Mol cell Bio exam 2 ch 15
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all slides and notes from class done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Analogy for how protein synthesis in the side of soul find their way to membrane and organelles
Mail distribution: parcels find their way through ZIP Codes and addresses
Largest to smallest membrane in compartments by percentage volume (8)
Cytosol 54%, mitochondrion 22%, ER with membrane-bound poly ribosomes 12%, nucleus 6%, golgi apparatus 3%, endosome 1%, lysosome 1%, peroxisome 1%
Three functions of the cytosol
Signaling, cytoskeleton, protein synthesis
endosome function
Sorting of endocytosed material
peroxisome function
Oxidation of toxic molecules
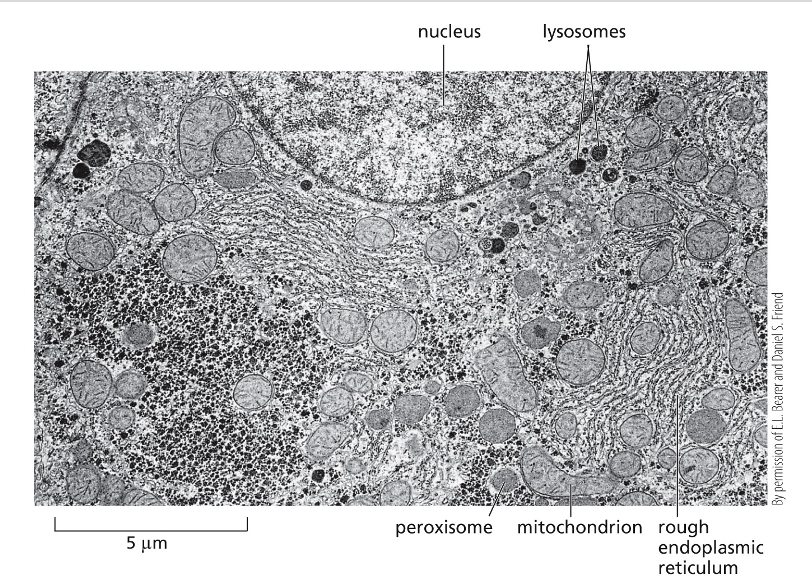
What does this image show?
Electron micrograph of part of a liver cell, small black granules between the compartments are aggregates of glycogen and the enzymes that control its synthesis and breakdown
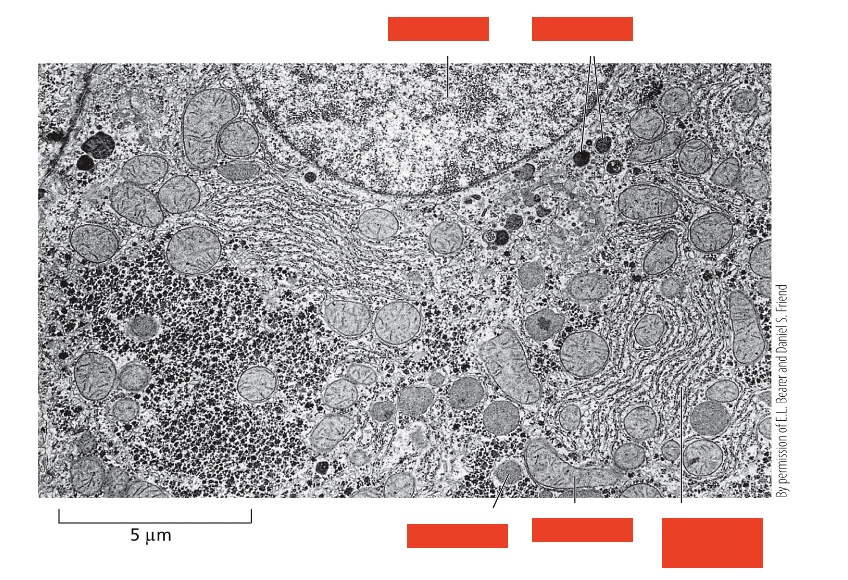
Label the top two
Nucleus, lysosomes

Label the bottom three
Peroxisome, mitochondrion, rough endoplasmic reticulum
Two advantages of compartmentalization
It separates processes, e.g. lysosomes can be extremely acidic, which would be detrimental for the rest of the cytoplasm, processes are able to be concentrated
how did compartmentalization arise? (3 steps)
Endo-symbiotic theory: aerobic prokaryotic cell was phagocytosed by an anaerobic prokaryotic cell, aerobic prokaryotic cell lost surrounding membranes derived from pre-eukaryotic cell, finally you have an early aerobic eukaryotic cell containing a mitochondria with a double membrane
three ways of transport to organelles
Transport through nuclear pores, transport across membranes, transported by vesicles
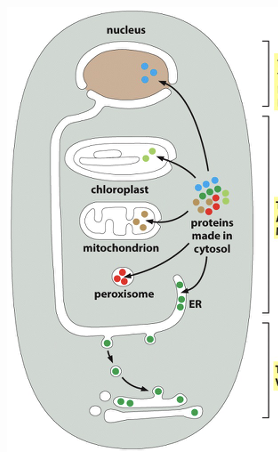
label the transport ways top to bottom
Transport through nuclear pores, transport across membranes, transported by vesicles
what determines where a molecules is transported to, some examples of what signal they can have (3)?
Certain peptides (signal sequences), import into ER, retention in lumen of ER, import into mitochondria
what do proteins have to contain to be transported?
Signal peptides
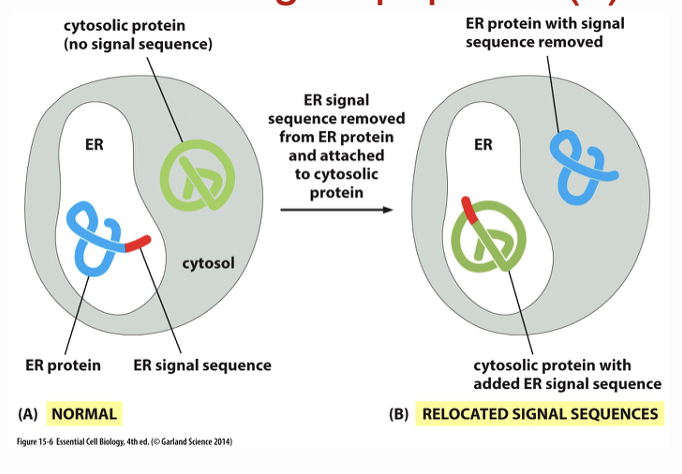
What does this image show?
depending on the red signal peptide a protein is either translocated to the ER or to the cytosol, scientists can use this to make proteins that will enter the ER (picture to the right)
why are nuclear pores important?
Many things have to enter and exit the nucleus
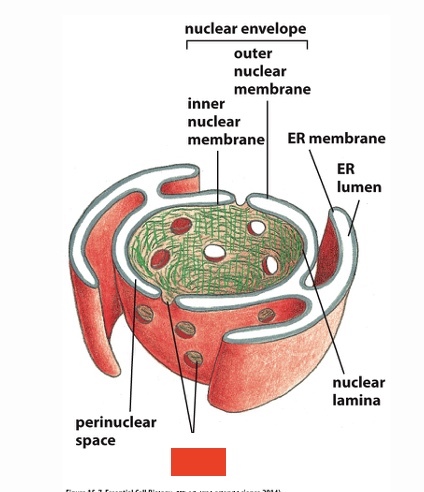
Label
nuclear pores
Label
Nuclear pore complexes
label bottom 4
nuclear basket, pore complex proteins, nuclear lamina, inner nuclear membrane

Label right 3 top to bottom
Cytosolic fibrils, outer nuclear membrane, nuclear envelope
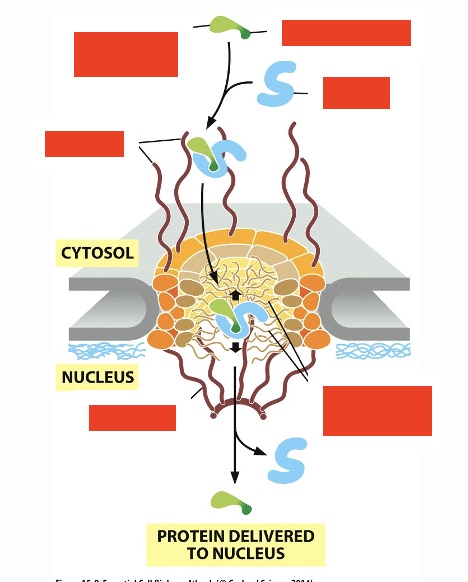
steps of proteins migrating to the nucleus (1), what do they need (2)?
need nuclear localization signal, nuclear import receptor, together this will lead to delivery from cytoplasm to nucleus
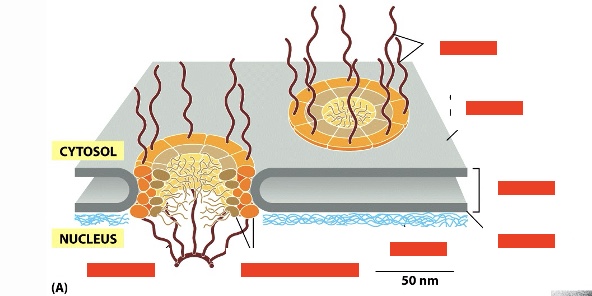
label top three (left to right)
Perspective nuclear protein (cargo), nuclear localization signal, nuclear import receptor

Label bottom three (top then bottom left then bottom right)
cytosolic fibrils, nuclear basket, gel-like meshwork of nuclear fibrils
what drives nuclear transport
Energy by GTP hydrolysis
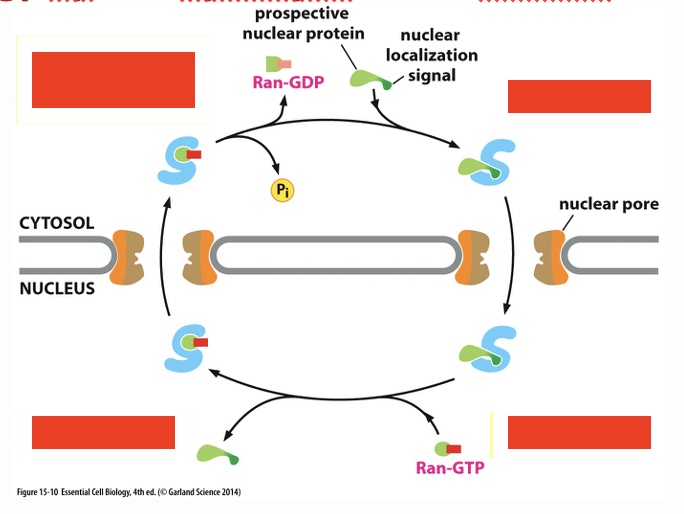
label steps of how GTB hydrolysis provides energy for nuclear transport (start top left, following arrows)
ran hydrolyzes it's bound GTP, ran-GDP dissociates from receptor; protein binds to receptor; ran-GTP binds to receptor; protein delivered to nucleus
How does transport across membranes happen (6 steps)
precursor protein has a signal sequence which binds to import receptors, these receptors deliver the protein to a translocation apparatus at a contact site where mitochondrion’s two membranes are close together, precursor protein snakes in a unfolded state though two protein translocators (1 in each membrane), inside the mitochondrion chaperon proteins pull protein in and prevent backsliding back through the protein translocators, once inside signal peptidase cleaves signal sequence, chaperone proteins released and protein folds and matures
chaperone proteins two functions
prevents protein from preforming its function prematurely, prevents protein from backsliding
How is a protein transported into the ER?
proteins made in the cytoplasm/ER, it binds with an ER signal sequence to a signal receptor particle (SRP), this binds to a receptor in proximity to the protein translocator, SRP is displaced which causes the protein to be imported into the ER lumen
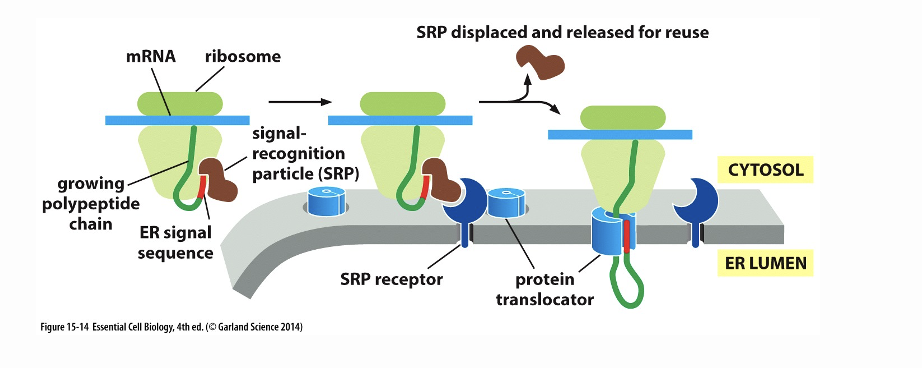
What does this image show?
How to transport into the ER happens
What happens with soluble proteins?
Their signal sequence is cleaved
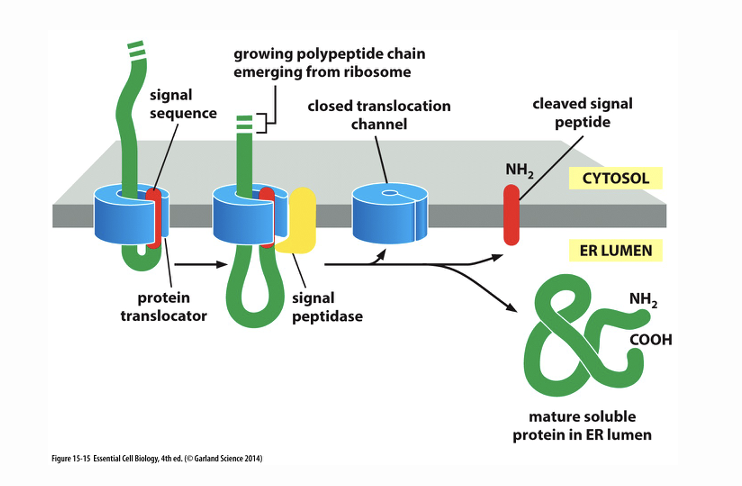
What does this image show
How transport happens with soluble proteins, the signal sequence is cleaved
How does transport happen with membrane proteins? (3 points)
hydrophobic part has to be delivered into the membrane (has a stop transfer sequence and ends with hydrophobic part in membrane), signal peptide is recognized by the protein translator facilitating the import of the peptide, not all of it is transported in since it has a part spanning of the membrane
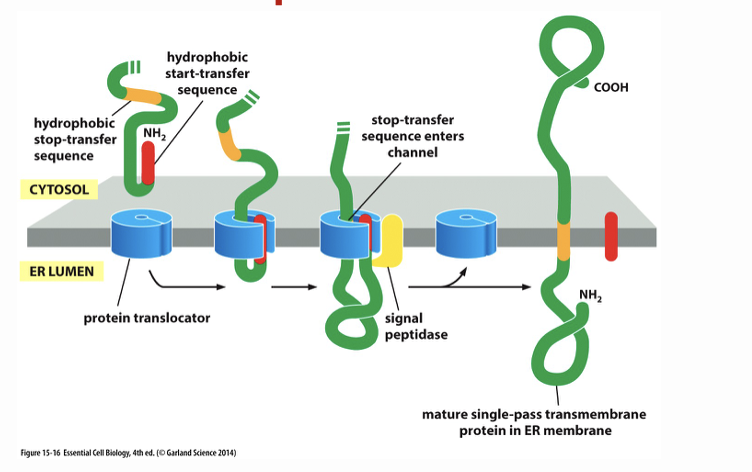
What does this image show?
How does transport across membranes happen with membrane proteins?
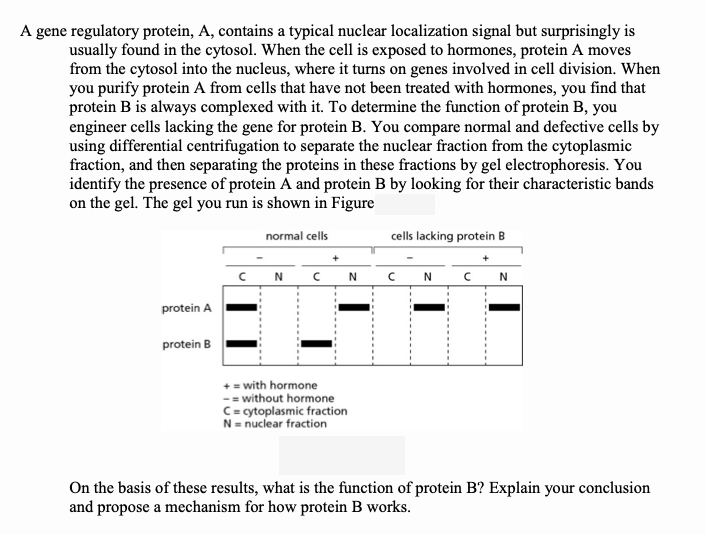


two types of vesicular transport
endocytosis (from outside cell to inside) and exocytosis (buds from inside cell to outside)
Steps post endocytosis (4)
Endocytosis, early endosome (also includes vesicles from golgi apparatus), late endosome, lysosome
Steps pre-exocytosis (3)
Golgi apparatus, transport vesicles, exocytosis
what is vesicular budding driven by?
assembly of a protein coat
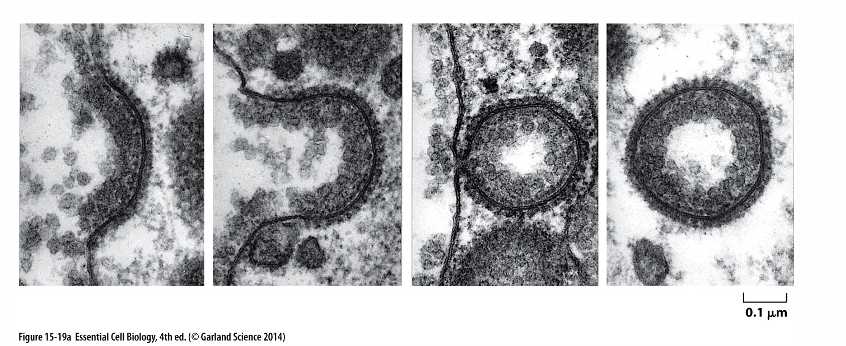
what does this image show?
vesicular budding
what are the components and functions of the protein coat parts (4)
cargo receptor - holds cargo molecules and connects them to adaptin
adaptin - between the cargo receptor and clarithin
clarithrin - assembles into a basketlike lattice structure that distorts the membrane and drives vesicle budding
dynamin - cuts the internally budding vesicle from the membrane
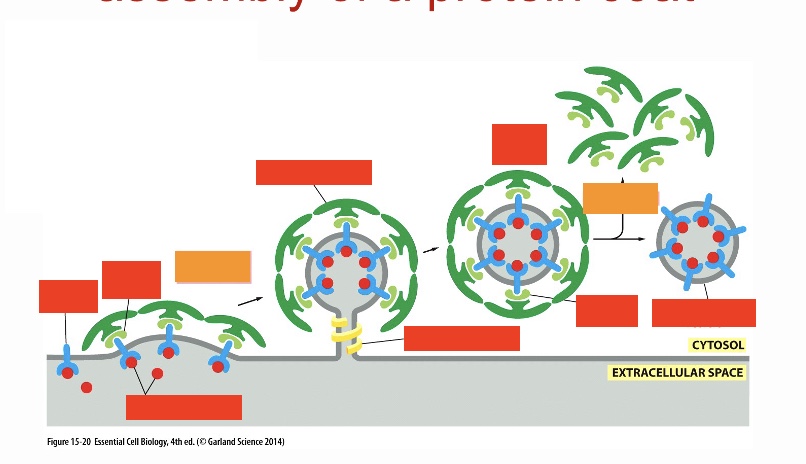
vesicular budding: label the red top row 4 going from left to right
cargo receptor, adaptin, clarithin coat, coated vesicle

vesicular budding: label the red bottom row 4 going from left to right
cargo molecules, dynamin, adaptin, naked transport vesicle

label the orange (steps of what is happening)
vesicle formation, uncoating
what is important for membrane fusion?
snares
proteins involved in exocytosis (4) + functions)
cargo protein (protein to be released after exocytosis), v-snare (on vesicle combines with T snare), receptor (holds docking protein), t-snare (in target membrane, combines with v-snare)
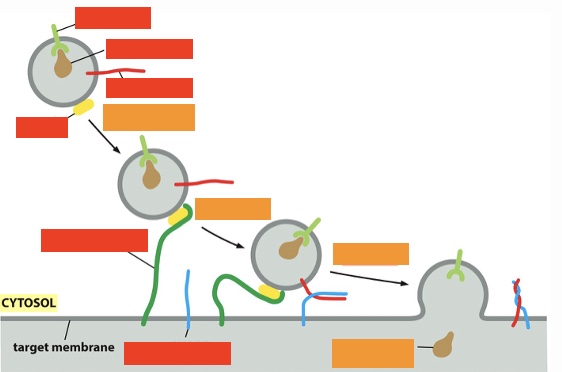
exocytosis: label the processes (orange) (top left to bottom right)
tethering, docking, fusion, cargo protein delivered

exocytosis: label the top 3 proteins on right (top to bottom)
Receptor, cargo protein, v-snare

exocytosis: label the lower 3 proteins on left (top to bottom)
Rab, tethering protein, t-snare
how can movement of molecules be visualized in vivo
using green fluorescent protein
2 types of secretory pathways w/ descriptions
Constitutive of secretion: without external signals
Regulated exocytosis: extra cellular stimulus is needed for release of cargo of the vesicles that are in the cytoplasm
constitutive exocytosis pathway steps from movie (9 steps)
fluorescently labeled membrane proteins synthesized in ER, dispersed through extensive membrane network of ER, move to exit sites that form in random locations in the membrane network, at each of these sites membrane proteins concentrated and packaged in transport vescicles, clusters of transport vesicles fuse to form transport intermediates, transport intermediates move along microtubule track to golgi, exit golgi moving on transport vesicles that are pulled outward on microtubules, delivered to plasma membrane, there it fuses and contents are dispersed
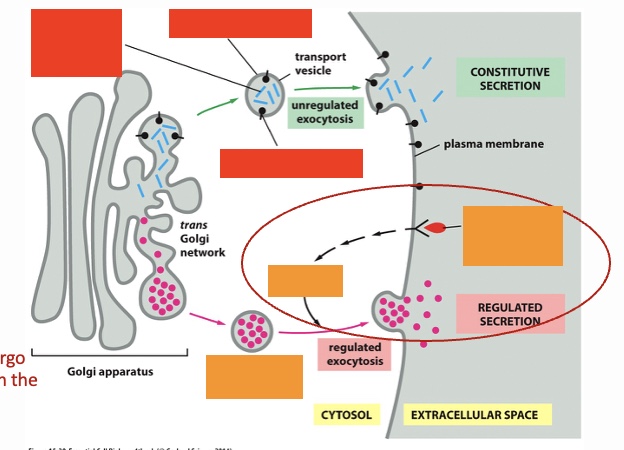
secretory pathways: label the red top two and then bottom (unregulated exocytosis)
newly synthesized soluble proteins for constitutive secretion, newly synthesized plasma membrane lipids, newly synthesized plasma membrane protein

secretory pathways: label the orange left to right (regulated exocytosis)
Secretary vesicles storing secretory proteins, signal transduction, extracellular signal such as hormone or neurotransmitter
endocytosis- “eating and drinking” of the cell, name and describe
pinocytosis- drinking, fluid containing smaller vesicles (<150nm)
phagocytosis- eating, larger particles (>250nm), bacteria, RBCs/defective cells
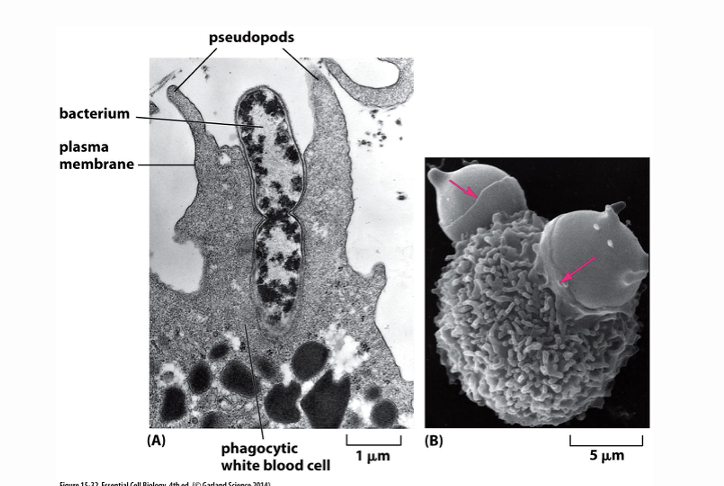
What does this image image show?
phagocytic white blood cell phagocytosing a bacterium
how does cholesterol enter cells, from where
it circulates in the bloodstream, then enters through receptor mediated endocytosis
in what form does cholesterol circulate?
cholesterol molecules are derivatized and packed inside LDL particles, they are surrounded by a protein and phospholipid layer
Steps of receptor, mediated endocytosis with cholesterol (9 steps)
protein of cholesterol recognized by LDL receptors in plasma membrane, adaptin (adaptor molecule) binds to tail of LDL receptor that protrudes into the cytosol, adaptin recruits clarithin which starts coating the membrane, assembly of the clarithin coat causes the membrane to bend inward forming a vesicle that buds off inside the cell taking with it cholesterol, once inside cell vesicle uncoats and fuses with endosome, endosomes low pH causes LDL receptors to release their cargo, (empty LDL receptors are recycled: bud off and return to membrane), endosome fuses with lysosome and LDL particles disassembled, free cholesterol is released to be used in synthesis of new membranes
endosome function
intracellular compartment that first receives all endocytosed material, has low pH
how often do LDL receptors make round trips from plasma membrane to endosome?
every 10 mins
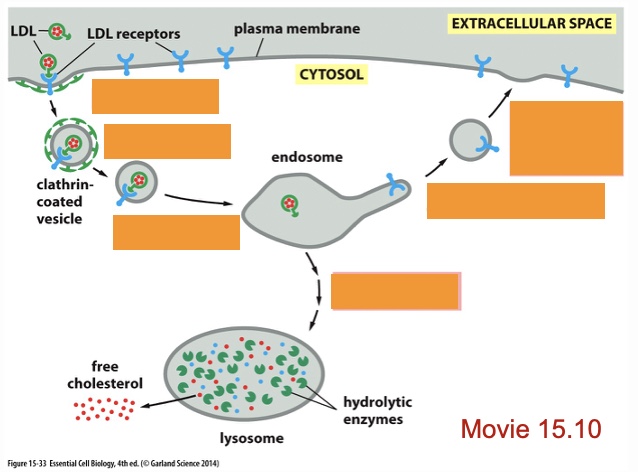
receptor mediated endocytosis: label processes, left top to bottom
Endocytosis, uncoating, fusion with endosome

receptor mediated endocytosis: label processes, right top to bottom
return of the LDL receptors to plasma membrane, budding off of transport, vesicles, delivery of LDL to lysosome
what is the fate of endosomes (3)
recycling, degradation (in lysosome), transcytosis
function of lysosomes, how does it achieve that?
degradation, using many acid hydrolyses and a very acidic environment, H+ pump keeps acidity inside
autophagy description
cell eats itself and obsolete parts are removed
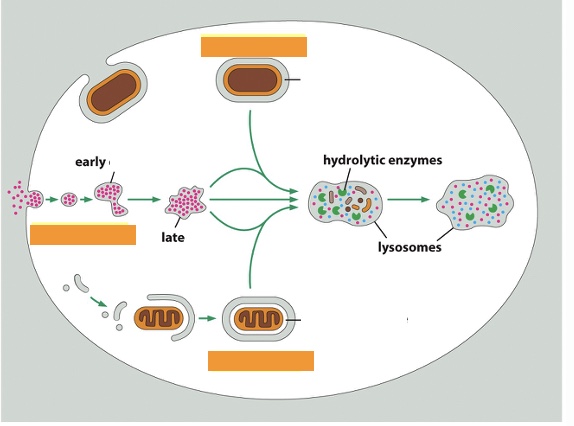
label the three processes top to bottom
phagocytosis, endocytosis, autophagy