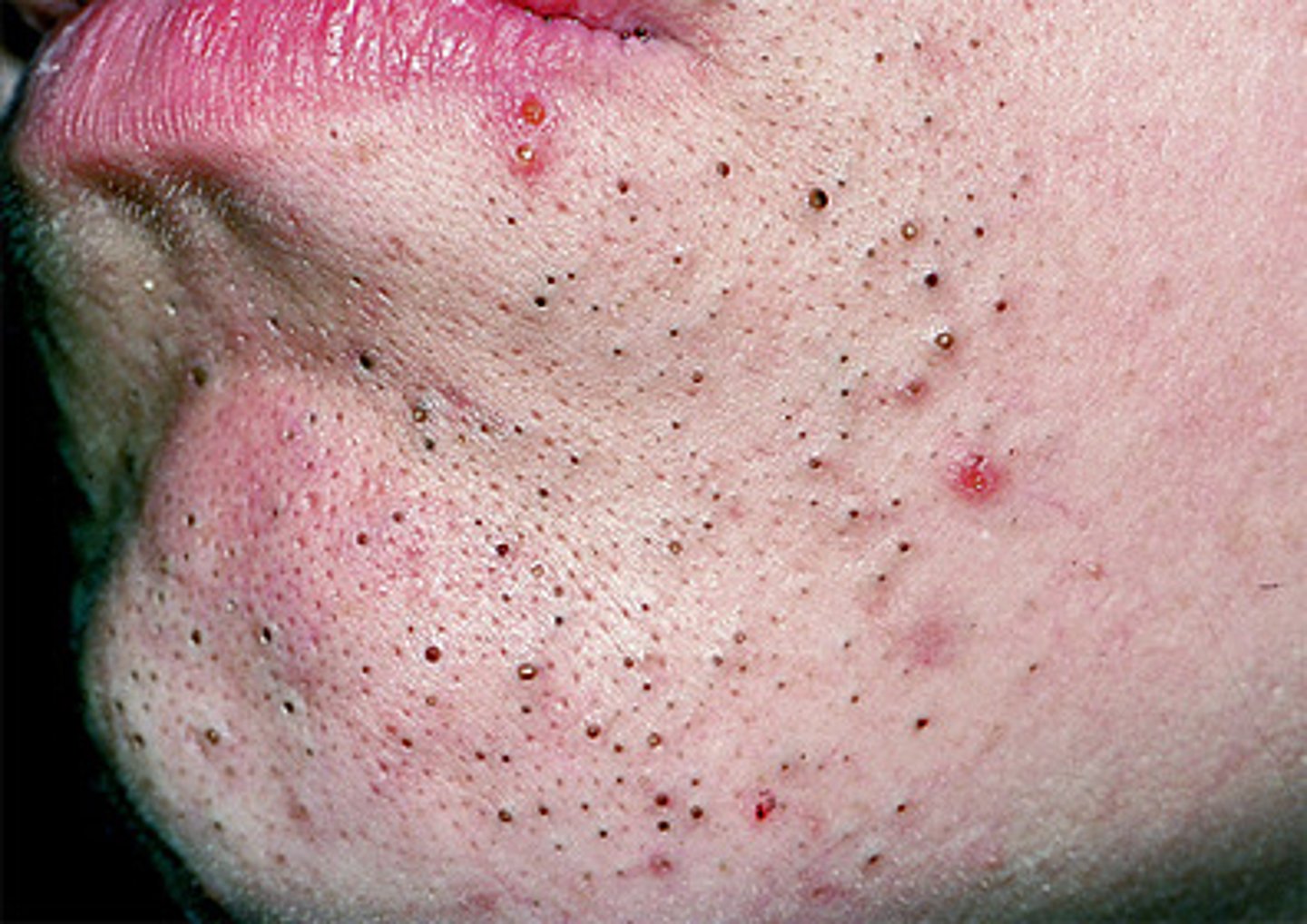
non inflammatory acne lesions usually ~1mm yellowish papules called whiteheads
Closed comedones
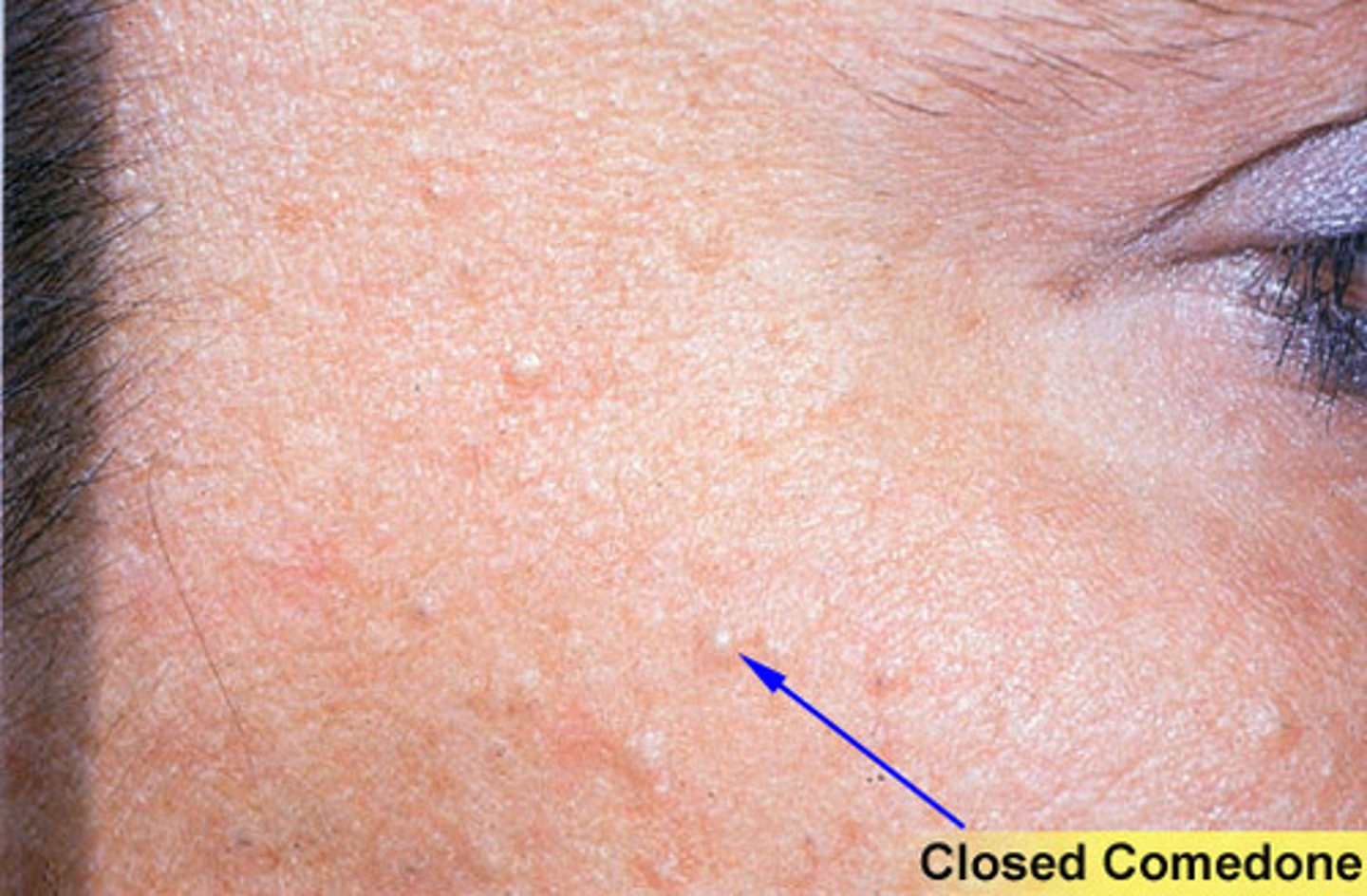
______ can cause Post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Acne vulgarism
What are the 4 things that cause acne?
1. Excess skin (plugged follicles)
2. Excess oil (inc. sebum)
3. Bacteria (cutibacterium)
4. Inflammation (rupture of follicle)
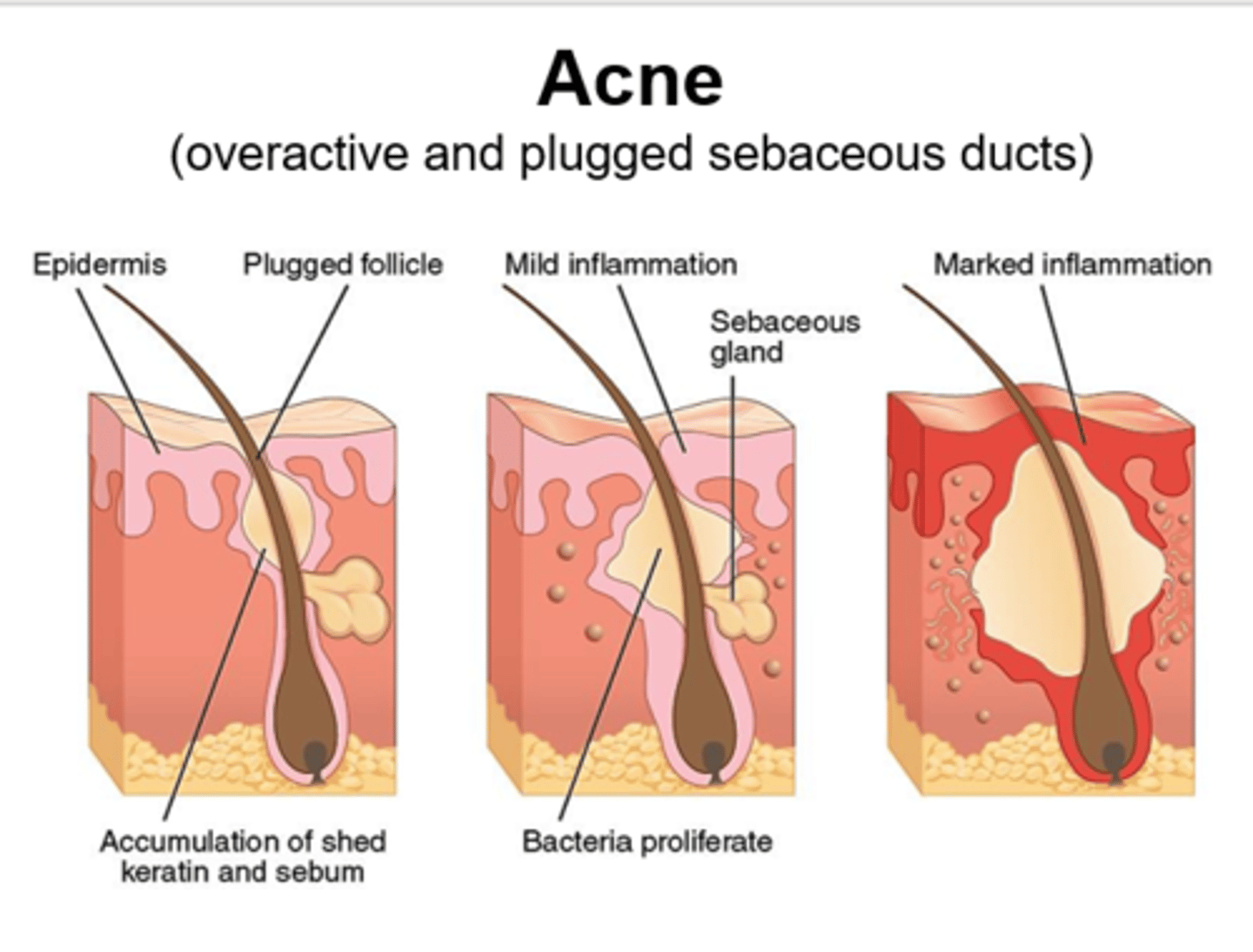
An excessive buildup of dead skin cells/keratinized cells - plugged follicles
Hyperkeratinization
Overuse of _____ can cause rebound acne
Oral steroids
What is the only food in the literature with a supported relationship to acne?
Dairy
What are some common retinoids used in the tx of AV?
1. Tretinoin
2. adapalene
3. tazarotene