Agricultural poisons
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Insecticides:organophosphorous, carbamates, organochlorines
Rodenticides: Phosphorous, anticoagulants, strychnine
Herbicides
Fungicides
Nematicides
Acaricides
Types of agricultural poisons
Alkyl -
HETP
OMPA
TEPP
Malathion
Trichlorfon
Demeton
Dimefox
Isopestox
Aryl- Parathion, Paraoxon, Methyl-parathion, Chlorothion, Diazinon
Types of organophosphate compounds
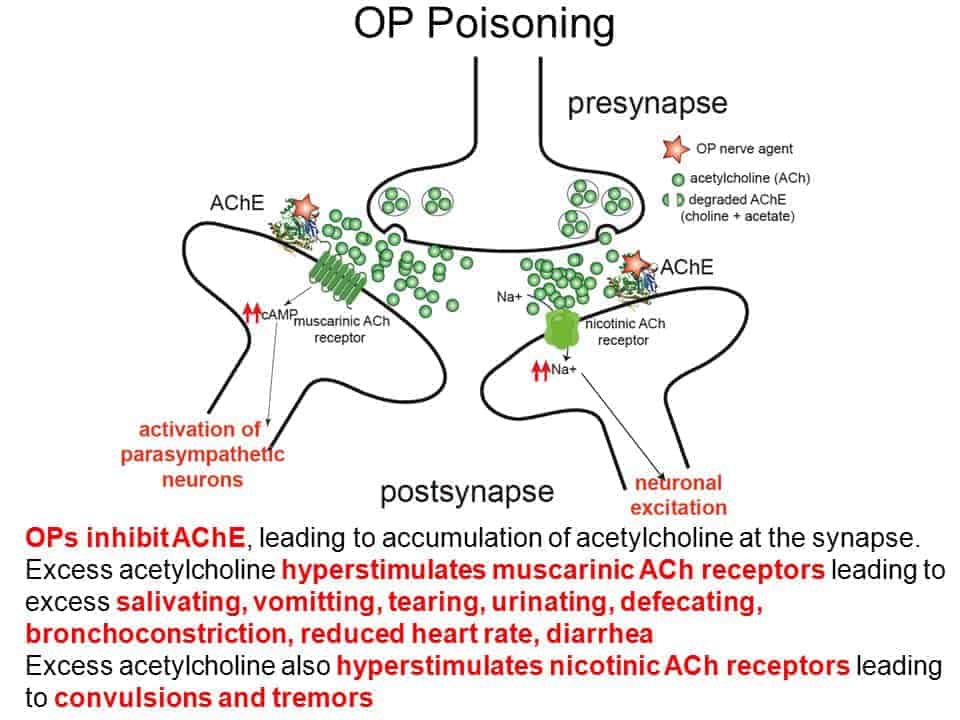
Action of OP
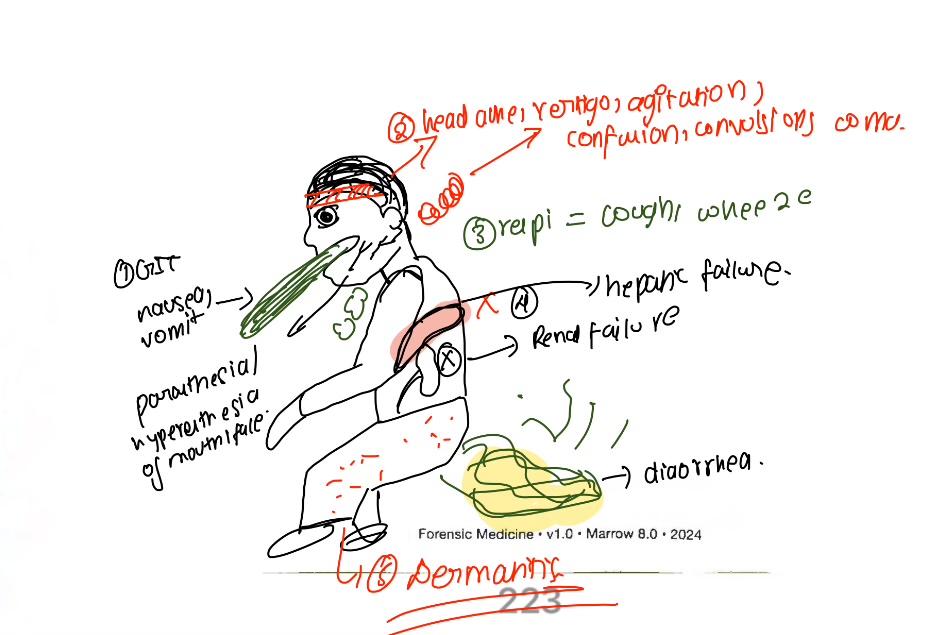
Acute cholinergic syndrome(<1day)
Intermediate Syndrome (1-4 days)
Delayed Polyneuropathy(1-4weeks)
Signs and symptoms of OP is divided as
Muscarinic-
DUMBBELS
diarrhea, urination, miosis, bradycardia, bronchorrhea, emesis, lacrimation(chromodacryorrhea-red tears due to protoporphyrin excretion), salivation
Nicotinic effects-
MATCH
Muscle weakness and fasciculation
Adrenal medulla activity increase
Tachycardia
Cramps in muscle
Hypertension
CNS effects- irritability, apprehension, convulsions, restlessness, fine fibrillary tremors in hands, eyelids, face
Features of acute cholinergic syndrome
due to release of OP stored in fat tissue
includes proximal muscle weakness and the neck flexors muscles——areas innervated by cranial nerves
cranial nerve palsies
Intermediate syndrome includes
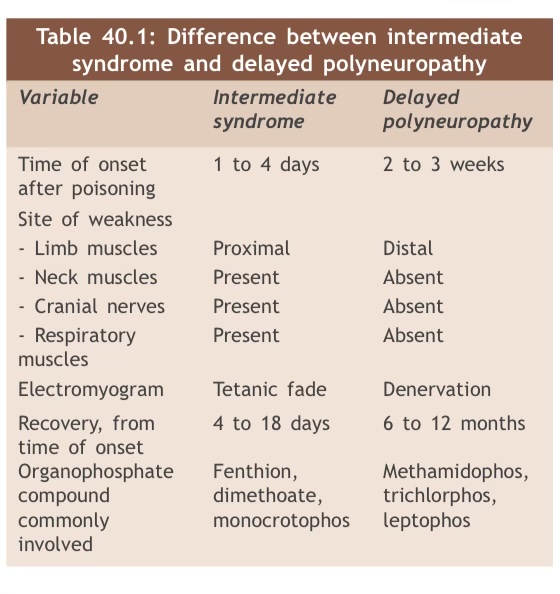
due to the inhibition of the enzyme neurotoxic esterase with nerve demyelination
paralysis is usually limited to distal muscles of the limbs, cranial nerves and proximal muscles are sparede
-foot drop
-flaccid symmetrical paralysis
-muscle wasting
Delayed polyneuropathy is
History
Clinical features
Cholinesterase level:Rbc cholinesterase and plasma cholinesterase—-<50% fall.
Colorimetric method
Paper chromatography
P-nitrophenol test
Thin layer chromatography
Gas chromatography
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
High performance liquid chromatography
ECG-Right axis deviation, ST depression, T wave inversion
Diagnosis of OPP
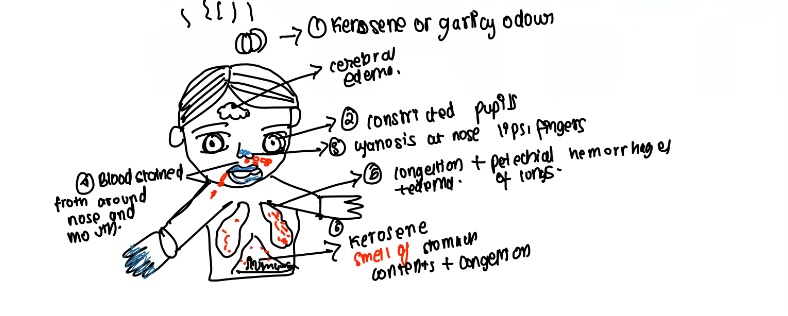
PM findings of OP poisoning
Stabilisation
Decontamination
Antidote_atropine sulfate-reverses the muscarininc effect but cannont reverse nicotinic effect.2-4 mgIV
Oximes-regeneration of acetylcholinesterase at the muscarinic, nicotinic and CNS sites. Pralidoxime-500mg/20ml infusion at a dose of 1-2gm.
For convulsions-diazepamm
Antibiotics
Oxygen administraion, ventilator
Treatment of Opp
insecticides
include carboaryl,carbfuran, methomyl, popoxur, aldicarb, triallate
causes reversible inhibition of ACE by binding to its anionic site
What are carbamates
-anionic site is not available for oximes to bind and they themselves have anticholinesteric efffect hence not given
Why is oxime not given in carbamates poisoning
Respiratory failure
Cerebral hypoxia
Hyperthermia
Hepatic failure
Renal failure
Causes of death in OP poisoning
Organochlorines are chlorinated hydrocarbons used for pesticides
They include
-DDT
-Benzene hexachloride group-BHC, Lindane
-Cyclodienes-endosulfan,endrin,dieldrin
-Toxaphene and related compounds
What are organichlorines
DDT——> blocs sodium channels and sodium conductance across the axons
Lindanes and Cyclodienes inhibit GABA-medicated chloride channels.
MOA of organochlorines are
mydriasis
Clinical features of Organochlorine poisoning
when it comes in contact with water it produces phosgene gas. phosgene gas is absorbed and itis a protoplasmic poison which inhibits cytochrome oxidase.
Aluminium phosphide moa
Weaknes
Ataxia
Tremors
Weight loss
Pseudotumor cerebri
Abnormal mental changes
Oligospermia
Thrombocytopenic purpura
Aplastic anemia
Liver cancer
Leukaemia
Chronic poisoning with organochlorines causes
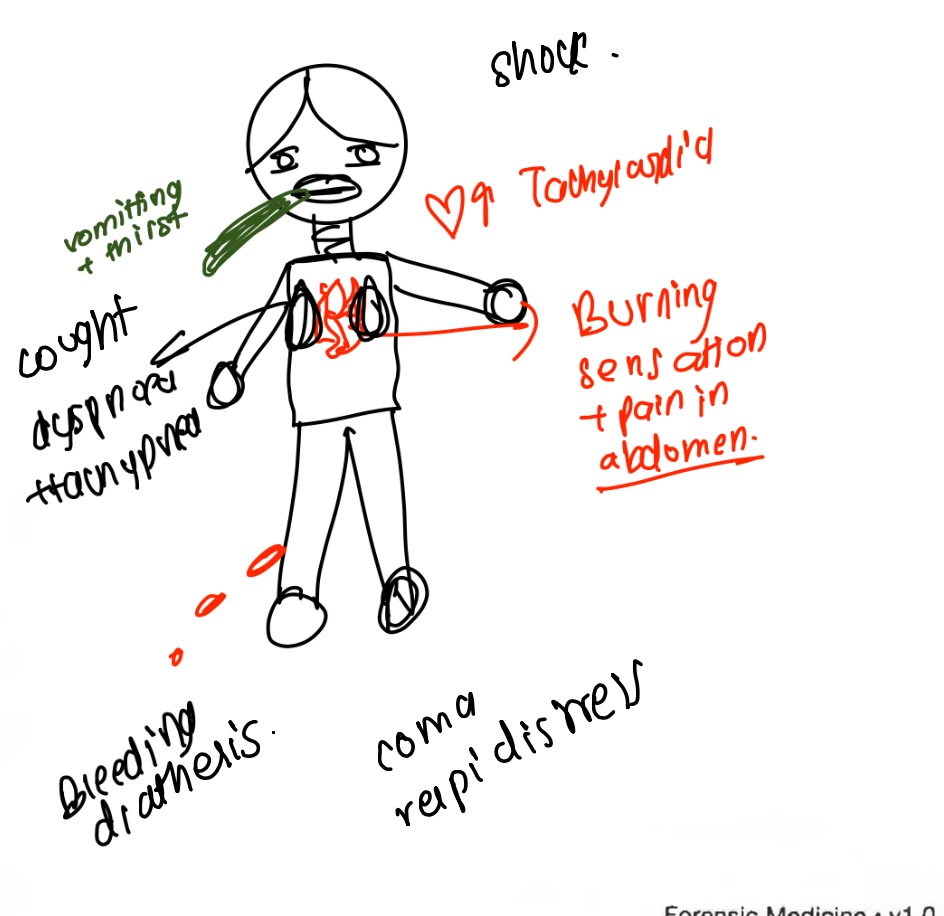
clinical features of AP poisoning
Garlicky odour breath
Abnormal LFT
Urinalysis- occult blood, glucose, albumin, bilirubin
ABG- Metabolic acidosis
Silver nitrate test- black color
Diagnosis of aluminium phosphide poisoning
Undergoes nicotinamide dependent reduction to form free radiacals which inturn combines with o2 to form cations. superoxide free radicals and hydroxyl radicals are produced which disrupts cellular function, structure and death.
MOA of paraquat
Prolongs the inactivation of sodium channels by binding to it in the open state.
MOA of pyrethrin compounds