4.1.5 (a) - trading blocs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is a trading bloc
a group of countries who come together and agree to reduce or eliminate any barriers to trade that exist between them
aka economic integration
are there levels to this?
yes!
v low economic integration = bilaterial agreements
v high economic integration = monetary unions (eg. Eurozone)
4 types of trade blocs
free trade areas
customs unions
common markets
monetary unions
free trade areas
countries abolish trade restrictions (like tarriffs) between themselves, but maintain their own restrictions with whoever else
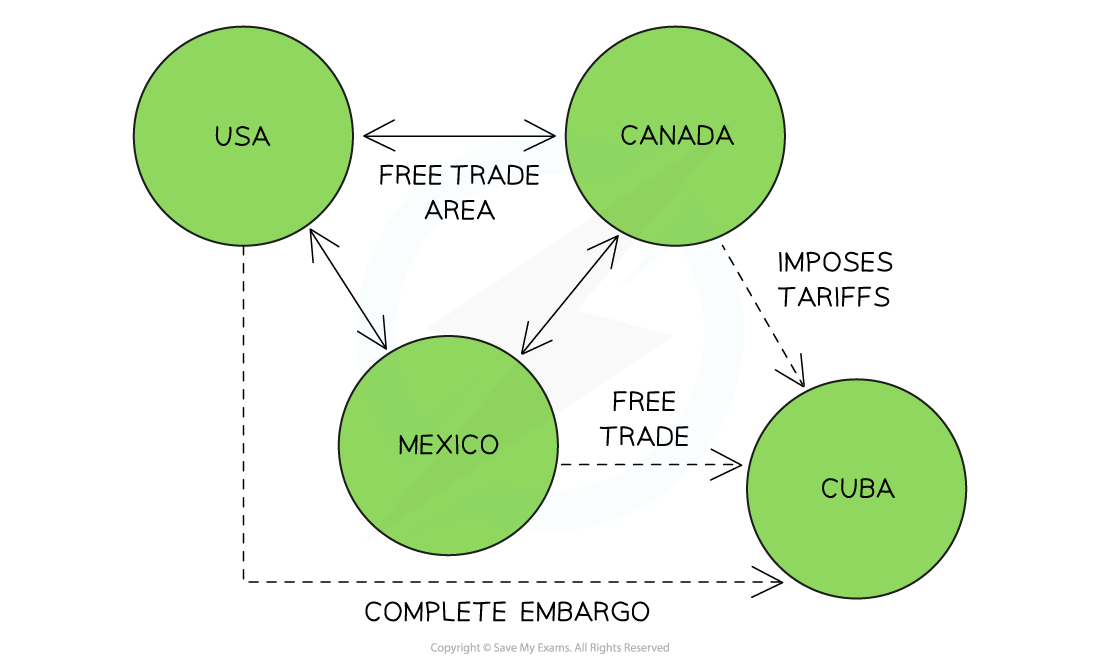
example of free trade area
CUSMA —> Canada - US - Mexico Agreement
they free trade with each other but deal with cuba as they like
customs unions
all g+s produced by member countries are traded tarrif free
AND
member countries agree on a common tarrif rate for imports from third party countries (common external barriers)
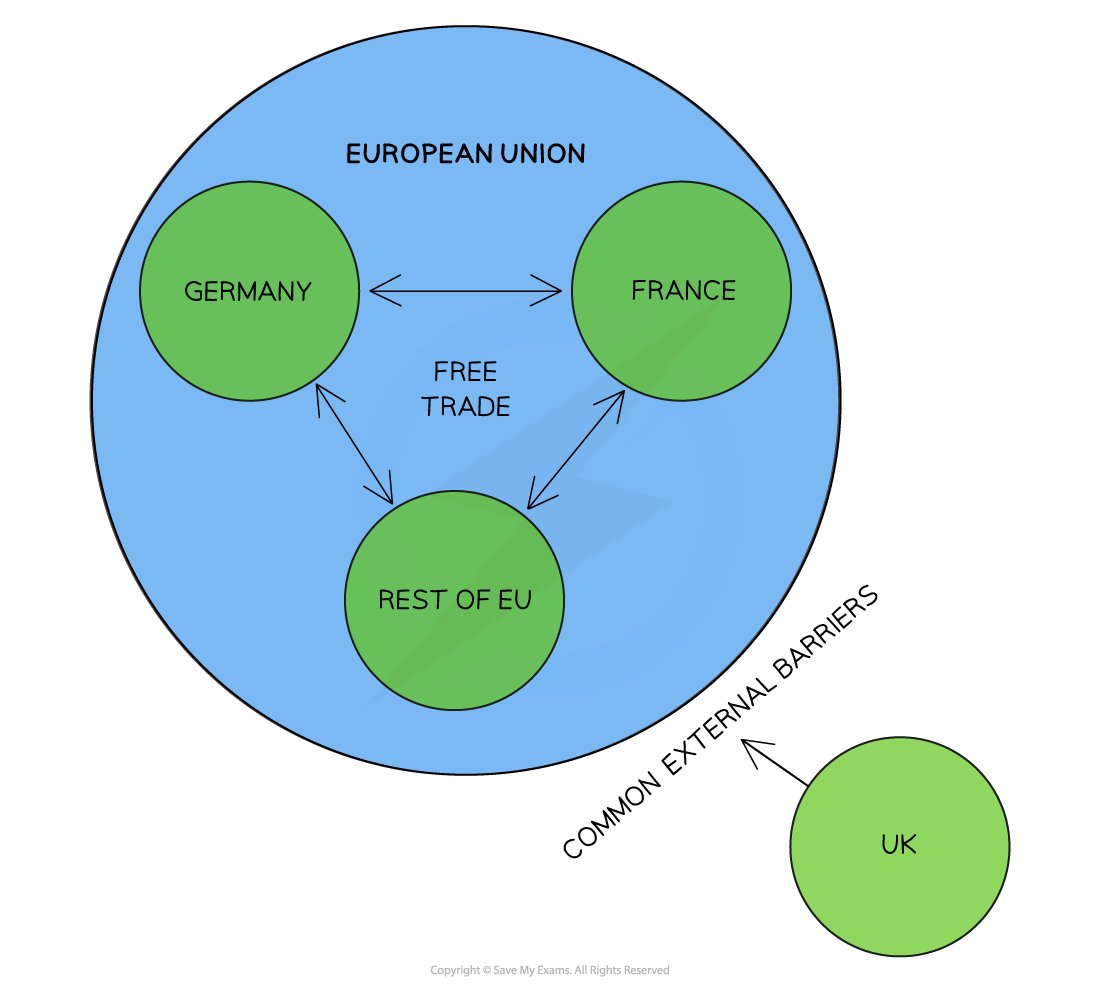
example of customs union
EU
common markets
g+s traded tariff free, common external tarriffs are in place
AND
fops flow freely between member countries
why the free flow of fops
improve allocation of resources
lower costs of production
example of common market
EU
monetary unions
same as customs union + common market
AND
a common currency issued by a common central bank
example of monetary union
Eurozone
4 essential conditions for a successful monetary union
movement of labour
similar trade cycles
mobility of finance
fiscal transfers
movement of labour
labour can move freely without any barriers (including language)
similar trade cycles
avoids tension
EG. southern europe in depression vs northern europe in temporary recession after 2008 crisis
mobility of finance
prices + wages can adjust based on market conditions of member nations
fiscal transfers
automatic fiscal transfers important to help economies
(because they have lost monetary policy so they rely wholly on fiscal)
benefits/costs of a free trade area
trade creation - ↑ efficiency + ↑ income
trade diversion - countries reallocate trade to partners = ↓ global efficiency
benefits/costs of a customs union or common market
tariffs eliminated = cheaper imprts
common tariffs to 3rd parties simplifies trade
structural unemployment
↑ neg externalities of production
benefits/costs of a monetary union
simplifies trading costs - no exchange rate to deal with
can benefit from improved monetary policy (union interest rates may be lower than individual)
expensive to transition to monetary union (menu change prices)
loss of monetary policy
loss of sovereignty (decision making authority)