BIOL 108L: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, BIO 108L final, BIOLOGY 108L FINAL REVIEW, Biology 108L Review Notes, BIO 108L Midterm (Kapros), Bio 108 Lab Final Review, Biology 108 Lab Final UMKC, Mendelian Genetics, BIOLOGY LAB PHOTOSYNTHESIS
1/489
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
490 Terms
a process of introducing specific genes from one organism into another
recombinant DNA technology
an organism with a gene from another species
transgenic organism
enzymes function to cut DNA molecule at a specific sites and have become one of the basic tools of molecular biology
restriction enzymes
a process that scientists make many copies (molecular clones) of an isolated DNA
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
is used to identify criminals in cases of rape and murder
DNA fingerprinting
a technique is used to sort and separate DNA fragments by their size
electrophoresis
what happens at the electrodes during electrophoresis?
electrolysis and pH effects
the flow of current through the ___ results in the ___ of water and an accompanying change in the ___
buffer
electrolysis
pH
reaction occurs at cathode (- electrode) results in more basic solution
2e⁻ + 2H₂O → 2OH⁻ + H₂
HA + OH⁻ ↔ A⁻ + H₂O
reaction occurs at -anode (+ electrode) results in more acidic solution
H₂O → 2H+ + 1/2 O₂ + 2e⁻
H+ + A⁻ ↔ HA
why are there more bubbles produced at the cathode?
the difference in the production of the hydrogen and oxygen gas at the cathode and anode, respectively, affords a direct way of determining electrode polarity. Twice as much hydrogen gas is produced at the cathose as oxygen at the anode. This is readily apparent by the larger number of bubbles at the cathode than at the anode
why does the buffer is so important in electrophoresis?
the change in pH resulting from the hydrolysis of water underscores the importance of the buffer in electrophoresis
where do restrictin enzymes come from?
these enzymes happen to be an adaptation of bacteria that act as a defense mechanism againsnt viruses known as bacteriophages. The addition of methyl groups to restriction enxymes only recognize and cut the phage DNA, thereby preventing infection
Explain the basic principle of how restriction enzymes work
→Restriction enzymes recognize a sequence of nucleotides, usually 4 to 8 base pair long, call a recognition site
→At a specific nucleotides within the sequence, the enzyme will break the phosphodiester bonds in the DNA backbone
→The recognition sites are usually palindromic, meaning that the sequence seads the same forwards and backwards
→When the palindrome is found on complementary strands of DNA molecule it is called an interted-repeat panlindrome
→Restriction enzymes can leave different types of ends once the DNA is cleaved: sticky ends and blunt ends
→Sticky ends leave 3' to 5' overhangs while blunt ends leaves no overhangs
→The type of end dictates how the DNA fragment isolated by the restriction enzyme digest will be recombined with other DNA fragments in a process known as ligation
restriction enzymes recognize a sequence of nucleotides, usually 4 to 8 base pair long
recognition site
explain why the recognition sites are usually palindromic?
the sequence heads the same forwards and backwards
when the palindrome is found on complementary strands of DNA molecule
interted-repeat panlindrome
leave 3' to 5' overhangs
sticky ends
Via restriction exonucleases
leaves no overhangs
blunt ends
Via restriction endonucleases
the type of end dictates how the DNA fragment isolated by the restriction enzyme digest will be recombined with other DNA fragments in a process known as
ligation
DNA fragments of various sizes are loaded into a porous gell made from ___ , a carbohydrate found in red algae
agarose
how do the fragments of DNA migrate through the gell when an electric field in applied?
because of the negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA nucleotides, the fragments will be attacted to the positive anode
___ pieces of DNA will more easily migrate through the gell than ___ fragments, which have more difficult time moving through the gell matrix
smaller
larger
the presence of fragment of interest can be confirmed based on its ___ , which is determined by comparing the relative lovation of the test sample to the fragments of the ladder
size
anode (+ charged)
red
cathode (- charged)
black
how to find size of unknown DNA from known size DNA?
measure how far DNA travel whose size known to find out direct relationship of linear scale (distance of DNA migration mm) and log scale (DNA size - base pairs)
blunt ends or sticky ends are cut smaller?
sticky ends
Mapping
Initial process of finding size and order of DNA
via gene sequencing and bioinformatics
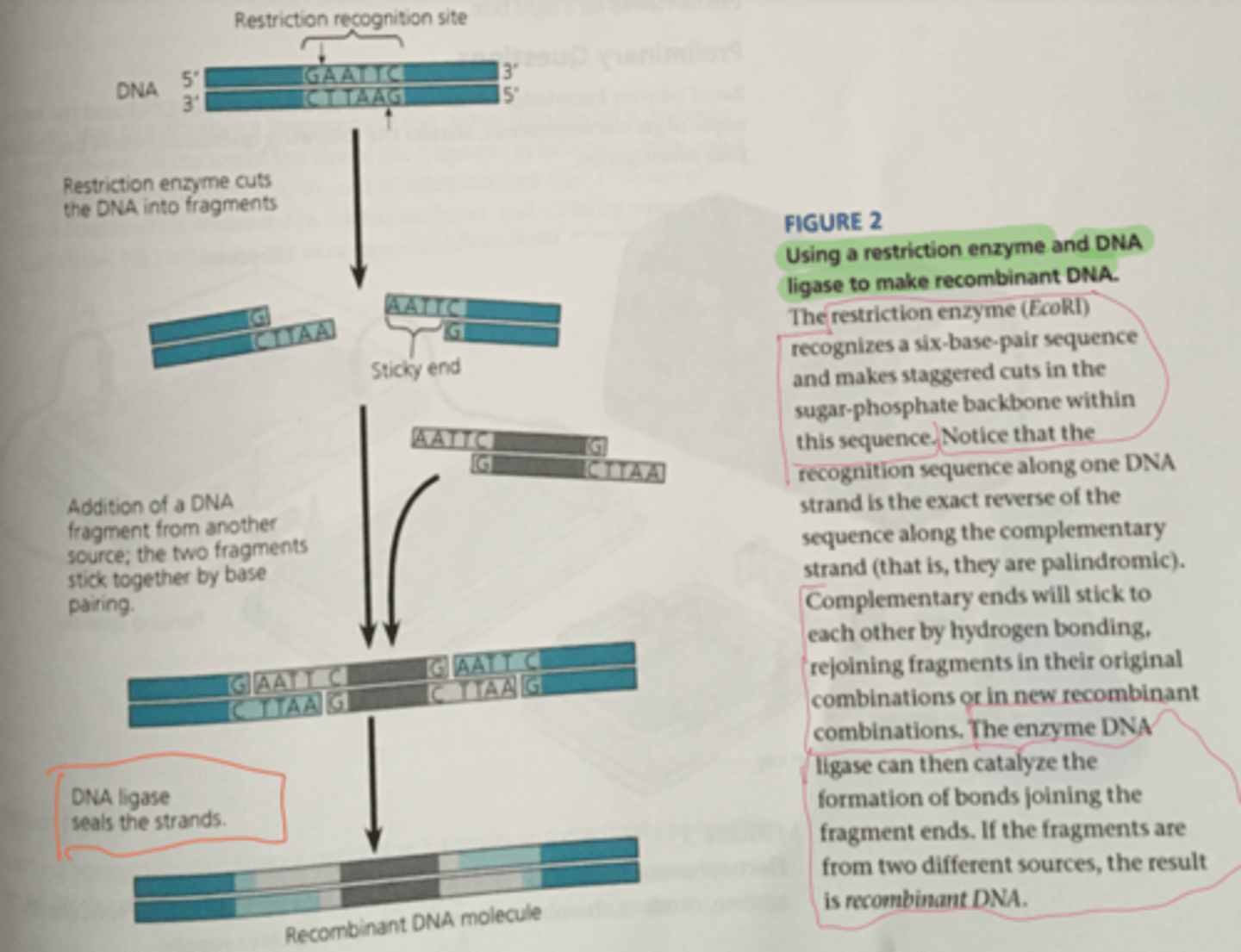
Restriction endonucleases (restriction enzymes) *
Help manipulate DNA molecules.
restriction enzymes recognizes a six-base-pair sequence and makes staggered cuts in sugar-phosphate backbone w/i sequence
i.e. Bacteria use restriction enzymes as defense against virus infections by recognizing and cutting foreign DNA
Nuclease
Digestion of a nucleic acid
i.e. DNA
Cutting (aka Restricting, or digesting)
Requires energy; ATP
Involves a physical cleaving of chemical bonds.
Palindromic
Sequences of complementary strands read the same on both strands from 5' to 3'
i.e. race car
Plasmid
A plasmid is a smaller extrachromosomal ring of DNA sometimes found in bacteria and yeast.
It replicates independently of the bacterial chromosome.
PCR
uses synthetic primer (the primer may be RNA or DNA oligonucleotides) to clone DNA (rapidly amplify).
Taq polymerase (heat
stable) + nucleotides + primers + salts (buffer) necessary.
Making solutions from dry chemicals
Grams of solute = formula weight* (in grams) x volume (in liters) x molarity
*FW of NaCl: 58.44 g/mole
Make 100 ml 5M NaCl solution
58.44g x 0.1 x 5 = 29.22g
How to make dilutions
How to dilute?
(Concentration that you want/Concentration of stock solution you have) X final volume (ml)
make 250 ml 0.5M NaCl solution from a 5M NaCl stock
How many ml of 5M NaCl and how many ml of water should be used?
(0.5M/5M) X 250 ml = 25 ml
Therefore to 25 ml 5M NaCl add water (225 ml) in a graduated cylinder to bring the volume to 250 ml
What gas fixes during photosynthesis? (Q6)
CO2
Name an important factor that determined how far pigments separated in the paper? (Q6)
Polarity or solubility
What was our dependent variable in the spectrophotometer experiment? (Q6)
absorption
What was the independent variable in the spectrophotometer experiment?(Q6)
wavelength
Why does calibrating (setting to zero absorbance) the machine on the black gave us more accurate results?(Q6)
subtracts acetones from pigments
The third step of the PCR machine is called synthesis or extension. What is extended?(Q11)
primers
Why can't RNA polymerase be used in a PCR machine?(Q11)
to high of temperature
What happens if you don't bring temperature down enough during the second stage of PCR.(Q11)
target doesn't stick
Why do we want to select for antibiotic resistant colonies after bacteria transformation?(Q11)
...
What is most likely to be a restriction site? (Q9)
CTTAAG
DNA fragments in a agrose gel separate from one another because of ________.(Q9)
size
What gas is released at the negative electrode of the gel apparatus?(Q9)
hydrogen
Towards which electrode do DNA fragments typically migrate during electolosis?(Q9)
positive
Which axis of the graph did we use for distance DNA fragments traveled in the gel?(Q9)
linear distance
What was Darwin's major contribution to the theory of evolution?
Natural Selection (descent with modification)
The gradual change in a species over time
Evolution
What are the requirements for Hardy Weinberg
1 - No mutations.
2 - No gene flow.
3 - Random mating must occur (i.e. individuals must pair by chance)
4 - Large POP so no genetic drift.
5 - No selection can occur so that certain alleles are not selected for, or against.
What is the major selective pressure that leads to an increase in the number of antibiotic resistant bacteria?
antibiotic
Define population
group of individuals of the same species in some parameter
A number of individuals of specific species in a given area.
What is a gene pool?
aggregate of all copies of every type of allele at all loci in every individual in a population. The term is also used in a more restricted sense as the aggregate of alleles for just one or a few loci in a population.
The total number of genes in a give population.
What does HARDY Weinberg state about gene frequency?
That under the right (5) conditions it will reach a state of equilibrium where the allele frequency will stay constant
Name two requirements for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Large population
no gene flow
Name an important difference between genetic drift and natural selection
genetic drift is random
natural selection is not
Which requirement of Hardy Weinberg is violated by genetic drift?
population size
Restriction endonuclease have a protective function in bacteria. What is it?
Cuts phage DNA.
amplify DNA
In general, what is the purpose of using PCR?
(Taq Polymerase) thermostable
What is the special property of the enzyme used in PCR?
primers
Approximately 20 base pairs making up single strand DNA that starts a DNA replication
What gives specifity to the PCR reaction?
1. Only a tiny amount of target DNA is needed
2. It is quick
What are the benefits of PCR?
1. Denaturation (95 degrees C) to break H-bonds
2. Annealing (50-65 degrees C) reduce temperature so primers can stick
3. Synthesis or extension (most sensitive to time)4. Repeat
What are the steps of PCR?
random change in population of alleles
What is genetic drift?
large population
Which criterion of HW equilibrium is violated by bottleneck?
In the bottleneck effect, the frequency alleles in the population has been changed due to ___.
chance alone
p=.3
q=.7
In a population of 50, there are 5 AA, 20Aa and 25aa. What is the value of q and p?
mimicry and camouflage
What are two of the salamanders adaptions used in California?
genetic drift is random, natural selection is not random
Important difference between natural selection and genetic drift.
group of organisms of the same species that occur in the same area and have the opportunity to interbreed or share a common gene pool
Population
variable number in tandem repeats
in DNA fingerprinting, the DNA fragments compared are different lengths. What causes this difference?
very large in size, matings are random, no natural selection, no mutations, no migration
name the requirements for HW equilibrium.
stays the same from generation to generation if population is at equilibrium
What did Hardy-Weinberg state about gene frequencies?
.42
In a H-W population, the frequency of a recessive disorder is 0.09.
What is the frequency of heterozygotes?
to determine if the values in change are significant or not.
What was our purpose of using "chi square test" for a genetic cross?
yes. p>0.05
In a chi square test, the expected genotype distribution is 1:2:1.
Would you compare this to your own observed distribution at q=.05, you find that p=.06.
Would you still think that your observed distribution is 1:2:1?
Observed variable in an experiment or study
whose changes are determined by the presence or degree of one or more independent variables
Dependent variable.
A manipulated variable in an experiment or study
whose presence or degree determines the change in the dependent variable
Independent variable.
enzymes cut up phage DNA (destroy invading DNA their own DNA is not cut up because it is menthylated).
Restriction endonucleases have a protective function in bacteria. What is it?
about the same size (about the same number of base pairs).
Why do fragments "gather" in bands at specific locations in agarose gel?
positive
Toward which electrode do DNA fragments typically migrate during electrophoresis?
hydrogen
what gas is produced at the negative electrode during electrophoresis?
oxygen
what gas is produced at the positive electrode during electrophoresis?
based on observable phenomenon
-what can be observed with 5 senses
what does it mean that science is based on empirical knowledge?
science comes from observations and testing
based on empirical knowledge
commitment to experimentation
Name some characteristics of science.
what they do is important for what we do.
what does it mean that "science depends on interactions within he scientific community"?
We fail to reject the null hypothesis
If significant level is .05 and you find that p=.06.
What would you do with your null hypothesis?
States the lack of significant difference between the expected and observed results
difference is due to chance - sampling error
this states that the difference between the expected and observed results is not significant - random fluctuations data by choice
Null hypothesis?
Testing the significance of chance of error or to test the goodness of fit.
What was the purpose of using a chi square test last time from a genetic cross?
.32
In a HW population the frequencies of individuals affected by recessive disorder is 0.04
What is the frequency of the heterozygous in the same population?
Stays the same through generation if in equilibrium
What did Hardy-Weinberg state about gene frequencies.
No mutation, no natural selection, and large population
Name three requirements for a population to be Hardy Weinberg equilibrium?
all the alleles at all gene loci of all individuals in the population
What is a gene pool?
populations
Do populations or individuals evolve?
Changes of genetic frequencies in a small population
Genetic Drift?