IB Bio Review- D3.2 Inheritance
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Female (XX) only produce eggs containing the _ chromosome
X
Male (XX) can produce sperm containing either the _ or the _ chromosome
X Y
sex chromosomes are ___, and there are many genes on the x-chromosome not on the y-chromosome
non-homologous
sex-linked traits are those which are carried on the __-______ in the non-homologous region
x-chromosome
sex-linked traits are more common in ____
males
what is colorblindness?
inability or decreased ability to see color, or perceive color differences
caused by a genetic mutation affecting the photopigments in the cones of the retina
X-linked recessive disorder
since males have one X and one Y chromosome, they are more likely to be colorblind if they inherit the mutation.
females, with two X chromosomes, are less likely to be affected because they would need the mutation on both X chromosomes to be colorblind.
females can be _____ or _____ with respect to sex-linked genes
homozygous or heterozygous
_____ females are carriers of colorblindness and haemophilia
heterozygous
what is the genotype of a carrier female
X^N X^n
N = normal vision
n = red-green color blindness
what is the genotype of a normal male
X^N Y
(notice that there is no allele attached to the Y)
N = normal vision
n = red-green color blindness
what is blood clotting?
metabolic pathway of enzyme-controlled biochemical reactions
requires globular proteins called clotting factors
recessive X-linked mutations causes these factors to not be produced
what is haemophilia?
impairs the body's ability to make blood clots, a process needed to stop bleeding
X-linked recessive disorder (carried by the X-chromosome)
since males have only one X chromosome, a single defective gene can cause the disorder
females have two X chromosomes, so a defective gene on one X chromosome is often compensated by the other X chromosome.
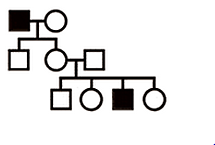
sex-linked, recessive:
trait is able to skip generations
males are predominately affected
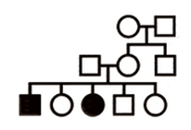
autosomal, recessive:
trait is able to skip generations
no major sex-bias in expression
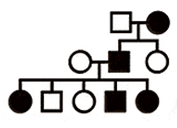
autosomal dominant:
trait cannot skip generations
no major sex-bias in expression
what is a genotype?
the combination of alleles of a gene carried by an organism
what is a phenotype?
the expression of alleles of a gene carried by an organism
what is a centromere?
joins chromatids in cell division
what is an allele?
different versions of a gene
dominant allele = capital letter
recessive allele = lower case letter
what is a carrier?
heterozygous carrier of a recessive disease-causing allele
what does homozygous dominant mean?
having 2 copies of the same dominant allele (AA)
what does homozygous recessive mean?
having 2 copies of the same recessive allele (aa)
recessive alleles are only expressed when homozygous
what does codominant mean?
pairs of alleles which are both expressed when present
what does heterozygous mean?
having 2 different alleles, the dominant allele is expressed
what is gene loci?
specific position on a chromosome
who discovered the principles of inheritance with pea plant experiments?
gregor mendel, 1866
why were pea plants used for conducting genetic crosses?
Short life cycle for generational studies.
Can produce hybrids
Self-pollinate
Easy control of pollination for experiments.
Distinct traits for clear inheritance.
High offspring numbers for increased data accuracy.
what are mendel’s 3 laws?
law of segregation
law of independent assortment
principle of dominance
what is the law of segregation?
gametes are haploid and have 1 allele of each gene
when male and female gamete fuse the diploid cell will have 2 alleles of each gene
many genes have 2 allels w one dominant, one recessive, producing:
AA (homozygous dominant)
Aa (heterozygous)
aa (homozygous recessive)
what is reductive division?
each haploid gets only one of 2 alleles parent has for each gene
what is the law of independent assortment?
the two alleles of each gene are randomly separated into different haploid daughter nuclei during meiosis.
thus, the inheritance of one trait (determined by a gene) doesn't influence the inheritance of another trait (determined by a different gene).
what is the principle of dominance?
dominant alleles always show their encoded trait when present in an organism
masking recessive alleles
recessive alleles only express their encoded traits when no other alleles are present
CODOMINANT alleles can have joint effects if both are present
_____ is the combination of alleles in an organism
genotype
____ is the observale traits of an organism
phenotype
what is phenotype plasticity?
when organisms change their gene expression pattern of proteins to become adapted to specific environmental conditions