ANSC 102 Meats
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
safety
risk of hazard (ex. having non-edible product in meat)
quality
sensory acceptance
wholesomeness
impact on health
What is meat science
combination of several different types of science to study the end product of animal agrictulrue
What different components make up meat sciences
muscle biology (muscle growth), harvest procedures (ethically, legally, biochemical), meat fabriciation (how can we optimize harvest), meat processing (help limit waste), meat in the diet, food safety
What are the two types of muscle growth
hyperplasia and hypertrophy
hyperplasia
increase in the number of muscle cells - done prior to birth (born with all muscle cells), environment and maternal health is very improtant
hypertrophy
increase in muscle cell size, primarily diameter - after birth, can select genetically, use nutrition and management
Definition of meat
animal tissue that is suitable for use as food
what type of muscle typically composes meat
skeletal muscle
What are the catergories of meat
red (from 4 footed domestic animals), poultry, seafood (anything from water), game (anything undomesticated)
Meat composition
78% water, 18.5% protein, 3% lipid 1% carbohydrate, 1% inorganic material (ash)
What are the steps in turning muscle to meat
immobilization, exsanguination, shift in metabolism, decrease pH, rigor mortis
immobilization
stun animal/render unconcious, requried since 1950s, electrical/mechanical/co2 gas
exsanguination
bleed, kills animal and turns into carcass, changes the biochemistry
What happens biochemically when an animal is exsanguinated
o2 transport around the body is stoped which leds to a shift in metabolism and causes lactic acid to build up, ph drop, and proteins change in shape so they can no longer slide
rigor mortis/muscle
when proteins change in shape so muscle cannot slipe or move
Quality problems
PSE and dark cutter
what causes Pale, soft, exudative (PSE)
actue stress
What happens to metabolism with Pale, soft, exudative (PSE)
rapid pH decline before death, pH continues to drop too fast
What is the result with Pale, soft, exudative (PSE)
excessive protein denaturation, proteins have poor water holding capacity
What is the effect on meat of with Pale, soft, exudative (PSE)
very pale in color, very dry
What causes dark cutter
chronic stress
What is the effect of metabolism with dark cutter
slow pH decline
What is the result with dark cutter
limited protein denaturation, exceptional water holding
What effect on meat is there with dark cutter
very ugly, juciy but off flavored
Quantity problems
bruises and broken bones = loss
What are the principles of meat cutting
separate tender cuts from less tender cuts, separate lean cuts from tender cut, separate thick from thin cuts, separate valueable cuts from less valuable cuts
Rules of thumb related to fat and tenderness
limbs are less tender, animals fatten from front to rear - separate limsb and body
What are the different suasage types
fresh, uncooked, fully cooked, luncheon, dry and semi-dry
fresh
raw, losing market share - not as easy to use
uncooked, smoked
mainly found in europe, still raw
fully cooked
aka RTE/ready to eat
luncheon loaves
fully cooked, larger in diameter, like lunch meat
dry and semi dry
ex. salomi, summer sausauge, good for larger preservation
Processing ingredients
water, salt, phsophates, sweetners, flavorings, nitrate
Why do we add water
to add juciness, get more from our product
why do we add salt
helps proteins hold water
why do we add phosphates
help improve water holding, help bring pH up
why do add weetners
help counter balance salt and helps with fermentation
why do we add flavorings
to give meat its identity``
Why do we add nitrate to meet
gives meat its color
Why do we need meat in our diet
provides protein (9 essential amino acids in right concentrations), provides minerals (iron and zinc, b vitamins)
What type of iron does meat provide and why is it significant
it provides hemiron, which the body can absorb 40% of compared to 10% of nonhemiron that plants contain
What is the recommended daily amount of meat to consume
5-7 oz
What are the 3 catergories of food safety hazards
biological, physical, chemical
Physical food safety hazards
non-edible items getting into food, ex. plastic
chemical food safety hazards
allergens, cleaning solutions
What are the major allergies
wheat, soy, fish, shellfish, eggs, seasame
biological food hazards
bacteria, fungi, parasites
What is the danger zone for biological food hazards
40 - 140 degrees F for more than 4 hours
Ways to control food borne illness
keep microbes out (sanitation, hygiene), kill microbes that get in (refrigeration, cooking), control microbes that are ther (refridgeration, cooking, cooling), thawing, reheating
What are the 3 ways to thaw food
refrigderation, cold water, microwave
quality traits
attributes that will improve the quality to the consumer (apperance and palatability)
Palatability
the sensory perception of tenderness, flavor, and juiciness
What is the primary purpose of food safety plans
to remove/eliminate hazards or to reduce the level of hazard to an acceptable level
What are the 3 traits considered when evaluating carcasses and meat
trimness, muscling, and quality
trimness
the amount of fat present
What traits are most important for beef carcasses
quality followed by muscling and trimness tied
What traits are most important for pork and lamb carcasses
trimness followed by muscling and quality if there is a significant quality defect
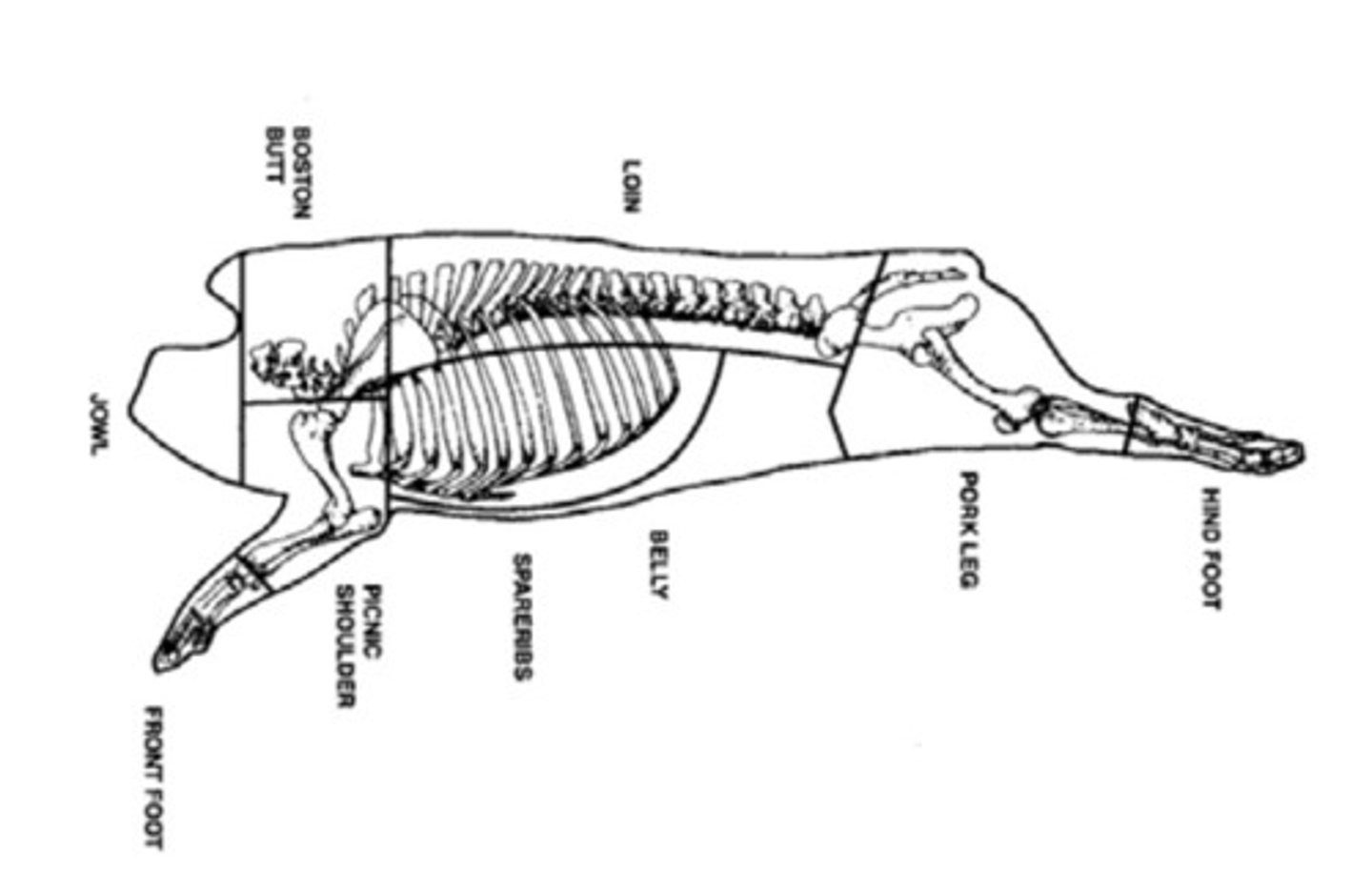
What are the parts of a pork carcass
boston butt, picnic shoulder, loin, belly, ham
Why do we process meat
to make new products, extend the shelf-life, and improve the overall quality and palatability
What is the most sinficiatn catergory of processed meat
sausage
What are the basic steps of sausage production
grinding (reducing particle size), mixing (incorporating functional ingredients), stuffing (putting sausage into casings or packing to improve uniforminity)
Why do you want to cook meat at a certain temp
to meet a min to make sure food is safe and not exceeding a max which would reduce quality
What are some guidelines for reading a thermometer
never read while on the cooking element, insert into the side of the meet/thickest part